Experimental Study on Millisecond Laser Percussion Drilling of Heat-Resistant Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Simulation and Experimental Protocol Design
2.1. COMSOL Fluid Dynamics Simulation
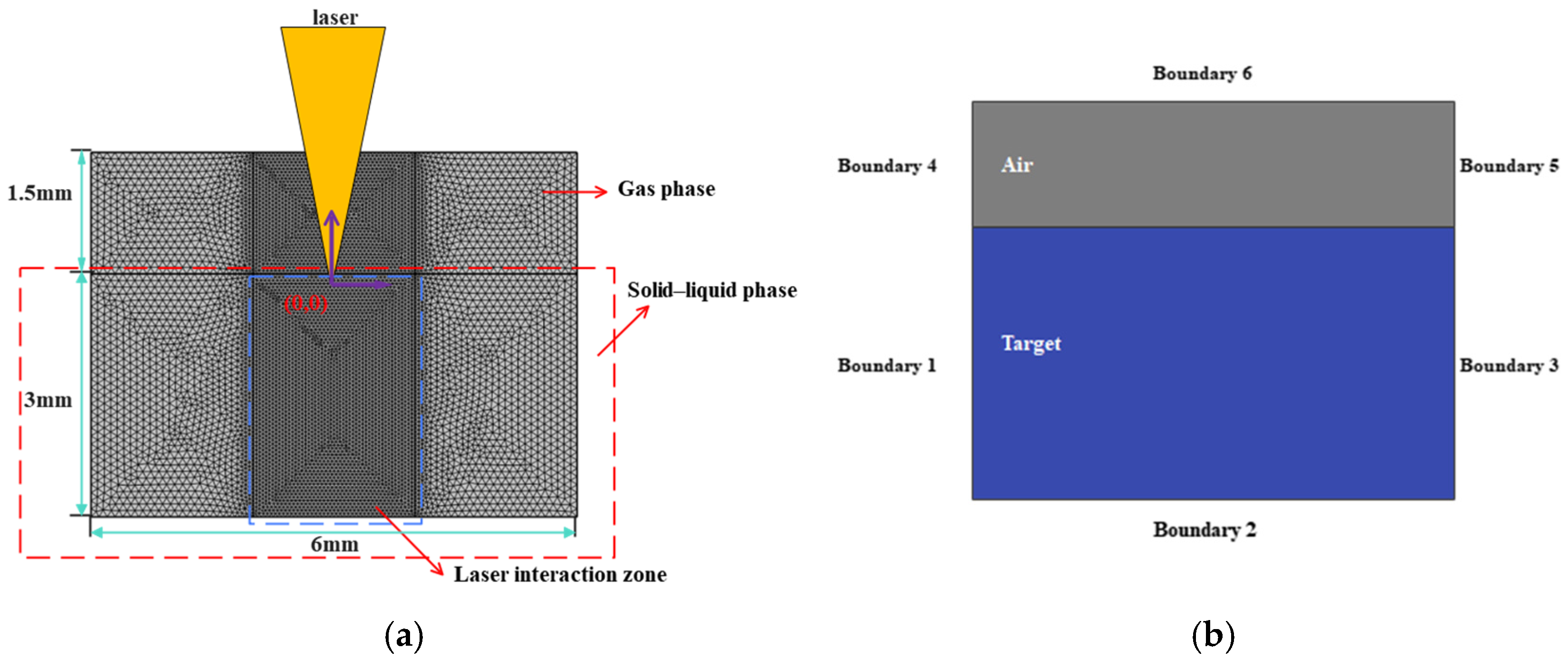
2.1.1. Modeling and Mesh Generation
2.1.2. Heat Source Model
2.1.3. Initial Conditions and Boundary Conditions
- Initial Conditions
- 2.
- Boundary Conditions
- (1)
- Chemical reactions between the high-temperature molten material and the surrounding gas are neglected.
- (2)
- The molten liquid within the melt pool is considered an incompressible Newtonian fluid.
- (3)
- The solid/liquid region is treated as an isotropic porous medium.
- (4)
- The effects of plasma formation are ignored.
2.1.4. Material Thermophysical Properties
2.2. Experiment
2.2.1. Experimental Materials
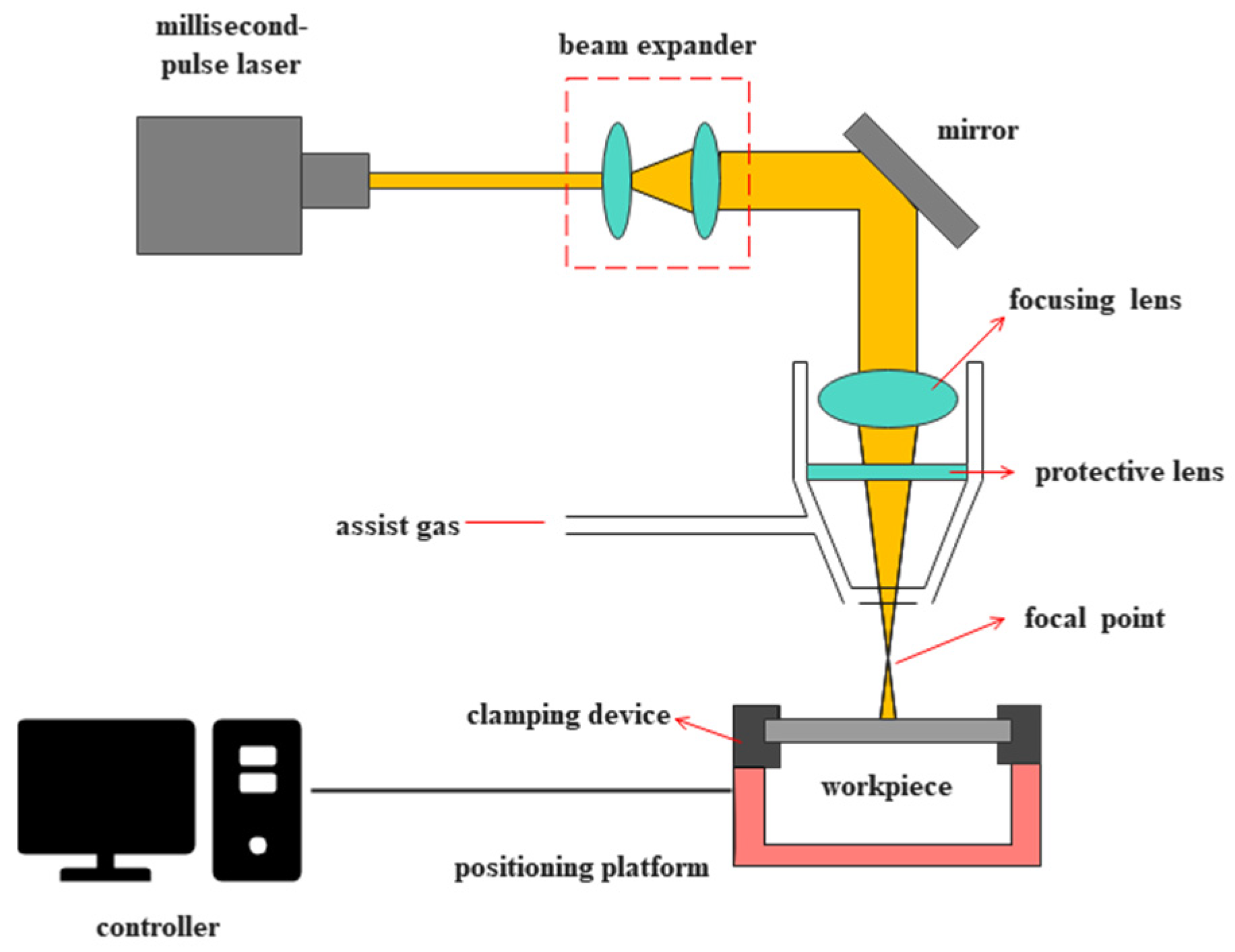
2.2.2. Experimental Equipment
2.2.3. Experimental Method
3. Experimental Results and Analysis
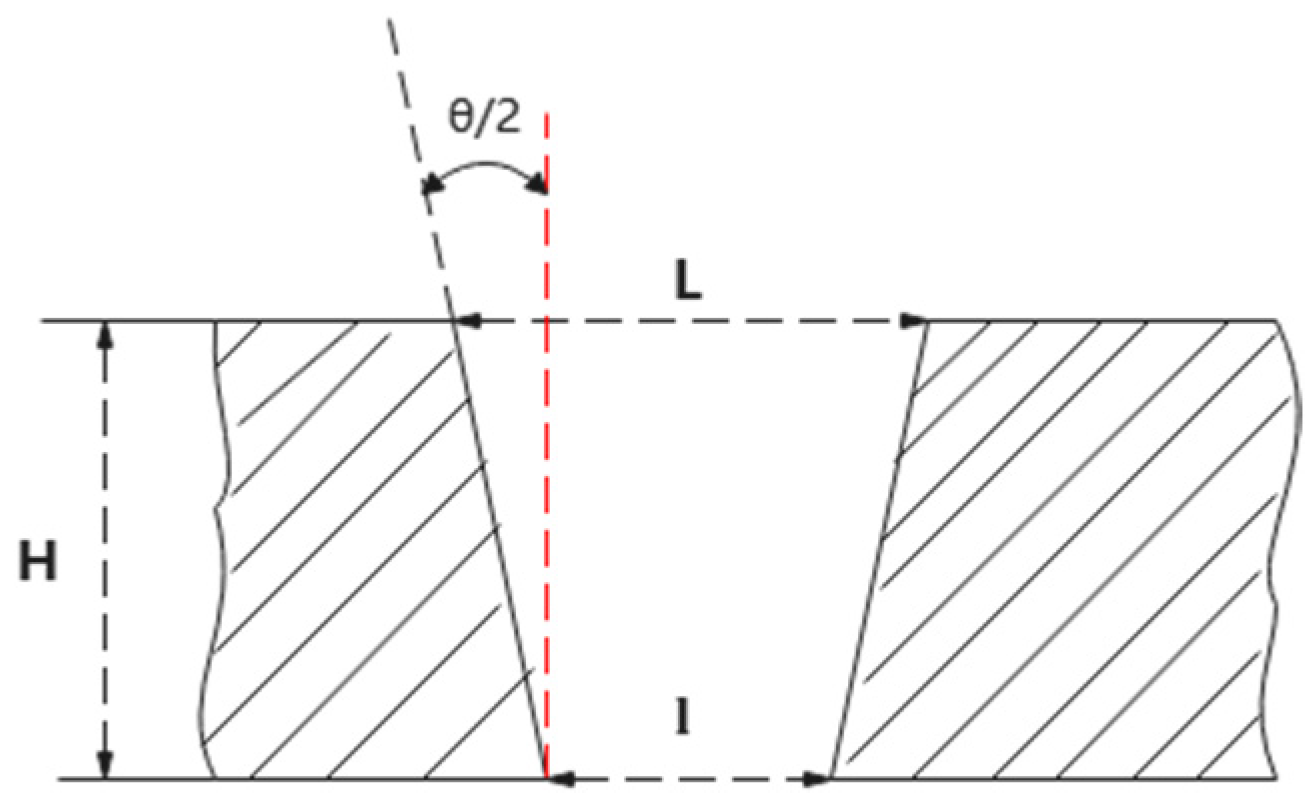
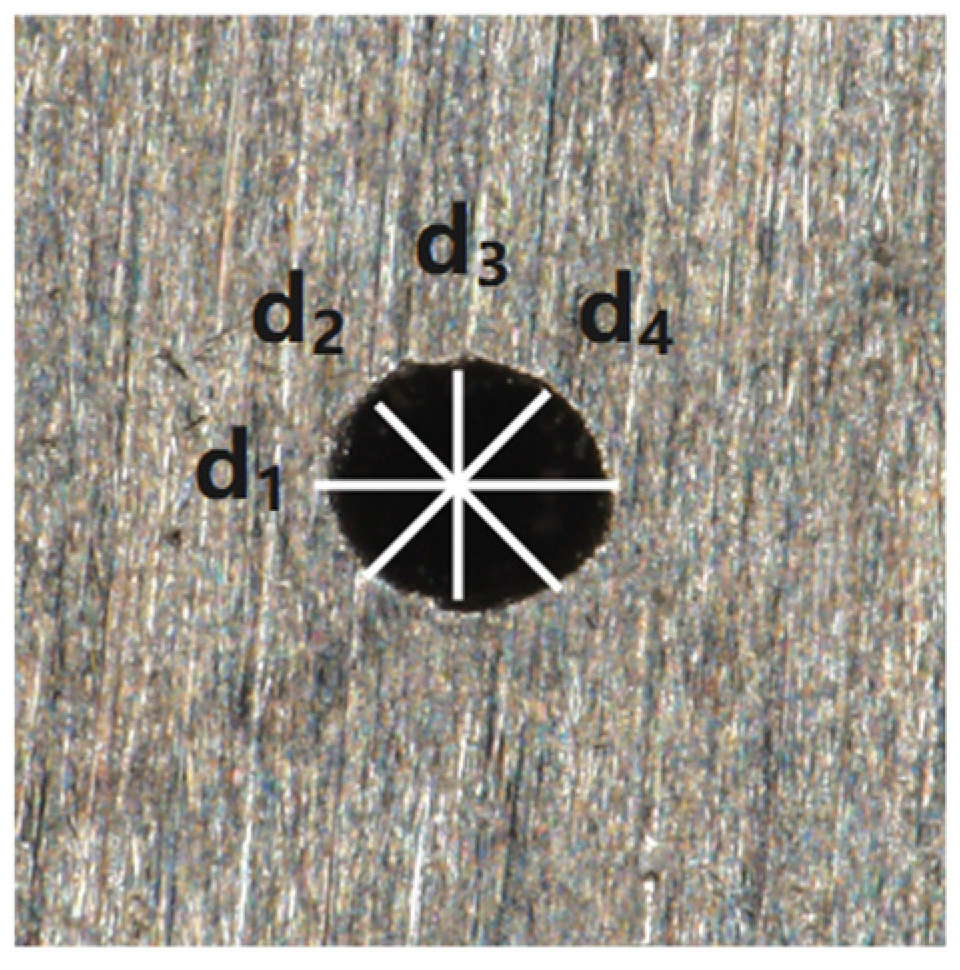
3.1. Through-Hole Research
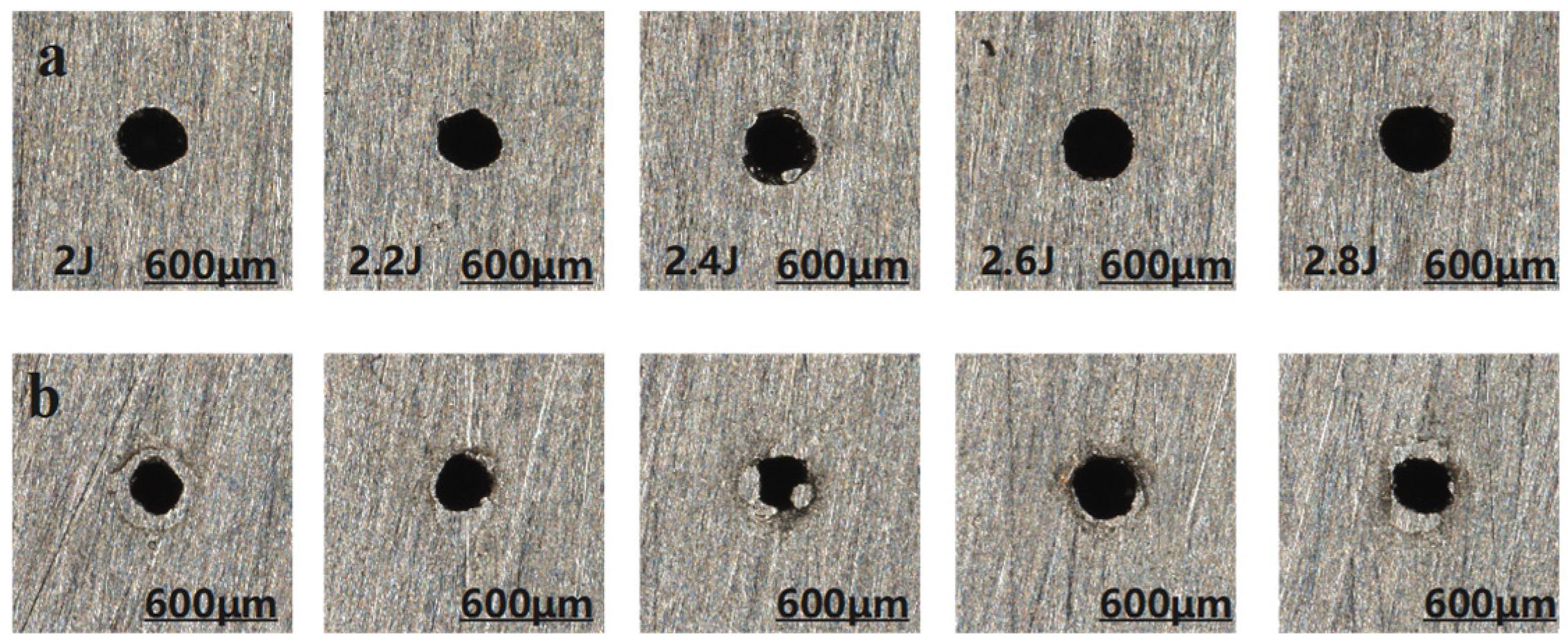
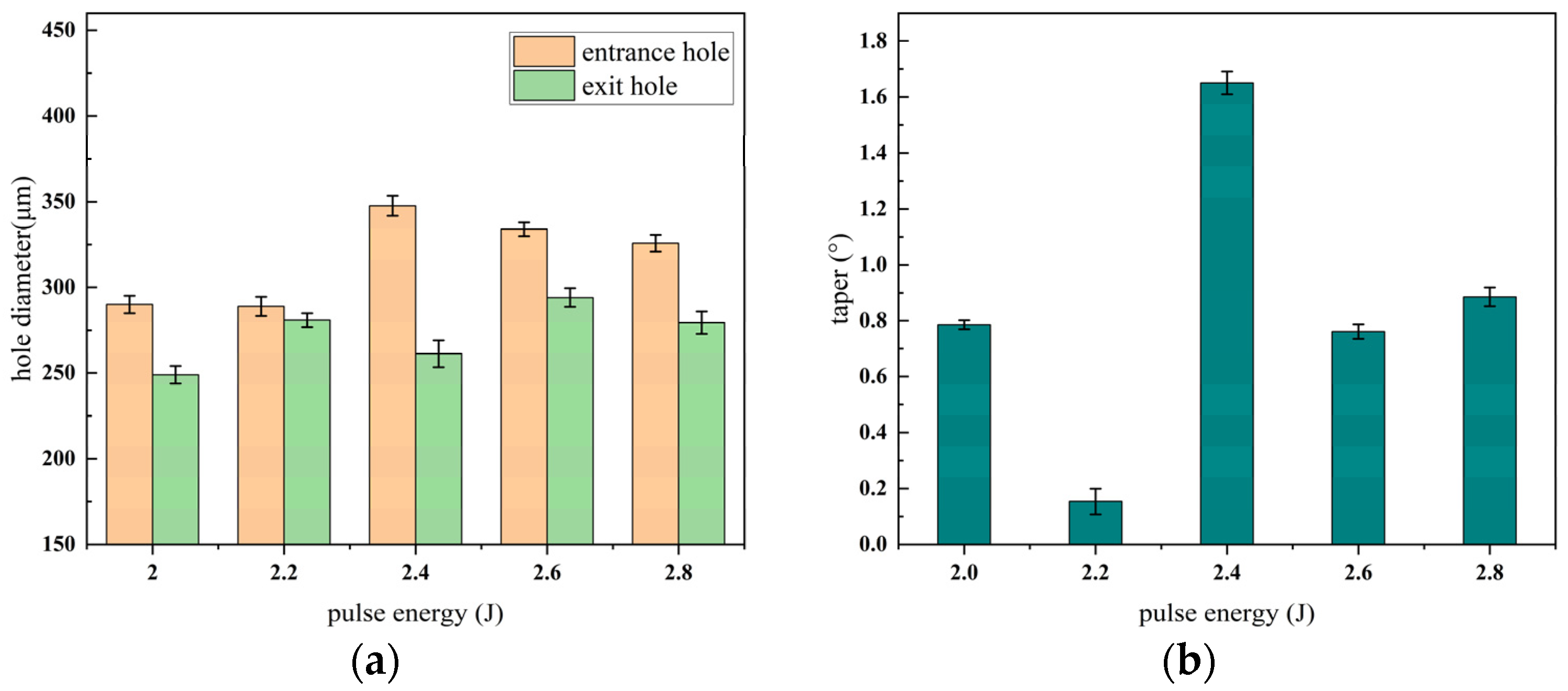
