Research on the Structural Design and Mechanical Properties of T800 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials in Flapping Wings
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
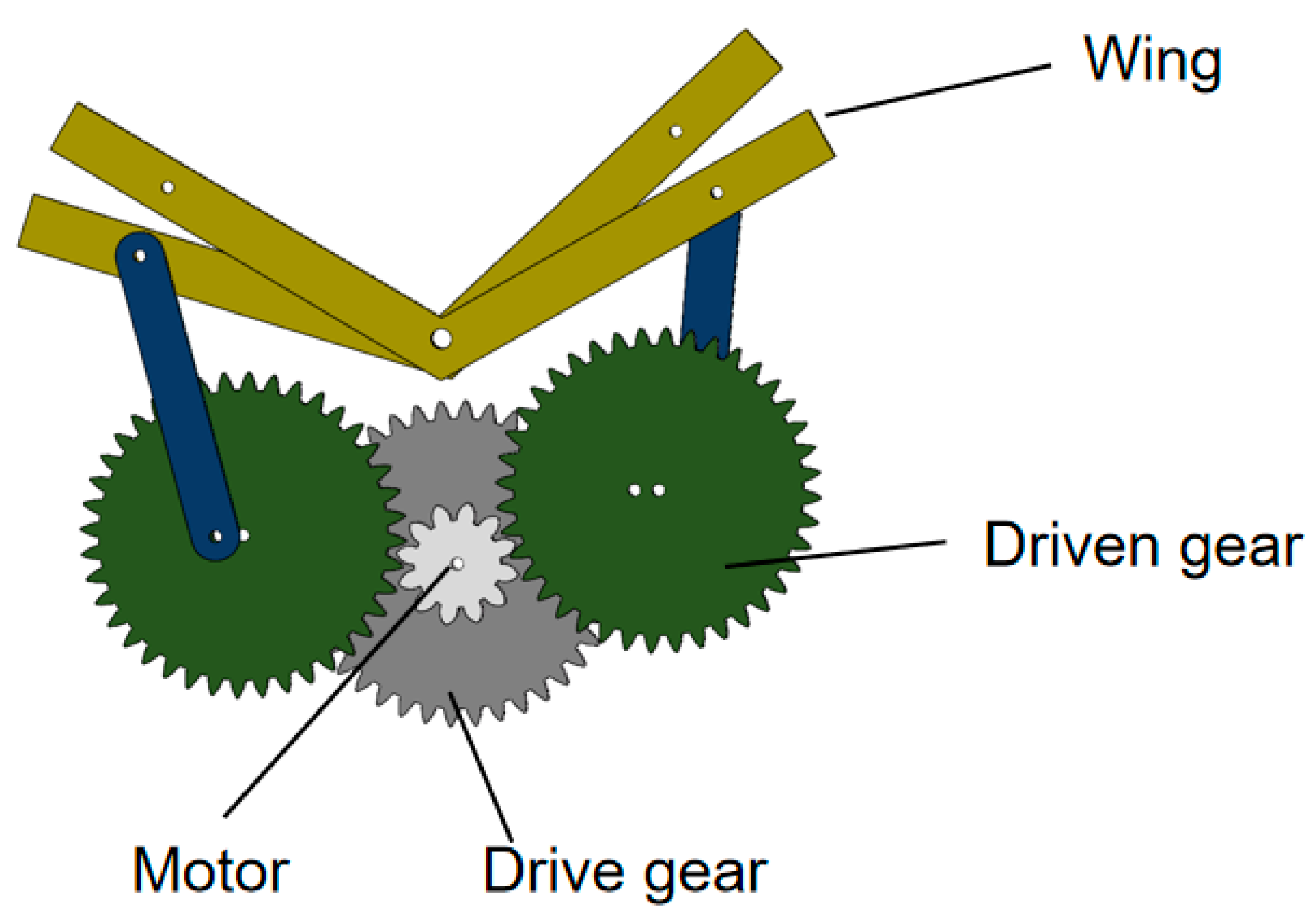
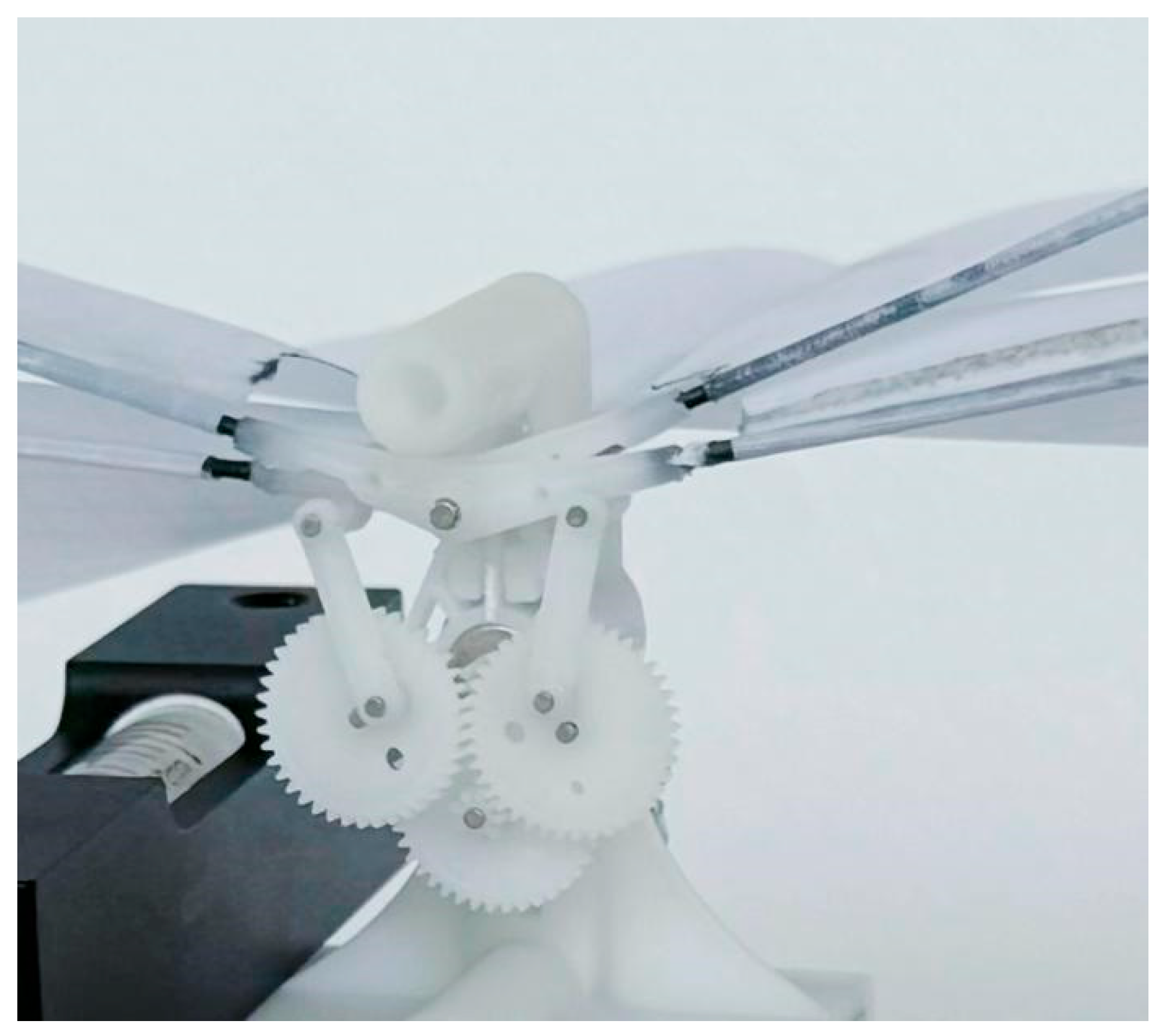
Single-Degree-of-Freedom Fluttering Mechanism
