Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
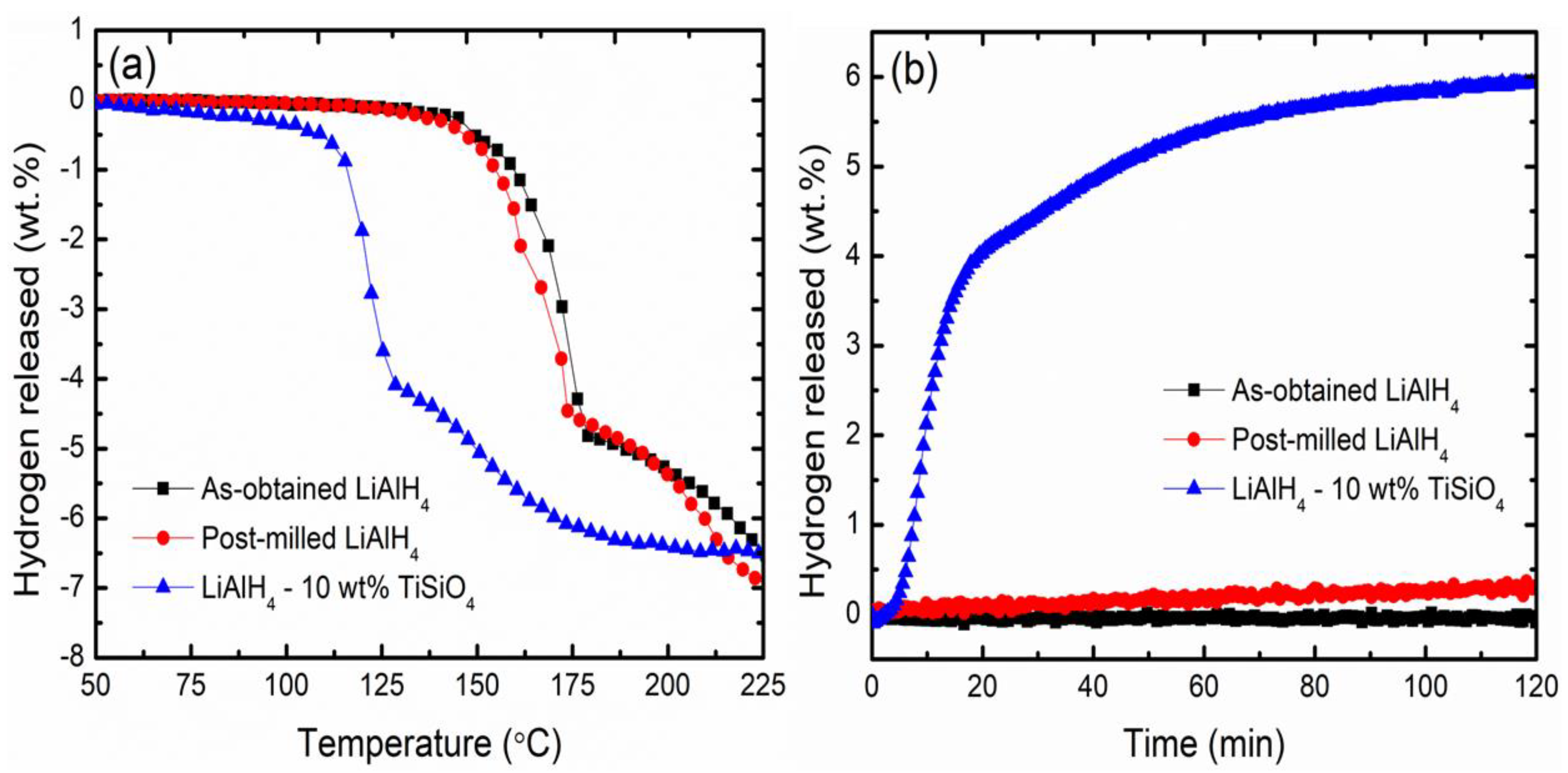
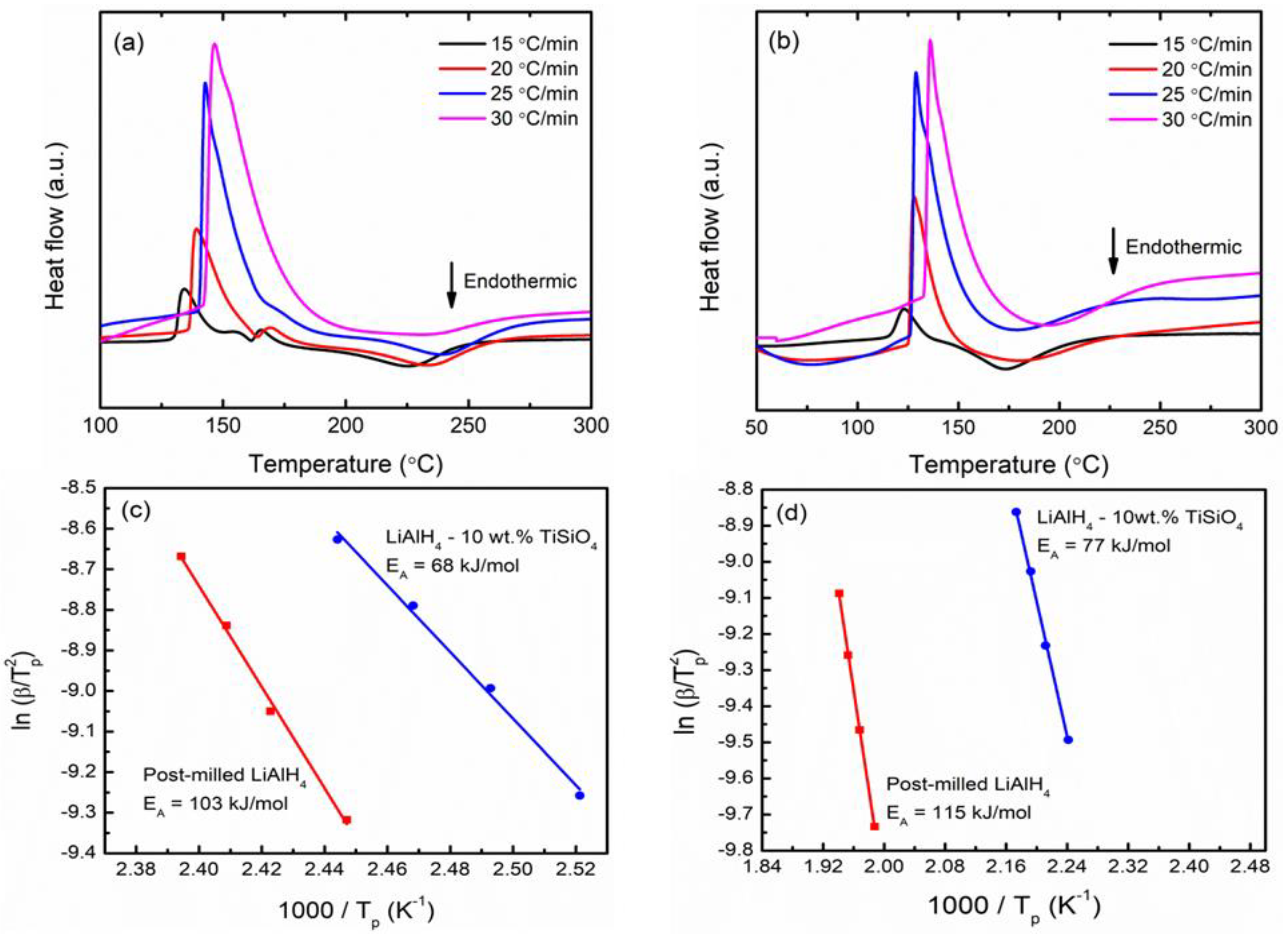
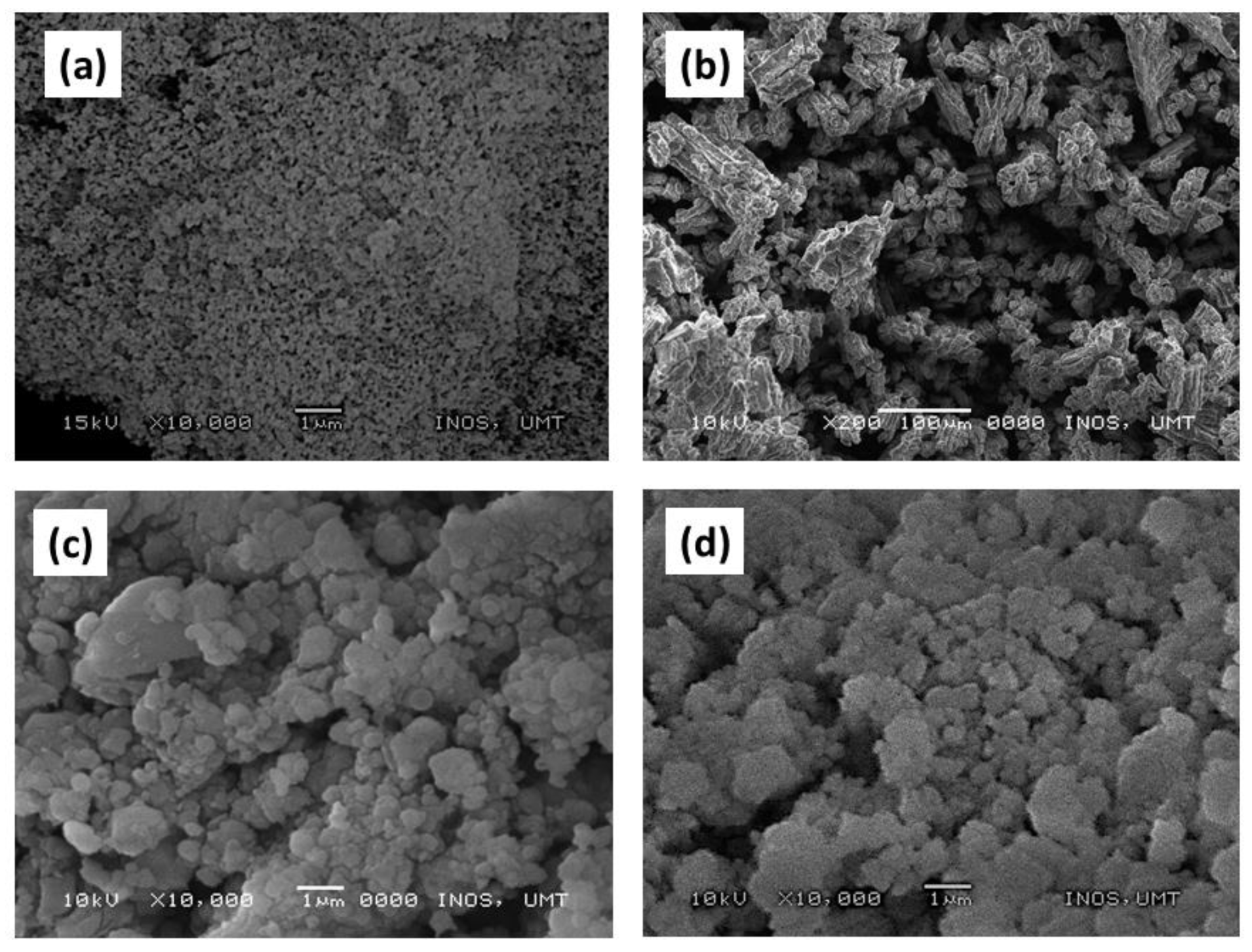
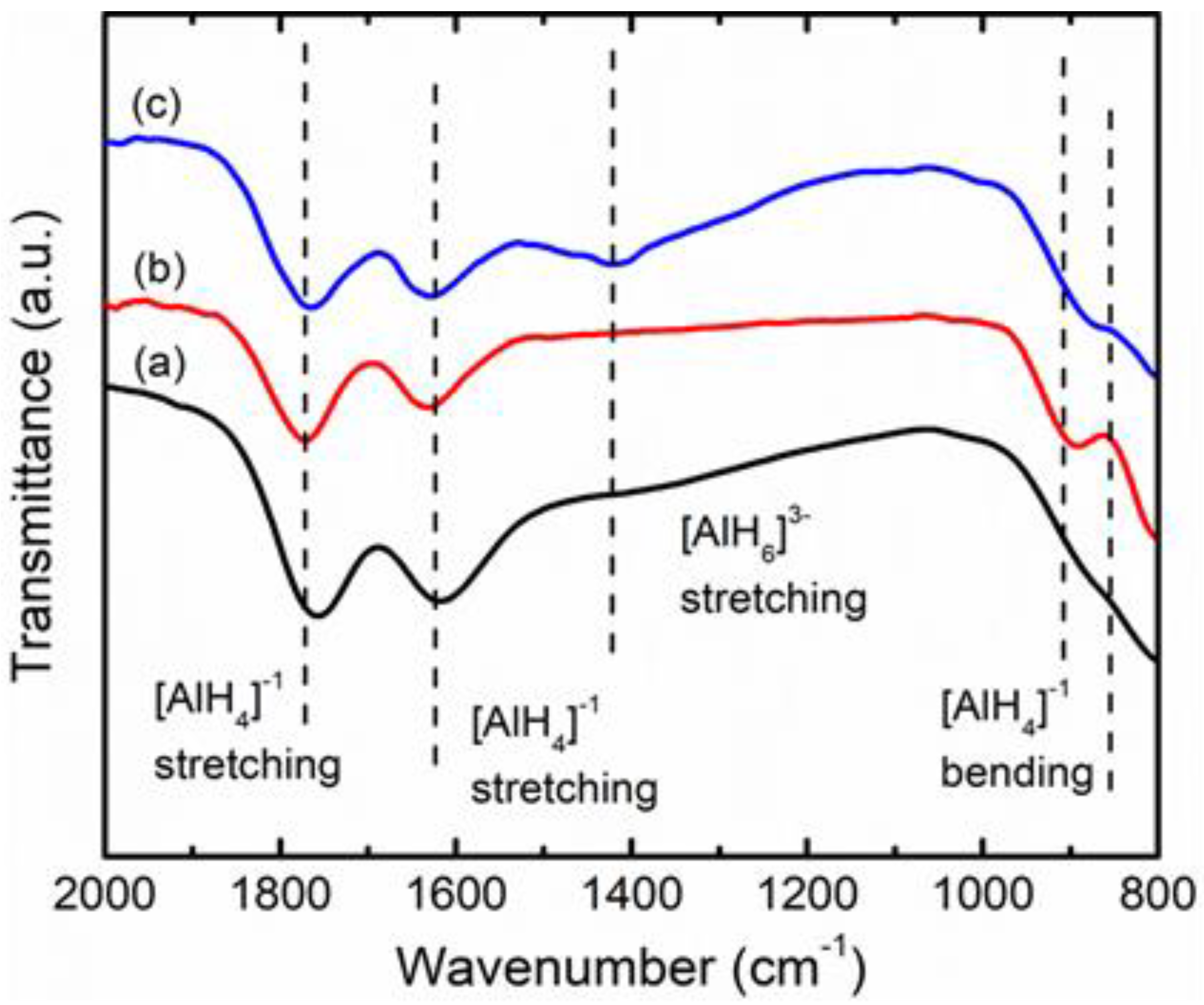
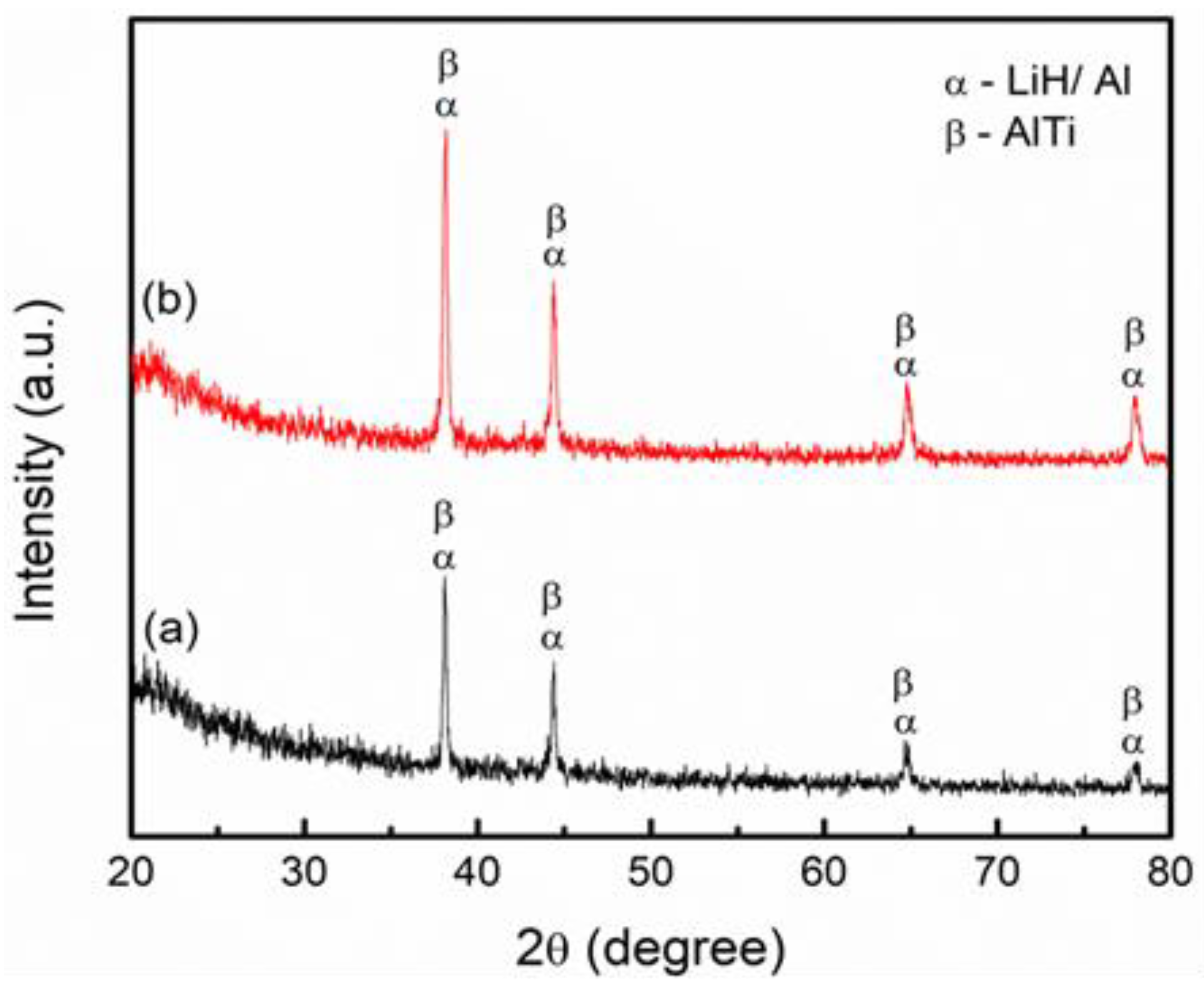
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, Y.; Lu, J.; Ding, J.; Wang, W.; Yan, J. Numerical simulation on the storage performance of a phase change materials based metal hydride hydrogen storage tank. Appl. Energy 2020, 278, 115682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Zhang, J. A review of high density solid hydrogen storage materials by pyrolysis for promising mobile applications. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2021, 60, 2737–2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivard, E.; Trudeau, M.; Zaghib, K. Hydrogen storage for mobility: A review. Materials 2019, 12, 1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, J.; Shabani, B. A critical study of stationary energy storage policies in Australia in an international context: The role of hydrogen and battery technologies. Energies 2016, 9, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schlapbach, L.; Züttel, A. Hydrogen-storage materials for mobile applications. J. Nat. 2001, 414, 353–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mustafa, N.S.; Yahya, M.S.; Itam Sulaiman, N.N.; Yap, F.A.H.; Ismail, M. Enhanced the hydrogen storage properties and reaction mechanisms of 4MgH2+ LiAlH4 composite system by addition with TiO2. Int. J. Energy Res. 2021, 45, 21365–21374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehabadi, A.; Umar, M.F.; Ahmad, A.; Ahmad, M.I.; Ismail, N.; Rafatullah, M. Carbon-based nanocomposites in solid-state hydrogen storage technology: An overview. Int. J. Energy. Res. 2020, 44, 11044–11058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egeland-Eriksen, T.; Hajizadeh, A.; Sartori, S. Hydrogen-based systems for integration of renewable energy in power systems: Achievements and perspectives. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 31963–31983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DOE Technical Targets for Onboard Hydrogen Storage for Light-Duty Vehicles. Available online: https://www.energy.gov/eere/fuelcells/doe-technical-targets-onboard-hydrogen-storage-light-duty-vehicles (accessed on 19 February 2023).
- Aziz, M.; Wijayanta, A.T.; Nandiyanto, A.B.D. Ammonia as effective hydrogen storage: A review on production, storage and utilization. Energies 2020, 13, 3062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Liu, F.; Wang, H.; Liu, J.; Yang, X.