Flexural Behavior Characteristics of Steel Tubes Filled with SFRCCs Incorporating Recycled Materials
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Program
2.1. Test Specimens
2.2. Materials
2.3. Mechanical Properties of Cement Composites
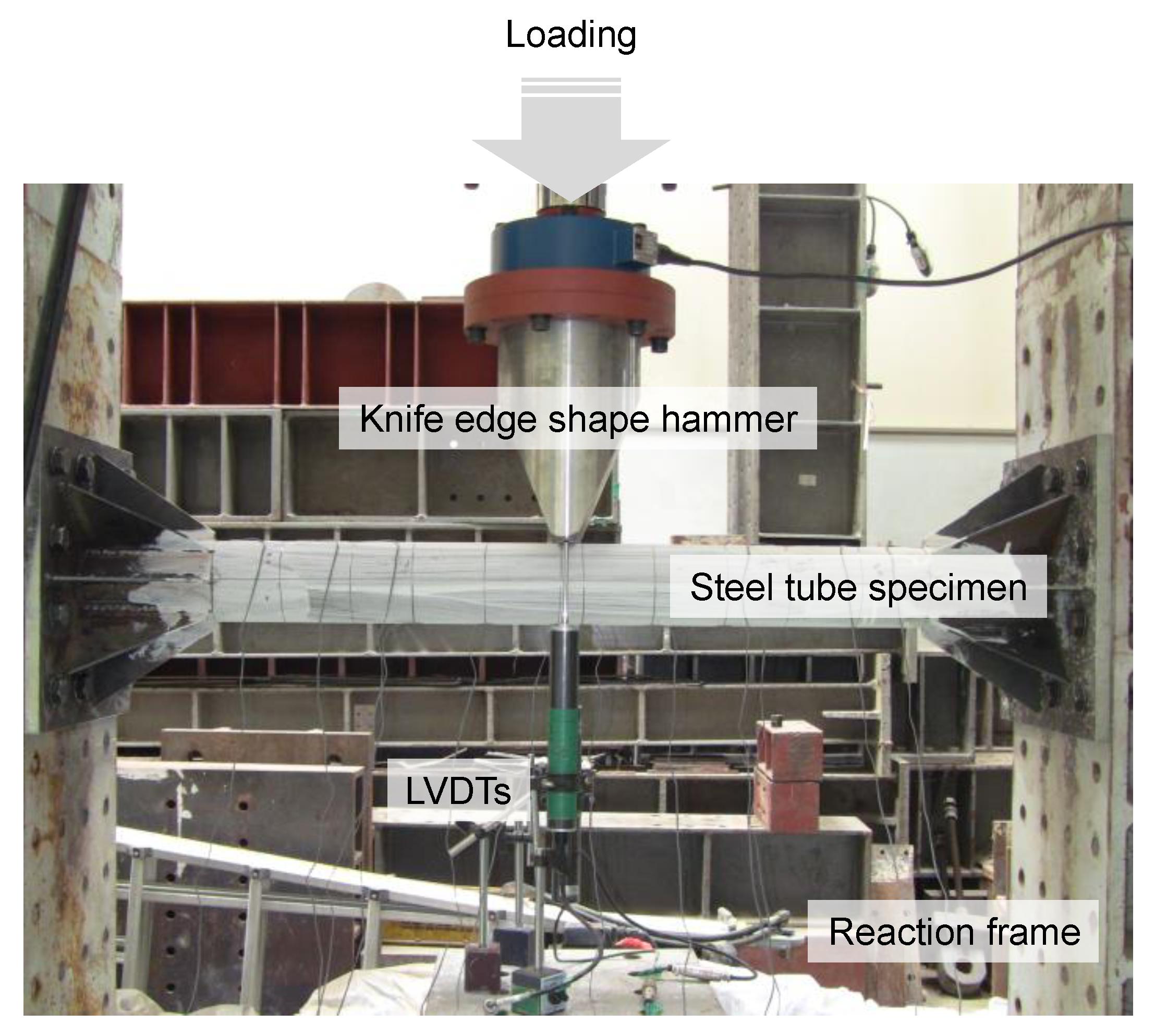
