Advances in Polypyrrole Nanofiber Composites: Design, Synthesis, and Performance in Tissue Engineering
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Structural Classification of PPy-Based Electrospun Nanofiber Composites
2.1. Randomly Distributed PPy-Based Nanofibers
2.2. Aligned PPy-Based Nanofibers
2.3. Core–Shell Structure PPy-Based Nanofibers
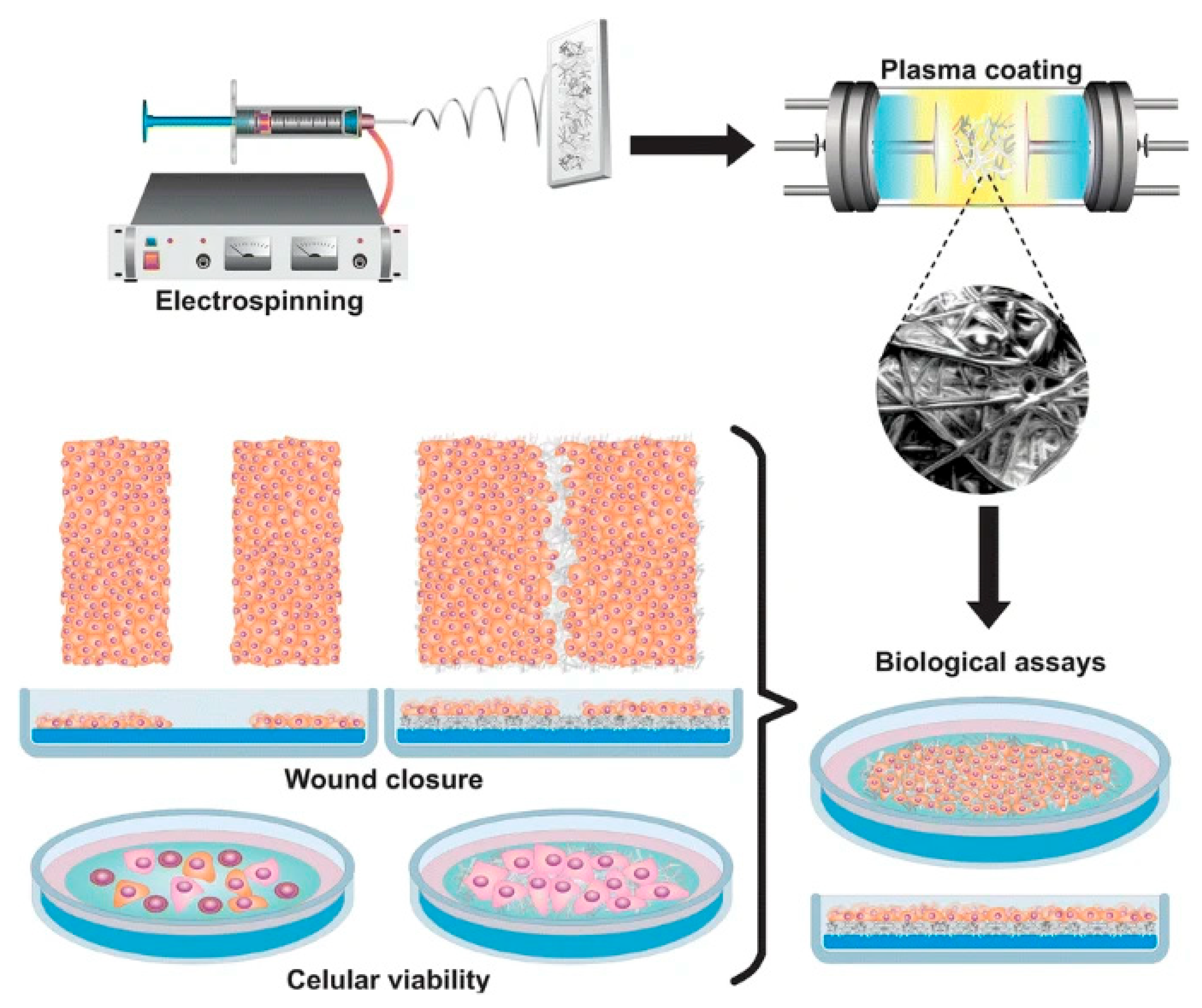
3. Application of Electrospun PPy-Based Composites in Tissue Engineering
3.1. Bone Tissue Engineering
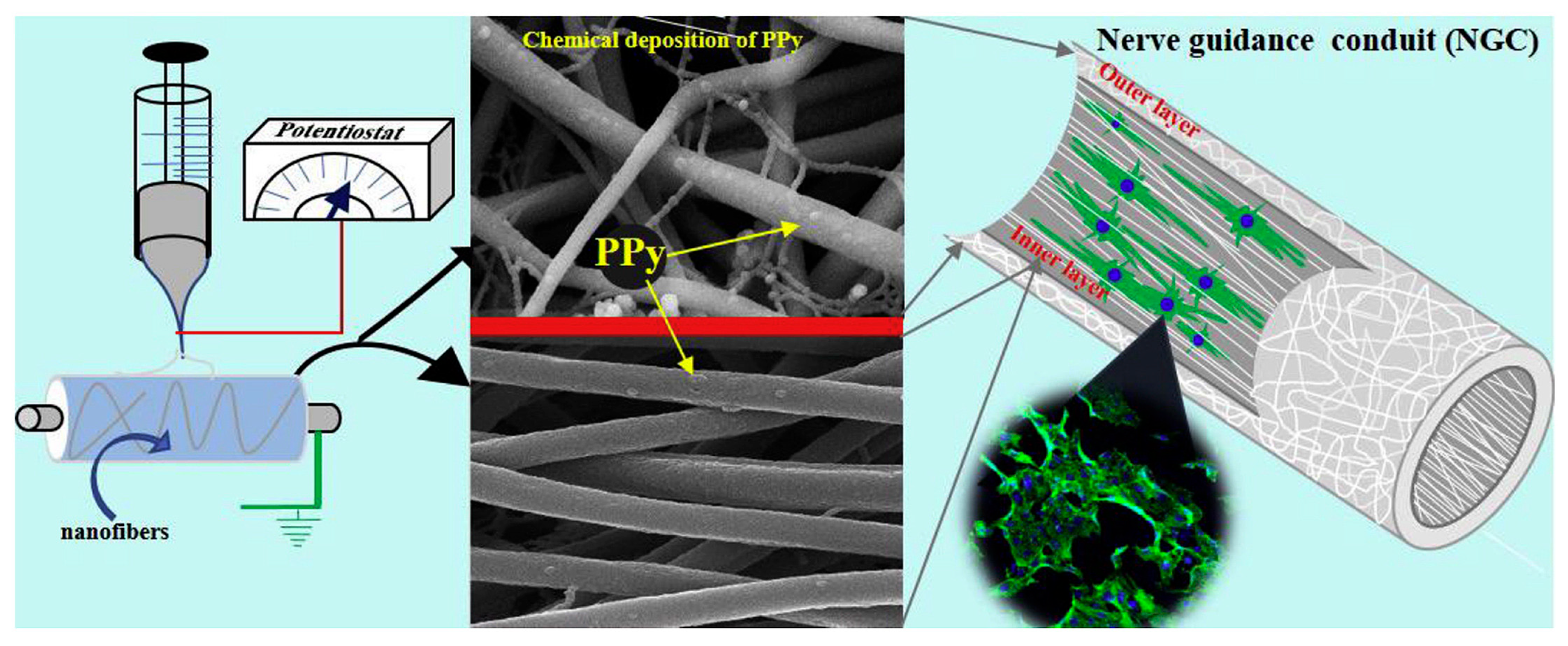
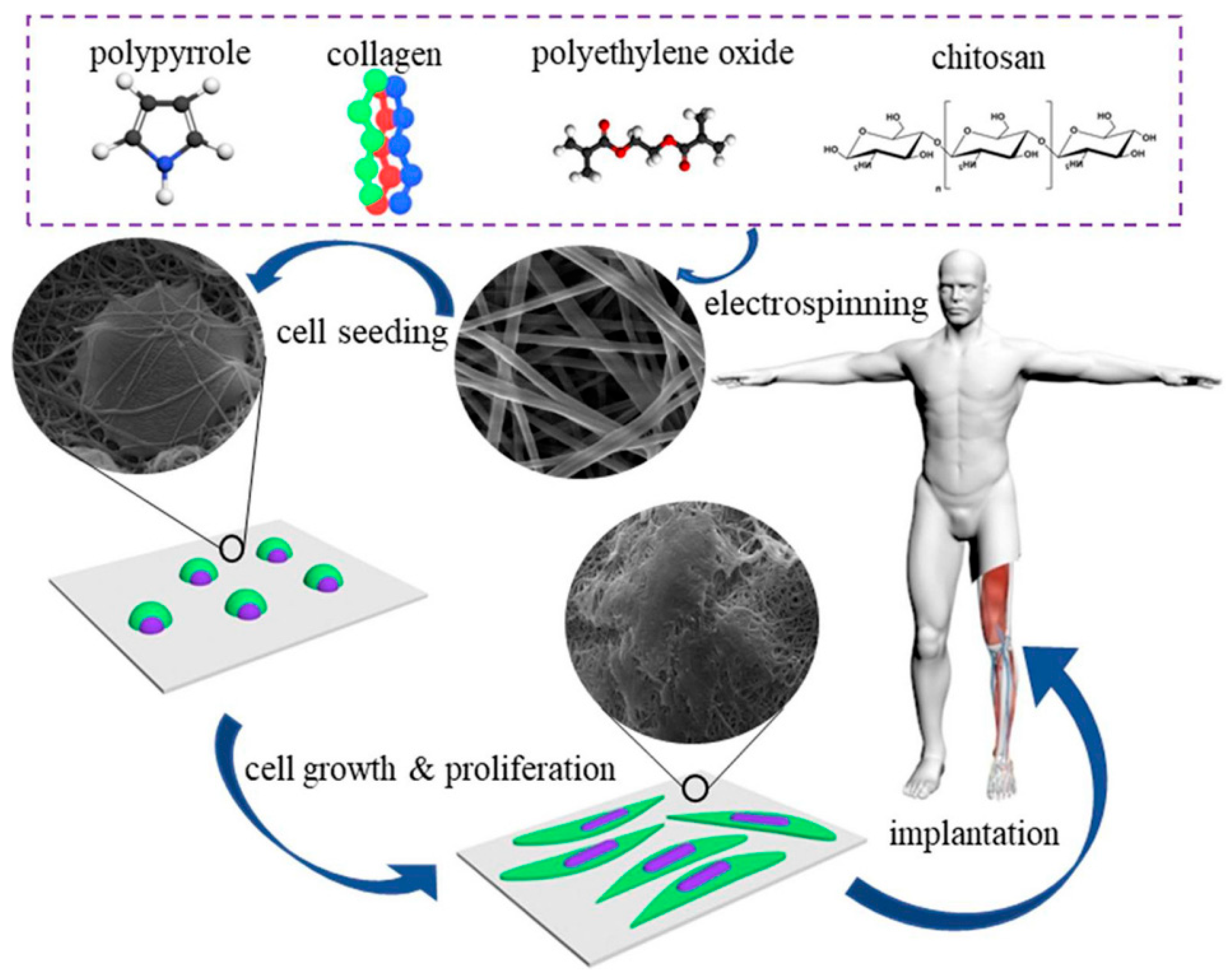
3.2. Neural Tissue Engineering
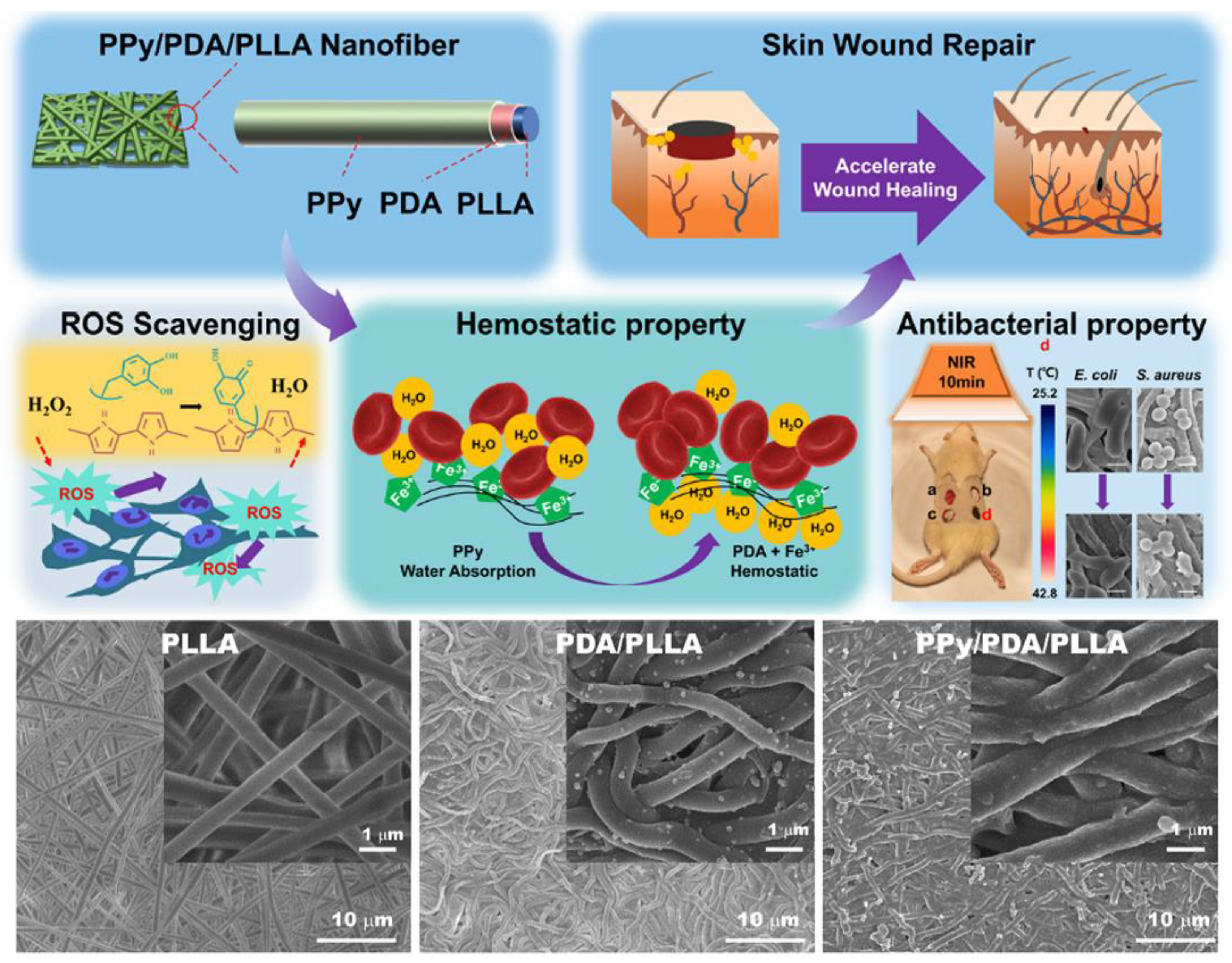
3.3. Skin Tissue Engineering
3.4. Skeletal Muscle Tissue Engineering
3.5. Myocardial Tissue Engineering
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Secchi, E.; Marbach, S.; Niguès, A.; Stein, D.; Siria, A.; Bocquet, L. Massive radius-dependent flow slippage in carbon nanotubes. Nature 2016, 537, 210–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, J.; Zhao, Z.; Kumar, A.; Boughton, R.I.; Liu, H. Recent progress in design, synthesis, and applications of one-dimensional TiO2 nanostructured surface heterostructures: A review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 6920–6937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Luan, D.; Gao, S.; Lou, X.W. Rational Design and Engineering of One-Dimensional Hollow Nanostructures for Efficient Electrochemical Energy Storage. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2021, 60, 20102–20118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Kouamé, N.A.; Ramos, L.; Remita, S.; Dazzi, A.; Deniset-Besseau, A.; Beaunier, P.; Goubard, F.; Aubert, P.-H.; Remita, H. Conducting polymer nanostructures for photocatalysis under visible light. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 505–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.; Wu, H.; Meng, Y.; Wei, Z. Conducting Polymer Nanowire Arrays for High Performance Supercapacitors. Small 2013, 10, 14–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Shi, X.-L.; Dargusch, M.; Di, C.; Zou, J.; Chen, Z.-G. Conducting polymer-based flexible thermoelectric materials and devices: From mechanisms to applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 121, 100840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nezakati, T.; Seifalian, A.; Tan, A.; Seifalian, A.M. Conductive Polymers: Opportunities and Challenges in Biomedical Applications. Chem. Rev. 2018, 118, 6766–6843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanavicius, S.; Ramanavicius, A. Conducting Polymers in the Design of Biosensors and Biofuel Cells. Polymers 2021, 13, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, J.; Zhang, Z. Polypyrrole as Electrically Conductive Biomaterials: Synthesis, Biofunctionalization, Potential Applications and Challenges. In Cutting-Edge Enabling Technologies for Regenerative Medicine; Springer: Singapore, 2018; Volume 1078, pp. 347–370. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, S.; Jang, L.K.; Jang, M.; Lee, S.; Hardy, J.G.; Lee, J.Y. Electrically Conductive Polydopamine–Polypyrrole as High Performance Biomaterials for Cell Stimulation In Vitro and Electrical Signal Recording In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 33032–33042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Hu, X.; Lu, L.; Ye, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, Z. Electrical regulation of Schwann cells using conductive polypyrrole/chitosan polymers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2010, 93A, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, I.; Han, H.S.; Edwards, J.R.; Jeon, H. Electrospun Fibrous Scaffolds for Tissue Engineering: Viewpoints on Architecture and Fabrication. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 17, 745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahmati, M.; Mills, D.K.; Urbanska, A.M.; Saeb, M.R.; Venugopal, J.R.; Ramakrishna, S.; Mozafari, M. Electrospinning for tissue engineering applications. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2021, 117, 20102–20118. [Google Scholar]