-S.; Sun, L.; Zhu, M. Magnesium-based hydrogen storage compounds: A review. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 832, 154865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, L.; Chen, K.; Jiang, J.; Yang, X.-S.; Zhu, M. Hydrogen storage in light-metal based systems: A review. J. Alloy. Compd. 2020, 829, 154597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Ismail, M. Advanced hydrogen storage of the Mg–Na–Al system: A review. J. Magnes. Alloy 2021, 9, 1111–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ismail, M. An overview of reactive hydride composite (RHC) for solid-state hydrogen storage materials. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 31674–31698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Idris, N.H.; Din, M.M.; Ismail, M. Desorption properties of LiAlH4 doped with LaFeO3 catalyst. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 11953–11960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Mustafa, N.S.; Sazelee, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Modifying the hydrogen storage performances of NaBH4 by catalyzing with MgFe2O4 synthesized via hydrothermal method. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2019, 44, 6720–6727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim Yap, F.A.; Ali, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Catalytic effect of MgFe2O4 on the hydrogen storage properties of Na3AlH6–LiBH4 composite system. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2018, 43, 20882–20891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juahir, N.; Mustafa, N.S.; Yap, F.A.H.; Ismail, M. Study on the hydrogen storage properties and reaction mechanism of NaAlH4–Mg(BH4)2 (2:1) with and without TiF3 additive. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2015, 40, 7628–7635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Yahya, M.S.; Ali, N.A.; Idris, N.H.; Ismail, M. Enhancement of dehydrogenation properties in LiAlH4 catalysed by BaFe12O19. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 835, 155183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.; Fang, F.; Zhou, G.; Chen, G.; Ouyang, L.; Zhu, M.; Sun, D. Hydrogen storage properties of space-confined NaAlH4 nanoparticles in ordered mesoporous silica. Chem. Mater. 2008, 20, 3954–3958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigma-Aldrich. Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/MY/en/campaigns/connected-lab-instrumentation (accessed on 20 February 2023).
