Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel 310 Manufactured via WAAM
Abstract
1. Introduction
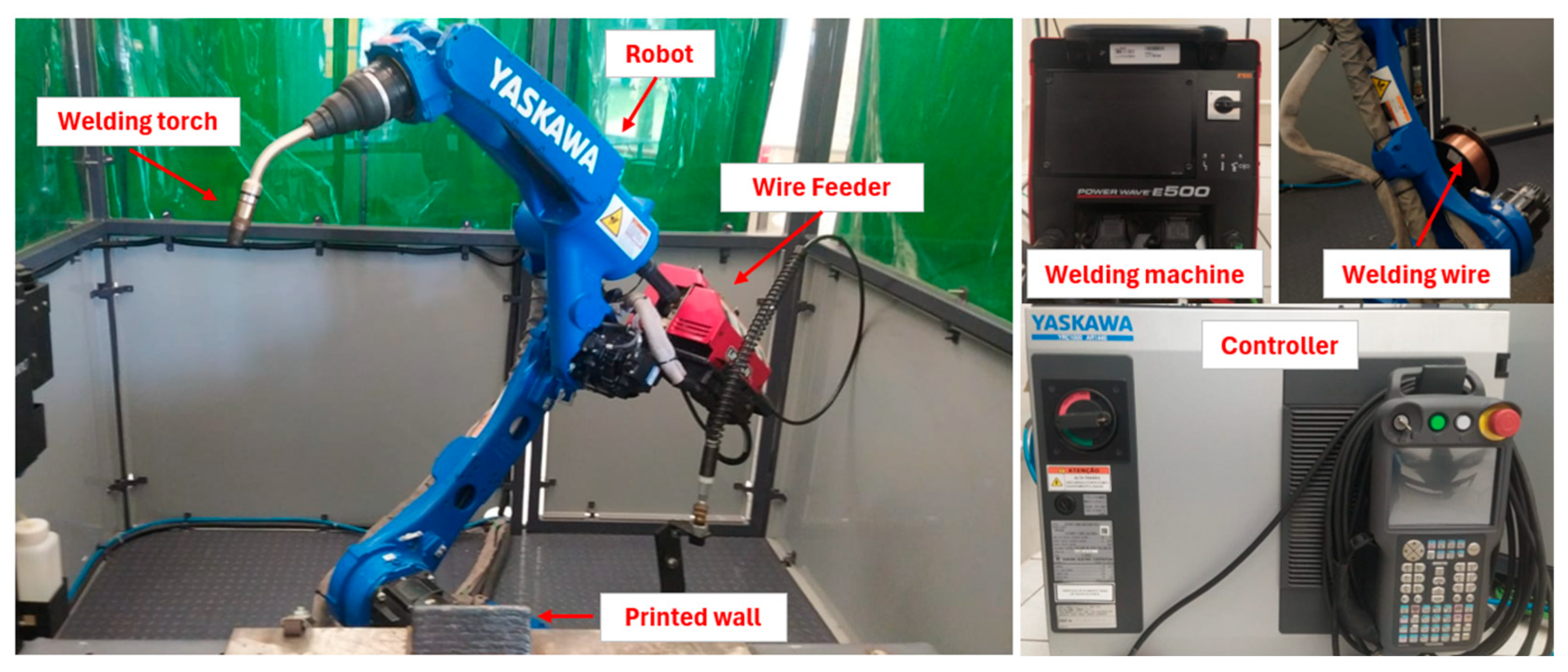
2. Experimental Procedure
- V = voltage (V).
- A = current (A).
- Travel speed (mm/min).
- Result in joules per millimeter (J/mm).
- Area = = cross-sectional area of the wire (mm2).
- d = wire diameter (mm).
- vw = wire feed speed (mm/min).
- ρ = density of stainless steel 310 = (7.9 g/cm3 or 0.0079 g/mm3) [26].
- m = deposition rate (g/min).
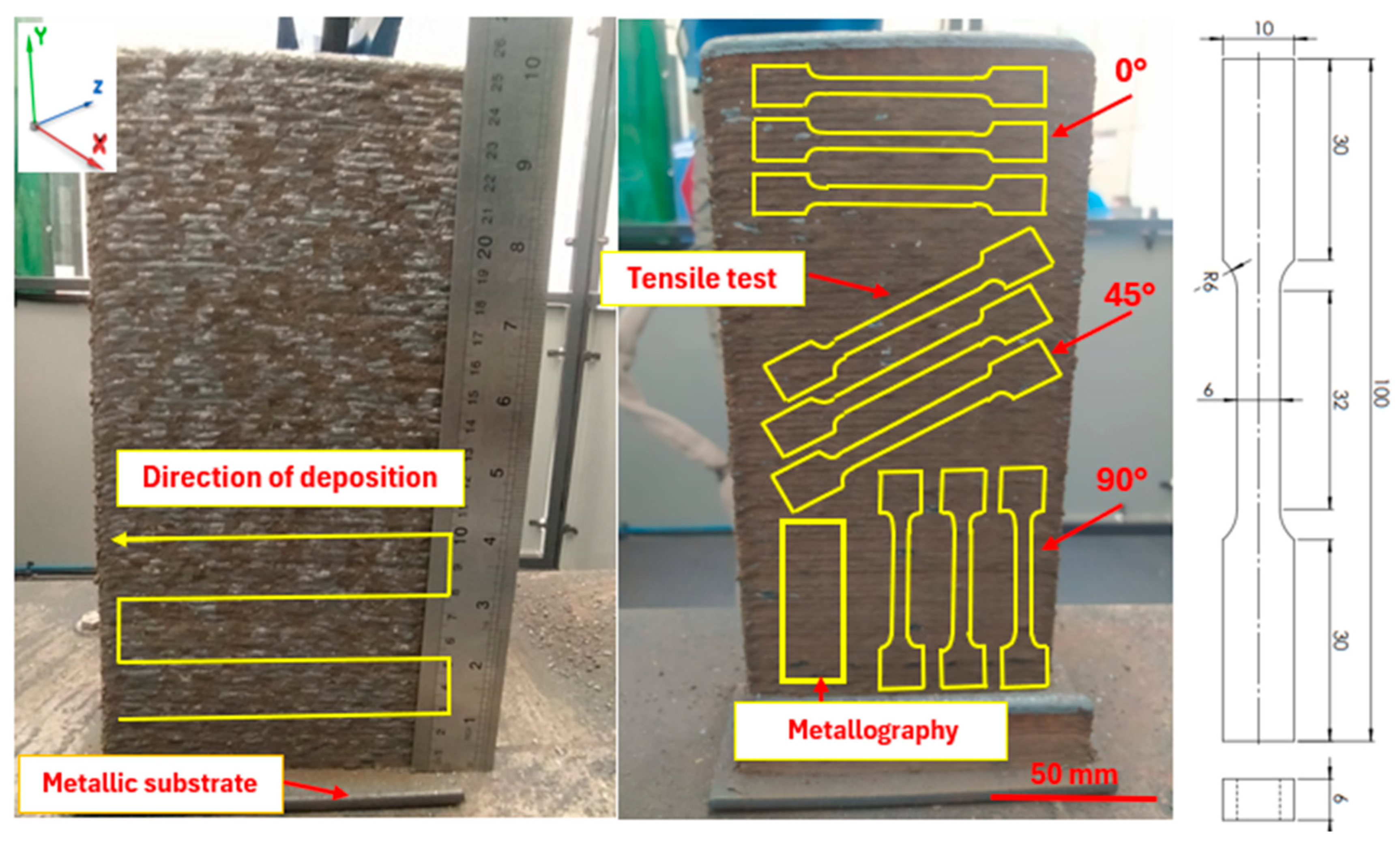
2.1. Microstructural Characterization
2.2. Tensile Testing
2.3. Optical Emission Spectrometry (OES)
2.4. Characterization of Pore Distribution
3. Results and Discussion
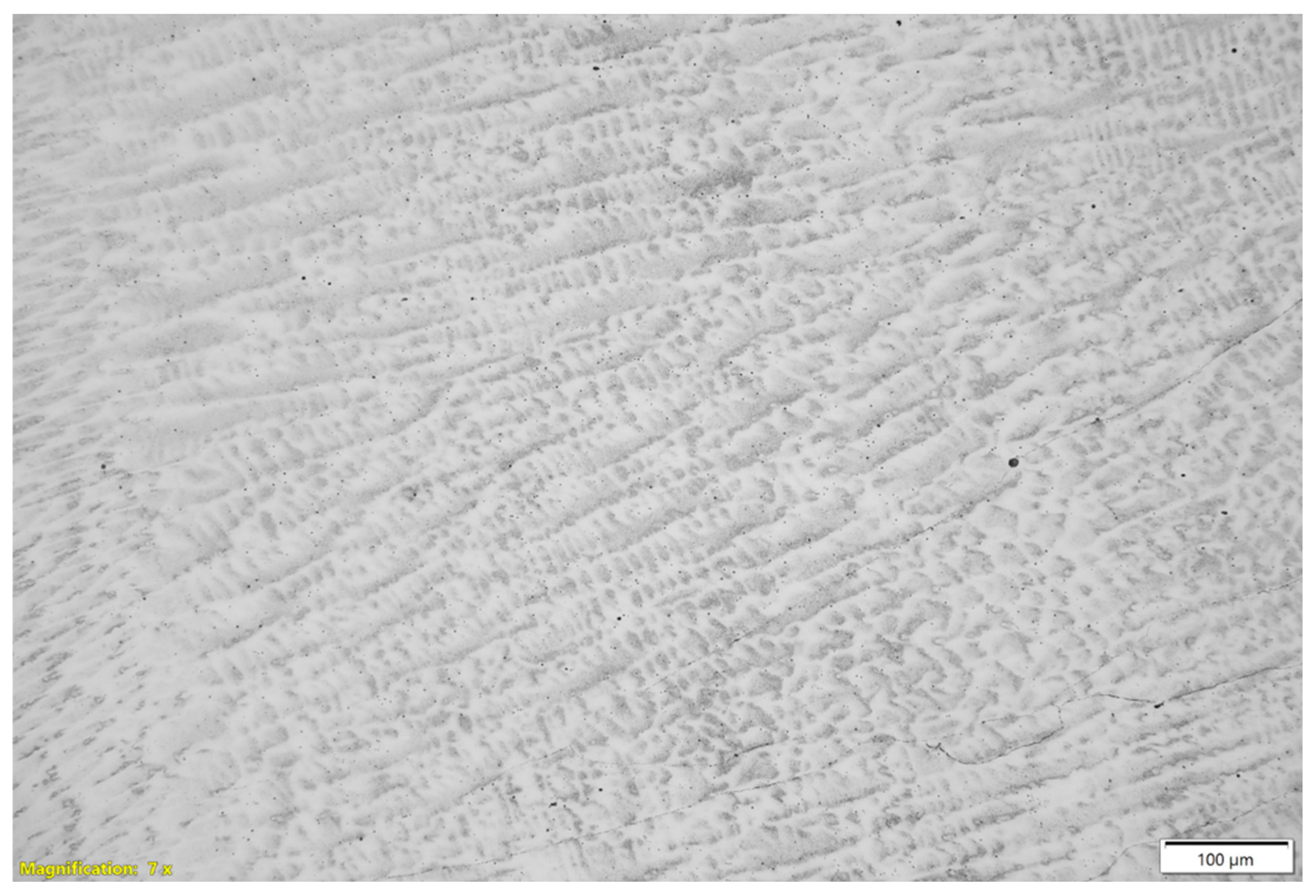
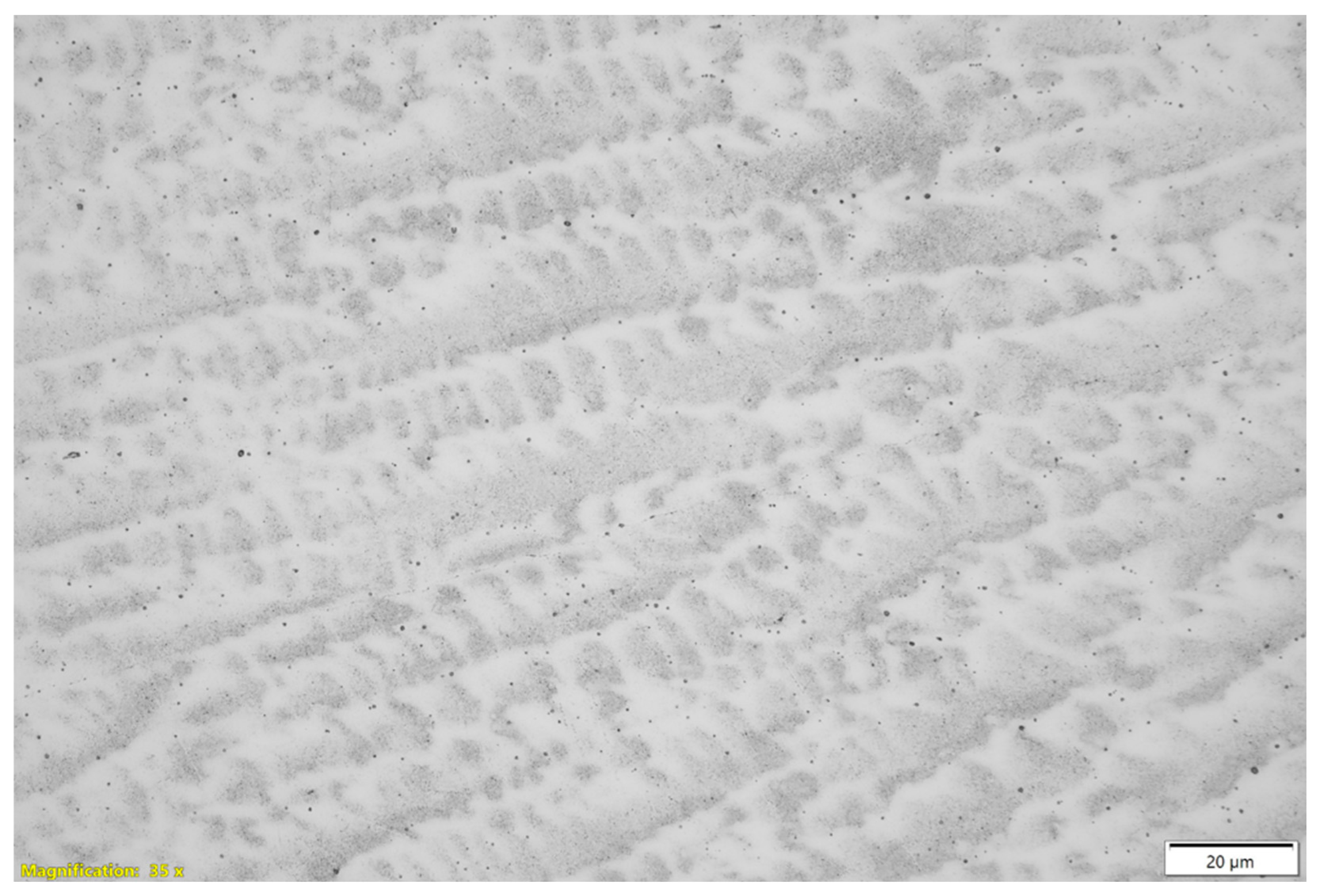
3.1. Metallographic Analysis Using an Optical Microscope on 310 Austenitic Steel
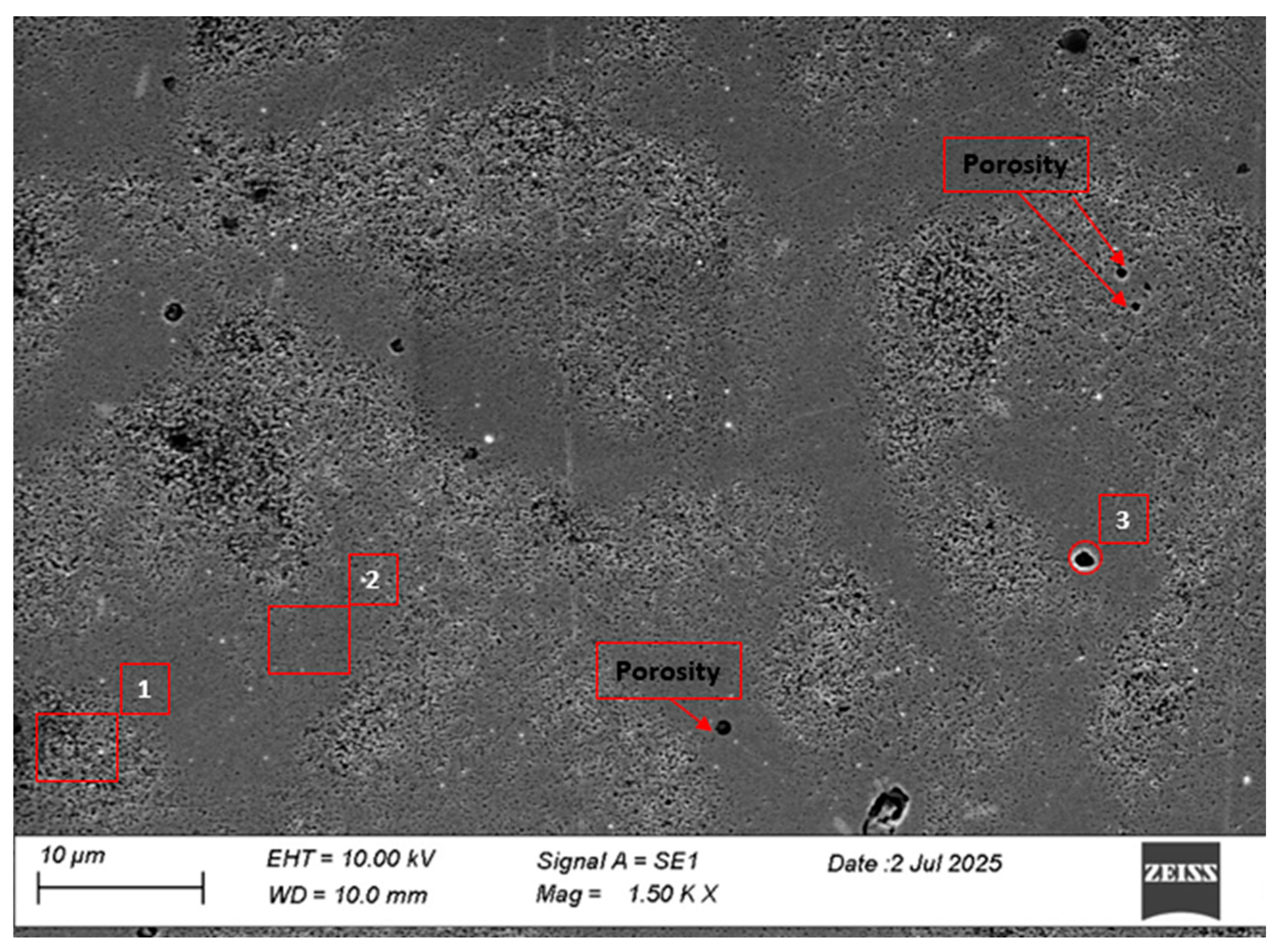
3.2. Scanning Microscope Metallographic Analysis of 310 Austenitic Steel
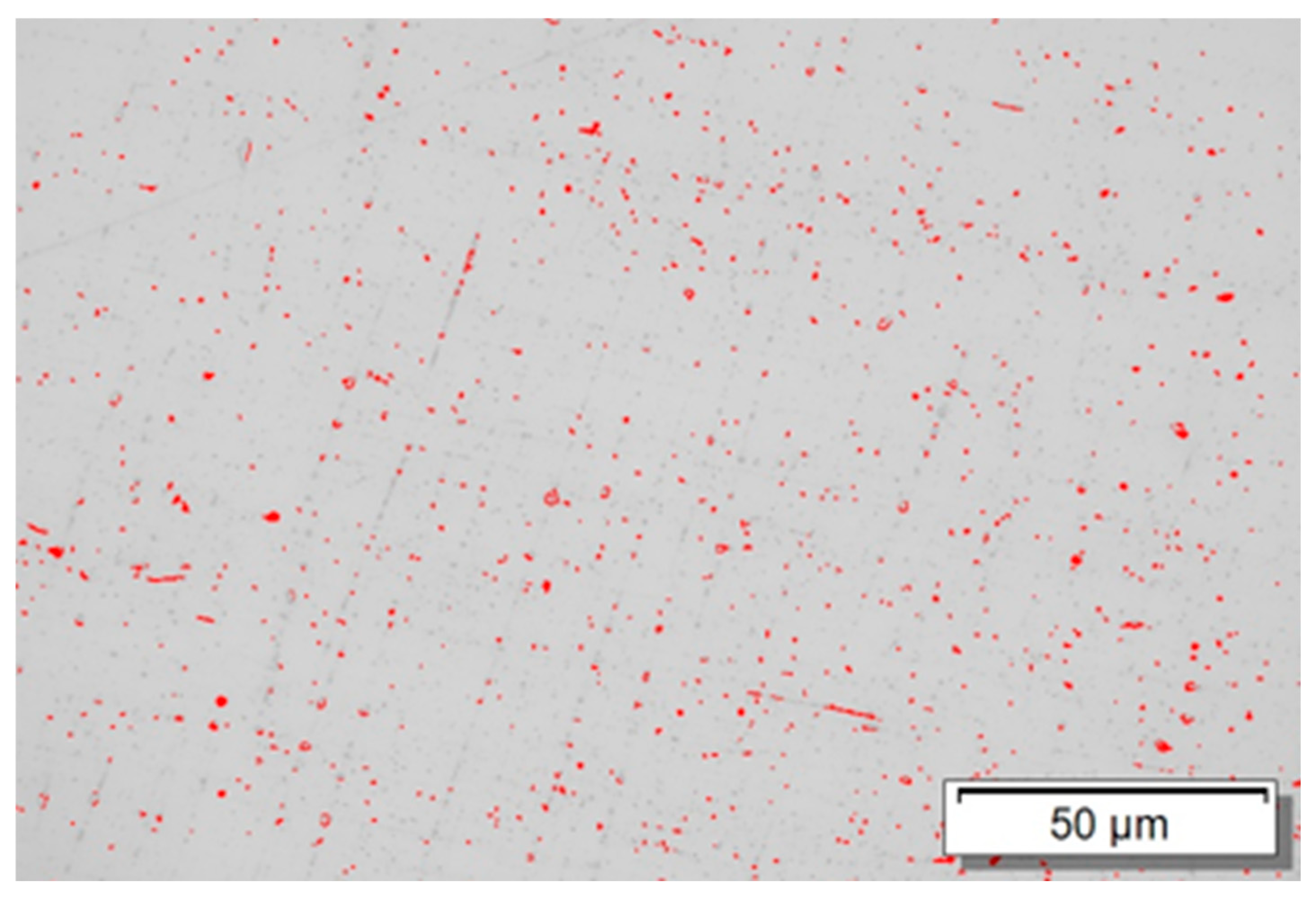
3.3. Mapping of Porosity in the Sample
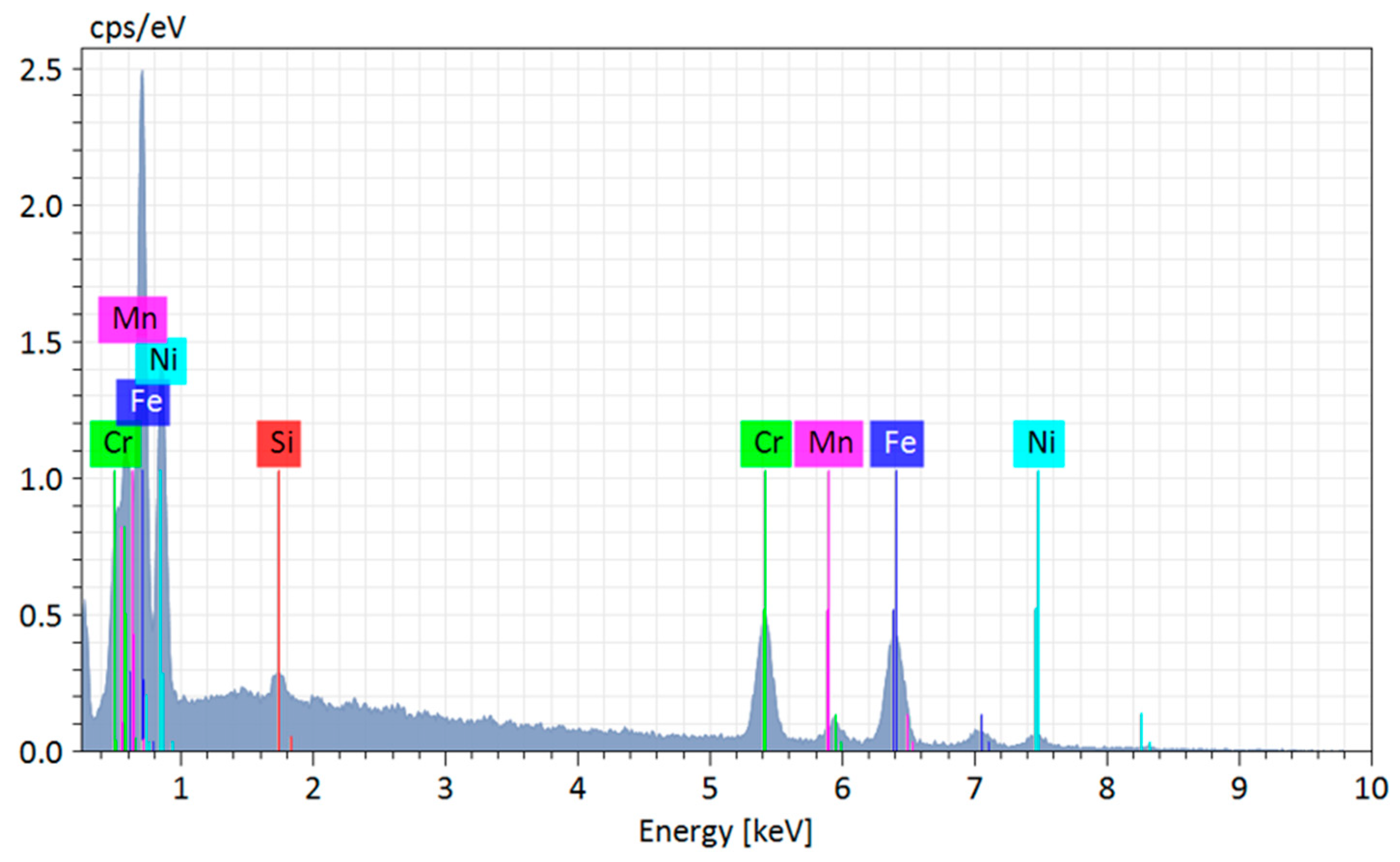
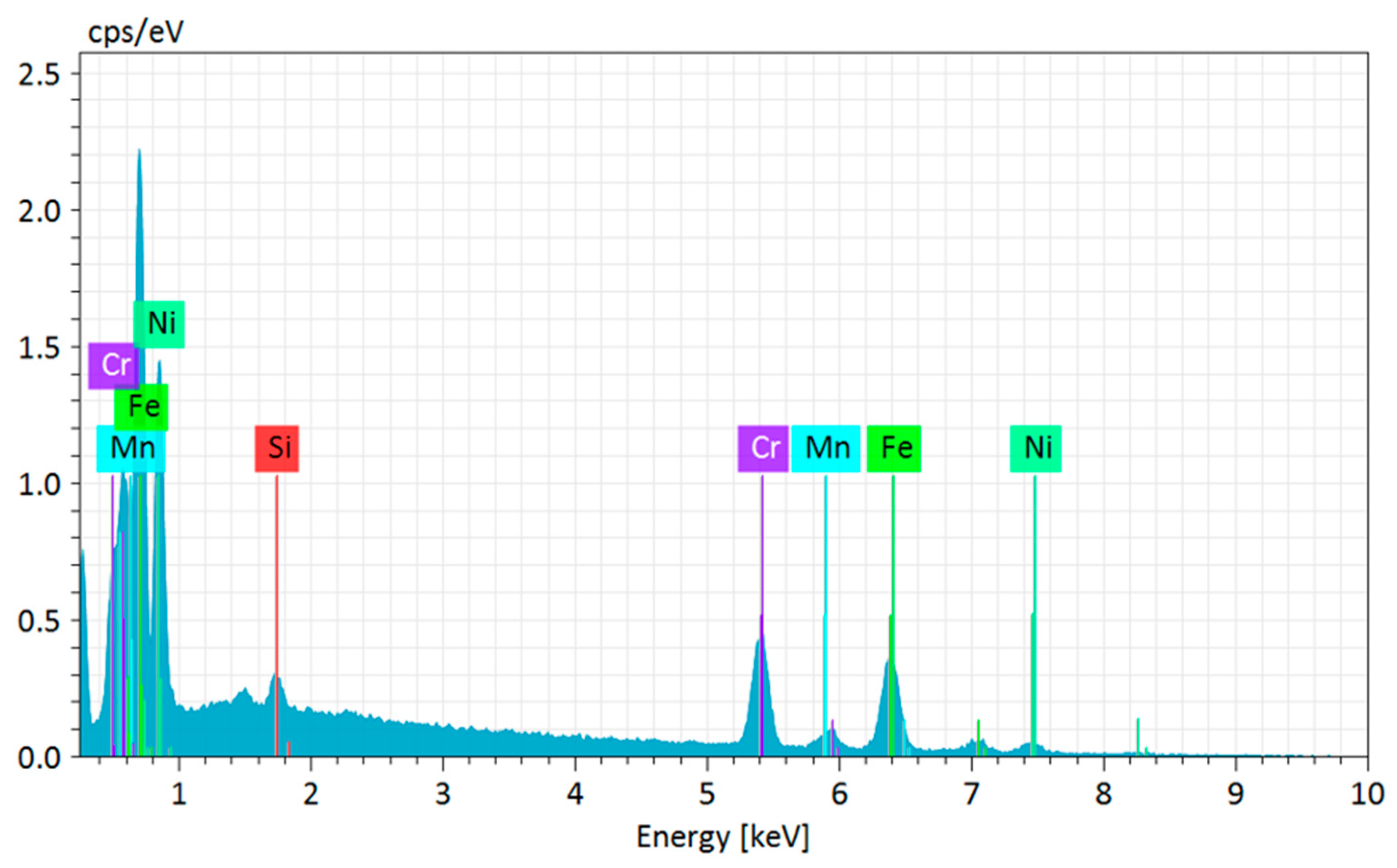
3.4. Optical Emission Spectrometry for the Chemical Characterization of AISI 310 Stainless Steel
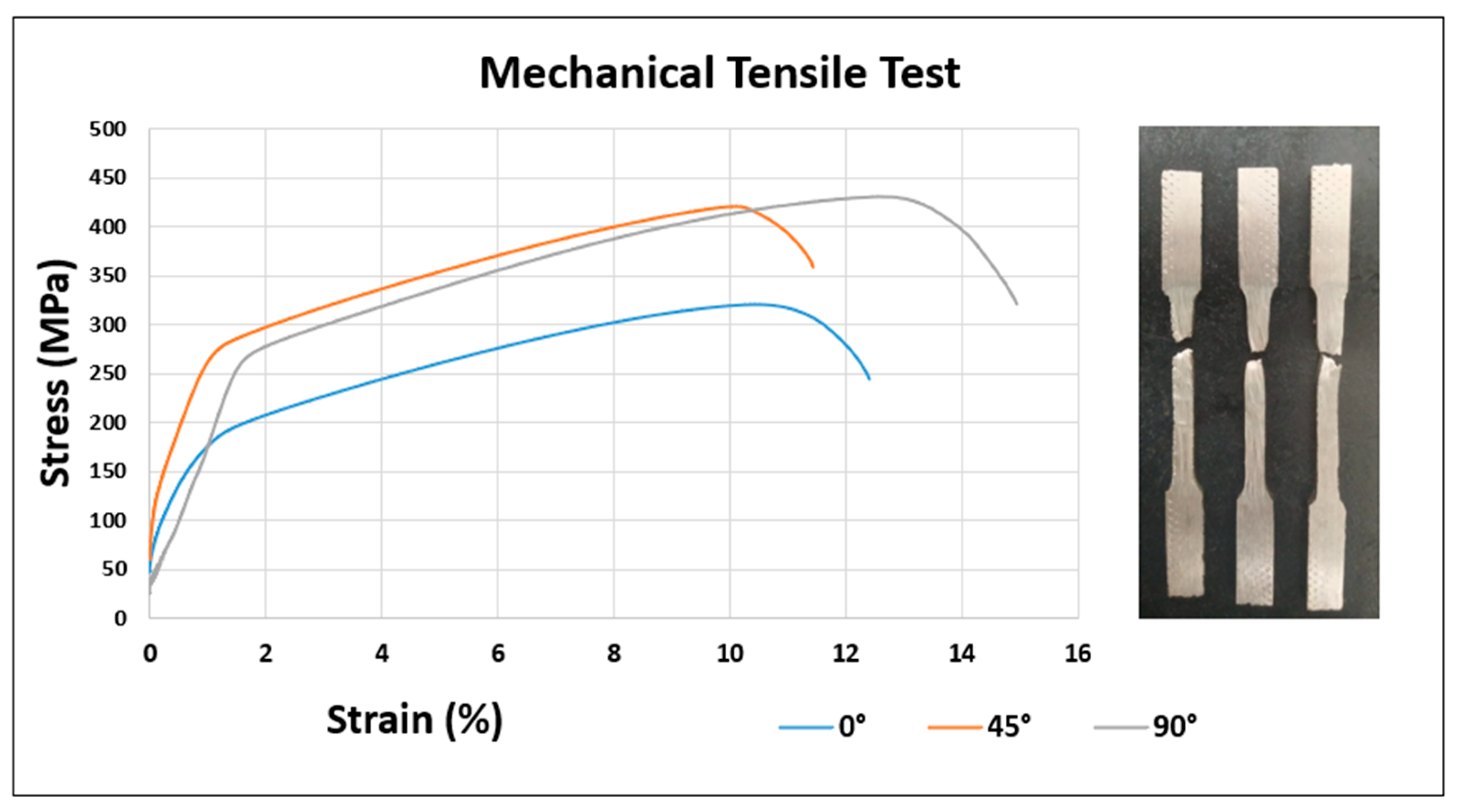
3.5. Mechanical Tensile Test on 310 Austenitic Steel
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahimi, A.; Yazdizadeh, M.; Ara, M.V.; Pouranvari, M. CMT wire-arc additive manufacturing of 310 austenitic stainless steel: Microstructure-properties relationships. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2025, 35, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, É.A.; Bomfim, M.H.S.; Liberato, F.M. A evolução da fabricação: Comparação e sinergia entre manufatura aditiva e subtrativa. Res. Soc. Dev. 2005, 14, e9114548869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cunningham, C.R.; Flynn, J.M.; Shokrani, A.; Dhokia, V.; Newman, S.T. Invited review article: Strategies and processes for high quality wire arc additive manufacturing. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 22, 672–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Li, H.; Gong, H.; Wu, H.; Ahmad, A.S.; Chen, X. Effect of rolling force on tensile properties of additively manufactured Inconel 718 at ambient and elevated temperatures. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 884, 161050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frazier, W.E. Metal Additive Manufacturing: A Review. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2014, 23, 1917–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Kim, D. Repair of damaged parts using wire arc additive manufacturing in machine tools. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 16, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeffus, L.F. Welding and Applications; Cengage Learning: Boston, MA, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Gao, M.; Zeng, X. Wire arc additive manufacturing of Al-6Mg alloy using variable polarity cold metal transfer arc as power source. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 711, 415–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, T.A.; Duarte, V.; Miranda, R.M.; Santos, T.G.; Oliveira, J. Current Status and Perspectives on Wire and Arc Additive Manufacturing (WAAM). Materials 2019, 12, 1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campatelli, G.; Montevecchi, F.; Venturini, G.; Ingarao, G.; Priarone, P.C. Integrated WAAM-subtractive versus pure subtractive manufacturing approaches: An energy efficiency comparison. