New Biodegradable Polyester–Polyurethane Biocompositions Enriched by Urea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Polymer Compositions
2.3. Injection Molding of Shapes for Testing Mechanical Properties
2.4. Methods
2.4.1. Mechanical Tests
2.4.2. Scanning Electron Microscopy
2.4.3. Infrared Spectroscopy Measurements
2.4.4. Biodegradability Test
3. Results and Discussion
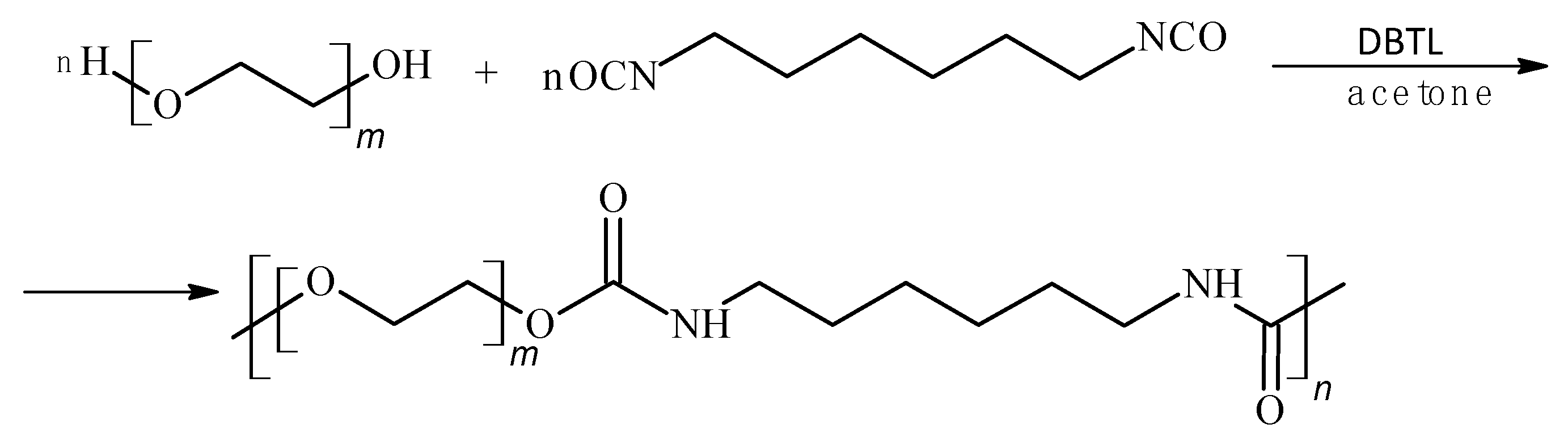
3.1. Formulation and Manufacturing of Biodegradable P3HB–PU–Urea Compositions
3.2. Analysis of the Processing Conditions of P3HB–PU–Urea Blends
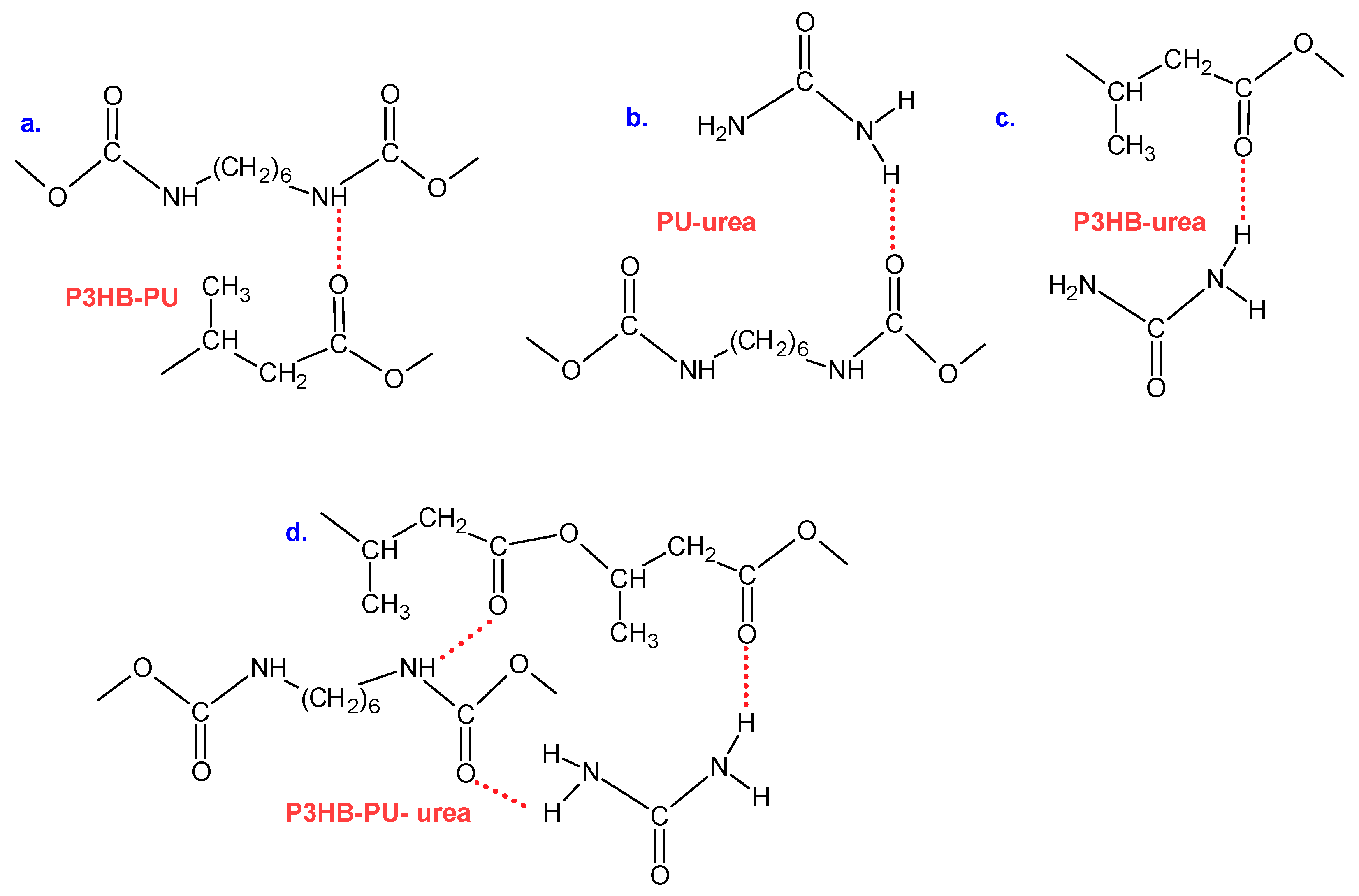
3.3. FTIR Analysis of Material Structure and Intermolecular Interactions
3.4. Effect of Urea and Aliphatic Polyurethane Additives on the Fracture Surface Morphology of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Compositions
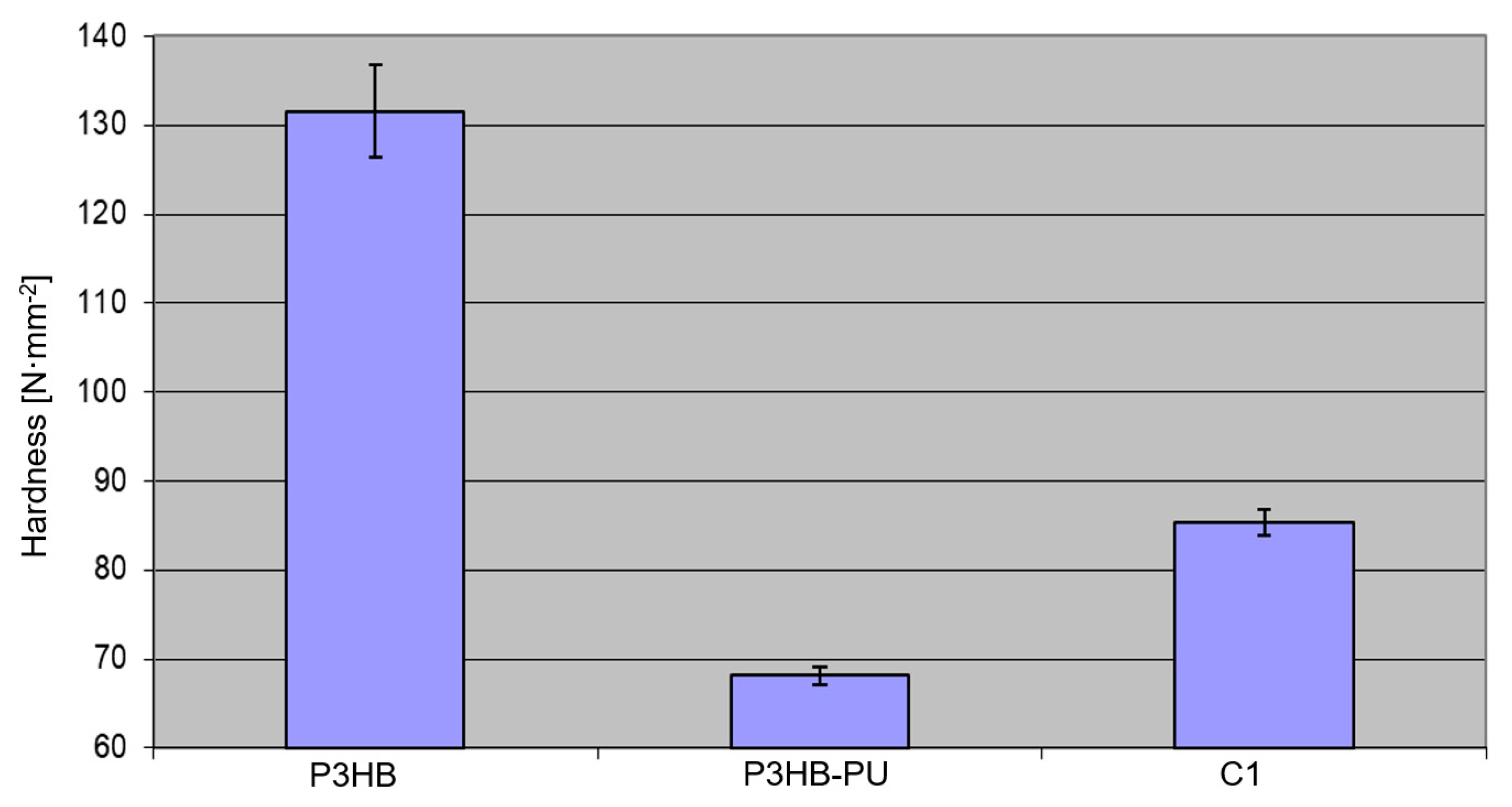
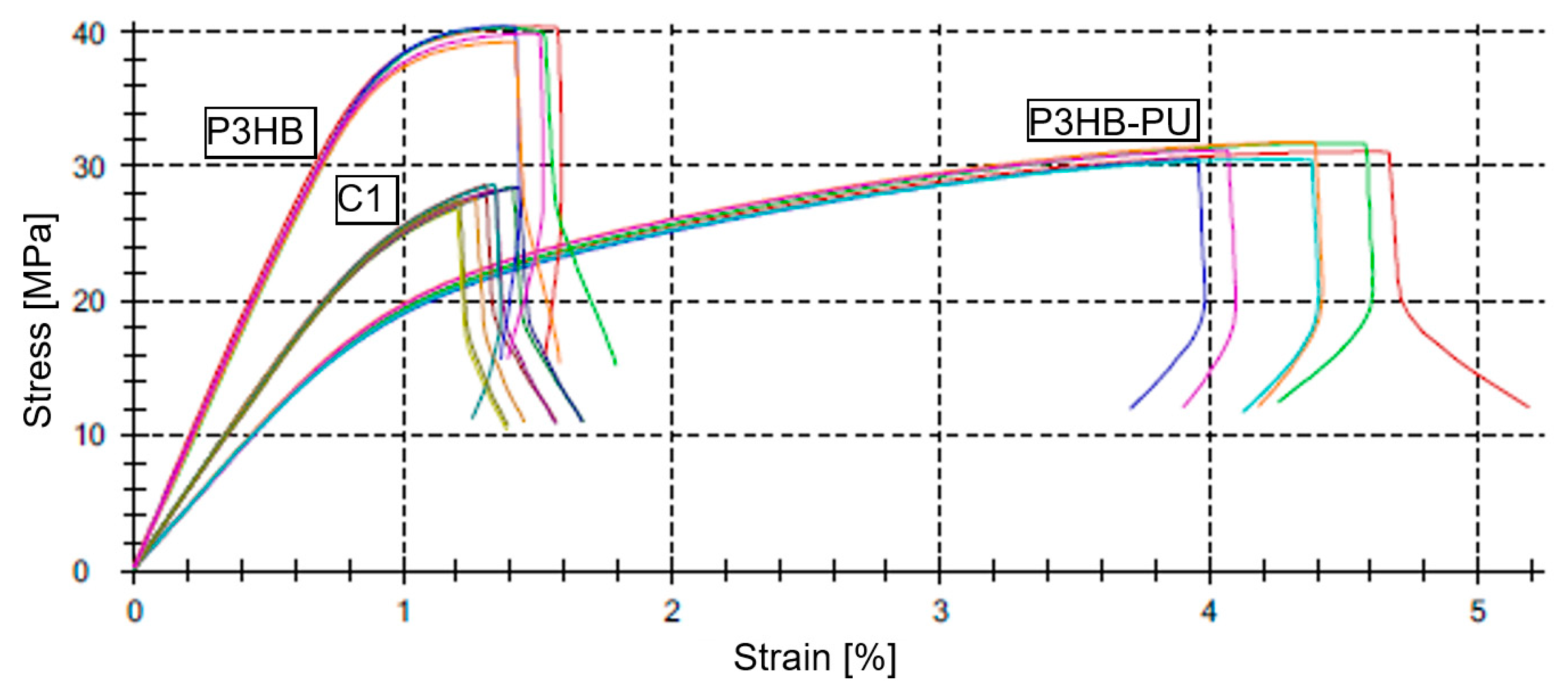
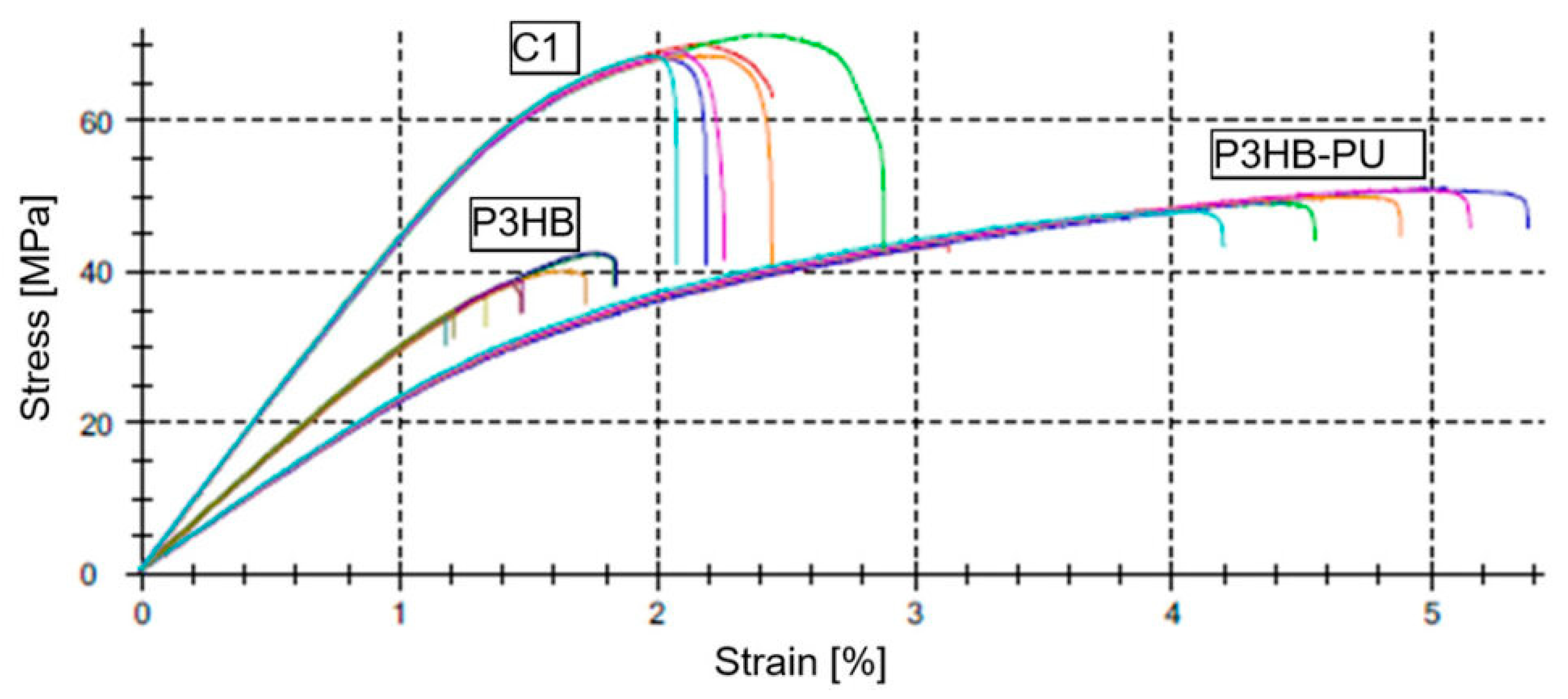
3.5. Mechanical Properties of the Polymer–Urea Biocompositions
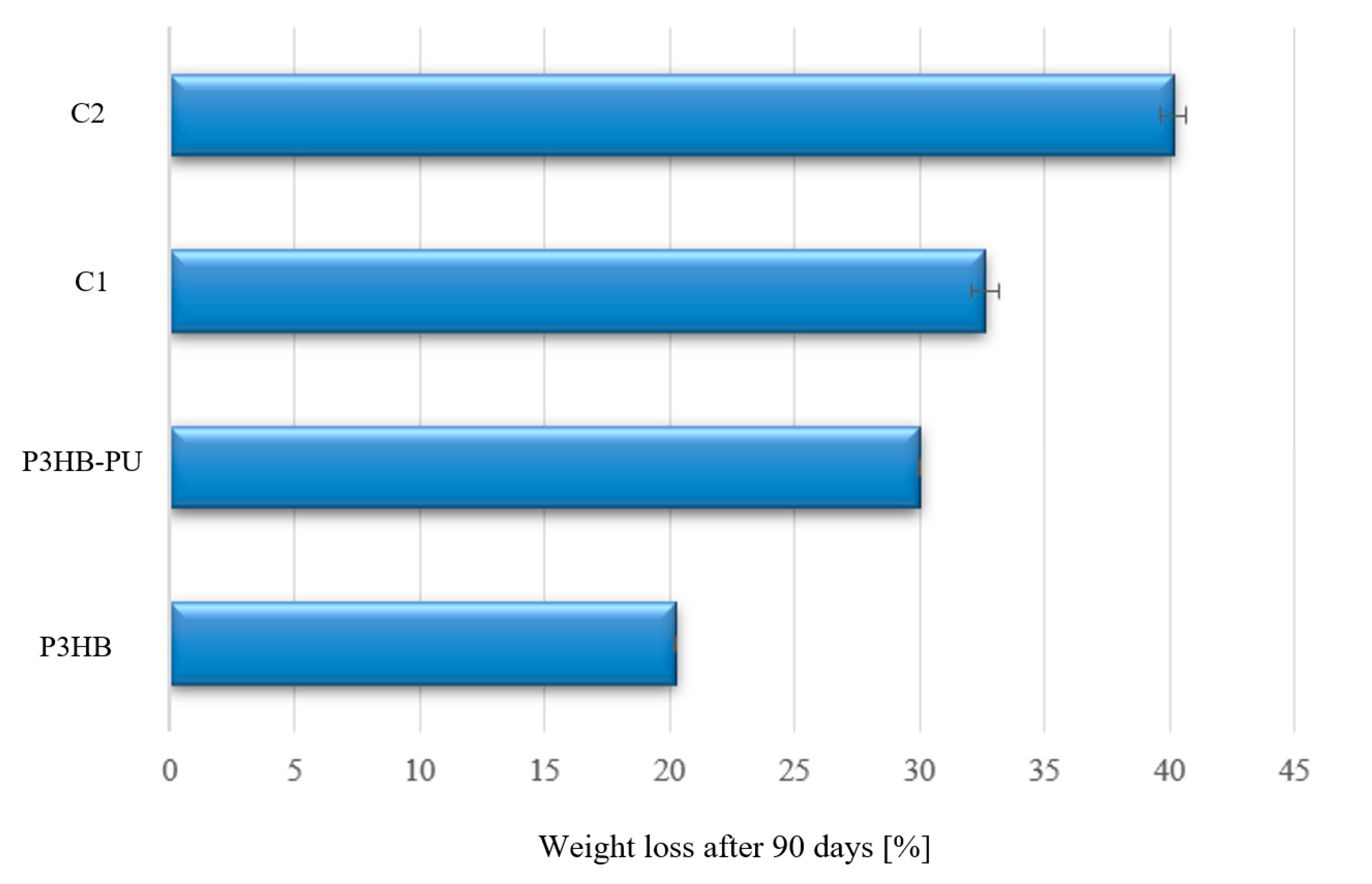
3.6. Biodegradability Assessment of Biocomposites
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, Use, and Fate of All Plastics Ever Made. Sci. Adv. 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopewell, J.; Dvorak, R.; Kosior, E. Plastics Recycling: Challenges and Opportunities. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2115–2126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, G.Q.; Wu, Q. The Application of Polyhydroxyalkanoates as Tissue Engineering Materials. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 6565–6578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudesh, K.