Optimization of the Mechanical and Structural Performance of Bamboo by Microwave–Compression as a Function of Moisture Content
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Microwave-Compression Treatment Method
2.3. Mechanical Property Testing
2.4. Water Resistance Performance Testing
2.5. Microscopic Structure Testing
2.6. Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) Testing
2.7. X-Ray Diffraction (XRD) Testing
3. Results and Discussion
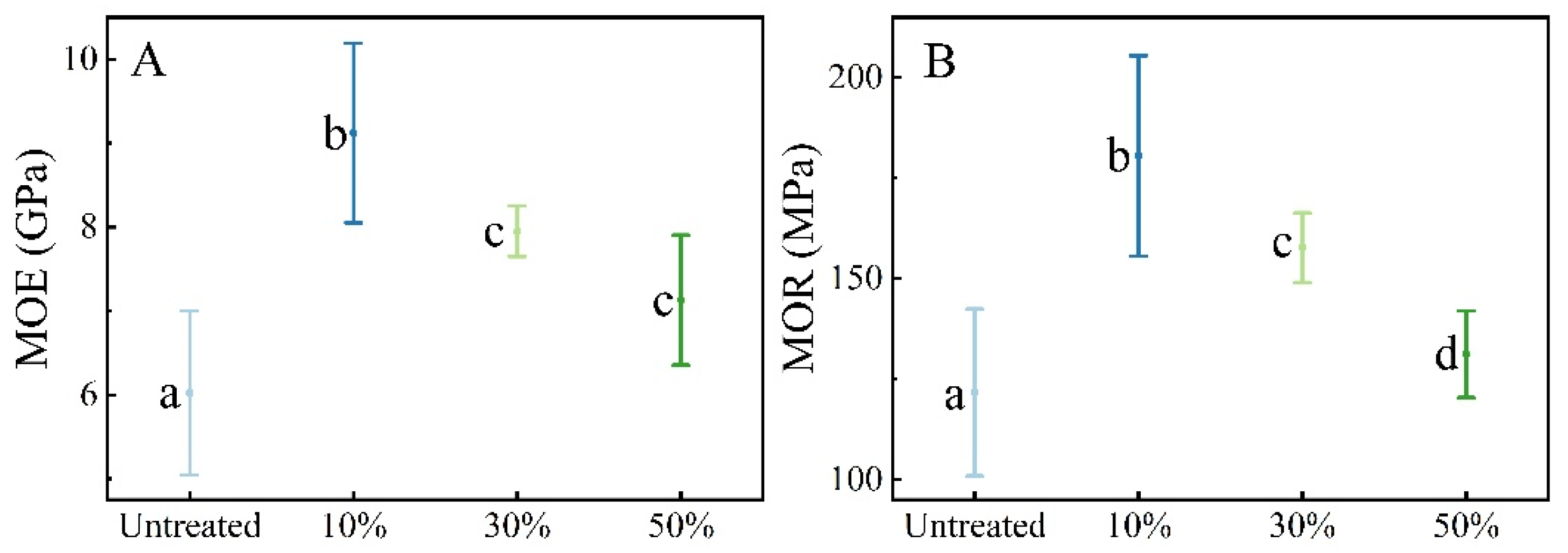
3.1. Mechanical Properties
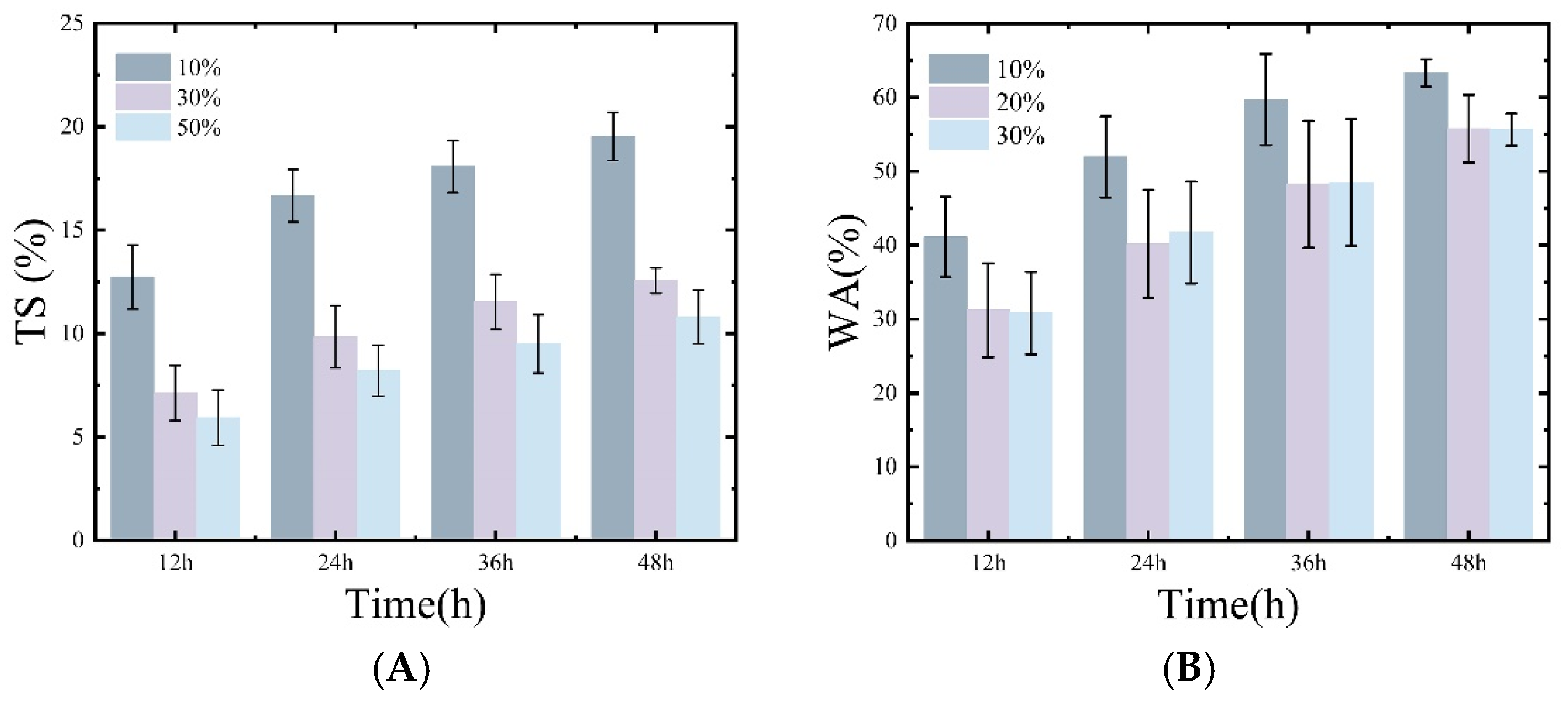
3.2. Water Absorption and Dimensional Stability
3.3. FTIR Analysis
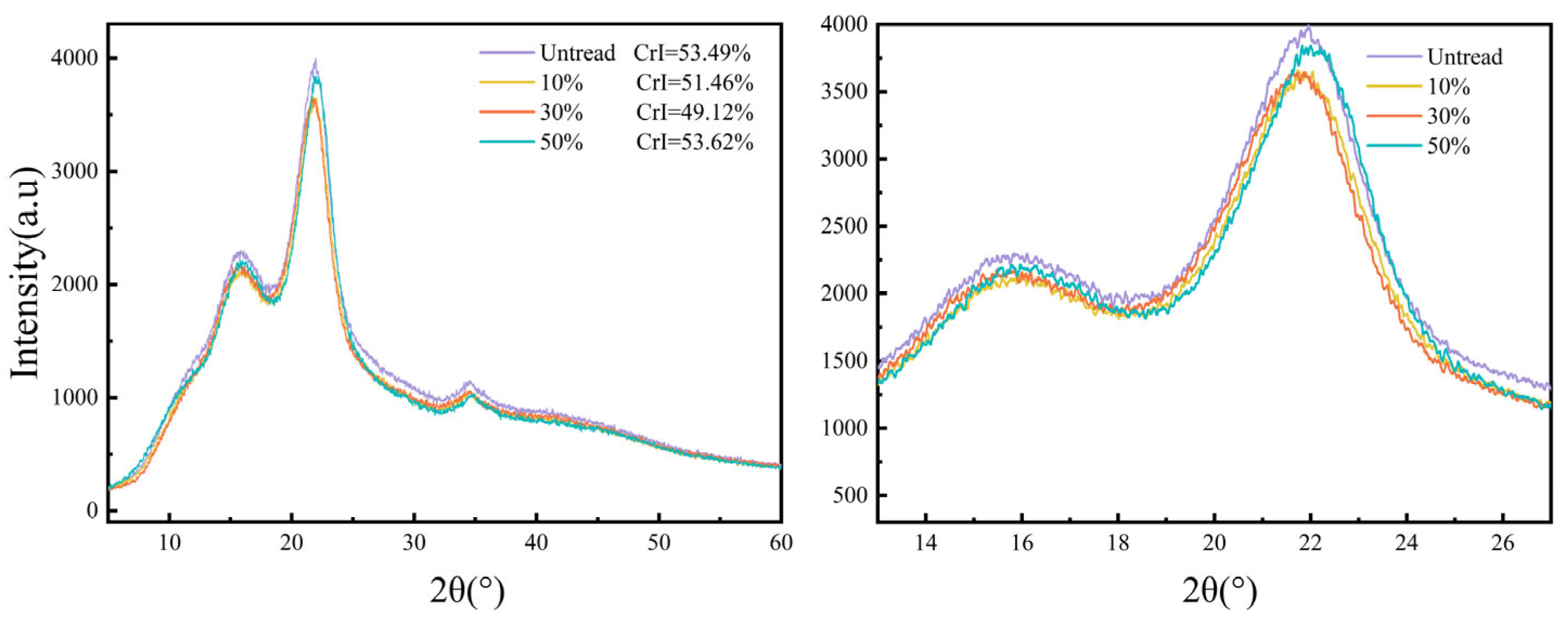
3.4. Changes in Crystallinity
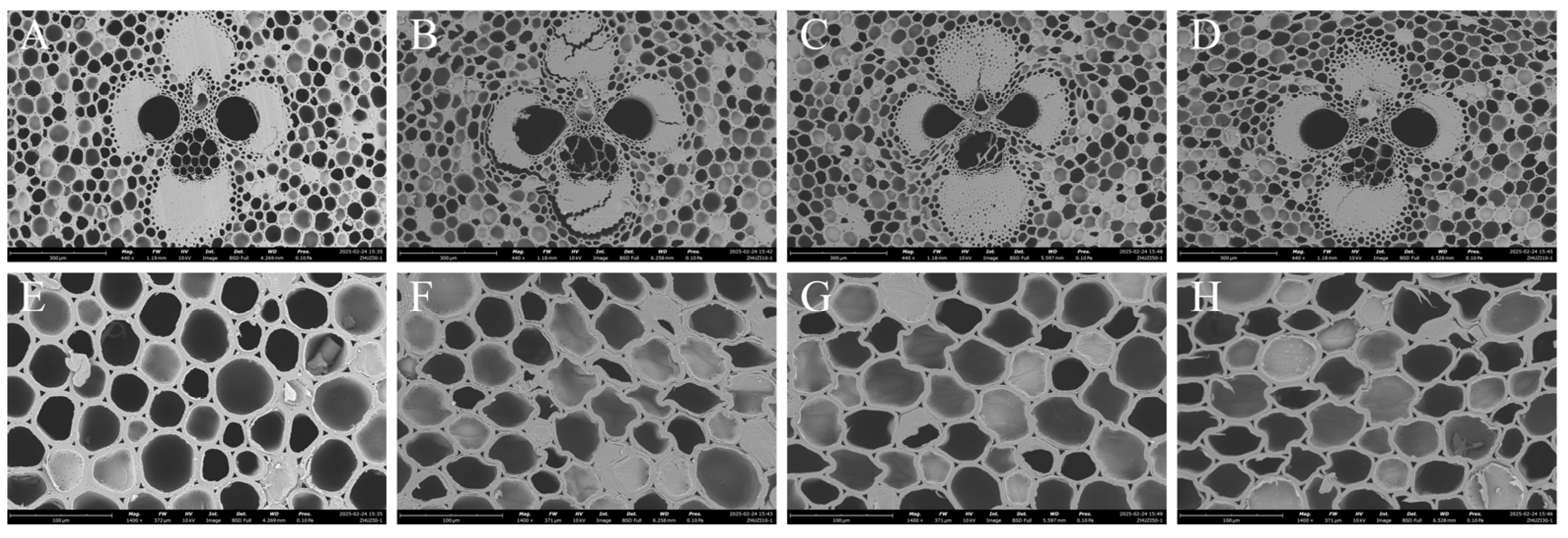
3.5. Changes in Cell Structure
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Y.Y.; Yin, H. Analysis on significance of bamboo products based on sustainable development. Adv. Mater. Res. 2014, 1010–1012, 1944–1948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Hu, Q.; Chen, B.; Fang, H.; Ke, Q.; Song, S. Study on the visual cognition of laminated bamboo furniture. For. Prod. J. 2021, 71, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Fei, B.; Liu, S. The relationship between moisture content and shrinkage strain in the process of bamboo air seasoning and cracking. Dry. Technol. 2022, 40, 571–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norhisham, A.; Faizah, A.; Zaidon, A. Effects of moisture content on the bamboo border. J. Trop. For. Sci. 2015, 27, 334–341. [Google Scholar]