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 7, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabernero, I.; Paskuala, A.; Álvarezb, P.; Suárezcb, A. Study on Arc Welding processes for High Deposition Rate Additive Manufacturin. In Proceedings of the CIRP Conference on Electro Physical and Chemical Machinin, Bilbao, Spain, 20 April 2018; Volume 68, pp. 358–362. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, L.; Chen, Y.; Liou, F. Additive manufacturing of functionally graded metallic materials using laser metal deposition. Addit. Manuf. 2020, 31, 100901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.; Schaeffer, L.; Daleffe, A.; Castelan, J.; Casagrande, H.; March, G.M.A. Hybrid Manufacturing Process and Hot Forging: Preform Manufacturing Through Localized Melting Material Deposition Using UTP AF DUR 600 Wire. RGSA J. Soc. Environ. Manag. 2025, 19, e012427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, H.C.; Daleffe, A.; Ferreira, C.A.; Milanez, A.; March, G.; Schaeffer, L. Additive Manufacturing in the Forging Process: Preform Manufacturing Through Localized Melting Material Deposition Using Low Carbon Wire. RGSA J. Soc. Environ. Manag. 2025, 19, e012422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, H.C.; Daleffe, A.; Ferreira, C.; Fritzen, D.; March, G.; Castelan, J. Processo de fabricação de peças metálicas por manufatura aditiva com fusão localizada de aços baixa liga. Open Sci. Res. 2023, 11, 997–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Chen, W.; Gong, N.; Pu, H.; Luo, J.; Zhang, D.Z.; Murr, L.E. A critical review on wire-arc directed energy deposition of high-performance steels. J. Mater. Res. Tecnol. 2023, 24, 9369–9412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.A.; Prasad, R.V.S. Chapter 2—Basic Principles of Additive Manufacturing: Different Additive Manufacturing Technologies. In Additive Manufacturing. A Tool for Industrial Revolution 4.0; Woodhead Publishing Reviews: Mechanical Engineering Series; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2021; pp. 17–35. [Google Scholar]
- ASTM international F2792-12A; Standard Terminology for Aditive Manufacturing Technologies. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012; pp. 918–928.
- Uralde, V.; Veiga, F.; Aldalur, E.; Suarez, A.; Ballesteros, T. Symmetry and Its Application in Metal Additive Manufacturing (MAM). Symmetry 2022, 14, 1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korkut, I.; Kasap, M.; Ciftci, I.; Seker, U. Determination of optimum cutting parameters during machining of AISI 304 austenitic stainless steel. Mater. Des. 2004, 25, 303–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pixer, F.; Arnoldt, A.; Unger, M.; Scneider-Broskamp, C.; Bharadwaj, K.; Mayrhofer, F.; Gradinger, R.; Klein, T. On the viability of in-situ alloying via process gas mixtures in wire arc directed energy deposition of austenitic stainless steel. J. Mech. Work. Technol. 2025, 337, 118738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kou, S. Welding Metallurgy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons Incorporated: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Lippold, J.C. Welding Metallurgy and Weldability; Ohio State University: Columbus, OH, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Yi, M.; Wu, H.; Fang, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B.; Zhou, K.; Liaw, P.K. Fine-grain-embedded dislocation-cell structures for high strength and ductility in additively manufactured steels. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 790, 139736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardner, L.; Talja, A.; Baddoo, N.R. Structural design of high-strength austenitic stainless steel. Thin-Walled Struct. 2006, 44, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASM Specialty Handbook: Stainless Steels; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1994.
- Sousa, J.M.B.A. Influência dos elementos de liga nos aços inoxidáveis duplex e superduplex utilizados na indústria do petróleo: Uma revisão. Trabalho de Conclusão de Curso apresentado ao curso de Engenharia Metalúrgica do Departamento de Engenharia Metalúrgica e de Materiais da Universidade Federal do Ceará. 2021. Available online: https://repositorio.ufc.br/bitstream/riufc/60634/3/2021_tcc_jmbasousa.pdf (accessed on 27 June 2025).
- Souza, V.P.; Labiapari, W.S.; Lins, V.F.C. Stainless steels as a solution for corrosion and erosion problems involving grains in agribusiness sector applications. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 30, 5605–5621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Srivastava, M.; Jain, K. Design and fabrication of wire arc additive manufacturing setup and enhanced tailored properties of dissimilar steel additively deposited by WAAM process. Estruturas 2025, 72, 108228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blakey-Milner, B.; Gradl, P.; Snedden, G.; Brooks, M.; Pitot, J.; Lopez, E.; Leary, M.; Berto, F.; Plessis, A. Metal additive manufacturing in aerospace: A review. Mater. Des. 2021, 209, 110008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanni, R.A. On High-Temperature Matersials: A Case on Creep and Oxidation of a Fully Austenitic Heat-Resistant Super-alloy Stainless Steel Sheet. J. Mater. 2013, 1, 124649. [Google Scholar]
- Liao, H.; Wang, Z.; Chi, P.; Zhang, B.; Ding, T.; Zhangc, Q. Evolutions of microstructure and mechanical property of 308L stainless steel repaired by the local dry underwater wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2024, 898, 146365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamim, M.; Darmadi, D.B.; Purnowidodo, A.; Widodo, T.D.; Ismail, Z. Influence of the welding thermal cycle on δ-ferrite evolution in the first layer of austenitic stainless steel (ASS) 308L produced by WAAM-GTAW. Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 64, 105489, Erratum in Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2024, 64, 105575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, F.; Bi, W.; Zhang, K.; Sun, X.; Ma, G.; Wu, D. Additive manufacturing of 304 stainless steel integrated component by hybrid WAAM and LDED. Mater. Today Commun. 2023, 35, 106227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, D.G.; Tankova, T.; Zhu, C.; Silva, L.S.; Rodrigues, D.M. Mechanical properties of 3D printed CMT-WAAM 316LSi stainless steel walls. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2024, 215, 108527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vinoth, V.; Sathiyamurthy, S.; Natarajan, U.; Venkatkumar, D.; Prabhakaran, J.; Prakash, S.K. Examination of microstructure properties of AISI 316L stainless steel fabricated by wire arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Proc. 2022, 66, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Guo, S.; Xuan, Y.; Xu, J.; Li, S.; Fang, W.; Zhou, Q.; Wang, K. Influence of different deposition strategies on the microstructure and mechanical properties of the laminated heterostructured material with ER130S-G HSS and 316 L SS fabricated by WAAM. Mater. Charact. 