3.1.1. Influence of Different Pulse Energy on Micro-Hole Quality
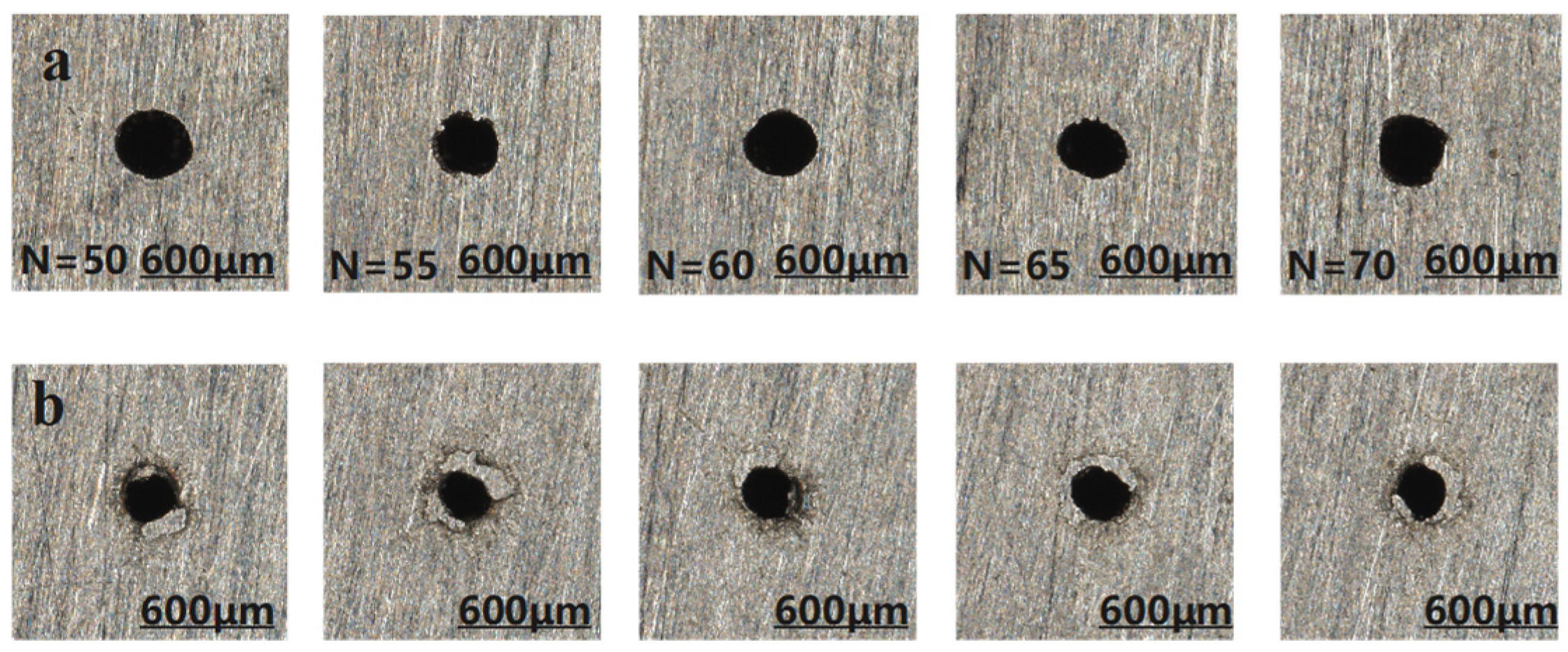
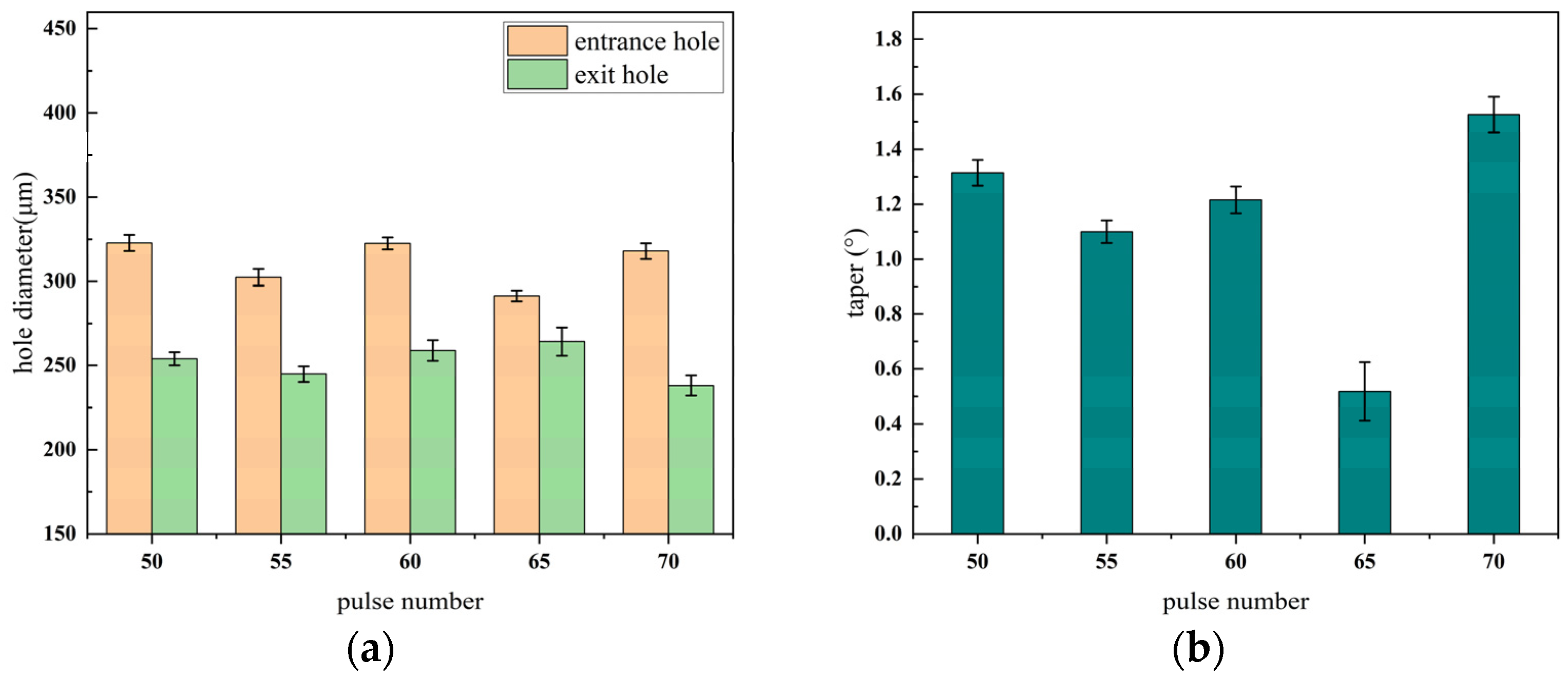
3.1.2. Effect of Different Pulse Number on the Quality of Micro-Hole
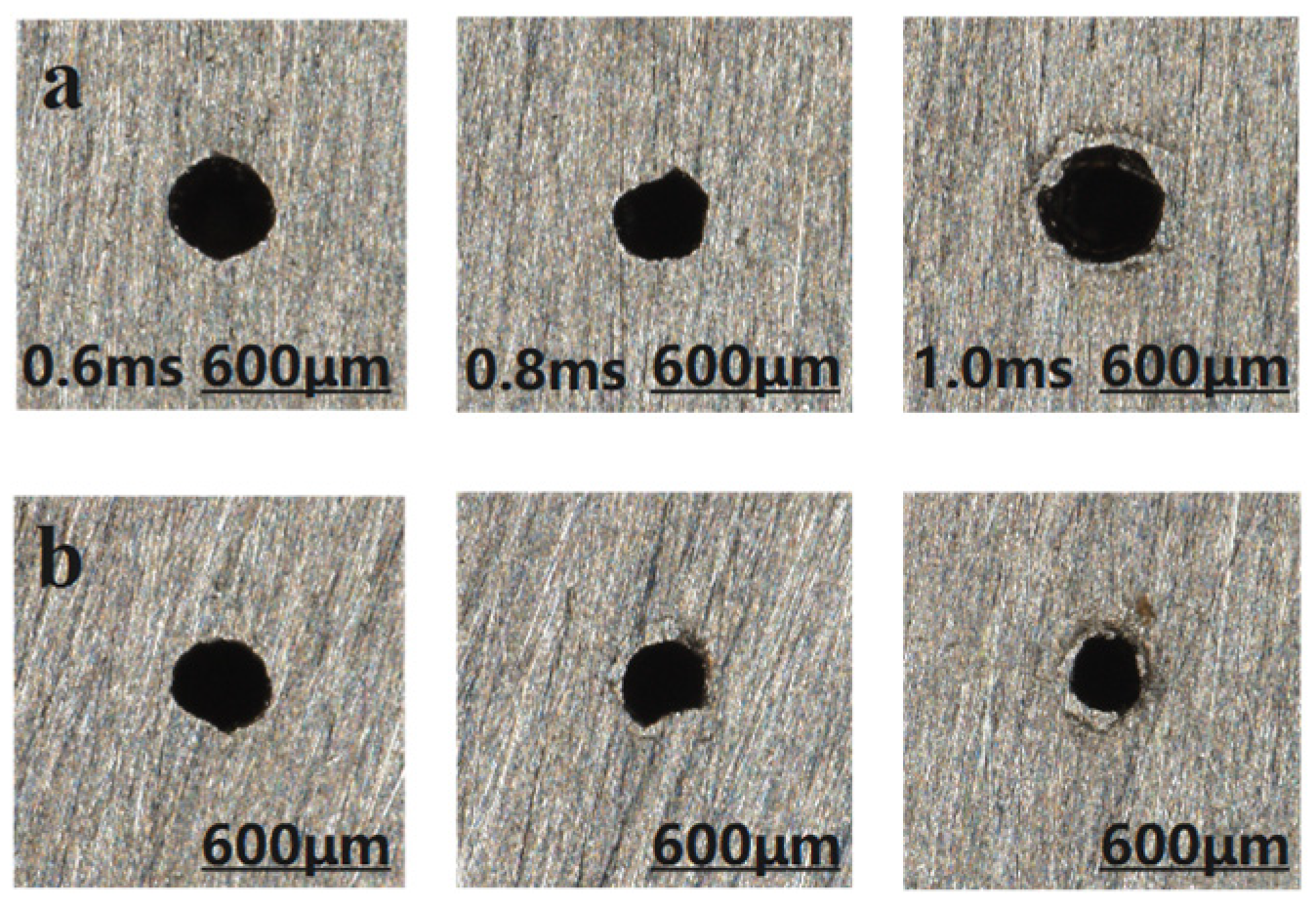
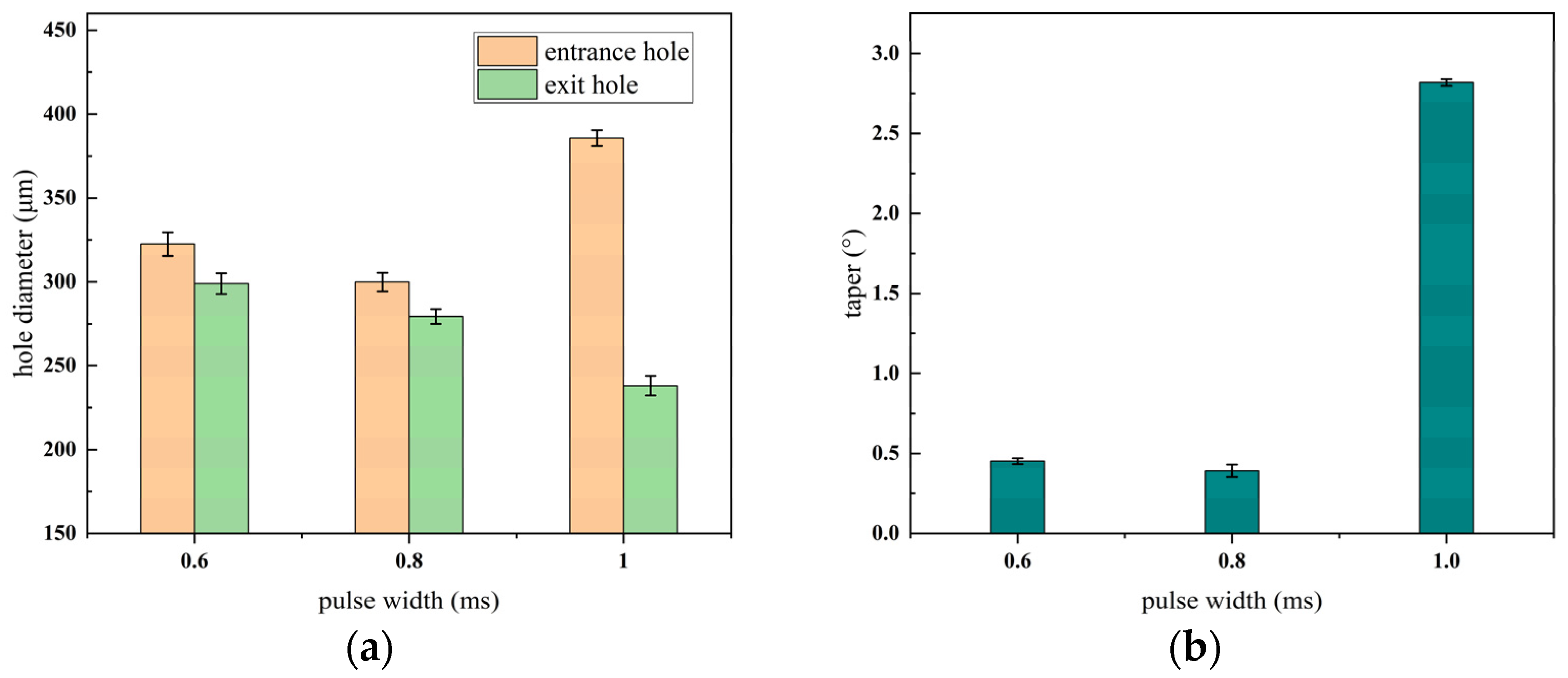
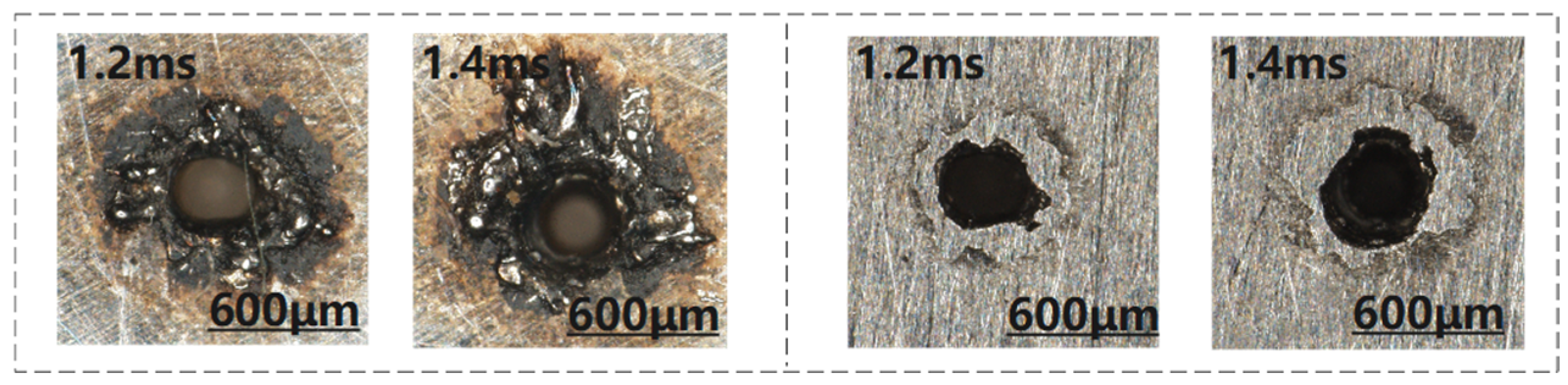
3.1.3. Effect of Different Width of Pulses on the Quality of Micro-Hole
3.2. Research on Blind Holes
3.2.1. Effect of Different Width of Pulses on the Quality of Blind Hole
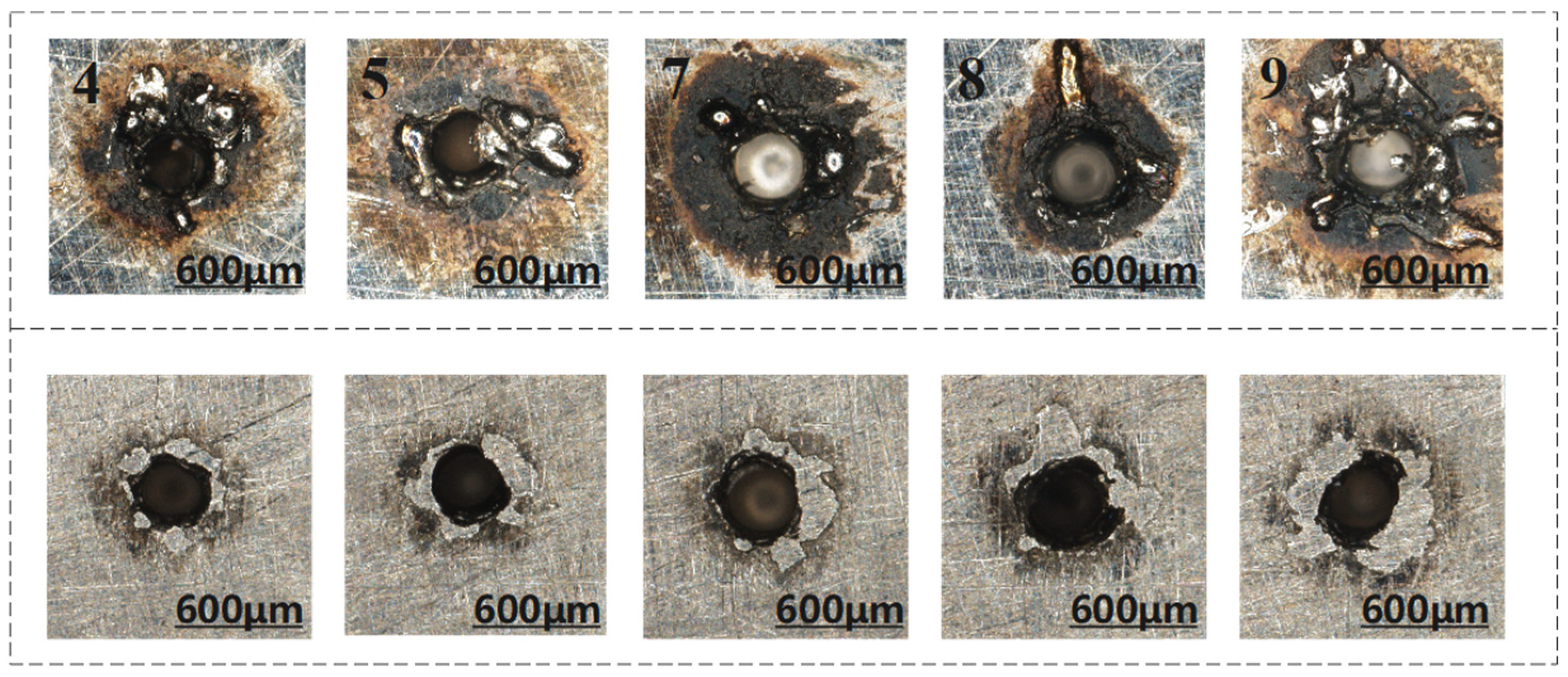
3.2.2. The Effect of Other Parameters on the Morphology of Blind Holes
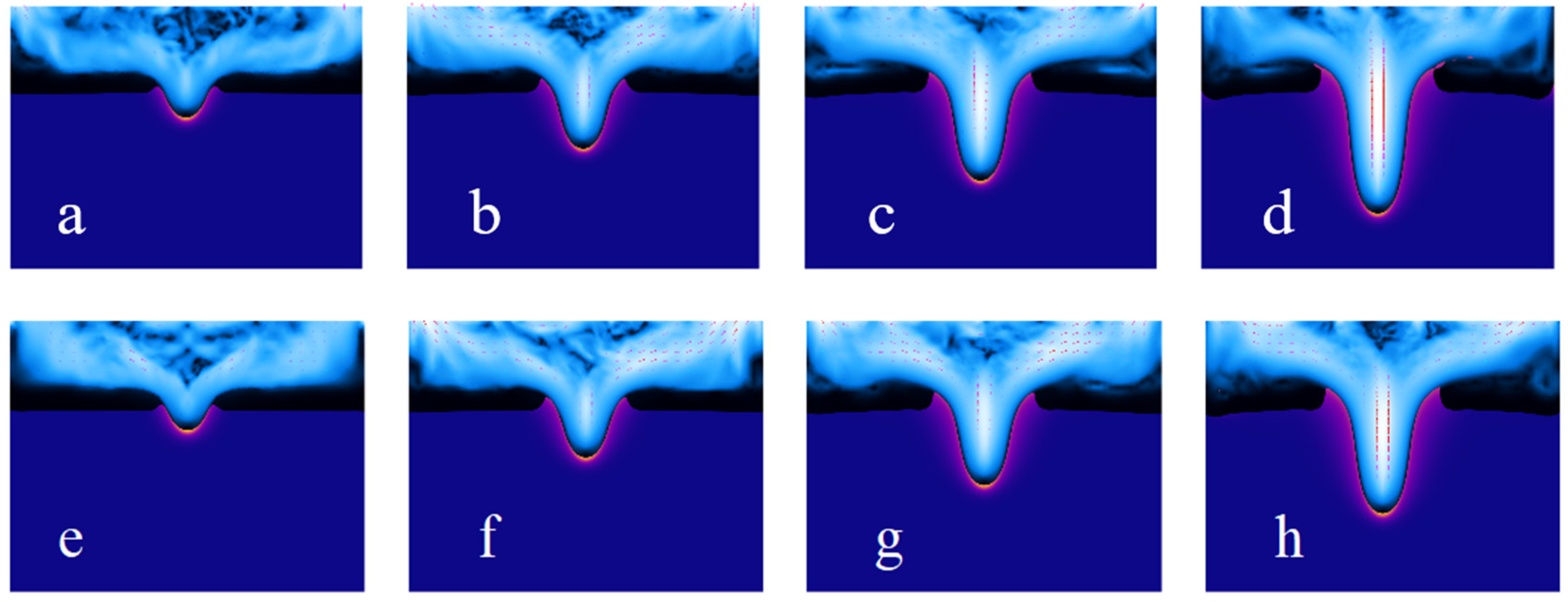
4. Numerical Simulation Analysis
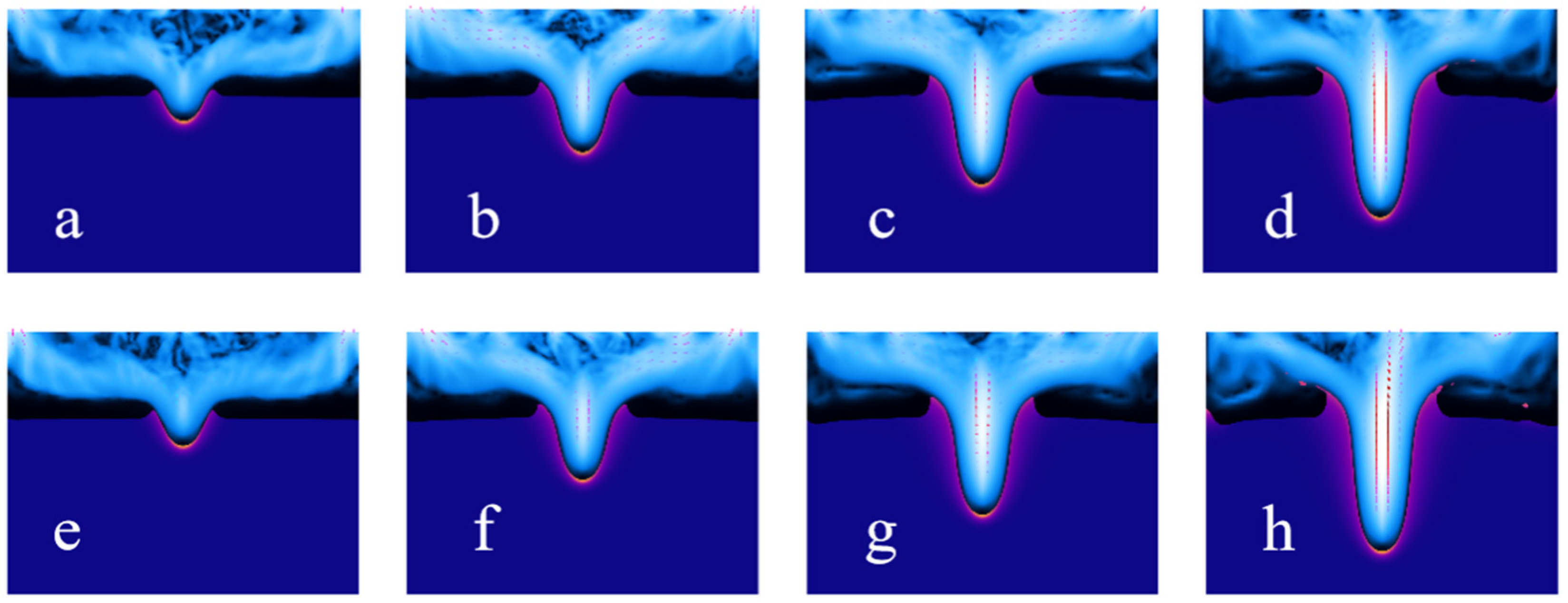
4.1. Effect of Pulse Energy
4.2. Effect of Pulse Width
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balakrishnan, T.S.; Sultan, M.T.H.; Shahar, F.S.; Saravanakumar, Y.N.; Chandran, N.K. Aerospace Steel: Properties, Processing, and Applications. In Aerospace Materials; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2025; pp. 275–290. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, J.; Cao, Y.; Ma, Y.; Zheng, K.; Zhang, M.; Hei, H.; Gong, H.; Yu, S.; Kuai, P.; Liu, K. Wear, corrosion, and biocompatibility of 316L stainless steel modified by well-adhered Ta coatings. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2022, 31, 8784–8798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, X.; Deng, R.; Yu, X.; Deng, W.; Shen, P. Tool wear and surface integrity analysis of austenitic stainless-steel machining with variable-length restricted contact tools at large depth of cut. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2025, 131, 107217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, A.A.; Li, M.J.; Mahmoud, S. On miniature hole quality and tool Wear when mechanical Drilling of Mild Steel. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 2020, 45, 8917–8929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, A.K.; Yadava, V. Laser beam machining—A review. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2008, 48, 609–628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdum, V.B.; Kittur, J.K.; Kulkarni, S.C. Surface roughness optimization in laser machining of stainless steel 304 using response surface methodology. Mater. Today Proc. 2022, 59, 540–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A.; Chatterjee, P.; Mondal, R.S.; Husain, M.M. Effect of Laser Beam Machining Process on Stainless Steel Performance Characteristic. SAE Int. J. Mater. Manuf. 2022, 15, 207–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahu, A.K.; Malhotra, J.; Jha, S. Laser-based hybrid micromachining processes: A review. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 146, 107554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, J.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Hayasaki, Y.; Kim, D.; Sun, S. Experimental study of nickel-based superalloy IN792 with femtosecond laser drilling method. Opt. Laser Technol. 2021, 143, 107335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Rong, Y.; Xu, L.; Wu, C.; Xia, K. Process Optimization on Trepanning Drilling in Titanium Alloy Using a Picosecond Laser via an Orthogonal Experiment. Micromachines 2025, 16, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattanayak, S.; Panda, S.; Dhupal, D. Laser micro drilling of 316L stainless steel orthopedic implant: A study. J. Manuf. Process. 