MXenes: Manufacturing, Properties, and Tribological Insights
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Overview of MXenes
2.1. What Are MXenes and Why Do They Matter?
2.2. MXene Manufacturing
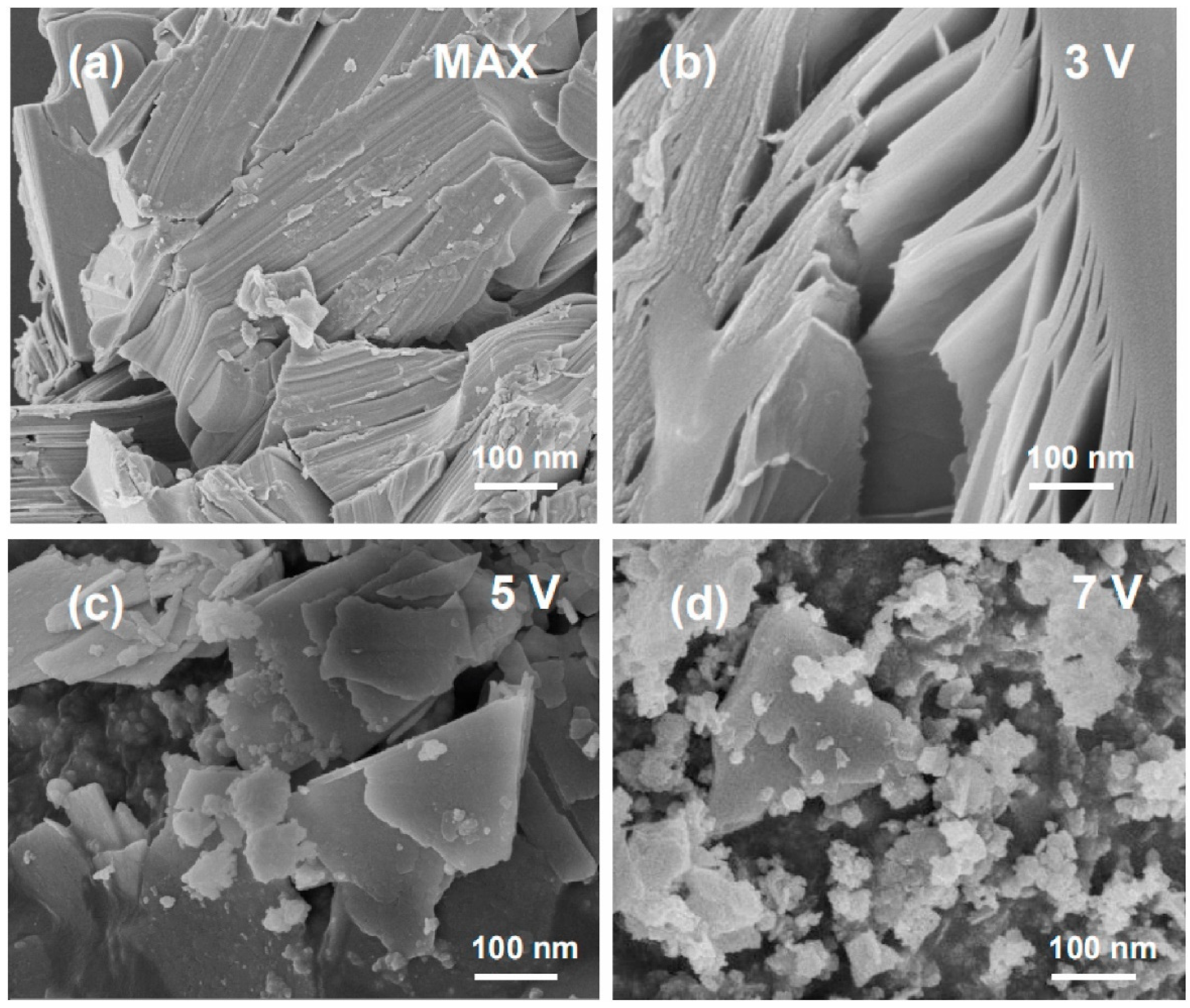
2.2.1. Fluoride Etching
2.2.2. Molten Salt Etching
2.2.3. Electrochemical Etching
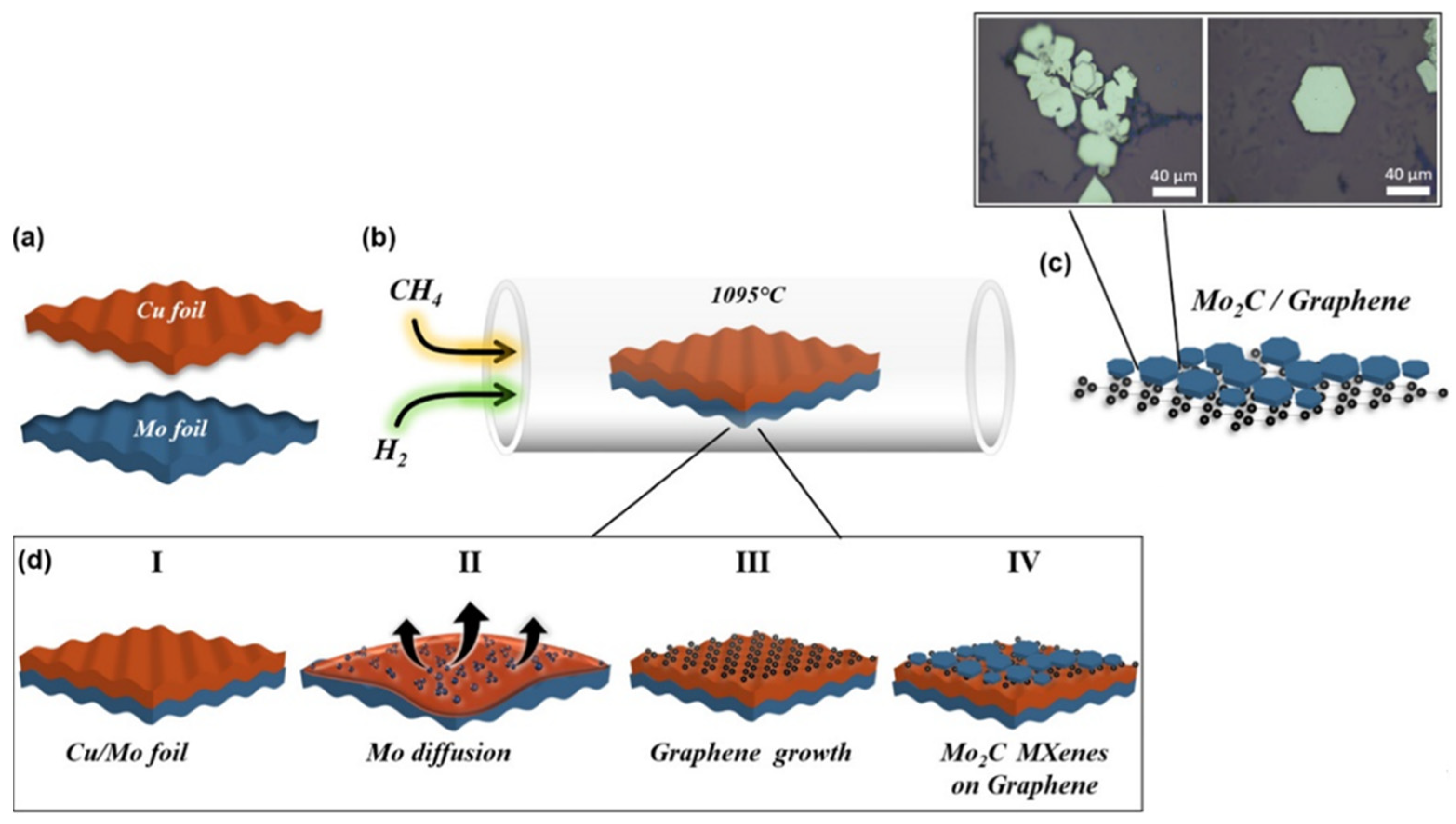
2.2.4. Chemical Vapor Deposition Synthesis
2.2.5. Fluoride and Acid-Free Etching
3. Properties of MXenes
3.1. Mechanical, Electrical, and Thermal Properties
3.2. Surface Chemistry and Hydrophilicity
4. Application of MXene in the Field of Tribology
4.1. Solid Lubricants
4.2. Lubricant Additives
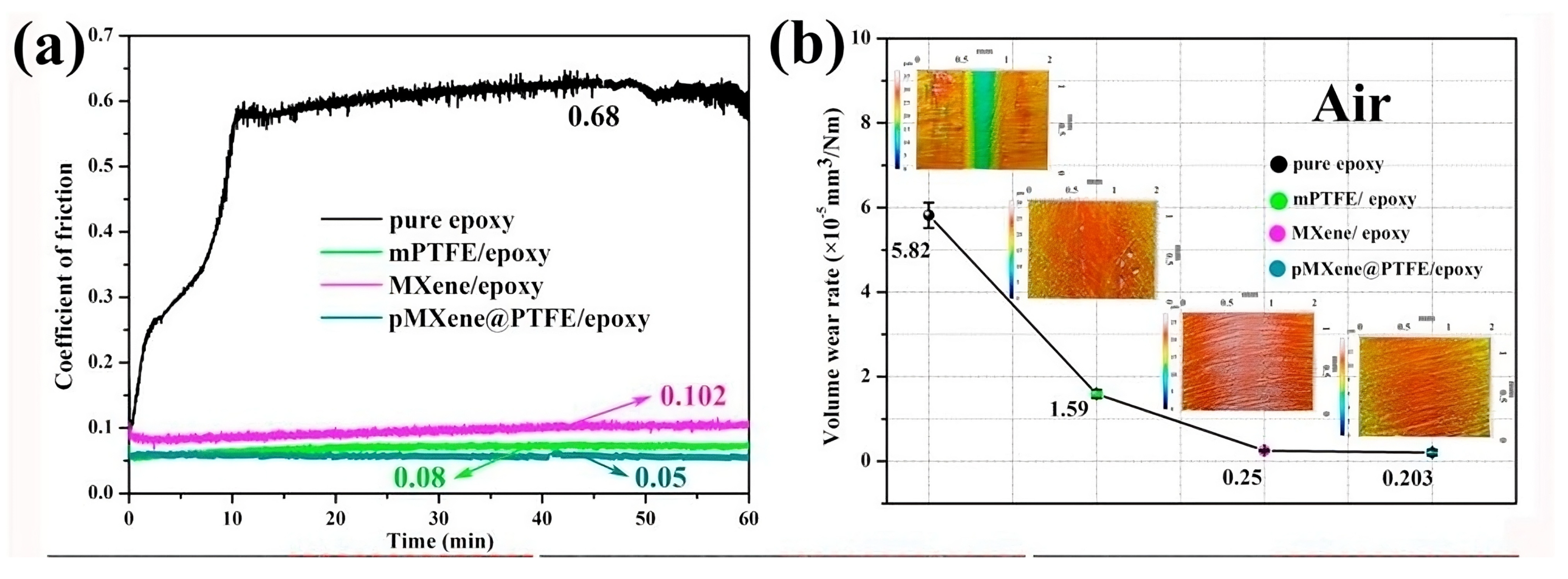
4.3. Coatings
4.4. Emerging Applications in Triboelectronics
5. Challenges, Opportunities, and Future Directions
5.1. Obstacles in Manufacturing and Usage
5.2. Safety and Environmental Factors
5.3. Opportunities and Future Directions
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- AhadiParsa, M.; Dehghani, A.; Ramezanzadeh, M.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Rising of MXenes: Novel 2D-Functionalized Nanomaterials as a New Milestone in Corrosion Science—A Critical Review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2022, 307, 102730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, M.; Mochalin, V.N.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. 25th Anniversary Article: MXenes: A New Family of Two-Dimensional Materials. Adv. Mater. 2014, 26, 992–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, Y.; Wu, X.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, H.-B.; Yu, Z.-Z. Highly Sensitive, Robust and Anisotropic MXene Aerogels for Efficient Broadband Microwave Absorption. Compos. Part. B Eng. 2020, 200, 108263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khazaei, M.; Mishra, A.; Venkataramanan, N.S.; Singh, A.K.; Yunoki, S. Recent Advances in MXenes: From Fundamentals to Applications. Curr. Opin. Solid. State Mater. Sci. 2019, 23, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenkranz, A.; Righi, M.C.; Sumant, A.V.; Anasori, B.; Mochalin, V.N. Perspectives of 2D MXene Tribology. Adv. Mater. 2023, 35, 2207757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, X.; Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, S. MXenes in Tribology: Current Status and Perspectives. Adv. Powder Mater. 2023, 2, 100092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, J.; Guo, X.; Xiao, J.; Li, X.; Chen, W.; Wu, W.; Liu, H.; Wang, Y.; Wu, M.; Wang, G. Nanoengineering of 2D MXene-Based Materials for Energy Storage Applications. Small 2021, 17, 1902085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Huang, Z.; Shuck, C.E.; Liang, G.; Gogotsi, Y.; Zhi, C. MXene Chemistry, Electrochemistry and Energy Storage Applications. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2022, 6, 389–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Z. MXene-Based Materials for Electrochemical Energy Storage. J. Energy Chem. 2018, 27, 73–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kumar, A.; Ebenso, E.E. MXenes and MXene-Based Nanomaterials for Corrosion Protection. Mater. Lett. 2023, 335, 133789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajmal, Z.; Qadeer, A.; Singh, K.; Mahmud, A.A.; Lakhan, M.N.; Pradeep, H.; Hussain, B.; Ullah, A.; Khan, H.R.; Ibrahim, E.H.; et al. A Comprehensive Review on MXenes for Various Applications. Appl. Energy 2025, 397, 126136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Web of Science Platform | Clarivate. Available online: https://clarivate.com/academia-government/scientific-and-academic-research/research-discovery-and-referencing/web-of-science/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Naguib, M.; Kurtoglu, M.