2024, 210, 113838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezende, R.F.; Árias, A.R.; Lima, E.J.; Coelho, F.G.F. Pulsed GMAW-based WAAM–Influence of droplet detachment mode on the geometry and mechanical properties of 308 L stainless steel. J. Adv. Join. Process. 2025, 11, 100286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, A.; Srivastava, M.; Jain, P.K.; Rathee, S. Microstructure transformations and improving wear resistance of austenitic stainless steel additively fabricated by arc-based DED process. Def. Technol. 2024, 38, 194–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Zhao, X.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Liang, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, C. Study on properties of 304 wire arc additive manufacturing stainless steel TIG welded joints. Mater. Lett. 2024, 361, 136107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, O.S.; Kuriachen, B.; Anantharam, G.S.; Eldose, K.K. Influence of microstructure on the anisotropic tribocorrosion behaviour of WAAM-fabricated SS304L in marine environments. Tribol. Int. 2025, 209, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Xue, J.; Wang, Q. Correlation between arc mode, microstructure, and mechanical properties during wire arc additive manufacturing of 316L stainless steel. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 751, 183–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayan, Y.; Kahraman, N. Investigation of tensile and fatigue properties of an austenitic stainless steel part fabricated by WAAM. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2024, 315, 128937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, P.; Lin, H.; Wu, W.; Tang, H. Influence of Duty Ratio and Current Mode on Robot 316L Stainless Steel Arc Additive Manufacturing. Metals 2021, 11, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Yin, Y.; Li, C.; LI, C.; Zhang, K. Influence of thermal behavior on microstructure evolution of TIG arc additive manufacture for 316L stainless steel. Trans. Mater. Heat. Treat. 2020, 41, 97–105. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Huang, J.; Liu, C.; Ma, Y.; Han, Y.; Xu, T.; Lu, J.; Fang, H. Fabricating Pyramidal Lattice Structures of 304 L Stainless Steel by Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing. Materials 2020, 13, 3482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, K.; Wang, Z.; Gao, M.; Li, X.; Zeng, X. Effects of processing parameters on tensile properties of selective laser melted 304 stainless steel. Materials 2013, 50, 581–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Prasad, A.; Bermingham, M.J.; Todaro, C.J.; Benoit, M.J.; Patel, M.N.; Qiu, D.; StJohn, D.; Qian, M.; Easton, M.A. Grain Refinement of Alloys in Fusion-Based Additive Manufacturing Processes. Metall. Mater. Trans. 2020, 51, 4341–4359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, H.; Kuang, Y.; Zhou, D.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, X.; Xu, L.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z. Achieving fine-grained structure with larger ferrite fraction via local dry underwater WAAM to enhance corrosion behavior of 308 L stainless steel. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 457, 139510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinasa, A.; Weber, B.; Meng, X.; Zhang, R.; Nitawaki, M.; Gardner, L. Influence of process parameters on the physical and material properties of WAAM steels. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 479, 141078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belhadj, M.; Werda, S.; Kromer, R.; Darnis, P. Influence of operating parameters on the mechanical and geometric properties of 316L Stainless Steel structures fabricated by WAAM-CMT. Procedia CIRP 2025, 133, 585–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Chen, W.; Wang, D.; Hou, H.; Zhao, Y. Phase-field modeling and Experimental investigation for rapid solidification in wire and arc additive manufacturing. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2024, 28, 4585–4599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurol, U.; Kocaman, E.; Dilibal, S.; Koçak, M. A comparative study on the microstructure, mechanical properties, wear and corrosion behaviors of SS 316 austenitic stainless steels manufactured by casting and WAAM Technologies. CIRP J. Manuf. Sci. Technol. 2023, 47, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertsch, K.M.; Bellefon, G.M.; Kuehl, B.; Thoma, D.J. Origin of dislocation structures in an additively manufactured austenitic stainless steel 316L. Acta Mater. 2020, 199, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Ouyang, H.; Fan, C.; Guo, Q.; Li, Z.; Yan, W.; Li, Z. The origino f high-density dislocations in additively manufactured metals. Mater. Res. Lett. 2020, 8, 283–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derekar, K.S. A review of wire arc additive manufacturing and advances in wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminium. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 895–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendez-Morales, M.; Jesus, J.S.; Branco, R.; Tankova, T.; Rebelo, C. Fatigue crack growth of untreated and heat-treated WAAM ER70S-6 carbon steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2025, 198, 109008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kun, L.; Ping, Y.; Sindo, K. Solidification Cracking Susceptibility of Stainless Steels: New Test and Explanation. Weld. Res. 2020, 99, 225–270. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, M.; Zeng, X. Workpiece vibration augmented wire arc additive manufacturing of high strength aluminum alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2019, 217, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, N.A.; Muzamil, M.; Jamil, T.; Hussain, G. Heat sources in wire arc additive manufacturing and their impact on macro-microstructural characteristics and mechanical properties—An overview. Smart Mater. Manuf. 2025, 3, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vimal, K.E.K.; Srinivas, M.N.; Rajak, S. Wire arc additive manufacturing of aluminium alloys: A review. Mater. Today Proc. 2021, 41, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strano, G.; Hao, L.; Everson, R.M.; Evans, K.E. Surface roughness analysis, modelling and prediction in selective laser melting. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2013, 213, 589–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; Yazdizadeh, M.; Ara, M.V.; Pouranvari, M. Strength and ductility of additively manufactured 310 austenitic stainless steel via wire-arc directed energy deposition: The role of columnar grain growth and ductility-dip cracking. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2025, 920, 147554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E8; Standard Test Methods for Tension Testing of Metallic Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024.
