Effect of Elemental Iron Containing Bauxite Residue Obtained After Electroreduction on High-Pressure Alkaline Leaching of Boehmitic Bauxite and Subsequent Thickening Rate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
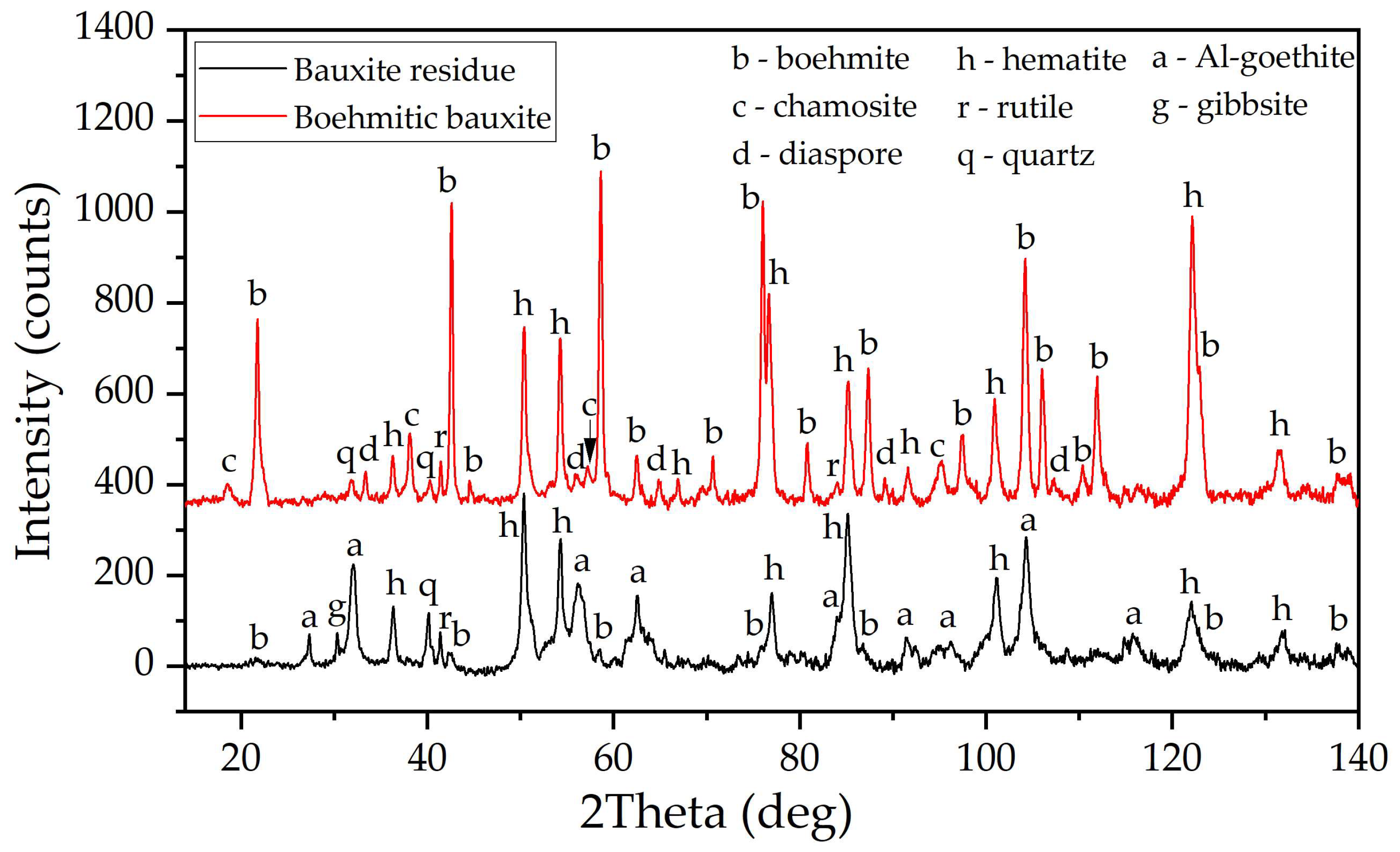
2.1. Materials and Reagents
2.2. Analytical Methods
