Modification Effects and Mechanism of Cement Paste Wrapping on Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Significance
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Parent Concrete
3.3. No-Sulfate Recycled Aggregate and Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate
3.4. Recycled Aggregate Treated by Cement Paste Wrapping
3.5. Test Methods
3.5.1. Compressive Strength of Parent Concrete
3.5.2. Physical Properties of Recycled Aggregate
3.5.3. Microhardness Characteristics of Recycled Aggregate
3.5.4. Microstructure of Recycled Aggregate
4. Results and Discussion
4.1. Effect of Sulfate on the Properties of Concrete and of Recycled Aggregate
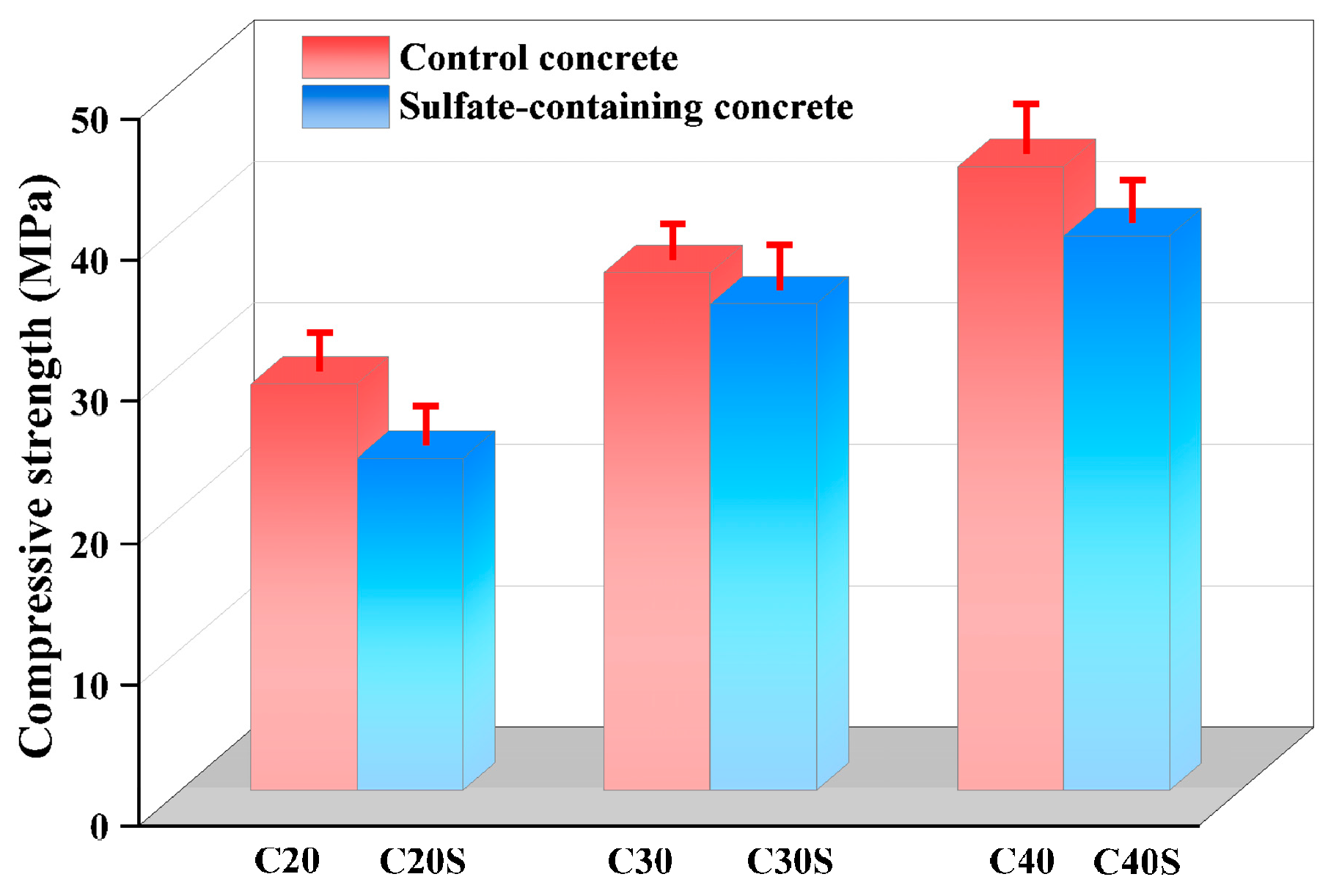
4.1.1. Compressive Strength of Concrete
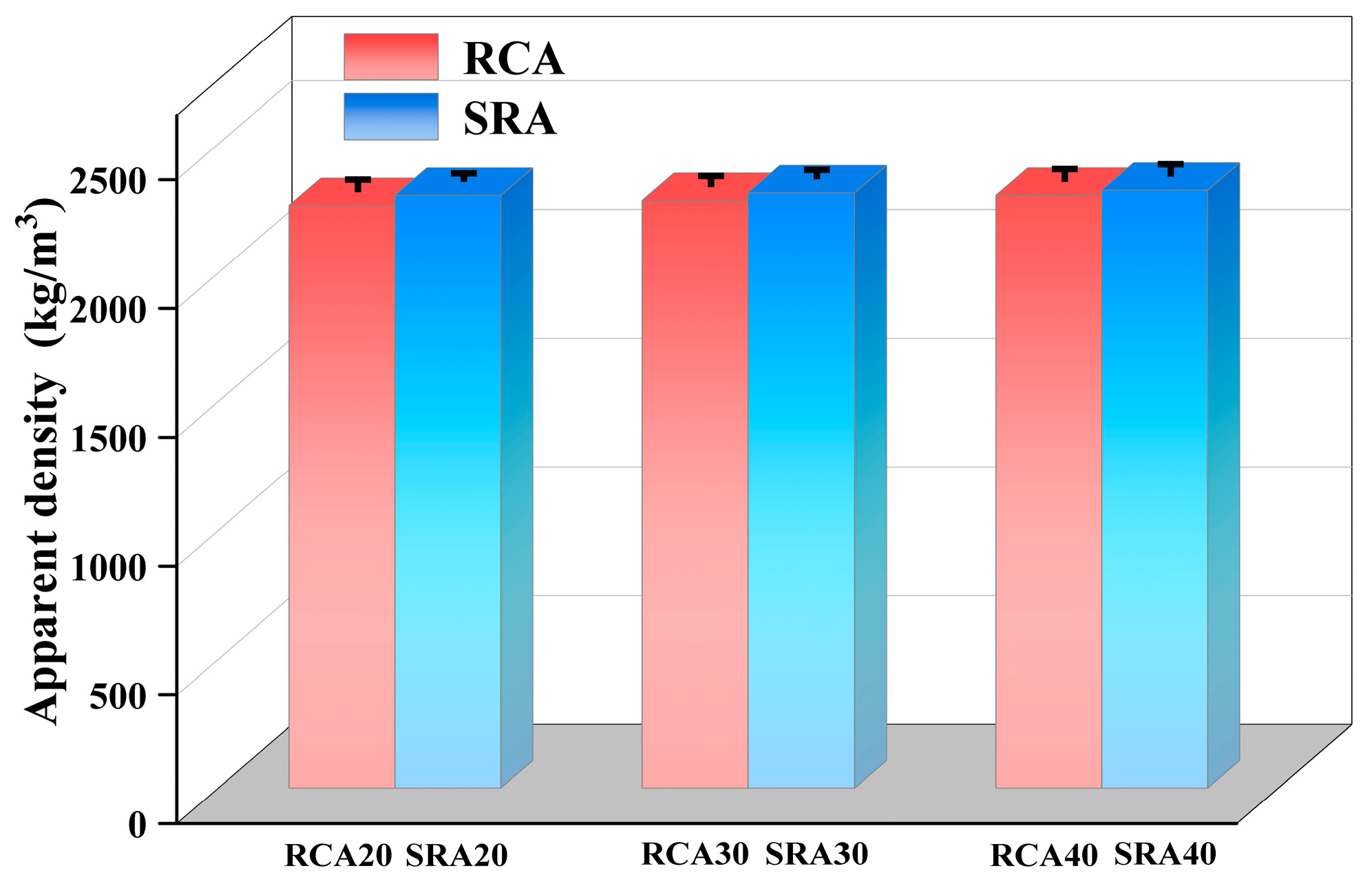
4.1.2. Apparent Density of SRA