- Xiong, J.; Tzempelikos, A.; Bilionis, I.; Awalgaonkar, N.; Lee, S.; Konstantzos, I.; Sadeghi, S.; Karava, P. Inferring personalized visual satisfaction profiles in daylit offices from comparative preferences using a Bayesian approach. Build. Environ. 2018, 138, 74–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felice, I.; Shen, J.; Barragan, A.F.; Moura, I.A.; Li, B.; Wang, B.; Khodaverdi, H.; Mohri, M.; Schell, N.; Ghafoori, E.; et al. Wire and arc additive manufacturing of Fe-based shape memory alloys: Microstructure, mechanical and functional behavior. Mater. Des. 2023, 231, 112004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alagha, A.; Hussain, S.; Zaki, W. Additive manufacturing of shape memory alloys: A review with emphasis on powder bed systems. Mater. Des. 2021, 204, 109654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, L.; Lu, J.; Liua, C.; Jing, C.; Fan, H.; Ma, S. Microstructure and mechanical properties of 304L steel fabricated by arc additive manufacturing. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Electronic Information Technology and Computer Engineering (EITCE 2017), Sibiu, Romania, 7–9 June 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Sasikumar, C.; Oyyaravelu, R. Mechanical properties and microstructure of SS 316 L created by WAAM based on GMAW. Mater. Commun. 2024, 38, 107807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, P.; Wen, D.; Min, J.; Zheng, Z.; Li, J.; Liu, Y. Microstructure Evolution and Mechanical Properties of a Wire-Arc Additive Manufactured Austenitic Stainless Steel: Effect of Processing Parameter. Materials 2021, 14, 1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omiyale, B.; Ogedengbe, I.; Olugbade, T.; Farayibi, P. Corrosion Performance of Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing of Stainless Steel: A Brief Critical Assessment. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2024, 11, e572–e585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Brito Neto, F.M.; Ferreira, M.O.A.; dos Santos, S.A.C.; Pereira, J.N.; Meza, D.L.C.; Ahmed, W.; Nossa, T.d.S.; Moreto, J.A.; Pinto, H.C.; Arantes, V.L. Mechanical and corrosion behaviour of 316L stainless steel processed by wire arc additive manufacturing (WAAM). Prog. Addit. Manuf. 2025, 10, 6453–6469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Gong, Z.; Zhang, T.; Zuo, W.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, O.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Z. Mechanical behavior of austenitic stainless steels produced by wire arc additive manufacturing. Thin-Walled Struct. 2024, 196, 111455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasai, B.; Malarvizhi, S.; Balasubramanian, V. Mechanical Properties and microstructural characteristics of wire arc aditive manufactured 308L stainless steel cylindrical componentes made by gas metal arc and colda metal transfer arc welding processes. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2022, 307, 117655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlina, A.I.; Kondratyev, V.V.; Balanovskiy, A.E.; Astafyeva, N.A.; Yamshchikova, E.A. Porosity reduction in metal with hybrid wire and arc additive manufacturing technology (WAAM). CIS Iron and Steel Review. 