3. Preparation of Flapping Wing Prototype
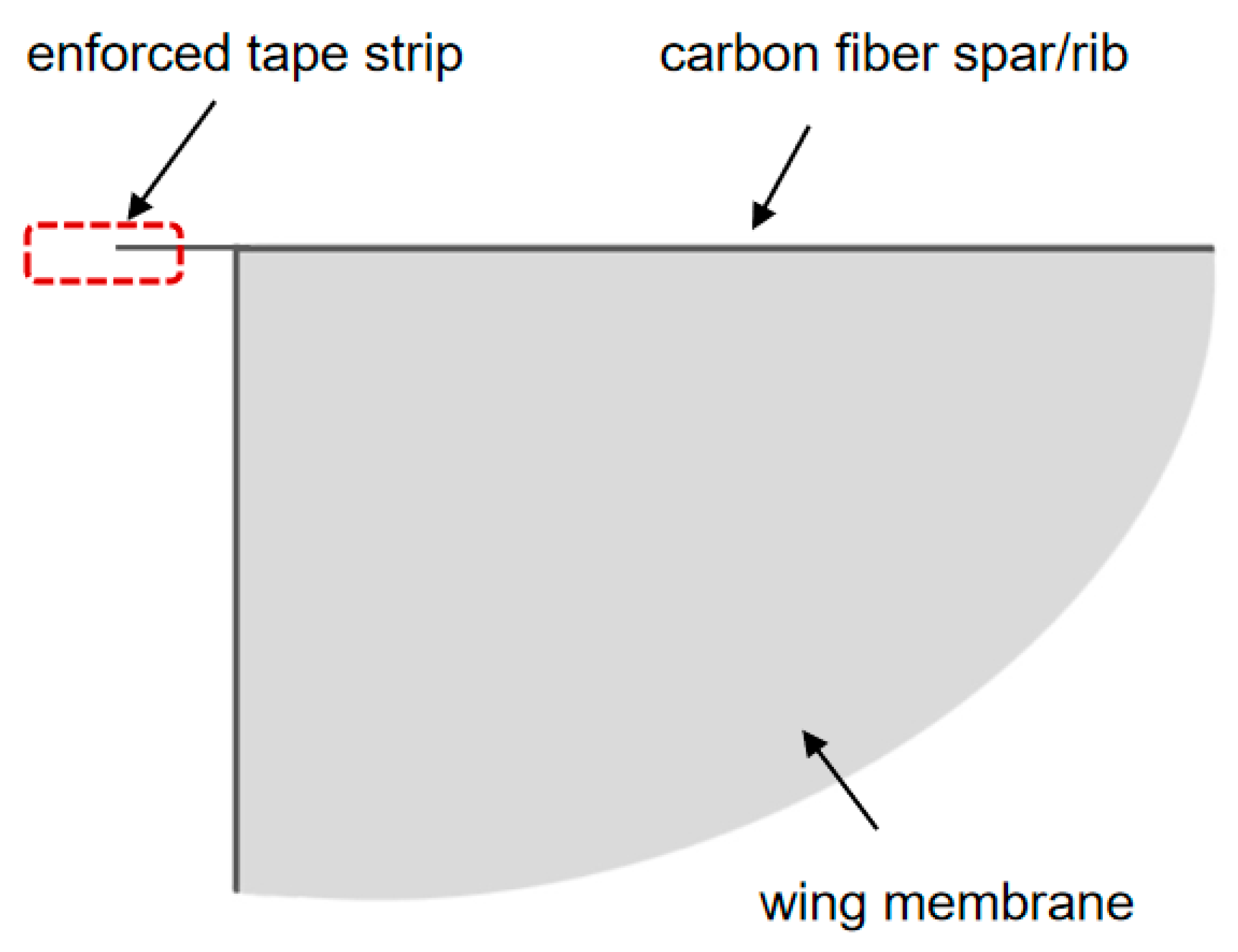
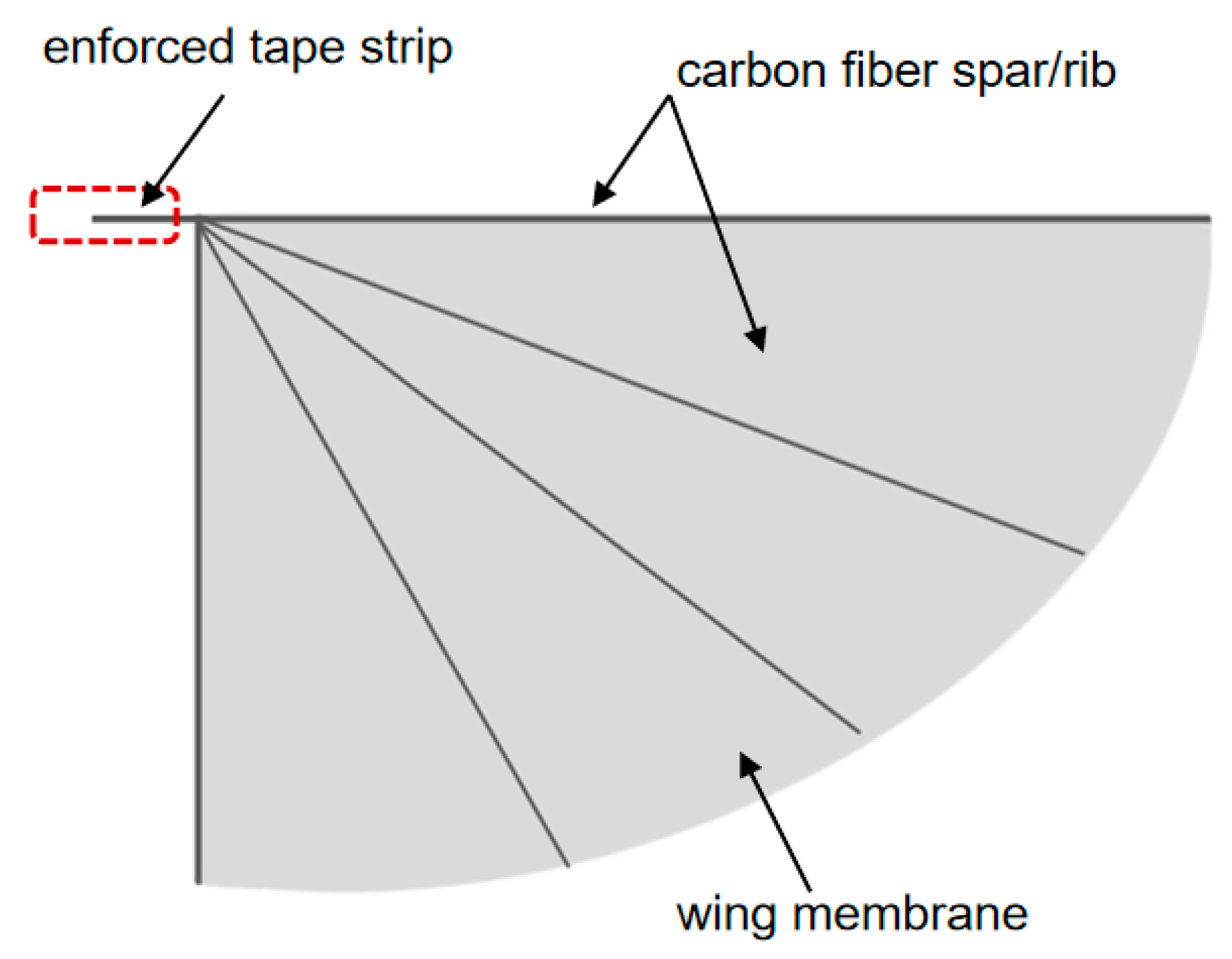
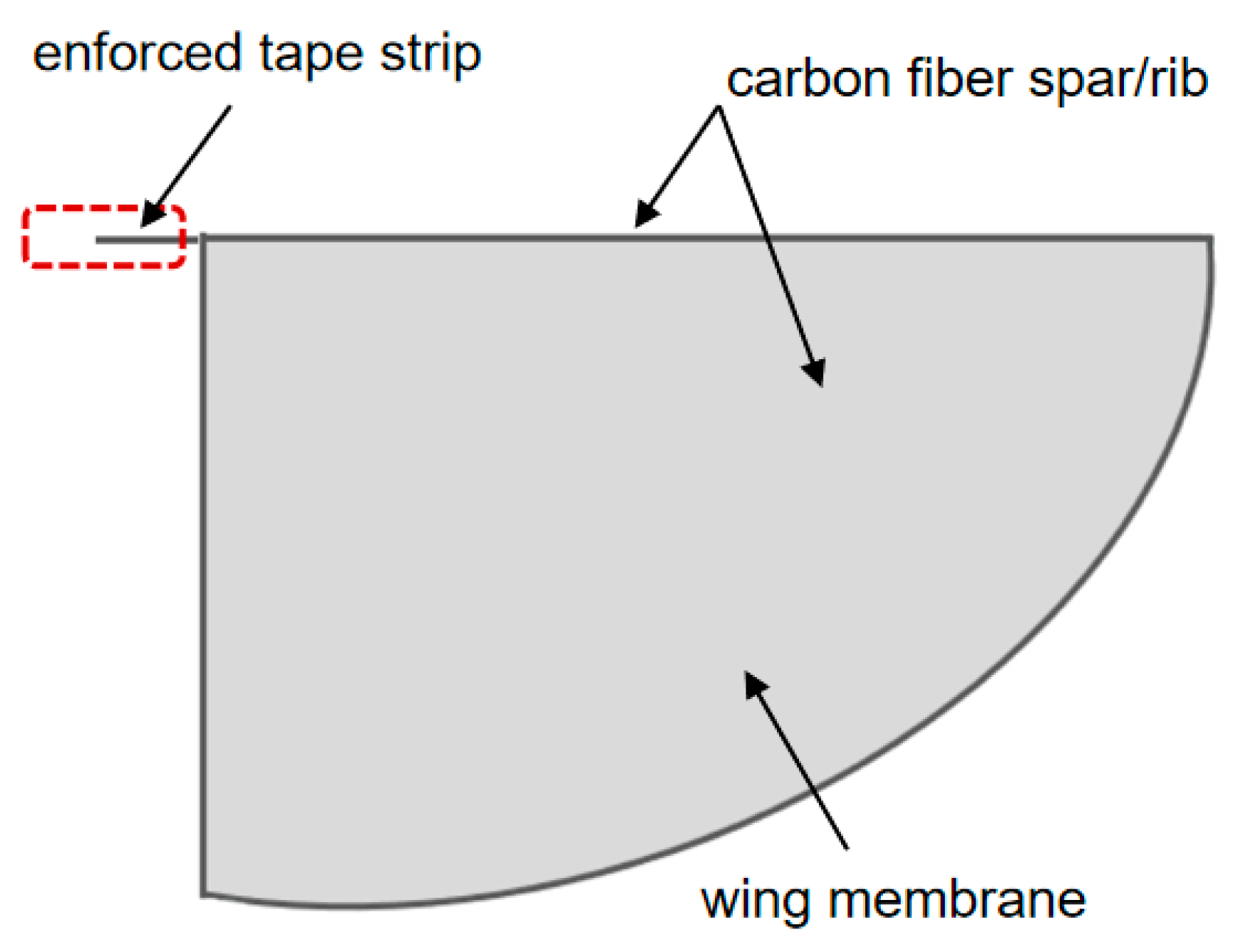
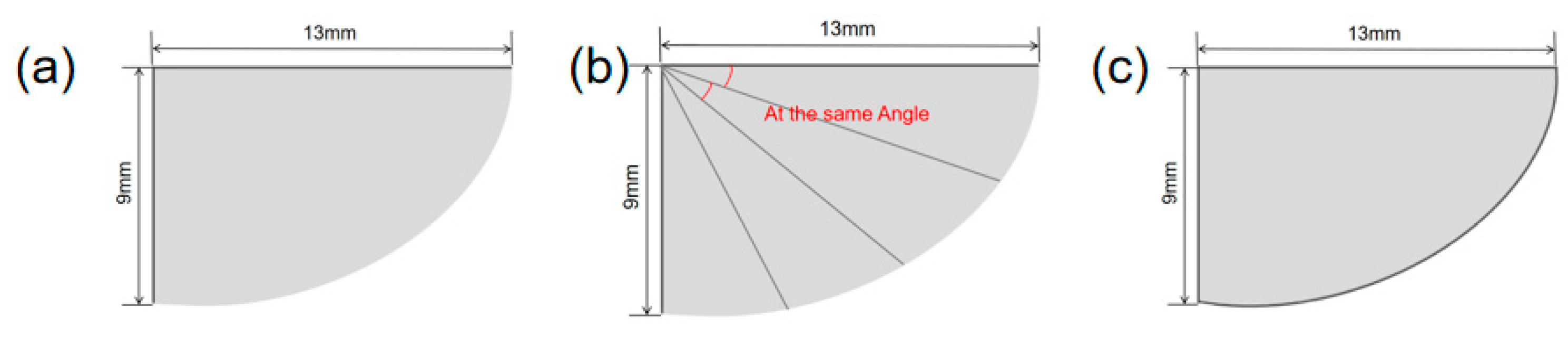
3.1. Flapping Wing Shape Design
3.2. Selection of Flapping Wing Materials
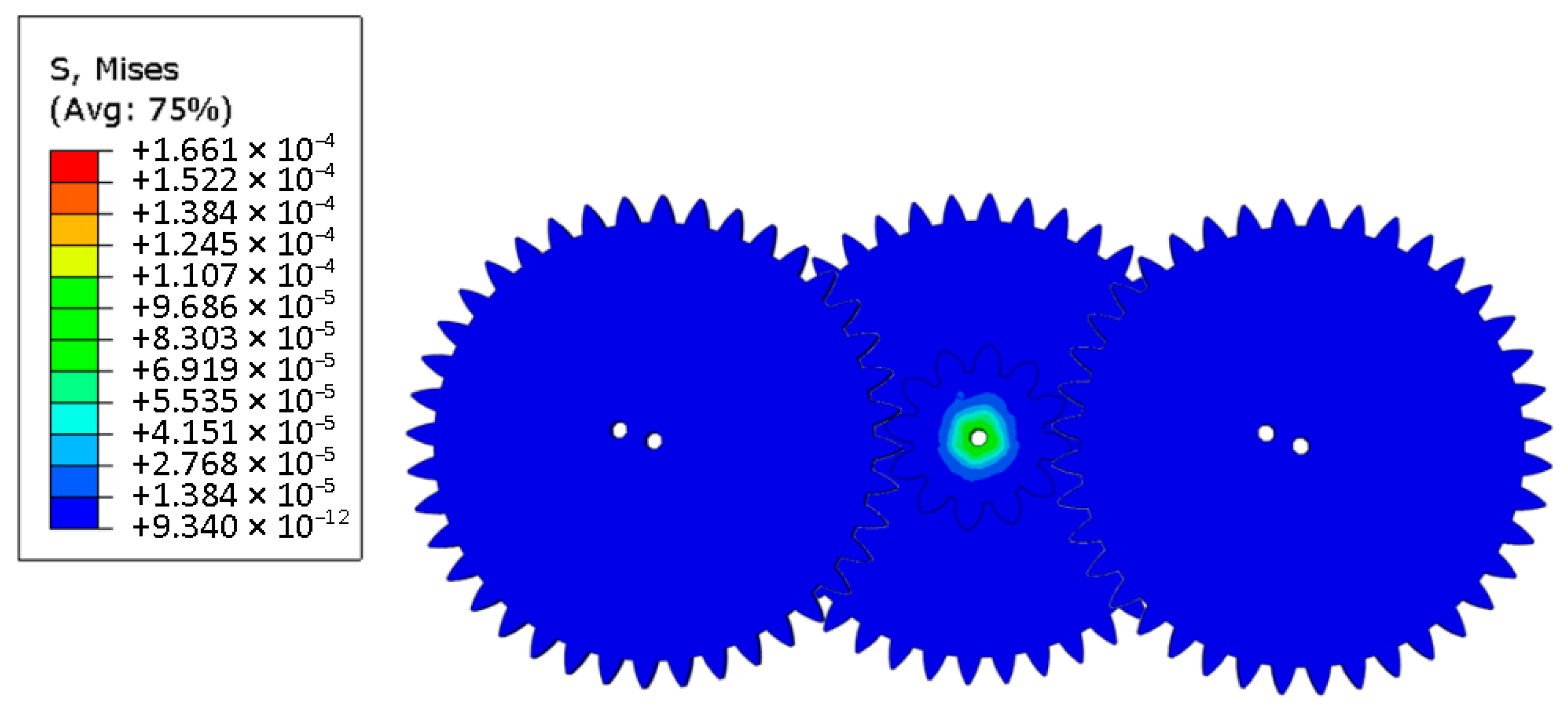
