The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
2.2. Fabrication of Catalysts
2.3. Characterization of Catalysts
2.4. Hydrolysis Measurements of NaBH4
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Coatings, Microstructure and Morphology Studies
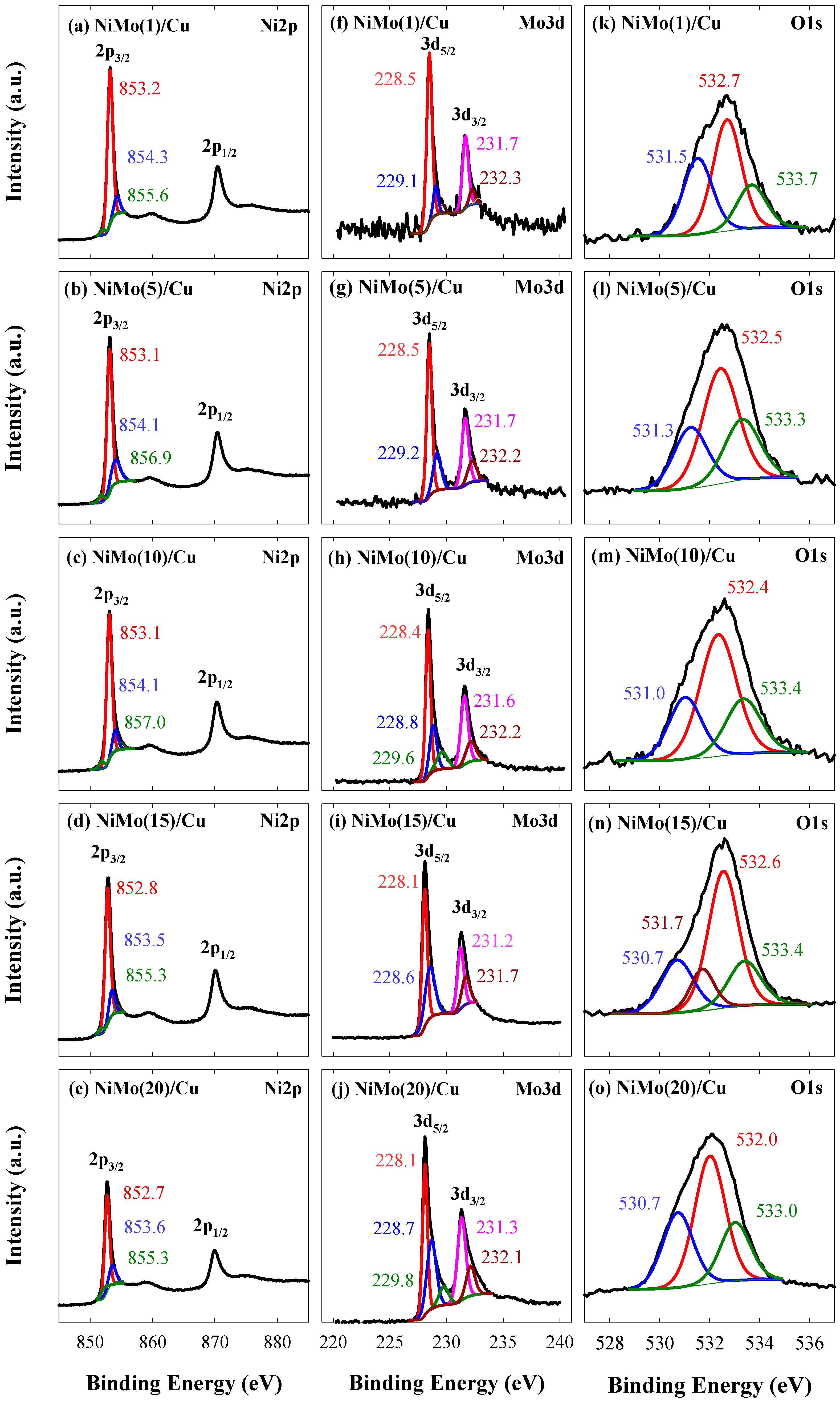
3.2. XPS Analysis of the Prepared Catalysts
3.3. XRD Analysis of the Prepared Catalysts
