Abstract
Cyclodextrins (CDs) are cyclic oligosaccharides that emerged as industrial excipients in the early 1970s and are currently found in at least 130 marketed pharmaceutical products, in addition to numerous other consumer products. Although CDs have been the subject of close to 100,000 publications since their discovery, and although their structure and properties appear to be trivial, CDs are constantly surprising investigators by their unique physicochemical properties. In aqueous solutions, CDs are solubilizing complexing agents of poorly soluble drugs while they can also act as organic cosolvents like ethanol. CDs and their complexes self-assemble in aqueous solutions to form both nano- and microparticles. The nanoparticles have diameters that are well below the wavelength of visible light; thus, the solutions appear to be clear. However, the nanoparticles can result in erroneous conclusions and misinterpretations of experimental results. CDs can act as penetration enhancers, increasing drug permeation through lipophilic membranes, but they do so without affecting the membrane barrier. This review is an account of some of the unexpected results the authors have encountered during their studies of CDs as pharmaceutical excipients.
1. Introduction
About half a century ago, a group of cyclic oligosaccharides called cyclodextrins (CDs) emerged as enabling excipients for solubilization and stabilization of poorly soluble drugs in aqueous solutions. They rapidly gained the attention of pharmaceutical formulators in their constant search for new ways to solubilize and stabilize drug candidates. Currently, CDs can be found in at least 130 marketed pharmaceutical products, as well as in numerous other industrial products, including food, cosmetic, and toiletry products, most of which have been marketed during the past few decades [1,2,3,4,5]. CDs were first described as bacterial digest of starch by Antoine Villiers in 1891 [6]. In the following decades, their chemistry, structure, and physiochemical properties were investigated, including their ability to form water-soluble inclusion complexes of poorly soluble compounds [1,7,8,9,10,11,12,13]. In the beginning, only small amounts of relatively impure CDs were available, and this hampered their industrial applications; however, in the 1970s, biotechnological advances allowed large-scale production of pure CDs and their industrial application as enabling excipients. Since their discovery, CDs have been the subject of close to 100,000 publications, including about 61,000 peer-reviewed scientific articles and about 32,000 patents, most of which have been published during the past few decades (SciFinder; American Chemical Society, February 2023). Hence, scientific and industrial interest in CDs is significant and rapidly growing. Nevertheless, CDs are still surprising investigators with their unexpecting and, sometimes, hard-to-explain properties. This is an account of some of the unexpected results the authors have encountered during their studies of CDs as pharmaceutical excipients. It starts with a short theoretical background that might help to explain some of these CD oddities.
2. Cyclodextrins as Complexing Agents
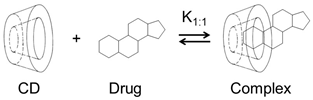
The most abundant natural CDs are formed by 6 (αCD), 7 (βCD), and 8 (γCD) (1→4)-linked α-D-glucose units that form a doughnut-shaped oligosaccharide with a hydrophilic outer surface and a somewhat hydrophobic central cavity [14,15,16,17,18,19]. Natural CDs have rather limited solubility in water, but freely soluble CD derivatives have been synthesized that are better suited for, e.g., parenteral solutions (Table 1). In aqueous solutions, CDs form water-soluble inclusion complexes with many poorly soluble drugs (or other poorly soluble substrates) by taking up lipophilic moieties of the drug molecules into the hydrophobic cavity. No covalent bonds are broken or formed during the complex formation, and, in aqueous solutions, drug molecules bound within the complex are in dynamic equilibrium with unbound molecules where the complexes are constantly being formed and dissembled on a milli- to microsecond timescale [20]. The classification of drug/CD complexes is based on the work by Higuchi and Connors and their studies of solubilizing complexes and phase-solubility profiles (Figure 1) [21]. Water-soluble complexes form A-type phase solubility profiles. Linear AL-type phase-solubility profiles are observed when the complex formed is first-order with respect to the CD (i.e., the ligand) and first- or higher-order with respect to the drug (e.g., 1:1 and 2:1 drug/CD complexes). Profiles displaying positive deviation from linearity (i.e., AP-type profiles) are, for example, observed when the complex is first-order with respect to the drug and second- or higher-order with respect to the CD (e.g., 1:2 drug/CD complex). B-type phase solubility profiles are observed when the complex has limited solubility in water (Figure 1).

Table 1.
Cyclodextrins with monographs in USP–NF and Ph. Eur., and formation of 1:1 drug/CD inclusion complex.
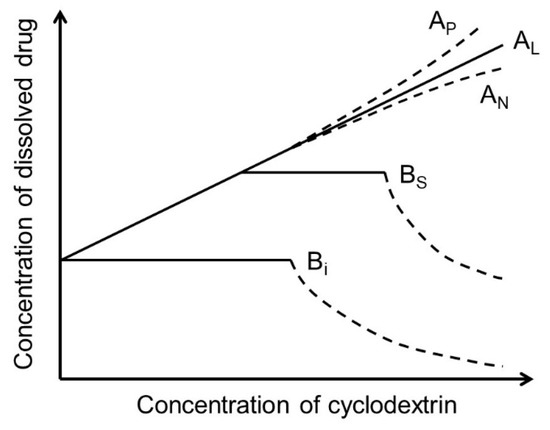
Figure 1.
Phase-solubility profiles and classification of drug/CD complexes according to Higuchi and Connors [21].
Most frequently, one drug molecule forms an inclusion complex with one CD molecule to give a 1:1 drug/CD complex (see figure in Table 1). In this case, a linear phase-solubility diagram is observed (i.e., AL-type) with a slope that is less than unity, and the stability constant (K1:1) can be obtained from the following equation:
where S0 is the drug solubility in the aqueous solution when no CD is present, frequently referred to as the intrinsic drug solubility. S0 represents the thermodynamic equilibration solubility of the drug in the complexation medium in identical conditions (i.e., same pH, same temperature, etc.) when CD is not present. S0 is the y-intercept (i.e., Sint) of the phase-solubility profile. Stepwise formation of 1:2 drug/CD complexes, where a 1:2 complex is formed following formation of a 1:1 complex, results in AP-type profiles where the stability constants (i.e., K1:1 and K1:2) can be obtained by, e.g., curve fitting to a quadratic model:
where [CD] represents the concentration of free CD molecules in the aqueous solution [21,23]. Higuchi and Connor did not work with CDs but based their classification system on studies of aqueous solubility of poorly soluble drugs, such as sulfathiazole, that form water-soluble but simple non-inclusion complexes with low-molecular-weight complexing agents, such as caffeine (MW 194 Da; logP −0.6) [24]. Such complexing agents have relatively few hydrogen bond acceptors (H-acceptors) and donors (H-donors), while the much larger CD molecules are very hydrophilic with numerous H-acceptors and H-donors (Table 1). Consequently, in aqueous solutions, CD molecules interact more strongly than the low-molecular-weight complexing agents, both with each other and with the surrounding water molecules.