- Stewart, E.; Kobayashi, N.R.; Higgins, M.J.; Quigley, A.F.; Jamali, S.; Moulton, S.E.; Kapsa, R.M.; Wallace, G.G.; Crook, J.M. Electrical stimulation using conductive polymer polypyrrole promotes differentiation of human neural stem cells: A biocom-patible platform for translational neural tissue engineering. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods 2015, 21, 385–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hermenegildo, B.; Ribeiro, C.; Peřinka, N.; Martins, P.; Trchová, M.; Hajná, M.; Stejskal, J.; Lanceros-Méndez, S. Electroactive poly(vinylidene fluoride) electrospun fiber mats coated with polyaniline and polypyrrole for tissue regeneration applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2022, 170, 105118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.; Ma, P.X. Conducting polymers for tissue engineering. Biomacromolecules 2018, 19, 1764–1782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Pech, J.C.; Rosales-Ibáñes, R.; Cauich-Rodriguez, J.V.; Carrillo-Escalante, H.J.; Rodríguez-Navarrete, A.; Avila-Ortega, A.; Hernández-Sánchez, F. Design, synthesis, characterization, and cytotoxicity of PCL/PLGA scaffolds through plasma treatment in the presence of pyrrole for possible use in urethral tissue engineering. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 34, 840–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatamzadeh, M.; Sarvari, R.; Massoumi, B.; Agbolaghi, S.; Samadian, F. Liver tissue engineering via hyperbranched polypyrrole scaffolds. Int. J. Polym. Mater. Polym. Biomater. 2020, 69, 1112–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjo, M.; Kesküla, A.; Leemets, K.; Khorram, M.S.; Saar, R.; Järvekülg, M.; Tamm, T.; Kiefer, R. Polypyrrole coatings on gelatin fiber scaffolds: Material and electrochemical characterizations in organic and aqueous electrolyte. Synth. Met. 2017, 232, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, F.G.; García-Bernabé, A.; Moreno, V.C.; Martínez-Ramos, C.; Pradas, M.M. Solid Polymer Electrolytes Based on Polylactic Acid Nanofiber Mats Coated with Polypyrrole. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2020, 306, 2000584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Zhou, Z.; Li, D.; Wu, T.; Zheng, H.; Liu, J.; Wang, G.; Yu, Y.; Mo, X. Polypyrrole-coated poly(l-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofibrous nerve guidance conduit induced nerve regeneration in rat. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 94, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancino, C.; Hendrickson, T.; Whitney, L.V.; Paradiso, F.; Abasi, S.; Tasciotti, E.; Taraballi, F.; Guiseppi-Elie, A. Electrospun electroconductive constructs of aligned fibers for cardiac tissue engineering. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2022, 44, 102567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Qiao, T.; Jiang, S.; Li, T.; Song, P.; Zhang, B.; Song, X. Aligned poly (glycolide-lactide) fiber membranes with conducting polypyrrole. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2016, 28, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, F.G.; Estellés, J.M.; Pradas, M.M.; Martínez-Ramos, C. Axonal extension from dorsal root ganglia on fibrillar and highly aligned poly(lactic acid)-polypyrrole substrates obtained by two different techniques: Electrospun nanofibres and extruded microfibres. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 163, 1959–1969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nekouian, S.; Sojoodi, M.; Nadri, S. Fabrication of conductive fibrous scaffold for photoreceptor differentiation of mesen-chymal stem cell. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 15800–15808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, A.; Huang, Z.; Yin, G.; Pu, X. Fabrication of aligned, porous and conductive fibers and their effects on cell adhesion and guidance. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2015, 134, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortés-Ortiz, E.; Olayo-Valles, R.; Rodríguez-Talavera, R.; González-Torres, M.; Vargas-Muñoz, S.; Olayo, R.; Godinez-Fernández, R.; Juárez, O.E.U.; Morales-Corona, J. Plasma Functionalized Scaffolds of Polyhydroxybutyrate Electrospun Fibers for Pancreatic Beta Cell Cultures. Front. Mater. 2021, 8, 600738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengupta, P.; Ghosh, A.; Bose, N.; Mukherjee, S.; Roy Chowdhury, A.; Datta, P. A comparative assessment of poly(vinylidene fluoride)/conducting polymer electrospun nanofiber membranes for biomedical applications. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2020, 137, 49115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yardimci, A.I.; Baskan, O.; Yilmaz, S.; Mese, G.; Ozcivici, E.; Selamet, Y. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells on random and aligned PAN/PPy nanofibrous scaffolds. J. Biomater. Appl. 2019, 34, 640–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Shrestha, B.K.; Kim, J.I.; Ko, S.W.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. Electrodeless coating polypyrrole on chitosan grafted polyurethane with functionalized multiwall carbon nanotubes electrospun scaffold for nerve tissue engineering. Carbon 2018, 136, 430–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osorio-Londoño, D.M.; Godínez-Fernández, J.R.; Acosta-García, M.C.; Morales-Corona, J.; Olayo-González, R.; Morales-Guadarrama, A. Pyrrole Plasma Polymer-Coated Electrospun Scaffolds for Neural Tissue Engineering. Polymers 2021, 13, 3876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, M.; Min, J.H.; Hong, M.H.; Lee, H.J.; Kang, S.; Yi, S.; Koh, W.G. Culture of neural stem cells on conductive and microgrooved polymeric scaffolds fabricated via electrospun fiber-template lithography. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 045007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Y.; Huang, Z.; Pu, X.; Yin, G.; Zhang, J. Fabrication of Chitosan/Polypyrrole-coated poly(L-lactic acid)/Polycaprolactone aligned fibre films for enhancement of neural cell compatibility and neurite growth. Cell Prolif. 2019, 52, e12588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elashnikov, R.; Rimpelová, S.; Děkanovský, L.; Švorčík, V.; Lyutakov, O. Polypyrrole-coated cellulose nanofibers: Influence of orientation, coverage and electrical stimulation on SH-SY5Y behavior. J. Mater. Chem. B 2019, 7, 6500–6507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, F.; Wei, S.; Sheng, H.; Wu, S.; Liu, Z.; Cui, W.; Sun, Y.; Wu, Y.; Li, B.; Xuan, H.; et al. Three-layer core-shell structure of polypyrrole/polydopamine/poly(l-lactide) nanofibers for wound healing application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 222, 1948–1962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, W.; Shi, J.; Liu, S.; Xu, Z.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Y. Preparation and properties of fiber-based conductive composite scaffolds for pe-ripheral nerve regeneration. Chin. J. Reparative Reconstr. Surg. 2019, 33, 356–362. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, W.; Yang, Z.; Qin, X.; Wei, Y.; Li, C.; Huang, R.; Zhou, C.; Wang, H.; Jin, L.; Wang, H. Fabrication and Characterization of the Core-Shell Structure of Poly(3-Hydroxybutyrate-4-Hydroxybutyrate) Nanofiber Scaffolds. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 8868431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Ao, Q.; Wang, L.; Huang, Z.; Cai, Q.; Chen, G.; Yang, X.; Zhong, W. Constructing conductive conduit with conductive fibrous infilling for peripheral nerve regeneration. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 345, 566–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Wang, K.; Xing, Y.; Yu, Q. Lysine-doped polypyrrole/spider silk protein/poly(l-lactic) acid containing nerve growth factor composite fibers for neural application. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2015, 56, 564–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golbabaei, M.H.; Varnoosfaderani, M.S.; Hemmati, F.; Barati, M.R.; Pishbin, F.; Ebrahimi, S.A.S. Machine learning-guided morphological property prediction of 2D electrospun scaffolds: The effect of polymer chemical composition and processing parameters. RSC Adv. 2024, 14, 15178–15199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, L.; Ouyang, J.; Zhang, L.; Xue, J.; Zhang, H.; Tao, W. Electroactive electrospun nanofibers for tissue engineering. Nano Today 2021, 39, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ning, C.; Zhou, Z.; Tan, G.; Zhu, Y.; Mao, C. Electroactive polymers for tissue regeneration: Developments and perspectives. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2018, 81, 144–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohki, T.; Yamato, M.; Ota, M.; Takagi, R.; Kondo, M.; Kanai, N.; Okano, T.; Yamamoto, M. Application of regenerative medical technology using tissue-engineered cell sheets for endoscopic submucosal dissection of esophageal neoplasms. Dig. Endosc. 