3.3. Pulsating Mechanism Printing
4. Experiment
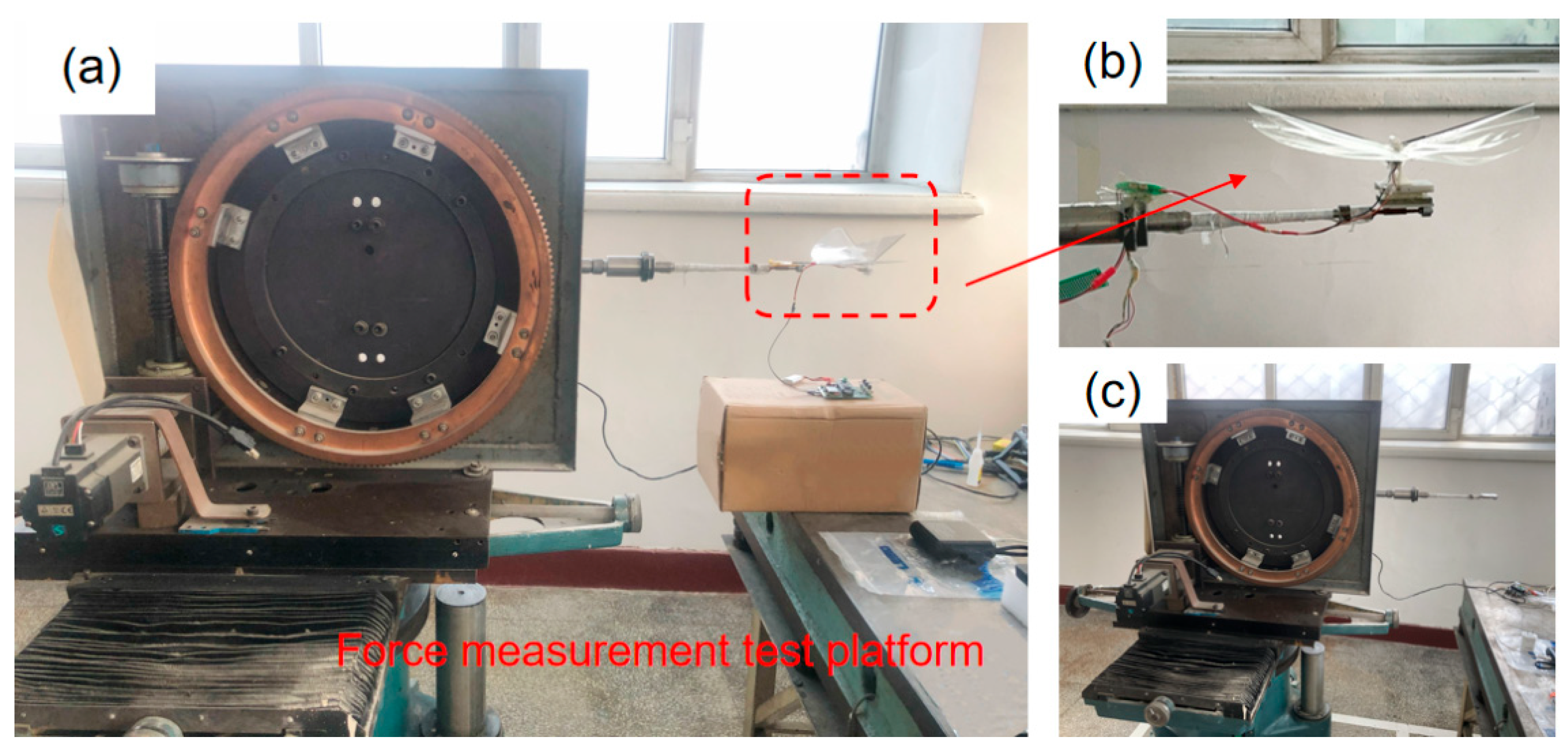
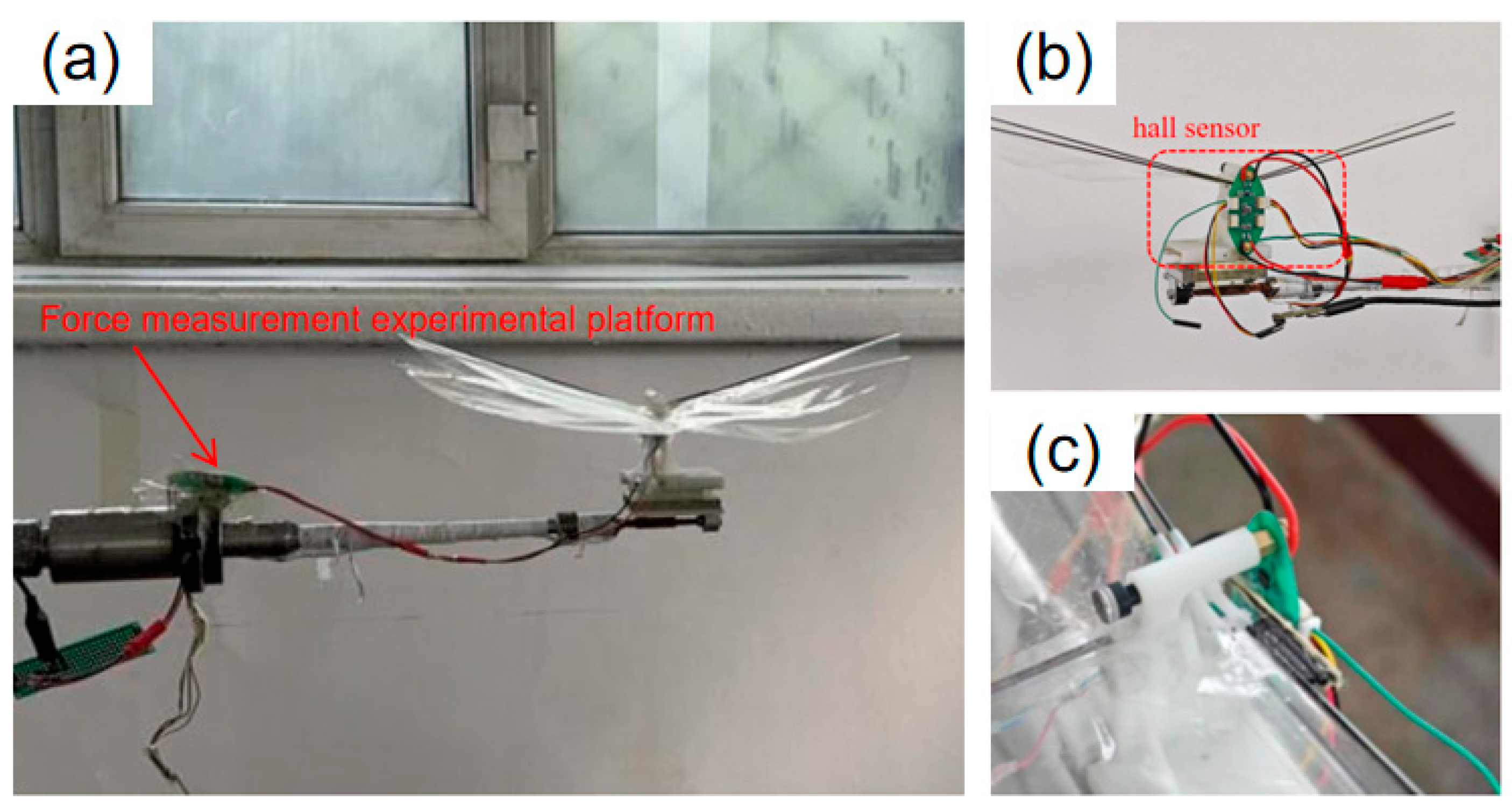
4.1. Construction of the Force Measurement Experiment Platform
4.2. Experimental Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
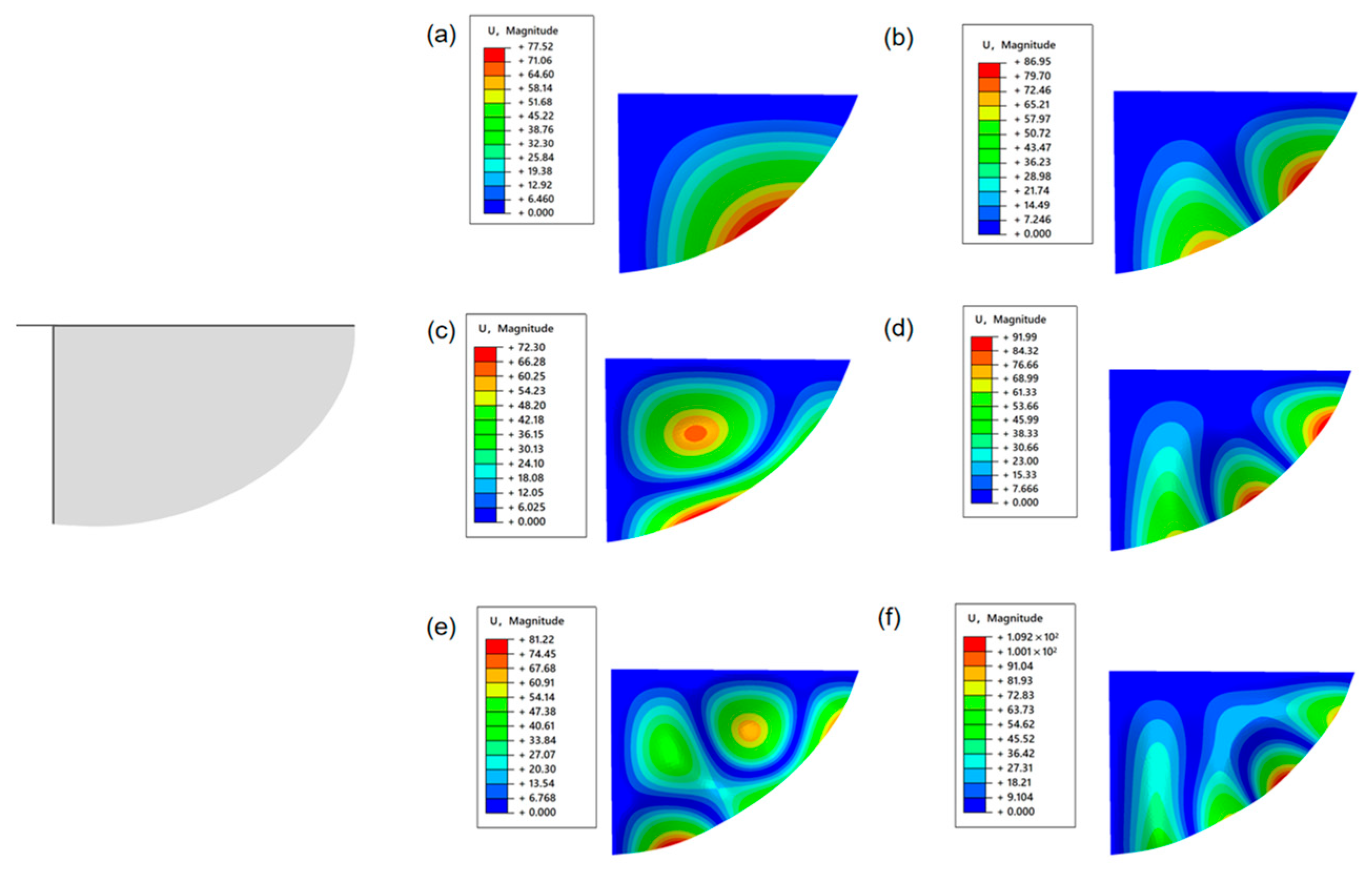