2024, 27, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, W.; Zhang, C.; Jin, S.; Tian, Y.; Wellmann, D.; Liu, W. Wire Arc Additive Manufacturing os Stainless Steels: A Review. Materials 2020, 10, 1563. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, T.; Lindwall, G.; Ghosh, S.; Ma, L.; Lane, B.M.; Zhang, F.; Kattner, U.R.; Lass, E.A.; Heigel, J.C.; Idell, Y.; et al. Application of Finite Element, Phase-field, and CALPHAD-based Methods to Additive Manufacturing of Ni-based Superalloys. Mater. Sci. 2017, 139, 244–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedjad, S.; Yildiz, M.; Saboori, A. Solidification behaviour os austenitic stainless steels during welding and directed energy deposition. Sci. Technol. Weld. Join. 2023, 28, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotecki, D.J.; Lippold, J.C. Welding Metallurgy and Weldability of Stainless Steels; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Ettefagh, A.H.; Guo, S.; Raush, J. Corrosion performance of additively manufactured stainless steel parts: A review. Addit. Manuf. 2021, 37, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Charmi, A.; Falkenberg, R.; Ávila, L.; Mohr, G.; Sommer, K.; Ulbricht, A.; Sprengel, M.; Neumann, R.S.; Skrotzki, B.; Evans, A. Mechanical anisotropy of additively manufactured stainless steel 316L: An experimental and numerical study. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 799, 140154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jiang, P.; Yang, G.; Yan, Y. An Investigation of the Anisotropic Mechanical Properties of Additive-Manufactured 316L SS with SLM. Materials 2024, 17, 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, T.G.; Zhu, P.; Lu, Y.H.; Shoji, T. Study on microstructure and tensile properties of 316L stainless steel fabricated by CMT wire and arc additive manufacturing. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2020, 796, 140006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajay, V.; Nakrani, J.; Mishra, N.K.; Shrivastava, A. Anisotropic fatigue crack propagation in wire arc additively manufactured 316L stainless steel. Int. J. Fatigue 2023, 177, 107976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, T.H.; Kumar, P.; Ramamurty, U. Fracture and fatigue in additively manufactured metals. Acta Mater. 2021, 219, 117240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez, N.; Vázquez, L.; Huarte, I.; Arruti, E.; Tabernero, I.; Alvarez, P. Wire and arc additive manufacturing: A comparison between CMT and TopTIG processes applied to stainless steel. Weld. World 2018, 62, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laghi, V.; Palermo, M.; Tonelli, L.; Gasparini, G.; Ceschini, L.; Trombetti, T. Tensile properties and microstructural features of 304L austenitic stainless steel produced by wire-and-arc additive manufacturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2020, 106, 3693–3705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM A276-13a; Standard Specification for Stainless Steel Bars and Shapes. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2013.
