Estimation of the Kinetic Coefficient of Friction of Asphalt Pavements Using the Top Topography Surface Roughness Power Spectrum
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Persson’s Friction Theory Without Consideration of Top Texture
2.1. Persson’s Rubber Friction Theory
2.2. Top Topography PSD
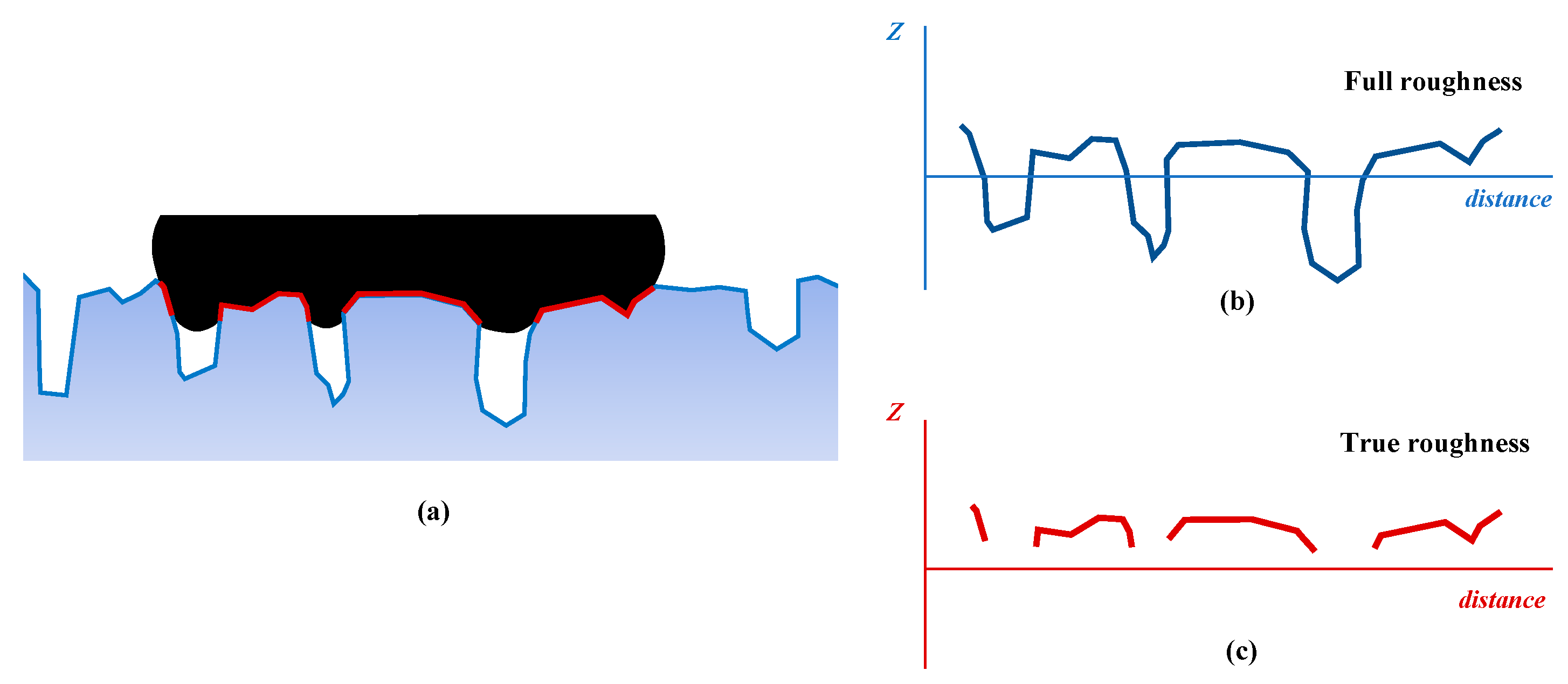
2.3. Optimal Cutting Plane of Top Topography
3. Materials and Methods
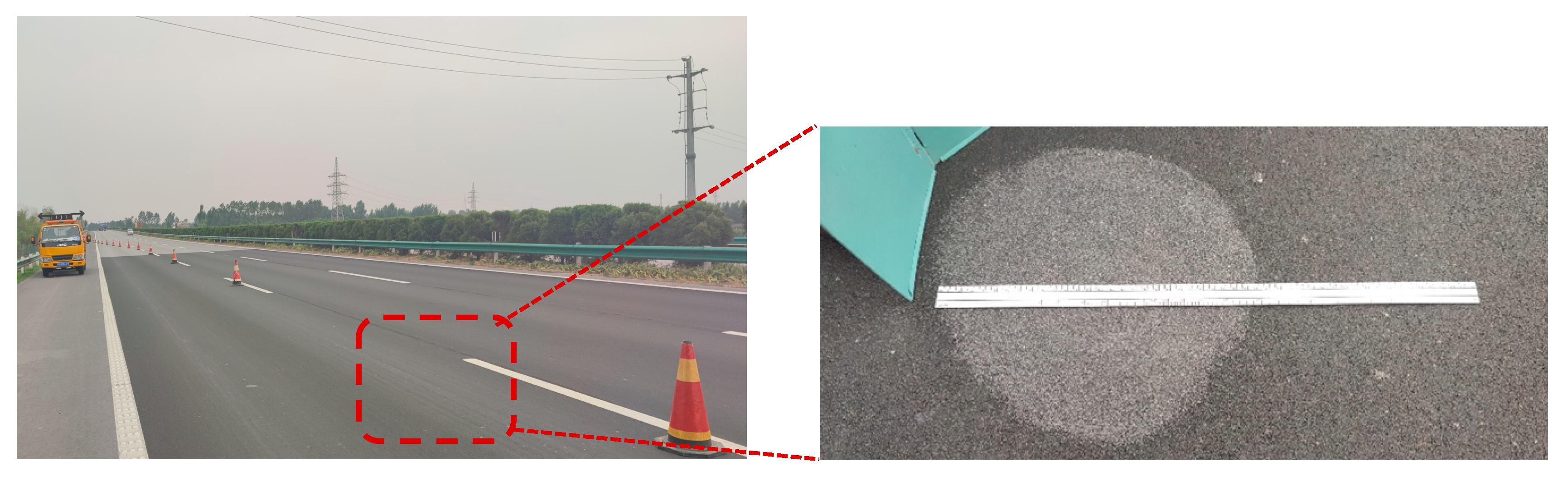
3.1. Pavement Samples
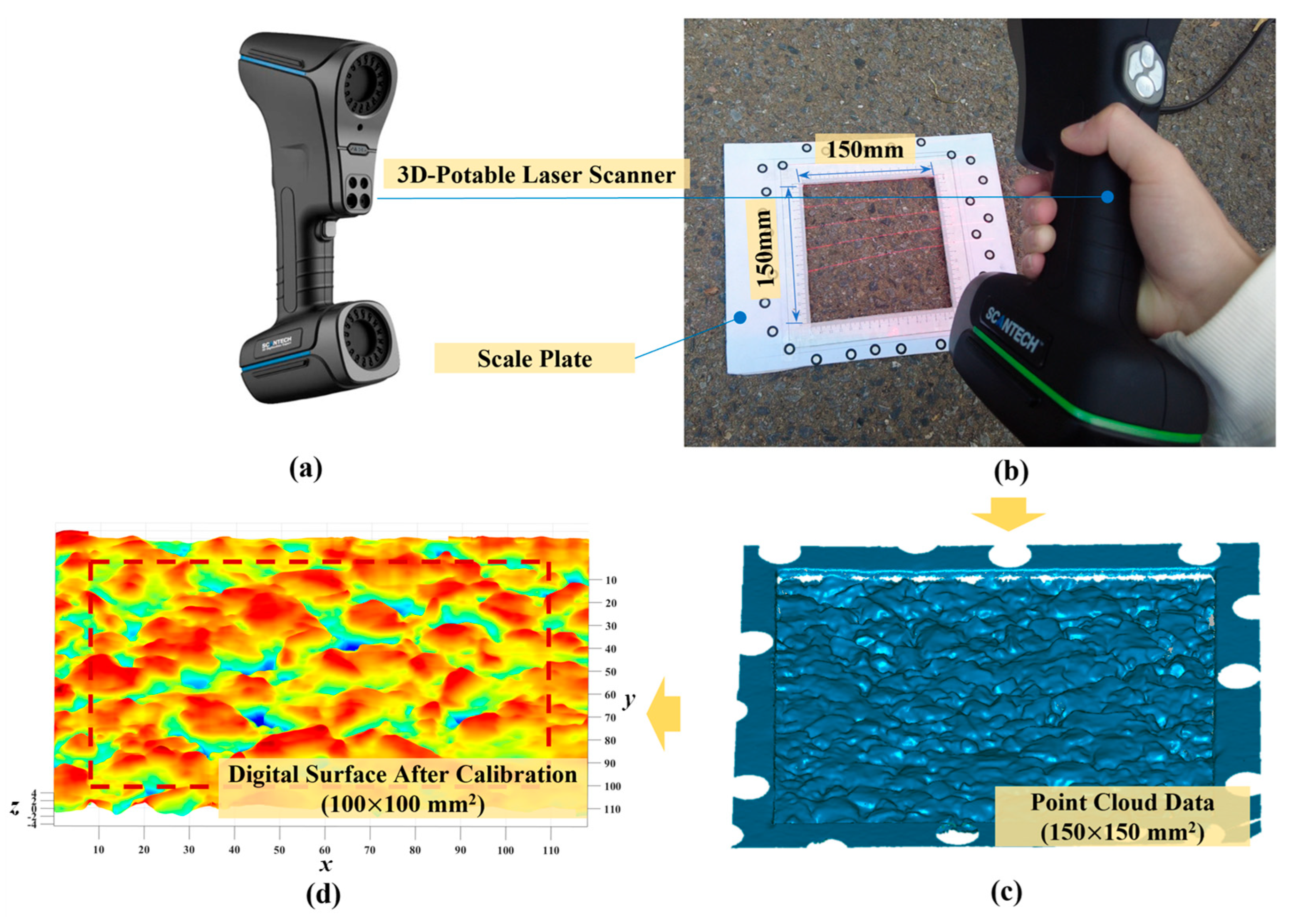
3.2. Data Acquisition and Preprocessing
3.2.1. Digitized Pavement Texture by 3D Laser Scanning
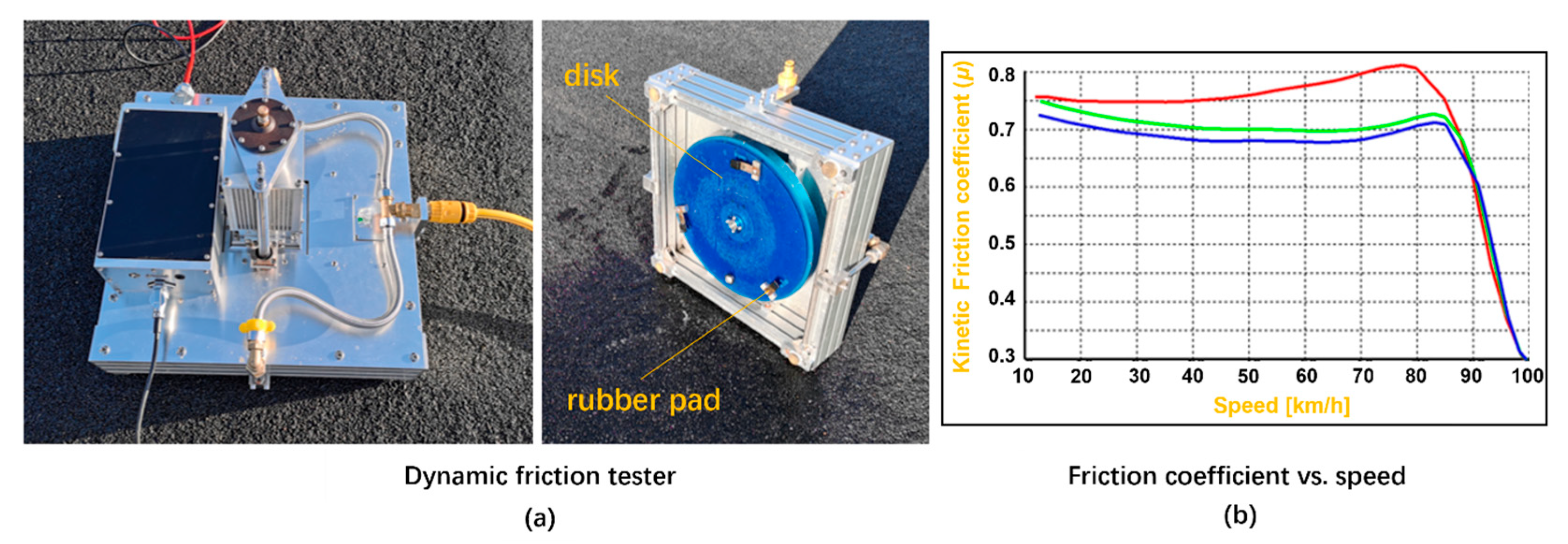
3.2.2. Dynamic Friction Test
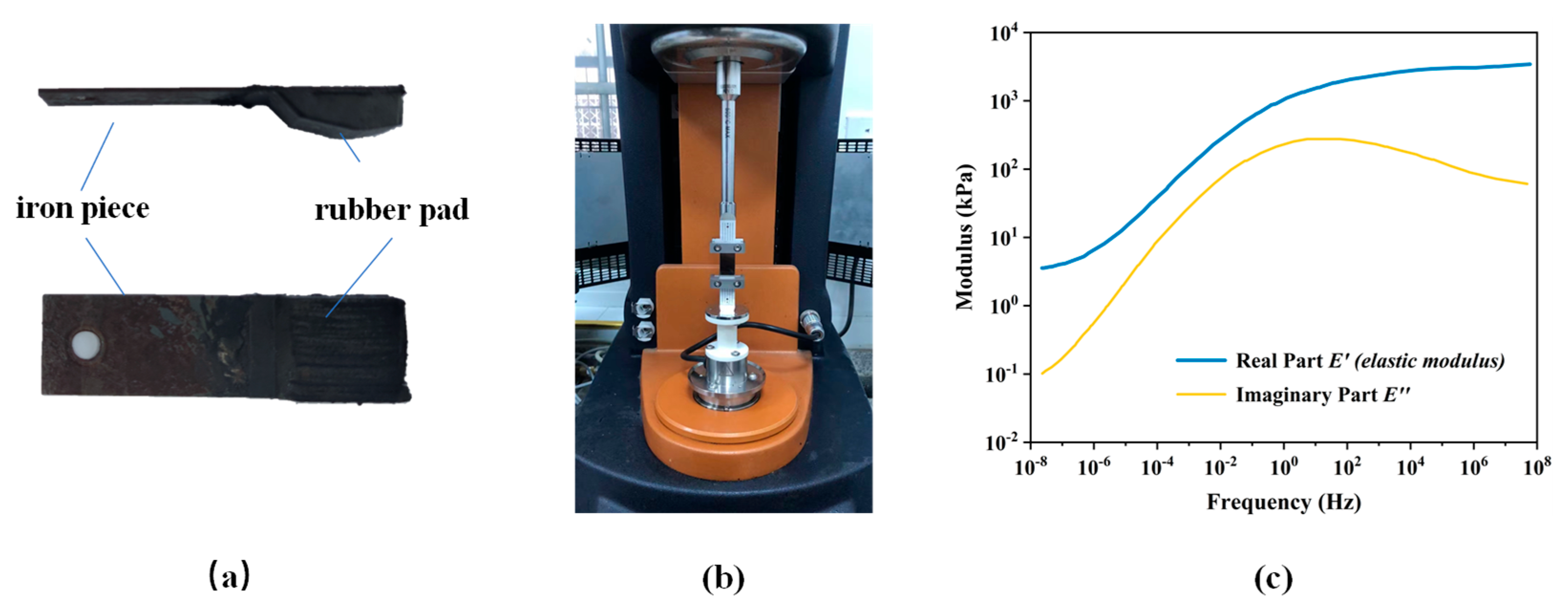
3.2.3. Modulus of Rubber
4. Discussions and Results
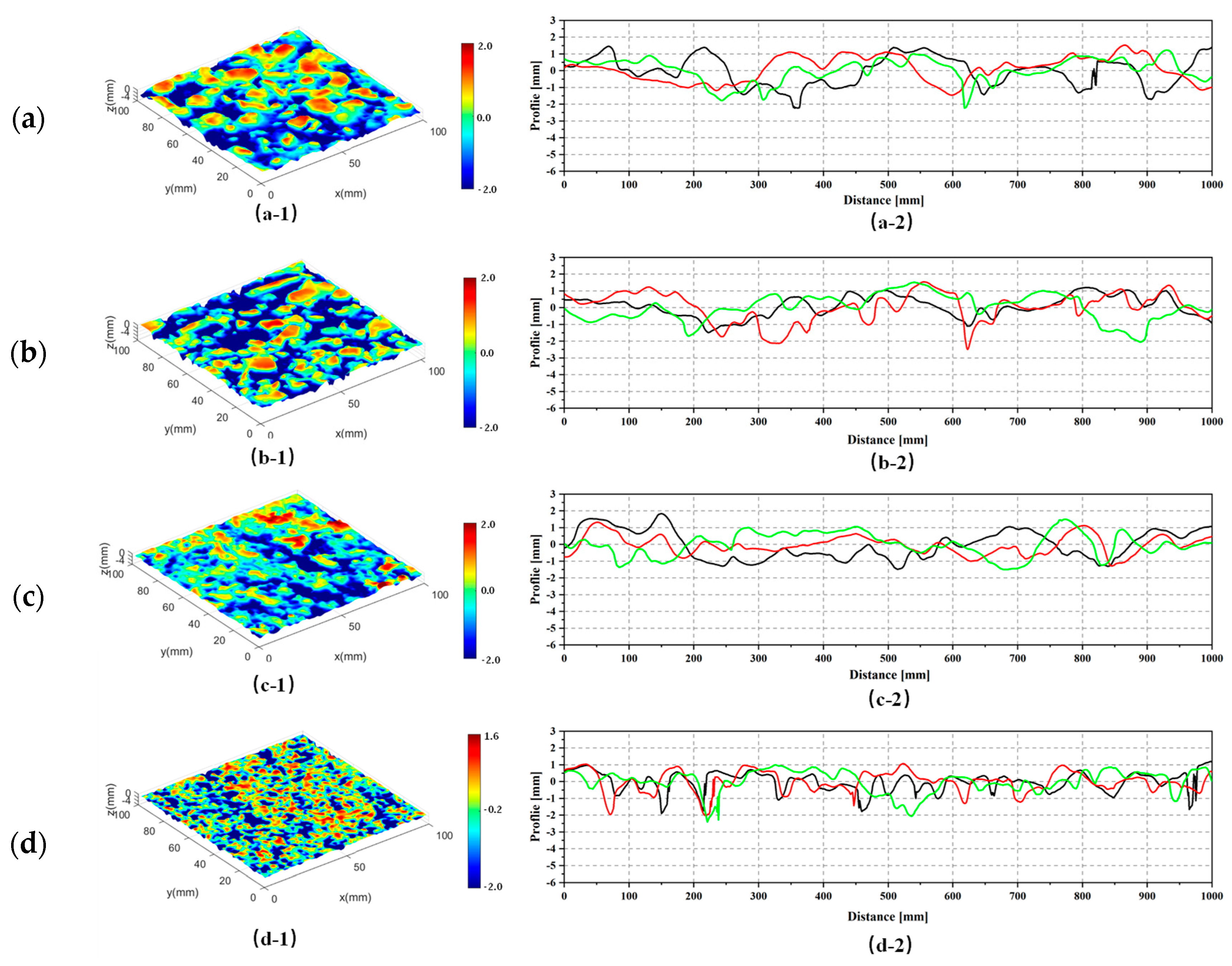
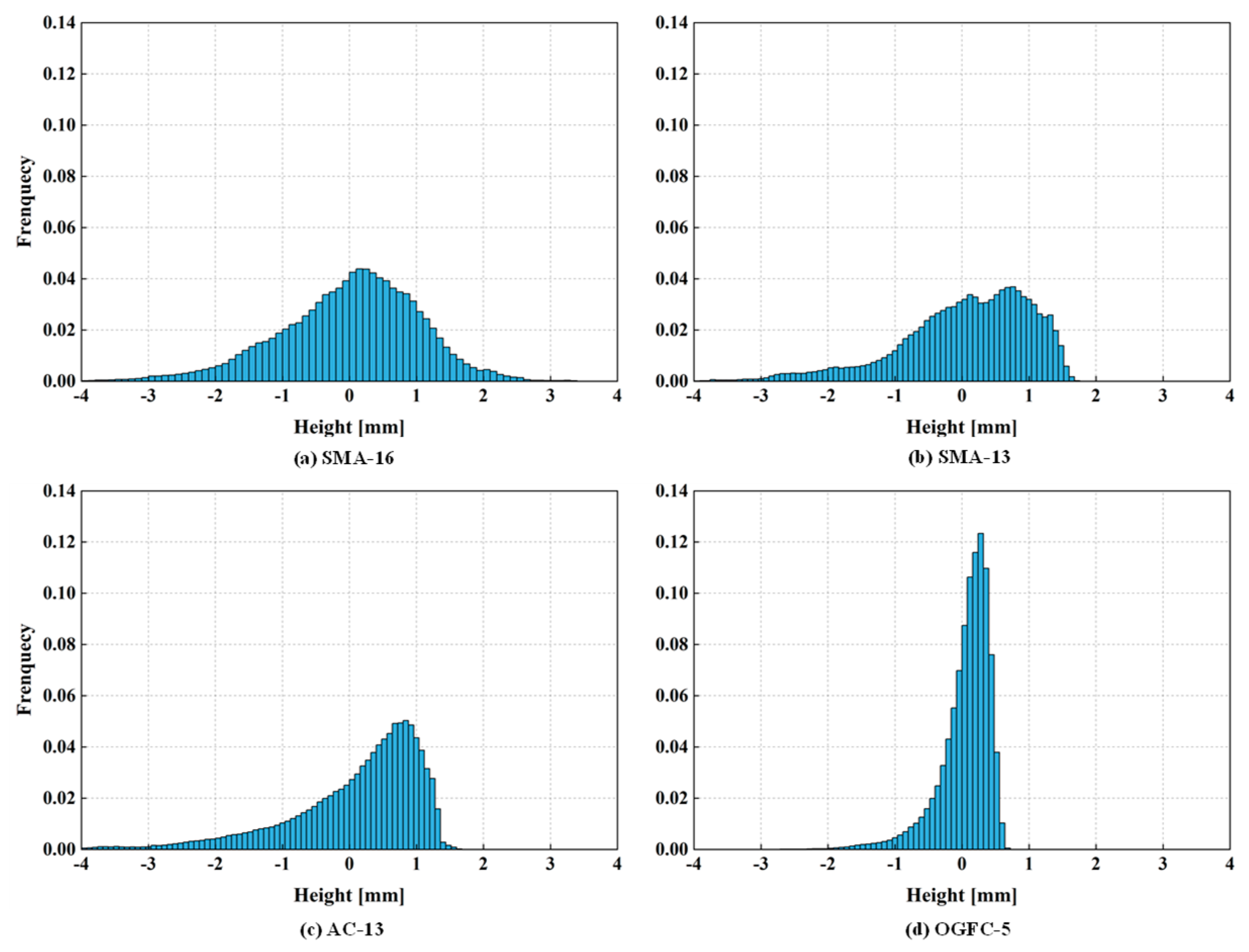
4.1. Texture Characterization
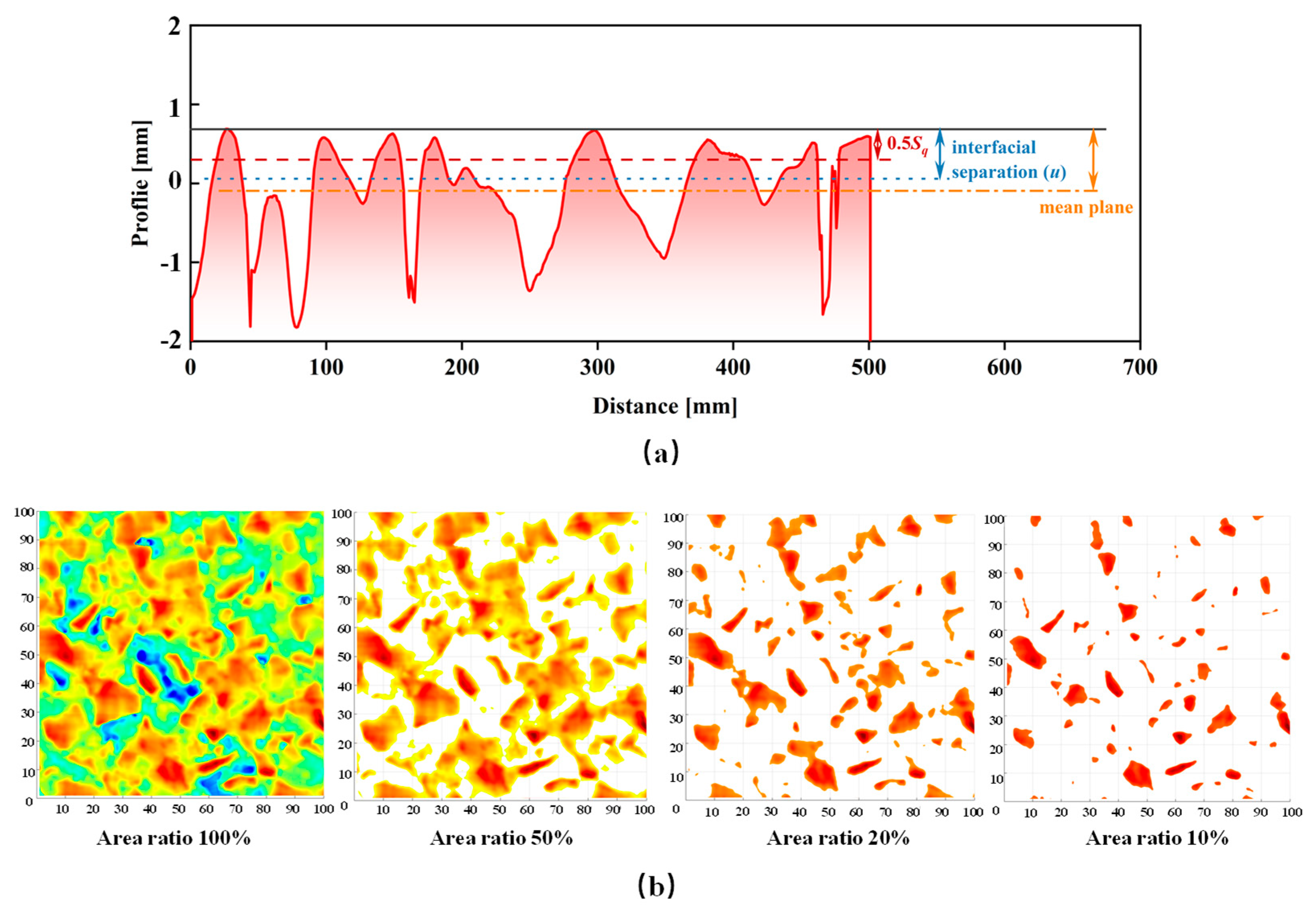
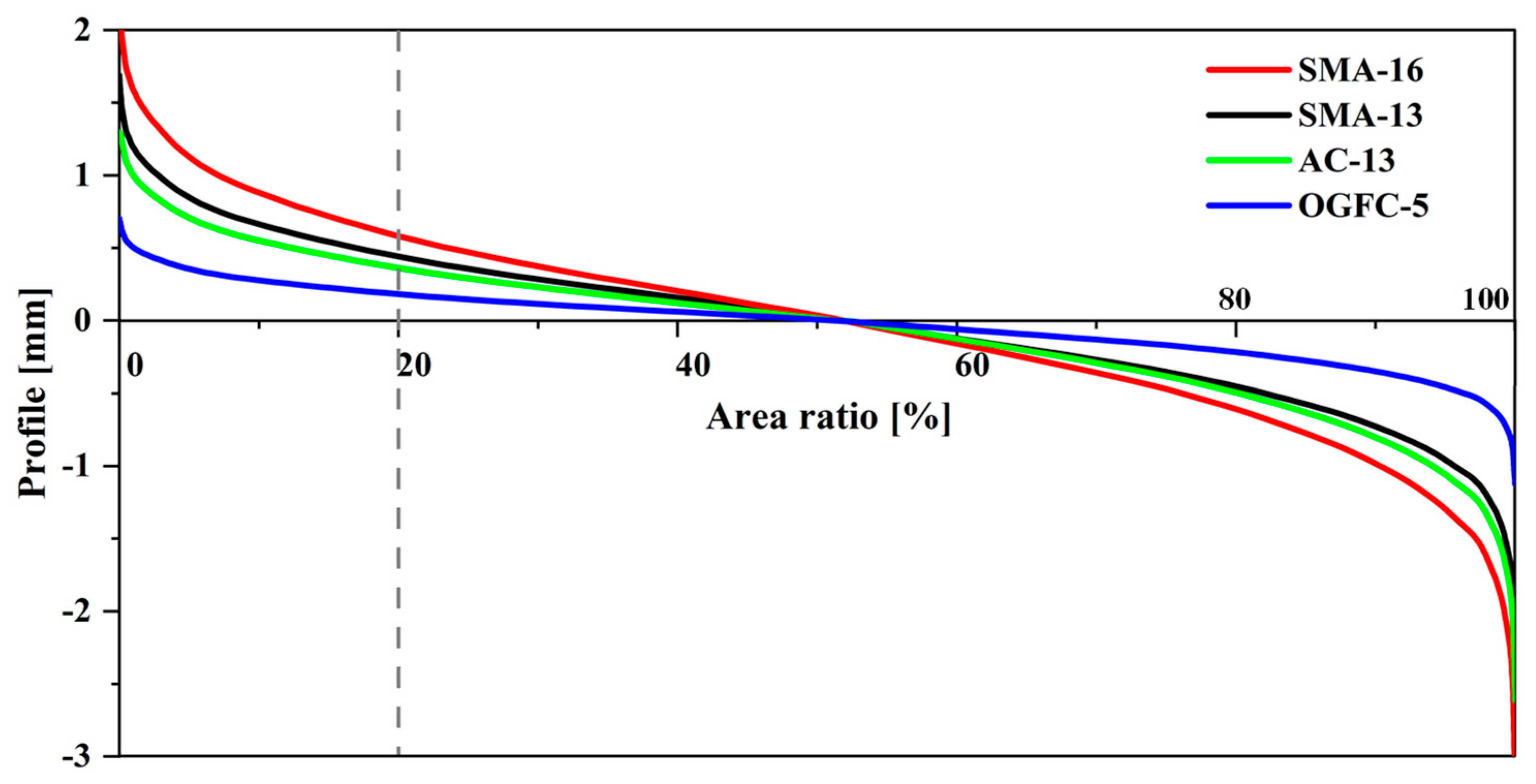
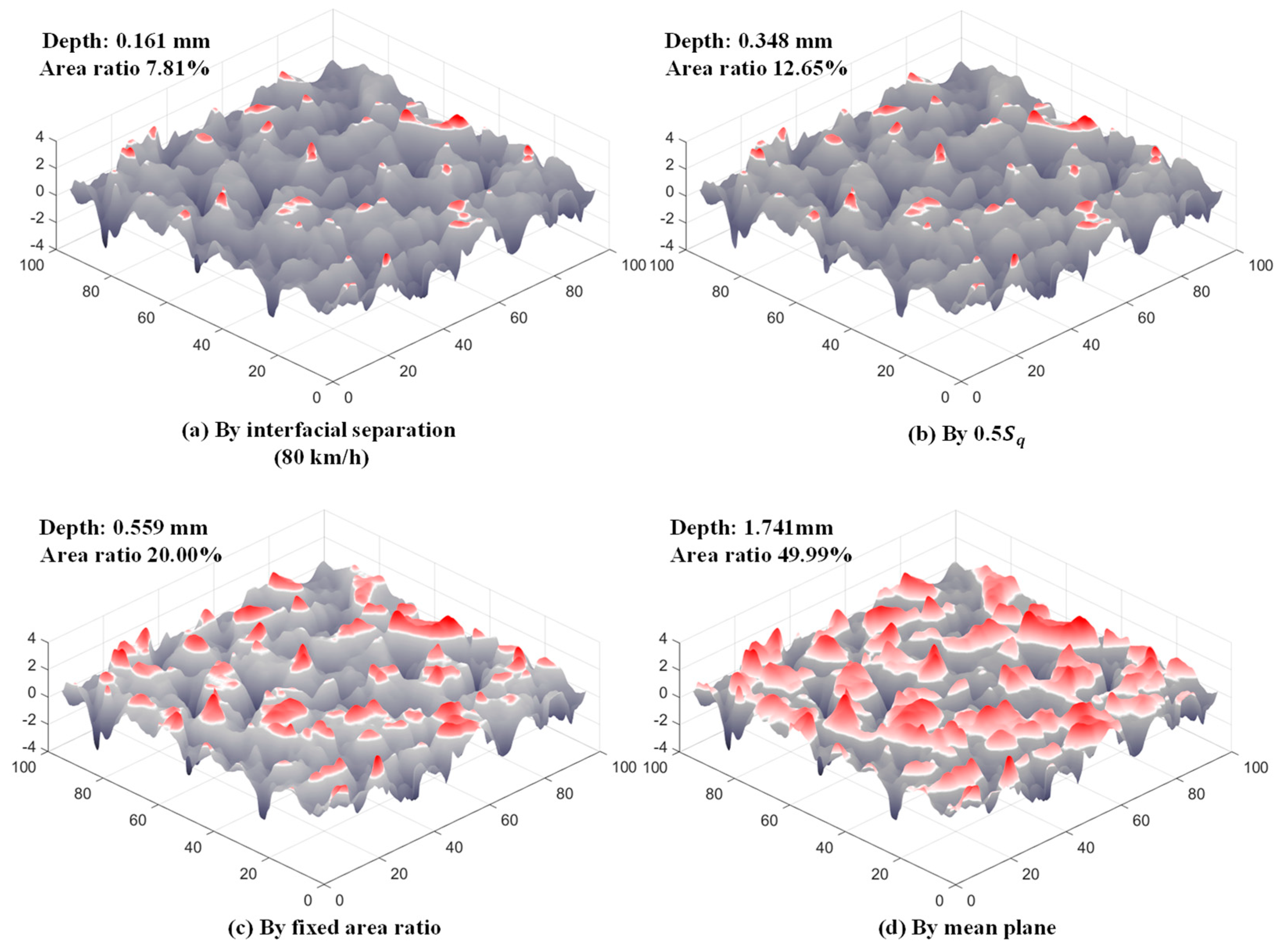
4.2. Top Topography and the Cutting Depth
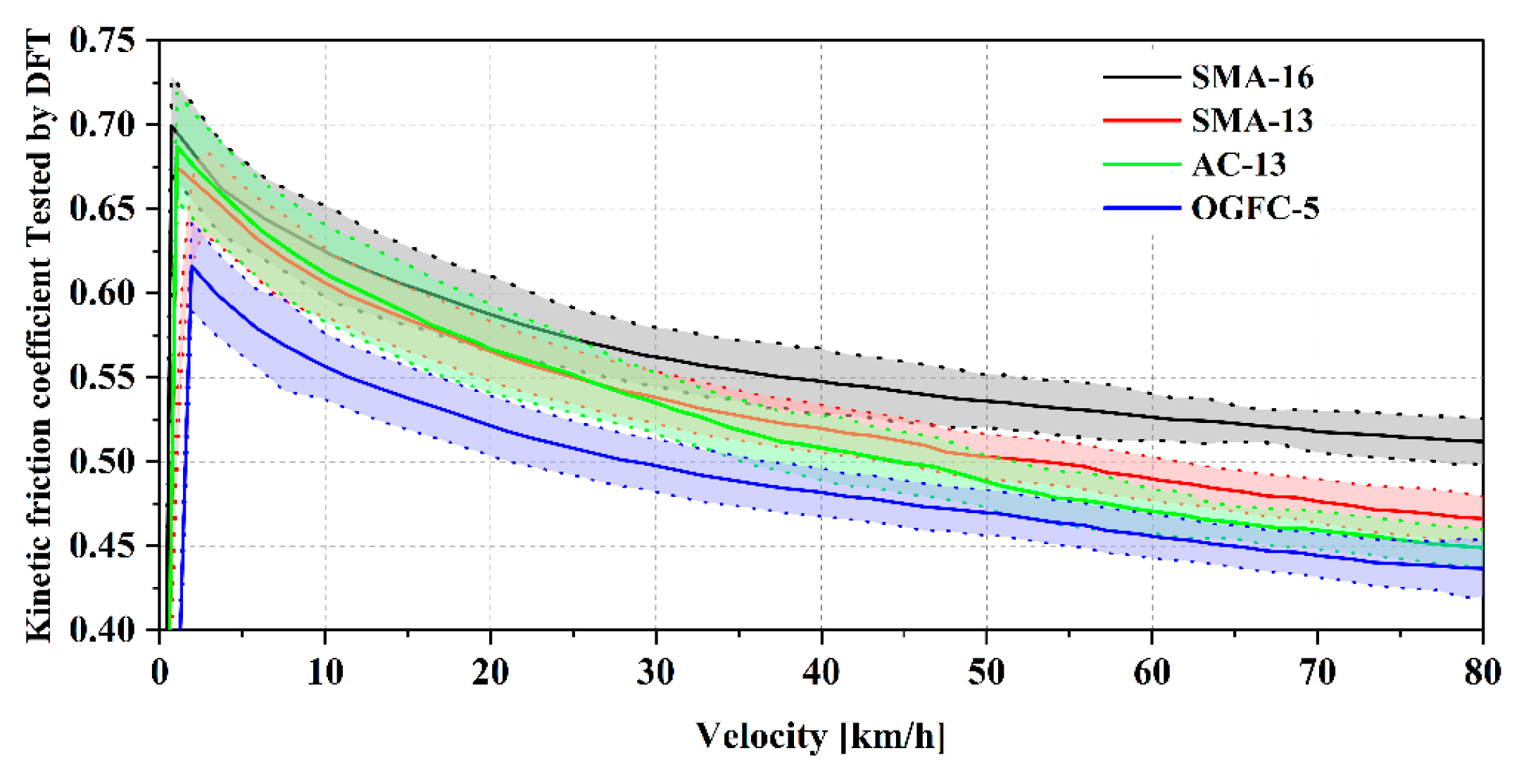
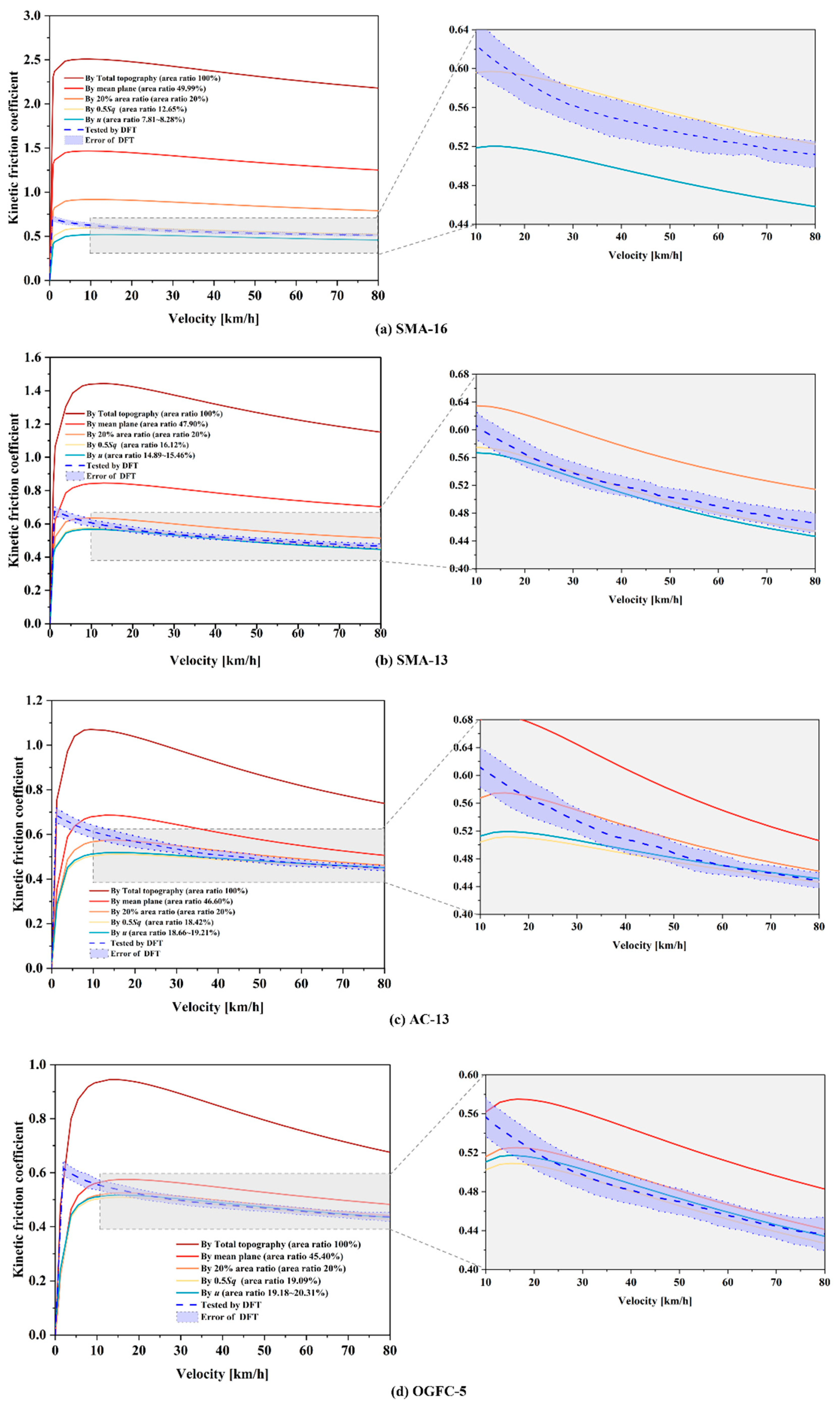
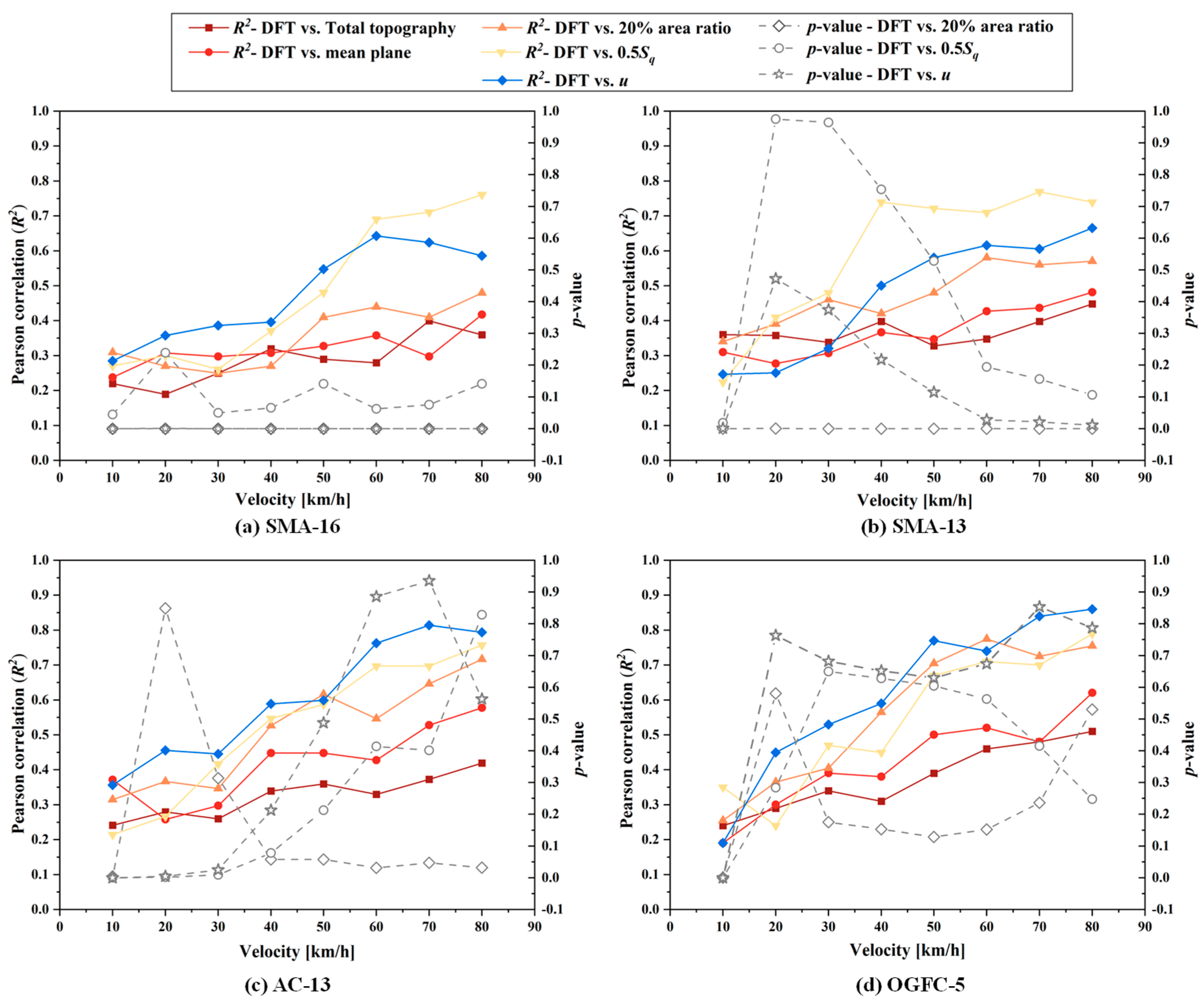
4.3. Kinetic Coefficient of Friction: Experimental vs. Theoretical