2015, 27, 182–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jadoun, S.; Riaz, U.; Budhiraja, V. Biodegradable conducting polymeric materials for biomedical applications: A review. Med. Devices Sens. 2021, 4, e10141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarei, M.; Samimi, A.; Khorram, M.; Abdi, M.M.; Golestaneh, S.I. Fabrication and characterization of conductive polypyrrole/chitosan/collagen electrospun nanofiber scaffold for tissue engineering application. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 168, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores-Sánchez, M.G.; Islas-Arteaga, N.C.; Raya-Rivera, A.M.; Esquiliano-Rendon, D.R.; Morales-Corona, J.; Uribe-Juarez, O.E.; Vivar-Velázquez, F.I.; Ortiz-Vázquez, G.P.; Olayo, R. Effect of a plasma synthesized polypyrrole coverage on polylactic acid/hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2021, 109, 2199–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Castro, J.G.; Rodrigues, B.V.M.; Ricci, R.; Costa, M.M.; Ribeiro, A.F.C.; Marciano, F.R.; Lobo, A.O. Designing a novel nanocomposite for bone tissue engineering using electrospun conductive PBAT/polypyrrole as a scaffold to direct nanohydroxyapatite electrodeposition. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 32615–32623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elias, C.d.M.V.; Filho, A.L.M.M.; da Silva, L.R.; do Amaral, F.P.d.M.; Webster, T.J.; Marciano, F.R.; Lobo, A.O. In Vivo Evaluation of the Genotoxic Effects of Poly (Butylene adipate-co-terephthalate)/Polypyrrole with Nanohydroxyapatite Scaffolds for Bone Regeneration. Materials 2019, 12, 1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Wang, X.; Chen, T.; Zhang, N.; Wei, Q.; Tian, J.; Wang, Y.; Ma, C.; Lu, Y. Hydroxyapatite/silver electrospun fibers for anti-infection and osteoinduction. J. Adv. Res. 2020, 21, 91–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, W.; Huang, Y.; Wei, P.; Cai, Q.; Yang, X.; Zhong, W. Roles of electrical stimulation in promoting osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs on conductive fibers. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 1443–1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, K.; Zhang, S.; Wang, S.; Zhu, F.; Liu, M.; Gu, X.; Li, P.; Fan, Y. Positive effect of magnetic-conductive bifunctional fibrous scaffolds on guiding double electrical and magnetic stimulations to pre-osteoblasts. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2019, 15, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Wei, S.; Jin, W.; Lu, B.; Xu, Y. Preparation and structure–property relationship study of piezoelectric–conductive composite polymer nanofiber materials for bone tissue engineering. Polymers 2024, 16, 1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peña, B.; Laughter, M.; Jett, S.; Rowland, T.J.; Taylor, M.R.G.; Mestroni, L.; Park, D. Injectable hydrogels for cardiac tissue engineering. Macromol. Biosci. 2018, 18, e1800079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maharjan, B.; Kaliannagounder, V.K.; Jang, S.R.; Awasthi, G.P.; Bhattarai, D.P.; Choukrani, G.; Park, C.H.; Kim, C.S. In-situ polymerized polypyrrole nanoparticles immobilized poly(ε-caprolactone) electrospun conductive scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 114, 111056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardy, J.G.; Villancio-Wolter, M.K.; Sukhavasi, R.C.; Mouser, D.J.; Aguilar, D.; Geissler, S.A.; Kaplan, D.L.; Schmidt, C.E. Electrical Stimulation of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Conductive Nanofibers Enhances their Differentiation toward Osteogenic Outcomes. Macromol. Rapid Commun. 2015, 36, 1884–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ding, S.; Zhang, K.; Mao, H.-Q.; Yang, Y. Application of conductive PPy/SF composite scaffold and electrical stimulation for neural tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2020, 255, 120164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.-H.; Niu, C.-M.; Shi, J.-Q.; Wang, Y.-Y.; Yang, Y.-M.; Wang, H.-B. Novel conductive polypyrrole/silk fibroin scaffold for neural tissue repair. Neural Regen. Res. 2018, 13, 1455–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhosseini, S.N.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Karkhaneh, A.; Dodel, M.; Khalili, M.; Arshaghi, T.E.; Elahirad, E.; Mozafari, M. Improved cellular response on functionalized polypyrrole interfaces. J. Cell Physiol. 