2.3. Bauxite Residue Pretreatment Using Electrolysis
2.4. Experimental
3. Results and Discussion
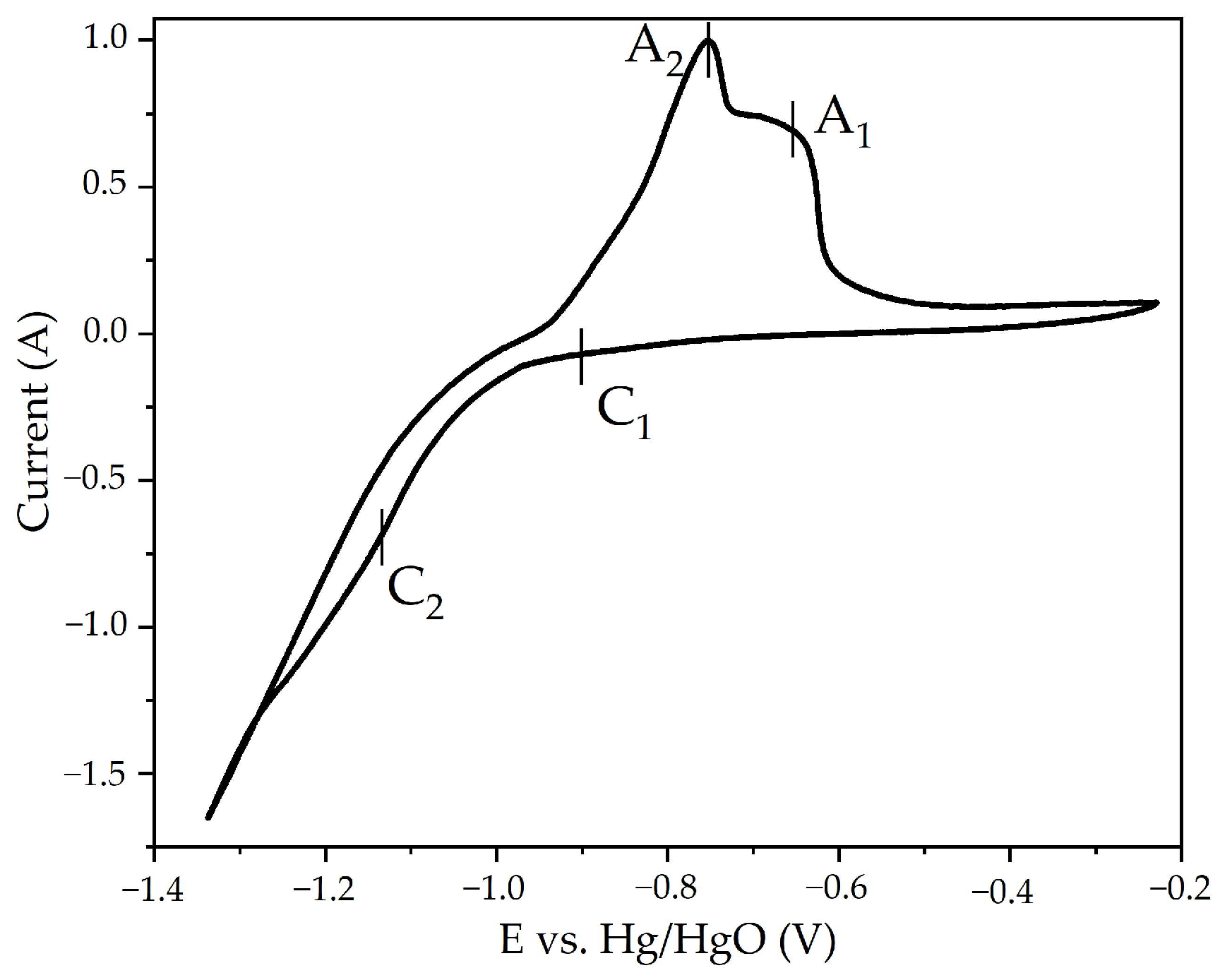
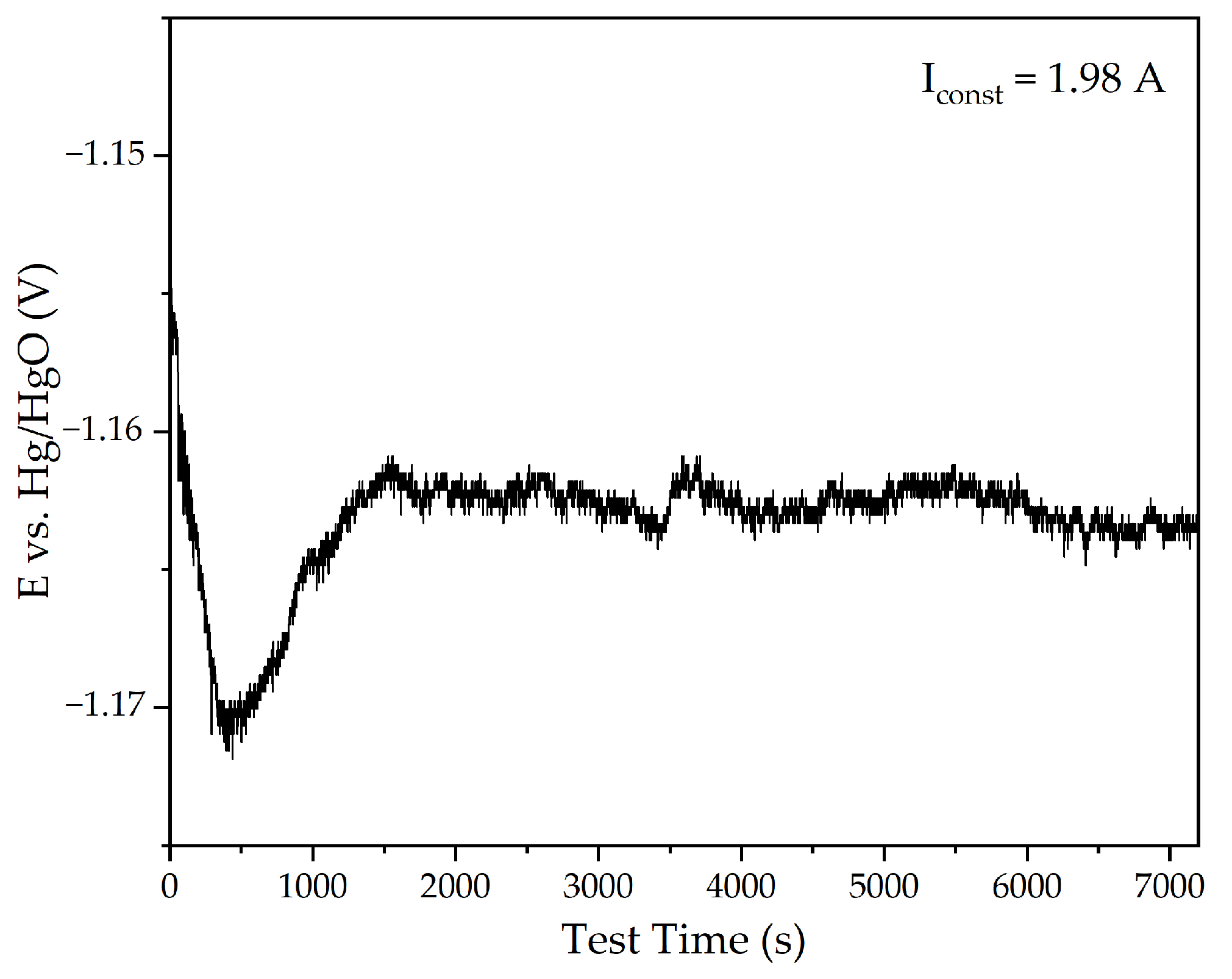
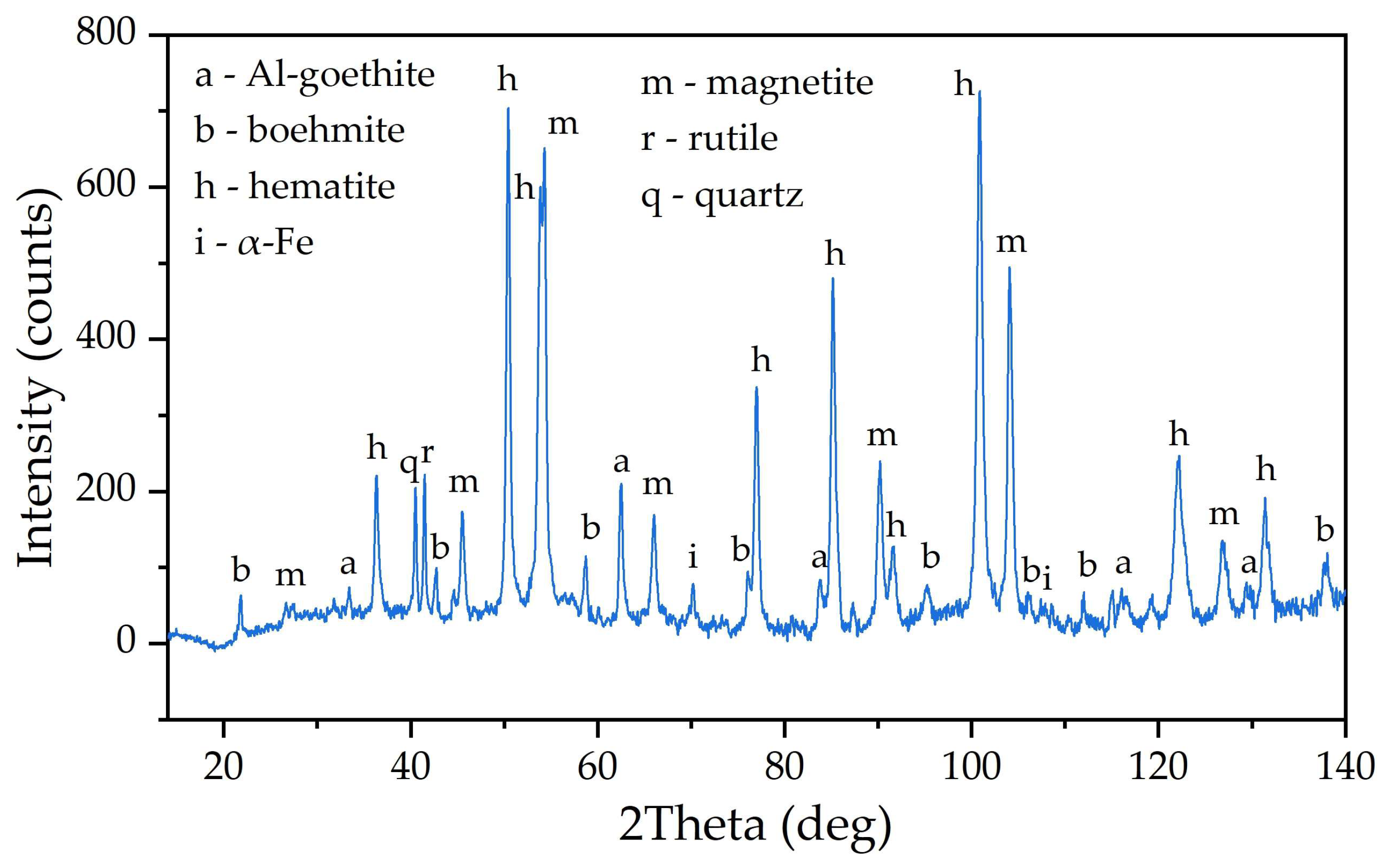
3.1. Electroreduction of Al-Goethite Containing Bauxite Residue
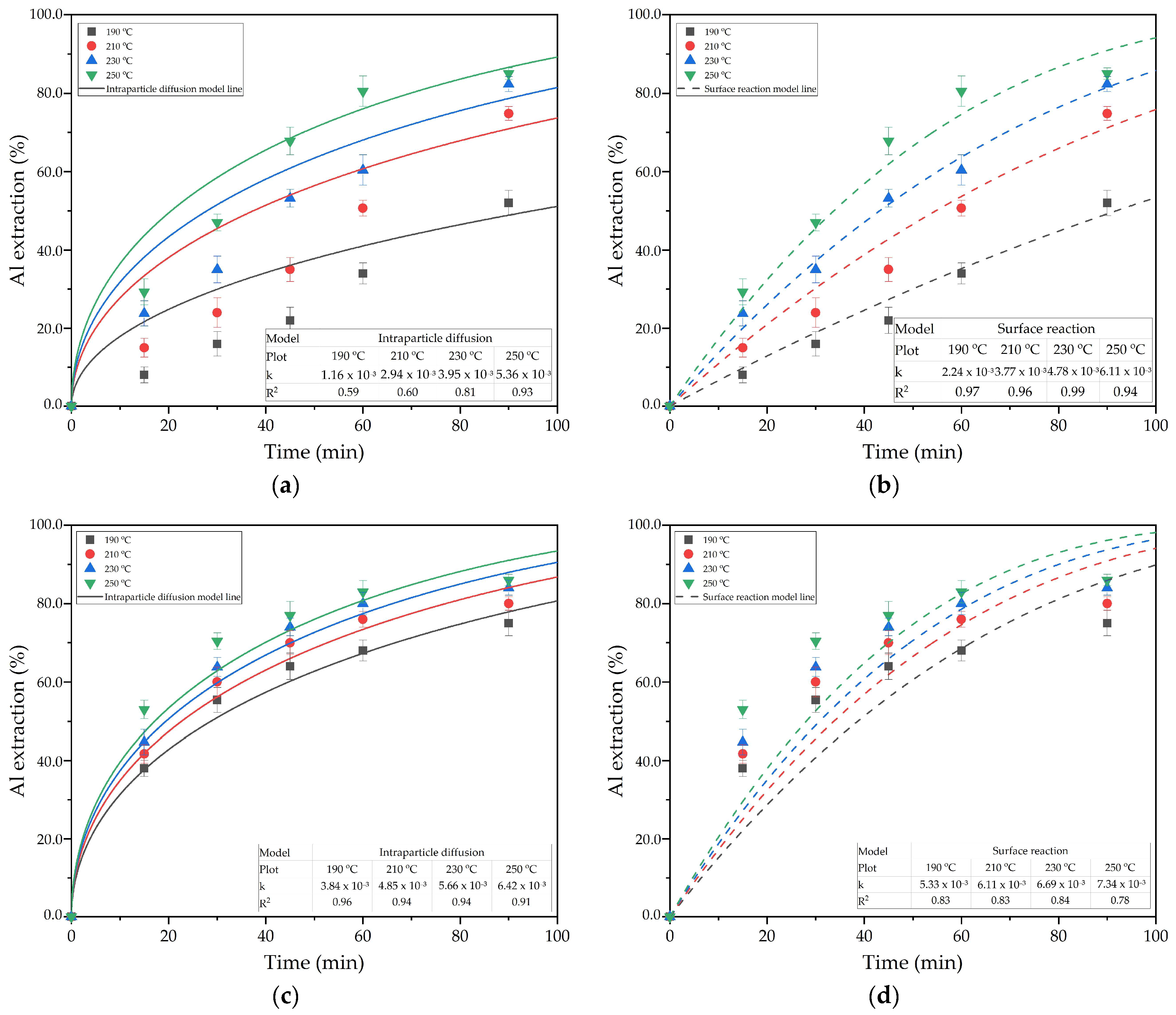