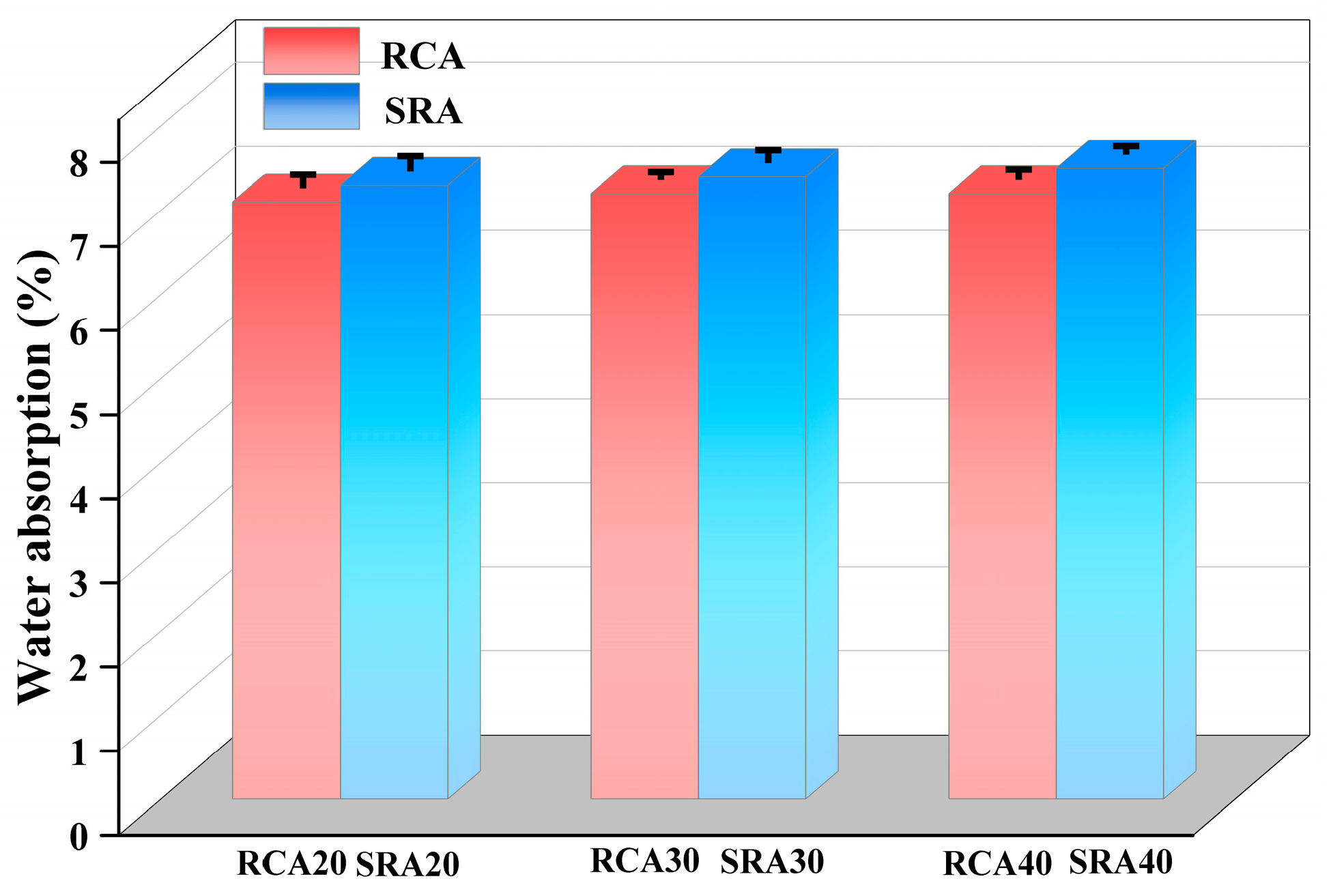
4.1.3. Water Absorption of SRA
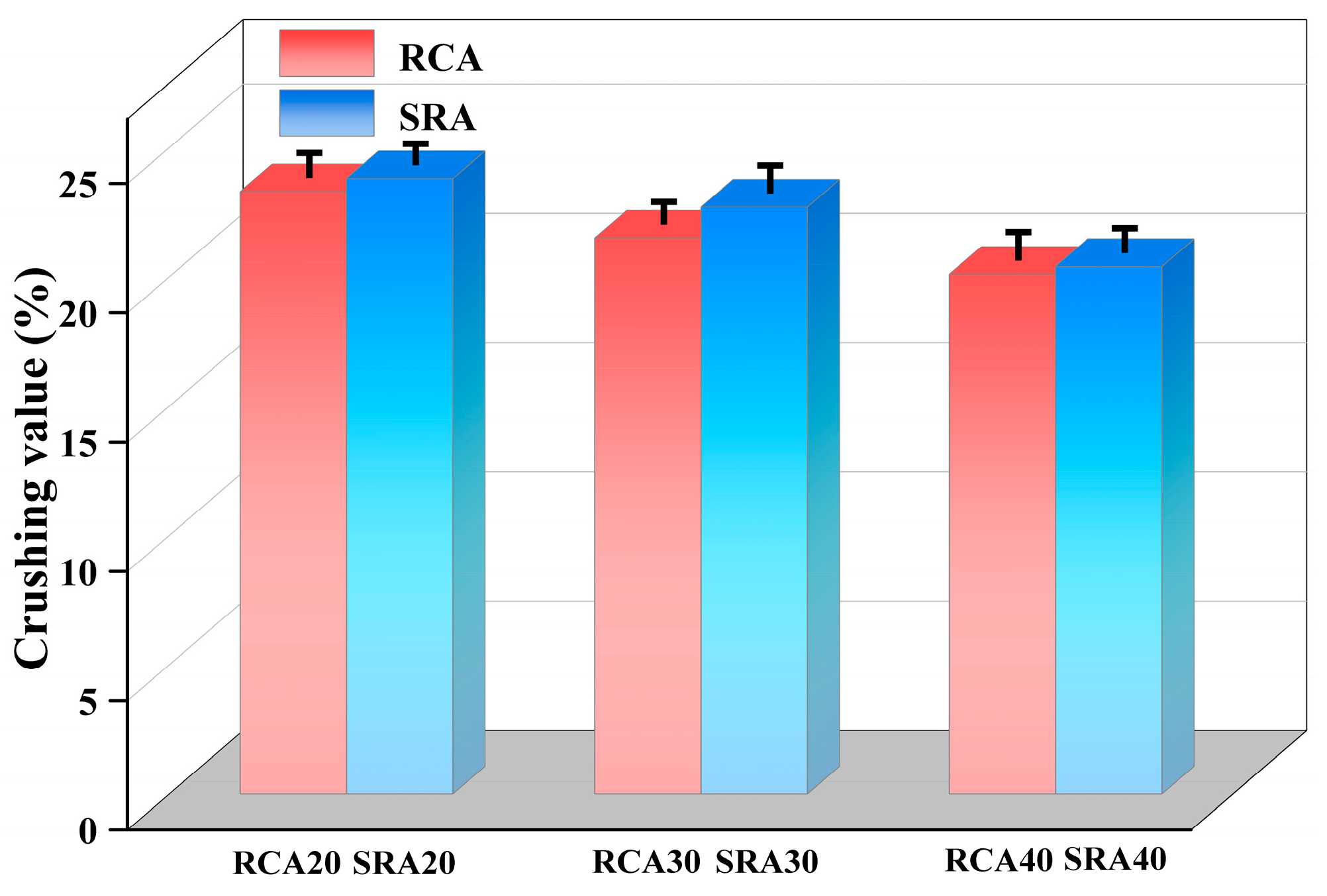
4.1.4. Crushing Value of SRA
4.2. Properties of Paste Wrapped Recycled Aggregate
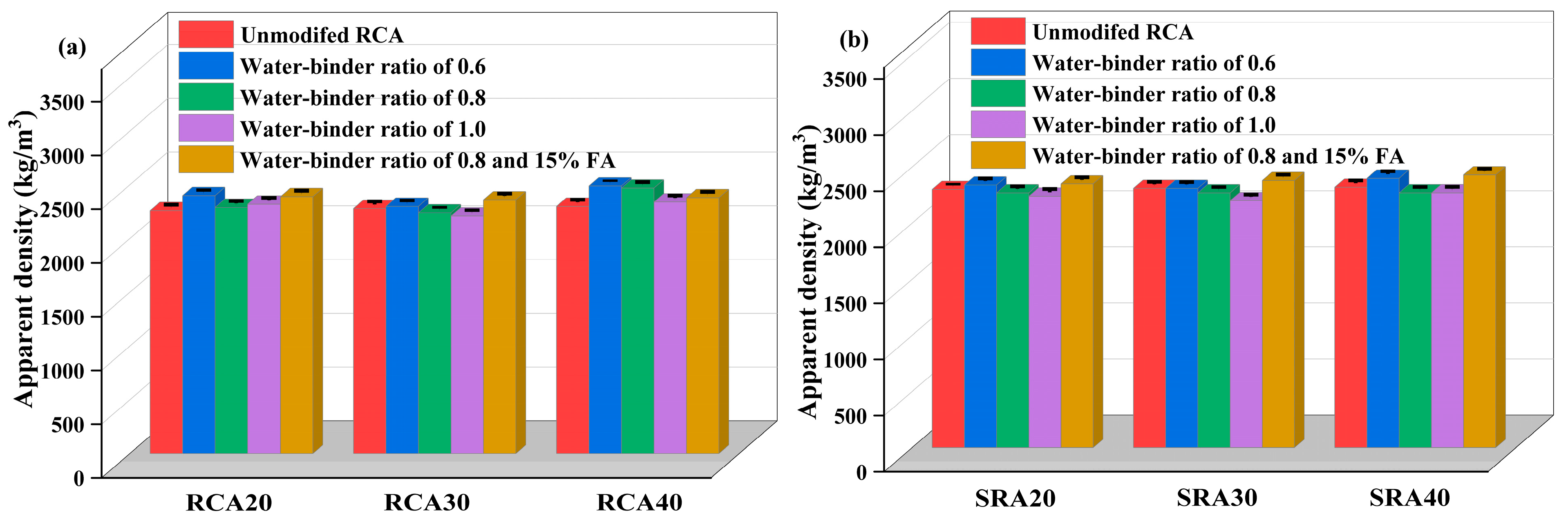
4.2.1. Apparent Density
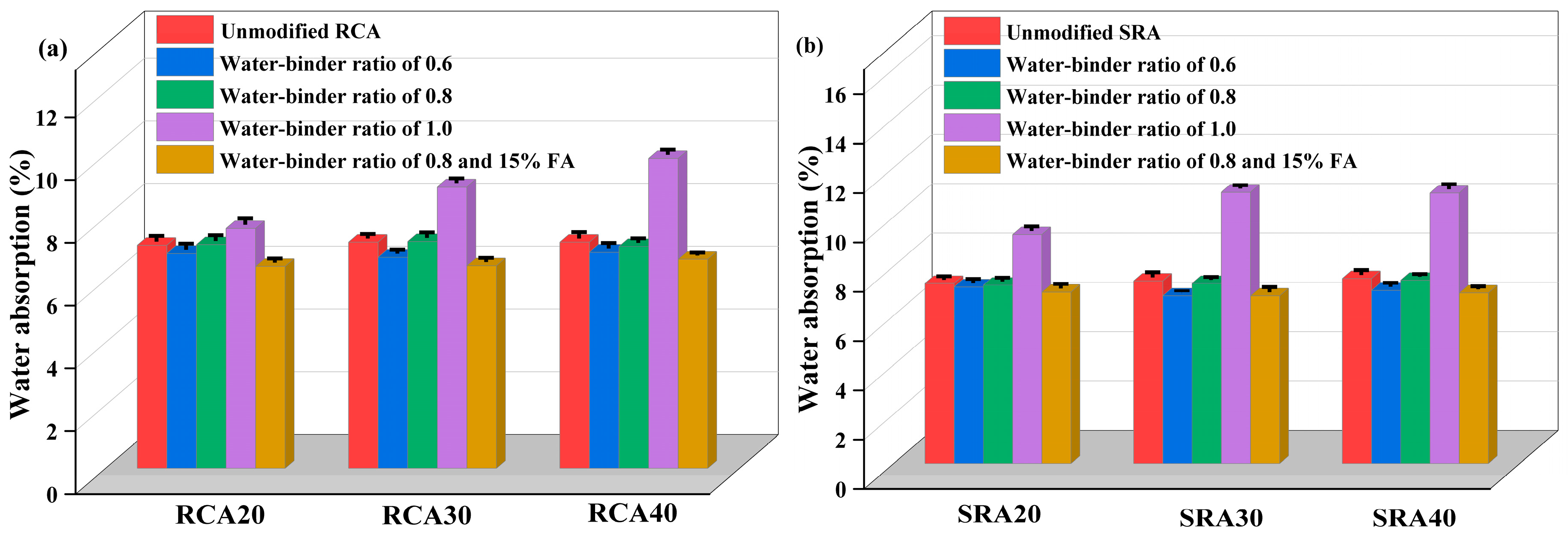
4.2.2. Water Absorption
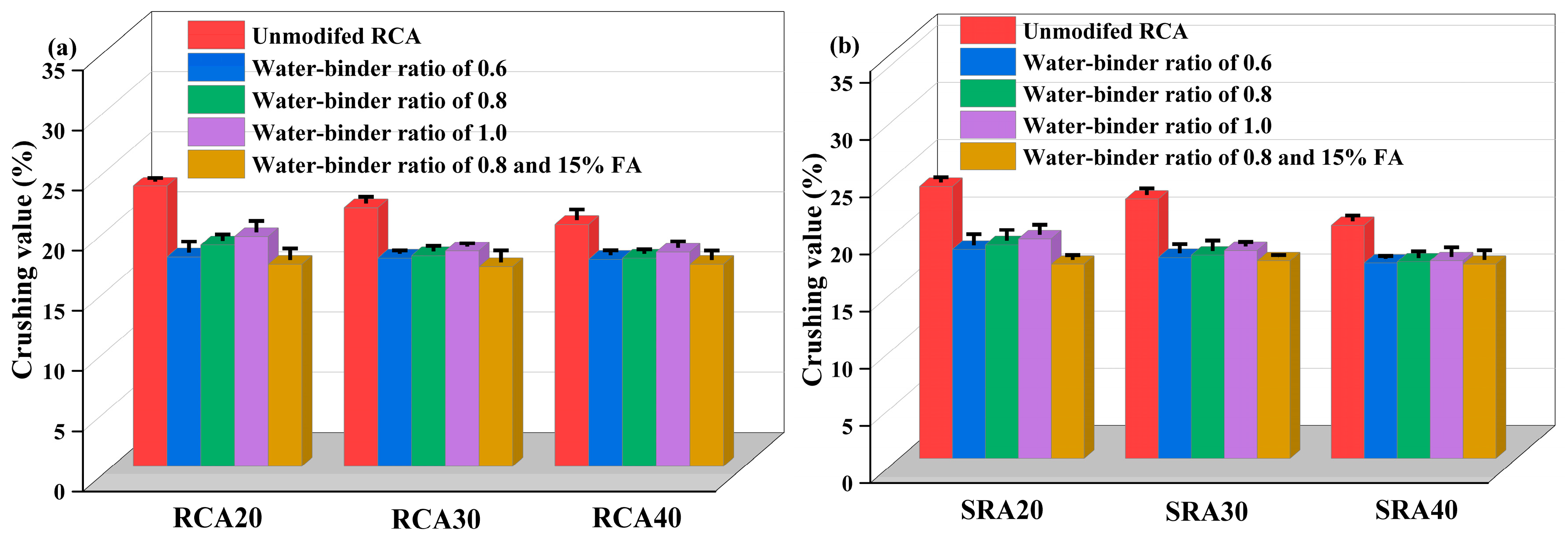
4.2.3. Crushing Value
4.3. ANOVA Analysis