2019, 234, 15279–15287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thunberg, J.; Kalogeropoulos, T.; Kuzmenko, V.; Hägg, D.; Johannesson, S.; Westman, G.; Gatenholm, P. In situ synthesis of conductive polypyrrole on electrospun cellulose nanofibers: Scaffold for neural tissue engineering. Cellulose 2015, 22, 1459–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnan-Prema, V.; Mohanan, A.; Shivaram, S.B.; Madhusudanan, P.; Raju, G.; Menon, D.; A Shankarappa, S. Electrical stimulation of co-woven nerve conduit for peripheral neurite differentiation. Biomed. Mater. 2020, 15, 065015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Wu, T.; Wang, J.; Li, D.; Wang, J.; Gao, Q.; Bhutto, M.A.; El-Hamshary, H.; Al-Deyab, S.S.; Mo, X. Polypyrrole-coated poly(L-lactic acid-co-ε-caprolactone)/silk fibroin nanofibrous membranes promoting neural cell proliferation and differentiation with electrical stimulation. J. Mater. Chem. B 2016, 4, 6670–6679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.-F.; Zhang, F.; Wang, J.-G.; Chen, Q.-C.; Yang, W.-Z.; He, N.; Jiang, Y.-Y.; Chen, F.; Liu, J.-J. Electrospinning of PELA/PPY Fibrous Conduits: Promoting Peripheral Nerve Regeneration in Rats by Self-Originated Electrical Stimulation. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2016, 2, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namhongsa, M.; Daranarong, D.; Sriyai, M.; Molloy, R.; Ross, S.; Ross, G.M.; Tuantranont, A.; Tocharus, J.; Sivasinprasasn, S.; Topham, P.D.; et al. Surface-Modified Polypyrrole-Coated PLCL and PLGA Nerve Guide Conduits Fabricated by 3D Printing and Electrospinning. Biomacromolecules 2022, 23, 4532–4546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granato, A.E.; Ribeiro, A.C.; Marciano, F.R.; Rodrigues, B.V.; Lobo, A.O.; Porcionatto, M. Polypyrrole increases branching and neurite extension by Neuro2A cells on PBAT ultrathin fibers. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2018, 14, 1753–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Q.; Jin, L.; Li, C.; Kuddannayai, S.; Zhang, Y. The effect of electrical stimulation on cortical cells in 3D nanofibrous scaffolds. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 11027–11035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Yang, A.; Huang, Z.; Yin, G.; Pu, X.; Jin, J. Enhancement of Neurite Adhesion, Alignment and Elongation on Conductive Polypyr-role-Poly(lactide acid) Fibers with Cell-Derived Extracellular Matrix. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2017, 149, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Sun, B.; Mo, X. Electrospun polypyrrole-coated polycaprolactone nanoyarn nerve guidance conduits for nerve tissue engineering. Front. Mater. Sci. 2018, 12, 438–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
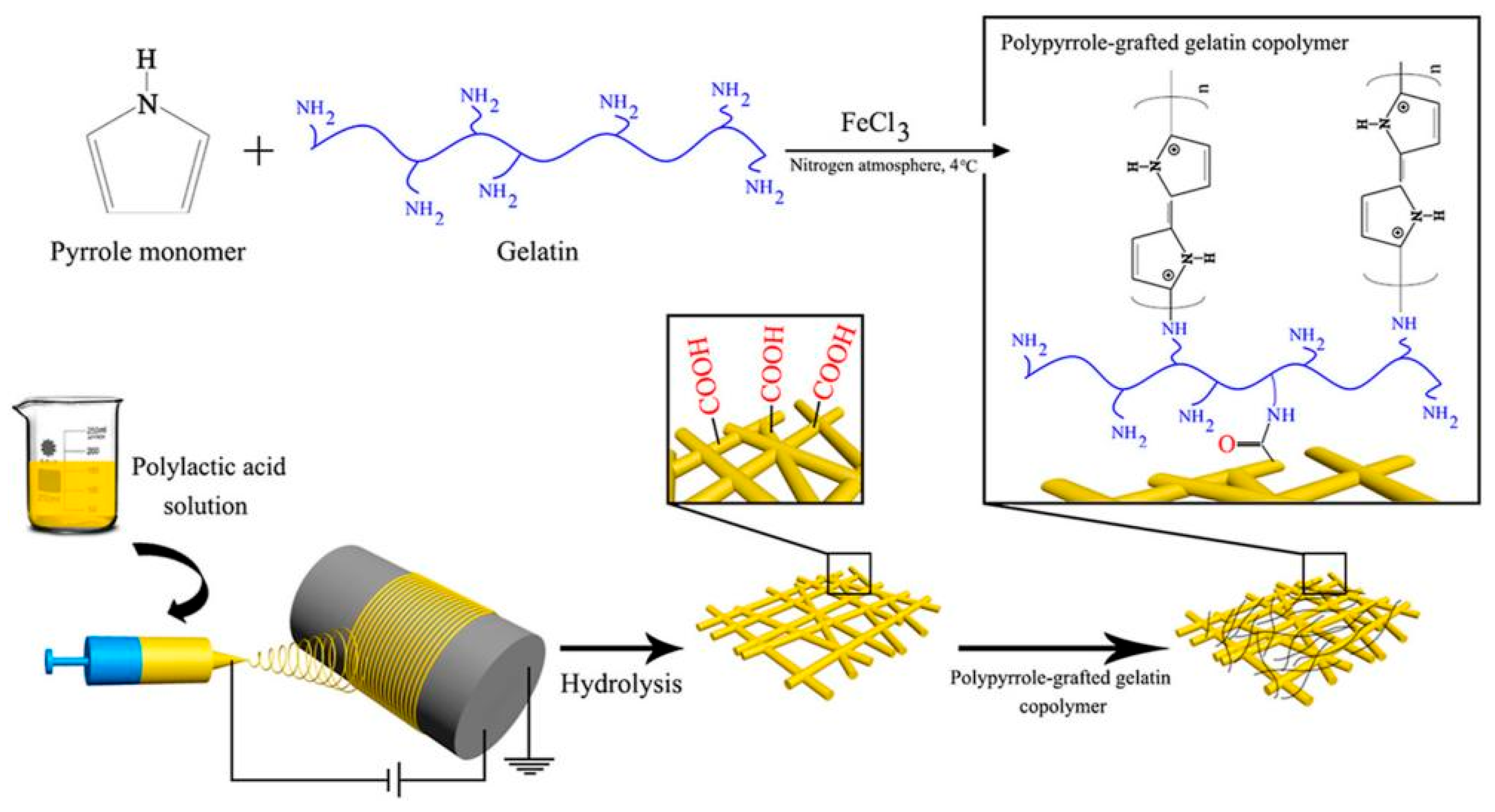
- Imani, F.; Karimi-Soflou, R.; Shabani, I.; Karkhaneh, A. PLA electrospun nanofibers modified with polypyrrole-grafted gelatin as bioactive electroconductive scaffold. Polymer 2021, 218, 123487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.-F.; Wang, Y.-G.; Cheng, L.; Wu, Z.; Sun, X.-D.; Peng, J. Preparation of polypyrrole-embedded electrospun poly(lactic acid) nanofibrous scaffolds for nerve tissue engineering. Neural Regen. Res. 2016, 11, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar]
- Talebi, A.; Labbaf, S.; Atari, M.; Parhizkar, M. Polymeric Nanocomposite Structures Based on Functionalized Graphene with Tunable Properties for Nervous Tissue Replacement. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2021, 7, 4591–4601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Liu, C.; Huang, Z.; Pu, X.; Shang, L.; Yin, G.; Xue, C. Preparation of carboxylic graphene oxide-composited polypyrrole conduits and their effect on sciatic nerve repair under electrical stimulation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 2784–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadeghi, A.; Moztarzadeh, F.; Mohandesi, J.A. Investigating the effect of chitosan on hydrophilicity and bioactivity of conductive electrospun composite scaffold for neural tissue engineering. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 625–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafei, S.; Foroughi, J.; Chen, Z.; Wong, C.S.; Naebe, M. Short Oxygen Plasma Treatment Leading to Long-Term Hydrophilicity of Conductive PCL-PPy Nanofiber Scaffolds. Polymers 2017, 9, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, L.; Prabhakaran, M.P.; Hu, J.; Chen, M.; Besenbacher, F.; Ramakrishna, S. Synergistic effect of topography, surface chemistry and conductivity of the electrospun nanofibrous scaffold on cellular response of PC12 cells. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2016, 145, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zha, F.; Chen, W.; Lv, G.; Wu, C.; Hao, L.; Meng, L.; Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Effects of surface condition of conductive electrospun nanofiber mats on cell behavior for nerve tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 120, 111795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zha, F.; Chen, W.; Hao, L.; Wu, C.; Lu, M.; Zhang, L.; Yu, D. Electrospun cellulose-based conductive polymer nanofibrous mats: Composite scaffolds and their influence on cell behavior with electrical stimulation for nerve tissue engineering. Soft Matter 2020, 16, 6591–6598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, B.; Aziz, M.R.F.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Li, D.; Li, R.-K. An Electro-spun Tri-component Polymer Biomaterial with Optoelectronic Properties for Neuronal Differentiation. Acta Biomater. 2022, 139, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debels, H.; Hamdi, M.; Abberton, K.; Morrison, W. Dermal matrices and bioengineered skin substitutes: A critical review of current options. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2015, 3, e284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Massoumi, B.; Hatamzadeh, M.; Firouzi, N.; Jaymand, M. Electrically conductive nanofibrous scaffold composed of poly(ethylene glycol)-modified polypyrrole and poly(ε-caprolactone) for tissue engineering applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 98, 300–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Román-Doval, R.; Tellez-Cruz, M.M.; Rojas-Chávez, H.; Cruz-Martínez, H.; Carrasco-Torres, G.; Vásquez-Garzón, V.R. Enhancing electrospun scaffolds of PVP with polypyrrole/iodine for tissue engineering of skin regeneration by coating via a plasma process. J. Mater. Sci. 2019, 54, 3342–3353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Lei, T.; Yang, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; He, S.; Fan, J. Electrically Conductive Polypyrrole@keratin Nanofber Membranes with Potential for Tissue Restoration. Fibers Polym. 2024, 25, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjo, M.; Torop, J.; Järvekülg, M.; Tamm, T.; Kiefer, R. Electrochemomechanical Behavior of Polypyrrole-Coated Nanofiber Scaffolds in Cell Culture Medium. Polymers 2019, 11, 1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebadi, S.V.; Fashandi, H.; Semnani, D.; Rezaei, B.; Fakhrali, A. Overcoming the potential drop in conducting polymer artificial muscles through metallization of electrospun nanofibers by electroplating process. Smart Mater. Struct. 2020, 29, 085036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browe, D.; Freeman, J. Optimizing C2C12 myoblast differentiation using polycaprolactone–polypyrrole copolymer scaffolds. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2019, 107, 220–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baei, P.; Hosseini, M.; Baharvand, H.; Pahlavan, S. Electrically conductive materials for in vitro cardiac microtissue engineering. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 1203–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmi, A.; Cieslar-Pobuda, A.; de Muinck, E.; Los, M.; Rafat, M.; Jager, E.W.H. Direct Mechanical Stimulation of Stem Cells: A Beating Electromechanically Active Scaffold for Cardiac Tissue Engineering. Adv. Healtc. Mater. 2016, 5, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Mitriashkin, A.; Lim, T.T.; Goh, J.C.-H. Conductive polypyrrole-encapsulated silk fibroin fibers for cardiac tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2021, 276, 121008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fakhrali, A.; Semnani, D.; Salehi, H.; Ghane, M. Electro-conductive nanofibrous structure based on PGS/PCL coated with PPy by in situ chemical polymerization applicable as cardiac patch: Fabrication and optimization. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2022, 139, 52136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, M.R.F.; Wlodarek, L.; Alibhai, F.; Wu, J.; Li, S.; Sun, Y.; Santerre, J.P.; Li, R. A Polypyrrole-Polycarbonate Polyurethane Elastomer Alleviates Cardiac Arrhythmias via Improving Bio-Conductivity. Adv. Health Mater. 