3.2. Effect of Addition of Reduced Bauxite Residue on Al Extraction
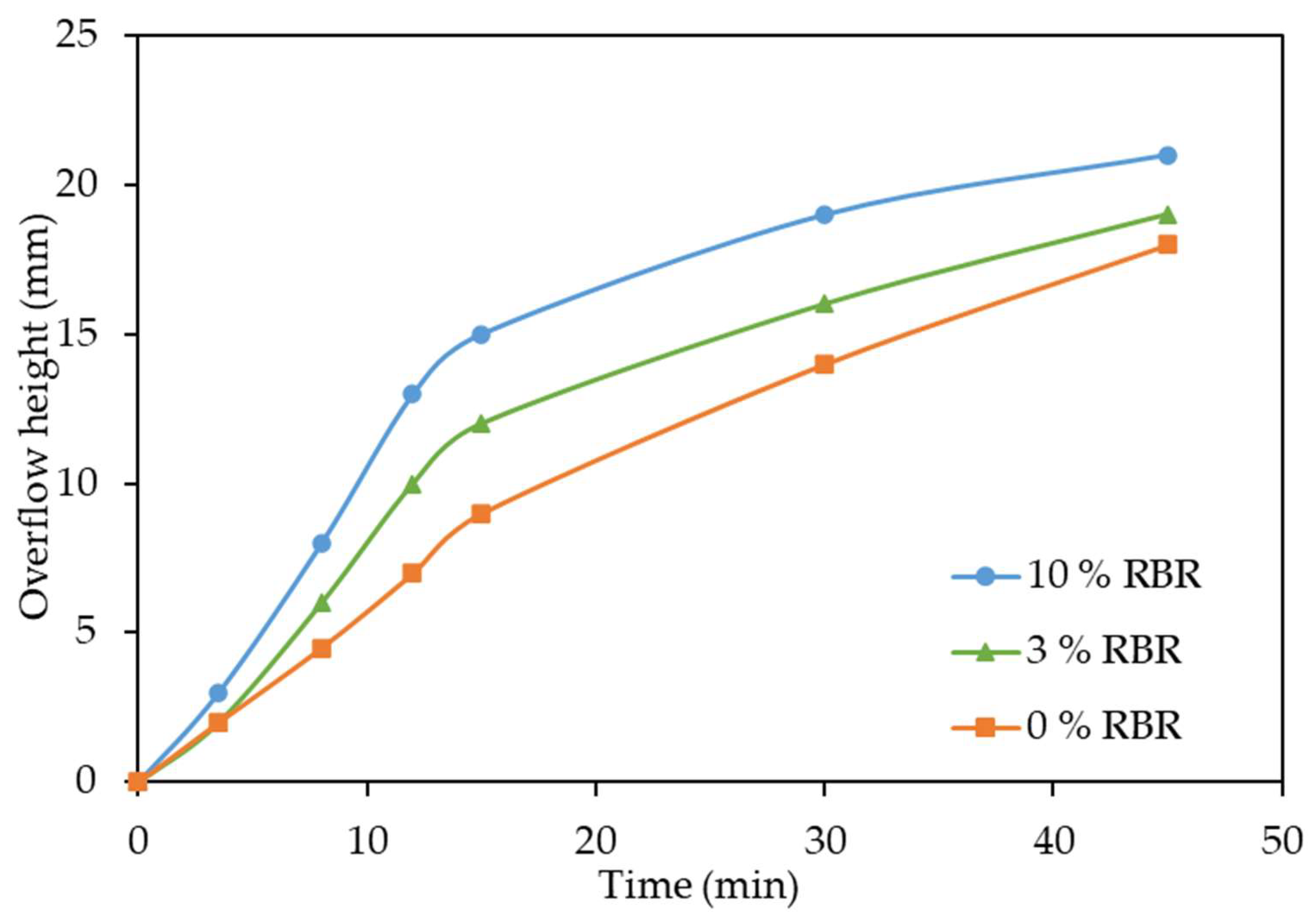
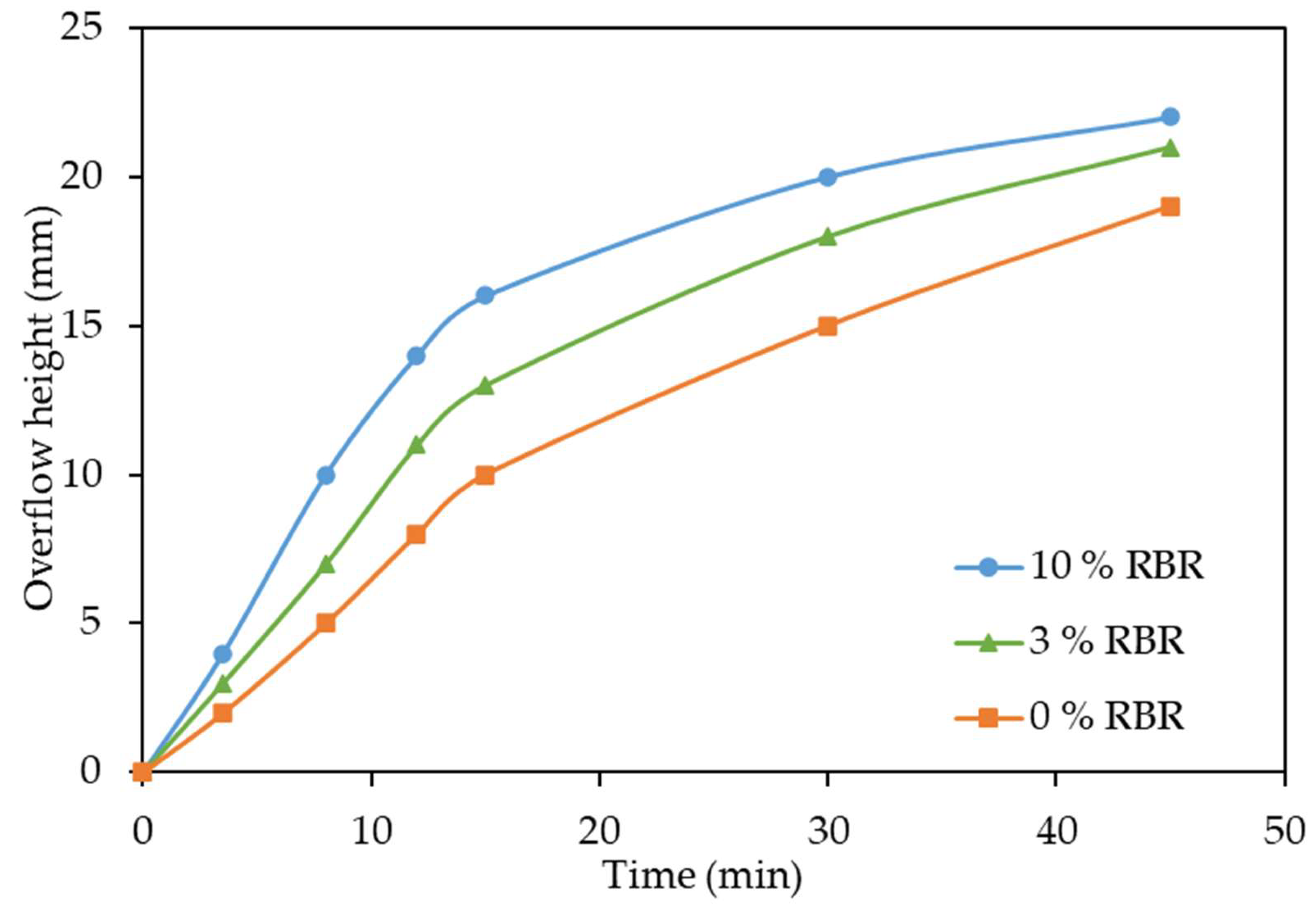
3.3. Effect of Addition of Reduced Bauxite Residue on Thickening of the Pulp
3.4. Effect of Addition of Reduced Bauxite Residue on the Chemical Composition of Solid Residue and Na2O Losses
3.5. Evaluation of the Feasibility of the Process
4. Conclusions
- The electrolytic reduction of iron minerals in the suspension of Al-goethite containing BR in an alkaline solution using a bulk cathode results in more than a 55% reduction degree after 2 h with the current efficiency higher than 73%.