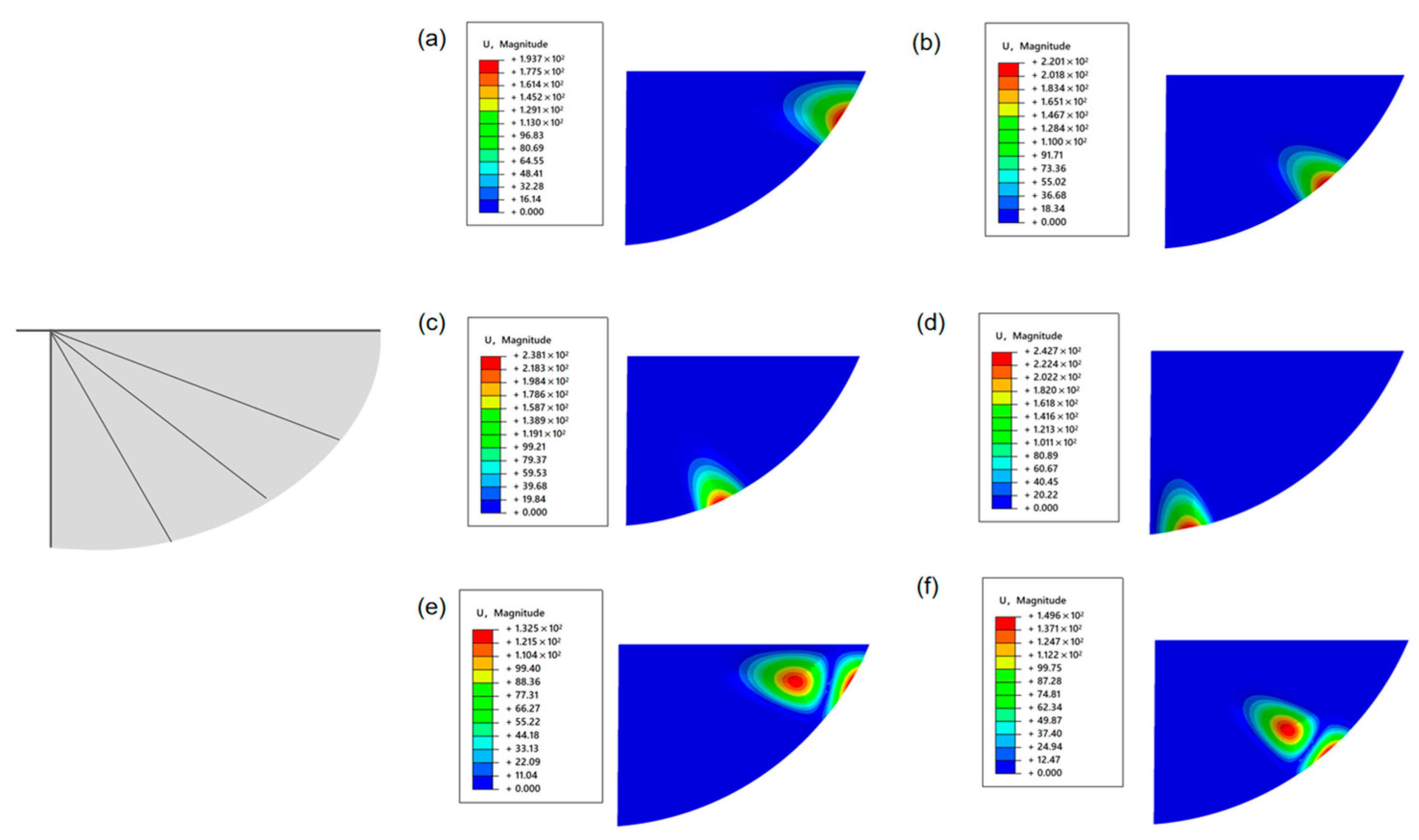
- By introducing the T800 carbon fiber composite material-designed biomimetic “wing membrane-wing vein” structure in specific areas of the wing membrane, the local structural stiffness was effectively enhanced, and the structural vibration was suppressed, thereby improving the stability of flapping-wing flight.
- Under low-voltage driving conditions, although the semi-covered structure has lower stiffness, its lift performance is superior to the other two structures, demonstrating good lightweighting and lift balance, and having certain potential for engineering applications.