5. Summary and Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chen, S.; Liu, X.; Luo, H.; Yu, J.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, T.; Huang, X. A state-of-the-art review of asphalt pavement surface texture and its measurement techniques. J. Road Eng. 2022, 2, 156–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Wang, K.C.; Li, J.Q. Multiresolution analysis of three-dimensional (3D) surface texture for asphalt pavement friction estimation. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2021, 22, 1882–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; You, Z.; Wu, G.; Kong, L.; Liu, C.; Gao, J. Measurement and modeling of skid resistance of asphalt pavement: A review, Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 119878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fwa, T. Determination and prediction of pavement skid resistance–connecting research and practice. J. Road Eng. 2021, 1, 43–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Williamson, J.B.P. The contact of nominally-flat surfaces Contact of Nominally Flat Surfaces. Int. Res. Symp. Electr. Contact Phenom. 1964, 295, 300–319. [Google Scholar]
- Hertz, H. Miscellaneous Papers; Macmillan: New York, NY, USA, 1896. [Google Scholar]
- Greenwood, J.A.; Tabor, D. Deformation properties of friction junctions. Proc. Phys. Soc. Sect. B 1955, 68, 609–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KlüpPel, M.; Heinrich, G. Rubber friction on self-affine road tracks. Rubber Chem. Technol. 