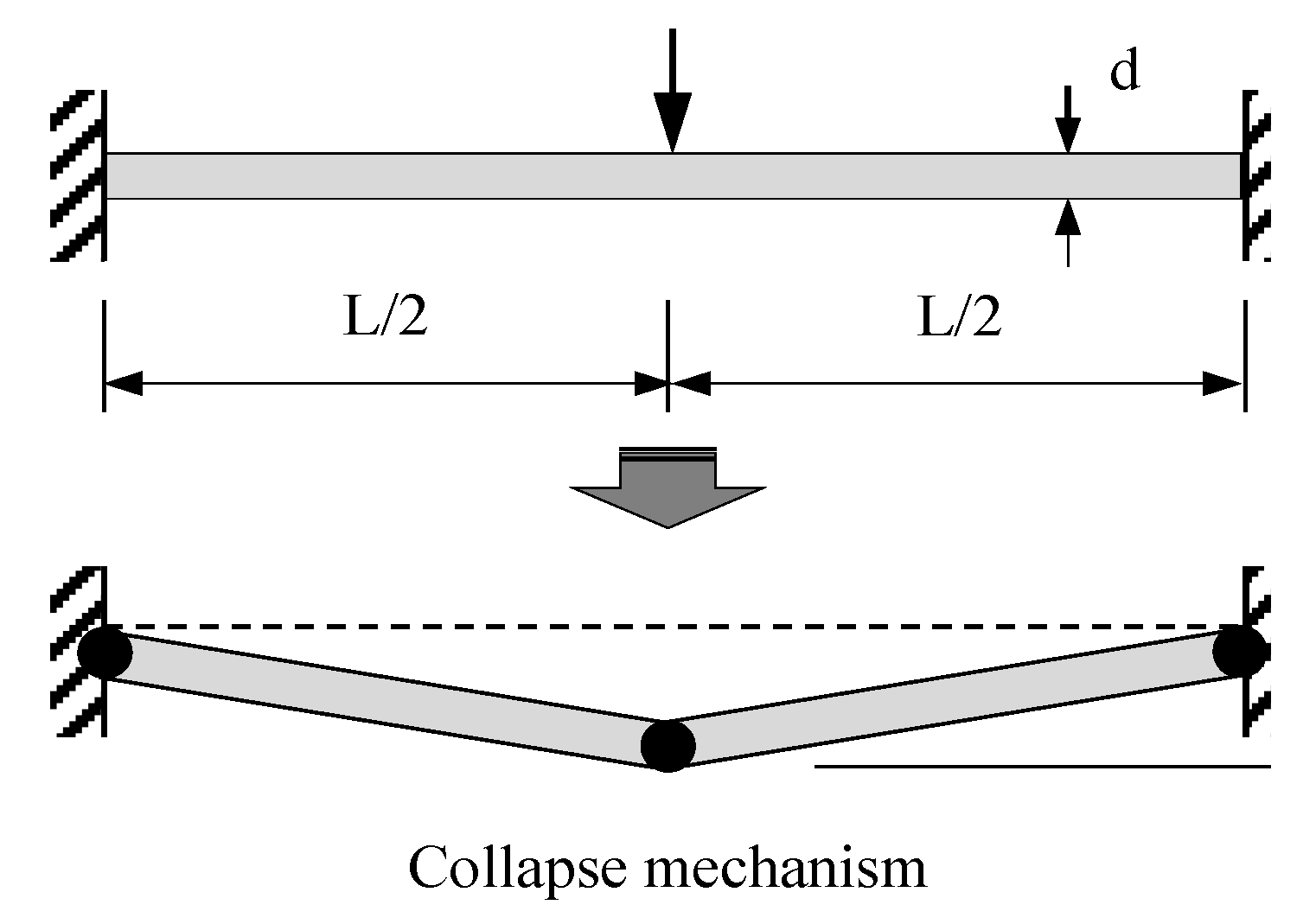
2.4. Flexural Test Method
3. Experimental Results and Discussion
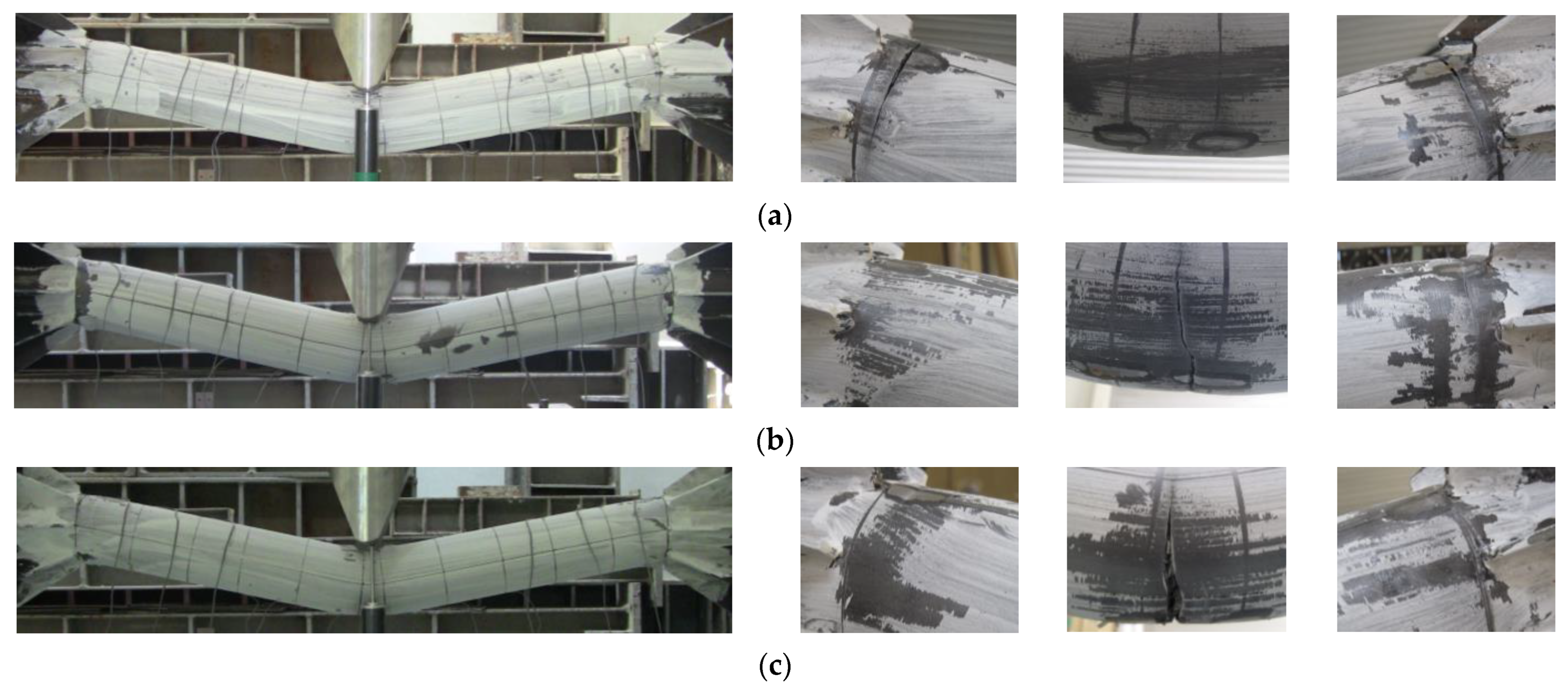
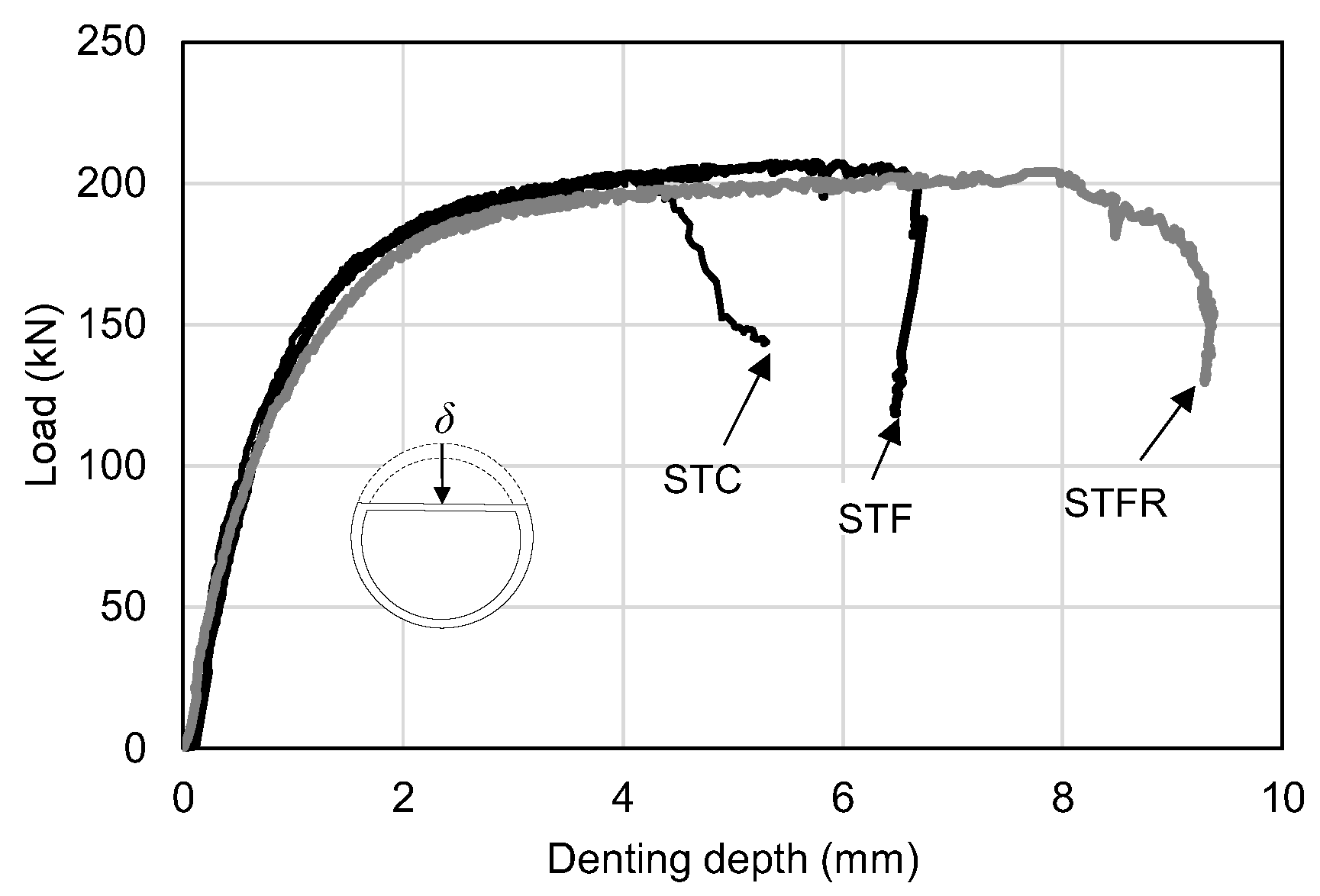
3.1. Failure Modes
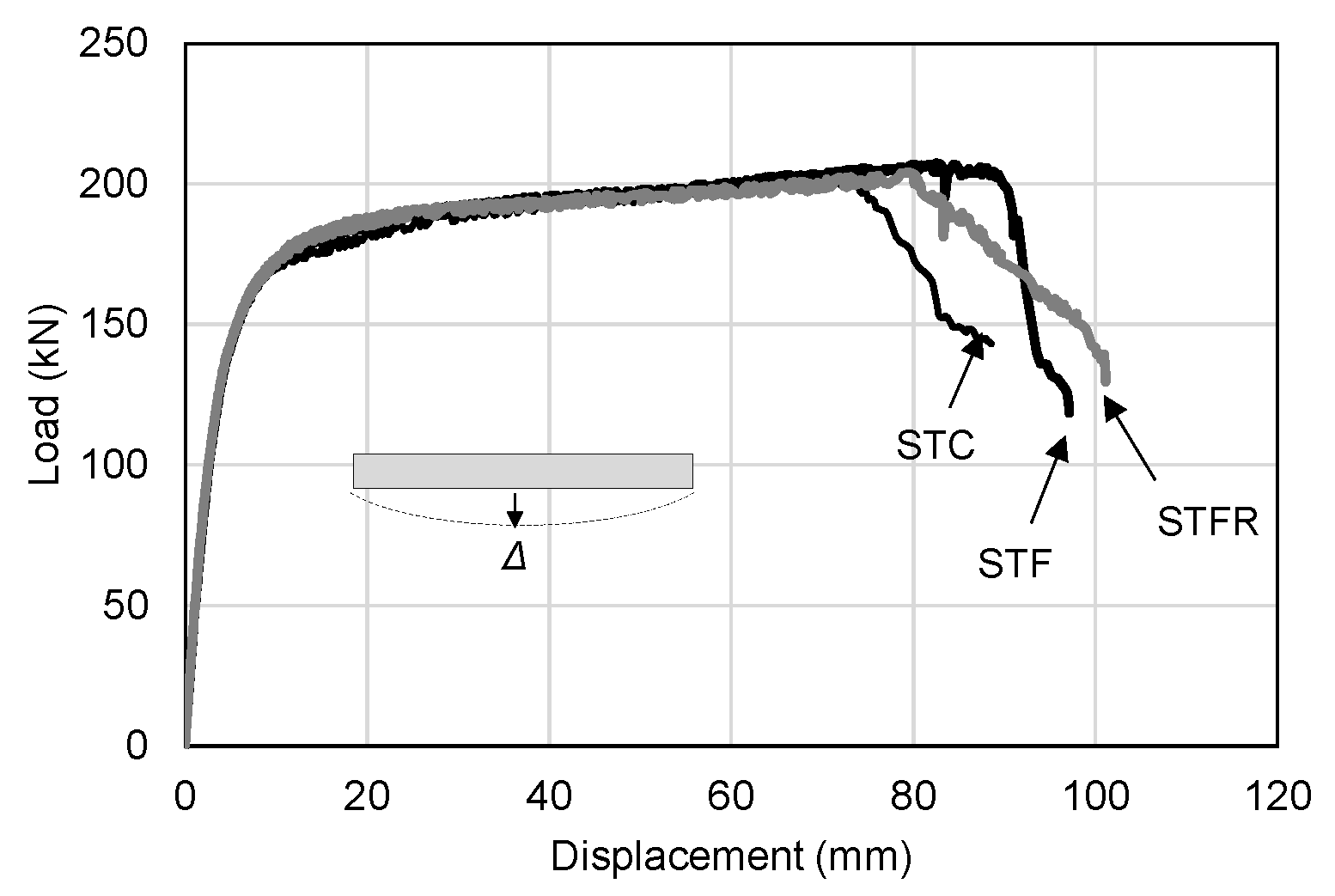
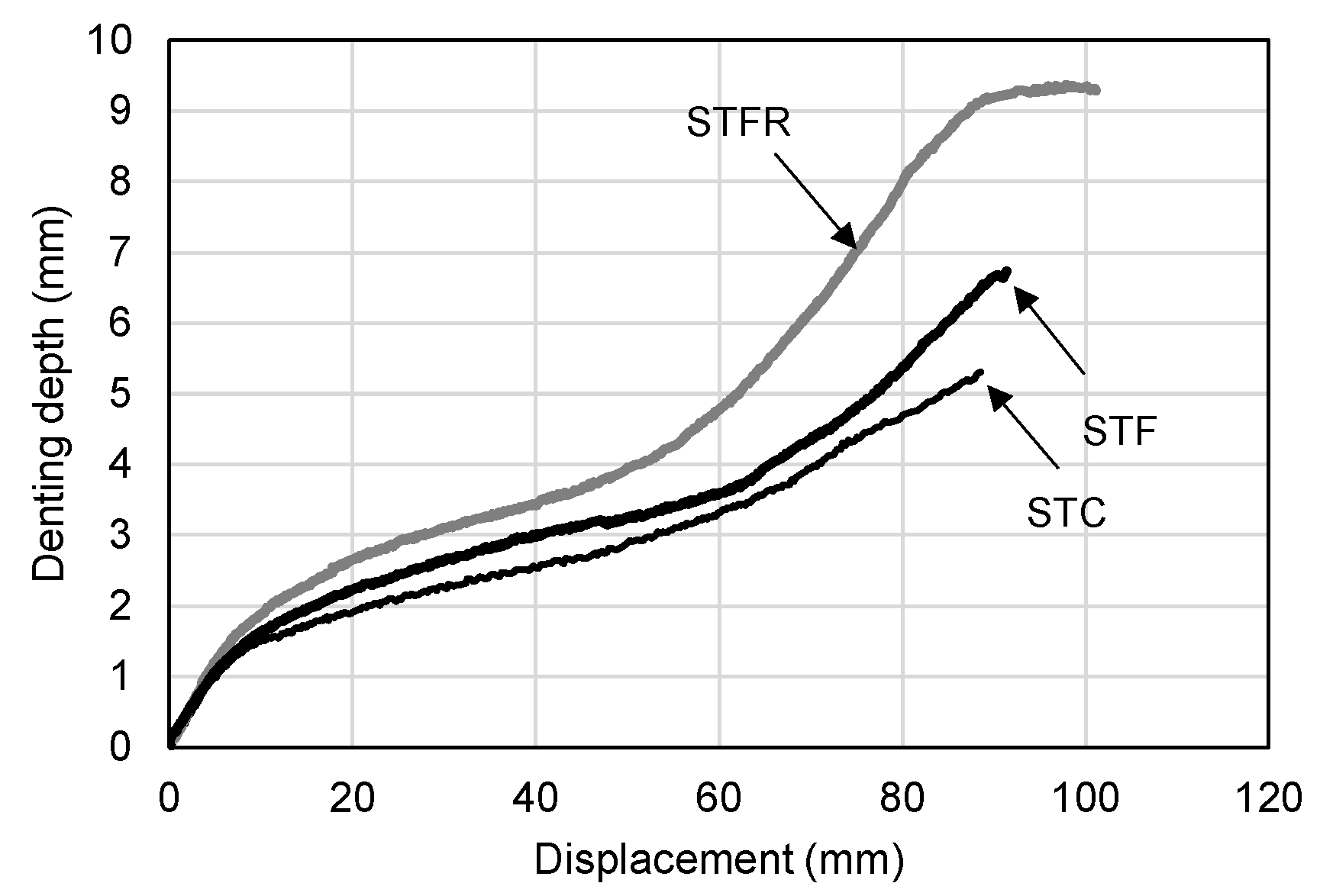