2023, 12, e2203168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhrali, A.; Tamimi, M.; Semnani, D.; Salehi, H.; Ghodsi, A.; Rajabi, S.; Pezeshki-Modaress, M.; Ebadi, S.V.; Abdi, S.; Ghane, M. Electroconductive Nanofiber/Myocardium Gel Scaffolds Applicable for Myocardial Infarction Therapy. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2024, 6, 5593–5607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olvera, D.; Molina, M.S.; Hendy, G.; Monaghan, M.G. Electroconductive Melt Electrowritten Patches Matching the Mechanical Anisotropy of Human Myocardium. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020, 30, 1909880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feiner, R.; Fleischer, S.; Shapira, A.; Kalish, O.; Dvir, T. Multifunctional degradable electronic scaffolds for cardiac tissue engineering. J. Control. Release 2018, 281, 189–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chronakis, I.S.; Grapenson, S.; Jakob, A. Conductive polypyrrole nanofibers via electrospinning: Electrical and morphological properties. Polymer 2006, 47, 1597–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhu, K.; Xu, Q.; Tang, M. Novel electrochemical biosensor based on functional composite nanofibers for sensitive detection of p53 tumor suppressor gene. Anal. Chim. Acta 2013, 765, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Liu, S.-L.; Long, Y.-Z.; Liu, L.-Z.; Zhang, H.-D.; Zhang, J.-C.; Han, W.-P.; Liu, Y.-C. Fabrication of p-type ZnO nanofibers by electrospinning for field-effect and rectifying devices. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 104, 042105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-H.; Kong, H.-Y.; Yang, R.-R.; Dou, H.; Faraz, N.; Wang, L.; Feng, C. Review on fiber morphology obtained by bubble electrospinning and blown bubble spinning. Therm. Sci. 2012, 16, 1263–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Zhang, L.; Sun, X.-F.; Liu, J.; Fan, J.; Huang, D.-W. Multi-jet electrospinning via auxiliary electrode. Mater. Lett. 2015, 141, 153–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brettmann, B.K.; Tsang, S.; Forward, K.M.; Rutledge, G.C.; Myerson, A.S.; Trout, B.L. Free surface electrospinning of fibers containing microparticles. Langmuir 2012, 28, 9714–9721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Persano, L.; Camposeo, A.; Tekmen, C.; Pisignano, D. Industrial upscaling of electrospinning and applications of polymer nano-fibers: A review. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2013, 298, 504–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, B.; Long, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, M.; Duvail, J.; Jiang, X.; Yin, H. Advances in three-dimensional nanofibrous macrostructures via electrospinning. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2014, 39, 862–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.D.; Vaquette, C.; Farrugia, B.L.; Dargaville, T.R.; Brown, T.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Electrospinning and additive manufacturing: Converging technologies. Biomater. Sci. 2013, 1, 171–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalton, P.D.; Klinkhammer, K.; Salber, J.; Klee, D.; Möller, M. Direct in vitro electrospinning with polymer melts. Biomacromolecules 2006, 13, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Direct writing by way of melt electrospinning. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 5651–5657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Slotosch, A.; Thibaudeau, L.; Taubenberger, A.; Loessner, D.; Vaquette, C.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Design and fabrication of tubular scaffolds via direct writing in a melt electrospinning mode. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 13–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, T.D.; Dalton, P.D.; Hutmacher, D.W. Melt electrospinning today: An opportune time for an emerging polymer process. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2016, 56, 116–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Fabrication Method | Composition of the Composite | Arrangement Patterns of Nanofiber Scaffolds | Cell Type | In Vitro Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrospinning | PAN/PPy | Aligned and random | Mouse bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells | Alignment process increased the tensile strength of nanofibers 3.9-fold, while the tensile strain of nanofibers decreased by 78% | [29] |