- Gowthaman, P.S.; Jeyakumar, S.; Sarathchandra, D.T. Experimental characteristics of 316L stainless steel thin wall processed in wire-based arc additive manufacturing process. Inst. Mech. Eng. 2023, 239, 1712–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, S.; Haldar, N.; Datta, S.; Das, A. Experimental investigation on microstructure and mechanical property of wire arc additively manufactured SS308L built part. Sadhana 2023, 48, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, K.U.; Kumar, R.; Mahapatra, M.M.; Mulik, R.S.; Swierczynska, A.; Fydrych, D.; Pandey, C. Wire Arc Additive Manufactured Mild Steel and Austenitic Stainless Steel Components: Microstructure, Mechanical Properties and Residual Stresses. Materials 2022, 15, 7094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASM Handbook, Volume 1. Properties and Selection: Irons, Steels, and High Performance Alloys Section: Publication Information and Contributors; ASM international: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1990.




| Variables | Parameters |
|---|---|
| Voltage (V) | 19 |
| Current (A) | 165 |
| Gas flow rate (L/min) | 16 |
| Wire feed speed (m/min) | 5.5 |
| Power (kW) | 3.135 |
| CNC travel speed (mm/min) | 300 |
| Wire diameter (mm) | 1.2 |
| Variables | Values |
|---|---|
| Average thickness (mm) | 10 |
| Average layer height (mm) | 2.5 |
| Number of deposited layers | 100 |
| Deposition time per bead (S) | 26 |
| Total active fabrication time (min) | 43 |
| Shielding gas argon (%) | 100 |
| Elements | Values |
|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.120 |
| Silicon (Si) | 0.476 |
| Manganese (Mn) | 1.320 |
| Chromium (Cr) | 26.70 |
| Nickel (Ni) | 20.10 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 0.140 |
| Iron (Fe) | 51.144 |
| Variables: Position | 0° | 45° | 90° |
|---|---|---|---|
| Yield strength (MPa) | 198 ± 7.20 | 280 ± 5.13 | 269 ± 10.21 |
| Ultimate tensile strength (MPa) | 320 ± 4.16 | 419 ± 12.66 | 430 ± 12.06 |
| Strain (%) | 12.5 ± 0.98 | 11.5 ± 2.72 | 15 ± 1.69 |
| Reference | Alloy | Tested Orientations | Ys (MPa) | UTS (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gowthaman et al., 2023 [89] (WAAM) | 316L | Horizontal (0°) | 302 | 576 | 35 |
| Vertical (90°) | 295 | 469 | 39 | ||
| Anand et al., 2023 [90] (WAAM) | 308L | Horizontal (0°) | 364 | 548 | 38 |
| Rani et al., 2022 [91] (WAAM) | 304 | Horizontal (0°) | - | 600 | - |
| Vertical (90°) | - | 597 | - | ||
| ASM Handbook 1990 [92] (Sheet) | 310 | Horizontal (0°) | 240 | 570 | 40 |
| Vertical (90°) | 240 | 600 | 46 | ||
| ASM Handbook 1990 [92] (Forging) | 310L | Vertical (90°) | 260 | 585 | 54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cipriano, A.; Malfatti, C.d.F.; Casagrande, H.C.; Daleffe, A.; Castelan, J.; Possamai, P.H.M. Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel 310 Manufactured via WAAM. Materials 2025, 18, 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163855
Cipriano A, Malfatti CdF, Casagrande HC, Daleffe A, Castelan J, Possamai PHM. Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel 310 Manufactured via WAAM. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163855
Chicago/Turabian StyleCipriano, Aline, Célia de Fraga Malfatti, Henrique Cechinel Casagrande, Anderson Daleffe, Jovani Castelan, and Pedro Henrique Menegaro Possamai. 2025. "Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel 310 Manufactured via WAAM" Materials 18, no. 16: 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163855
APA StyleCipriano, A., Malfatti, C. d. F., Casagrande, H. C., Daleffe, A., Castelan, J., & Possamai, P. H. M. (2025). Analysis of the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Austenitic Stainless Steel 310 Manufactured via WAAM. Materials, 18(16), 3855. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163855