3.2. Load–Displacement Relationships
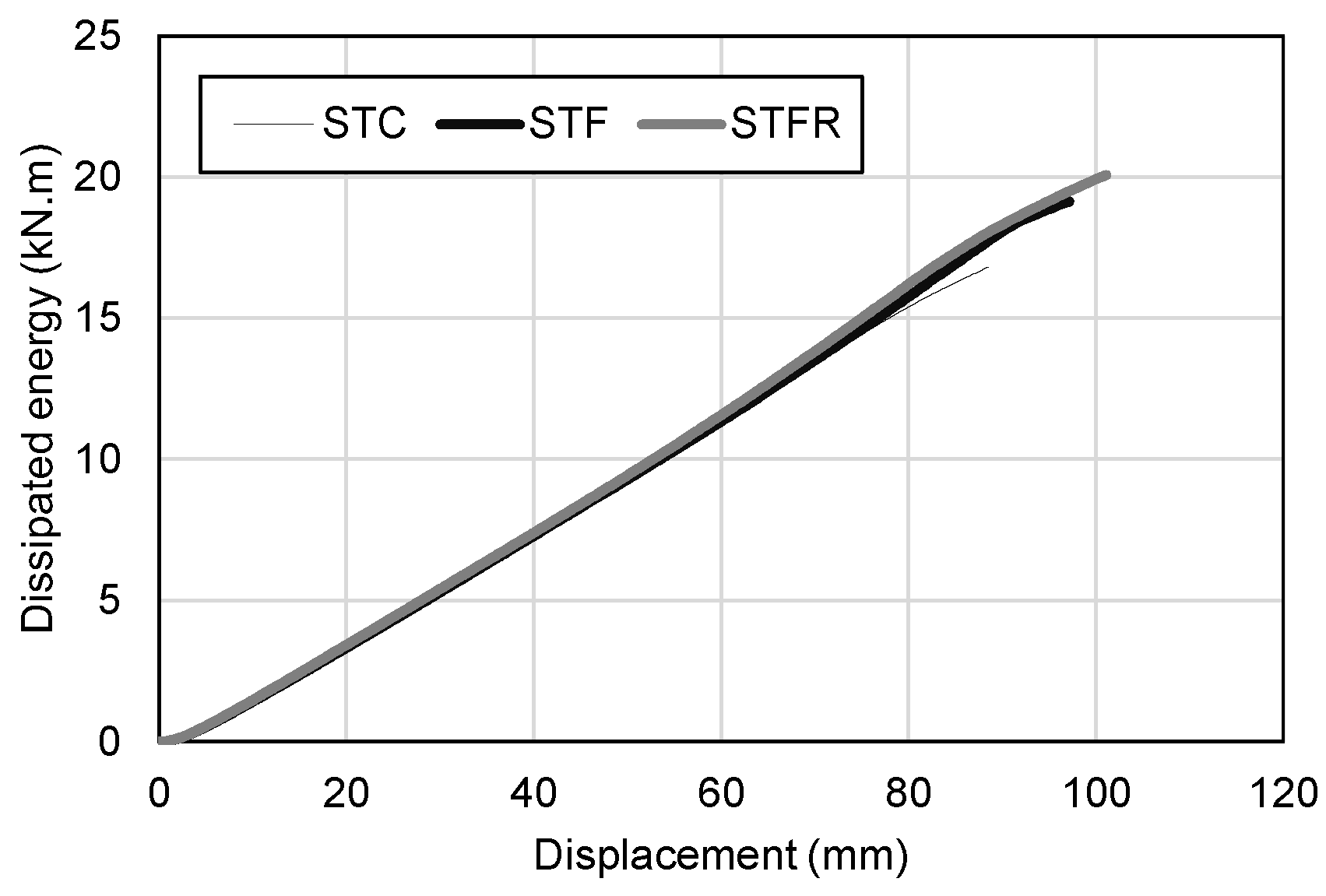
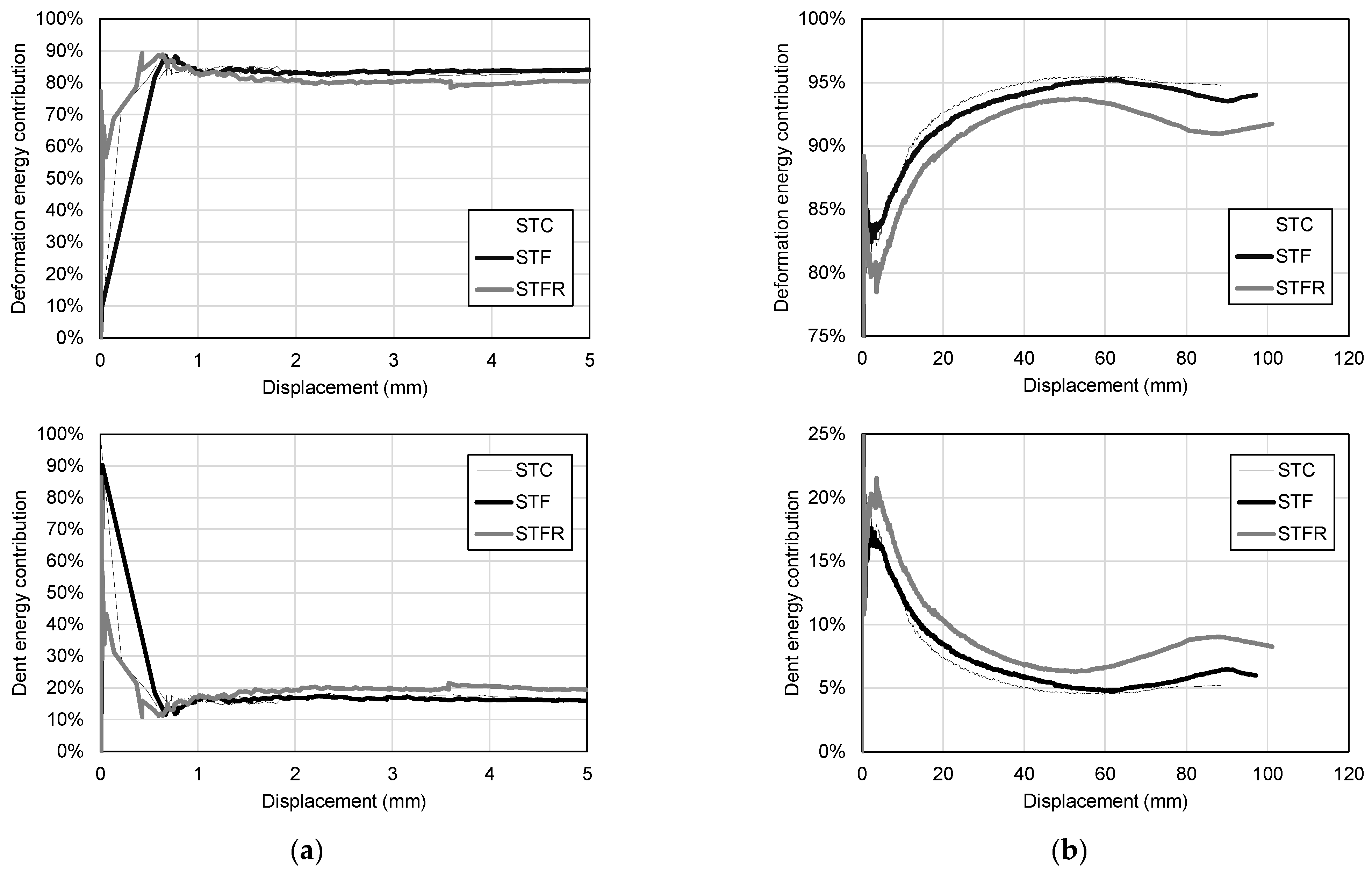
3.3. Energy Dissipation Characteristics
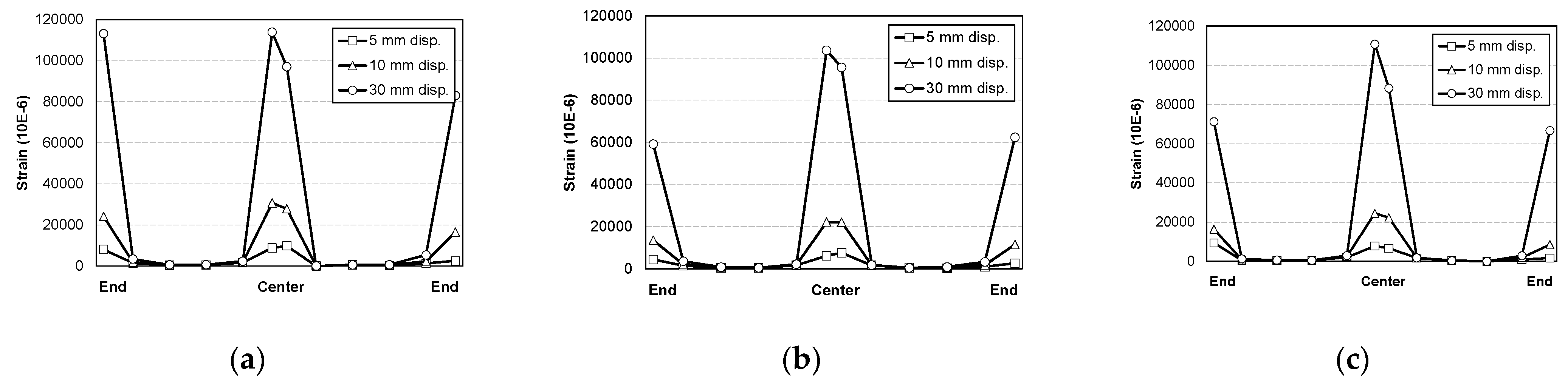
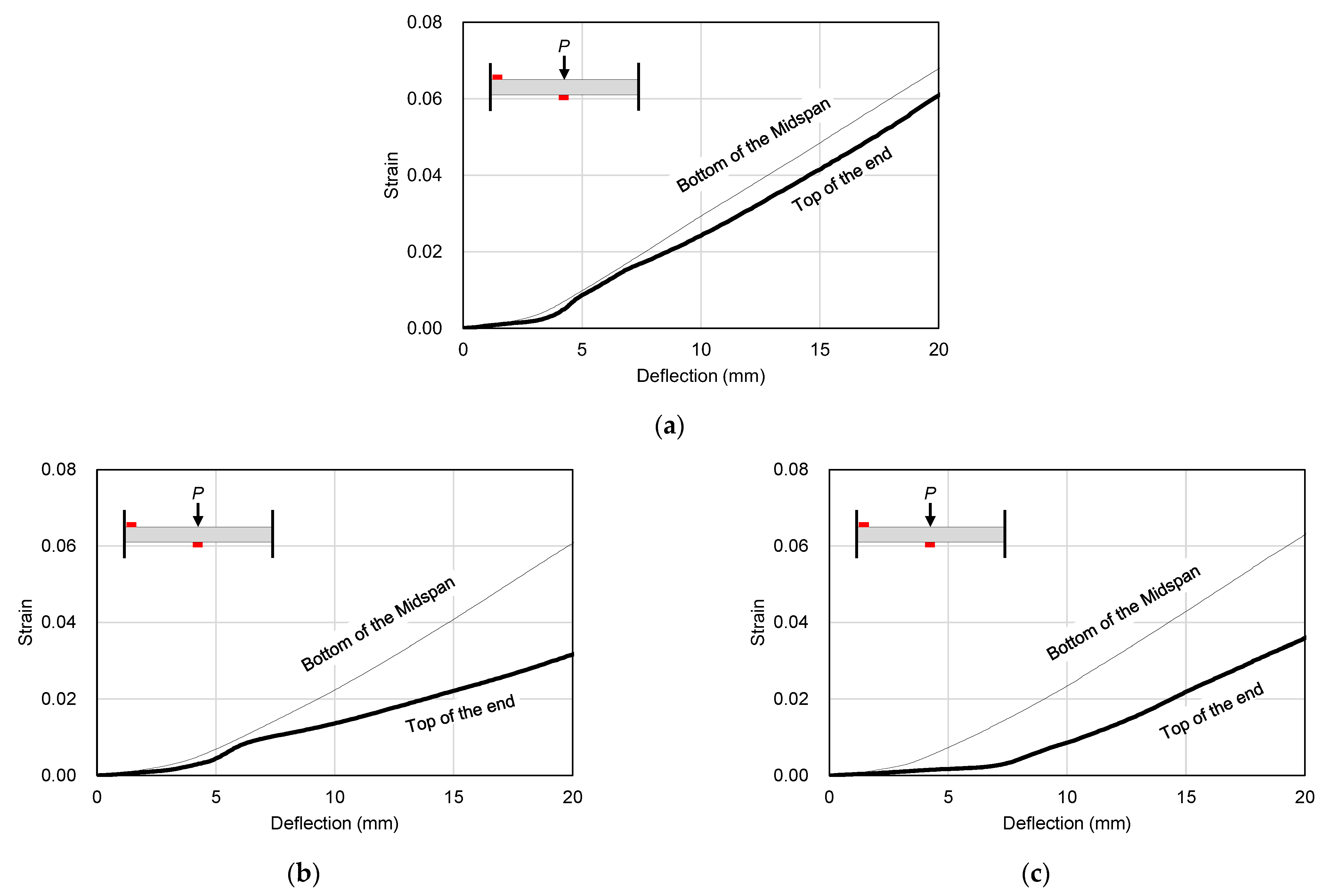
3.4. Steel Strain Characteristics