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Synthesis, Structure and Properties of Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biological Polyesters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1503–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koller, M.; Atlić, A.; Dias, M.; Reiterer, A.; Braunegg, G. Microbial PHA Production from Waste Raw Materials. In Plastics from Bacteria; Springer: Berlin, Germany, 2010; pp. 85–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philip, S.; Keshavarz, T.; Roy, I. Polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biodegradable Polymers with a Range of Applications. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 2007, 82, 233–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basnett, P.; Lukasiewicz, B.; Marcello, E.; Knowles, J.C. Novel Polyhydroxyalkanoate Copolymers for Tissue Engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 1154–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrovic, Z.S. Polyurethane from Renewable Resources. Polym. Rev. 2008, 48, 109–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javni, I.; Petrovic, Z.S.; Guo, A.; Fuller, R. Thermal Stability of Polyurethanes Based on Vegetable Oils. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2000, 77, 1723–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guelcher, S.A. Biodegradable Polyurethanes: Synthesis and Applications in Regenerative Medicine. Tissue Eng. Part B Rev. 2008, 14, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malucelli, G.; Fabbri, P.; Messori, M. Advances in Aliphatic Polyurethanes for Biomedical Applications: A Review. Polym. Int. 2018, 67, 401–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, H.; Zhang, J.; Hou, D.; Li, Y. Biodegradable Film with Controlled-Release Fertilizer Properties Based on Starch/Polyvinyl Alcohol Blends. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 96, 103–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, R.; Liu, M.; Xu, Y. Controlled Release Urea Encapsulated by Starch-g-Poly(lactic acid). Carbohydr. Polym. 2015, 115, 20–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.; Wu, Z.; He, Y.; Han, Y.; Tong, Y. Characterization of p(AA-co-AM)/bent/urea and Its Swelling and Slow Release Behavior in a Simulative Soil Environment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 133, 43082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaganesh, B.; Malarvizhi, P.; Chandra Sekaran, N.; Jeyakumar, P.; Latha, K.R.; Lakshmanan, A. Effect of Biodegradable Polymer Coated Urea Fertilizers for the Growth and Yield of Hybrid Maize (Zea mays L.). Pharma Innov. J. 2021, 10, 2495–2501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bátori, V.; Åkesson, D.; Zamani, A.; Taherzadeh, M.J.; Sárvári Horváth, I. Anaerobic Degradation of Bioplastics: A Review. Waste Manag. 2018, 80, 406–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharath, K.N.; Basavarajappa, S. Applications of Biocomposite Materials Based on Natural Fibers from Renewable Resources: A Review. Materials 2016, 23, 123–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Si, W.-J.; Yang, L.; Weng, Y.-X.; Zhu, J.; Zeng, J.-B. Poly(lactic acid)/biobased polyurethane blends with balanced mechanical strength and toughness. Polym. Test. 2018, 69, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.-J.; Huang, H.