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Niu, J.; Heon, M.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nanocrystals Produced by Exfoliation of Ti3AlC2. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 4248–4253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Decade of Discovery: A Review of MXenes, the Family of 2D Transition Metal Carbides and Nitrides. Available online: https://drexel.edu/news/in-the-news/2021/June/June-15-Gogotsi-Mohammadi-American-Ceramic-Society (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Rasool, K.; Pandey, R.P.; Rasheed, P.A.; Buczek, S.; Gogotsi, Y.; Mahmoud, K.A. Water Treatment and Environmental Remediation Applications of Two-Dimensional Metal Carbides (MXenes). Mater. Today 2019, 30, 80–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Fu, Y.; Mo, A. Multilayered Titanium Carbide MXene Film for Guided Bone Regeneration. Int. J. Nanomed. 2019, 14, 10091–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fei, M.; Lin, R.; Lu, Y.; Zhang, X.; Bian, R.; Cheng, J.; Luo, P.; Xu, C.; Cai, D. MXene-Reinforced Alumina Ceramic Composites. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 17206–17210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Gogotsi, Y. MXenes: Trends, Growth, and Future Directions. Graphene 2D Mater. 2022, 7, 75–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Anasori, B. The Rise of MXenes. ACS Nano 2019, 13, 8491–8494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmud, S.T.; Hasan, M.M.; Bain, S.; Rahman, S.T.; Rhaman, M.; Hossain, M.M.; Ordu, M. Multilayer MXene Heterostructures and Nanohybrids for Multifunctional Applications: A Review. ACS Mater. Lett. 2022, 4, 1174–1206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; Li, X.; Chen, Y.; Liu, N.; Du, Y.; Dou, S.; Jiang, L.; Cheng, Q. High-Strength Scalable MXene Films through Bridging-Induced Densification. Science 2021, 374, 96–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Ma, T.; Erdemir, A.; Li, Q. Tribology of Two-Dimensional Materials: From Mechanisms to Modulating Strategies. Mater. Today 2019, 26, 67–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androulidakis, C.; Zhang, K.; Robertson, M.; Tawfick, S. Tailoring the Mechanical Properties of 2D Materials and Heterostructures. 2D Mater. 2018, 5, 032005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solangi, N.H.; Karri, R.R.; Mubarak, N.M.; Mazari, S.A.; Azad, A.K. Emerging 2D MXenes as Next-Generation Materials for Energy Storage Applications. J. Energy Storage 2023, 70, 108004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogotsi, Y.; Huang, Q. MXenes: Two-Dimensional Building Blocks for Future Materials and Devices. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 5775–5780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Fan, R.; Zou, B.; Yan, J.; Shi, Q.; Guo, G. Roles of MXenes in Biomedical Applications: Recent Developments and Prospects. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2023, 21, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- From 2D Flake to Stable 3D Crystal: Researchers Demonstrate Potential of MXenes as Additives in Ultrahigh-Temperature Ceramics—The American Ceramic Society. Available online: https://ceramics.org/ceramic-tech-today/from-2d-flake-to-stable-3d-crystal-researchers-demonstrate-potential-of-mxenes-as-additives-in-ultrahigh-temperature-ceramics/ (accessed on 4 August 2025).