3. The Anomalous Properties of Water
Water has some unique or anomalous physiochemical properties [25,26,27,28,29]. The water molecule consists of a highly electronegative oxygen atom that is covalently bound to two weakly electropositive hydrogen atoms that form a 104.5° angle, giving the molecule a close-to-tetrahedral structure. The electrostatic molecular surface forms a dipole where the oxygen atom is partially negative and the hydrogen atoms are partly positive. In liquid water, the polarity of each water molecule results in an intermolecular attraction and hydrogen bond formations. On average, each water molecule forms about 3.6 hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules; however, importantly, the exchange of hydrogen-bond partners via breaking and reforming occurs in a time range between 1 and 5 picoseconds (ps) [26,30]. Hydrogen bonds are relatively strong (~5–40 kJ/mol) compared to van der Waals interactions (~1–10 kJ/mol) but much weaker than covalent bonds (~200–1000 kJ/mol). Intermolecular hydrogen bonding of water molecules leads to enhanced molecular cohesion that affects the physiochemical properties. For example, the melting and boiling points of hydrogen sulfide (H2S; MW 34 Da) are −85 °C and −60 °C, respectively, compared to 0 °C and 100 °C, respectively, for water (H2O; MW 18 Da). In fact, if water did not possess this extensive molecular adhesion, its boiling point would not be 100 °C but about −90 °C. This extensive hydrogen bonding also affects other physiochemical properties of liquid water such as its dielectric constant (ε 78.5 at 25 °C), density (1.000 g/mL at 3.98 °C), surface tension, and heat of vaporization (40.65 kJ/mol), making them all higher than expected [25]. The dielectric constants of organic solvents, such as ethanol (ε 24.3 at 25 °C) and glycerol (ε 42.5 at 25 °C), are much lower than that of water. Due to self-ionization of the water molecule, protons and hydroxide ions diffuse through water at much faster rate than other ions. For example, protons in the form of hydronium ions (H3O+) diffuse about seven times faster through water than Na+, and OH− diffuses about 2.5 times faster than Cl− [25]. In solutions, water molecules form intermolecular and directional interactions that give rise to a wide variety of molecular networks that are constantly being formed and disassembled.
In aqueous solutions, hydration shells of structured water molecules are formed around solute molecules and at membrane surfaces [26,31]. In the case of hydrophilic solutes, such as polar molecules (e.g., CDs), the partly positive and partly negative surfaces of the water molecule form hydrogen bonds with the solute molecules. Formation of hydrogen bonds is thermodynamically favored. Nonpolar solutes, like many Class II drugs of the biopharmaceutics classification system (BCS), are hydrophobic and unable to form hydrogen bonds with water. Instead, water molecules form structured layers of water around the hydrophobic solute molecules that tend to aggregate to minimize the contact area of the hydrophobic surface with water. Hydration of hydrophobic solutes involves disruption hydrogen bonds and loss of entropy; thus, it is not thermodynamically favored, which can explain their low aqueous solubility. The structured water layers at membrane surfaces can hamper the permeation of drug molecules through membrane surfaces and decrease the rate of drug permeation through biomembranes such as mucosa [32,33,34,35].
Stable CD hydrates contain several water molecules. For example, in the solid state 2, 6, and 8.8 water molecules are present in the αCD, βCD, and γCD cavities, respectively, and 4.4, 3.6, and 5.4 water molecules, respectively, are spread around the CD exterior [22]. In bulk water, each water molecule forms on the average 3.6 hydrogen bonds, whereas, inside the αCD, βCD, and γCD cavities, each water molecule forms 1.5, 1.9, and 2.2 hydrogen bonds, respectively [36]. Thus, expulsion of water from the central CD cavity by a lipophilic drug moiety is thermodynamically favored. In aqueous solution, each glucose repeat unit of a CD molecule forms about 4–5 hydrogen bonds with surrounding water molecules, which create the first hydration shell, in addition to intramolecular hydrogen bonds between C2–OH on one glucose unit and C3–OH of the adjacent glucose unit [36,37]. It has been proposed that the ability of αCD, βCD, and γCD to form intra- and intermolecular hydrogen bonds can explain their differences in aqueous solubility (Table 1) [14,38,39]. Chemical substitution of OH groups of the CD molecules (e.g., in HPβCD and SBEβCD) has a significant effect on the hydrogen bonding of water molecules in the CD hydration shell [40]. Nevertheless, the main reason for the enhanced aqueous solubility of HPβCD and SBEβCD (Table 1) is the average degree of substitution (i.e., number of substituents per cyclodextrin molecule) and the random distribution of the substituents that results in amorphous mixtures of substituted CD isomers. The βCD molecule contains 21 hydroxyl functional groups that allow numerous possible combinations for substitution. Furthermore, the 2-hydroxypropyl moiety contains an additional optical center and, thus, the number of geometrical and optical isomers of HPβCD can be astronomical [41]. Studies have shown that both the molar substitution and the location of the substituents can influence the aqueous solubility and complexing behavior of HPβCD, as well as of other substituted CDs [42].
4. The Anomalous Properties of Cyclodextrins
CDs are small cyclic glucose polymers, or oligosaccharides, with molecular weight between 973 and 1297 Da. In spite of their rather trivial structure, their physiochemical properties have been shown to be far from predictable. In fact, these rather simple molecules are constantly surprising pharmaceutical formulators with their unexpected properties, especially in aqueous solutions, most of which can be explained by their inter- and intramolecular hydrogen bonding, as well as by the anomalous properties of water. It should also be mentioned that, while theoretical chemistry is frequently based on studies in close-to-ideal solutions (i.e., very dilute solutions), pharmaceutical solutions are nonideal solutions (i.e., concentrated solutions of drugs and excipients) and, thus, can deviate from the classical physicochemical principles.
4.1. Aggregation of CDs and CD Complexes
Like other saccharides and carbohydrate polymers, CD molecules and their complexes self-associate in aqueous solutions to form nanoparticles, even at relatively low CD concentrations [43,44,45,46,47,48]. Although association of CD molecules was first mentioned in the scientific literature some 40 years ago [49], and although formation of nanosized CD aggregates is observed at CD concentrations below 1% (Table 2), the effects of CD aggregates and CD complex aggregates are frequently overlooked. The reason might be that the aggregate weight fraction of the total CD mass can be low (e.g., 0.001%), and their diameters are frequently well below the wavelength of the visible light; thus, CD solutions appear clear even though they contain CD aggregates of various types and shapes [45,50,51,52]. Furthermore, nanosized aggregates are frequently transient and, thus, can be difficult to detect using conventional analytical techniques [48]. Depending on their size and physicochemical properties, the observed aggregates can be characterized as unstable nanoclusters of CD molecules and CD complexes that are constantly being formed and dissembled in aqueous solutions [43,44], as somewhat stable nano- or microparticles [53], and as unstable macroclusters [54] (Table 3). In most cases, the formation of nanosized CD complex aggregates does not affect the shape of the phase-solubility diagrams. However, due to CD complex aggregation, AL-type phase-solubility diagrams with slope less than unity do not necessarily indicate formation of 1:1 drug/CD inclusion complexes, and AP-type diagrams do not necessarily indicate formation of 1:2 drug/CD inclusion complexes [48,55,56]. Drug/CD complexes of more than one stoichiometry can also coexist in aqueous solutions [57].