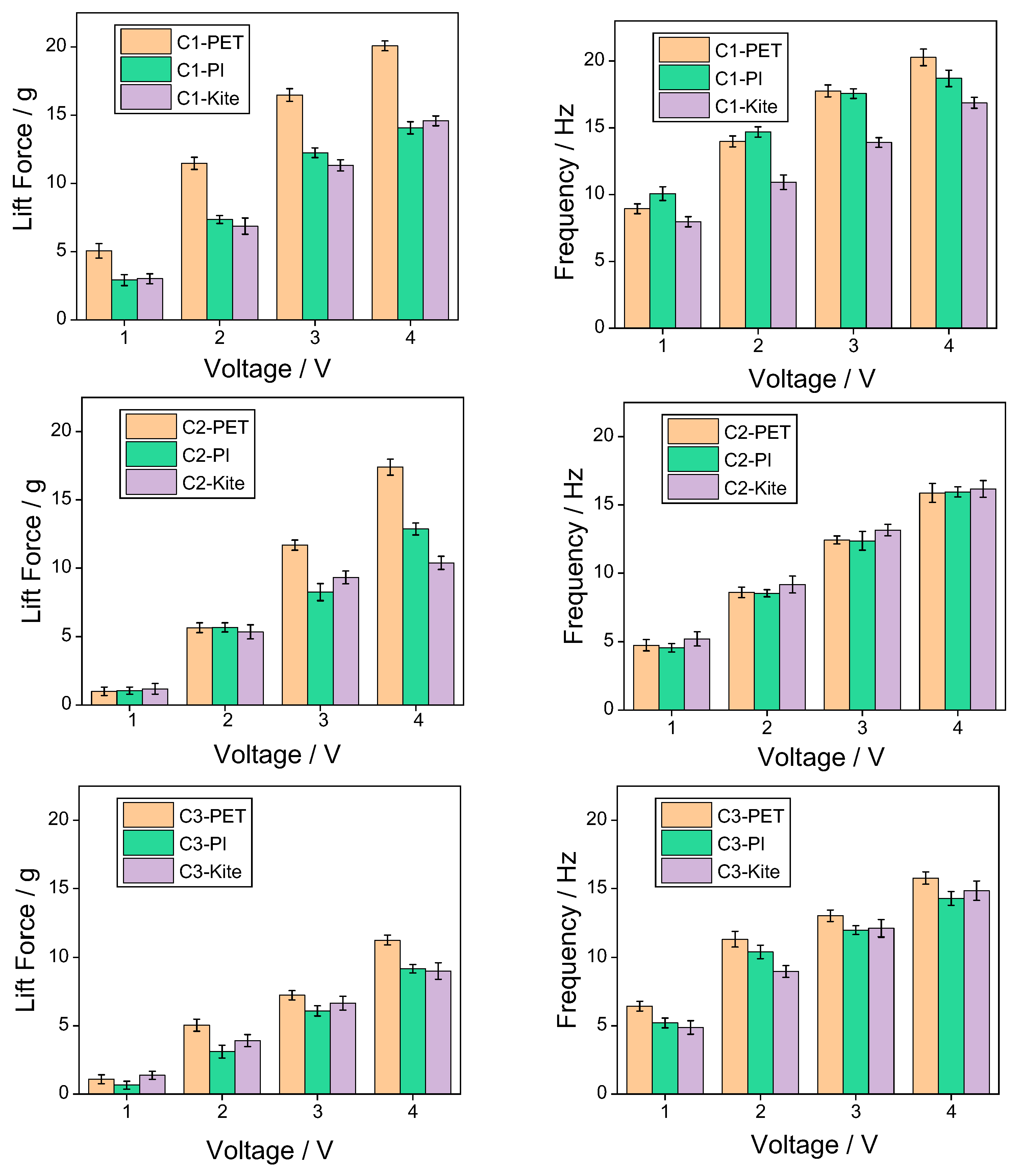
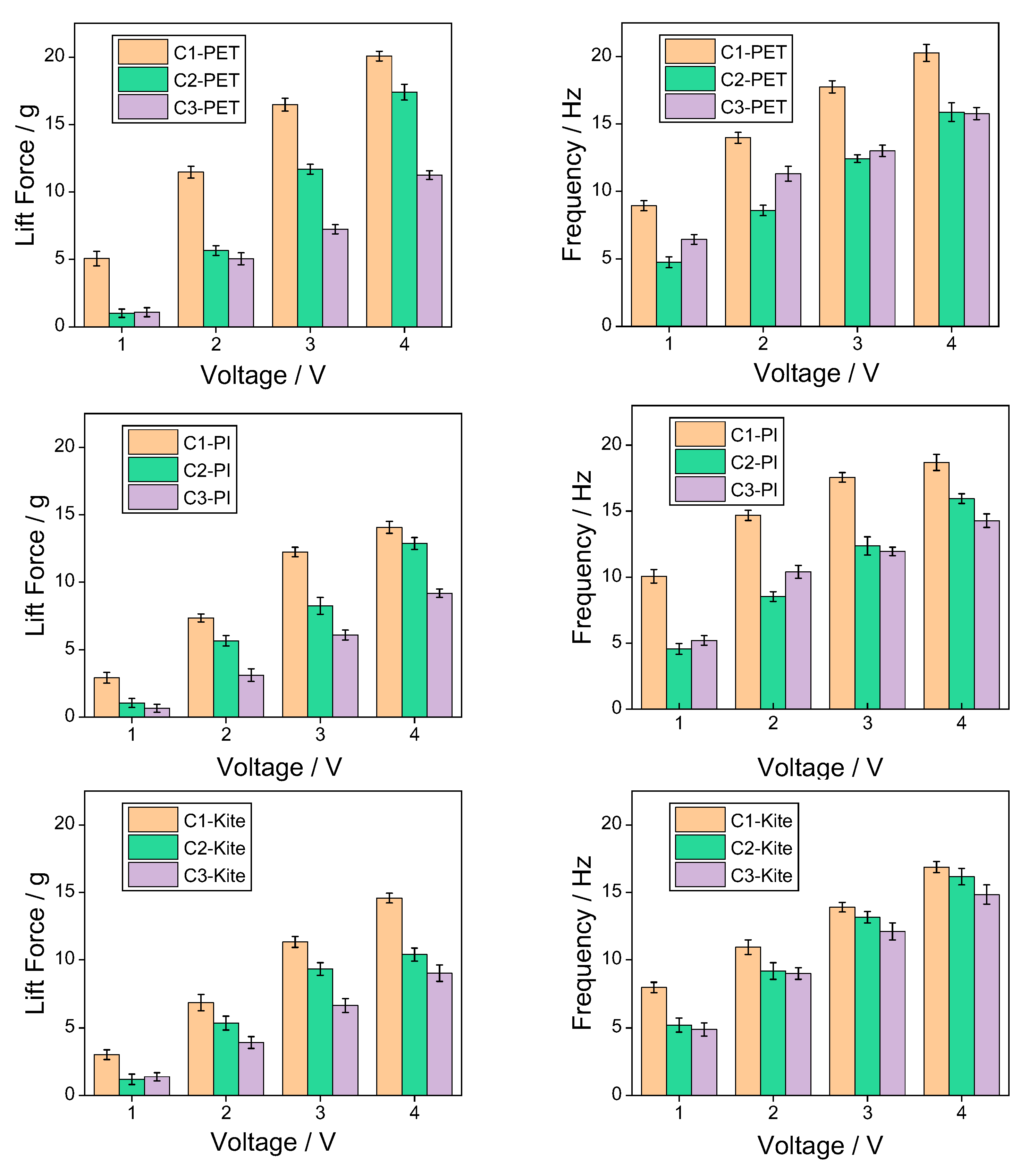
- Under the same configuration, the lift performance of the wing surface using PET membrane material is significantly better than that of polyimide membrane and kite fabric materials.