2020, 52, 220–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Geng, D.; Chen, T.; Lu, D.; Chen, B. Second-derivative laser-induced fluorescence spectroscopy combined with chemometrics for authentication of the adulteration of camellia oil. CyTA J. Food 2018, 16, 747–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; He, Y.; Ji, J.; Fu, Y. Numerical simulation and experimental study of the shape variation influence on stainless steel drilling with picosecond laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2025, 181, 112021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Dai, X.; Xu, Y.; Liu, J.; Shan, J.; Ren, N.; Ren, X. Real-time observation with metallurgical examination for laser percussion drilling in stainless steel sheets using simultaneous magnetic-ultrasonic assistance. Opt. Commun. 2021, 493, 126869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bara, A.; Sahoo, S.K.; Naik, S.S.; Sahu, A.K.; Mahapatra, S.S. Multi response optimization of Nd: YAG laser micro drilling characteristics of 304 stainless steel using desirability function approach. Mater. Today Proc. 2018, 5, 18975–18982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Mao, Y.; Kang, M.; Ma, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. Fabrication of high aspect ratio micro-holes on 304 stainless steel via backside-water-assisted laser drilling. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2023, 162, 107426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Xu, Y.; Zheng, H.; Zhou, W.; Ren, N.; Ren, X.; Li, T. Monitoring and analysis of millisecond laser drilling process and performance with and without longitudinal magnetic assistance and/or assist gas. J. Manuf. Process. 2019, 48, 297–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhu, S.; Xu, G.; Zhou, W.; Li, L.; Zhang, D.H.; Ren, N.; Xia, K.; Shi, C. Influence of ultrasonic vibration on percussion drilling performance for millisecond pulsed Nd: YAG laser. Opt. Laser Technol. 2018, 104, 133–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, C.; Chen, X.; Li, J. Physical study of spatter and melt pool dynamics during millisecond laser metals drilling. Opt. Commun. 2021, 482, 126627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Wu, C.; Wu, T. Defocusing effect and energy absorption of plasma in picosecond laser drilling. Opt. Commun. 2021, 478, 126410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Physical Properties | Heat-Resistant Steel 310 |