The aggregation and hydration of CDs in aqueous solutions can also affect the rate of drug dissolution in aqueous CD media by decreasing the ability of dissolved CD molecules to form water-soluble inclusion complexes. Both CD aggregation and CD hydration decrease with increasing temperature, while the intrinsic solubility of both the drug and CD increases. Thus, heating the aqueous complexation medium, followed by equilibration at the desired temperature, can result in more reliable solubility data and better solubilization [23,58].

Table 2.
The apparent critical aggregation constant (cac) of some CDs at ambient temperature in pure water as determined by permeation through a semipermeable membrane with MWCO of 3.3–5 kDa [44], proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) [59], and dynamic light scattering (DLS) [59].
Table 2.
The apparent critical aggregation constant (cac) of some CDs at ambient temperature in pure water as determined by permeation through a semipermeable membrane with MWCO of 3.3–5 kDa [44], proton nuclear magnetic resonance (1H-NMR) [59], and dynamic light scattering (DLS) [59].
| Cyclodextrin | Critical Aggregation Concentration (% w/v) | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Permeation | 1H-NMR | DLS | |
| αCD | 2.5 | ||
| βCD | 0.8 | ||
| γCD | 0.9 | ||
| HPβCD | 11.8 | 2.1 | 1.8 |
| SBEβCD | 1.9 | 2.5 | |
| HPγCD | 2.2 | 1.7 | |

Table 3.
Classification of aggregates that have been observed in aqueous CD solutions. Adapted with permission from Ref. [44].
Table 3.
Classification of aggregates that have been observed in aqueous CD solutions. Adapted with permission from Ref. [44].
| Type of Aggregate | Approx. Diameter (µm) | Properties | When Observed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nanoclusters | <0.5 | Transient clusters that are unstable and dissemble upon agitation and filtration. | Aqueous CD solutions. The nanoclusters consist of free CD and/or drug/CD complexes. |
| Nanoparticles | <0.5 | Somewhat stable particles that can tolerate centrifugation and filtration but dissemble upon medium dilution. | Aqueous αCD, βCD, and γCD solutions, frequently at relatively low CD concentrations. The nanoparticles consist of free CD and/or drug/CD complexes. |
| Microparticles | 1–50 | Stable particles that can precipitate from aqueous media but disassemble upon medium dilution. | Aqueous αCD, βCD, and γCD solutions, containing poorly soluble drugs and at relatively high CD concentrations. The microparticles consist of drug/CD complexes. |
| Macroclusters | >1000 | Very unstable transient clusters that can be visible to the naked eye but dissemble upon agitation and filtration. | Transient clusters (or transient particulate matter) that are sometimes observed in aqueous parenteral solutions containing a relatively high concentration of water-soluble CD derivatives, such as HPβCD. |
4.2. S0 Is Not Always Equal to Sint
One of the basic assumptions of the phase-solubility technique used to determine the stability constants of solubilizing complexes is that the solubility of a drug (i.e., the substrate) in the aqueous complexation medium (i.e., the intrinsic solubility or S0) when no complexing agent (i.e., ligand) is present is equal to the y-intercept (Sint) of the phase-solubility diagram (Figure 2A) [21]. However, this is not always the case, especially for lipophilic drugs with limited solubility in water. Such molecules tend to form small aggregates in aqueous solutions. Even many hydrophilic drugs of poor aqueous solubility (e.g., doxorubicin, solubility 0.5 mg/mL and logD −1.6 at pH 7) form aggregates in aqueous solutions [60]. In aqueous solutions, most often only the drug monomer can enter the CD central cavity to form an inclusion complex (Figure 2B), while the observed intrinsic drug solubility (S0) represents the concentration of both drug monomers and nanosized drug aggregates; thus, S0 can be greater than Sint (Figure 2C). Consequently, values of stability constants of drug/CD complexes that are derived from phase-solubility diagrams are frequently incorrect, such as values of K1:1 obtained from Equation (1). The complexation efficiency (CE in Figure 2C) of a given CD at a given condition only depends on the slope of the phase-solubility diagram and, thus, is independent of both S0 and Sint [61]. In addition to drug aggregation, drug–excipient interactions (e.g., formation of water-soluble drug–polymer complexes) can result in S0 > Sint [62,63].
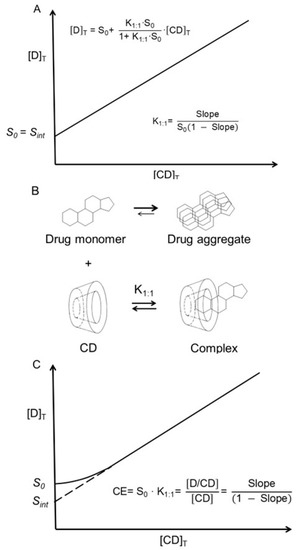
Figure 2.
In general, one drug molecule (D) forms a complex with one CD molecule in pure water, and, if the complex is water-soluble, an AL-type phase-solubility diagram is observed (Table 1). (A) Classical AL-type phase-solubility profile of a 1:1 drug/CD complex (D/CD) according to Higuchi and Connors [21]. [D]T is the total concentration of dissolved drug, and [CD]T is the total concentration of CD in solution. In this case, S0 is equal to the intercept (Sint). (B) Aggregation of drug molecules in water where only the monomeric drug can form a 1:1 complex with CD. (C) Drug aggregation, where S0 is the concentration of not only dissolved monomeric drug but also dissolved nanosized drug aggregates (S0 > Sint). Here, the stability constant (K1:1) of the complex cannot be determined from the slope and intercept, and the complexation efficiency (CE) is used to evaluate the CD solubilization [61].
4.3. The Value of K Is Method-Dependent
Both the stoichiometry and the aggregation of drug/CD complexes are affected by the drug and CD concentrations in the aqueous complexation medium. In addition, analytical methods applied to determine the stability constants (i.e., the K values) can be affected by the CD and drug/CD complex aggregation. Thus, experimental K values can be both concentration- and method-dependent [64,65,66]. For example, the phase-solubility diagrams of diflunisal in pure aqueous HPβCD solutions have slopes between 1.2 and 1.3, indicating 2:1 stoichiometry (i.e., [diflunisal]:[HPβCD] ratio) of the diflunisal/HPβCD complex, although other studies have clearly shown that only 1:1 inclusion complexes are formed in the solutions [56]. A possible explanation can be that additional diflunisal solubilization is obtained through non-inclusion complexation and/or a micellar-like solubilization by diflunisal/HPβCD complex aggregates. It is known that diflunisal/HPβCD complexes aggregate in aqueous solutions [55,56]. The value of K1:1 for the diflunisal/HPβCD complex can be obtained by other techniques but the value is highly method-dependent (Table 4).

Table 4.
The stability constant (K1:1) of diflunisal/HPβCD complex at 23 to 25 °C and neutral pH (i.e., the pH ranged from 7 to 7.4). At 25 °C, the pKa of diflunisal is 2.9 and, thus, the drug is fully ionized at neutral pH.