- Wang, Y.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y. Chemistry of Two-Dimensional MXene Nanosheets in Theranostic Nanomedicine. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, X.; Liu, H.; Xu, H.; Wu, X.; Han, X.; Kang, J.; Reddy, K.M. A Simple Approach to Synthesis Cr2CTx MXene for Efficient Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Mater. Today Energy 2021, 20, 100668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghidiu, M.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Zhao, M.-Q.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Conductive Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide ‘Clay’ with High Volumetric Capacitance. Nature 2014, 516, 78–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Naguib, M.; Ghidiu, M.; Pan, L.-M.; Gu, J.; Nanda, J.; Halim, J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Nb-Based M4C3 Solid Solutions (MXenes). J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2016, 99, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Zhou, A.; Chen, J.; Jia, J.; Zhou, W.; Wang, L.; Hu, Q. Preparation of Ti3C2 and Ti2C MXenes by Fluoride Salts Etching and Methane Adsorptive Properties. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 416, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Geng, W.-C.; Liu, C.; Gu, J.; Zhang, Z.; Tang, Y. Ultrahigh Areal Capacitance of Flexible MXene Electrodes: Electrostatic and Steric Effects of Terminations. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 8257–8265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Li, J.; Wang, Y.; Han, W.; Xu, S.; Lu, M.; Zhang, W.; Li, H. Surface Terminations of MXene: Synthesis, Characterization, and Properties. Symmetry 2022, 14, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, H.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Chai, Z.; Huang, Q. Layered Transition Metal Carbides/Nitrides: From Chemical Etching to Chemical Editing. Acc. Mater. Res. 2025, 6, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Wang, R.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, L.; Gao, X.; Zhou, B.; Hu, P.; Chen, Y. Ultrathin Molybdenum Carbide MXene with Fast Biodegradability for Highly Efficient Theory-Oriented Photonic Tumor Hyperthermia. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1901942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, A.; Yu, Y.; Jiang, F.; Wang, Y.; Mi, L.; Yu, Y.; Song, L. Fabrication and Thermal Stability of NH4HF2-Etched Ti3C2 MXene. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 6322–6328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C.; Zhao, X.; Xiong, Y.; Tang, Y.; Ma, X.; Tao, Q.; Sun, C.; Xu, W. A Review of Etching Methods of MXene and Applications of MXene Conductive Hydrogels. Eur. Polym. J. 2022, 167, 111063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbankowski, P.; Anasori, B.; Makaryan, T.; Er, D.; Kota, S.; Walsh, P.L.; Zhao, M.; Shenoy, V.B.; Barsoum, M.W.; Gogotsi, Y. Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Titanium Nitride Ti4N3 (MXene). Nanoscale 2016, 8, 11385–11391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruger, D.D.; García, H.; Primo, A. Molten Salt Derived MXenes: Synthesis and Applications. Adv. Sci. 2024, 11, 2307106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ming, F.; Liang, H.; Huang, G.; Bayhan, Z.; Alshareef, H.N. MXenes for Rechargeable Batteries Beyond the Lithium-Ion. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslam, M.K.; Niu, Y.; Xu, M. MXenes for Non-Lithium-Ion (Na, K, Ca, Mg, and Al) Batteries and Supercapacitors. Adv. Energy Mater. 2021, 11, 2000681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poonam; Sharma, K.; Arora, A.; Tripathi, S.K. Review of Supercapacitors: Materials and Devices. J. Energy Storage 2019, 21, 801–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, J. A Review of Electrode Materials for Electrochemical Supercapacitors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 797–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanati, S.; Morsali, A.; García, H. First-Row Transition Metal-Based Materials Derived from Bimetallic Metal–Organic Frameworks as Highly Efficient Electrocatalysts for Electrochemical Water Splitting. Energy Env. Sci. 2022, 15, 3119–3151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Zhang, P.; Wang, F.; Ricciardulli, A.G.; Lohe, M.R.; Blom, P.W.M.; Feng, X. Fluoride-Free Synthesis of Two-Dimensional Titanium Carbide (MXene) Using A Binary Aqueous System. Angew. Chem. 2018, 130, 15717–15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Mishra, A.; Mizuseki, H.; Lee, K.-R.; Singh, A.K. Mechanistic Insight into the Chemical Exfoliation and Functionalization of Ti3C2 MXene. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2016, 8, 24256–24264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.; Oh, M.S.; Cho, A.; Ryu, J.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kang, H.; Cho, S.-Y.; Im, S.G.; Kim, S.J.; Jung, H.-T. Simple Approach to Enhance Long-Term Environmental Stability of MXene Using Initiated Chemical Vapor Deposition Surface Coating. ACS Nano 2023, 17, 10898–10905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, L.; Guo, J.; Kang, N.; Ma, X.-L.; Cheng, H.-M.; Ren, W. Large-Area High-Quality 2D Ultrathin Mo2C Superconducting Crystals. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 1135–1141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, D.; Zhao, X.; Chen, Z.; Sun, W.; Fu, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Zhou, W.; Loh, K.P. Direct Synthesis of Large-Area 2D Mo2C on In Situ Grown Graphene. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravuri, S.; Wrobel, P.S.; Gorantla, S.; Bazioti, C.; Sunding, M.F.; Lis, K.; Jedrzejewski, R.; Sartori, S.; Diplas, S.; Gunnæs, A.E.; et al. High Yield and Wide Lateral Size Growth of α-Mo2 C: Exploring the Boundaries of CVD Growth of Bare MXene Analogues. Nanotechnology 2024, 35, 155601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alnoor, H.; Elsukova, A.; Palisaitis, J.; Persson, I.; Tseng, E.N.; Lu, J.; Hultman, L.; Persson, P.O.Å. Exploring MXenes and Their MAX Phase Precursors by Electron Microscopy. Mater. Today Adv. 2021, 9, 100123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Q.; Zhuang, W.; Attia, M.; Djugum, R.; Zhang, M. Recent Progress in Additive Manufacturing of Bulk MAX Phase Components: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 131, 30–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naguib, M.; Mashtalir, O.; Carle, J.; Presser, V.; Lu, J.; Hultman, L.; Gogotsi, Y.; Barsoum, M.W. Two-Dimensional Transition Metal Carbides. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 1322–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Yao, L.; Liu, Q.; Gu, J.; Luo, R.; Li, J.; Yan, X.; Wang, W.; Liu, P.; Chen, B.; et al. Fluorine-Free Synthesis of High-Purity Ti3C2Tx (T=OH, O) via Alkali Treatment. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2018, 57, 6115–6119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Lu, J.; Luo, K.; Li, Y.; Chang, K.; Chen, K.; Zhou, J.; Rosen, J.; Hultman, L.; Eklund, P.; et al. Element Replacement Approach by Reaction with Lewis Acidic Molten Salts to Synthesize Nanolaminated MAX Phases and MXenes. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 141, 4730–4737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arole, K.; Blivin, J.W.; Saha, S.; Holta, D.E.; Zhao, X.; Sarmah, A.; Cao, H.; Radovic, M.; Lutkenhaus, J.L.; Green, M.J. Water-Dispersible Ti3C2Tz MXene Nanosheets by Molten Salt Etching. iScience 2021, 24, 103403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.C.; Guan, X.; Zhang, T.; Lin, K.; Huang, Y.; Lei, L.; Georgantas, Y.; Gogotsi, Y.; Bissett, M.A.; Kinloch, I.A. The Fabrication of Ti3C2 and Ti3 CN MXenes by Electrochemical Etching. J. Mater. Chem. A 2024, 12, 25165–25175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, T.; Li, Y.; Wang, R.; Al-Hartomy, O.A.; Al-Ghamdi, A.; Wageh, S.; Luo, X.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H. Synthesis of Ti3C2Fx MXene with Controllable Fluorination by Electrochemical Etching for Lithium-Ion Batteries Applications. Ceram. Int. 2021, 47, 28642–28649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, Y.; Tian, Y.; Man, Q.; Shen, H.; Liu, C.; Xiong, S.; Feng, J. Fluorine- and Acid-Free Strategy toward Scalable Fabrication of Two-Dimensional MXenes for Sodium-Ion Batteries. Nano Lett. 2023, 23, 5217–5226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronchi, R.M.; Arantes, J.T.; Santos, S.F. Synthesis, Structure, Properties and Applications of MXenes: Current Status and Perspectives. Ceram. Int. 2019, 45, 18167–18188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palladino, D.L.; Baino, F. MXenes: Properties, Applications, and Potential in 3D Printing. Ceramics 2025, 8, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhari, N.K.; Jin, H.; Kim, B.; San Baek, D.; Joo, S.H.; Lee, K. MXene: An Emerging Two-Dimensional Material for Future Energy Conversion and Storage Applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 24564–24579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, I.; Amna, R.; Kalidasan, B.; Rani, G.M.; Bandi, H.; Venkateswarlu, S.; Khan, S.A.; Mohapatra, D.; Zhang, K. MXenes for Various Applications: Recent Trends and Future Aspects. SmartMat 2025, 6, e70012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilibana, M.P. Electrochemical Properties of MXenes and Applications. Adv. Sens. Energy Mater. 2023, 2, 100080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Jia, X.; Zhou, H.; Ren, S.; Han, D.; Li, S.; Gao, Z. Applications of MXenes in Wearable Sensing: Advances, Challenges, and Prospects. Mater. Today 2024, 75, 359–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mim, M.; Habib, K.; Farabi, S.N.; Ali, S.A.; Zaed, M.A.; Younas, M.; Rahman, S. MXene: A Roadmap to Sustainable Energy Management, Synthesis Routes, Stabilization, and Economic Assessment. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 32350–32393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandey, M.; Anju, C.; Praveen, B.V.S.; Dashan, A.; Verma, R.K.; Ramezanzadeh, B. Fabrication, Progress and Future Perspective of MXene/Polymeric Nano Composites for Electromagnetic Shielding Application—A Review. Compos. Part. Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2025, 190, 108682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, S.M.; Walczak, M.; Stefano, M.D.; Ruggiero, A.; Rosenkranz, A.; Marian, M. 2D Materials for Tribo-Corrosion and -Oxidation Protection: A Review. Adv. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2024, 331, 103243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Protyai, M.I.H.; Rashid, A.B. A Comprehensive Overview of Recent Progress in MXene-Based Polymer Composites: Their Fabrication Processes, Advanced Applications, and Prospects. Heliyon 2024, 10, e37030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yang, H.; Han, Z.; Bo, Z.; Yan, J.; Cen, K.; Ostrikov, K.K. MXene-Based Electrodes for Supercapacitor Energy Storage. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 2390–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, A.Y.S.; Awan, H.T.A.; Cheng, F.; Zhang, M.; Tan, M.T.T.; Manickam, S.; Khalid, M.; Muthoosamy, K. Recent Advances in the Use of MXenes for Photoelectrochemical Sensors. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 482, 148774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, M.; Li, J.; Ma, Z.; Pan, L.; Shi, Y. MXenes and Their Applications in Wearable Sensors. Front. Chem. 2020, 8-2020, 297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragimova, R.; Erhart, P.; Rinke, P.; Komsa, H.-P. Surface Functionalization of 2D MXenes: Trends in Distribution, Composition, and Electronic Properties. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 2377–2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; An, Y.; Xu, B. MXene-Based Materials for Advanced Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2022, 101, 107556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; An, Y.; Feng, J.; Qian, Y. MXenes and Their Derivatives for Advanced Aqueous Rechargeable Batteries. Mater. Today 2022, 52, 225–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Xu, L.; Lu, L.; Alhalili, Z.; Zhou, X. Thermal Properties of MXenes and Relevant Applications. ChemPhysChem 2022, 23, e202200203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Sun, D.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, B.; Hu, Q.; Zhou, A. Synthesis and Thermal Stability of Two-Dimensional Carbide MXene Ti3C2. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 2015, 191, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesterova, V.; Korostelev, V.; Klyukin, K. Unveiling the Role of Termination Groups in Stabilizing MXenes in Contact with Water. J. Phys. Chem. Lett. 2024, 15, 3698–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, B.; Bashir, T.; Zhang, H.; Ali, T.; Raza, S.; He, D.; Liu, Y.; Bai, J. Impact of Various 2D MXene Surface Terminating Groups in Energy Conversion. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 199, 114506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, J.L.; Hantanasirisakul, K.; Lang, A.C.; Anasori, B.; Pinto, D.; Pivak, Y.; van Omme, J.T.; May, S.J.; Gogotsi, Y.; Taheri, M.L. Control of MXenes’ Electronic Properties through Termination and Intercalation. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, T.; Ismail, S.A.; Wang, J.; Zhu, W.; Zhao, J.; Gao, L. MXene Terminating Groups O, -F or -OH, -F or O, -OH, -F, or O, -OH, -Cl? J. Energy Chem. 2023, 76, 90–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Yu, B.; Zhu, J.; Li, K.; Tian, S. Hierarchical ZnO/MXene (Nb2C and V2C) Heterostructure with Efficient Electron Transfer for Enhanced Photocatalytic Activity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2022, 590, 153095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Björk, J.; Rosen, J. Functionalizing MXenes by Tailoring Surface Terminations in Different Chemical Environments. Chem. Mater. 2021, 33, 9108–9118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, R.K.; Sarkar, J.; Verma, K.; Chianella, I.; Goel, S.; Nezhad, H.Y. Exploring Transformative and Multifunctional Potential of MXenes in 2D Materials for Next-Generation Technology. Open Ceram. 2024, 18, 100596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Y.; Zhang, M.; Qin, J.; Ma, X.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Hydrophilicity-Dependent Distinct Frictional Behaviors of Different Modified MXene Nanosheets. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 13664–13671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Guo, Y.; Wang, D.; Xu, Q. Nano Friction and Adhesion Properties on Ti3C2 and Nb2C MXene Studied by AFM. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berman, D.; Deshmukh, S.A.; Sankaranarayanan, S.K.R.S.; Erdemir, A.; Sumant, A.V. Extraordinary Macroscale Wear Resistance of One Atom Thick Graphene Layer. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 6640–6646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adomaviciute-Grabusove, S.; Popov, A.; Ramanavicius, S.; Sablinskas, V.; Shevchuk, K.; Gogotsi, O.; Baginskiy, I.; Gogotsi, Y.; Ramanavicius, A. Monitoring Ti3C2Tx MXene Degradation Pathways Using Raman Spectroscopy. ACS Nano 2024, 18, 13184–13195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekhirev, M.; Shuck, C.E.; Sarycheva, A.; Gogotsi, Y. Characterization of MXenes at Every Step, from Their Precursors to Single Flakes and Assembled Films. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 120, 100757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarycheva, A.; Gogotsi, Y. Raman Spectroscopy Analysis of the Structure and Surface Chemistry of Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chem. Mater. 2020, 32, 3480–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Chen, Q.; Li, P.; Zhou, A.; Cao, X.; Hu, Q. Preparation, Mechanical and Anti-Friction Performance of MXene/Polymer Composites. Mater. Des. 2016, 92, 682–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wang, T. MXene-Al2O3 Synergize to Reduce Friction and Wear on Epoxy-Steel Contacts Lubricated with Ultra-Low Sulfur Diesel. Tribol. Int. 2021, 153, 106588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Yang, G.; Hou, K.; Wang, H.; Wang, N.; Yang, S.; Wang, J. Environmentally-Adaptive Epoxy Lubricating Coating Using Self-Assembled pMXene@polytetrafluoroethylene Core-Shell Hybrid as Novel Additive. Carbon. 2021, 184, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Li, S.; Zhang, J.; Chang, Q.; Yu, W.; Zhou, Y. Mechanical Properties and Frictional Resistance of Al Composites Reinforced with Ti3C2Tx MXene. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 996–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Han, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, C. Fabrication and Assessment of Dry Sliding Behavior of Ti3C2Tx-MXene Reinforced Nickel Aluminide Composites. Tribol. Int. 2024, 200, 110131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, T.; Guan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, B.; Shen, X. Improved Tribological and Thermo-mechanical Properties of Epoxy Resin with Micro-nano Structured ZrO2/Ti3C2 Particles. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2021, 138, 51209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Z.; Shen, X.; Wang, T.; Yang, Y.; Yi, J.; Cao, M.; Shen, J.; Xiao, Y.; Guan, J.; Jiang, X.; et al. Investigation on Tribological and Thermo-Mechanical Properties of Ti3C2 Nanosheets/Epoxy Nanocomposites. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 29184–29191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Qi, H.; Lei, Y.; Yu, J.; Guo, B.; Zhang, D. Ti3C2 MXene Induced High Tribological Performance of Polyimide/Polyurea Copolymer at a Wide Temperature Range. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2023, 608, 155157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, L.; Xu, Q.; Meng, C.; Lei, S.; Zhang, G.; Tang, M.; Zhai, W.; Yu, H.; Liu, X.; Du, C.-F. Achieving the Ultra-Low Friction and Wear Rate of PEEK-PTFE Composites by Ti3C2Tx MXene Reinforcement. Tribol. Int. 2024, 199, 110030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, T.; Li, W.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Ti3C2Tx MXenes—An Effective and Long-Storable Oil Lubricant Additive. Tribol. Int. 2023, 180, 108273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Tang, H.; Shi, X.; Xue, Y.; Huang, Q. Effect of Ti3C2 MXenes Additive on the Tribological Properties of Lithium Grease at Different Temperatures. Wear 2023, 526–527, 204953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Wang, X.; Zhao, L.; Yang, S.; Zhang, X. Synergistic Tribological Effects of Ti3C2Tx MXene and ZDDP under Simple Grafting Strategies for Efficient Lubrication. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 59096–59108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Yang, J.; Dou, M.; Zou, S.; Wei, L.; Huang, F. Modified Ti3C2TX MXene/GO Nanohybrids: An Efficient Lubricating Additive for Tribological Applications. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2024, 49, 10349–10361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xue, S.; Wang, T.; Liu, S.; Ye, Q.; Zhou, F.; Liu, W. Core-Rim Structured MXene@SiO2 Composites as Oil-Based Additives for Enhanced Tribological Properties. Friction 2024, 12, 1728–1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Liu, Z.; Chen, X.; Dou, X.; Ye, Q.; Liu, X. Synergistic Tribological Performance of Ti3C2Tx MXene Functionalized with Ionic Liquids. Tribol. Int. 2024, 194, 109526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, W.; Li, T.; Fang, Z.; Li, W.; Tang, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Qiao, Z. Ti3C2Tx MXenes Modified with Dodecylphosphonic Acid as an Effective Lubricant Additive. Tribol. Int. 2023, 186, 108565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marian, M.; Song, G.C.; Wang, B.; Fuenzalida, V.M.; Krauß, S.; Merle, B.; Tremmel, S.; Wartzack, S.; Yu, J.; Rosenkranz, A. Effective Usage of 2D MXene Nanosheets as Solid Lubricant—Influence of Contact Pressure and Relative Humidity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 531, 147311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Q.; Sun, S.; Gao, S.; Chen, J.; Zhang, F. MXene Coatings Based on Electrophoretic Deposition for the High-Temperature Friction Reduction of Graphite for Mechanical Seal Pairs. Coatings 2024, 14, 1567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wicklein, B.; Valurouthu, G.; Yoon, H.; Yoo, H.; Ponnan, S.; Mahato, M.; Kim, J.; Ali, S.S.; Park, J.Y.; Gogotsi, Y.; et al. Influence of MXene Composition on Triboelectricity of MXene-Alginate Nanocomposites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2024, 16, 23948–23959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y.; Mallineni, S.S.K.; Maleski, K.; Behlow, H.; Mochalin, V.N.; Rao, A.M.; Gogotsi, Y.; Podila, R. Metallic MXenes: A New Family of Materials for Flexible Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2018, 44, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, S.; Kim, J.-N.; Oh, S.; Kim, J.; Ahn, C.W.; Oh, I.-K. Ti3C2Tx MXene for Wearable Energy Devices: Supercapacitors and Triboelectric Nanogenerators. APL Mater. 2020, 8, 110701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pabba, D.P.; Satthiyaraju, M.; Ramasdoss, A.; Sakthivel, P.; Chidhambaram, N.; Dhanabalan, S.; Abarzúa, C.V.; Morel, M.J.; Udayabhaskar, R.; Mangalaraja, R.V.; et al. MXene-Based Nanocomposites for Piezoelectric and Triboelectric Energy Harvesting Applications. Micromachines 2023, 14, 1273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kedambaimoole, V.; Harsh, K.; Rajanna, K.; Sen, P.; Nayak, M.M.; Kumar, S. MXene Wearables: Properties, Fabrication Strategies, Sensing Mechanism and Applications. Mater. Adv. 2022, 3, 3784–3808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghorbanzadeh, S.; Zhang, W. Advances in MXene-Based Triboelectric Nanogenerators. Nano Energy 2024, 125, 109558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jussambayev, M.; Shakenov, K.; Sultakhan, S.; Zhantikeyev, U.; Askaruly, K.; Toshtay, K.; Azat, S. MXenes for Sustainable Energy: A Comprehensive Review on Conservation and Storage Applications. Carbon. Trends 2025, 19, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marquez, K.P.; Sisican, K.M.D.; Ibabao, R.P.; Malenab, R.A.J.; Judicpa, M.A.N.; Henderson, L.; Zhang, J.; Usman, K.A.S.; Razal, J.M. Understanding the Chemical Degradation of Ti3C2Tx MXene Dispersions: A Chronological Analysis. Small Sci. 2024, 4, 2400150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hansen, S.F.; Nielsen, M.B.; Skjolding, L.M.; Kaur, J.; Desivyana, N.; Hermansson, F.; Bird, J.; Barg, S.; Khort, A.; Odnevall, I.; et al. Maximizing the Safety and Sustainability of MXenes. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 31030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oyehan, T.A.; Salami, B.A.; Abdulrasheed, A.A.; Hambali, H.U.; Gbadamosi, A.; Valsami-Jones, E.; Saleh, T.A. MXenes: Synthesis, Properties, and Applications for Sustainable Energy and Environment. Appl. Mater. Today 2023, 35, 101993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S.A.; Habib, K.; Zaed, M.A.; Saidur, R. Cost-Effective Synthesis of Vanadium Carbide MXene from Recycled Waste Precursors for Phase Change Material Applications in Heat Sink Cooling. Results Eng. 2025, 26, 105598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Zhu, J.; Tong, H.; Zou, R. Advanced Perspectives on MXene Composite Nanomaterials: Types Synthetic Methods, Thermal Energy Utilization and 3D-Printed Techniques. iScience 2023, 26, 105824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anasori, B.; Lukatskaya, M.R.; Gogotsi, Y. 2D Metal Carbides and Nitrides (MXenes) for Energy Storage. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 16098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Ma, H.; Li, C. Host–Guest Intercalation Chemistry in MXenes and Its Implications for Practical Applications. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 15502–15537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, D.; Sun, N.; Chen, L.; Bu, J.; Jiang, C. Piezoelectricity in Monolayer and Multilayer Ti3C2Tx MXenes: Implications for Piezoelectric Devices. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2022, 5, 1034–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishna Paul, T.; Parvez, M.S.; Mashfik Ahmed, C. Recent Progress and Prospects of MXene/Cellulose-Based Composite Electrodes: A Sustainable Pathway towards Supercapacitor Application. ChemElectroChem 2024, 11, e202300435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antony Jose, S.; Cowan, N.; Davidson, M.; Godina, G.; Smith, I.; Xin, J.; Menezes, P.L. A Comprehensive Review on Cellulose Nanofibers, Nanomaterials, and Composites: Manufacturing, Properties, and Applications. Nanomaterials 2025, 15, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iqbal, A.; Kwon, J.; Hassan, T.; Park, S.W.; Lee, W.-H.; Oh, J.-M.; Hong, J.; Lee, J.; Naqvi, S.M.; Zafar, U.; et al. Environmentally Stable and Highly Crystalline MXenes for Multispectral Electromagnetic Shielding up to Millimeter Waves. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2025, 35, 2409346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, G.P.; Soon, C.F.; Ma, N.L.; Morsin, M.; Nayan, N.; Ahmad, M.K.; Tee, K.S. Cytotoxicity of MXene-Based Nanomaterials for Biomedical Applications: A Mini Review. Environ. Res. 2021, 201, 111592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Dai, X.; Feng, W.; Chen, Y. Biomedical Applications of MXenes: From Nanomedicine to Biomaterials. Acc. Mater. Res. 2022, 3, 785–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, I.; Sayed, M.; Saeed, T.; Rehman, F.; Naeem, A.; Gul, S.; Khan, Q.; Naz, K.; ur Rehman, M. Unveiling Cutting-Edge Progress in the Fundamentals of MXene: Synthesis Strategies, Energy and Bio-Environmental Applications. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2024, 511, 215870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, W.; Liu, H.; Ding, H.; Yan, Y.; Chen, R. Influencing Factors on Synthesis and Properties of MXene: A Review. Processes 2022, 10, 1744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amani, A.M.; Abbasi, M.; Najdian, A.; Mohamadpour, F.; Kasaee, S.R.; Kamyab, H.; Chelliapan, S.; Ardeshiri, H.; Tayebi, L.; Vafa, E.; et al. A Potentially Fruitful Path toward a Cleaner and Safer Environment: MXenes Uses in Environmental Remediation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 297, 118222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dmytriv, T.; Lushchak, V. Potential Biosafety of Mxenes: Stability, Biodegradability, Toxicity and Biocompatibility. Chem. Rec. N. Y. N. 2024, 24, e202300338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jangra, S.; Kumar, B.; Sharma, J.; Sengupta, S.; Das, S.; Brajpuriya, R.K.; Ohlan, A.; Mishra, Y.K.; Goyat, M.S. A Review on Overcoming Challenges and Pioneering Advances: MXene-Based Materials for Energy Storage Applications. J. Energy Storage 2024, 101, 113810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kumari, N.; Seo, Y. MXenes: Versatile 2D Materials with Tailored Surface Chemistry and Diverse Applications. J. Energy Chem. 2024, 90, 253–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


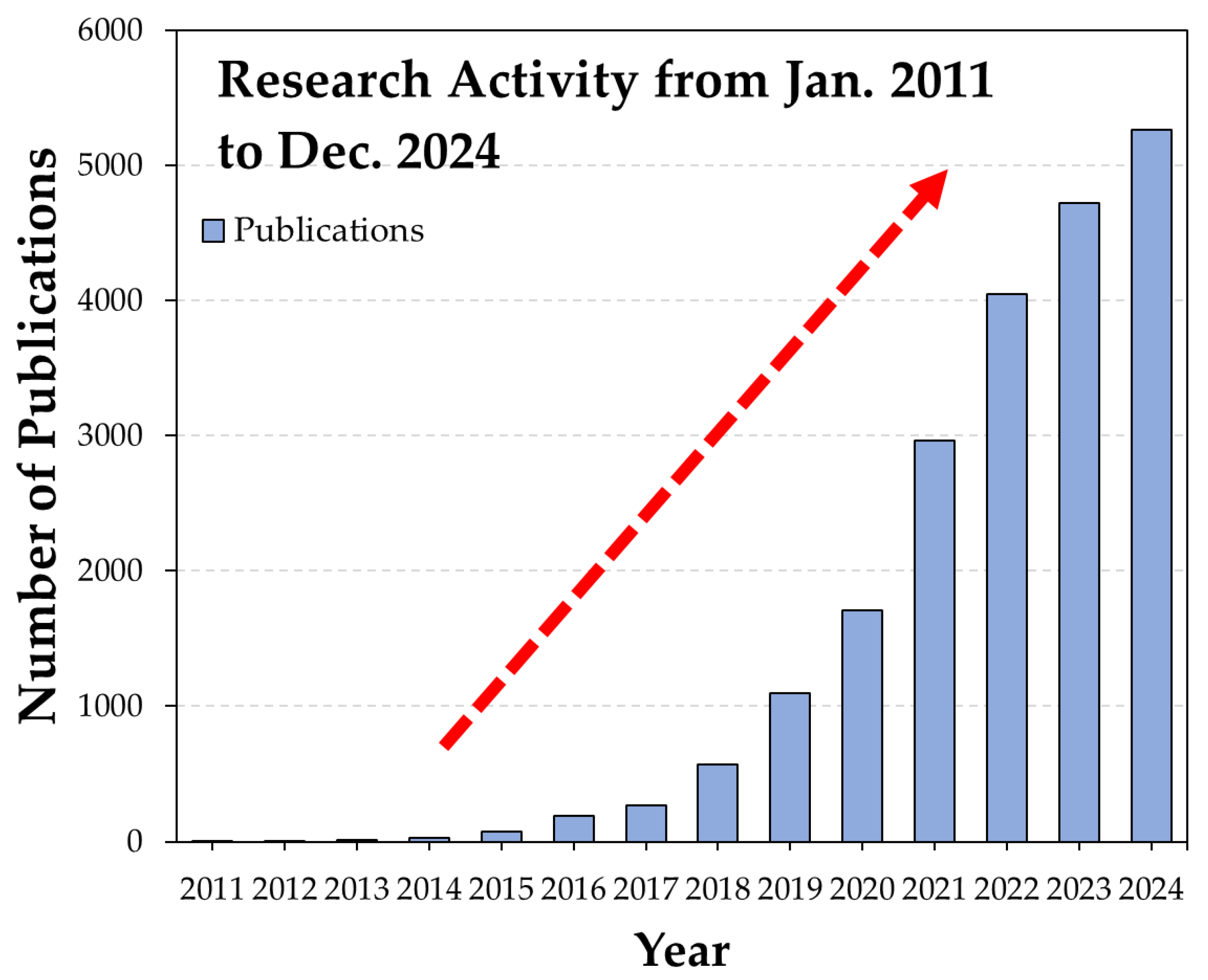
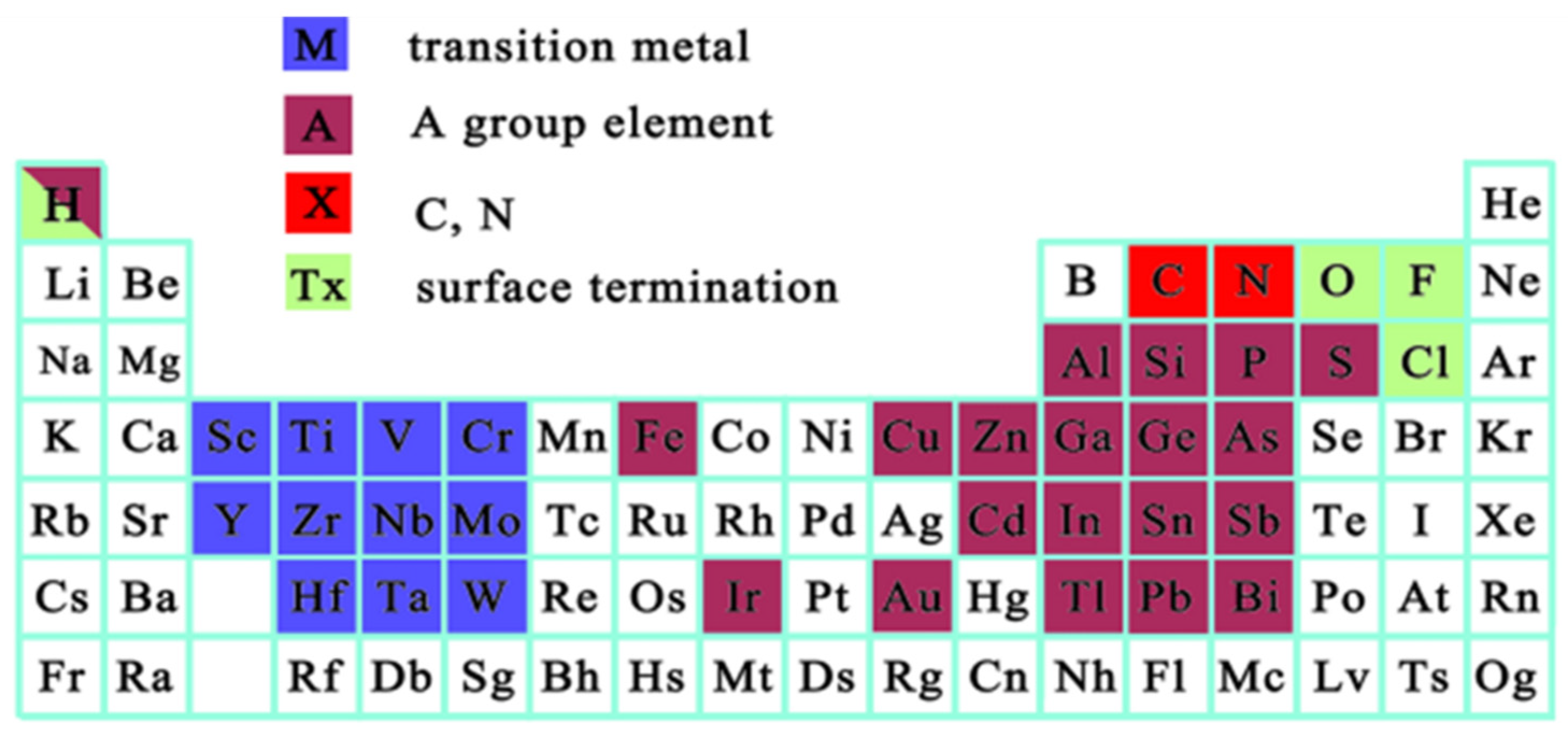
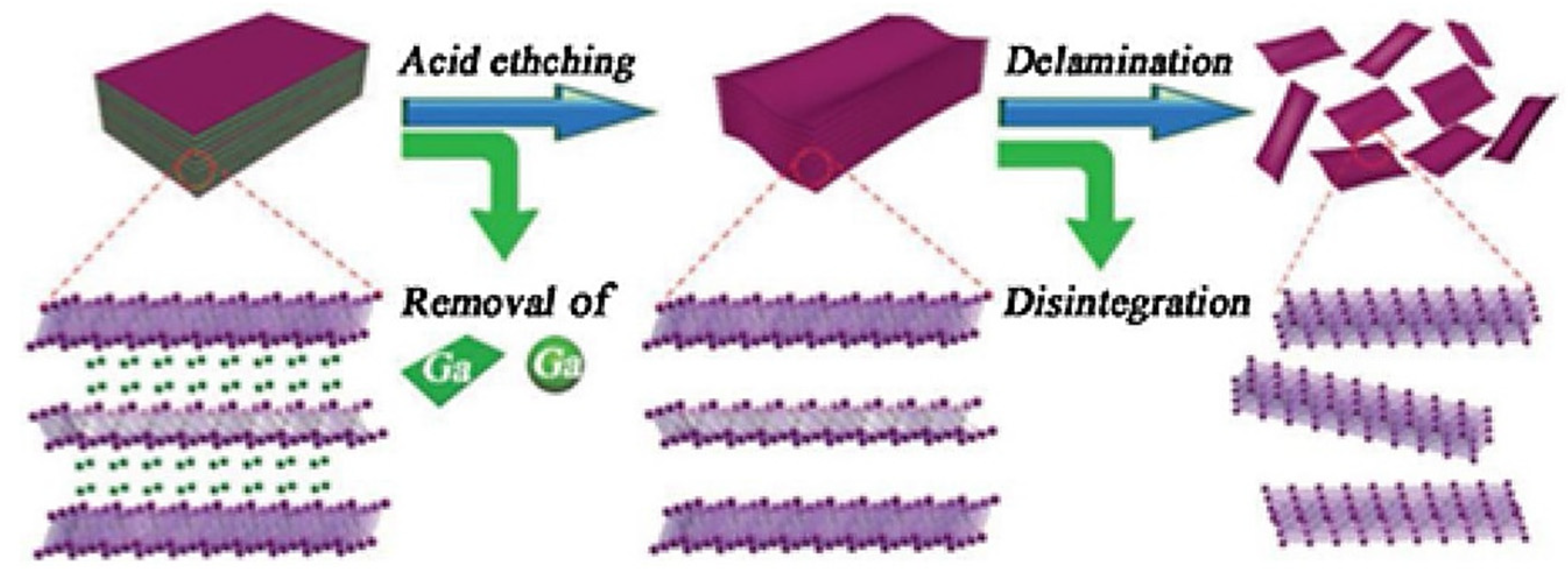

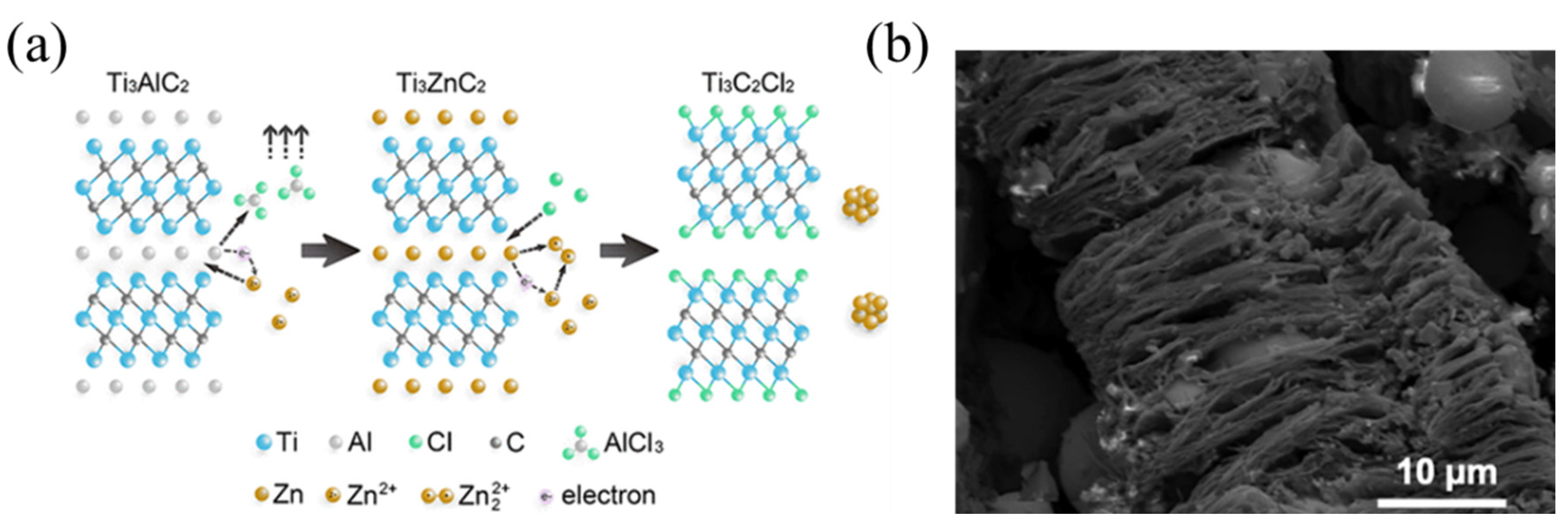


| Database Used for the Search | Web of Science |
|---|---|
| Keywords Used for the Search | (1) MXene |
| (2) MXenes | |
| (3) MAX Phase Etching | |
| (4) MXene Synthesis | |
| (5) MXene Fabrication | |
| (6) MXene Properties | |
| Timespan of Search | January 2011–December 2024 |
| Language | Any |
| Types of Research | Review and Research Journal Publications, Books, Book Chapters, and Patents |
| MXene Manufacturing Route | Summarization | Parameters That Control Structural Features | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| HF Etching | This process consists of selectively dissolving the A element of the MAX phase through an HF solution | Parameters include etching time, the concentration of HF, and the operational temperature | [25,27,28,29,30,31,32,33,34,35,36,37] |