- Ahmad, M.A.N.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Ismail, M. Enhancing the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4 using K2NiF6 as additive. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 24843–24851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, J. Advanced Doping Techniques and Dehydrogenation Properties of Transition Metal-Doped LiAlH4 for Fuel Cell Systems. Ph.D Thesis, Dresden University of Technology, Dresden, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Orimo, S.-I.; Nakamori, Y.; Eliseo, J.R.; Züttel, A.; Jensen, C.M. Complex hydrides for hydrogen storage. Chem. Rev. 2007, 107, 4111–4132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liang, C.; Zhou, H.; Gao, M.; Pan, H.; Wang, Q. A novel catalyst precursor K2TiF6 with remarkable synergetic effects of K, Ti and F together on reversible hydrogen storage of NaAlH4. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 1740–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreasen, A.; Vegge, T.; Pedersen, A.S. Dehydrogenation kinetics of as-received and ball-milled LiAlH4. J. Solid State Chem. 2005, 178, 3672–3678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Sun, L.-X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, F.; Zhang, J.; Chu, H.-L.; Fan, M.Q.; Zhang, T.; Song, X.Y.; Grolier, J.P. Effect of ball milling time on the hydrogen storage properties of TiF3-doped LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 8079–8085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; McGrady, G.S.; Langmi, H.W.; Jensen, C.M. Facile cycling of Ti-doped LiAlH4 for high performance hydrogen storage. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5032–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Li, P.; Wan, Q.; Zhai, F.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, K.; Wang, L.; Lü, S.; Zou, L.; Qu, X.; et al. Dehydrogenation improvement of LiAlH4 catalyzed by Fe2O3 and Co2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2013, 117, 18343–18352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Resan, M.; Hampton, M.D.; Lomness, J.K.; Slattery, D.K. Effects of various catalysts on hydrogen release and uptake characteristics of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2005, 30, 1413–1416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, V.P.; Wiench, J.W.; Dennis, K.W.; Pruski, M.; Pecharsky, V.K. Titanium catalyzed solid-state transformations in LiAlH4 during high-energy ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2001, 329, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shenglin, L.; Qiuhua, M.; Xueping, Z.; Xin, F.; Guo, X.; Jiaojiao, Z. Influences of Y2O3 doping on hydrogen release property of LiAlH4. Rare Metal Mat. Eng. 2014, 43, 287–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Ouyang, L. Catalytic effect of ScCl3 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 762, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Zbroniec, L. Fast and slow dehydrogenation of ball milled lithium alanate (LiAlH4) catalyzed with manganese chloride (MnCl2) as compared to nanometric nickel catalyst. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, S736–S739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sazelee, N.A.; Ismail, M. Recent advances in catalyst-enhanced LiAlH4 for solid-state hydrogen storage: A review. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2021, 46, 9123–9141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, F.; Li, P.; Sun, A.; Wu, S.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y.; Cui, L.; Qu, X. Significantly improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 destabilized by MnFe2O4 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11939–11945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.; Nevirkovets, I.; Dou, S. Significantly improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 catalysed with TiO2 nanopowder. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 8327–8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuanhui, Q.; Ping, L.; Zhang, L.; Ahmad, M. Hydrogen sorption improvement of LiAlH4 catalyzed by Nb2O5 and Cr2O3 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2011, 115, 13088–13099. [Google Scholar]