-X. Preparation and characterization of biodegradable polylactide/thermoplastic polyurethane elastomer blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2011, 120, 3217–3223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pablos, J.L.; Munoz-Bonilla, A.; Fernández-García, M. Polymeric blends based on PLA for food packaging applications. Eur. Polym. J. 2019, 112, 264–277. [Google Scholar]
- Sartori, S.; Boffito, M.; Serafini, P.; Caporale, A.; Silvestri, A.; Bernardi, E.; Sassi, M.P.; Boccafoschi, F.; Ciardelli, G. Synthesis and Structure–Property Relationship of Polyester-Urethanes and Their Evaluation for the Regeneration of Contractile Tissues. React. Funct. Polym. 2013, 73, 1366–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panaitescu, D.M.; Melinte, V.; Frone, A.N.; Nicolae, C.A.; Gabor, A.R.; Capră, L. Influence of Biobased Polyurethane Structure on Thermal and Mechanical Properties of Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)−Polyurethane Blends. J. Polym. Environ. 2023, 31, 1584–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xie, J.; Xiao, X.; Chen, S.; Wang, Y. Development of Nontoxic Biodegradable Polyurethanes Based on Polyhydroxyalkanoate and L-lysine Diisocyanate with Improved Mechanical Properties as New Elastomers Scaffolds. Polymers 2019, 11, 1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, R.-B.; Zhang, X.; Xing, Q. Sustainable Polylactide/Polycaprolactone Based Polyurethane Blends Fabricated via Reactive Compatibilization. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2024, 35, e6282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joo, Y.S.; Cha, J.R.; Gong, M.S. Biodegradable Shape-Memory Polymers Using Polycaprolactone and Isosorbide Based Polyurethane Blends. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2018, 91, 426–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nofar, M.; Mohammadi, M.; Carreau, P.J. Effect of TPU Hard Segment Content on the Rheological and Mechanical Properties of PLA/TPU Blends. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Panaitescu, D.M.; Gabor, A.R.; Nicolae, C.A.; Ghiurea, M.; Bradu, C. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) Modified with Thermoplastic Polyurethane and Microfibrillated Cellulose: Hydrolytic Degradation and Thermal and Mechanical Properties. Polymers 2024, 16, 3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, S.H.; Hsieh, C.T.; Sun, Y.M. Synthesis and Characterization of Waterborne Polyurethane Containing Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) as New Biodegradable Elastomers. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 9089–9097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdo, S.M.; Youssef, A.M.; El-Liethy, M.A.; Ali, G.H. Preparation of Simple Biodegradable, Nontoxic, and Antimicrobial PHB/PU/CuO Bionanocomposites for Safely Use as Bioplastic Material Packaging. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 2024, 14, 28673–28683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.C.; Xiang, H.X.; Wang, R.L.; Peng, C.; Zhou, Z.; Zhu, M.F. Morphology and Properties of Renewable Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate) Blends with Thermoplastic Polyurethane. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2014, 54, 1113–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Abad, A.; González-Ausejo, J.; Lagarón, J.M.; Cabedo, L. Biodegradable Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/Thermoplastic Polyurethane Blends with Improved Mechanical and Barrier Performance. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2016, 132, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajesh, K.A.; Panicker, A.M.; Varghese, T.O. Effect of Compatibilization of Thermoplastic Polyurethane with Poly(lactic acid) for the Preparation of Sustainable Blends. Polym. Sci. Ser. A 2022, 63, S46–S57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.P.; Hu, H.; Wang, X.; Yu, X.L.; Zhou, W.Y.; Peng, S.X. Super Tough Poly(lactic Acid) Blends: A Comprehensive Review. RSC Adv. 2020, 10, 13316–13368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ajili, S.H.; Ebrahimi, N.G.; Soleimani, M. Polyurethane/Polycaprolactone Blend with Shape Memory Effect as a Proposed Material for Cardiovascular Implants. Acta Biomater. 2009, 5, 1519–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.J.; Xing, Q.; Li, R.B.; Dong, X. Toward Highly Toughened Polylactide/Polycaprolactone-Based Polyurethane Blends with Shape Memory Property via Reactive Blending. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2025, 142, e56490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarzyka, I.; Czerniecka-Kubicka, A.; Hęclik, K.; Dobrowolski, D.; Pyda, M.; Leś, K.; Walczak, M.; Białkowska, A.; Bakar, M. Thermally stable biopolymer composites based on poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) modified with linear aliphatic polyurethanes—Preparation and properties. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2021, 23, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EN ISO 527:2019; Plastics-Determination of Tensile Properties—Part 1: General Principles. International Organization for Standardization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2019.