| Molten Salt Etching | This process consists of utilizing molten salts to chemically react with the A element of the MAX phase | Parameters include the chemistry of the molten salts, the temperature of the molten salts, and the submersion time | [38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45] |
| Electrochemical Etching | This process consists of inducing a chemical reaction with the MAX phase and selectively removing the A element | Parameters include the electrolyte solution, etching time, current density, and voltage | [37,40,46,47] |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | This process consists of using CVD to allow for metal precursors to react with gases to form the MXenes | Parameters include operational temperature, the gas flow rate, the concentration of the precursors, and the operational pressure | [38,48,49,50,51] |
| Synthesis Method | Yield | Scalability | Environmental Impact | Cost | Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HF Etching | High | Moderate | High (toxic HF handling) | Low to moderate | Widely used, high-quality MXenes | Hazardous chemicals, disposal issues |
| Molten Salt Etching | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Moderate | Fluoride-free; accordion-like morphology | Requires high temperature; salt recovery needed |
| Electrochemical Etching | Moderate | High | Low | Low | Environmentally friendly; tunable structure | Longer processing time; uniformity issues |
| Chemical Vapor Deposition | Variable | Low to moderate | Low | High | Fluoride-free; direct synthesis of 2D sheets | Expensive setup; not yet widely adopted |
| Fluoride and Acid-Free Etching | Moderate | High | Very low | Low | Green, scalable, safe | Under development, limited types |
| Termination | Reactivity Characteristics | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| -O | Lewis acidic, stable | Oxidation reactions |
| -OH | Bronsted basic, hydrophilic | Biomolecule adsorption |
| -F | Electron-withdrawing, hydrophobic | Fluorination reactions |
| Mixed | Tunable acid-based properties | Multifunctional catalysis |
| MXene Material | Matrix | Synthesis Method | Tribological Testing | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx (3 wt.%) | Aluminum | Pressureless sintering followed by extrusion | COF ~0.2 at 5 N normal load against GCr15 steel ball (~2.5 times reduction) | [95] |
| Ti3C2Tx (15%) | Ni3Al | Sparks plasma sintering | COF = ~0.5 (29% reduction) and wear rate = 1.64 × 10−4 mm3/m (93% reduction) | [96] |
| Ti3C2 (2 wt.%) | UHMWPE | Pressure molded | COF~0.13 (31% reduction) | [92] |
| Ti3C2Tx (3 wt.%) by HF leaching method | Epoxy + 3% Al2O3 | Curing | COF ~0.02 against steel (COF of epoxy + 3% Al2O3 = 0.07 | [93] |
| Ti3C2Tx (0.5 wt.%) | Epoxy | Curing | COF ~0.65 (28% reduction) and wear rate reduced by 79% | [97] |
| Ti3C2Tx (1 wt.%) by HF leaching with ultrasound-assisted delamination | Epoxy | Curing | COF = 0.65 (26% less) and wear 6.61 × 10−14 m3/N·m (63% lesser) | [98] |
| Ti3C2Tx coated on PTFE particles | Epoxy | Curing | [94] |
| MXene | Base Lubricant | Result | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ti3C2Tx + N, N-dimethylformamide | 5750 oil | Reduction in wear rate by 92% under 100 N against GCr15 bearing steel | [101] |
| Ti3C2 (2 wt.%) | Lithium grease | COF = 0.045 and wear rate = 5.8 × 10−8 mm3N−1m−1 reduced by 56.7% and 26.6% compared to MoS2 lithium grease for 42CrMo steel and E52100 steel tribo pair | [102] |
| hexadecylphosphonic acid grafted Ti3C2Tx + zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP) | Polyalkylene glycol | COF ~0.1 (33% reduction) | [103] |
| tetradecylphosphonic acid (TDPA) modified Ti3C2TX + Graphene oxide | Polyalphaolefins base oil | COF = 0.09 (54% reduction) and wear rate = 4.4 × 10–6 mm3/Nm (90.0% reduction) for steel to steel tribo pair | [104] |
| Ti3C2Tx with in situ grown SiO2 | Mineral oil (500 SN) | COF = 0.1 (44% reduction), and wear reduced by 73% | [105] |
| Ti3C2Tx grafted on ionic liquid (1-aminoethyl-3-methylimidazolium bromide [NH2C2MIm] [Br]) | Mineral oil (500 SN) | COF = 0.12 (40% reduction) and 81% reduction in wear volume for AISI 52100 steel tribo pair | [106] |
| Ti3C2Tx MXenes modified with dodecyl phosphonic acid | OSP-46 | COF = 0.09 (24% reduction) and 85% reduction in wear rate for AISI-52100 GCr15 steel tribo pair | [107] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antony Jose, S.; Ralls, A.M.; Kasar, A.K.; Antonitsch, A.; Neri, D.C.; Image, J.; Meyer, K.; Zhang, G.; Menezes, P.L. MXenes: Manufacturing, Properties, and Tribological Insights. Materials 2025, 18, 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173927
Antony Jose S, Ralls AM, Kasar AK, Antonitsch A, Neri DC, Image J, Meyer K, Zhang G, Menezes PL. MXenes: Manufacturing, Properties, and Tribological Insights. Materials. 2025; 18(17):3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173927
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntony Jose, Subin, Alessandro M. Ralls, Ashish K. Kasar, Alexander Antonitsch, Daniel Cerrillo Neri, Jaybon Image, Kevin Meyer, Grace Zhang, and Pradeep L. Menezes. 2025. "MXenes: Manufacturing, Properties, and Tribological Insights" Materials 18, no. 17: 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173927
APA StyleAntony Jose, S., Ralls, A. M., Kasar, A. K., Antonitsch, A., Neri, D. C., Image, J., Meyer, K., Zhang, G., & Menezes, P. L. (2025). MXenes: Manufacturing, Properties, and Tribological Insights. Materials, 18(17), 3927. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18173927