- The mechanical property data of the three types of wing membrane materials (C2 and C3) indicate that in engineering practice, a solution can be adopted that combines the artificial wing membrane-wing vein structure with lightweight and high-performance wing membrane materials to enhance the aerodynamic performance and structural reliability of micro flapping-wing aircraft.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lentink, D. Biomimetics: Flying like a fly. Nature 2013, 498, 306–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ward, T.A.; Fearday, C.J.; Salami, E.; Binti Soin, N. A bibliometric review of progress in micro air vehicle research. Int. J. Micro Air Veh. 2017, 9, 146–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, T. A Review of Design and Fabrication of the Bionic Flapping Wing Micro Air Vehicles. Micromachines 2019, 10, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohsan, S.A.H.; Othman, N.Q.H.; Khan, M.A.; Amjad, H.; Zywiolek, J. A Comprehensive Review of Micro UAV Charging Techniques. Micromachines 2022, 13, 977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, M.; Wu, R.; Ye, M.; Gao, K.; Chen, B.; Tao, X.; Fan, Z. The Structural Design and Optimization of a Novel Independently Driven Bionic Ornithopter. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Li, N.; Childs, P.R.N. Light-weighting in aerospace component and system design. Propuls. Power Res. 2018, 7, 103–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Haddad, L.A.; Jaber, A.A.; Giernacki, W.; Khan, Z.H.; Ali, K.M.; Tawafik, M.A.; Humaidi, A.J. Quadcopter Unmanned Aerial Vehicle Structural Design Using an Integrated Approach of Topology Optimization and Additive Manufacturing. Designs 2024, 8, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, C.; Li, T.; Fu, H. Optimization of Composite Wheel Fender for Manned Lunar Vehicle. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2024, 2882, 012013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Mohite, P.M.; Kamle, S. Dragonfly Inspired Nanocomposite Flapping Wing for Micro Air Vehicles. J. Bionic Eng. 2019, 16, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, S.; Li, S.; Zhu, J.; Tang, Y. Additive manufacturing of polymeric composites from material processing to structural design. Compos. Part B Eng. 2021, 219, 108903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shema, A.; Yu, C.; Wang, F. Fibrous Orientation Effects on the Deformation and Stress of an Insect-like Flapping-wing Micro Aerial Vehicle Based on ACP. IOP Conf. Ser. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 585, 012060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potes, F.C.; Silva, J.M.; Gamboa, P.V. Development and characterization of a natural lightweight composite solution for aircraft structural applications. Compos. Struct. 2016, 136, 430–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Zhang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Wu, J. Topology optimization in lightweight design of a 3D-printed flapping-wing micro aerial vehicle. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2020, 33, 3206–3219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Truong, T.; Nguyen, Q.-V.; Luong, H.T.; Nguyen, Q.S.; Au, T.K.L. Experimental and numerical analysis of an optimized flapping wing mechanism for flapping wing robots. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 035506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiński, C.; Żbikowski, R. Materials challenges in the design of an insect-like flapping wing mechanism based on a four-bar linkage. Mater. Des. 2007, 28, 783–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Govindarajan, G.; Sharma, R. Experimental investigation on a flapping beam with smart material actuation for underwater application. Mech. Adv. Mater. Struct. 2019, 28, 1020–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCroix, B.W.; Ifju, P.G. Aeroelastic Model for Macrofiber Composite Actuators on Micro Air Vehicles. J. Aircr. 2017, 54, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.; Ali, T.; Zuber, M.; Basri, A.A.; Mazlan, N.; Hamidon, M.N.; Basri, E.I.; Ahmad, K.A.; Hegde, N.T.; Vaz, A.C. Micro aerial vehicle flapping actuation: An experimental analysis of crank and sliding lever mechanisms. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 015511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Hui, Z.; Tian, F.; Chen, G. Review on bio-inspired flight systems and bionic aerodynamics. Chin. J. Aeronaut. 2021, 34, 170–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, R.; Nagpal, R.; Wei, G.Y. Flight of the robobees. Sci. Am. 2013, 308, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaughan, O. RoboBee breaks free. Nat. Electron. 2019, 2, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karasek, M.; Muijres, F.T.; De Wagter, C.; Remes, B.D.W.; de Croon, G. A tailless aerial robotic flapper reveals that flies use torque coupling in rapid banked turns. Science 2018, 361, 1089–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rashmikant; Ishihara, D.; Suetsugu, R.; Ramegowda, P.C. One-wing polymer micromachined transmission for insect-inspired flapping wing nano air vehicles. Eng. Res. Express 2021, 3, 045006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quadrini, F.; Bellisario, D.; Iorio, L.; Santo, L. Shape memory polymer composites by molding aeronautical prepregs with shape memory polymer interlayers. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 115711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Cui, L.; Wang, H.; Zhang, F.; Liu, Z.; Wang, G. Insect-inspired passive wing collision recovery in flapping wing microrobots. Bioinspir. Biomim. 