- PN-EN ISO 178:2019; Plastics-Determination of Flexural Properties. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2010.
- PN-EN ISO 2039-1:2004; Plastics-Determination of Hardness—Part 1: Ball Indentation Method. Polish Committee for Standardization: Warsaw, Poland, 2004.
- DIN EN 13432:2002; Packaging—Requirements for Packaging Recoverable Through Composting and Biodegradation. The European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2002.
- Bayari, S.; Severcan, F. FTIR study of biodegradable biopolymers: P(3HB), P(3HB-co-4HB) and P(3HB-co-3HV). J. Mol. Struct. 2005, 744–747, 529–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kansiz, M.; Billman-Jacobe, H.; McNaughton, D. Quantitative determination of the biodegradable polymer poly(β-hydroxybutyrate) in a recombinant Escherichia coli strain by use of mid-infrared spectroscopy and multivariative statistics. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2000, 66, 3415–3420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.C. Infrared Spectroscopy of Polymers XIII: Polyurethanes. Spectroscopy 2023, 38, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolińska-Grabczyk, A.; Kaczmarczyk, B.; Jankowski, A. Investigations of hydrogen bonding in the poly(urethane-urea)-based membrane materials by using FTIR spectroscopy. Pol. J. Chem. Technol. 2008, 10, 53–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grdadolnik, J.; Maréchal, Y. Urea and urea-water solutions—An infrared study. J. Mol. Struct. 2002, 615, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manivannan, M.; Rajendran, S. Investigation of inhibitive action of urea-Zn2+ system in the corrosion control of carbon steel in sea water. Int. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. 2011, 3, 8421–8426. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Park, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, J. Comparison of acellular and cellular bioactivity of poly 3-hydroxybutyrate/hydroxyapatite nanocomposite and poly 3-hydroxybutyrate scaffolds. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2013, 18, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pétriz Reyes, A.; Martínez Torres, A.; Carreón Castro, M.d.P.; Rodríguez Talavera, J.R.; Vargas Muñoz, S.; Velázquez Aguilar, V.M.; González Torres, M. Novel Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-g-vinyl alcohol) Polyurethane Scaffold for Tissue Engineering. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 31140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hebda, E.; Pielichowski, K. Biomimetic Polyurethanes in Tissue Engineering. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janković, B.; Dodevski, V.; Janković, M.; Milenković, M.; Samaržija-Jovanović, S.; Jovanović, V.; Marinović-Cincović, M. Synthesis and Characterization of Bio-Composite Based on Urea–Formaldehyde Resin and Hydrochar: Inherent Thermal Stability and Decomposition Kinetics. Polymers 2025, 17, 1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naser, A.Z.; Deiab, I.; Defersha, F.; Yang, S. Expanding Poly(lactic acid) (PLA) and Polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) Applications: A Review on Modifications and Effects. Polymers 2021, 13, 4271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, H.M.C.C.; Raman, S.N.; Mohotti, D.; Mutalib, A.A.; Badri, K.H. The use of polyurethane for structural and infrastructural engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 995–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frone, A.N.; Nicolae, C.A.; Eremia, M.C.; Tofan, V.; Ghiurea, M.; Chiulan, I.; Radu, E.; Damian, C.M.; Panaitescu, D.M. Low Molecular Weight and Polymeric Modifiers as Toughening Agents in Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate) Films. Polymers 2020, 12, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.; Sharma, S.K.; Raj, A. Handbook of Biodegradable Polymers, 2nd ed.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2014; 731p, ISBN 978-1-84735-526-3. [Google Scholar]