4.4. Water-Soluble Polymers Can Enhance the Solubilizing Efficiency of CDs
Polymers are known to interact with a variety of particulate systems such as nanoparticles, micelles, and cyclodextrin aggregates [69,70,71]. It is also well documented that polymers enhance micellar solubilization of lipophilic compounds in aqueous media [72,73,74]. Some years ago, it was observed that, in aqueous solutions, polymers have synergistic effects on CD solubilization of poorly soluble drugs, and it is assumed that this effect is analogous to that of micellar solubilization, and that the effect is related to the aggregation of CD complexes [75,76,77,78,79]. To avoid the formation of polymer–CD inclusion complexes and rotaxanes that might result in decreased CE, the diameter of the polymer should preferably be greater than that of the CD cavity [80]. Then, through hydrogen bonding, the polymers stabilize the drug/CD complex aggregates, as well as individual drug/CD complexes, resulting in enhanced complexation efficacy and increased drug solubilization [77]. If the drug/CD complex has limited solubility in aqueous complexation media, addition of a water-soluble polymer will enhance the solubility through solubilization of the nanosized drug/CD complex aggregates [81]. For example, the aqueous solubility of βCD in pure water was determined to be 18.6 ± 0.4 mg/mL when no PVP was present, increasing to 20.5 ± 0.8 mg/mL when 2.5 mg/mL PVP was present (~10%) [81]. However, when the aqueous medium is saturated with both βCD and carbamazepine, the βCD solubility is increased by about 150% (Figure 3). The figure shows that the solubility of βCD is about 18 mg/mL in pure water, about 33 mg/mL when the solution is saturated with both βCD and carbamazepine, and about 53 mg/mL when 0.75 mg/mL of PVP is added to the βCD and carbamazepine-saturated solution. Furthermore, the solubility of carbamazepine in the saturated βCD solution increases from about 2.2 to 4.6 mg/mL when 1 mg/mL PVP is present.
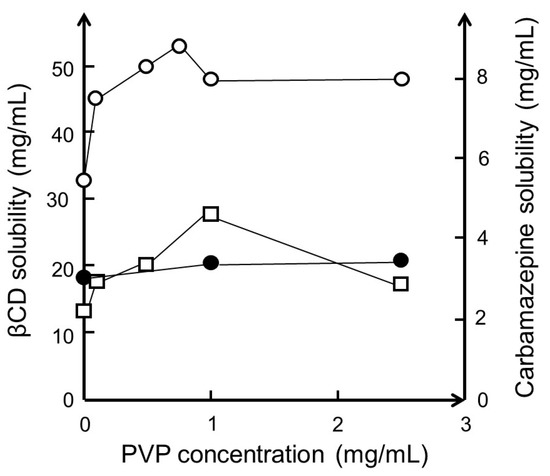
Figure 3.
The effect of polyvinylpyrrolidone with a molecular weight of 40,000 (PVP) on the solubility of βCD and carbamazepine in water at room temperature (23 °C). Solubility of βCD when no carbamazepine is present (●). Solubility of βCD (○) and carbamazepine (□) when the complexation medium contains both excess βCD and excess carbamazepine. Unpublished results based on experiments described in [81].
4.5. Effects of Ions on βCD Solubilization of Drugs
Hydroxy acids, such as lactic acid, citric acid, and tartaric acid, enhance the aqueous solubility of βCD due to their ability to influence intra- and intermolecular hydrogen-bonding [82]. Studies have shown that hydroxy acids enhance the complexation efficacy and aqueous solubility of the complex when a poorly soluble basic drug forms a salt with the acid while the acid is able to interact with the hydroxyl groups on the wider external rim of a CD molecule [83]. However, other organic acids and bases, such as sodium acetate, sodium benzoate, and benzalkonium chloride, are also able to enhance the solubility of drug/βCD complexes, presumably through solubilization of drug/βCD aggregates, even for drugs that are unable to form salts [84]. For example, the aqueous solubility of hydrocortisone (a neutral drug) at room temperature was determined to be 0.4 mg/mL in pure water, 2.1 mg/mL in aqueous 4% (w/v) βCD solution, and 7.1 mg/mL in aqueous 4% (w/v) βCD solution containing 1% (w/v) sodium acetate (Figure 4).
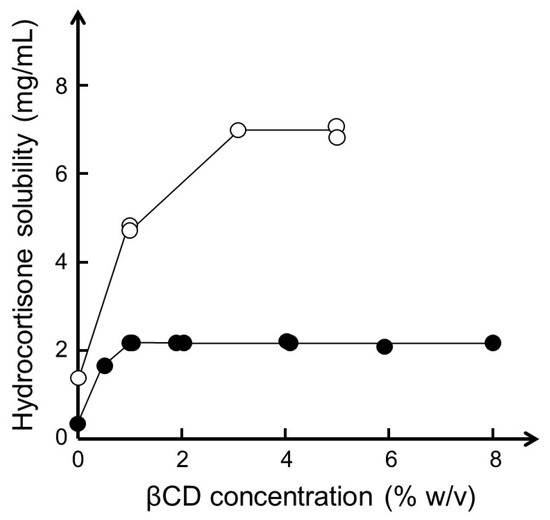
Figure 4.
Phase-solubility diagram of hydrocortisone in aqueous βCD medium with (○) and without (●) 1% (w/v) sodium acetate at room temperature (22–23 °C) and pH 6.9. Based on data with permission from [84].
4.6. In Aqueous Solutions, CDs Frequently Resemble Organic Cosolvents
In chemistry, the word complex usually refers to molecules or molecular assembles formed by association of substrates (e.g., a drug molecule) and ligands (e.g., a CD molecule); in aqueous solutions, noncovalent complexes are in dynamic equilibrium with unbound substrates and ligands [85]. With only few exceptions, drug/CD complexes have stability constants (e.g., K1:1) below 104 M−1, and the complexes are transient in aqueous solutions, constantly being formed and dissembled on a milli- to microsecond timescale [20]. Consequently, the release of a drug molecule from the CD cavity will generally not be a limiting factor, such as during drug permeation from an aqueous CD solution through a lipophilic biological membrane. One exception is the effect of CDs on the thermodynamic activity of drugs in aqueous solutions, which can result in reduced drug permeation [86]. In this respect, the effect of CDs on drug permeation from the aqueous exterior through biological membranes is similar to that of organic cosolvents. It is common practice in reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatography to increase the concentration of organic solvents, such as methanol and acetonitrile, in the aqueous mobile phase to shorten the drug retention time. The same effect can be obtained by adding CDs, such as βCD and HPβCD, to the mobile phase [66,87]. Numerous studies have shown that the transient drug/CD complexes with K1:1 below 105 M−1 do not affect the drug pharmacokinetic parameters after parenteral administration such as the half-life and volume of distribution [54,88]. In aqueous parenteral solutions, CDs behave as organic cosolvents. This is due to the very rapid release of drug molecules from the CD cavities upon intravenous administration, as well as the consequent medium dilution and drug binding to plasma proteins [89]. Although one would expect that aqueous drug/CD complex solutions behave like disperse systems (e.g., colloids), these and other observations indicate that, due to the transient nature of CD complexes and their aggregates, aqueous CD solutions can resemble aqueous solutions containing organic cosolvents.
