Influence of Laser Power and Rotational Speed on the Surface Characteristics of Rotational Line Spot Nanosecond Laser Ablation of TC4 Titanium Alloy
Abstract
1. Introduction
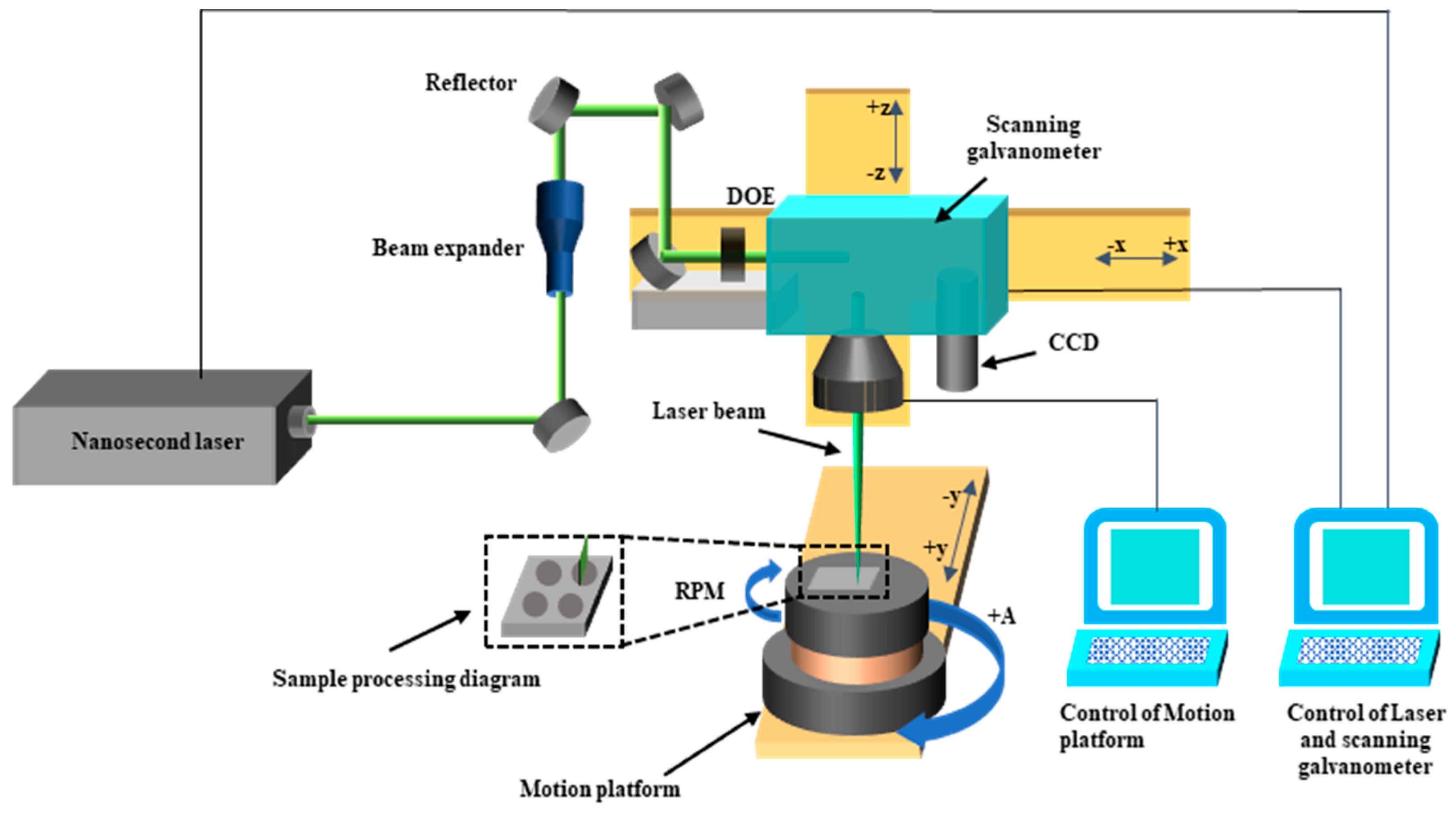
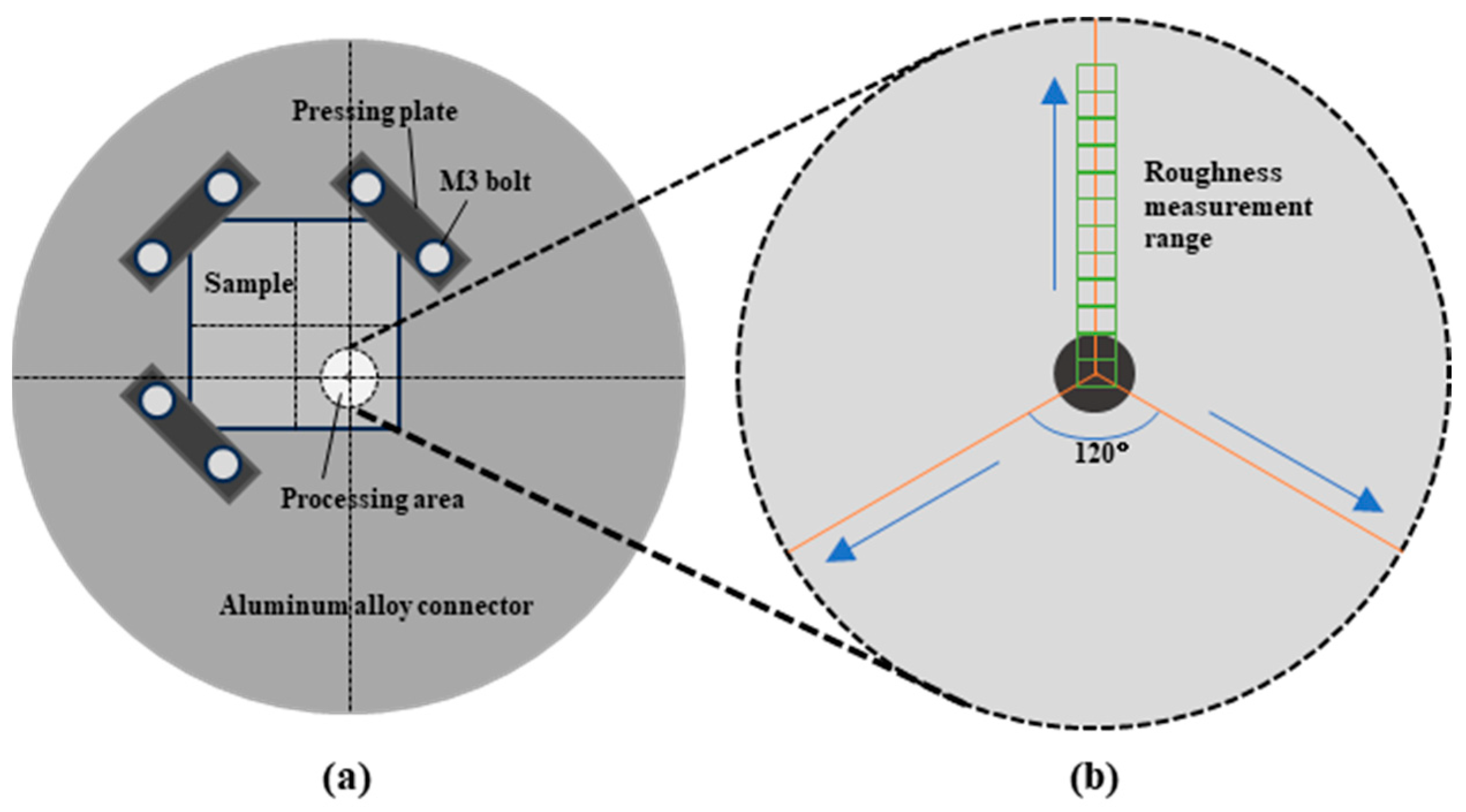
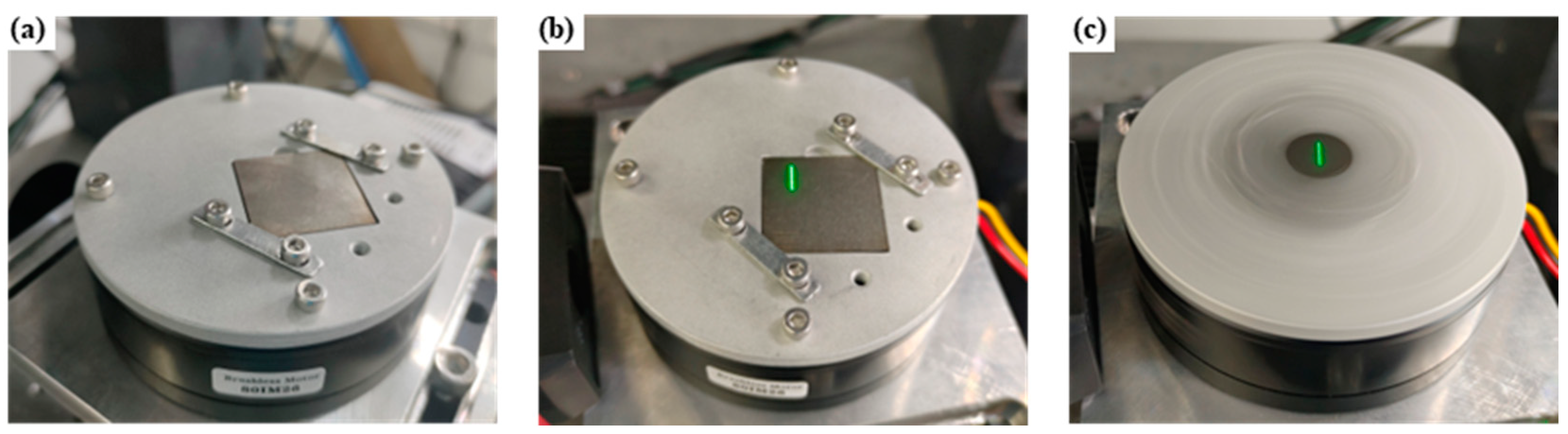
2. Experimental Setting
3. Results and Discussion
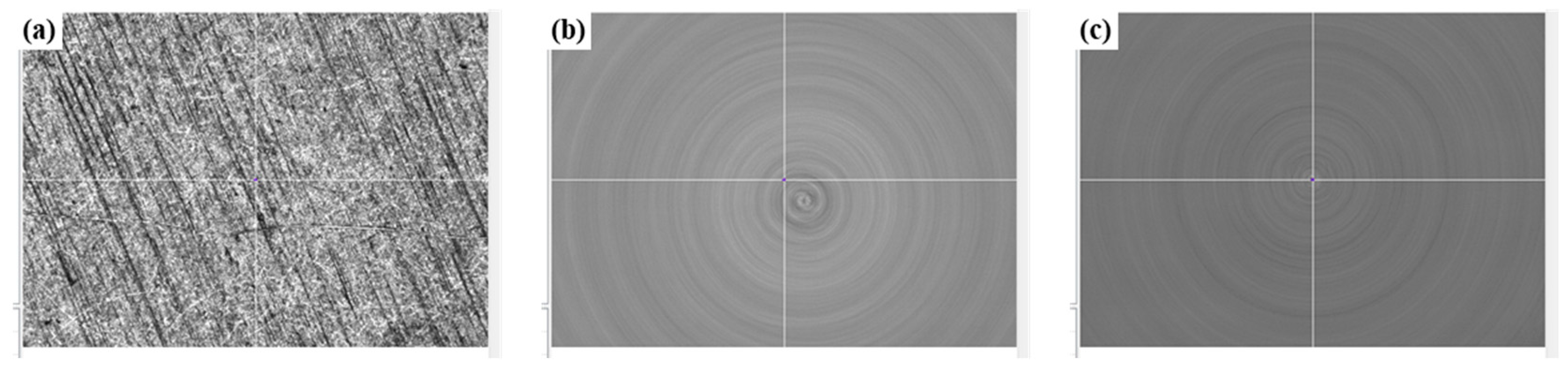
3.1. Surface Roughness and Surface Morphologies
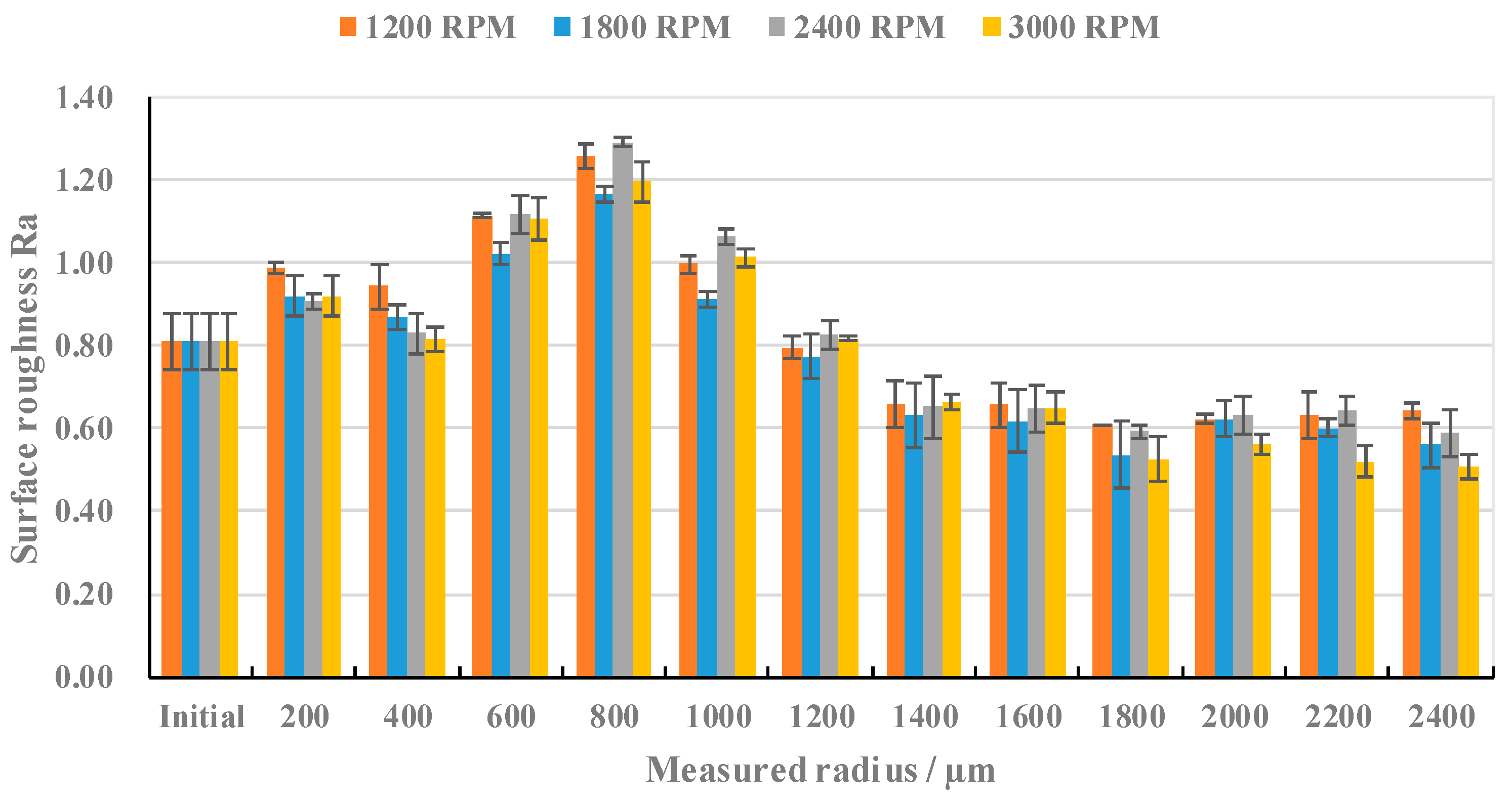
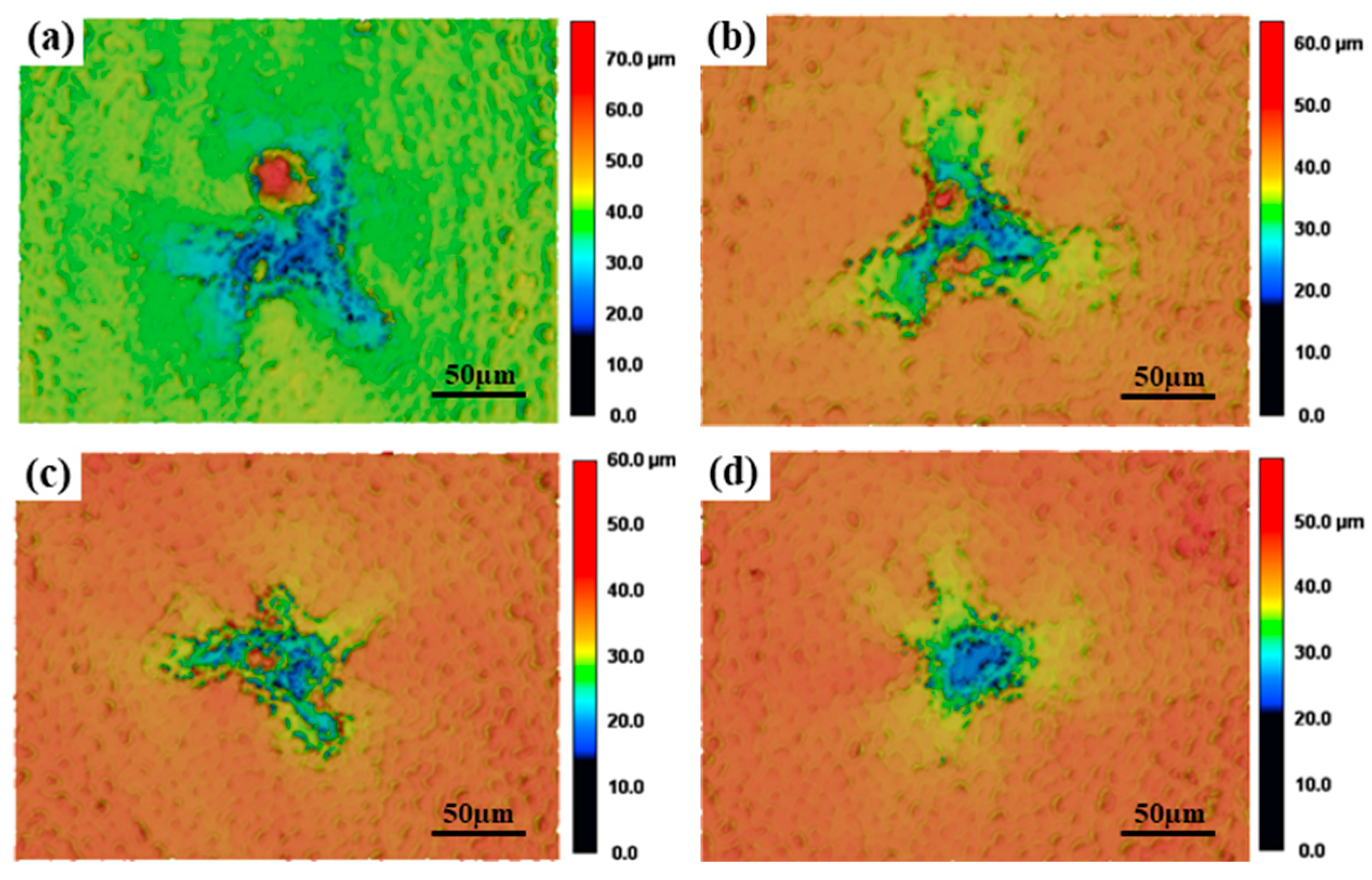
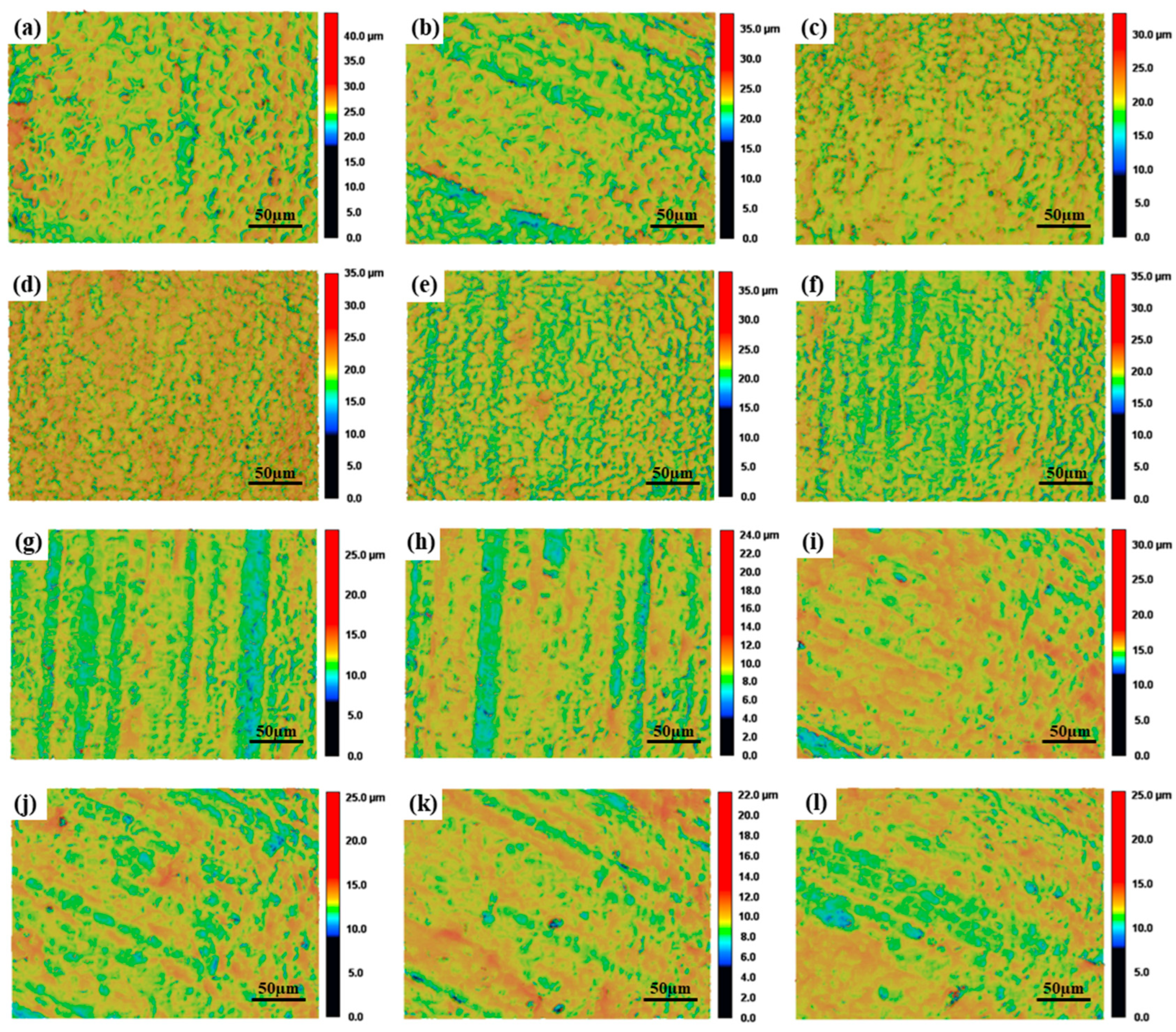
3.1.1. Effects of Rotational Speed on the Surface Roughness and Surface Morphologies
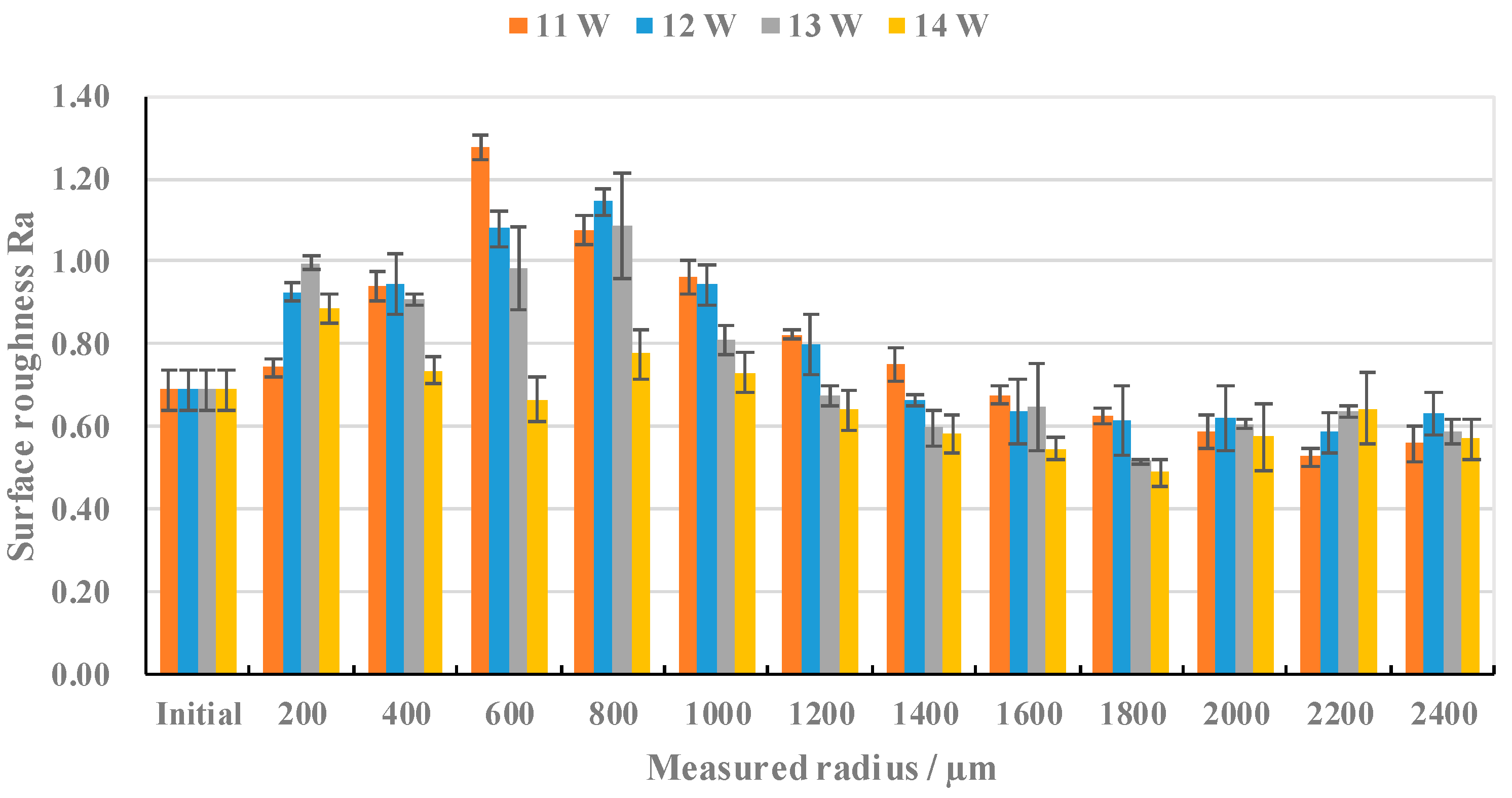
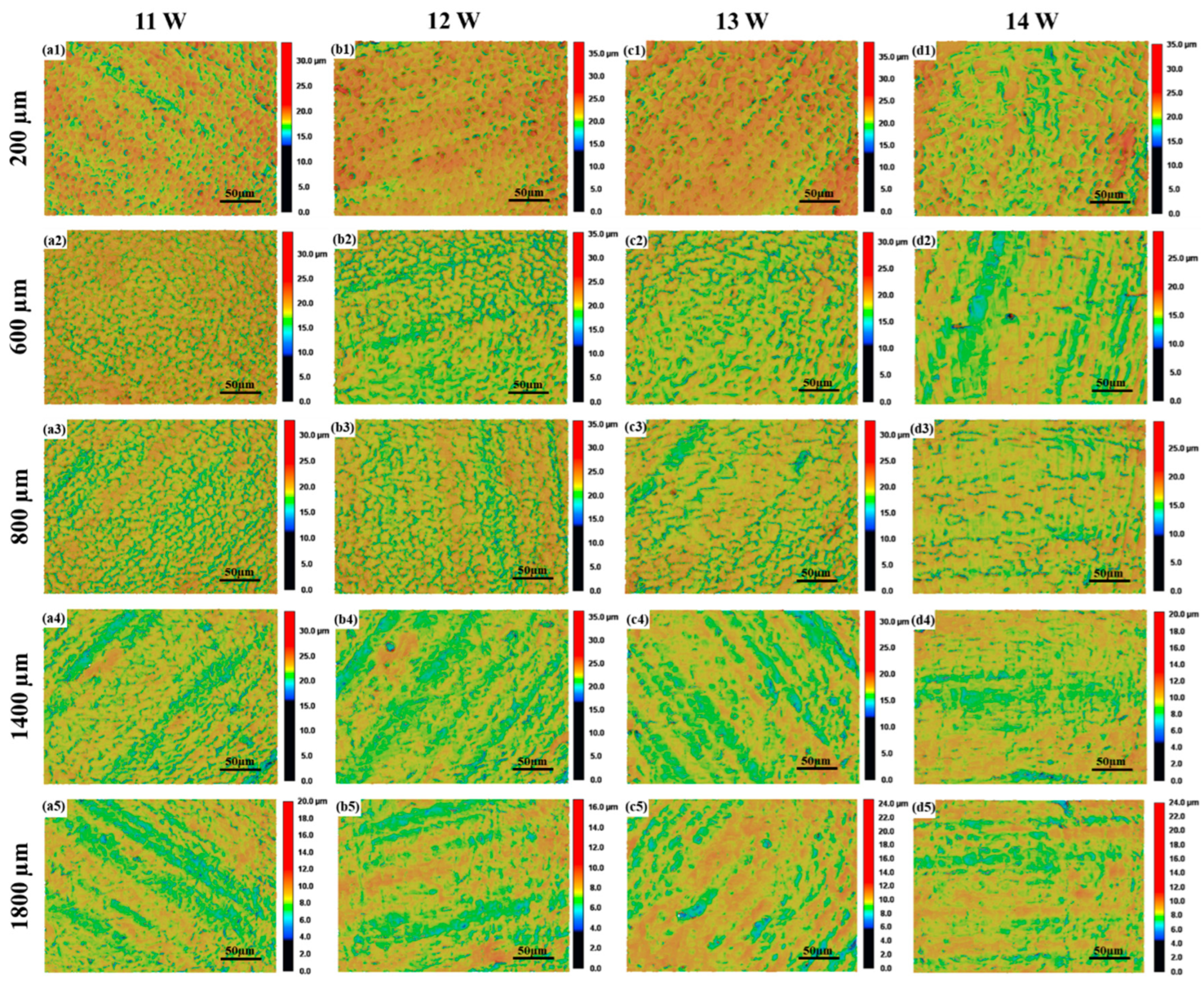
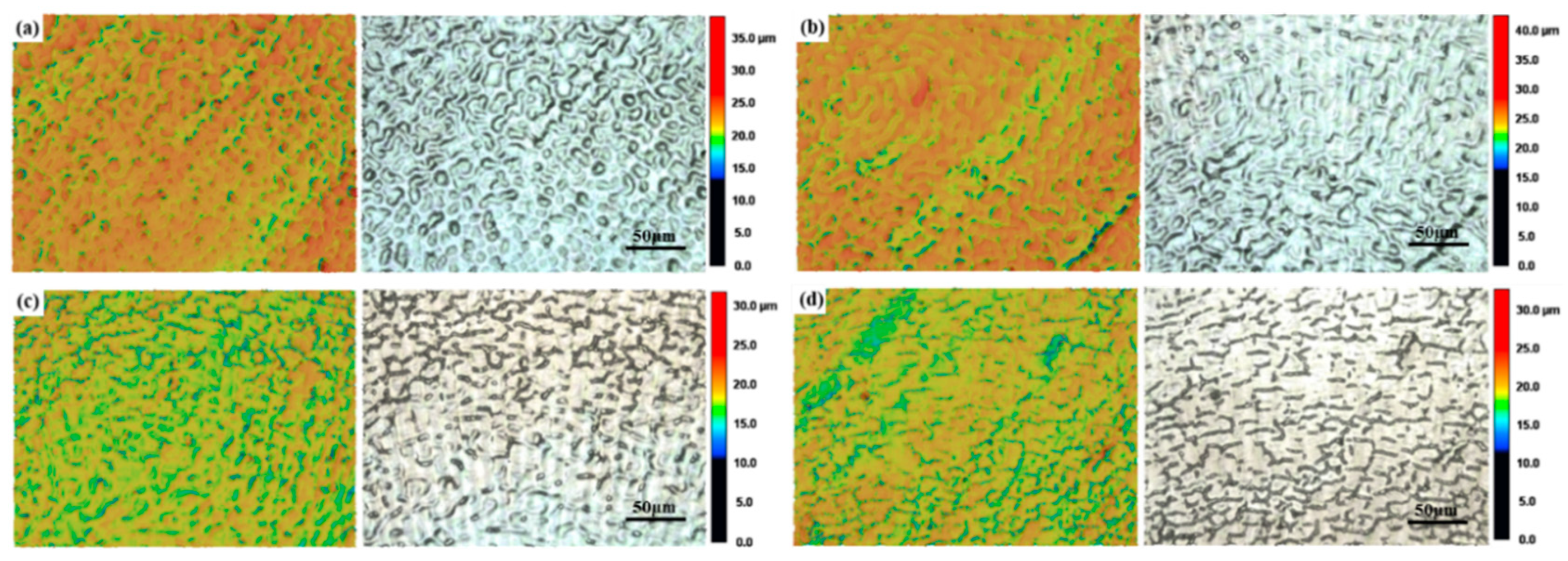
3.1.2. Effects of Laser Power on Surface Roughness and Surface Morphologies
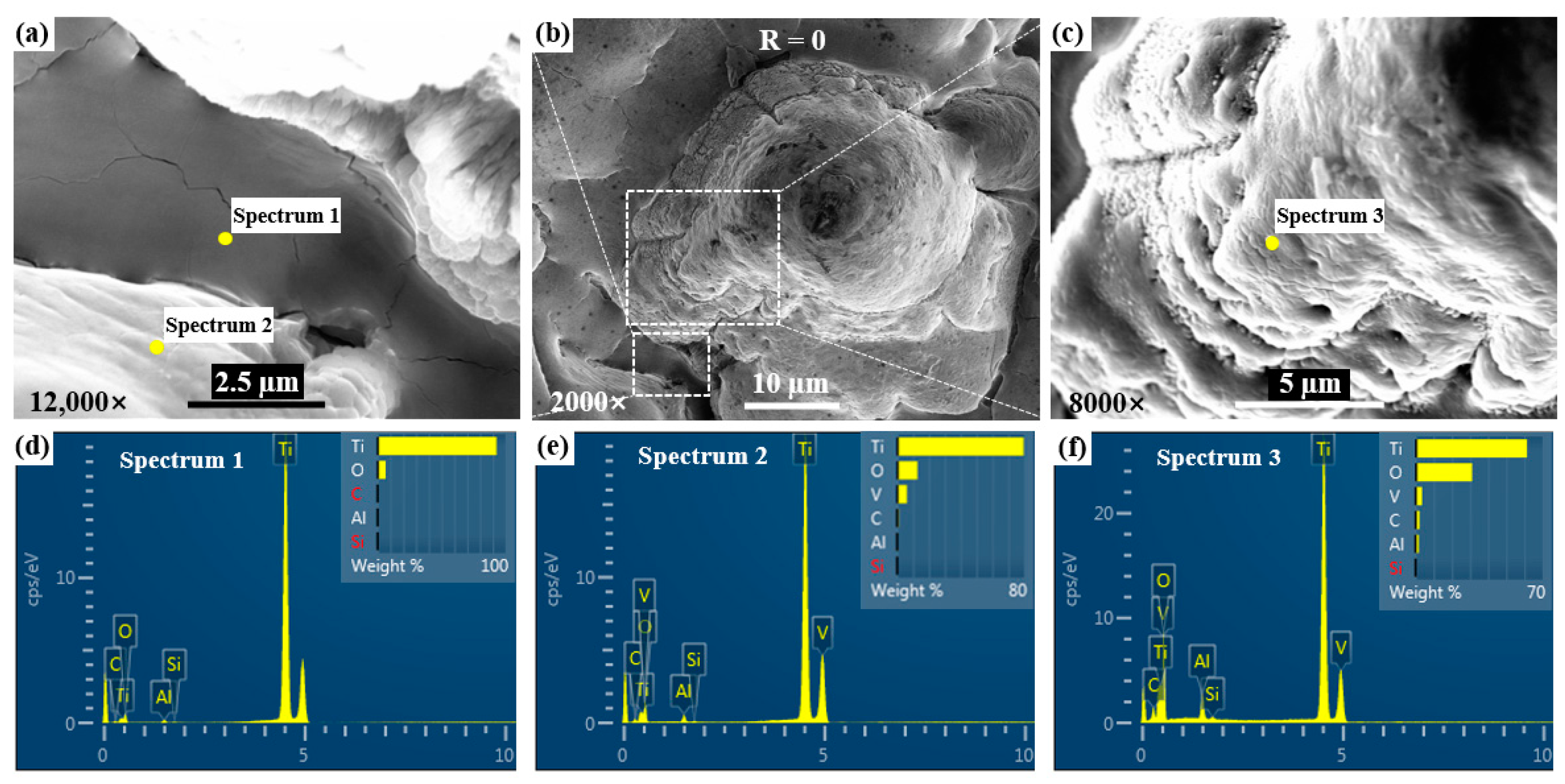
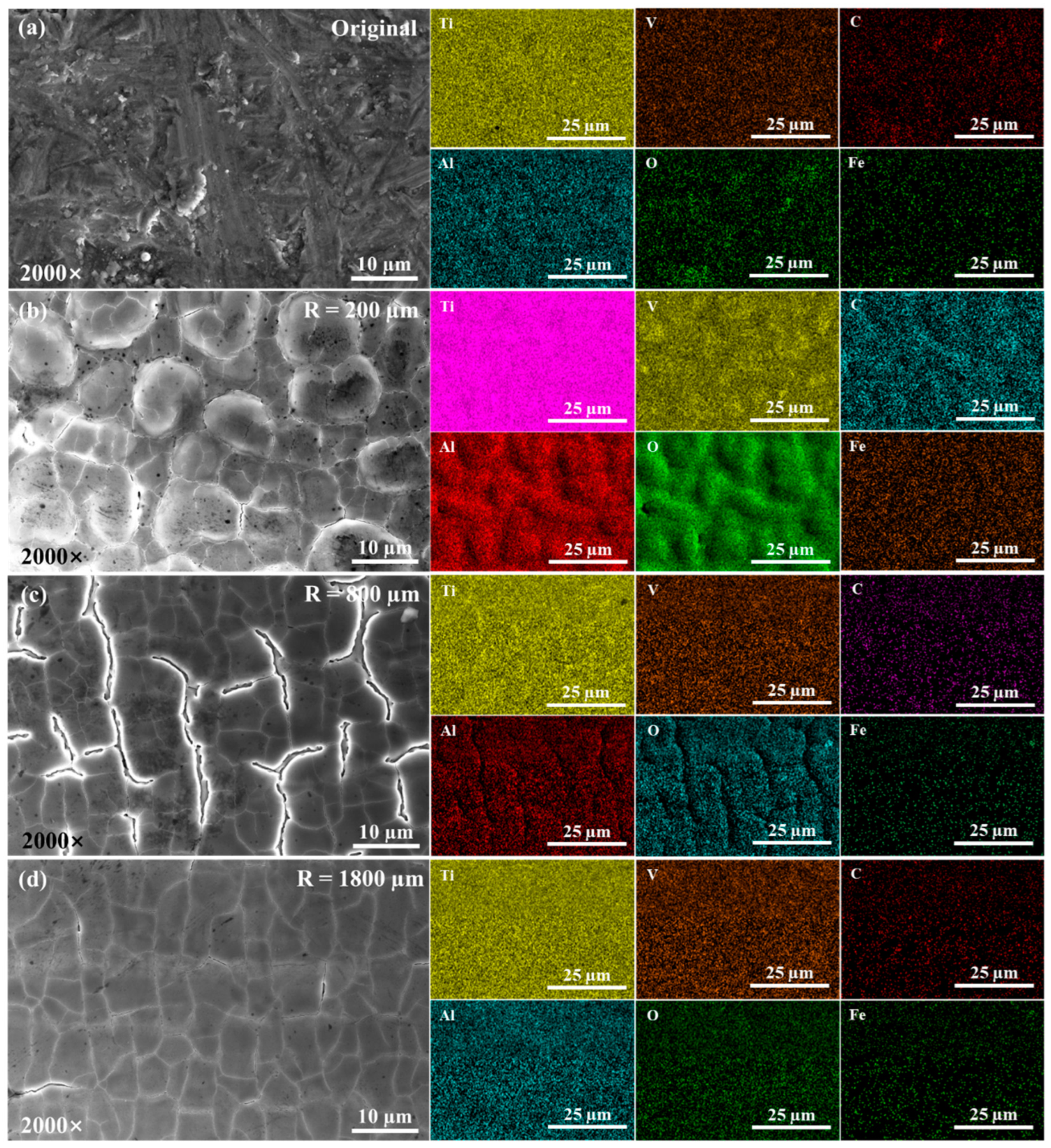
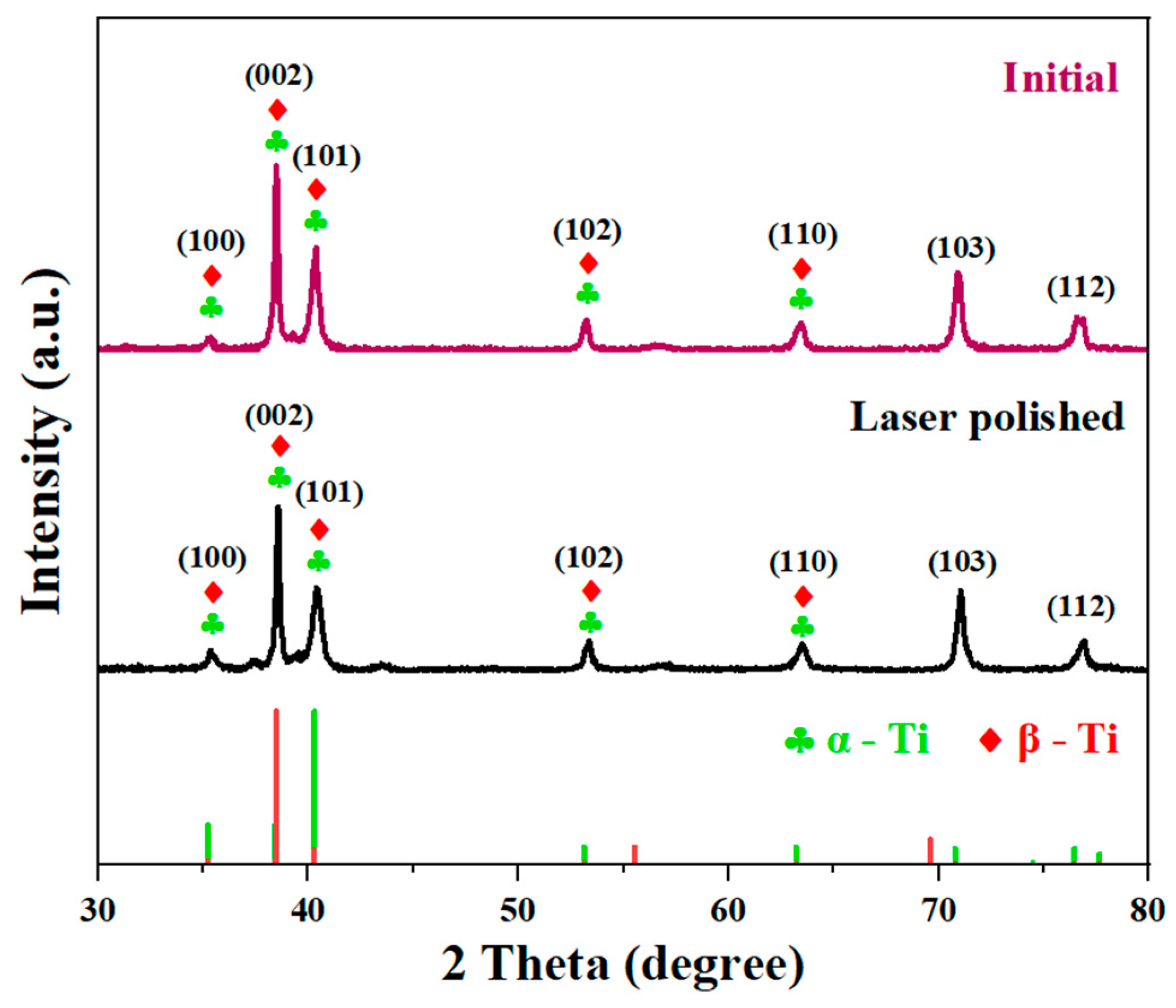
3.2. Micro-Morphologies and Microstructure Analysis
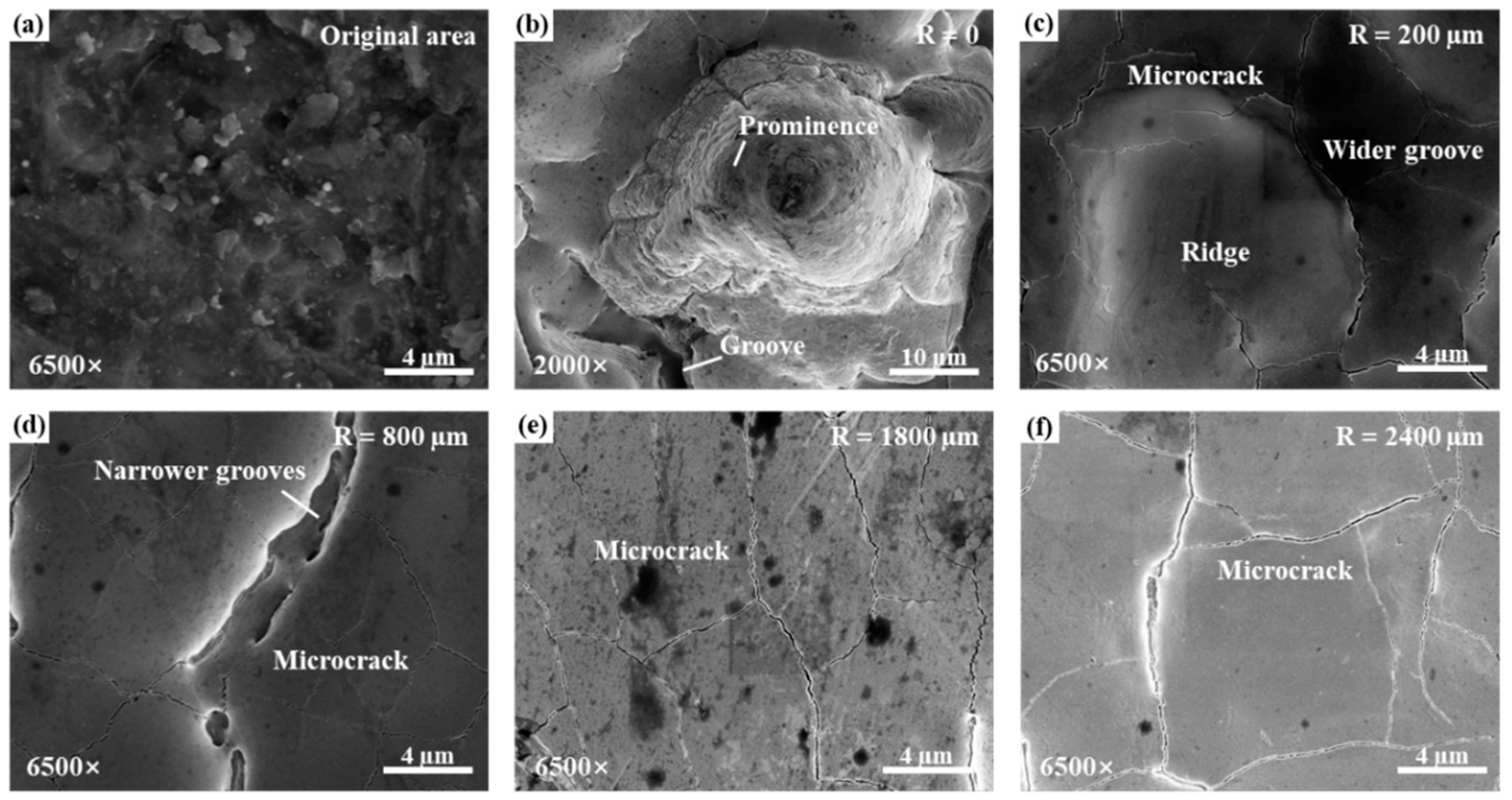
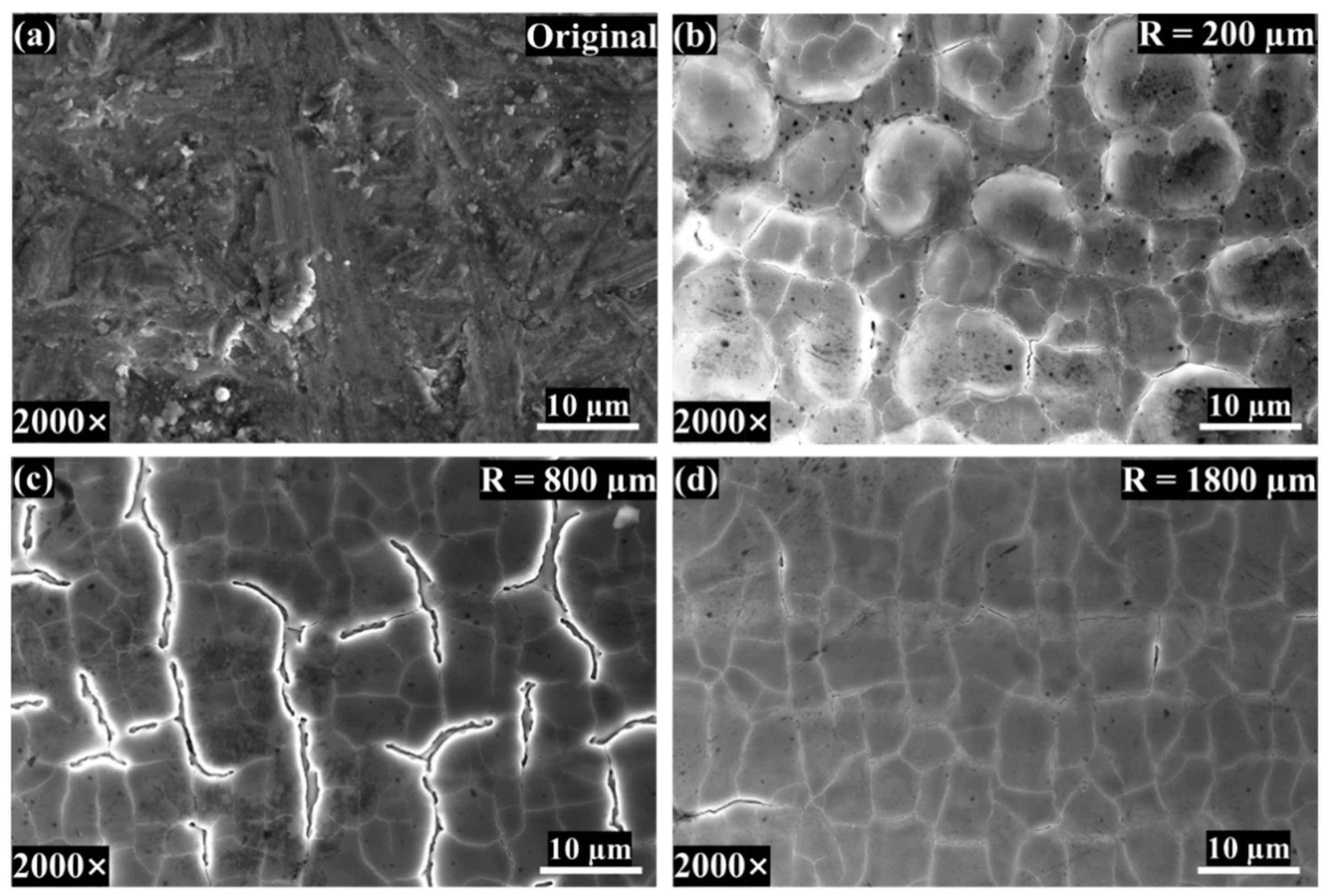
3.2.1. Microscopic Morphologies
3.2.2. Element Distributions
3.2.3. Analysis of XRD Pattern