2025, 20, 026004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Yu, S.; Duan, S.; Zhang, P. Design and flight verification of passive wing folding for bionic flapping-wing aerial vehicle based on flexible joints. Eng. Res. Express 2025, 7, 035508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, S.I.; Chiang, C.H. The Influence of Wing Membrane Elasticity on Aerodynamics in a Bat-Inspired Flapping Robot. Biomimetics 2025, 10, 161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, R.; Zhang, H.; Xu, L.; Xie, P.; Wu, J.; Wang, C.; Avanzini, G. Mechanism and Kinematics for Flapping Wing Micro Air Vehicles Maneuvering Based on Bilateral Wings. Int. J. Aerosp. Eng. 2022, 2022, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jafferis, N.T.; Helbling, E.F.; Karpelson, M.; Wood, R.J. Untethered flight of an insect-sized flapping-wing microscale aerial vehicle. Nature 2019, 570, 491–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shankar, V.; Shirakawa, N.; Ishihara, D. Novel Computational Design of Polymer Micromachined Insect-Mimetic Wings for Flapping-Wing Nano Air Vehicles. Biomimetics 2024, 9, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, D.; Sheng, J.; Meng, Q.; Wu, D.; Wang, L.; Xiao, J.; Lv, W.; Chen, Q.; Sun, D. Biomimetic Beetle-Inspired Flapping Air Vehicle Actuated by Ionic Polymer-Metal Composite Actuator. Appl. Bionics Biomech. 2018, 2018, 3091579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.; Tang, J.; Hu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Fu, Z. Three-dimensional vibration investigation of the thin web gear pair based on Timoshenko beam. Thin-Walled Struct. 2023, 184, 110507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Hu, B.; Wu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Tang, J. A Comprehensive Optimization Model of Tooth Surface Parameters for the Minimization of Contact Stress of Helical Face Gears by Considering the Avoidance of Edge Contact. Mathematics 2022, 10, 3102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, L.; Yao, S.; Guan, C.; Zhang, D.; Wang, B.; Zhong, S. Curing simulation and experimental analysis of composite segmented tools for aerospace applications. Polym. Compos. 2025, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Shi, J.; Xu, W.; Sun, N.; Zeng, J.; Yang, G.; Song, K.; Zheng, J. A Study on the Failure Behavior and Force Transmission of Composite Skin-Stringer Structures Under a Compressive Load. Materials 2025, 18, 1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Zhong, X.Y.; Jia, H.; Zhang, L.W.; Liu, H.S.; Sun, M.C.; Liu, T.W.; Bao, J.W.; Bai, J.B.; Ge, S.C. Study on the Transverse Properties of T800-Grade Unidirectional Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polymers. Materials 2025, 18, 816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szafran, K.; Jurak, M.; Mroczka, R.; Wiacek, A.E. Preparation and Surface Characterization of Chitosan-Based Coatings for PET Materials. Molecules 2023, 28, 2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aktas, C.; Bhethanabotla, V.; Ayyala, R.S.; Sahiner, N. Modifying wetting properties of PI Film: The impact of surface texturing and CF4 and O2 plasma treatment. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2024, 656, 159729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Yu, M. Effect of atmospheric-pressure air/He plasma on the surface properties related to ink-jet printing polyester fabric. Vacuum 2017, 137, 42–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


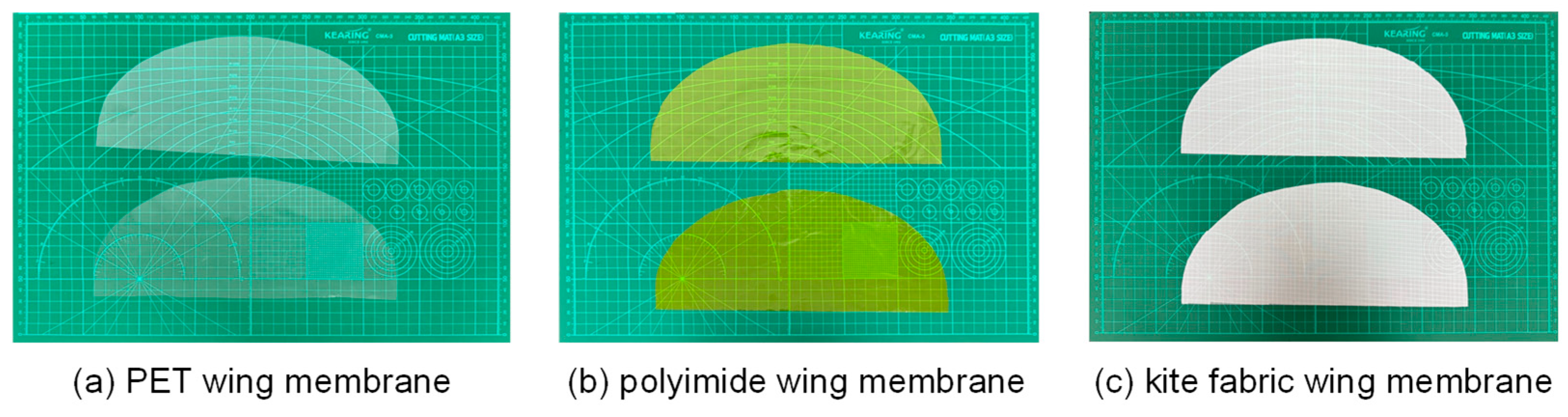

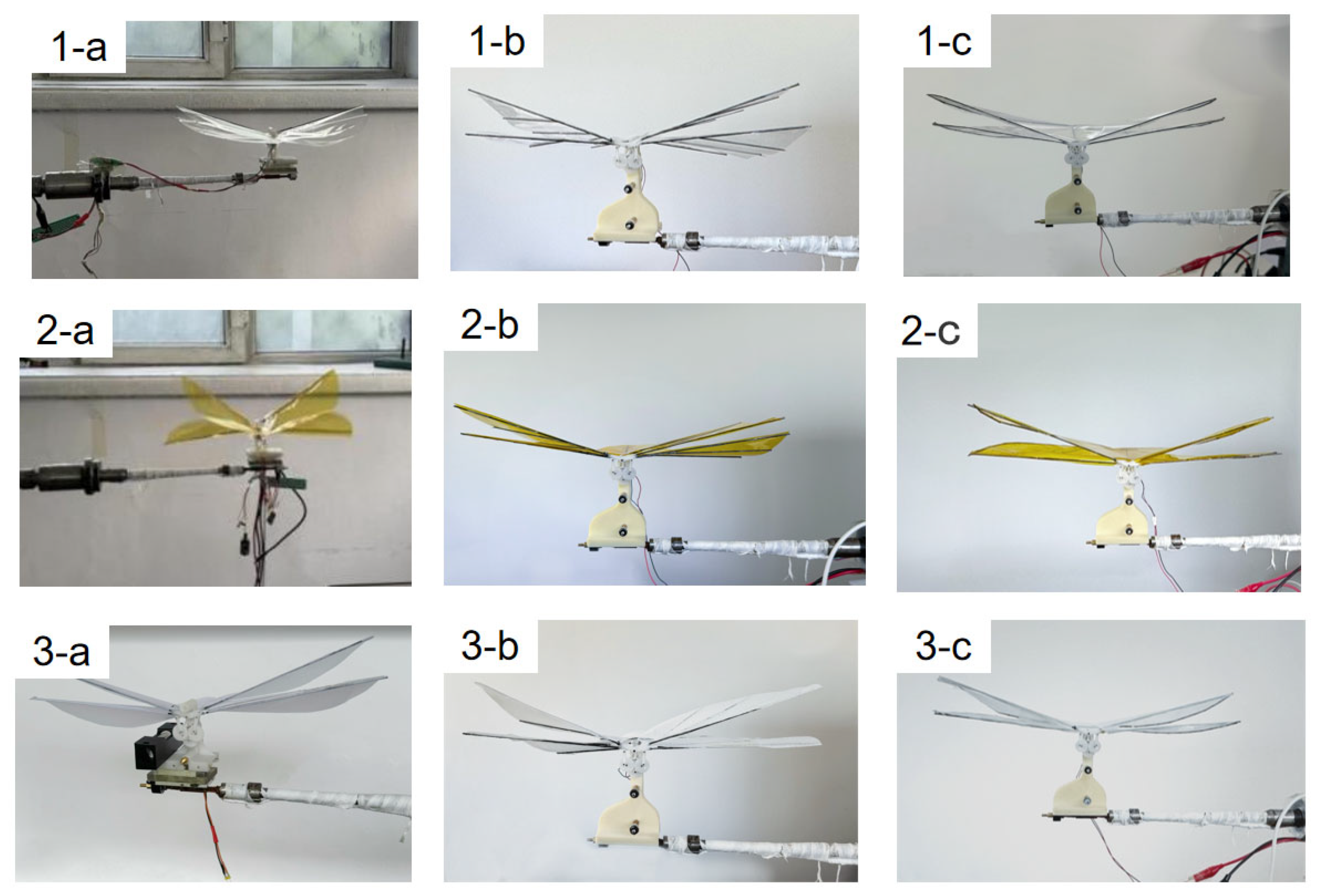
| Material Type | Density (g/cm3) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Elongation at Break (%) | Surface Energy (mJ/m3) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PET | 1.38 | 50–80 | 2–4 | 50–150 | 40–45 |
| polyimide | 1.42 | 150–300 | 2.5–4 | 20–50 | 40–50 |
| kite fabric | 0.9–1.2 | 100–300 | _ | 10–30 | _ |
| Voltage | C1-PET | C2-PET | C3-PET | C1-PI | C2-PI | C3-PI | C1-Kite | C2-Kite | C3-Kite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 V | 5.07 g | 1.01 g | 1.09 g | 2.91 g | 1.05 g | 0.66 g | 3.02 g | 1.19 g | 1.38 g |
| 2 V | 11.47 g | 5.66 g | 5.05 g | 7.36 g | 5.69 g | 3.11 g | 6.87 g | 5.36 g | 3.92 g |
| 3 V | 16.48 g | 11.69 g | 7.24 g | 12.25 g | 8.25 g | 6.09 g | 11.32 g | 9.32 g | 6.66 g |
| 4 V | 20.07 g | 17.40 g | 11.25 g | 14.04 g | 12.87 g | 9.18 g | 14.77 g | 10.39 g | 9.01 g |
| Voltage | C1-PET | C2-PET | C3-PET | C1-PI | C2-PI | C3-PI | C1-Kite | C2-Kite | C3-Kite |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 V | 8.94 Hz | 4.75 Hz | 6.44 Hz | 10.07 Hz | 4.56 Hz | 5.21 Hz | 7.97 Hz | 5.21 Hz | 4.88 Hz |
| 2 V | 13.98 Hz | 8.59 Hz | 11.32 Hz | 14.69 Hz | 8.53 Hz | 10.41 Hz | 10.93 Hz | 9.17 Hz | 8.98 Hz |
| 3 V | 17.76 Hz | 12.43 Hz | 13.01 Hz | 17.56 Hz | 12.37 Hz | 11.95 Hz | 13.90 Hz | 13.15 Hz | 12.11 Hz |
| 4 V | 20.27 Hz | 15.88 Hz | 15.77 Hz | 18.66 Hz | 15.95 Hz | 14.28 Hz | 16.87 Hz | 16.17 Hz | 14.84 Hz |
| Voltage | Voltage (V) | Lift (g) | Weight (g) | Lift to Weight | Flapping Frequency (Hz) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1-PET | 4.3 | 20.07 | 5.3 | 3.79 | 20.27 |
| Robobee | 100 | 0.7 | 0.175 | 4 | 120 |
| Defly Nimble | 8.4 | 45 | 29 | 1.55 | 17 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, R.; Jiang, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, L.; Yin, W. Research on the Structural Design and Mechanical Properties of T800 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials in Flapping Wings. Materials 2025, 18, 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153474
Wang R, Jiang Z, Zhang Y, Fan L, Yin W. Research on the Structural Design and Mechanical Properties of T800 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials in Flapping Wings. Materials. 2025; 18(15):3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153474
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Ruojun, Zengyan Jiang, Yuan Zhang, Luyao Fan, and Weilong Yin. 2025. "Research on the Structural Design and Mechanical Properties of T800 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials in Flapping Wings" Materials 18, no. 15: 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153474
APA StyleWang, R., Jiang, Z., Zhang, Y., Fan, L., & Yin, W. (2025). Research on the Structural Design and Mechanical Properties of T800 Carbon Fiber Composite Materials in Flapping Wings. Materials, 18(15), 3474. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18153474