4. Conclusions
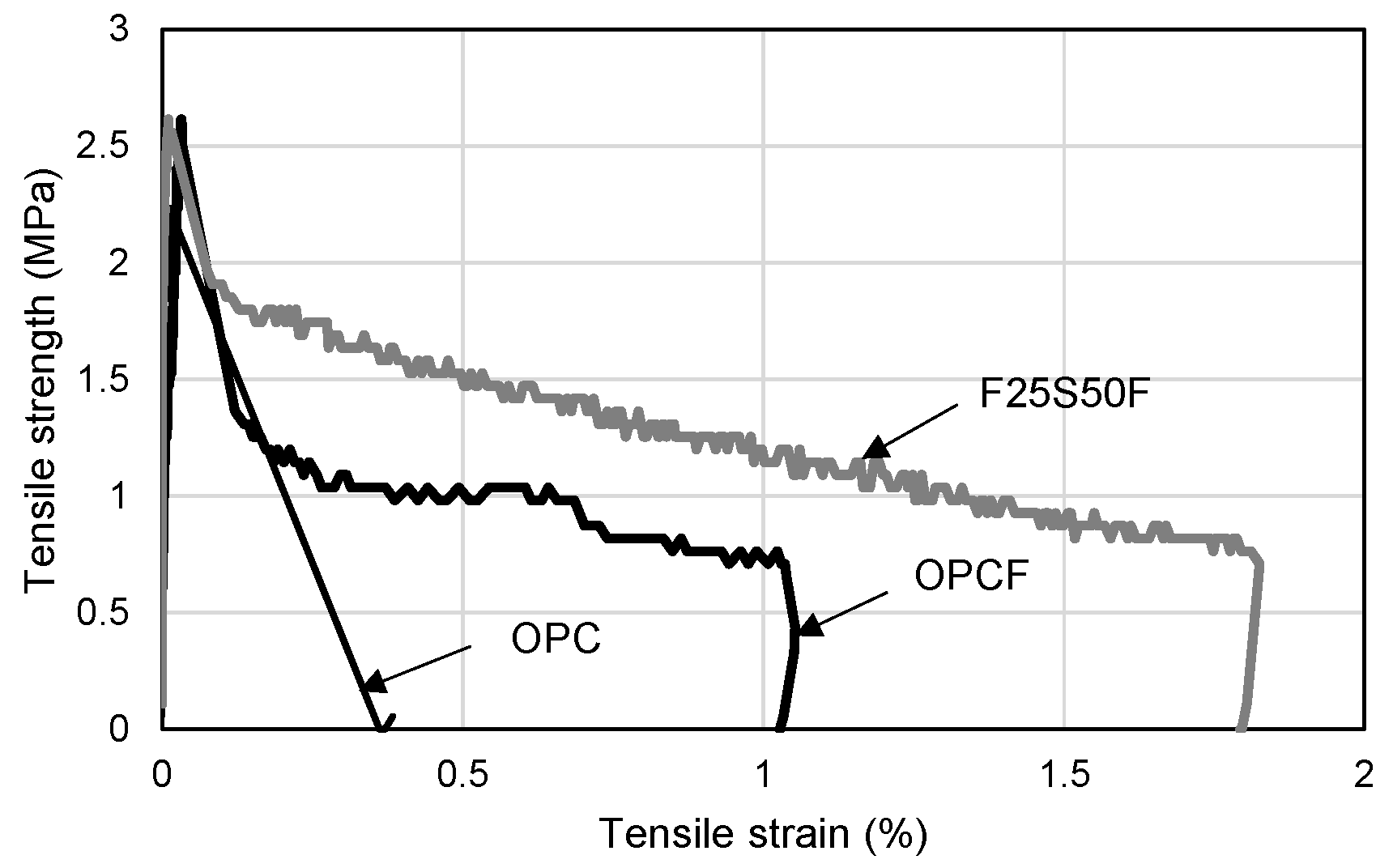
- The compressive strength and modulus of elasticity of cement composites tended to decrease, and the Poisson’s ratio tended to increase slightly, due to the incorporation of steel fibers and the substitution of recycled materials. In addition, when steel fibers were mixed, the flexural strength was 15 to 16% higher than that of the OPC mixture, and the retardation of brittle fractures due to the fiber crosslinking stress after the initial tensile crack was exhibited during the tensile test.