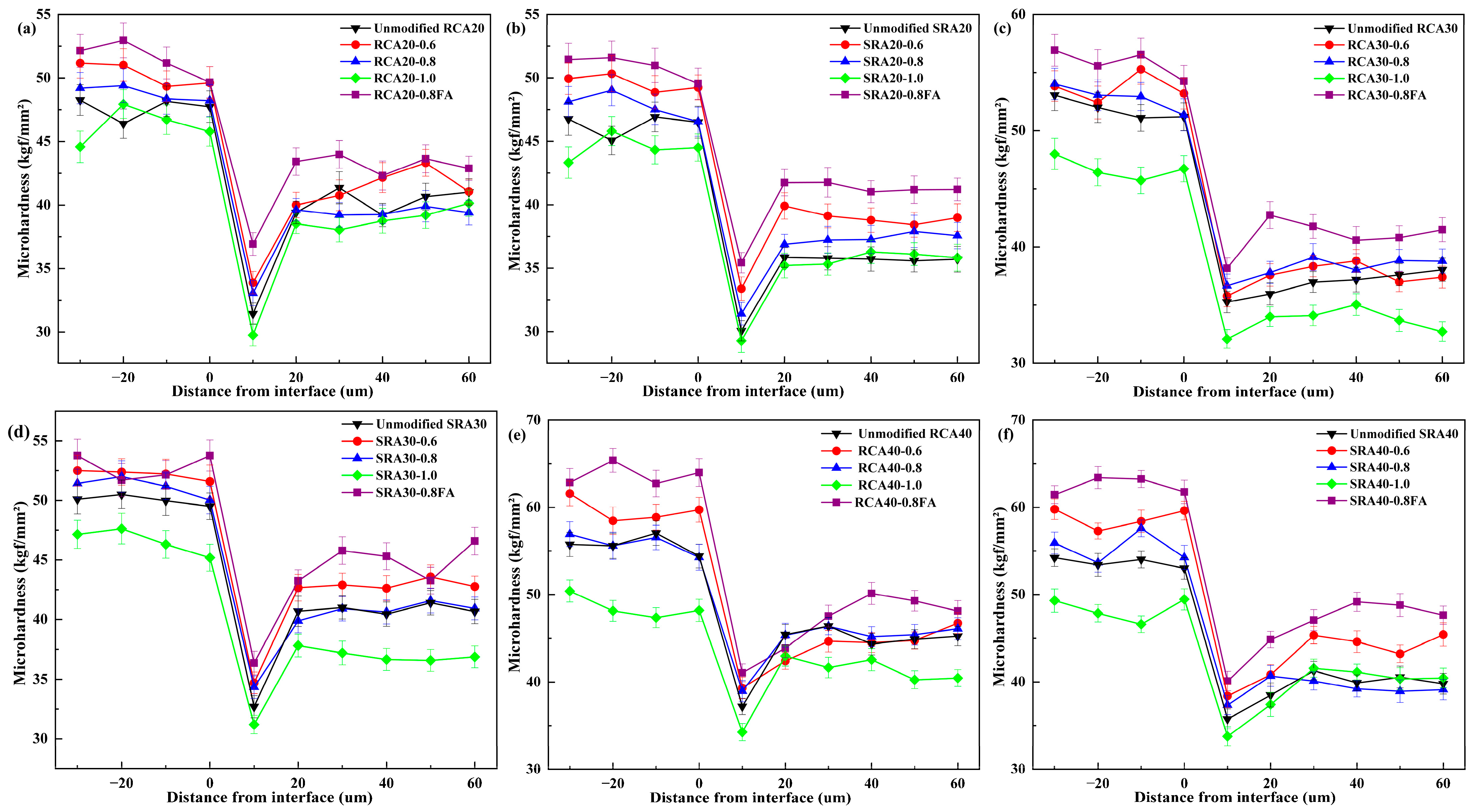
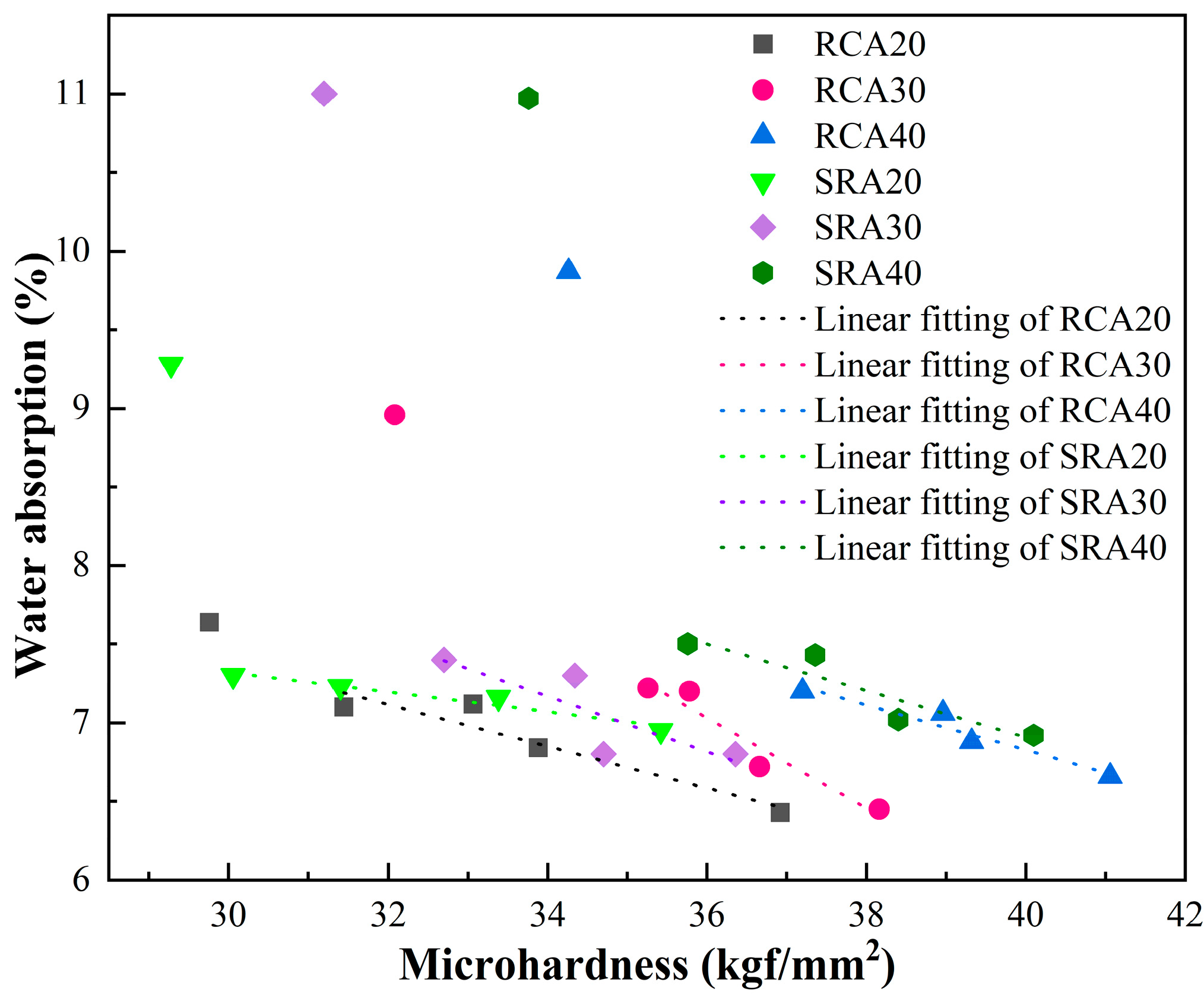
4.4. Microhardness
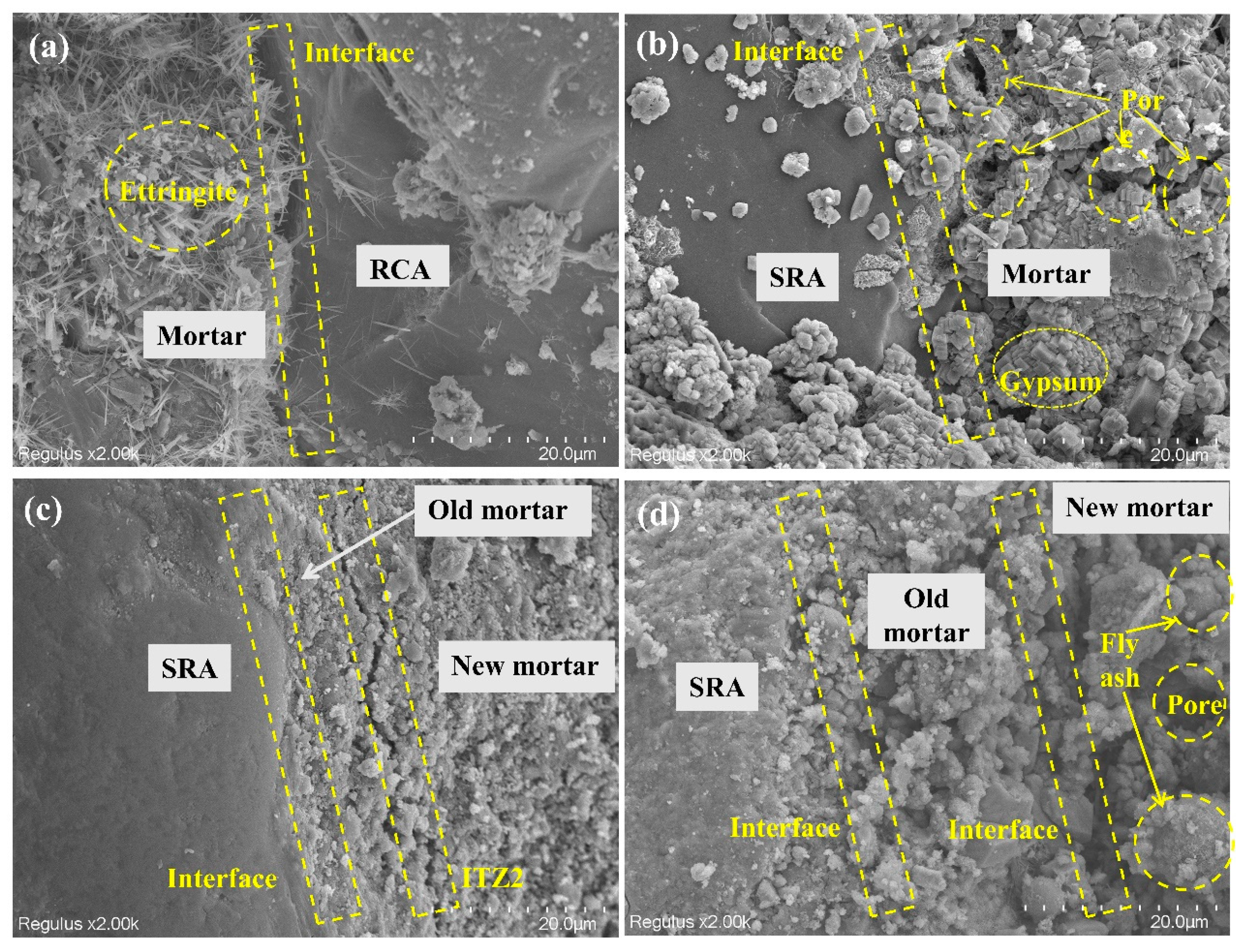
4.5. SEM
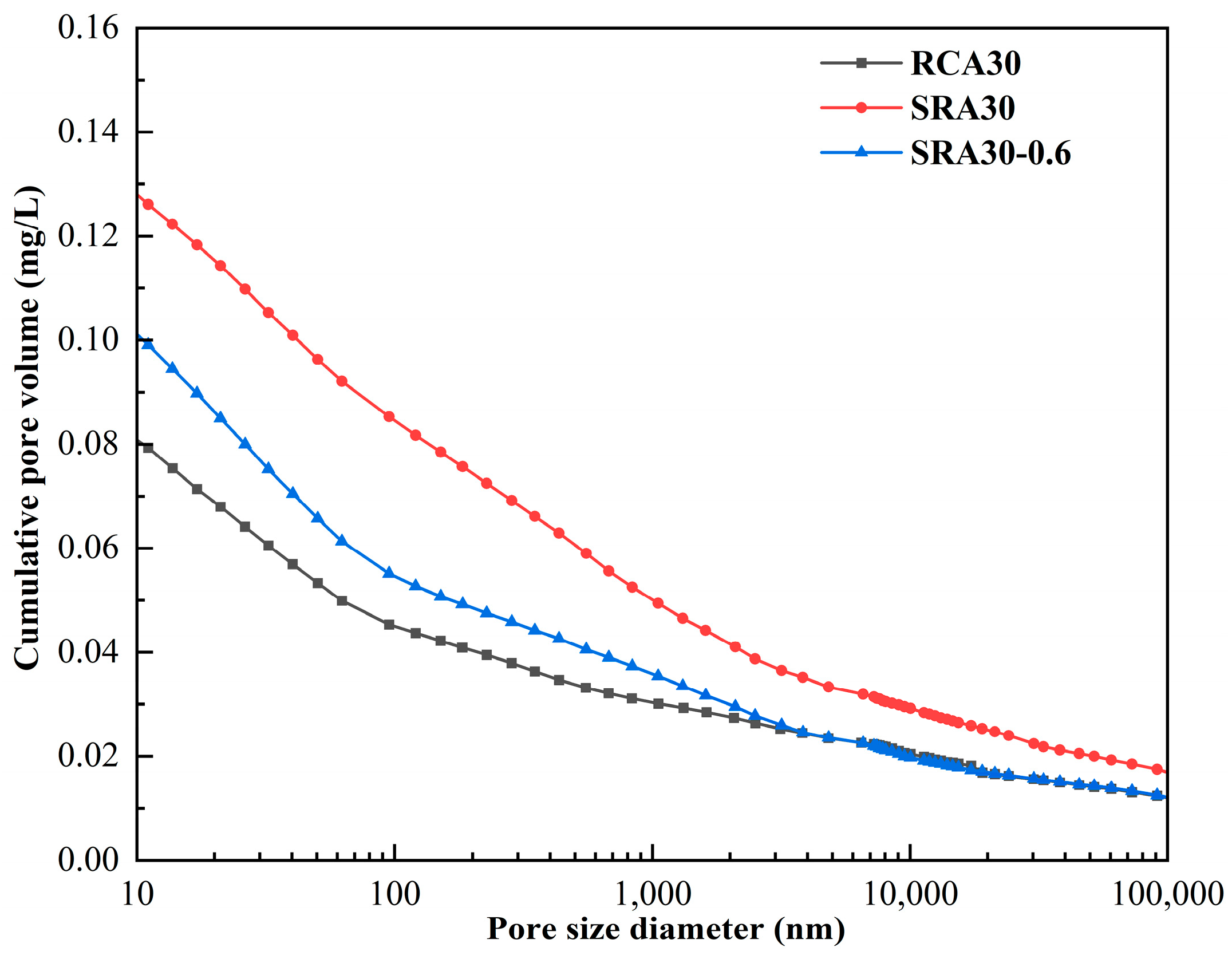
4.6. MIP
5. Conclusions
- A 2% sulfate addition to the parent concrete resulted in strength decrease. Furthermore, the corresponding sulfate-containing recycled aggregate showed a decrease in crushing value and water absorption rate, whereas its apparent density increased.
- The performance of traditional recycled aggregates and sulfate-containing recycled aggregates can be optimized by adopting an appropriate cement paste proportion. Their performance showed a decreasing trend with the increase in the water–binder ratio from 0.6 to 1.0. Notably, the water–binder ratio of 1.0 induced a notable deterioration in aggregate performance compared to unmodified aggregate.
- The optimal wrapping paste proportion identified in this study was a 0.8 water–binder ratio and 15% fly ash, which modified sulfate-containing aggregates more effectively than traditional recycled aggregates. Considering the superior wrapping performance of a 0.6 water–binder ratio over 0.8, decreasing the water–binder ratio further and adding fly ash may lead to a more substantial modifying effect.