- Dixon, P.G.; Semple, K.E.; Kutnar, A.; Kamke, F.A.; Smith, G.D.; Gibson, L.J. Comparison of the flexural behavior of natural and thermo-hydro-mechanically densified Moso bamboo. Eur. J. Wood Wood Prod. 2016, 74, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Chen, C.; Mi, R.; Gan, W.; Dai, J.; Jiao, M.; Xie, H.; Yao, Y.; Xiao, S.; Hu, L. A Strong, Tough, and Scalable Structural Material from Fast-Growing Bamboo. Adv. Mater. 2020, 32, 1906308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Archila-Santos, H.F.; Ansell, M.P.; Walker, P. Elastic Properties of Thermo-Hydro-Mechanically Modified Bamboo (Guadua angustifolia Kunth) Measured in Tension. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 600, 111–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, M.; Gauss, C.; Stanislas, T.T.; Ahrar, A.J.; Charca, S.; Savastano, H. Effect of bamboo species and pre-treatment method on physical and mechanical properties of bamboo processed by flattening-densification. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2022, 291, 126746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gašparík, M.; Gaff, M. Changes in Temperature and Moisture Content in Beech Wood Plasticized by Microwave Heating. BioResources 2013, 8, 3372–3384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D7264-15; Standard Test Method for Flexural Properties of Polymer Matrix Composite Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2015.
- ASTM D1037-12; Standard Test Methods for Evaluating Properties of Wood-Base Fiber and Particle Panel Materials. ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2012.
- Kadivar, M.; Gauss, C.; Ghavami, K.; Savastano, H. Densification of bamboo: State of the art. Materials 2020, 13, 4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Yang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Shu, X.; Cao, W.; Xu, B.; Fei, B. Effects of microwave drying on the cell wall structures of round bamboo. BioResources 2023, 18, 