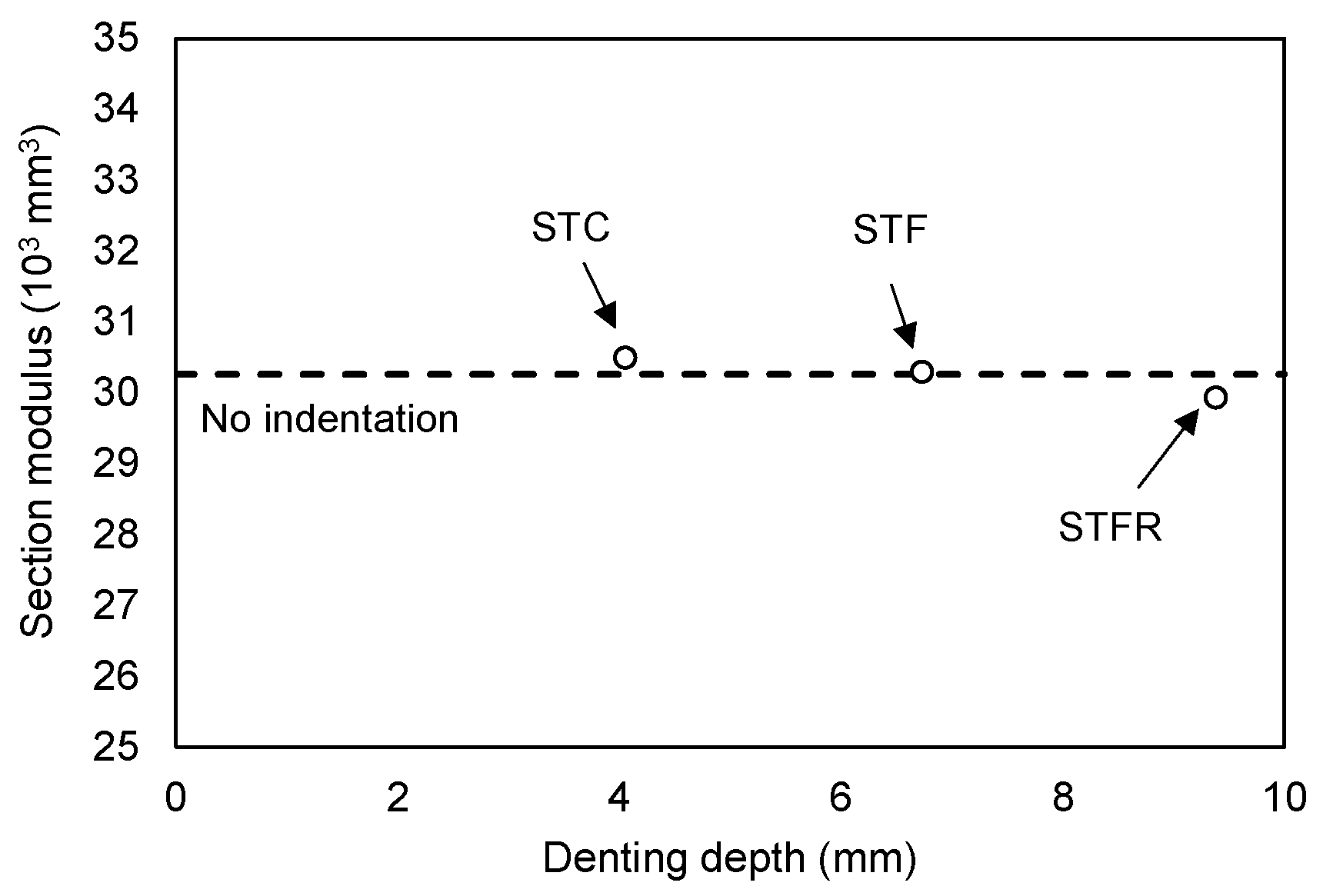
- The STF specimens filled with SFRCCs showed a slight increase in denting depth according to the increase in deflection compared to the STC specimens that were not reinforced with steel fibers. In particular, for the STFR test specimen with the recycled material, the denting depth at the loading part tended to increase noticeably due to the lower elastic modulus and higher Poisson’s ratio of the cementitious composite compared to the OPC mixture.
- In all specimens, the tendency to increase the energy dissipation capacity according to deflection was similar regardless of the type of mixture for the cement composite. However, in the case of the STFR specimen, the contribution to the energy dissipation capacity due to the damage at the loading part was larger than those of the STC and STF specimens, indicating that the ability to redistribute local damage was improved.
- In all specimens, the steel strain at the top of the supporting part was larger than that at the bottom of the midspan of the test specimen, which is considered to be due to the dispersion of cracks at the loading part due to the mixing of steel fibers. In particular, in the STFR test specimen, which was an SFRCC-filled steel tube with recycled materials, the lowest steel strain was observed at the top of the supporting part, and steel deformation was delayed the longest. Thus, it is determined that the stress distribution was stable.