2000, 73, 578–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, G.; Klüppel, M.; Vilgis, T. Vilgis, Evaluation of self-affine surfaces and their implication for frictional dynamics as illustrated with a Rouse material. Comput. Theor. Polym. Sci. 2000, 10, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, G.; Klüppel, M. Rubber friction, tread deformation and tire traction. Wear 2008, 265, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Theory of rubber friction and contact mechanics. J. Chem. Phys. 2001, 115, 3840–3861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. On the fractal dimension of rough surfaces. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 54, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, S.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Huang, X. Numerical study of tire hydroplaning based on power spectrum of asphalt pavement and kinetic friction coefficient. Adv. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2017, 2017, 5843061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Huang, X. Evaluation of Vehicle Braking Performance on Wet Pavement Surface using an Integrated Tire-Vehicle Modeling Approach. Transp. Res. Rec. 2019, 2673, 295–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafi, M.M.; Tuononen, A.J. Tuononen, Application of three-dimensional printing to pavement texture effects on rubber friction. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2017, 18, 865–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, B.; Oh, Y.R.; Nam, S.K.; Jeon, S.H.; Persson, B.N.J. Persson, Rubber friction on road surfaces: Experiment and theory for low sliding speeds. J. Chem. Phys. 2015, 142, 194701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Tartaglino, U.; Albohr, O.; Tosatti, E. Rubber friction on wet and dry road surfaces: The sealing effect. Phys. Rev. B-Condens. Matter Mater. Phys. 2005, 71, 035428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J.; Albohr, O.; Tartaglino, U.; Volokitin, A.I.; Tosatti, E. On the nature of surface roughness with application to contact mechanics, sealing, rubber friction and adhesion. J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 2004, 17, R1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, B.; Persson, B.N.J.; Dieluweit, S.; Tada, T. Rubber friction: Comparison of theory with experiment. Eur. Phys. J. E 2011, 34, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hartikainen, L.; Petry, F.; Westermann, S. Frequency-wise correlation of the power spectral density of asphalt surface roughness and tire wet friction. Wear 2014, 317, 111–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Q.; Zhan, Y.; Liu, C.; Qiu, Y.; Zhang, A. Multiscale power spectrum analysis of 3D surface texture for prediction of asphalt pavement friction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 293, 123506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, S.; Wang, K.C.; Yang, E.; Zhan, Y. Influence of effective texture depth on pavement friction based on 3D texture area. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 287, 123002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogbara, R.B.; Masad, E.A.; Woodward, D.; Millar, P. Relating surface texture parameters from close range photogrammetry to Grip-Tester pavement friction measurements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 227–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Qin, B.; Weng, Z.; Wu, D.; Liu, C. Promoting the pavement skid resistance estimation by extracting tire-contacted texture based on 3D surface data. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 307, 124729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafi, M.M.; Tuononen, A.J. Top topography surface roughness power spectrum for pavement friction evaluation. Tribol. Int. 2017, 107, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persson, B.N.J. Relation between interfacial separation and load: A general theory of contact mechanics. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 125502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kogbara, R.B.; Masad, E.A.; Kassem, E.; Scarpas, A.; Anupam, K. A state-of-the-art review of parameters influencing measurement and modeling of skid resistance of asphalt pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 114, 602–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhasan, A.; Smadi, O.; Bou-Saab, G.; Hernandez, N.; Cochran, E. Pavement Friction Modeling using Texture Measurements and Pendulum Skid Tester. Transp. Res. Rec. 2018, 2672, 440–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueckermann, A.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M.; Steinauer, B. A contribution to non-contact skid resistance measurement. Int. J. Pavement Eng. 2014, 16, 646–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Ueckermann, A.; Schacht, A.; Oeser, M.; Steinauer, B.; Persson, B.N.J. Tire-road contact stiffness. Tribol. Lett. 2014, 56, 397–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vieira, T.; Sandberg, U.; Erlingsson, S. Negative texture, positive for the environment: Effects of horizontal grinding of asphalt pavements. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2021, 22, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miljković, M.; Radenberg, M.; Gottaut, C. Characterization of Noise-Reducing Capacity of Pavement by Means of Surface Texture Parameters. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2014, 26, 240–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meegoda, J.N.; Gao, S. Evaluation of pavement skid resistance using high speed texture measurement. J. Traffic Transp. Eng. 2015, 2, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Huang, X.; Zheng, B.; Zhao, R.; Liu, X.; Cao, Q.; Zhu, S. Real-time identification system of asphalt pavement texture based on close-range photogrammetry. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 226, 910–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.-Q.; Yu, H.-P.; Wang, Q.-F.; Lu, G. Effects of coagulation processes on properties of epoxidized natural rubber. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 109, 1944–1949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Huang, X.; Rongyan, T.; Ding, H.; Huang, J.; Wang, D.; Liu, Y.; Hong, Z. Advanced method for measuring asphalt viscosity: Rotational plate viscosity method and its application to asphalt construction temperature prediction. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 301, 124129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ech, M.; Morel, S.; Yotte, S.; Breysse, D.; Pouteau, B. An original evaluation of the wearing course macrotexture evolution using the abbot curve. Road Mater. Pavement Des. 2009, 10, 471–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanafi, M.M. Radially Averaged Surface Roughness Power Spectrum (PSD) Only on Top or Bottom Part of a Topography. 2023. Available online: https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/60771-radially-averaged-surface-roughness-power-spectrum-psd-only-on-top-or-bottom-part-of-a-topography (accessed on 23 July 2025).