4.7. CDs as Permeation Enhancers
Biomembranes, such as mucosa, form membrane barriers toward drug permeation from, e.g., the gastrointestinal tract to the systemic blood circulation. Although drugs can be transported actively through biomembranes, the capacity of the active absorption is frequently limited; thus, passive drug permeation through the membrane is dominating. Most often, membrane barriers consist of an unstirred water layer (UWL) at the exterior surface of a lipophilic membrane [33]. In the gastrointestinal tract, the UWL is the relatively thick (can be several hundred µm in humans) and viscous mucus layer that covers the lipophilic mucosal epithelium [90,91]. Figure 5 is a schematic presentation of permeation of a lipophilic drug through a simple two-layer biomembrane showing passive drug permeation first through an UWL and then through a lipophilic membrane. Passive drug permeation follows Fick’s first law that states that the drug flux (J) is the product of the permeation coefficient (P) and drug concentration gradient over the barrier. A greater concentration gradient results in faster permeation of the drug molecules (i.e., a larger value of J) [86]. A higher concentration of a dissolved lipophilic drug in the aqueous gastrointestinal fluid results in faster absorption of the drug through the mucosa into the systemic blood circulation and more complete absorption (i.e., higher drug bioavailability). In vitro studies have shown that CDs only enhance drug permeation through artificial membranes (e.g., PAMPA) and cellular tissues (e.g., Caco-2 membrane) when the permeation resistance of the UWL at the membrane surface contributes significantly to the overall permeation resistance of the membrane [92,93,94]. Moreover, the dissolution rate also affects the overall bioavailability, and CDs usually enhance the drug dissolution rate. An understanding of absorption barriers of a given drug is, however, essential for optimal formulation design [95]. The diffusional and kinetic parameters for drug diffusion through the UWL from aqueous CD formulations can be predicted by a simple experimental/mathematical approach [96]. In general, CDs enhance the permeation without affecting the barrier function of the mucosa. Most permeation enhancers increase the delivery of drugs through mucosal membranes by permeating into the lipophilic membrane where they disrupt the membrane structure, which results in faster drug permeation. CDs are very hydrophilic and, thus, unable to partition from the aqueous exterior into the lipophilic membrane. Furthermore, maximum absorption is obtained when the aqueous exterior is saturated with the drug, i.e., when CA is equal to drug-saturated solubility (Figure 5) [86]. Under such conditions, the dissolved drug molecules have the maximum ability to leave the aqueous exterior and partition into the lipophilic membrane. Lastly, it has been noted that drug/CD complex aggregates can reduce drug irritation in the gastrointestinal tract [97].
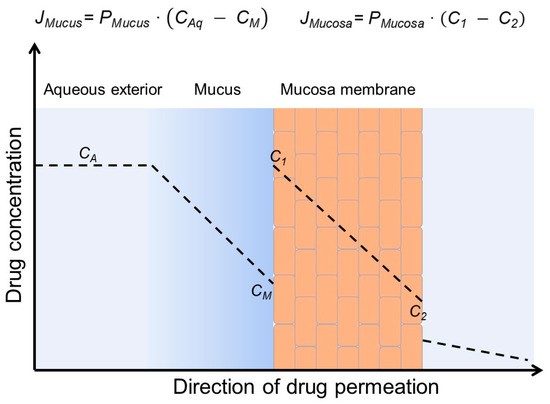
Figure 5.
Passive permeation of a lipophilic drug from an aqueous exterior through mucus (a viscous unstirred water layer) to the mucosal surface where the drug partitions into the mucosa (a lipophilic membrane barrier) and then permeates the mucosa. The concentration gradient within the mucus layer (CA − CM) is the driving force for drug permeation through the mucus layer (i.e., diffusion barrier), and the concentration gradient within the mucosa (C1 − C2) is the driving force for drug permeation through the mucosa (i.e., membrane barrier). JMucus, JMucosa, PMucus and PMucosa are the drug fluxes and permeation coefficients through the aqueous mucus layer and the mucosa, respectively.
4.8. CDs Can Stabilize Supersaturated Solutions
When the concentration of dissolved drug in an aqueous solution is higher than the drug’s thermodynamic equilibrium solubility, the solution is said to be supersaturated. A supersaturated drug solution is unstable and can result in rapid drug precipitation. Pharmaceutical excipients that inhibit nucleation and crystal growth are referred to as drug precipitation inhibitors and include numerous polymers, such as hydroxypropyl methylcellulose and polyvinylpyrrolidone, cocrystals, and surfactants, as well as CDs [98,99,100]. The mechanism of inhabitation may include changes in surface tension, an increase in viscosity, and adsorption to the crystal layer, thereby blocking crystal growth. Although several common pharmaceutical excipients can stabilize supersaturated solutions, CDs have been shown to both enhance the drug dissolution rate and stabilize the resulting supersaturated drug solution.
According to the Noys–Whitney equation, the dissolution rate (dC/dt) is proportional to the difference between the drug concentration in the aqueous solution (Ct) at time t and the drug solubility at the solid drug surface (S) [101].
where k is a constant. dC/dt increases with increasing S and decreases with increasing Ct. S of poorly soluble drugs can, for example, be increased through the formation of salts of ionizable drugs, by converting crystalline drugs to amorphous ones or through the addition of surface-active agents to the solid drug dosage form, but also through formation of water-soluble drug/CD complexes. In some cases, the drug dissolution is fast enough to produce drug concentrations that are above the thermodynamic equilibrium solubility (S0). In this case, CA is greater than S0, resulting in even faster drug permeation (Figure 5). Figure 6 shows how both HPβCD and SBEβCD form supersaturated itraconazole solutions that are stable for at least 120 min. TPGS forms a supersaturated solution that is stable for about 40 min, while the other surface-active agents tested form instable supersaturated itraconazole solutions. Other investigators have observed that drug/CD complexes both enhance the rate of drug dissolution and stabilize the supersaturated drug solution formed from about 0.5 to about 12 h [102,103,104]. The influence of CDs on drug dissolution has been referred to as the spring (i.e., fast dissolution) and parachute (i.e., stabilization of supersaturated drug solution) effect [105,106].
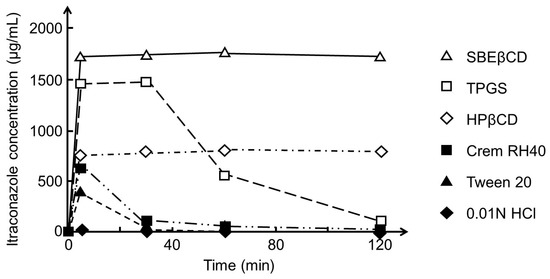
Figure 6.
Effect of sulfobutylether β-cyclodextrin (SBEβCD), α-tocopheryl succinate esterified to polyethylene glycol 1000 (TPGS), 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin (HPβCD), Cremophor RH40 (Crem RH40), and polysorbate 20 (Tween 20) in aqueous 0.01 M HCl solution on the solubility of itraconazole. An excess amount of dissolve itraconazole (50 mg/mL) in dimethylformamide (DMF) was added to a medium containing no or 2.5% (w/v) of the excipients, and the itraconazole concentration was monitored for 120 min. The equilibrium solubility (S0) of itraconazole was determined to be 21 µg/mL in the HPβCD medium and 206 µg/mL in the SBEβCD medium. Adapted from Brewster et al. with permission [107].