- The interface of sulfate-containing recycled aggregates was primarily composed of gypsum crystals. Cement paste wrapping significantly improved the old interface structure, despite a new interface being observed in the modified aggregates.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Trivedi, S.S.; Snehal, K.; Das, B.B.; Barbhuiya, S. A comprehensive review towards sustainable approaches on the processing and treatment of construction and demolition waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 393, 132125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robalo, K.; Soldado, E.; Costa, H.; Carvalho, L.; do Carmo, R.; Júlio, E. Durability and Time-Dependent Properties of Low-Cement Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 3583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhtar, A.; Sarmah, A.K. Construction and demolition waste generation and properties of recycled aggregate concrete: A global perspective. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 186, 262–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Sun, Z.; Cao, Y. Modification of recycled aggregate and conservation and application of recycled aggregate concrete: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 431, 136567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bian, Y.D.; Zhao, J.H.; Wang, Y.R.; Qiu, X.; Liu, Q. Sustainable building materials-recycled aggregate and concrete: A systematic review of properties, modification techniques, and environmental impacts. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 20814–20852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivamani, J.; Renganathan, N.T.; Palaniraj, S. Enhancing the quality of recycled coarse aggregates by different treatment techniques-a review. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 60346–60365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, R.; Zhao, H.Y.; Zhong, Y.; Wang, J.J.; Xu, L.; Lin, S.Y.; Li, L.; Zhang, X. Enhancing quality and strength of recycled coarse and fine aggregates through high-temperature and ball milling treatments: Mechanisms and cost-effective solutions. J. Mater. Cycles Waste Manag. 2025, 27, 270–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bru, K.; Touzé, S.; Bourgeois, F.; Lippiatt, N.; Ménard, Y. Assessment of a microwave-assisted recycling process for the recovery of high-quality aggregates from concrete waste. Int. J. Miner. Process. 2014, 126, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, V.W.Y.; Tam, C.M.; Le, K.N. Removal of cement mortar remains from recycled aggregate using pre-soaking approaches. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 50, 82–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Bayati, H.K.A.; Das, P.K.; Tighe, S.L.; Baaj, H. Evaluation of of various treatment methods for enhancing the physical and morphological properties of coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 112, 284–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etxeberria, M.; Castillo, S. How the Carbonation Treatment of Different Types of Recycled Aggregates Affects the Properties of Concrete. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Cui, J.Z.; Chen, M.; Yang, J.L.; Yan, Z.G.; Zhang, M.Z. Durability of concrete containing carbonated recycled aggregates: A comprehensive review. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2025, 156, 105865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, M.; Zhao, Y.; Ji, A.; Ding, Z.Q. Enhancing recycled aggregates quality through biological deposition treatment. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 100, 111681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Z.H.; Lv, Z.Y.; Xiao, J.Z.; Liu, C.; Nong, X.Y. Study on the Performance of Recycled Coarse and Fine Aggregates as Microbial Carriers Applied to Self-Healing Concrete. Materials 2023, 16, 2371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Q.; Tian, A.R.; Ling, C.; Huang, Y.C.; Gu, F. Physical and mechanical properties of recycled aggregates modified by microbially induced calcium carbonate precipitation. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 382, 135409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.F.; Jin, M.; Wang, F.; Jacques, D.; Shen, X.Y.; Zhang, J.; Gao, C.; Zeng, H.Y.; Liu, J.W.; Liu, J.P. Heating-induced transformations in calcium silicate hydrate (C-S-H): In-situ investigations of composition, structure, and morphology. Cem. Concr. Res. 2025, 190, 107819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.H.; Wang, S.D.; Lu, L.C.; Gong, C.C. Evaluation of pre-coated recycled aggregate for concrete and mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 43, 191–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.H.; Li, Z.D.; Cai, J.G.; Jin, B.H. Axial compression performance of slurry-wrapping recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tube short columns under freeze-thaw cycles. Struct. Concr. 2025, 26, 3416–3429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Q.; Qiao, H.X.; Li, Q.; Su, R.; An, B.F. Study on enhancing recycled aggregate concrete using high belite sulfoaluminate cement. J. Build. Eng. 2025, 108, 112792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.C.; Chen, W.; He, Z.M.; Zhu, P.H.; Yang, L.; Dong, Y.L.; Jiang, L.H.; Yang, W. Recyclability and mechanism of recycled aggregate concrete incorporating layered double hydroxides after fatigue loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 458, 139675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, X.D.; Zhu, P.H.; Chen, C.H.; Wang, X.J.; Yang, W.; Zong, M.R. Carbonation treatment to repair the damage of repeatedly recycled coarse aggregate from recycled concrete suffering from coupling action of high stress and freeze-thaw cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 349, 128688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.H.; Chen, W.; Yan, X.C.; He, Z.M.; Liu, H.; Ma, T.Y.; Qiao, S.; Zhao, X.L. Improving sulfate resistance of 100% recycled coarse aggregate concrete by simultaneous application of limestone powder and EDTA-2Na. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 418, 135390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.C.; He, Z.M.; Xia, Q.; Zhao, C.; Zhu, P.H.; Zong, M.R.; Hua, M.Q. A New Type of Self-Compacting Recycled Pervious Concrete Under Sulfate Drying-Wetting Exposure. Materials 2025, 18, 704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, L.; Yu, X.B.; Liang, Y.T.; Gong, X.L.; Du, Q.Y. Multi-scale deterioration and microstructure of polypropylene fiber concrete by salt freezing. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2023, 18, e01762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Guo, J.J.; Wang, J.; Zheng, Y.X.; Zhang, P.; Du, H.J. Numerical and experimental analysis of the effect of multi-ion electrical coupling on the sulfate convection zone in hydraulic concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 449, 138340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Tian, Y.G.; Lu, D.; Lu, X.; Ji, K.; Jia, K.; Zhang, J. Internal corrosion characteristics of endogenous sulfate introduced by recycled aggregates in recycled aggregates concrete: Insights into the macro-mechanical and meso-mechanical properties. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 426, 139085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 25177-2010; Recycled Coarse Aggregate for Concrete. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2010.
- Zhao, G.W.; Chen, Z.L.; Peng, F.Z.; Ding, S.J.; Wang, C. Utilization of tailing aggregates in cast-in-situ concrete: The enhancement in resistance to sulfate-chloride aggressive environment. J. Clean. Prod. 2025, 497, 145127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.W.; Li, J.P.; Shi, M.; Fan, H.H.; Cui, J.F.; Xie, F. Degradation mechanisms of cast-in-situ concrete subjected to internal-external combined sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 248, 118683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.F.; Wang, W. A semi-quantitative investigation of the free expansion stage of steel corrosion in fly ash concrete. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 34, 101941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GB/T 50081-2019; Standard for Test Methods for Mechanical Properties on Ordinary Concrete. China Architecture & Building Press: Beijing, China, 2019.
- JJG 148-2006; Vickers Hardness Reference Blocks. State Administration for Market Regulation: Beijing, China, 2006.