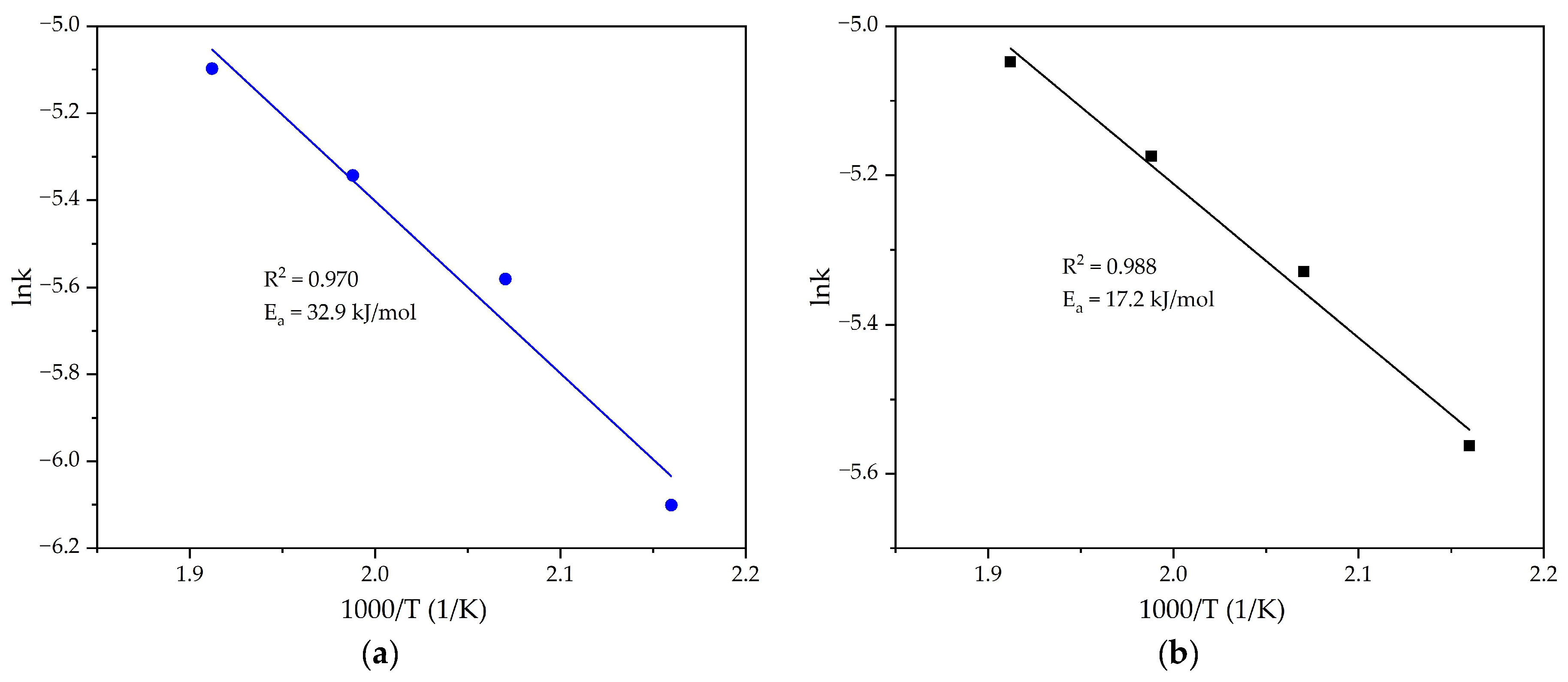
- The addition of reduced BR at the level of 10% of the bauxite mass leads to a change in the leaching mechanism. The activation energy was decreased from 32.9 to 17.2 kJ/mol. The limiting stage according to the shrinking core model changed from a surface chemical reaction to intraparticle diffusion due to easier Al extraction from Al-goethite and Al-hematite in the presence of Fe2+ ions.
- After high-pressure leaching with the addition of 3% reduced BR, the thickening rate increases by 1.33 times. Leaching of boehmitic bauxite with the addition of lime and reduced BR in the amount of 10% of the bauxite mass increases the thickening rate up to 1.7 times.
- Leaching of boehmitic bauxite with the addition of lime and reduced BR in the amount of 10% of the bauxite mass leads to Na2O losses being reduced by 15%.
- The Fe2O3 content in the solid residue of boehmitic bauxite leached with the addition of reduced BR reaches 50–52% against 46% in conventional leaching according to the Bayer process.