| Electrospinning | PPy/chitosan/collagen/PEO | Randomly arranged | Fibroblast cells | Enhanced the conductivity up to 164.274 × 10−3 s/m | [45] |
| Electrospinning and plasma polymerization | PLA/HA/Pyrrole/Iodine matrices | Randomly arranged and porous | Mesenchymal stem cells | Presenting a variety of apparent pore sizes to allow for the passage of nutrients to bone cells. The increased cell proliferation and significantly improved cell viability | [46] |
| Electrospinning and electrodepositing | Nanohydroxyapatite/PBAT/PPy | Randomly arranged | MG-63 cell | More hydrophilic with improved cell differentiation | [47] |
| Electrospinning and electrodepositing | PBAT/PPy/nHAp | Randomly arranged | Osteoblasts | Long-term antibacterial property, bioactivity, and osteoinductivity | [49] |
| Electrospinning | PLLA/PPy | An oriented direction and bead-free morphology | Bone mesenchymal stromal cells | Accelerated the osteogenic differentiation of the seeded cells | [50] |
| Electrospinning and in situ polymerization | PPy/Fe3O4/PLGA | Randomly arranged | MC3T3-E1 pre-osteoblasts | Good biocompatibility, hydrophilicity, and thermal stability | [51] |
| Electrospinning and in situ polymerization | PCL/PPy | Randomly arranged | MC3T3-E1 cell | Exhibited enhanced cell adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation in electrical stimulation conditions | [54] |
| Electrospinning and in situ polymerization | PCL/PPy/PSS | Randomly arranged | Human mesenchymal stem cells | Enhance the differentiation toward osteogenic outcomes | [55] |
| Fabrication Method | Composition of the Composite | Cell Type | In Vitro Performance | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Electrospinning | PPy coating (MWCNT/chitosan-g-polycarbamate) | S42 and PC12 | Supports better viability, growth, and axon formation. Aligned fiber arrangement positively regulates cell response. | [30] |
| Electrospinning and electrodeposition | Chitosan/PPy coating poly-L-lactone/poly (ε-caprolactone) | PC12 | Supports the viability, differentiation, and axon growth of cultured cells. Electrical stimulation improves genes (NF-L and Trk A). | [33] |
| Electrospinning | PPy-coated cellulose acetate butyrate | SH-SY5Y | The cell adhesion of the coating substrate is reduced. Aligned fibers and electrical stimulation positively regulate neurite outgrowth. | [34] |
| 3D Printing, electrodeposition and electrospinning | PPy-coated silk fibroin | Rat Schwann cells | Supports good cell attachment, growth, and axon growth. Printing parameters seriously affect cell response. | [57] |
| Electrospinning | PPy-coated PLCL/silk fibroin | PC12 | Showed better proliferation. Electrical stimulation improved cell response in terms of proliferation and differentiation phenotypes. | [61] |
| Electrospinning | PPy/PBAT | Neuro2A | Supports cell adhesion and axon growth. | [64] |
| Electrospinning | PPy-coated polyacrylonitrile | Rat neurons and glial cells | Forms cluster morphology and axon formation. Electrical stimulation induces cell proliferation and maturation. | [65] |
| Electrospinning | PPy-coated poly (ε-caprolactone) | Mouse Schwann cells | Supports cell growth. | [67] |
| Electrospinning | Polyornithine-coated polylactic acid/PPy | PC12 | Supports good cell viability and growth. Electrical stimulation and fiber arrangement significantly improved the differentiated cell phenotype. | [74] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hao, L.; Yu, D.; Hou, X.; Zhao, Y. Advances in Polypyrrole Nanofiber Composites: Design, Synthesis, and Performance in Tissue Engineering. Materials 2025, 18, 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132965
Hao L, Yu D, Hou X, Zhao Y. Advances in Polypyrrole Nanofiber Composites: Design, Synthesis, and Performance in Tissue Engineering. Materials. 2025; 18(13):2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132965
Chicago/Turabian StyleHao, Lu, Demei Yu, Xinyu Hou, and Yixuan Zhao. 2025. "Advances in Polypyrrole Nanofiber Composites: Design, Synthesis, and Performance in Tissue Engineering" Materials 18, no. 13: 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132965
APA StyleHao, L., Yu, D., Hou, X., & Zhao, Y. (2025). Advances in Polypyrrole Nanofiber Composites: Design, Synthesis, and Performance in Tissue Engineering. Materials, 18(13), 2965. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18132965