- Chen, W.F.; Huang, B.; Yuan, Y.X.; Deng, M. Deterioration Process of Concrete Exposed to Internal Sulfate Attack. Materials 2020, 13, 1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolski, M.E.G.; Munhoz, G.S.; Pereira, E.; Medeiros, R.A. Effect of crystalline admixture and polypropylene microfiber on the internal sulfate attack in Portland cement composites due to pyrite oxidation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 308, 125018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.T.; Zhu, X.Y. Performance of concrete containing sulfate-eroded recycled aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 424, 135955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colman, C.; Bulteel, D.; Thiery, V.; Rémond, S.; Michel, F.; Courard, L. Internal sulfate attack in mortars containing contaminated fine recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 272, 121851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.G.; Yan, X.H.; Zhang, M.Y.; Lu, D.; Yang, T.T.; Wang, Z.J.; Li, W.G. Internal transport and corrosion behaviors of sulfate corrosion media carried by recycled aggregate in concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 260, 120480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leklou, N.; Aubert, J.E.; Escadeillas, G. Influence of various parameters on heat-induced internal sulphate attack. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2013, 17, 141–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawaz, M.A.; Ali, B.; Qureshi, L.A.; Aslam, H.M.U.; Hussain, I.; Masood, B.; Raza, S.S. Effect of sulfate activator on mechanical and durability properties of concrete incorporating low calcium fly ash. Case Stud. Constr. Mater. 2020, 13, e00407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Liu, W.S.; Lin, X.J.; Su, S.L.; Zhao, B.J. To ameliorate the performance of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) by pre-treating aggregate in sulfoaluminate cement slurry and water glass solution. J. Build. Eng. 2021, 44, 103364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.R.; Ji, T.; Liu, H.; Su, S.L. Improving the sulfate resistance of recycled aggregate concrete (RAC) by using surface-treated aggregate with sulfoaluminate cement (SAC). Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 297, 123535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.K.; Rajhans, P. Optimizing mechanical and durability properties of recycled aggregate concrete using pozzolanic slurries and modified mixing approach. Eur. J. Environ. Civ. Eng. 2024, 28, 3661–3685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, G.S.; Sun, T.; Wang, Z.Y.; Lu, B.C.; Chen, M.L.; Mo, Z.L.; Guo, L.W. Consecutive pozzolanic layerings to depress internal-sulfate-attack corrosion of OPC by phosphogypsum-based cold bonded aggregates. Corros. Sci. 2024, 240, 112458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.F.; Zhang, J.H.; Cao, S.C.; Song, Y.; Chen, Z.Y. Surface reinforcement of recycled aggregates (RAs) by geopolymer and quantifying its morphological characteristics by machine learning. J. Build. Eng. 2024, 91, 109731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.X.; Kou, S.C.; Song, X.F.; Lu, M.R.; Wang, Q. Analysis of properties of pervious concrete prepared with difference paste-coated recycled aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 269, 121244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidorova, A.; Vazquez-Ramonich, E.; Barra-Bizinotto, M.; Roa-Rovira, J.J.; Jimenez-Pique, E. Study of the recycled aggregates nature’s influence on the aggregate-cement paste interface and ITZ. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 68, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.L.; Wang, S.D.; Zhao, P.Q.; Lu, L.C.; Cheng, X. Effect of the optimized triple mixing method on the ITZ microstructure and performance of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 203, 601–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouya, J.; Neji, M.; De Windt, L.; Péralès, F.; Socié, A.; Corvisier, J. Investigating chemical and cracking processes in cement paste exposed to a low external sulfate attack with emphasis on the contribution of gypsum. Constr. Build. Mater. 2024, 413, 134845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, F.; Möser, B.; Stark, J. Influence of sulfate solution concentration on the formation of gypsum in sulfate resistance test specimen. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, K.; Kang, W.; Xu, L.L.; Sun, D.D.; Wang, F.Z.; De Schutter, G. Damage evolution of blended cement concrete under sodium sulfate attack in relation to ITZ volume content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 452–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panghal, H.; Kumar, A. Enhancing concrete durability and strength: An innovative approach integrating abrasion and cement slurry treatment for recycled coarse aggregates. Struct. Concr. 2025, 26, 1455–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.; Zou, Z.Y.; Zeng, P.H. Mechanical properties of fly ash concrete after the coupling effects of sustained load and sulphate erosion. Constr. Build. Mater. 2025, 460, 139866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Z.Q.; Luo, L.; Qin, Y.J.; Bi, Y.; Liu, F.C.; Yang, Y.H. Influence of Accelerated Carbonation on the Performance of Recycled Concrete Containing Fly Ash, Recycled Coarse Aggregate, and Fine Aggregate. Materials 2024, 17, 5191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Types | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | CaO | K2O | SO3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 22.06 | 6.47 | 4.53 | 1.43 | 60.43 | 0.42 | 1.86 |
| Fly ash | 43.96 | 31.14 | 9.16 | 1.01 | 9.01 | 2.03 | 0.73 |
| ID | Cement | Coarse Aggregate | Fine Aggregate | Water | SP | Na2SO4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C20 | 408 | 821 | 778 | 212 | 2.04 | - |
| C20S | 408 | 821 | 778 | 212 | 2.04 | 8.14 |
| C30 | 460 | 858 | 735 | 196 | 2.30 | - |
| C30S | 460 | 858 | 735 | 195 | 2.30 | 9.17 |
| C40 | 503 | 890 | 700 | 182 | 2.51 | - |
| C40S | 503 | 890 | 700 | 181 | 2.51 | 10.05 |
| Codes | w/b = 0.6 | w/b = 0.8 | w/b = 1.0 | w/b = 0.8, 15% Fly Ash |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| RCA20 | RCA20-0.6 | RCA20-0.8 | RCA20-1.0 | RCA20-0.8FA |
| RCA30 | RCA30-0.6 | RCA30-0.8 | RCA30-1.0 | RCA30-0.8FA |
| RCA40 | RCA40-0.6 | RCA40-0.8 | RCA40-1.0 | RCA40-0.8FA |
| SRA20 | SRA20-0.6 | SRA20-0.8 | SRA20-1.0 | SRA20-0.8FA |
| SRA30 | SRA30-0.6 | SRA30-0.8 | SRA30-1.0 | SRA30-0.8FA |
| SRA40 | SRA40-0.6 | SRA40-0.8 | SRA40-1.0 | SRA40-0.8FA |
| Properties | Unmodified Recycled Aggregate | Modified Recycled Aggregate | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| F-Value | p-Value | F-Value | p-Value | |
| Apparent density | 3.37 | 0.039 | 28.32 | <0.001 |
| Water absorption | 2.03 | 0.145 | 76.04 | <0.001 |
| Crushing value | 22.26 | <0.001 | 78.83 | <0.001 |
| Pore Structure Parameter | RCA30 | SRA30 | SRA30-0.6 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porosity (%) | 16.7% | 23.3% | 20.8% |
| Total pore area (m2/g) | 12.78 | 20.51 | 18.18 |
| Medium pore diameter (nm) | 94.82 | 219.32 | 75.73 |
| Permeability (mdarcy) | 355.4 | 641.4 | 262.1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yan, X.; Chen, W.; He, Z.; Liu, H.; Xu, S.; Lu, S.; Hua, M.; Wang, X. Modification Effects and Mechanism of Cement Paste Wrapping on Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate. Materials 2025, 18, 3617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153617
Yan X, Chen W, He Z, Liu H, Xu S, Lu S, Hua M, Wang X. Modification Effects and Mechanism of Cement Paste Wrapping on Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153617
Chicago/Turabian StyleYan, Xiancui, Wen Chen, Zimo He, Hui Liu, Shengbang Xu, Shulin Lu, Minqi Hua, and Xinjie Wang. 2025. "Modification Effects and Mechanism of Cement Paste Wrapping on Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate" Materials 18, no. 15: 3617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153617
APA StyleYan, X., Chen, W., He, Z., Liu, H., Xu, S., Lu, S., Hua, M., & Wang, X. (2025). Modification Effects and Mechanism of Cement Paste Wrapping on Sulfate-Containing Recycled Aggregate. Materials, 18(15), 3617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153617