- Weng, Q.-H.; Hu, M.-H.; Wang, J.-F.; Hu, J.-J. Enhancing the Flexibility and Hydrophilicity of PLA via Polymer Blends: Electrospinning vs. Solvent Casting. Polymers 2025, 17, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iggui, K.; Le Moigne, N.; Kaci, M.; Bergeret, A. A biodegradation study of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyvalerate)/organoclay nanocomposites in various environmental conditions. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2015, 119, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzeska, J.; Jasik, G.; Sikorska, W.; Mendrek, B.; Karczewski, J.; Kowalczuk, M.; Rutkowska, M. Susceptibility to Degradation in Soil of Branched Polyesterurethane Blends with Polylactide and Starch. Polymers 2022, 14, 2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Material | Head | Zone 7 | Zone 6 | Zone 5 | Zone 4 | Zone 3 | Zone 2 | Zone 1 | Feed |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3HB | 158 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 150 | 145 | 55 |
| P3HB–PU | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 152 | 150 | 145 | 50 |
| C1 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 150 | 148 | 145 | 50 |
| C2 | 148 | 147 | 147 | 146 | 146 | 146 | 144 | 141 | 50 |
| Material | Rotational Speed [rpm] | Pressure [bar] | System Load [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| P3HB | 130 | 26 | 72 |
| P3HB–PU | 130 | 28 | 83 |
| C1 | 130 | 13 | 58 |
| C2 | 130 | 10 | 51 |
| Material | Plasticizing Pressure [bar] | Injection Pressure [bar] | Holding Pressure [bar] | Holding Time [s] | Injection Temperature [°C] | Cooling Time [s] | Mold Temperature [°C] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3HB | 190 | 600 | 400 | 25 | 165 | 25 | 30 |
| P3HB–PU | 200 | 550 | 350 | 26 | 176 | 25 | 40 |
| C1 | 50 | 200 | 180 | 24 | 167 | 24 | 40 |
| C2 | 50 | 200 | 180 | 24 | 167 | 24 | 40 |
| Sample | Et [MPa] | σM [MPa] | εM [%] | σB [MPa] | εB [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3HB | 4926 ± 27 | 33.5 ± 1.4 | 1.19 ± 0.05 | 33.5 ± 1.4 | 1.42 ± 0.05 |
| P3HB–PU | 2361 ± 48 | 31.1 ± 0.5 | 4.28 ± 0.24 | 28.0 ± 0.8 | 4.22 ± 0.21 |
| C1 | 3037 ± 46 | 28.1 ± 0.7 | 1.33 ± 0.08 | 28.1 ± 0.7 | 1.31 ± 0.08 |
| Sample | Ef [MPa] | σfC [MPa] | σfM [MPa] | εfM [%] | σfB [MPa] | εfB [%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P3HB | 4513 ± 35 | - | 69 ± 1.2 | 2.14 ± 0.15 | 69 ± 1.2 | 2.14 ± 0.15 |
| P3HB–PU | 2321 ± 36 | 47.1 ± 0.2 | 50 ± 1.3 | 4.62 ± 0.40 | 50 ± 1.3 | 4.62 ± 0.40 |
| C1 | 3054 ± 54 | - | 39 ± 3.1 | 1.47 ± 0.23 | 39 ± 3.1 | 1.47 ± 0.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zarzyka, I.; Krzykowska, B.; Hęclik, K.; Frącz, W.; Janowski, G.; Bąk, Ł.; Klepka, T.; Bieniaś, J.; Ostapiuk, M.; Tor-Świątek, A.; et al. New Biodegradable Polyester–Polyurethane Biocompositions Enriched by Urea. Materials 2025, 18, 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163842
Zarzyka I, Krzykowska B, Hęclik K, Frącz W, Janowski G, Bąk Ł, Klepka T, Bieniaś J, Ostapiuk M, Tor-Świątek A, et al. New Biodegradable Polyester–Polyurethane Biocompositions Enriched by Urea. Materials. 2025; 18(16):3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163842
Chicago/Turabian StyleZarzyka, Iwona, Beata Krzykowska, Karol Hęclik, Wiesław Frącz, Grzegorz Janowski, Łukasz Bąk, Tomasz Klepka, Jarosław Bieniaś, Monika Ostapiuk, Aneta Tor-Świątek, and et al. 2025. "New Biodegradable Polyester–Polyurethane Biocompositions Enriched by Urea" Materials 18, no. 16: 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163842
APA StyleZarzyka, I., Krzykowska, B., Hęclik, K., Frącz, W., Janowski, G., Bąk, Ł., Klepka, T., Bieniaś, J., Ostapiuk, M., Tor-Świątek, A., Droździel-Jurkiewicz, M., Białkowska, A., Tomczyk, A., Falkowska, A., & Kuciej, M. (2025). New Biodegradable Polyester–Polyurethane Biocompositions Enriched by Urea. Materials, 18(16), 3842. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18163842