- Techno-economic analysis suggests that the addition of reduced BR provides an optimum balance between capital and production costs to produce a BR suitable for subsequent magnetite concentrate separation.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kaußen, F.M.; Friedrich, B. Methods for Alkaline Recovery of Aluminum from Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2016, 2, 353–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hond, R.D.; Hiralal, I.; Rijkeboer, A. Alumina Yield in the Bayer Process Past, Present and Prospects. In Essential Readings in Light Metals; Donaldson, D., Raahauge, B.E., Eds.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013; pp. 528–533. ISBN 978-1-118-64786-8. [Google Scholar]
- Li, X.; Kong, L.-L.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z.-H.; Liu, G. Effect of Alumogoethite in Bayer Digestion Process of High-Iron Gibbsitic Bauxite. Zhongguo Youse Jinshu Xuebao/Chin. J. Nonferrous Met. 2013, 23, 543–548. [Google Scholar]
- Alkan, G.; Schier, C.; Gronen, L.; Stopic, S.; Friedrich, B. A Mineralogical Assessment on Residues after Acidic Leaching of Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) for Titanium Recovery. Metals 2017, 7, 458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, P.S.; Reddy, N.G.; Serjun, V.Z.; Mohanty, B.; Das, S.K.; Reddy, K.R.; Rao, B.H. Properties and Assessment of Applications of Red Mud (Bauxite Residue): Current Status and Research Needs. Waste Biomass Valorization 2020, 12, 1185–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Das, S.K.; Rao, B.H. Characterization of Coarse Fraction of Red Mud as a Civil Engineering Construction Material. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 679–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P. The Processing of High Silica Bauxites—Review of Existing and Potential Processes. Hydrometallurgy 2009, 98, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.; Lv, H.; Xie, M.; Li, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, F. Reaction Behavior of Quartz in Gibbsite-Boehmite Bauxite in Bayer Digestion and Its Effect on Caustic Consumption and Alumina Recovery. Ceram. Int. 2022, 48, 18676–18686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, T. Approaches to Improve Alumina Extraction Based on the Phase Transformation Mechanism of Recovering Alkali and Extracting Alumina by the Calcification-Carbonization Method. Hydrometallurgy 2019, 189, 105123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanna, R.; Konyukhov, Y.; Zinoveev, D.; Jayasankar, K.; Burmistrov, I.; Kravchenko, M.; Mukherjee, P.S. Red Mud as a Secondary Resource of Low-Grade Iron: A Global Perspective. Sustainability 2022, 14, 1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräfe, M.; Power, G.; Klauber, C. Bauxite Residue Issues: III. Alkalinity and Associated Chemistry. Hydrometallurgy 2011, 108, 60–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Sun, N.; Tang, H.; Sun, W. A Review on Comprehensive Utilization of Red Mud and Prospect Analysis. Minerals 2019, 9, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piirainen, V.Y.; Barinkova, A.A. Development of Composite Materials Based on Red Mud. Obogashchenie Rud. 2023, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eldeeb, A.B.; Brichkin, V.N.; Kurtenkov, R.V.; Bormotov, I.S. Study of the Peculiarities of the Leaching Process for Self-Crumbling Limestone-Kaolin Cakes. Obogashchenie Rud. 2021, 27–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ElDeeb, A.B.; Brichkin, V.N.; Kurtenkov, R.V.; Bormotov, I.S. Factors Affecting on the Extraction of Alumina from Kaolin Ore Using Lime-Sinter Process. In Topical Issues of Rational Use of Natural Resources 2019; Litvinenko, V., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2019; pp. 502–508. ISBN 978-1-00-301463-8. [Google Scholar]
- Vuković, J.; Perušić, M.; Stopić, S.; Kostić, D.; Smiljanić, S.; Filipović, R.; Damjanović, V. A Review of the Red Mud Utilization Possibilities. Ovidius Univ. Ann. Chem. 2024, 35, 165–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belviso, C.; Mancinelli, M.; Abdolrahimi, M.; Sturini, M.; Cavalcante, F.; Lettino, A.; Peddis, D. Red Mud Treated with KOH: Synthesis of Sustainable Materials from Waste for Water Treatment. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 45414–45424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damdinova, D.R.; Khardaev, P.K.; Pavlov, V.E.; Druzhinin, D.K.; Vtorushin, N.S.; Batorova, I.Y. Ash and Slag Wastes of Heat Power Engineering as Raw Materials for Obtaining Foamglasses. Bull. East. Sib. State Univ. Technol. Manag. 2016, 59, 9–14. [Google Scholar]