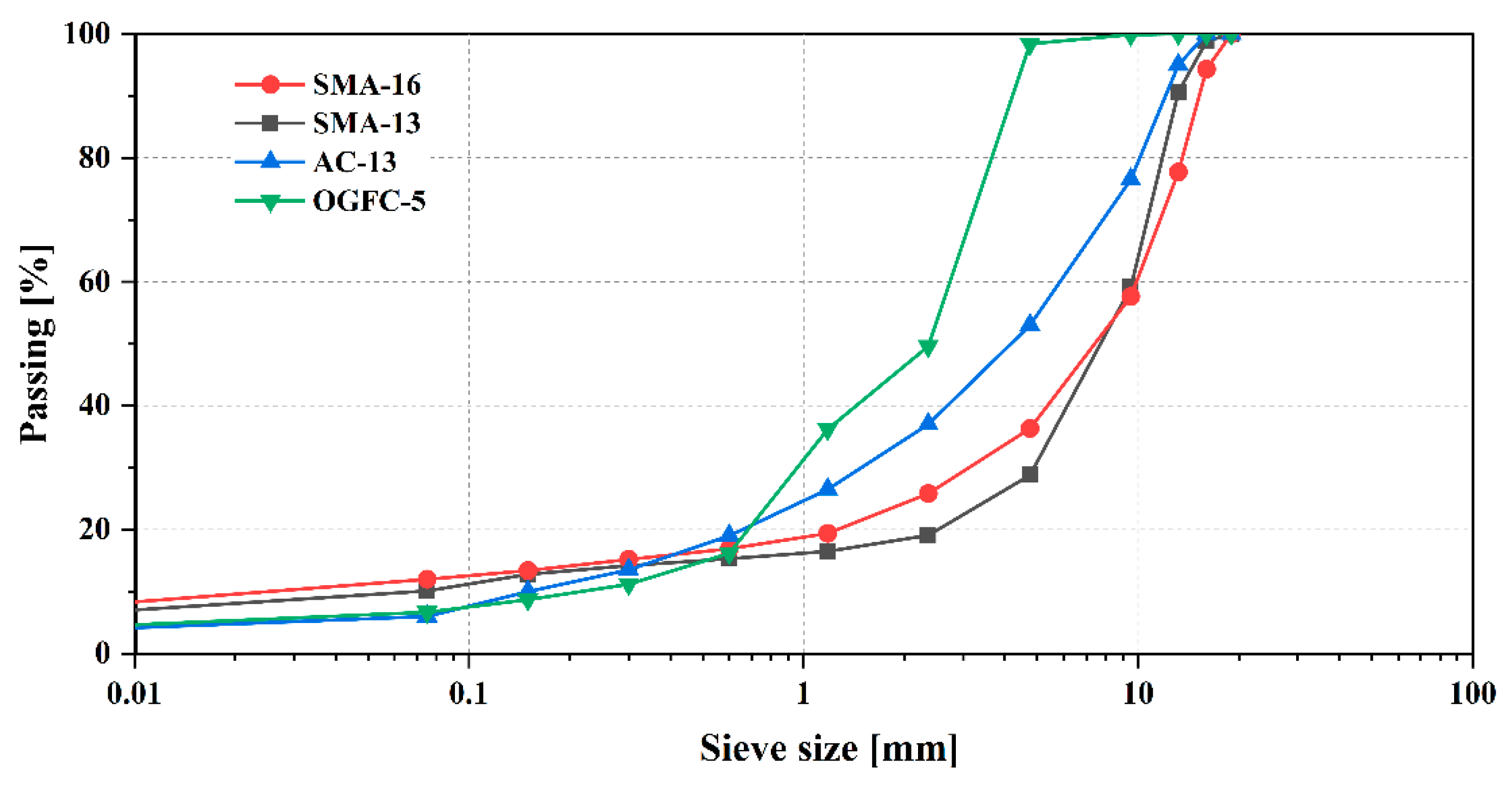


| Pavement Type | Location and Type of Roads | Binder Content | Additive | Asphalt Type |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA-16 | Part of the main line of S21 in Xinjiang | 4.9% | \ | SBS modified |
| SMA-13 | Main line of G4 in Henan | 6.5% | 0.055% fiber | SBS modified |
| AC-13 | Collector road of G4 in Xinjiang | 4.8% | \ | 70# asphalt |
| OGFC-5 | Part of the main line of S21 in Xinjiang | 5.5% | Polyester fiber | SBS modified |
| Surface | [mm] | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SMA-16 | 1.24 | 0.696 | −0.291 | 3.629 |
| SMA-13 | 0.91 | 0.970 | −0.940 | 4.835 |
| AC-13 | 0.83 | 1.026 | −1.294 | 6.331 |
| OGFC-5 | 0.53 | 0.386 | −1.829 | 8.019 |
| Surface | Depth of the Cut Plane [mm] | Area Ratio of the Cut Plane [%] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| By Mean Plane | By 20% Area Ratio | By Interfacial Separation (20~80 km/h) | By Mean Plane | By 20% Area Ratio | By Interfacial Separation (20~80 km/h) | |||
| SMA-16 | 1.741 | 0.348 | 0.559 | 0.161~0.180 | 49.99 | 12.65 | 20.00 | 7.81~8.28 |
| SMA-13 | 1.523 | 0.485 | 0.611 | 0.424~0.440 | 47.90 | 16.12 | 20.00 | 14.89~15.46 |
| AC-13 | 1.407 | 0.513 | 0.562 | 0.521~0.538 | 46.60 | 18.42 | 20.00 | 18.66~19.21 |
| OGFC-5 | 0.562 | 0.193 | 0.226 | 0.197~0.211 | 45.40 | 19.09 | 20.00 | 19.18~20.31 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, B.; Luo, H.; Rong, Y.; Yang, Y. Estimation of the Kinetic Coefficient of Friction of Asphalt Pavements Using the Top Topography Surface Roughness Power Spectrum. Materials 2025, 18, 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153643
Sun B, Luo H, Rong Y, Yang Y. Estimation of the Kinetic Coefficient of Friction of Asphalt Pavements Using the Top Topography Surface Roughness Power Spectrum. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153643
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Bo, Haoyuan Luo, Yibo Rong, and Yanqin Yang. 2025. "Estimation of the Kinetic Coefficient of Friction of Asphalt Pavements Using the Top Topography Surface Roughness Power Spectrum" Materials 18, no. 15: 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153643
APA StyleSun, B., Luo, H., Rong, Y., & Yang, Y. (2025). Estimation of the Kinetic Coefficient of Friction of Asphalt Pavements Using the Top Topography Surface Roughness Power Spectrum. Materials, 18(15), 3643. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153643