|---|---|
| Solid Specific Heat | 500 J/(kg·K) |
| Liquid Specific Heat | 800 J/(kg·K) |
| Solid Phase Density | 7990 kg/m3 |
| Liquid Phase Density | 7200 kg/m3 |
| Solid Phase Dynamic Viscosity | 1012 pa·s |
| Liquid Phase Dynamic Viscosity | 0.005 pa·s |
| Latent Heat of Fusion | 2.5 × 105 J/kg |
| Latent Heat of Vaporization | 2 × 106 J/kg |
| Solid Phase Thermal Conductivity | 15 W/m·K |
| Liquid Phase Thermal Conductivity | 10 W/m·K |
| Thermal Expansion Coefficient | 15 × 10−6/°C |
| Solidus Temperature | 1673.15 K |
| Liquidus Temperature | 1723.15 K |
| Melting Temperature | 1653.15 K |
| Vaporization Temperature | 3300 K |
| C | Mn | Ni | Si | P | S | Cr | Mo | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ≤0.03 | ≤2 | 10~14 | ≤1 | ≤0.045 | ≤0.030 | 16~18 | 2~3 | balance |
| Pulse Energy/J | Pulse Width/ms | Number of Pulses |
|---|---|---|
| 2.0, 2.2, 2.4, 2.6, 2.8 | 0.8 | 50 |
| 2.5 | 0.6, 0.8, 1.0, 1.2, 1.4 | 50 |
| 2.0 | 0.8 | 50, 55, 60, 65, 70 |
| Hole Number | Pulse Width/ms | Pulse Energy/J | Number of Pulses | Entrance Diameter/μm |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.8 | 2 | 50 | 302.542 |
| 2 | 0.8 | 2.2 | 55 | 311.630 |