5. Conclusions
Studies have shown that CDs possess peculiar properties that make them rather unique pharmaceutical excipients. CDs are solubilizing complexing agents that increase the aqueous solubility of poorly soluble drugs while also behaving like organic cosolvents such as ethanol. CDs and their complexes can self-assemble to form unstable aggregates that are able to solubilize poorly soluble compounds in a micellar-like fashion. Nanosized CD aggregates can self-assemble further to form stable microparticles that allow for sustained drug delivery after topical administration. CDs can enhance drug delivery through biological membranes without affecting the membrane barriers. CDs can increase drug dissolution in aqueous media and stabilize super-saturated solutions. Few if any other pharmaceutical excipients possess such diverse properties desired by drug formulators. However, at the same time, these properties can result in erroneous interpretations of experimental results.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, T.L.; writing—review and editing, T.L., H.H.S. and P.J.; project administration, T.L. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Loftsson, T.; Duchene, D. Cyclodextrins and their pharmaceutical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 329, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uekama, K. Design and evaluation of cyclodextrin-based drug formulation. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2004, 52, 900–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenyvesi, E.; Szente, L. Cyclodextrin in starchy foods. Acta Aliment. 2021, 50, 417–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puská, I.; Szent, L.; Szőcs, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Recent list of cyclodextrin-containing drug products. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poulson, B.G.; Alsulami, Q.A.; Sharfalddin, A.; El Agammy, E.F.; Mouffouk, F.; Emwas, A.-H.; Jaremko, L.; Jaremko, M. Cyclodextrins: Structural, Chemical, and Physical Properties, and Applications. Polysaccharides 2022, 3, 1–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villiers, A. Sur la fermentation de la fécule par l’action du ferment butyrique. Compt. Rend. Acad. Sci. 1891, 112, 536–538. [Google Scholar]
- Cramer, F. Einschlussverbindungen; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1954. [Google Scholar]
- Crini, G.; Fenyvesi, E.; Szente, L. Outstanding contribution of Professor Jozsef Szejtli to cyclodextrin applications in foods, cosmetics, drugs, chromatography and biotechnology: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2619–2641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; French, A.D.; Kainuma, K.; Jane, J.-L.; Szente, L. Contributions of Dexter French (1918–1981) to cycloamylose/cyclodextrin and starch science. Carbohydr. Polym. 2021, 257, 117620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G. Review: A History of Cyclodextrins. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10940–10975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krabicova, I.; Appleton, S.L.; Tannous, M.; Hoti, G.; Caldera, F.; Pedrazzo, A.R.; Cecone, C.; Cavalli, R.; Trotta, F. History of cyclodextrin nanosponges. Polymers 2020, 12, 1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morin-Crini, N.; Fourmentin, S.; Fenyvesi, E.; Lichtfouse, E.; Torri, G.; Fourmentin, M.; Crini, G. 130 years of cyclodextrin discovery for health, food, agriculture, and the industry: A review. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2021, 19, 2581–2617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; Rajewski, R.A. Sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 583, 119396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saokham, P.; Muankaew, C.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Solubility of Cyclodextrins and Drug/Cyclodextrin Complexes. Molecules 2018, 23, 1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhiman, P.; Bhatia, M. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins and their derivatives. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 98, 171–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, L.; Campos, J.; Veiga, F.; Cardoso, C.; Paiva-Santos, A.C. Cyclodextrin-based delivery systems in parenteral formulations: A critical update review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 178, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations II: Solubilization, binding constant, and complexation efficiency. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 363–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.-X.; Wang, Z.-L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, J.-C.; Zhang, Y.-F. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins. Xiandai Shengwuyixue Jinzhan 2016, 16, 3788–3792. [Google Scholar]
- Jambhekar, S.S.; Breen, P. Cyclodextrins in pharmaceutical formulations I: Structure and physicochemical properties, formation of complexes, and types of complex. Drug Discov. Today 2016, 21, 356–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; Rao, V.M.; Zannou, E.A.; Zia, V. Mechanisms of drug release from cyclodextrin complexes. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 1999, 36, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higuchi, T.; Connors, K.A. Phase Solubility Techniques. Adv. Anal. Chem. Instrum. 1965, 4, 117–212. [Google Scholar]
- Sabadini, E.; Cosgrove, T.; Egidio, F.C. Solubility of cyclomaltooligosaccharides (cyclodextrins) in H2O and D2O: A comparative study. Carbohydr. Res. 2006, 341, 270–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrins as functional excipients: Methods to enhance complexation efficiency. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 3019–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anderson, B.D. Chapter 3. Complexation. In Takero Higuchi: A Memorial Tribute; Equilibria and Thermodynamics; Riley, C.M., Rytting, J.H., Hkral, M.A., Eds.; Allen Press: Lawrence, KS, USA, 1991; Volume 3, pp. 175–426. [Google Scholar]
- Brini, E.; Fennell, C.J.; Fernandez-Serra, M.; Hribar-Lee, B.; Luksic, M.; Dill, K.A. How Water’s Properties Are Encoded in Its Molecular Structure and Energies. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 12385–12414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laage, D.; Elsaesser, T.; Hynes, J.T. Water Dynamics in the Hydration Shells of Biomolecules. Chem. Rev. 2017, 117, 10694–10725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jarisz, T.; Roy, S.; Hore, D.K. Surface Water as a Mediator and Reporter of Adhesion at Aqueous Interfaces. Acc. Chem. Res. 2018, 51, 2287–2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Physicochemical properties of water and its effect on drug delivery—A commentary. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaplin, M. Water Structure and Science. Available online: http://www1.lsbu.ac.uk/water/ (accessed on 10 February 2023).