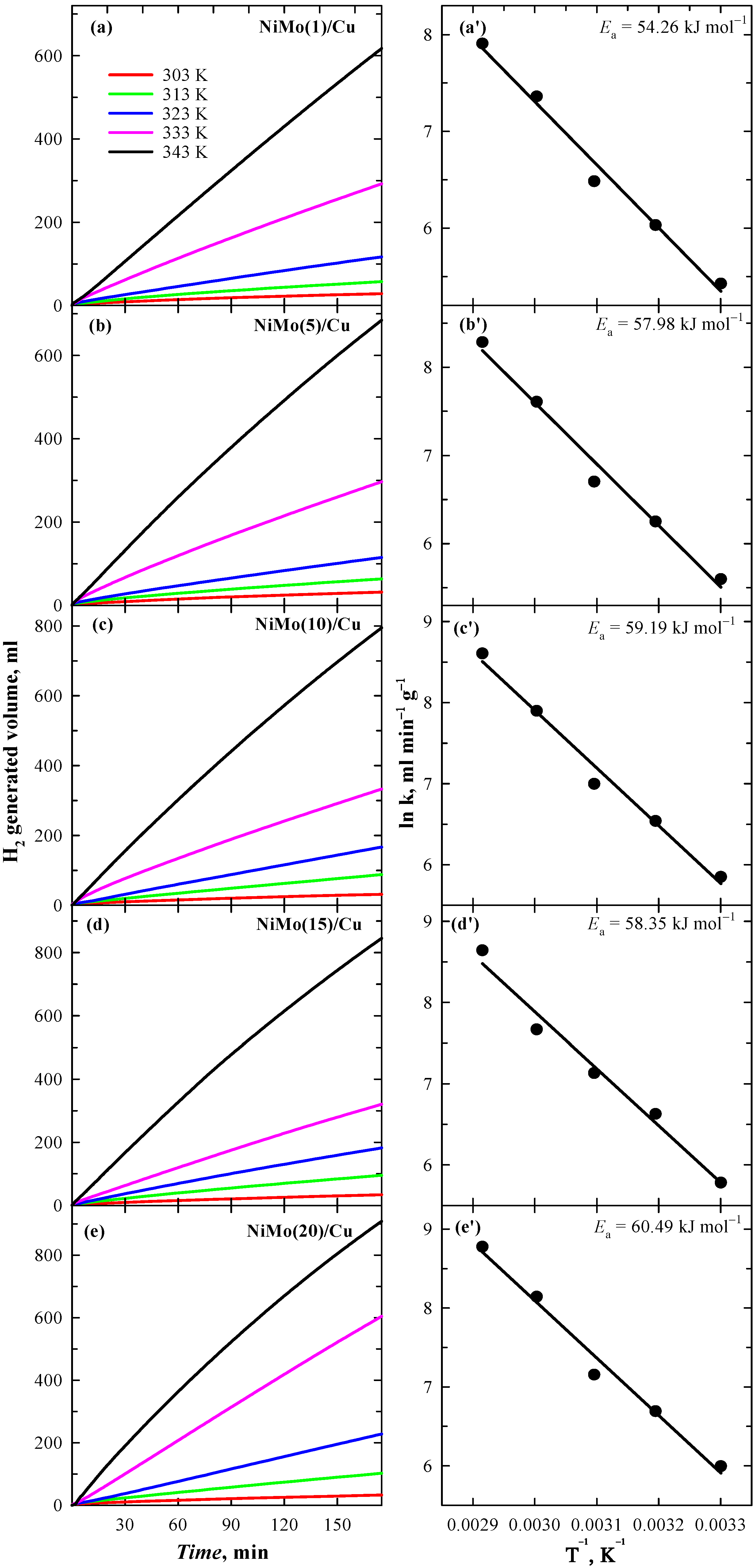
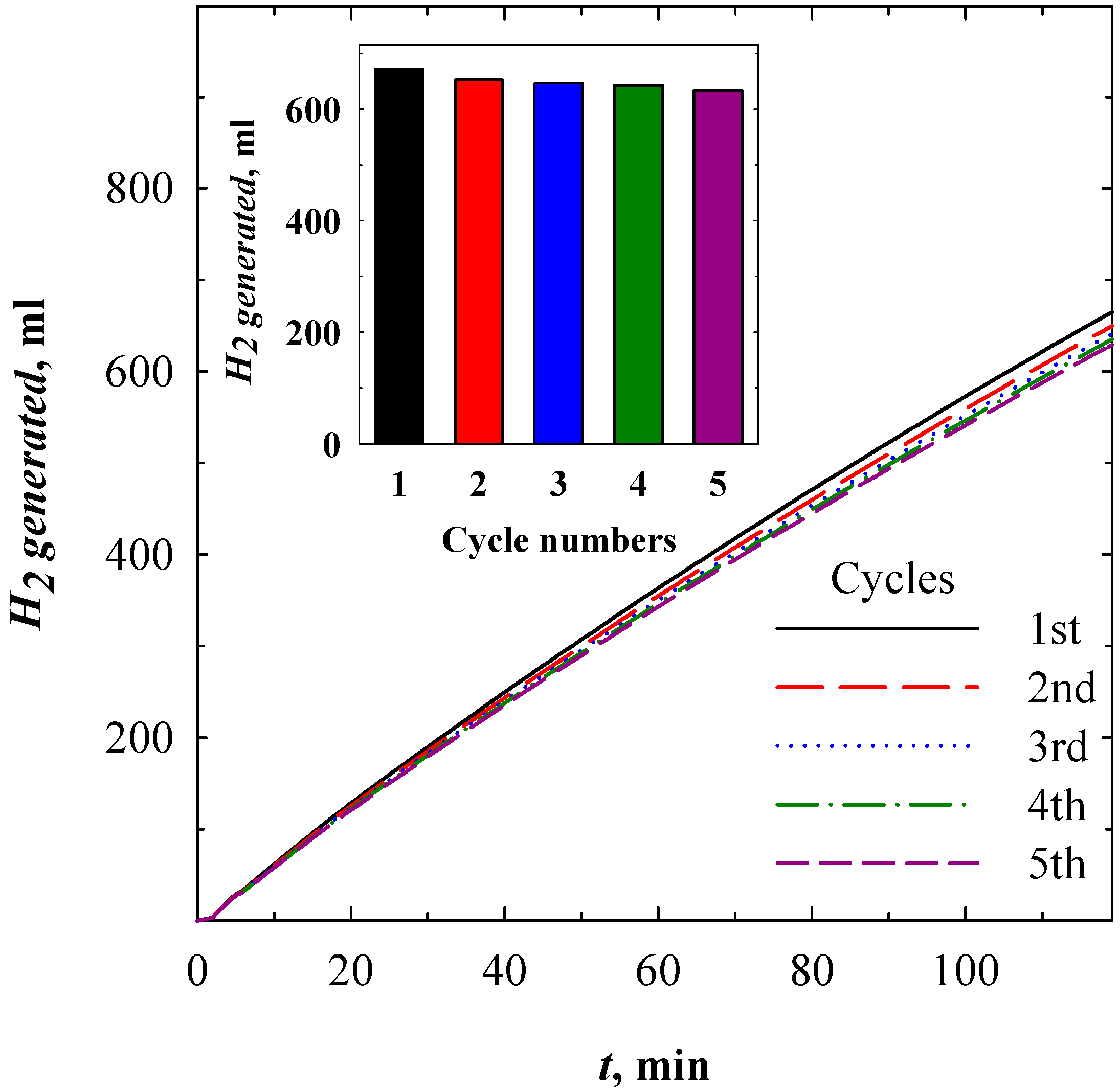
3.4. Catalysts Activity toward NaBH4 Hydrolysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alasali, F.; Abuashour, M.I.; Hammad, W.; Almomani, D.; Obeidat, A.M.; Holderbaum, W. A review of hydrogen production and storage materials for efficient integrated hydrogen energy systems. Energy Sci. Eng. 2024, 12, 1934–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramachandran, R.; Menon, R.K. An overview of industrial uses of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 1998, 23, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://www.iea.org/energy-system/low-emission-fuels/hydrogen (accessed on 22 August 2024).