| 3 | 0.8 | 2.4 | 60 | 329.365 |
| 4 | 1 | 2 | 60 | 357.709 |
| 5 | 1 | 2.2 | 50 | 376.210 |
| 6 | 1 | 2.4 | 55 | 346.845 |
| 7 | 1.2 | 2 | 55 | 395.830 |
| 8 | 1.2 | 2.2 | 60 | 453.470 |
| 9 | 1.2 | 2.4 | 50 | 456.587 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, L.; Wu, C.; Rong, Y.; Xu, L.; Xia, K. Experimental Study on Millisecond Laser Percussion Drilling of Heat-Resistant Steel. Materials 2025, 18, 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153699
Wang L, Wu C, Rong Y, Xu L, Xia K. Experimental Study on Millisecond Laser Percussion Drilling of Heat-Resistant Steel. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153699
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Liang, Changjian Wu, Yefei Rong, Long Xu, and Kaibo Xia. 2025. "Experimental Study on Millisecond Laser Percussion Drilling of Heat-Resistant Steel" Materials 18, no. 15: 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153699
APA StyleWang, L., Wu, C., Rong, Y., Xu, L., & Xia, K. (2025). Experimental Study on Millisecond Laser Percussion Drilling of Heat-Resistant Steel. Materials, 18(15), 3699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153699