- Roy, S.; Hore, D.K. Simulated Structure and Nonlinear Vibrational Spectra of Water Next to Hydrophobic and Hydrophilic Solid Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 22867–22877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monroe, J.; Barry, M.; DeStefano, A.; Aydogan Gokturk, P.; Jiao, S.; Robinson-Brown, D.; Webber, T.; Crumlin, E.J.; Han, S.; Shell, M.S. Water Structure and Properties at Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces. Annu. Rev. Chem. Biomol. Eng. 2020, 11, 523–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akamatsu, M.; Fujikawa, M.; Nakao, K.; Shimizu, R. In silico Prediction of Human Oral Absorption Based on QSAR Analyses of PAMPA Permeability. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1845–1866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korjamo, T.; Heikkinen, A.T.; Moenkkoenen, J. Analysis of unstirred water layer in in vitro permeability experiments. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4469–4479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Pharmaceutical applications of cyclodextrins: Effects on drug permeation through biological membranes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 63, 1119–1135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T. Drug permeation through biomembranes: Cyclodextrins and the unstirred water layer. Pharmazie 2012, 67, 363–370. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sandilya, A.A.; Natarajan, U.; Priya, M.H. Molecular View into the Cyclodextrin Cavity: Structure and Hydration. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 25655–25667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soe, H.M.S.H.; Maw, P.D.; Loftsson, T.; Jansook, P. Current Overview of Cyclodextrin-Based Nanocarriers for Enhanced Antifungal Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2022, 15, 1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szejtli, J. Introduction and General Overview of Cyclodextrin Chemistry. Chem. Rev. 1998, 98, 1743–1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, A.W.; Nicolis, I.; Keller, N.; Dalbiez, J.P. Aggregation of cyclodextrins: An explanation of the abnormal solubility of β-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Mol. Recognit. Chem. 1992, 13, 139–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottari, C.; Comez, L.; Paolantoni, M.; Corezzi, S.; D’Amico, F.; Gessini, A.; Masciovecchio, C.; Rossi, B. Hydration properties and water structure in aqueous solutions of native and modified cyclodextrins by UV Raman and Brillouin scattering. J. Raman Spectrosc. 2018, 49, 1076–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, M.E.; Brewster, M.E. Cyclodextrin-based pharmaceutics: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004, 3, 1023–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malanga, M.; Szemán, J.; Fenyvesi, É.; Puskás, I.; Csabai, K.; Gyémánt, G.; Fenyvesi, F.; Szente, L. “Back to the Future”: A New Look at Hydroxypropyl Beta-Cyclodextrins. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2921–2931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryzhakov, A.; Thi, T.D.; Stappaerts, J.; Bertoletti, L.; Kimpe, K.; Couto, A.R.S.; Saokham, P.; Van den Mooter, G.; Augustijns, P.; Somsen, G.W.; et al. Self-assembly of cyclodextrins and their complexes in aqueous solutions. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 105, 2556–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Saokham, P.; Sa Couto, A.R. Self-association of cyclodextrins and cyclodextrin complexes in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 560, 228–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.F.; Fu, P.; Shen, X.H.; Gao, H.C. Cyclodextrin-based aggregates and characterization by microscopy. Micron 2008, 39, 495–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cova, T.F.G.G.; Cruz, S.M.A.; Valente, A.J.M.; Abreu, P.E.; Marques, J.M.C.; Pais, A.C.C. Aggregation of cyclodextrins: Fundamental issues and applications. In Cyclodextrin Fundamentals, Reactivity and Analysis; Fourmentin, S., Crini, G., Lichtfouse, E., Eds.; Springer Nature Switzerland AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 45–65. [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Gaitano, G.; Rodriguez, P.; Isasi, J.R.; Fuentes, M.; Tardajos, G.; Sanchez, M. The aggregation of cyclodextrins as studied by photon correlation spectroscopy. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messner, M.; Kurkov, S.V.; Jansook, P.; Loftsson, T. Self-assembled cyclodextrin aggregates and nanoparticles. Int. J. Pharm. 2010, 387, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyajima, K.; Sawada, M.; Nakagaki, M. Viscosity B-cofficients, apparent molar volumes, and activity coefficients for α- and γ-cyclodextrins in aqueous solutions. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 1983, 56, 3556–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonini, M.; Rossi, S.; Karlsson, G.; Almgren, M.; Lo Nostro, P.; Baglioni, P. Self-assembly of β-cyclodextrin in water. Part 1: Cryo-TEM and dynamic and static light scattering. Langmuir 2006, 22, 1478–1484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Häusler, O.; Müller-Goymann, C.C. Properties and Structure of Aqueous Solutions of Hydroxypropyl-beta-Cyclodextrin. Starch-Stärke 1993, 45, 183–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, A.; Shen, X.; He, Y. Micrometer-sized rodlike structure formed by the secondary assembly of cyclodextrin nanotube. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 302, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Stefansson, E. Aqueous eye drops containing drug/cyclodextrin nanoparticles deliver therapeutic drug concentrations to both anterior and posterior segment. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 80, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins in Parenteral Formulations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 654–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Magnúsdóttir, A.; Másson, M.; Sigurjónsdóttir, J.F. Self-association and cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. J. Pharm. Sci. 2002, 91, 2307–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Magnusdottir, A.; Másson, M.; Loftsson, T. Self Association and Cyclodextrin Solubilization of NSAIDs. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2002, 44, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schönbeck, C.; Madsen, T.L.; Peters, G.H.; Holm, R.; Loftsson, T. Soluble 1:1 complexes and insoluble 3:2 complexes—Understanding the phase-solubility diagram of hydrocortisone and γ-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 531, 504–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, H.; Kumar, M.; Gupta, S.; Sekharan, T.R.; Tamilvanan, S. Influence of hydrophilic polymers addition into cinnarizine-β-cyclodextrin complexes on drug solubility, drug liberation behaviour and drug permeability. Polym. Bull. 2018, 75, 2987–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Do, T.T.; Van Hooghten, R.; Van den Mooter, G. A study of the aggregation of cyclodextrins: Determination of the critical aggregation concentration, size of aggregates and thermodynamics using isodesmic and K2–K models. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 521, 318–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fulop, Z.; Gref, R.; Loftsson, T. A permeation method for detection of self-aggregation of doxorubicin in aqueous environment. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 454, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Hreinsdottir, D.; Masson, M. The complexation efficiency. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2007, 57, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, L.N.C.; Tavares, A.C.M.; Ferreira, B.T.; Reis, A.K.C.A.; Katiki, L.M. Inclusion complexes and self-assembled cyclodextrin aggregates for increasing the solubility of benzimidazoles. Braz. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 55, e17776/1–e17776/11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Hreinsdottir, D.; Masson, M. Evaluation of cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2005, 302, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Másson, M.; Brewster, M.E. Self-Association of Cyclodextrins and Cyclodextrin Complexes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2004, 93, 1091–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Másson, M.; Sigurjónsdóttir, J.F.; Jónsdóttir, S.; Loftsson, T. Examination of 19F-NMR as a Tool for Investigation of Drug-Cyclodextrin Complexes. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2003, 29, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uekama, K.; Hirayama, F.; Nasu, S.; Matsuo, N.; Irie, T. Determination of the stability constants for inclusion complexes of cyclodextrins with various drug molecules by high performance liquid chromatography. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 1978, 26, 3477–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ugwu, S.O.; Alcala, M.J.; Bhardwaj, R.; Blanchard, J. Characterization of the complexation of diflunisal with hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 1999, 19, 391–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sideris, E.E.; Valsami, G.N.; Koupparis, M.A.; Macheras, P.E. Studies on the interaction of diflunisal ion with cyclodextrins using ion-selective electrode potentiometry. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 1999, 7, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguilar, N.M.; Perez-Aguilar, J.M.; Gonzalez-Coronel, V.J.; Soriano Moro, J.G.; Sanchez-Gaytan, B.L. Polymers as Versatile Players in the Stabilization, Capping, and Design of Inorganic Nanostructures. ACS Omega 2021, 6, 35196–35203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shvets, A. Theory of Colloidal Stabilization by Unattached Polymers; Cornell University Library: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Antunes, F.E.; Marques, E.F.; Miguel, M.G.; Lindman, B. Polymer–vesicle association. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2009, 147–148, 18–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Chatterjee, T.; Woo, S.H. Enhanced solubilization of phenanthrene in Triton X-100 solutions by the addition of small amounts of chitosan. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 163, 450–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attwood, D.; Florence, A.T. Surfactant Systems. Their Chemistry, Pharmacy and Biology; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 1983; p. 794. [Google Scholar]