4071–4084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, H.; Chen, M.; Ma, X.; Li, J.; Zhang, B.; Fang, C.; Fei, B. Effects of different drying methods on bamboo’s physical and mechanical properties. For. Prod. J. 2018, 68, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, M.; Zhao, S.; Tang, R.; Wei, J.; Bao, Y.; Li, N.; Lin, F.; Zhang, W. Effect of hygro-mechanical treatment combined with saturated steam on bamboo cell wall: Structural, chemical, and hygroscopic properties. Ind. Crops Prod. 2024, 219, 119085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dömény, J.; Brabec, M.; Rousek, R.; Rautkari, L.; Čermák, P. Effect of microwave and steam treatment on the thermo-hygro-plasticity of beech wood. BioResources 2021, 16, 8338–8352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, X.; Fang, X.; Gao, X.; Yi, S.; Zhou, Y. Effect of High-Intensity Microwave Treatment on Structural and Chemical Characteristics of Chinese Fir. Forests 2024, 15, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Zhang, F.; Ramaswamy, H.S.; Zhu, S.; Yu, Y. High-Pressure Treatment of Chinese Fir Wood: Effect on Density, Mechanical Properties, Humidity-Related Moisture Migration, and Dimensional Stability. BioResources 2016, 11, 10497–10510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Li, Y.; Semple, K.; Nasir, V.; Pineda, H.; He, M.; Dai, C. Manufacturing and Characterization of Wide-Bundle Bamboo Scrimber: A Comparison with Other Engineered Bamboo Composites. Materials 2022, 15, 7518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, L.Z.; Ma, M.G.; Ji, X.X.; Choi, S.E.; Si, C. Recent Developments and Applications of Hemicellulose From Wheat Straw: A Review. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 9, 690773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Zhao, S.; Pang, H.