- Guan, D.; Wang, B.; Zhang, J.; Shi, R.; Jiao, K.; Li, L.; Wang, Y.; Xie, B.; Zhang, Q.; Yu, J.; et al. Hydrogen society: From present to future. Energy Environ. Sci. 2023, 16, 4926–4943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, M.; Wietschel, M. The future of hydrogen—Opportunities and challenges. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 615–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pyza, D.; Gołda, P.; Sendek-Matysiak, E. Use of hydrogen in public transport systems. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 335, 130247–130259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Tan, G.L.; Li, G.W.; Liang, J.G.; Ahmad, S.M.; Bahadur, A.; Humayun, M.; Ullah, H.; Khan, A.; Bououdina, M. State-of-the-art hydrogen generation techniques and storage methods: A critical review. J. Energy Storage 2023, 64, 107196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albatayneh, A.; Juaidi, A.; Jaradat, M.; Manzano-Agugliaro, F. Future of electric and hydrogen cars and trucks: An Overview. Energies 2023, 16, 3230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.H.; Li, Z.P. A review: Hydrogen generation from borohydride hydrolysis reaction. J. Power Sources 2009, 187, 527–534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhammed, N.S.; Gbadamosi, A.O.; Epelle, E.I.; Abdulrasheed, A.A.; Haq, B.; Patil, S.; Al-Shehri, D.; Kamal, M.S. Hydrogen production, transportation, utilization, and storage: Recent advances towards sustainable energy. J. Energy Storage 2023, 73, 109207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, A.A.; Gasnier, A.; Gennari, F.C. From iron to copper: The effect of transition metal catalysts on the hydrogen storage properties of nanoconfined LiBH4 in a graphene-rich N-doped matrix. Molecules 2022, 27, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, B.L.; Allen, T.N.; Bowden, M.E.; Autrey, T.; Jensen, C.M. Effects of glymes on the distribution of Mg(B10H10) and Mg(B12H12) from the thermolysis of Mg(BH4)2. Inorganics 2021, 9, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Yang, N.; Cen, X.; Li, S.; Zhang, L.; Lu, Z.H. Exceptional activity of hollow porphyrin frameworks-confined Ni nanoparticles for hydrogen production from NaBH4 methanolysis. Fuel 2023, 354, 129332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiferraw, B.T.; Baye, A.F.; Kim, H. Mechanistic insights into the deprotonation of methanol by facile synthesized 3D flower-like BiOX (X¼ Cl, Br, I) catalysts for rapid hydrogen generation from NaBH4 methanolysis: The ‘X’ factor. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 435–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, W.; Zhou, D.; Fan, W.; Zou, R.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Y. A stable flow hydrogen production of sodium borohydride hydrolysis using millimeter-scale Ru/Al2O3 spheres as catalyst. J. Alloys Compd. 2024, 986, 174121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sengel, S.B.; Deveci, H.; Bas, H.; Butun, V. Carbon spheres as an efficient green catalyst for dehydrogenation of sodium borohydride in methanol. Catal. Commun. 2023, 177, 106650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darabi, R.; Gu, Q.; Mehrizi, A.A.; Altuner, E.E.; Alhrasishawi, W.; Gulbagca, F.; Tiri, R.N.E.; Tekeli, Y.; Seyrankaya, A.; Kaynak, I.; et al. Synthesis, characterization, and enhanced hydrogen generation from NaBH4 methanolysis of highly dispersed bimetallic PdNi nanoparticles supported on Vulcan carbon. Molecular Catal. 2023, 547, 113245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshammari, M.; Alshammari, K.; Alhassan, S.; Alshammari, A.H.; Alotibi, S.; Alotaibi, T.; Ismael, A.; Taha, T.A.M. A high-performance Cr2O3/CaCO3 nanocomposite catalyst for rapid hydrogen generation from NaBH4. Nanomaterials 2024, 14, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Gold nanoparticles AuNP decorated on fused graphene-like materials for application in a hydrogen generation. Materials 2023, 16, 4779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of platinum nanoparticles supported on fused nanosized carbon spheres derived from sustainable source for application in a hydrogen generation reaction. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 1994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, A.K.; Rezaei, M.; Varbar, M.; Alavi, S.M.; Akbari, E. Cobalt nanoparticle synthesis through the mechanochemical and chemical reduction method as a highly active and reusable catalyst for H2 production via sodium borohydride hydrolysis process. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2024, 51, 661–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onat, E. Synthesis of a cobalt catalyst supported by graphene oxide modified perlite and its application on the hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Synth. Metals 2024, 306, 117621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, X.; Fang, S.; Gao, Y.; Zhub, Y.; Zhang, C.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Pan, H.; Zeng, J.; Cao, Z.; et al. Ni-BTC-derived CoP-NiCoP/NC microspheres as an efficient catalyst for NaBH4 hydrolysis. J. Alloys Compd. 2023, 968, 171821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, S.; Wang, Y.; Du, B.; Cheng, L.; Sun, L.; Yan, P. Recoverable sepiolite coated B-CoP/cellulose hybrid aerogel as monolithic catalysts for hydrogen generation via NaBH4 hydrolysis. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 474, 145772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayouk, E.; Schechter, A.; Avrahami, I. A novel micro-reactor for hydrogen production from solid NaBH4 hydrolysis in a dual-cycle methodology. Heliyon 2024, 10, 25744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quach, Q.; Biehler, E.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Synthesis of palladium nanoparticles supported over fused graphene-like material for hydrogen evolution reaction. Catalysts 2023, 13, 1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nardo, A.D.; Portarapillo, M.; Russo, D.; Luciani, G.; Landi, G.; Ruoppolo, G.; Pezzella, A.; Benedetto, A.D. Cyan Hydrogen process: A new route for simultaneous hydrogen production and carbon valorization. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 7793–7805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biehler, E.; Quach, Q.; Abdel-Fattah, T.M. Silver-nanoparticle-decorated fused carbon sphere composite as a catalyst for hydrogen generation. Energies 2023, 16, 5053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosgun, S.; Hosgun, E.Z. Optimization of hydrogen generation rate with Co/MMT catalyst from NaBH4 using Box-Behnken method. Pamukkale Univ. J. Eng. Sci. 2024, 30, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, R.V.M.; Costa, J.A.S.; Romao, L.P.C. Bifunctional green nanoferrites as catalysts for simultaneous organic pollutants reduction and hydrogen generation: Upcycling strategy. J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 351, 119994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukackienė, Z.; Valeckytė, G.; Kepenienė, V.; Stalnionienė, I.; Jasulaitienė, V.; Vaičiūnienė, J.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L.; Stalnionis, G.; Norkus, E. Non-precious metals catalysts for hydrogen generation. Coatings 2023, 13, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Babajani, N. Preparation of the efficient nano-bimetallic cobalt-nickel catalysts supported on the various magnetic substrates for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride in alkaline solutions. Polyhedron 2020, 180, 114405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, M.; Zou, Y.C.; Huang, Y.M.; Wang, J.Q. Ni-Fe-B catalysts for NaBH4 hydrolysis. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2012, 37, 1568–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, D.; Wang, X.