- Goddard, E.D.; Ananthapadmanabhan, K.P. Interactions of Surfactants with Polymers and Proteins; CRC: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1992; p. 427. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Gao, H.; Ye, Z.; Deng, J.; Ouyang, D. In silico formulation prediction of drug/cyclodextrin/polymer ternary complexes by machine learning and molecular modeling techniques. Carbohydr. Polym. 2022, 275, 118712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chadha, R.; Bala, M.; Goyal, P.; Chadha, K.; Karan, M. Role of Polymers in Ternary Drug Cyclodextrin Complexes; Scrivener Publishing LLC: Beverly, MA, USA, 2015; pp. 413–438. [Google Scholar]
- Loftsson, T.; Fridriksdottir, H.; Sigurdardottir, A.M.; Ueda, H. The effect of water-soluble polymers on drug-cyclodextrin complexation. Int. J. Pharm. 1994, 110, 169–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Guðmundsdóttir, T.K.; Friðriksdóttir, H. The influence of water-soluble polymers and pH on hydroxylpropyl-β-cyclodextrin complexation of drugs. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 1996, 22, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suvarna, P.; Chaudhari, P.; Lewis, S.A. Cyclodextrin-Based Supramolecular Ternary Complexes: Emerging Role of Ternary Agents on Drug Solubility, Stability, and Bioavailability. Crit. Rev. Ther. Drug Carr. Syst. 2022, 39, 1–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harada, A.; Hashidzume, A.; Yamaguchi, H.; Takashima, Y. CD-based polymeric rotaxanes. Chem. Rev. 2009, 109, 5974–6023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Friðriksdóttir, H. The effect of water-soluble polymers on the aqueous solubility and complexing abilities of β-cyclodextrin. Int. J. Pharm. 1998, 163, 115–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fenyvesi, E.; Vikmon, M.; Szeman, J.; Redenti, E.; Delcanale, M.; Ventura, P.; Szejtli, J. Interaction of hydroxy acids with beta-cyclodextrin. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 1999, 33, 339–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Redenti, E.; Szente, L.; Szejtli, J. Drug/cyclodextrin/hydroxy acid multicomponent systems. Properties and pharmaceutical applications. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Matthiasson, K.; Masson, M. The effects of organic salts on the cyclodextrin solubilization of drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2003, 262, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Brewster, M.E. Complex formation. In Remington, the Science and Practice of Pharmacy, 22nd ed.; Allen, L.V., Ed.; Pharmaceutical Press: London, UK, 2013; Volume 1, pp. 681–692. [Google Scholar]
- Sripetch, S.; Prajapati, M.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins and Drug Membrane Permeation: Thermodynamic Considerations. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 111, 2571–2580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djajic, N.; Otasevic, B.; Malenovic, A.; Zecevic, M.; Holzgrabe, U.; Protic, A. Corona Charged Aerosol Detector in studying retention and β-cyclodextrin complex stability using RP-HPLC. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 193, 113711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loftsson, T.; Moya-Ortega, M.D.; Alvarez-Lorenzo, C.; Concheiro, A. Pharmacokinetics of cyclodextrins and drugs after oral and parenteral administration of drug/cyclodextrin complexes. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2016, 68, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stella, V.J.; He, Q. Cyclodextrins. Toxicol. Pathol. 2008, 36, 30–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyazaki, K.; Kishimoto, H.; Muratani, M.; Kobayashi, H.; Shirasaka, Y.; Inoue, K. Mucins are Involved in the Intestinal Permeation of Lipophilic Drugs in the Proximal Region of Rat Small Intestine. Pharm. Res. 2019, 36, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, M.E.V.; Sjövall, H.; Hansson, G.C. The gastrointestinal mucus system in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 10, 352–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, M.E.; Noppe, M.; Peeters, J.; Loftsson, T. Effect of the unstirred water layer on permeability enhancement by hydrophilic cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 2007, 342, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Vogensen, S.B.; Brewster, M.E.; Konradsdottir, F. Effects of cyclodextrins on drug delivery through biological membranes. J. Pharm. Sci. 2007, 96, 2532–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stappaerts, J.; Berben, P.; Cevik, I.; Augustijns, P. The effect of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin on the intestinal permeation through mucus. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 114, 238–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aihara, R.; Messerschmid, R.; Mizoguchi, M.; Wada, K.; Minami, K.; Higashino, H.; Takagi, T.; Kataoka, M.; Yamashita, S. In vitro-in vivo correlation in the effect of cyclodextrin on oral absorption of poorly soluble drugs. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 600, 120494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tzanova, M.M.; Moretti, F.; Grassi, G.; Stein, P.C.; Hiorth, M.; Abrami, M.; Grassi, M.; di Cagno, M.P. Modelling drug diffusion through unstirred water layers allows real-time quantification of free/loaded drug fractions and release kinetics from colloidal-based formulations. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2022, 178, 168–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truzzi, E.; Rustichelli, C.; de Oliveira Junior, E.R.; Ferraro, L.; Maretti, E.; Graziani, D.; Botti, G.; Beggiato, S.; Iannuccelli, V.; Lima, E.M.; et al. Nasal biocompatible powder of Geraniol oil complexed with cyclodextrins for neurodegenerative diseases: Physicochemical characterization and in vivo evidences of nose to brain delivery. J. Control. Release 2021, 335, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, S.; Dai, W.-G. Drug precipitation inhibitors in supersaturable formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvani, A.; Shayanfar, A. Solution Stability of Pharmaceutical Cocrystals. Cryst. Growth Des. 2022, 22, 6323–6337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Price, D.J.; Ditzinger, F.; Koehl, N.J.; Jankovic, S.; Tsakiridou, G.; Nair, A.; Holm, R.; Kuentz, M.; Dressman, J.B.; Saal, C. Approaches to increase mechanistic understanding and aid in the selection of precipitation inhibitors for supersaturating formulations—A PEARRL review. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2018, 71, 483–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dokoumetzidis, A.; Macheras, P. A century of dissolution research: From Noyes and Whitney to the Biopharmaceutics Classification System. Int. J. Pharm. 2006, 321, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anzai, K.; Mizoguchi, J.-i.; Yanagi, T.; Hirayama, F.; Arima, H.; Uekama, K. Improvement of Dissolution Properties of a New Helicobacter pylori Eradicating Agent (TG44) by Inclusion Complexation with β-Cyclodextrin. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2007, 55, 1466–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loftsson, T.; Sigurðsson, H.H.; Másson, M.; Schipper, N. Preparation of solid drug/cyclodextrin complexes of acidic and basic drugs. Pharmazie 2004, 59, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Torres-Labandeira, J.J.; Davignon, P.; Pitha, J. Oversaturated Solutions of Drug in Hydroxypropylcyclodextrins: Parenteral Preparation of Pancratistatin. J. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 80, 384–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustijns, P.; Brewster, M.E. Supersaturating Drug Delivery Systems: Fast is Not Necessarily Good Enough. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 101, 7–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada-Hirai, A.; Shimizu, S.; Ichii, R.; Tsunoda, C.; Hiroshige, R.; Fujita, M.; Li, Y.-P.; Shimada, Y.; Otsuka, Y.; Goto, S. Stabilization of the Metastable α–Form of Indomethacin Induced by the Addition of 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin, Causing Supersaturation (Spring) and Its Sustaining Deployment (Parachute). J. Pharm. Sci. 2021, 110, 3623–3630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Vandecruys, R.; Peeters, J.; Neeskens, P.; Verreck, G.; Loftsson, T. Comparative interaction of 2-hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin and sulfobutylether-β-cyclodextrin with itraconazole: Phase-solubility behavior and stabilization of supersaturated drug solutions. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 34, 94–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).