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, S.; Li, J. Developing Eco-friendly High-Strength Soy Adhesives with Improved Ductility through Multiphase Core-Shell Hyperbranched Polysiloxane. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2019, 7, 7784–7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.Q.; Trinh, L.T.P. Thermochemical Conversion of Cellulose and Hemicellulose. In Biomass Utilization: Conversion Strategies; Nghiem, N.P., Kim, T.H., Yoo, C.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 107–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadivar, M.; Gauss, C.; Tomazello-Filho, M.; Ahrar, A.J.; Ghavami, K.; Savastano, H. Optimization of thermo-mechanical densification of bamboo. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 298, 123860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Kocaefe, D.; Kocaefe, Y.; Boluk, Y.; Krause, C. Structural analysis of heat-treated birch (Betule papyrifera) surface during artificial weathering. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2013, 264, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, L.; Guo, W.; Luo, S. Investigation of changes in compressed moso bamboo (Phyllostachys pubescens) after hot-press molding. J. Wood Sci. 2018, 64, 557–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, L.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, L.; Xu, F. Efficient depolymerization of lignin through microwave-assisted Ru/C catalyst cooperated with metal chloride in methanol/formic acid media. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 1082341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Yan, M.; Yuan, S.; Sun, S.; Huo, Q. Effect of microwave treatment on the physicochemical properties of potato starch granules. Chem. Cent. J. 2013, 7, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoang, A.T.; Nižetić, S.; Ong, H.C.; Mofijur, M.; Ahmed, S.F.; Ashok, B.; Bui, V.T.V.; Chau, M.Q. Insight into the recent advances of microwave pretreatment technologies for the conversion of lignocellulosic biomass into sustainable biofuel. Chemosphere 2021, 281, 130878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furuta, Y.; Nakajima, M.; Nakanii, E.; Ohkoshi, M. The effects of lignin and hemicellulose on thermal-softening properties of water-swollen wood. J. Jpn. Wood Res. Soc. Jpn. 2010, 56, 132–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Chen, X.; Zhang, B.; Liu, X.; Fei, B. Research on the Physico-Mechanical Properties of Moso Bamboo with Thermal Treatment in Tung Oil and Its Influencing Factors. Materials 2019, 12, 599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muley, P.D.; Henkel, C.; Abdollahi, K.K.; Marculescu, C.; Boldor, D. A critical comparison of pyrolysis of cellulose, lignin, and pine sawdust using an induction heating reactor. Energy Convers. Manag. 2016, 117, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; Baker, J.O.; Himmel, M.E.; Parilla, P.A.; Johnson, D.K. Cellulose crystallinity index: Measurement techniques and their impact on interpreting cellulase performance. Biotechnol. Biofuels 2010, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, S.; Ji, J.; Yin, H.; Wang, X. The Influence of Treatment Methods on Bending Mechanical Properties of Bamboo Strips. Forests 2024, 15, 406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, Z.; Zheng, Z.; Yan, N.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, X.; Chen, S.; Xu, R.; Liu, C.; Xu, L. Modification and Application of Bamboo-Based Materials: A Review—Part II: Application of Bamboo-Based Materials. Forests 2023, 14, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