- In this study, based on numerous experiments on the mechanical properties of FRCC, three combinations with the best tensile performance were derived. However, when retrofitting is required at a construction site, materials such as self-compacting cementitious composites with excellent flowability are required. Therefore, verification of the structural applications as well as investigation of SFRCC materials that satisfy both high flowability and mechanical properties are necessary tasks for future research.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Subedi, N.; Thusoo, S.; Obara, T.; Kono, S.; Kaneko, O.; Hayakawa, T.; Watanabe, H.; Mukai, T. Flexural performance of cast-in-place concrete-filled steel tube piles under varying axial load. Thin Walled Struct. 2022, 174, 109130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Z.; Han, W.; Wang, Y.; Yang, X.; Huang, W. Shear behavior of high-strength square concrete filled steel tube members. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 196, 107423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, R.; Craveiro, H.D.; Lopes, M.; Simões, R.A.; Laím, L.; Rebelo, C. Concrete-filled cold-formed steel (CF-CFS) built-up columns under compression: Test and design. Thin Walled Struct. 2022, 179, 109603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, R.; Craveiro, H.D.; Simões, R.A.; Laím, L.; Santiago, A. Buckling resistance of concrete-filled cold-formed steel (CF-CFS) built-up short columns under compression. Thin Walled Struct. 2022, 170, 108638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Fan, F.; Lai, J. Strength behavior of circular concrete-filled steel tube stub columns under axial compression: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 322, 126144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ran, J.; Li, T.; Shang, L.; Jiang, H.; Li, W.; Zhang, S. Experimental and analytical investigation on flexural behaviors of cast-in-place concrete-filled flexible composite tube beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 329, 127202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.F.; Shao, Y.B.; Hassanein, M.F. Behaviour and confinement-based direct design of concrete-filled cold-formed stiffened steel tubular short columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 202, 107773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, M.H.; Lin, Y.H.; Jin, Y.Y.; Fei, Q.; Wang, Z.C.; Ho, J.C.M. Uni-axial behaviour of steel slag concrete-filled-steel-tube columns with external confinement. Thin Walled Struct. 2023, 185, 110562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, Y. Behavior of square geopolymer recycled brick aggregate concrete filled steel tubular stub columns under axial compression. Constr. Build. Mater. 2023, 363, 129823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, P.P.; Xu, F.; Chan, T.M. Load transfer mechanism in concrete-filled steel tubular columns: Developments, challenges and opportunities. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2023, 203, 107781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Xu, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, X.; Chen, Y.F. Seismic performance of concrete-encased column connections for concrete filled thin-walled steel tube piers. Eng. Struct. 2022, 269, 114803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, F.; Cao, L.; Li, H. Axial compressive behaviour of high-strength steel spiral-confined square concrete-filled steel tubular columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2022, 192, 107245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Zhu, M.; Chen, Z.; Wu, C.; Chen, B.; Li, C.; Li, L. Seismic performance evaluation of recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tubular columns with field strain detected via a novel mark-free vision method. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 37, pp. 426–441. [Google Scholar]
- Yazdi, H.A.; Hashemi, M.J.; Al-Mahaidi, R.; Gad, E. Multi-axis testing of concrete-filled steel tube columns forming ductile soft-story in multi-story buildings. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 183, 106736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Li, N.; Zhang, S. Energy dissipation and resilience of precast segmented concrete-filled steel tube self-centering column: Parameter study and design methodology. Eng. Struct. 2021, 244, 112747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Han, L.H.; Wang, Y.C. Effects of heating and loading histories on post-fire cooling behaviour of concrete-filled steel tubular columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2008, 64, 556–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.Q.; Zhu, M.C.; Clifton, G.C.; Ukanwa, K.U.; Lim, J.B. Performance of square steel-reinforced concrete-filled steel tubular columns subject to non-uniform fire. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 166, 105909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, R.; Craveiro, H.D.; Simões, R.A.; Santiago, A. Equivalent temperature prediction for concrete-filled cold-formed steel (CF-CFS) built-up column sections (part A). Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 33, 101928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, R.; Craveiro, H.D.; Simões, R.A.; Santiago, A. Equivalent temperature prediction for concrete-filled cold-formed steel (CF-CFS) built-up column sections (part B). Case Stud. Therm. Eng. 2022, 35, 102111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahnavard, R.; Craveiro, H.D.; Simoes, R.A.; Laím, L.; Santiago, A. Fire resistance of concrete-filled cold-formed steel (CF-CFS) built-up short columns. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 48, 103854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Chanh, N. Steel Fiber Reinforced Concrete. In Seminar Material; Faculty of Civil Engineering, University of Technology: Ho Chi Minh City, Vietnam, 2004; pp. 108–116. [Google Scholar]
- Li, V.C. On engineered cementitious composites (ECC) a review of the material and its applications. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2003, 1, 215–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunieda, M.; Rokugo, K. Recent progress on HPFRCC in Japan required performance and applications. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2006, 4, 19–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, P.; Mechtcherine, V. Behaviour of strain-hardening cement-based composites (SHCC) under monotonic and cyclic tensile loading: Part 1–experimental investigations. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, W.; Li, J.; Wu, K. Mechanical properties of hybrid fiber-reinforced concrete at low fiber volume fraction. Cem. Concr. Res. 2003, 33, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soroushian, P.; Bayasi, Z. Fiber type effects on the performance of steel fiber reinforced concrete. Mater. J. 1991, 88, 129–134. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, P.; Huang, Y.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Lu, Y. Experimental research on seismic performance of steel fiber-reinforced recycled concrete-filled circular steel tube columns. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 54, 104683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, W.; Zhou, W.; Chen, L.; Liao, Q.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, Y. Flexural performance of steel fiber reinforced concrete filled stainless steel tubular trusses. Compos. Struct. 2023, 303, 116266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, S.; Lu, Y.; Ma, W.; Yan, Y.; Lin, C. Behaviour of steel-fibre-reinforced recycled concrete-filled square steel tubular short columns under axial compressive load. Eng. Struct. 2022, 271, 114894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Ran, J.; Chen, D.; Du, Y.; Zhu, Q.; Zhang, H.; Li, W. Structural behaviors of steel fiber-reinforced concrete-filled geotextile tube stub columns under axial compression. In Structures; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2022; Volume 40, pp. 434–447. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, D.; Lu, Y.; Li, S. Eccentric loading behavior of steel tube columns filled with steel-fiber-reinforced recycled concrete. Struct. Concr. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naji, A.J.; Al-Jelawy, H.M.; Hassoon, A.; Al-Rumaithi, A. Axial Behavior of Concrete Filled-steel Tube Columns Reinforced with Steel Fibers. Int. J. Eng. 2022, 35, 1682–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalar, M.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Deifalla, A.F.; Aksoylu, C.; Arslan, M.H.; Ahmad, M.; Sabri, M.M.S. Improvement in bending performance of reinforced concrete beams produced with waste lathe scraps. Sustainability 2022, 14, 12660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.İ.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Zeybek, Ö.; Özdöner, N.; Tayeh, B.A. Performance assessment of fiber-reinforced concrete produced with waste lathe fibers. Sustainability 2022, 14, 11817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeybek, Ö.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Çelik, A.İ.; Deifalla, A.F.; Ahmad, M.; Sabri Sabri, M.M. Performance evaluation of fiber-reinforced concrete produced with steel fibers extracted from waste tire. Front. Mater. 2022, 692, 1057128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aksoylu, C.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Hadzima-Nyarko, M.; Işık, E.; Arslan, M.H. Investigation on improvement in shear performance of reinforced-concrete beams produced with recycled steel wires from waste tires. Sustainability 2022, 14, 13360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.C.; Li, L.J.; Feng, W.X.; Liu, F.; Liao, B. Seismic performance of recycled aggregate concrete–filled steel tube columns. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2017, 133, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, J.; Chen, Y.; Lui, E.M. Recycling and reuse of construction and demolition waste in concrete-filled steel tubes: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 641–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.C.; Han, L.H.; Hou, C. Performance of recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tubular columns under combined compression and shear load. Eng. Struct. 2022, 253, 113771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nour, A.I.; Güneyisi, E.M. Prediction model on compressive strength of recycled aggregate concrete filled steel tube columns. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 173, 106938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, W.Q.; Han, L.H.; Hou, C. Axial compressive behaviour and design calculations on recycled aggregate concrete-filled steel tubular (RAC-FST) stub columns. Eng. Struct. 2021, 241, 112452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Yang, J.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Z. Experimental study on recycled concrete confined by steel tube under axial compression. J. Build. Struct. 2011, 32, 92–98. [Google Scholar]