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Z.; Qi, N.; Wu, S.; Bai, S.; Li, G. Co–Fe–B as an effective catalyst for hydrogen production from NaBH4 hydrolysis. Mater. Lett. X 2021, 12, 100104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, J.; Chen, L.; Dong, Y.; Xie, P.; Li, Q. Hydrogen production through hydrolysis of sodium borohydride: Highly dispersed CoB particles immobilized in carbon nanofibers as a novel catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2020, 45, 32145–32156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Zou, Y.; Xiang, C.; Zhang, H.; Xu, F.; Sun, L.; He, K. Modulating valence band to enhance the catalytic activity of Co-Cr-B/NG for hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. J. Alloys Compd. 2022, 924, 166556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, F.; Zhao, S.; Xia, X. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NaBH4 based on high stable NiB/NiFe2O4 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 3971–3980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, X.; Wen, R.; Yue, G.H.; Peng, D.L. Facile synthesis of near-monodisperse Ag@Ni core–shell nanoparticles and their application for catalytic generation of hydrogen. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 195604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Wang, R.; Meng, L.; Wang, Y.; Li, G.; Xin, S.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, K. Hydrogen generation from alkaline NaBH4 solution using a dandelion-like Co-Mo-B catalyst supported on carbon cloth. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 9945–9951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liua, C.H.; Chen, B.H.; Hsueh, C.L.; Ku, J.R.; Jeng, M.S.; Tsau, F. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of sodium borohydride using Ni–Ru nanocomposite as catalysts. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2009, 34, 2153–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amber, H.; Vjūnova, K.; Sukackienė, Z.; Šimkūnaitė, D.; Vaičiūnienė, J.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L.; Norkus, E. Hydrogen production on CoFe, CoFeMn and CoFeMo coatings deposited on Ni foam via electroless metal plating. Chemija 2023, 34, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Miotello, A. Progress in Co-B related catalyst for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of boron-hydrides: A review and the perspectives to substitute noble metals. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2015, 40, 1429–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, Y.; Chen, R. Hydrogen storage via the hydrolysis of NaBH4 basic solution: Optimization of NaBH4 concentration. Energy Fuels 2006, 20, 2142–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Zhang, H.; Ye, W. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution using Pt/C catalyst. Catal. Commun. 2007, 8, 1767–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, N.; Patton, B.; Zanchetta, C.; Fernandes, R.; Guella, G.; Kale, A.; Miotello, A. Pd-C powder and thin film catalysts for hydrogen production by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Ozer, A.; Yurtcan, A.B. Development of effective catalysts for hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride: Ru, Pt, Pd nanoparticles supported on Co3O4. Energy 2019, 180, 702–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, X. Catalytic hydrolysis of sodium borohydride for hydrogen production using magnetic recyclable CoFe2O4-modified transition-metal nanoparticles. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 2021, 4, 11312–11320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lin, F.; Yang, L.; Dong, H. Highly dispersed Ru/Co catalyst with enhanced activity for catalyzing NaBH4 hydrolysis in alkaline solutions. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2020, 31, 2512–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.W.; Yang, G.; Xu, X.X.; Liu, Y.Y.; Li, B.J.; Wang, Y.Z.; Zhao, Y.X. Ultrafine Pt nanoparticles anchored on core–shell structured zeolite–carbon for efficient catalysis of hydrogen generation. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 7673–7681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Didehban, A.; Zabihi, M.; Shahrouzi, J.R. Experimental studies on the catalytic behavior of alloy and core-shell supported Co-Ni bimetallic nano-catalysts for hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of sodium borohydride. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 20645–20660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubisztal, J.; Budniok, A.; Lasia, A. Study of the hydrogen evolution reaction on nickel-based composite coatings containing molybdenum powder. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2007, 32, 1211–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Wang, H.; Guo, Q.; Ji, S. Catalytic behavior of carbon supported Ni–B, Co–B and Co–Ni–B in hydrogen generation by hydrolysis of KBH4. Fuel Process. Technol. 2011, 92, 1606–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozkurt, G.; Özer, A.; Yurtcan, A.B. Hydrogen generation from sodium borohydride with Ni and Co based catalysts supported on Co3O4. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2018, 43, 22205–22214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damian, A.; Omanovic, S. Ni and Ni-Mo hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts electrodeposited in a polyaniline matrix. J. Power Sources 2006, 158, 464–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jinlong, L.; Tongxiang, L.; Chen, W. Investigation of hydrogen evolution activity for the nickel, nickel-molybdenum nickel-graphite composite and nickel-reduced graphene oxide composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 366, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Karim, R.; Halim, J.; El-Raghy, S.; Nabil, M.; Waheed, A. Surface morphology and electrochemical characterization of electrodeposited Ni-Mo nanocomposites as cathodes for hydrogen evolution. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 530, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biesinger, M.C.; Payne, B.P.; Lau, L.W.M.; Gerson, A.; Smart, R.S.C. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopic chemical state quantification of mixed nickel metal, oxide and hydroxide systems. Surf. Interf. Anal. 2009, 41, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy (XPS) Reference Pages. Available online: http://www.xpsfitting.com/search/label/Molybdenum (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- NIST X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Database. Available online: http://srdata.nist.gov/xps/ (accessed on 2 August 2024).
- Mardiansyah, D.; Badloe, T.; Triyana, K.; Mehmood, M.Q.; Raeis-Hosseini, N.; Lee, Y.; Sabarman, H.; Kim, K.; Rho, J. Effect of temperature on the oxidation of Cu nanowires and development of an easy to produce, oxidation-resistant transparent conducting electrode using a PEDOT:PSS coating. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhou, X.; Li, T.; Li, H. Molybdenum induces the formation of high-performance nickel hydroxide with irregular shape. Mater. Res. Express 2019, 6, 125521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolabella, S.; Borzì, A.; Dommann, A.; Neels, A. Lattice strain and defects analysis in nanostructured semiconductor materials and devices by high-resolution X-Ray diffraction: Theoretical and practical aspects. Small Methods 2022, 6, 2100932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; To, D.T.; Myung, N.V. A review of nickel-molybdenum based hydrogen evolution electrocatalysts from theory to experiment. Appl. Catal. Gen. 2023, 651, 119013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Catalyst | Composition of Plating Solution (mol L−1) and Plating Conditions | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiSO4 | Na3C6H5O7 | MB | Na2MoO4 | pH | T, °C | t, min | |
| NiMo(1)/Cu | 0.1 | 0.04 | 0.2 | 0.0001 | 7 | 50 | 12 |
| NiMo(5)/Cu | 0.0005 | ||||||
| NiMo(10)/Cu | 0.0008 | ||||||
| NiMo(15)/Cu | 0.0010 | ||||||
| NiMo(20)/Cu | 0.0012 | ||||||