- Alam, S.; Das, B.K.; Das, S.K. Dispersion and Sedimentation Characteristics of Red Mud. J. Hazard. Toxic. Radioact. Waste 2018, 22, 04018025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaditager, M.; Sivakugan, N. Influence of Fly Ash–Based Geopolymer Binder on the Sedimentation Behavior of Dredged Mud. J. Waterw. Port. Coast. Ocean. Eng. 2017, 143, 04017012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Loginova, I.; Pankratov, D. Low-Temperature Treatment of Boehmitic Bauxite Using the Bayer Reductive Method with the Formation of High-Iron Magnetite Concentrate. Materials 2023, 16, 4678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera, R.M.; Ounoughene, G.; Malfliet, A.; Vind, J.; Panias, D.; Vassiliadou, V.; Binnemans, K.; Van Gerven, T. A Study of the Occurrence of Selected Rare-Earth Elements in Neutralized–Leached Bauxite Residue and Comparison with Untreated Bauxite Residue. J. Sustain. Metall. 2019, 5, 57–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. Cleaning Disposal of High-Iron Bauxite Residue Using Hydrothermal Hydrogen Reduction. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2022, 109, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. Comprehensive Utilization of Al-Goethite-Containing Red Mud Treated Through Low-Temperature Sodium Salt-Assisted Roasting–Water Leaching. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. A Clean Two-Stage Bayer Process for Achieving near-Zero Waste Discharge from High-Iron Gibbsitic Bauxite. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 405, 136991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasechnik, L.A.; Skachkov, V.M.; Bogdanova, E.A.; Chufarov, A.Y.; Kellerman, D.G.; Medyankina, I.S.; Yatsenko, S.P. A Promising Process for Transformation of Hematite to Magnetite with Simultaneous Dissolution of Alumina from Red Mud in Alkaline Medium. Hydrometallurgy 2020, 196, 105438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yu, S.; Dong, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Jiang, Y. Investigating the Effect of Ferrous Ion on the Digestion of Diasporic Bauxite in the Bayer Process. Hydrometallurgy 2015, 152, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, G.; Qi, T.; Zhao, J.; Peng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Shen, L. Increasing Iron Recovery from High-Iron Red Mud by Surface Magnetization. J. Sustain. Metall. 2023, 9, 795–805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Loginova, I. Novel Method of Bauxite Treatment Using Electroreductive Bayer Process. Metals 2023, 13, 1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes, D.V.; Ivanova, Y.A.; Kovalevsky, A.V.; Sarabando, A.R.; Frade, J.R.; Quina, M.J. Electrochemical Reduction of Hematite-Based Ceramics in Alkaline Medium: Challenges in Electrode Design. Electrochim. Acta 2019, 327, 135060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, J.F.; Ivanova, Y.A.; Kovalevsky, A.V.; Ivanou, D.K.; Frade, J.R. Reduction of Magnetite to Metallic Iron in Strong Alkaline Medium. Electrochim. Acta 2016, 193, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimov, K.; Shoppert, A.; Rogozhnikov, D.; Kuzas, E.; Zakhar’yan, S.; Naboichenko, S. Effect of Preliminary Alkali Desilication on Ammonia Pressure Leaching of Low-Grade Copper–Silver Concentrate. Metals 2020, 10, 812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levenspiel, O. Chemical Reaction Engineering, 3rd ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 1999; ISBN 0-471-25424-X. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.; Qi, T.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. Low-Temperature Thermal Conversion of Al-Substituted Goethite in Gibbsitic Bauxite for Maximum Alumina Extraction. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 4162–4174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shoppert, A.; Valeev, D.; Diallo, M.M.; Loginova, I.; Beavogui, M.C.; Rakhmonov, A.; Ovchenkov, Y.; Pankratov, D. High-Iron Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Valorization Using Hydrochemical Conversion of Goethite to Magnetite. Materials 2022, 15, 8423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, L.; Wang, Y.; Wang, B.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Zhou, Q.; Peng, Z.; Li, X. Phase Transformation of Desilication Products in Red Mud Dealkalization Process. J. Sustain. Metall. 2022, 8, 541–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinoveev, D.; Petelin, A.; Grudinsky, P.; Zakunov, A.; Dyubanov, V. Extraction of Iron from Russian Red Mud by a Carbothermic Reduction and Magnetic Separation Process. In Proceedings of the the 1st International Electronic Conference on Metallurgy and Metals, Virtual, 7 March 2021; p. 23. [Google Scholar]
- Stopic, S.; Kostić, D.; Schneider, R.; Sievers, M.; Wegmann, F.; Emil Kaya, E.; Perušić, M.; Friedrich, B. Recovery of Titanium from Red Mud Using Carbothermic Reduction and High Pressure Leaching of the Slag in an Autoclave. Minerals 2024, 14, 1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lin, Z.; Shen, L. Efficient Separation of Iron and Alumina in Red Mud Using Reduction Roasting and Magnetic Separation. Min. Metall. Explor. 2024, 41, 1543–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Li, X.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, B.; Qi, T.; Liu, G.; Peng, Z.; Pi, J.; Zhao, Z.; Wang, M. Reduction of Red Mud Discharge by Reductive Bayer Digestion: A Comparative Study and Industrial Validation. JOM 2020, 72, 270–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
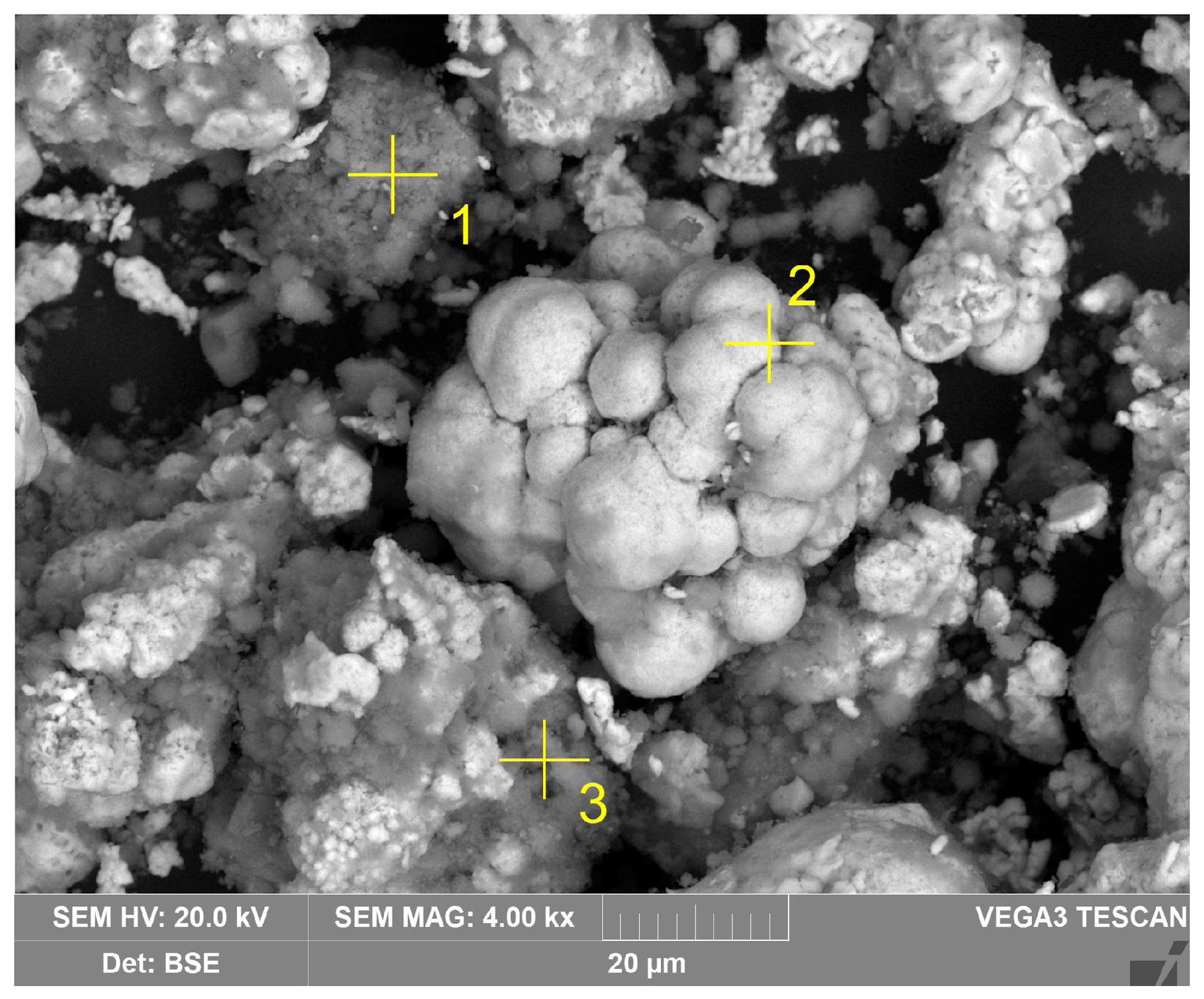

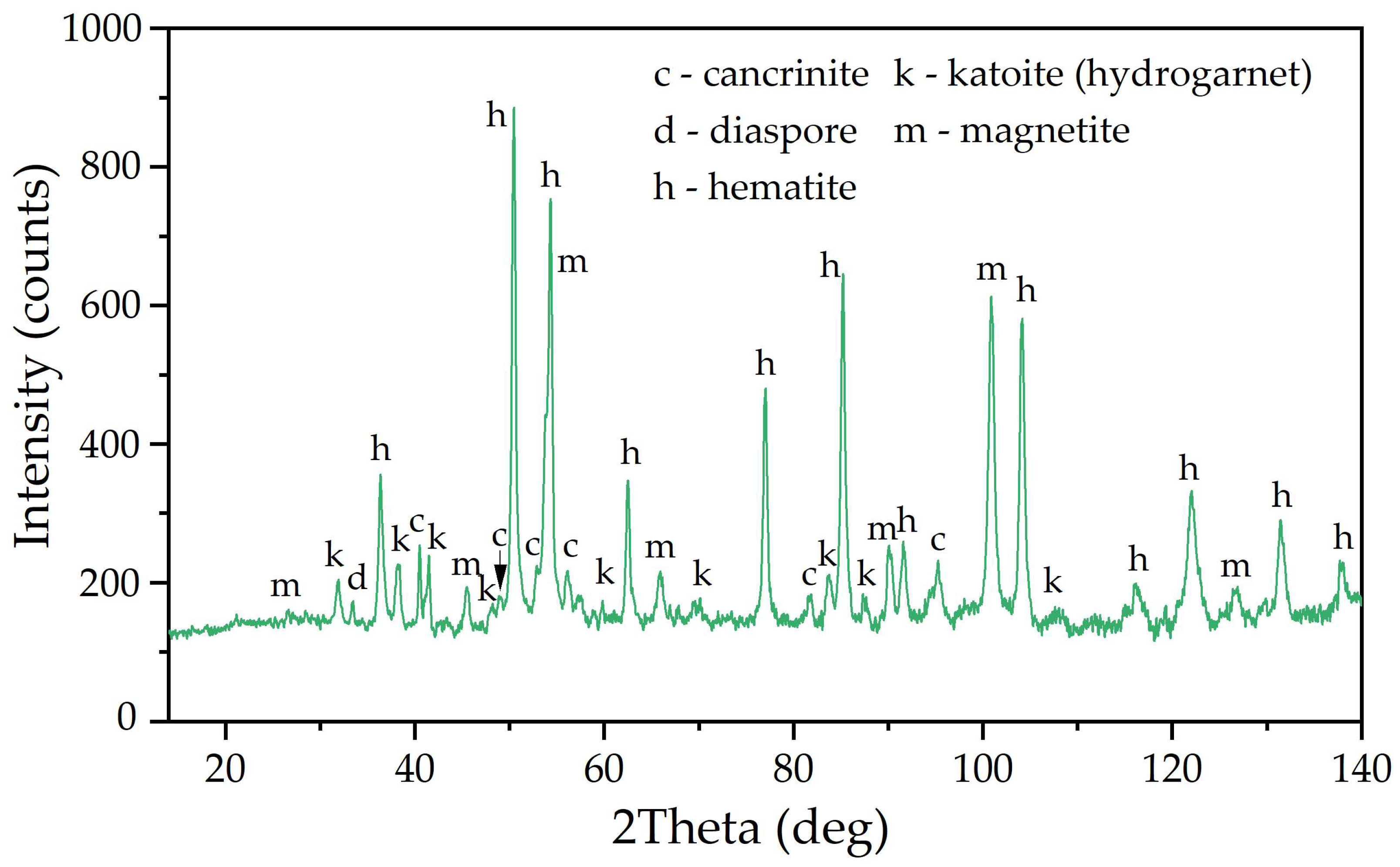

| Sample | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | Other | LOI 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bauxite | 25.5 | 51.7 | 6.4 | 2.7 | 0.1 | 0.5 | 0.4 | 0.02 | 0.3 | 1.1 | 11.3 |
| BR | 52.5 | 19.0 | 7.7 | 3.1 | 3.8 | 0.2 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 1.2 | 11.5 |
| Spectrum | 1 | 2 | 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| O | 55.2 | 2.6 | 44.5 |
| Al | 31.9 | 0.8 | 16.7 |
| Si | 0.1 | 0.3 | 14.4 |
| Fe | 8.4 | 96.1 | 13.0 |
| Ti | 1.0 | 0.3 | 0.6 |
| Na | 2.9 | 0.1 | 13.0 |
| Sample | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | SO3 | P2O5 | Other | LOI 1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced BR | 77.4 | 4.4 | 4.9 | 4.5 | 3.0 | 0.2 | 0.3 | 0.4 | 0.1 | 0.4 | 4.5 |
| Sample | Fe2O3 | Al2O3 | SiO2 | TiO2 | Na2O | CaO | MgO | SO3 | MnO | Other | LOI 1 | Na2O Losses, kg/t Al2O3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without additive | 45.9 | 13.8 | 14.3 | 5.7 | 6.8 | 2 | 1.5 | 1.6 | 1.1 | 1.3 | 6.0 | 48.4 |
| 10% RBR | 51.8 | 12.5 | 13.1 | 5.8 | 5.3 | 1.6 | 1.2 | 1.5 | 1 | 1.0 | 5.1 | 41.1 |
| 10% RBR + 3% CaO | 50.5 | 12.2 | 12.9 | 5.7 | 4.6 | 4.8 | 1.1 | 1.5 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 4.9 | 40.3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shoppert, A.; Loginova, I.; Diallo, M.M.; Valeev, D. Effect of Elemental Iron Containing Bauxite Residue Obtained After Electroreduction on High-Pressure Alkaline Leaching of Boehmitic Bauxite and Subsequent Thickening Rate. Materials 2025, 18, 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020224
Shoppert A, Loginova I, Diallo MM, Valeev D. Effect of Elemental Iron Containing Bauxite Residue Obtained After Electroreduction on High-Pressure Alkaline Leaching of Boehmitic Bauxite and Subsequent Thickening Rate. Materials. 2025; 18(2):224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020224
Chicago/Turabian StyleShoppert, Andrei, Irina Loginova, Malal Mamodou Diallo, and Dmitrii Valeev. 2025. "Effect of Elemental Iron Containing Bauxite Residue Obtained After Electroreduction on High-Pressure Alkaline Leaching of Boehmitic Bauxite and Subsequent Thickening Rate" Materials 18, no. 2: 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020224
APA StyleShoppert, A., Loginova, I., Diallo, M. M., & Valeev, D. (2025). Effect of Elemental Iron Containing Bauxite Residue Obtained After Electroreduction on High-Pressure Alkaline Leaching of Boehmitic Bauxite and Subsequent Thickening Rate. Materials, 18(2), 224. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18020224