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ren, D.; Jiang, Y.; Hu, X.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, X.; Huang, K.; Ling, H. Investigation of tensile and high cycle fatigue failure behavior on a TIG welded titanium alloy. Intermetallics 2021, 132, 107115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Gao, P.; Yu, J.; Jin, S.; Chen, S.; Zhan, M. Mesoscale deformation mechanisms in relation with slip and grain boundary sliding in TA15 titanium alloy during tensile deformation. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2022, 98, 72–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, Z.; Ozdemir, A.; Basim, G. Application of chemical mechanical polishing process on titanium based implants. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2016, 68, 383–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Ma, Y.; Peng, W.; Bao, Y.; Shi, Z. Evaluation of the effect of surface roughness parameters on fatigue of TC17 titanium alloy impeller using machine learning algorithm and finite element analysis. Eng. Fail. Anal. 2023, 153, 107586. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, R.; Pan, Y.; Chen, A.; Bin, G.; Li, H. Study on the influence of surface roughness on the erosion characteristics of compressor blades. Powder Technol. 2023, 430, 119037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.-Y.; Gao, J.; Guo, T.; Gao, K.-W.; Volinsky, A.A.; Pang, X.-L. Review of the fatigue behavior of hard coating-ductile substrate systems. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. Des. 2021, 28, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balyakin, A.; Goncharov, E.; Zhuchenko, E. The effect of preprocessing on surface quality in the chemical polishing of parts from titanium alloy produced by SLM. Mater. Today Proc. 2019, 19, 2291–2294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bezuidenhout, M.; Ter Haar, G.; Becker, T.; Rudolph, S.; Damm, O.; Sacks, N. The effect of HF-HNO3 chemical polishing on the surface roughness and fatigue life of laser powder bed fusion produced Ti6Al4V. Mater. Today Commun. 2020, 25, 101396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dogadkina, E.; Dontsov, M.; Parfenyuk, V. The effect of diffusion processes on surface smoothing upon chemical polishing of titanium. Prot. Met. Phys. Chem. Surf. 2016, 52, 947–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.-F.; Tsai, T.-H. Effect of organic acids on copper chemical mechanical polishing. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 2790–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wysocki, B.; Idaszek, J.; Buhagiar, J.; Szlązak, K.; Brynk, T.; Kurzydłowski, K.J.; Święszkowski, W. The influence of chemical polishing of titanium scaffolds on their mechanical strength and in-vitro cell response. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2019, 95, 428–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liao, Z.; La Monaca, A.; Murray, J.; Speidel, A.; Ushmaev, D.; Clare, A.; Axinte, D.; M’saoubi, R. Surface integrity in metal machining-Part I: Fundamentals of surface characteristics and formation mechanisms. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2021, 162, 103687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Li, R.W.; Perriman, D.M.; Chen, S.; Qin, Q.-H.; Smith, P.N. Laser polishing of thermoplastics fabricated using fused deposition modelling. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 2018, 96, 4295–4302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnan, A.; Fang, F. Review on mechanism and process of surface polishing using lasers. Front. Mech. Eng. 2019, 14, 299–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, J.; Bourell, D.; Beaman, J. Surface over-melt during laser polishing of indirect-SLS metal parts. MRS Online Proc. Lib. (OPL) 1999, 758, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zou, P.; Kang, D.; Wang, W.; Wang, A. Research on the formation mechanism of the surface structure in transition regime of laser polishing 304 stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2022, 149, 107906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, P.; Wang, Y.; Li, L.; Gong, Y.; Zhou, J.; Lu, J. Ablation oxidation and surface quality during laser polishing of TA15 aviation titanium alloy. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 23, 6101–6114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaritngama, P.; Tangwarodomnukuna, V.; Qib, H.; Dumkuma, C. Surface and subsurface characteristics of laser polished Ti6Al4V titanium alloy. Opt. Laser Technol. 2020, 126, 106102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, G.; Fu, G.; Wang, M.; Xu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Y.; Yao, J. Process and corrosion property of laser-chemical hybrid polishing of TC4 alloy. J. Manuf. Process. 2023, 101, 1374–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, D.; Zou, P.; Wu, H.; Wang, W.; Xu, J. Research on ultrasonic vibration-assisted laser polishing of the 304 stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 62, 403–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, G.; Sun, X.; Duan, J. Beam shaping technology for high efficiency laser fabrication. Laser Optoelectron. Prog. 2012, 49, 100002. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, J.; Wu, L.; Li, S.; Yang, Z.; Jia, X.; Starostenkov, M.D.; Dong, G. Beam shaping technology and its application in metal laser additive manufacturing: A review. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 4606–4628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tang, Y.; Kuang, Z.; Schille, J.; Loeschner, U.; Perrie, W.; Liu, D.; Dearden, G.; Edwardson, S. Multi imaging-based beam shaping for ultrafast laser-material processing using spatial light modulators. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2019, 112, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, C.; Chen, X.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, T.; Zhang, W. Effects of scanning speed and scanning times on surface quality of line spot laser polishing of nickel-based superalloys. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2023, 26, 2179–2190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu J, Zou P, Wang X, Wang, A.; Liu, L. Investigation into the laser polishing of an austenitic stainless steel. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 163, 109378. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Wang, D.; Liu, J.; Yu, M.; Yan, R.; Cui, E.; Liu, S.; Lei, C. Analysis of molten pool dynamics and surface smoothing time scale in laser polishing alloy materials. Opt. Laser Technol. 2023, 161, 109183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Tsai, H.-L. Fundamental study of the bulge structure generated in laser polishing process. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2018, 107, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Zou, P.; Wang, W. Theoretical and experimental study of bulge formation in laser polishing of 304 stainless steel. J. Manuf. Process. 2021, 66, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfefferkorn, F.E.; Duffie, N.A.; Li, X.; Vadali, M.; Ma, C. Improving surface finish in pulsed laser micro polishing using thermocapillary flow. CIRP Ann. 2013, 62, 203–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Guan, Y.; Zhou, W. Laser polishing of additive manufactured Ti alloys. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2017, 93, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Material | Al | V | Fe | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| TC4 | 5.5–6.8 | 3.5–4.5 | <0.30 | Balance |
| Experimental Parameters | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Laser repetition frequency f/(kHz) | 10 |
| Laser power P/(W) | 14 |
| Rotational speed n/(r/min) | 0, 1200, 1800, 2400, 3000 |
| Ablation time/(s) Beam spot size Material sample size | 8 14 μm × 5.3 mm 25 mm × 25 mm × 1 mm |
| Experimental Parameters | Parameter Value |
|---|---|
| Laser repetition frequency f/(kHz) | 10 |
| Laser power P/(W) | 11, 12, 13, 14 |
| Rotational speed n/(r/min) | 2000 |
| Ablation time/(s) | 8 |
| Beam spot size | 14 μm × 5.3 mm |
| Material sample size | 25 mm × 25 mm × 1 mm |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Shen, S.; Chen, X.; Chen, J.; Zhang, W. Influence of Laser Power and Rotational Speed on the Surface Characteristics of Rotational Line Spot Nanosecond Laser Ablation of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Materials 2024, 17, 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174271
Shen S, Chen X, Chen J, Zhang W. Influence of Laser Power and Rotational Speed on the Surface Characteristics of Rotational Line Spot Nanosecond Laser Ablation of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Materials. 2024; 17(17):4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174271
Chicago/Turabian StyleShen, Shunquan, Xiaoxiao Chen, Jianbo Chen, and Wenwu Zhang. 2024. "Influence of Laser Power and Rotational Speed on the Surface Characteristics of Rotational Line Spot Nanosecond Laser Ablation of TC4 Titanium Alloy" Materials 17, no. 17: 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174271
APA StyleShen, S., Chen, X., Chen, J., & Zhang, W. (2024). Influence of Laser Power and Rotational Speed on the Surface Characteristics of Rotational Line Spot Nanosecond Laser Ablation of TC4 Titanium Alloy. Materials, 17(17), 4271. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma17174271