- Ismail, M.; Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.A.; Suwarno, S. Catalytic effect of Al2TiO5 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2022, 47, 31903–31910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Suwarno, S. Catalytic effect of SrTiO3 on the dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 855, 157475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; An, C.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Qiu, F.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H. Enhancement of the H2 desorption properties of LiAlH4 doping with NiCo2O4 nanorods. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 4414–4420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.-S.; Li, Z.-B.; Jiao, C.-L.; Si, X.-L.; Yang, L.-N.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, H.Y.; Huang, F.L.; Gabelica, Z.; Schick, C.; et al. Improved reversible hydrogen storage of LiAlH4 by nano-sized TiH2. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 2770–2777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Ranjbar, A.; Dou, S.X. Improved hydrogen desorption in lithium alanate by addition of SWCNT–metallic catalyst composite. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 3593–3599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Zhao, Y.; Yu, X.B.; Dou, S.X. Effects of NbF5 addition on the hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2010, 35, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czujko, T.; Oleszek, E.E.; Szot, M. New aspects of MgH2 morphological and structural changes during high-energy ball milling. Materials 2020, 13, 4550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Révész, Á.; Gajdics, M. Improved H-storage performance of novel Mg-based nanocomposites prepared by high-energy ball milling: A review. Energies 2021, 14, 6400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varin, R.A.; Czujko, T.; Wronski, Z. Particle size, grain size and γ-MgH2 effects on the desorption properties of nanocrystalline commercial magnesium hydride processed by controlled mechanical milling. Nanotechnology 2006, 17, 3856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, J.; Zang, L.; Zhao, L.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Dehydrogenation characteristics of LiAlH4 improved by in-situ formed catalysts. J. Energy Chem. 2016, 25, 868–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, N.A.; Ahmad, M.A.N.; Yahya, M.S.; Sazelee, N.; Ismail, M. Improved dehydrogenation properties of LiAlH4 by addition of nanosized CoTiO3. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devrim, Y.; Erkan, S.; Bac, N.; Eroglu, I. Improvement of PEMFC performance with Nafion/inorganic nanocomposite membrane electrode assembly prepared by ultrasonic coating technique. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2012, 37, 16748–16758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balema, V.P.; Pecharsky, V.K.; Dennis, K.W. Solid state phase transformations in LiAlH4 during high-energy ball-milling. J. Alloys Compd. 2000, 313, 69–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, Y.; Zhang, H.; Sun, Y.; Sun, L.; Xu, F.; Sun, S.; Zhang, G.; Huang, P.; Du, Y.; Wang, J.; et al. Dehybridization effect in improved dehydrogenation of LiAlH4 by doping with two-dimensional Ti3C2. Mater. Today Nano 2019, 8, 100054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafi ud, d.; Zhang, L.; Ping, L.; Xuanhui, Q. Catalytic effects of nano-sized TiC additions on the hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4. J. Alloy. Compd. 2010, 508, 119–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zang, L.; Cai, J.; Zhao, L.; Gao, W.; Liu, J.; Wang, Y. Improved hydrogen storage properties of LiAlH4 by mechanical milling with TiF3. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 647, 756–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, M.; Yahya, M.S.; Sazelee, N.A.; Ali, N.A.; Yap, F.A.H.; Mustafa, N.S. The effect of K2SiF6 on the MgH2 hydrogen storage properties. J. Magnes. Alloy 2020, 8, 832–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranjbar, A.; Guo, Z.; Yu, X.; Attard, D.; Calka, A.; Liu, H.-K. Effects of SiC nanoparticles with and without Ni on the hydrogen storage properties of MgH2. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2009, 34, 7263–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurko, S.; Rašković, Ž.; Novaković, N.; Mamula, B.P.; Jovanović, Z.; Baščarević, Z.; Novaković, J.G.; Matović, L. Hydrogen storage properties of MgH2 mechanically milled with α and β SiC. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2011, 36, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yusnizam, N.Y.; Ali, N.A.; Sazelee, N.; Ismail, M. Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials 2023, 16, 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
Yusnizam NY, Ali NA, Sazelee N, Ismail M. Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials. 2023; 16(6):2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
Chicago/Turabian StyleYusnizam, Nurul Yasmeen, Nurul Amirah Ali, Noratiqah Sazelee, and Mohammad Ismail. 2023. "Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4" Materials 16, no. 6: 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178
APA StyleYusnizam, N. Y., Ali, N. A., Sazelee, N., & Ismail, M. (2023). Boosting the Dehydrogenation Properties of LiAlH4 by Addition of TiSiO4. Materials, 16(6), 2178. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16062178