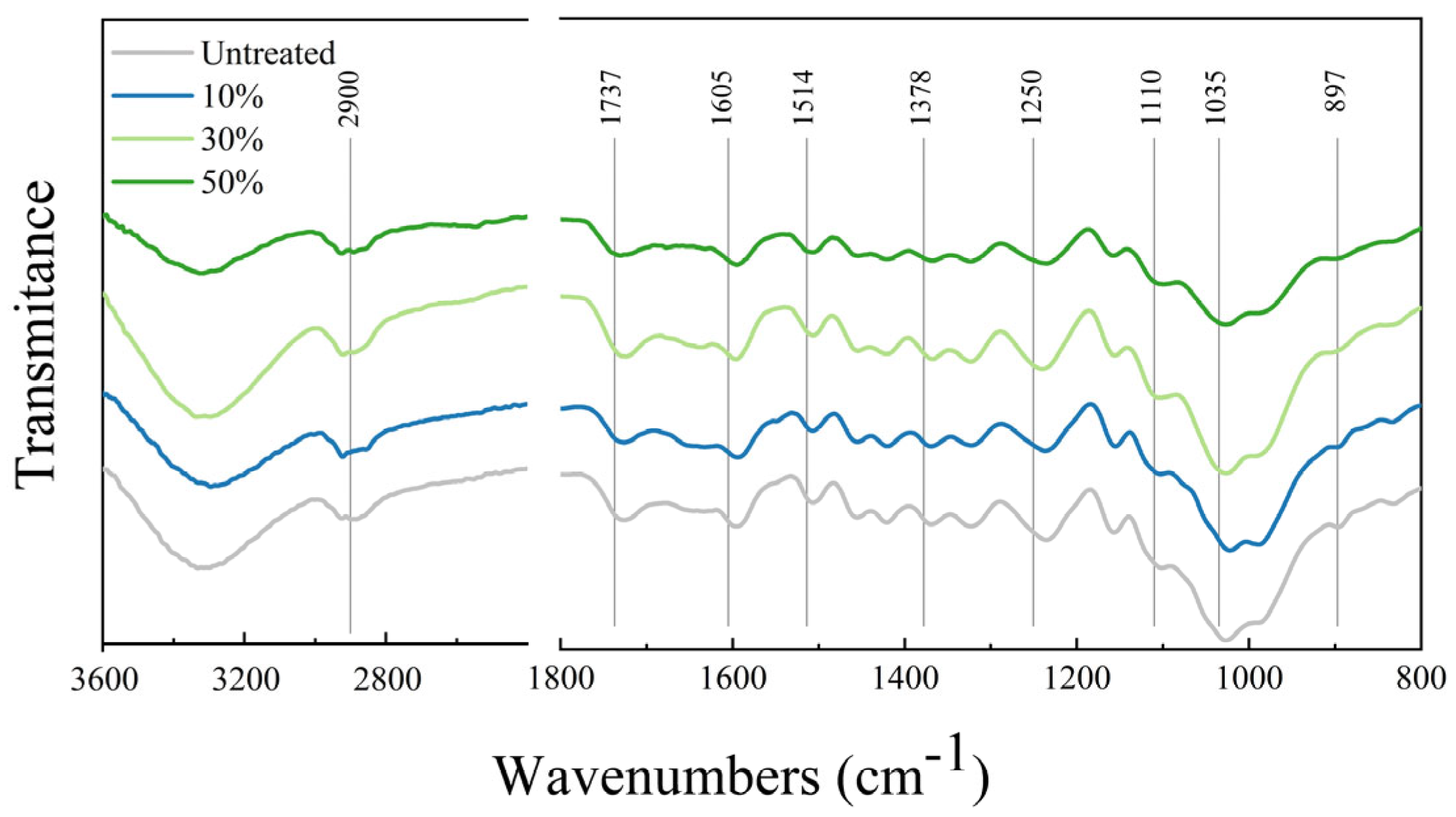
| I1737/I2900 | I1605/I2900 | I1514/I2900 | I1378/I2900 | I1250/I2900 | I1110/I2900 | I1035/I2900 | I896/I2900 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated | 0.8858 | 0.9058 | 0.8575 | 0.9027 | 0.9080 | 0.9731 | 1.1282 | 0.9098 |
| 10% | 0.8777 | 0.8864 | 0.8777 | 0.8864 | 0.8777 | 0.8864 | 0.8777 | 0.8864 |
| 30% | 0.8312 | 0.8486 | 0.8090 | 0.8476 | 0.8484 | 0.9241 | 1.1332 | 0.8384 |
| 50% | 0.9484 | 0.9731 | 0.9575 | 0.9659 | 0.9524 | 1.0088 | 1.0959 | 0.9649 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, H.; Liu, R.; An, R.; Liu, X.; Zhao, S.; Zhu, Z. Optimization of the Mechanical and Structural Performance of Bamboo by Microwave–Compression as a Function of Moisture Content. Materials 2025, 18, 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112551
Wang H, Liu R, An R, Liu X, Zhao S, Zhu Z. Optimization of the Mechanical and Structural Performance of Bamboo by Microwave–Compression as a Function of Moisture Content. Materials. 2025; 18(11):2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112551
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Huixiang, Rong Liu, Rui An, Xinyu Liu, Shiyu Zhao, and Zhaolong Zhu. 2025. "Optimization of the Mechanical and Structural Performance of Bamboo by Microwave–Compression as a Function of Moisture Content" Materials 18, no. 11: 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112551
APA StyleWang, H., Liu, R., An, R., Liu, X., Zhao, S., & Zhu, Z. (2025). Optimization of the Mechanical and Structural Performance of Bamboo by Microwave–Compression as a Function of Moisture Content. Materials, 18(11), 2551. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma18112551