| Catalyst | Element, wt.% | Element Loading, µg cm−2 | Deposition Rate, µm h−1 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Mo | Ni | Mo | Ni + Mo | ||
| NiMo(1)/Cu | 99.20 | 0.85 | 646.50 | 5.525 | 652.03 | 3.65 |
| NiMo(5)/Cu | 94.60 | 5.41 | 525.50 | 30.05 | 555.55 | 3.10 |
| NiMo(10)/Cu | 89.99 | 10.01 | 425.96 | 47.35 | 473.31 | 2.65 |
| NiMo(15)/Cu | 85.46 | 14.54 | 419.05 | 71.30 | 490.35 | 2.75 |
| NiMo(20)/Cu | 80.31 | 19.69 | 391.15 | 95.90 | 487.05 | 2.75 |
| Catalyst | Ea, kJ mol−1 | T, K | v, mL min−1 | v, L min−1 gcat−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NiMo(1)/Cu | 54.26 | 303 K | 0.30 | 0.23 |
| 313 K | 0.54 | 0.42 | ||
| 323 K | 0.85 | 0.65 | ||
| 333 K | 2.05 | 1.57 | ||
| 343 K | 3.55 | 2.72 | ||
| NiMo(5)/Cu | 57.98 | 303 K | 0.30 | 0.27 |
| 313 K | 0.58 | 0.52 | ||
| 323 K | 0.90 | 0.81 | ||
| 333 K | 2.24 | 2.01 | ||
| 343 K | 4.40 | 3.96 | ||
| NiMo(10)/Cu | 59.19 | 303 K | 0.33 | 0.35 |
| 313 K | 0.66 | 0.69 | ||
| 323 K | 1.04 | 1.09 | ||
| 333 K | 2.55 | 2.69 | ||
| 343 K | 5.17 | 5.46 | ||
| NiMo(15)/Cu | 58.35 | 303 K | 0.32 | 0.32 |
| 313 K | 0.74 | 0.76 | ||
| 323 K | 1.23 | 1.25 | ||
| 333 K | 2.10 | 2.14 | ||
| 343 K | 5.56 | 5.67 | ||
| NiMo(20)/Cu | 60.49 | 303 K | 0.39 | 0.40 |
| 313 K | 0.78 | 0.81 | ||
| 323 K | 1.25 | 1.28 | ||
| 333 K | 3.35 | 3.44 | ||
| 343 K | 6.32 | 6.48 |
| Catalyst | Electrolyte | Ea, kJ mol−1 | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| CoMoB/C | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 7 wt.% NaOH | 51.00 | [39] |
| Ni–Ru/50WX8 | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 5 wt.% NaOH | 52.73 | [40] |
| Ni–Fe–B | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 4 wt.% NaOH | 57.00 | [33] |
| Ag-Ni core-shell | 10 wt.% NaBH4 + 10 wt.% NaOH | 57.62 | [38] |
| Co-Ni/MSAC | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 5 wt.% NaOH | 63.27 | [32] |
| CoFeMo/Ni | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 66.80 | [41] |
| Ni | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.1 M NaOH | 67.90 | [31] |
| Ni-Co (Alloy) | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 5 wt.% NaOH | 68.84 | [50] |
| Ni | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 10 wt.% NaOH | 72.52 | [37] |
| NiMo(1)/Cu | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 54.26 | this study |
| NiMo(5)/Cu | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 57.98 | this study |
| NiMo(10)/Cu | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 59.19 | this study |
| NiMo(15)/Cu | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 58.35 | this study |
| NiMo(20)/Cu | 5 wt.% NaBH4 + 0.4 wt.% NaOH | 60.49 | this study |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sukackienė, Z.; Valeckytė, G.; Kepenienė, V.; Stalnionienė, I.; Jasulaitiene, V.; Vaičiūnienė, J.; Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L.; Pakštas, V.; Norkus, E. The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions. Materials 2024, 17, 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174353
Sukackienė Z, Valeckytė G, Kepenienė V, Stalnionienė I, Jasulaitiene V, Vaičiūnienė J, Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė L, Pakštas V, Norkus E. The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174353
Chicago/Turabian StyleSukackienė, Zita, Gitana Valeckytė, Virginija Kepenienė, Irena Stalnionienė, Vitalija Jasulaitiene, Jūratė Vaičiūnienė, Loreta Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, Vidas Pakštas, and Eugenijus Norkus. 2024. "The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions" Materials 17, no. 17: 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174353
APA StyleSukackienė, Z., Valeckytė, G., Kepenienė, V., Stalnionienė, I., Jasulaitiene, V., Vaičiūnienė, J., Tamašauskaitė-Tamašiūnaitė, L., Pakštas, V., & Norkus, E. (2024). The Dependence of NiMo/Cu Catalyst Composition on Its Catalytic Activity in Sodium Borohydride Hydrolysis Reactions. Materials, 17(17), 4353. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174353