- Qaidi, S.; Najm, H.M.; Abed, S.M.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Al Dughaishi, H.; Alosta, M.; Sabri, M.M.S.; Alkhatib, F.; Milad, A. Concrete containing waste glass as an environmentally friendly aggregate: A review on fresh and mechanical characteristics. Materials 2022, 15, 6222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, A.İ.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Zeybek, Ö.; Karalar, M.; Qaidi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.D.; Bejinariu, C. Mechanical Behavior of Crushed Waste Glass as Replacement of Aggregates. Materials 2022, 15, 8093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, M.; Agwa, I.S.; Mashaan, N.; Mahmood, S.; Abd-Elrahman, M.H. Investigation of the Physical Mechanical Properties and Durability of Sustainable Ultra-High Performance Concrete with Recycled Waste Glass. Sustainability 2023, 15, 3085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaran, B.; Kalkan, I.; Aksoylu, C.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Sabri, M.M.S. Effects of Waste Powder, Fine and Coarse Marble Aggregates on Concrete Compressive Strength. Sustainability 2022, 14, 14388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruengsillapanun, K.; Udtaranakron, T.; Pulngern, T.; Tangchirapat, W.; Jaturapitakkul, C. Mechanical properties, shrinkage, and heat evolution of alkali activated fly ash concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 299, 123954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalar, M.; Bilir, T.; Çavuşlu, M.; Özkiliç, Y.O.; Sabri, M.M.S. Use of recycled coal bottom ash in reinforced concrete beams as replacement for aggregate. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1064604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, A.; Siddique, R.; Ozbakkaloglu, T.; Shaikh, F.U.A.; Belarbi, R. Fly ash and ground granulated blast furnace slag-based alkali-activated concrete: Mechanical, transport and microstructural properties. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 257, 119548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeybek, Ö.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Karalar, M.; Çelik, A.İ.; Qaidi, S.; Ahmad, J.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.D.; Burduhos-Nergis, D.P. Influence of replacing cement with waste glass on mechanical properties of concrete. Materials 2022, 15, 7513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karalar, M.; Özkılıç, Y.O.; Aksoylu, C.; Sabri, M.M.S.; Beskopylny, A.N.; Stel’Makh, S.A.; Shcherban, E.M. Flexural behavior of reinforced concrete beams using waste marble powder towards application of sustainable concrete. Front. Mater. 2022, 9, 1068791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cha, J.H.; Song, S.H.; Jang, Y.H.; Jeon, E.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yun, H.D. Evaluation of mechanical properties of strain-hardening cement composite mixing fly ash and PET fiber. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2009, 21, 227–228. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Bang, J.W.; Hyun, J.H.; Seo, J.S.; Lee, E.S.; Lee, B.J.; Kim, Y.Y. The axial tensile properties of the Green SHCC in accordance with types of fly ash. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2013, 25, 323–324. (In Korean) [Google Scholar]
- Travanca, J.; Hao, H. Energy dissipation in high-energy ship-offshore jacket platform collisions. Mar. Struct. 2015, 40, 1–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Amdahl, J. A review of structural responses and design of offshore tubular structures subjected to ship impacts. Ocean. Eng. 2018, 154, 177–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinoddini, M.; Harding, J.E.; Parke, G.A.R. Effect of impact damage on the capacity of tubular steel members of offshore structures. Mar. Struct. 1998, 11, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeinoddini, M.; Parke, G.A.R.; Harding, J.E. Axially pre-loaded steel tubes subjected to lateral impacts: An experimental study. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2002, 27, 669–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Liu, K.; Ji, C.; Chen, D.; Wang, G.; Soares, C.G. Experimental and numerical investigations on the T joint of jack-up platform laterally punched by a knife edge indenter. Ocean. Eng. 2016, 127, 212–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Han, L.H.; Hou, C.C. Behavior of concrete filled steel tubular (CFST) members under lateral impact: Experiment and FEA model. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2013, 80, 188–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokgoz, S.; Dundar, C. Experimental study on steel tubular columns in-filled with plain and steel fiber reinforced concrete. Thin Walled Struct. 2010, 48, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Tuan, C.Y. Design of concrete-filled circular steel tubes under lateral impact. ACI Struct. J. 2013, 110, 691. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, L.; Fan, W.; Liu, B.; Liu, Y. Numerically efficient analysis of concrete-filled steel tubular columns under lateral impact loading. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 179, 106564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suksawang, N.; Wtaife, S.; Alsabbagh, A. Evaluation of elastic modulus of fiber-reinforced concrete. ACI Mater. J. 2018, 115, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Lv, Y. Behavior of ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete (UHPFRC) filled steel tubular members under lateral impact loading. Int. J. Impact Eng. 2019, 132, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Wu, C.; Li, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, X. Lateral impact behavior of double-skin steel tubular (DST) members with ultra-high performance fiber-reinforced concrete (UHPFRC). Thin Walled Struct. 2019, 144, 106351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- BS EN 10025-5; Steels with Improved Atmospheric Corrosion Resistance. British Standards Institute: London, UK, 2004.
- KS L 5201; Portland Cement. Korea Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016. (In Korean)
- KS L 5405; Fly Ash. Korea Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2016. (In Korean)
- KS L 2573; Recycled Aggregates for Concrete. Korea Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2014. (In Korean)
- KS L ISO 679; Methods of Testing Cements-Determination of Strength. Korea Standards Association: Seoul, Republic of Korea, 2006. (In Korean)
- Chen, G.M.; Yang, H.; Lin, C.J.; Chen, J.F.; He, Y.H.; Zhang, H.Z. Fracture behaviour of steel fibre reinforced recycled aggregate concrete after exposure to elevated temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 128, 272–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katkhuda, H.; Shatarat, N. Improving the mechanical properties of recycled concrete aggregate using chopped basalt fibers and acid treatment. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 140, 328–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, E.; Saadati, R.; Kordbacheh, N.; Parpinchi, Z.S.; Tang, W. Engineering and microstructural assessment of fibre-reinforced self-compacting concrete containing recycled coarse aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 168, 605–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.F.; Wang, Q.Y.; Guan, Z.W. Material properties of basalt fibre reinforced concrete made with recycled earthquake waste. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.B.; Yi, N.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Kim, J.H.J.; Song, Y.C. Material and structural performance evaluation of recycled PET fiber reinforced concrete. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2010, 32, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.F.U.; Mihashi, H. Strain hardening behavior of lightweight hybrid polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fiber reinforced cement composites. Mater. Struct. 2011, 44, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Cha, J.H.; Kim, Y.Y.; Yun, H.D. Mechanical properties of strain hardening cement-based composite (SHCC) with recycled materials. J. Korea Concr. Inst. 2010, 22, 727–736. (In Korean) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Li, V. Lightweight engineered cementitious composites (ECC). In Proceedings of 4th International RILEM Workshop on High Performance Fiber Reinforced Cement Composites (HPFRCC 4); RILEM Publications: Ann Arbor, MI, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- ANSI/AISC 360-16; Specification for Structural Steel Buildings (Revised June 2019). American Institute of Steel Construction: Chicago, IL, USA, 2019.
- Storheim, M.; Amdahl, J. Design of offshore structures against accidental ship collisions. Mar. Struct. 2014, 37, 135–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bambach, M.R.; Jama, H.; Zhao, X.L.; Grzebieta, R.H. Hollow and concrete filled steel hollow sections under transverse impact loads. Eng. Struct. 2008, 30, 2859–2870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
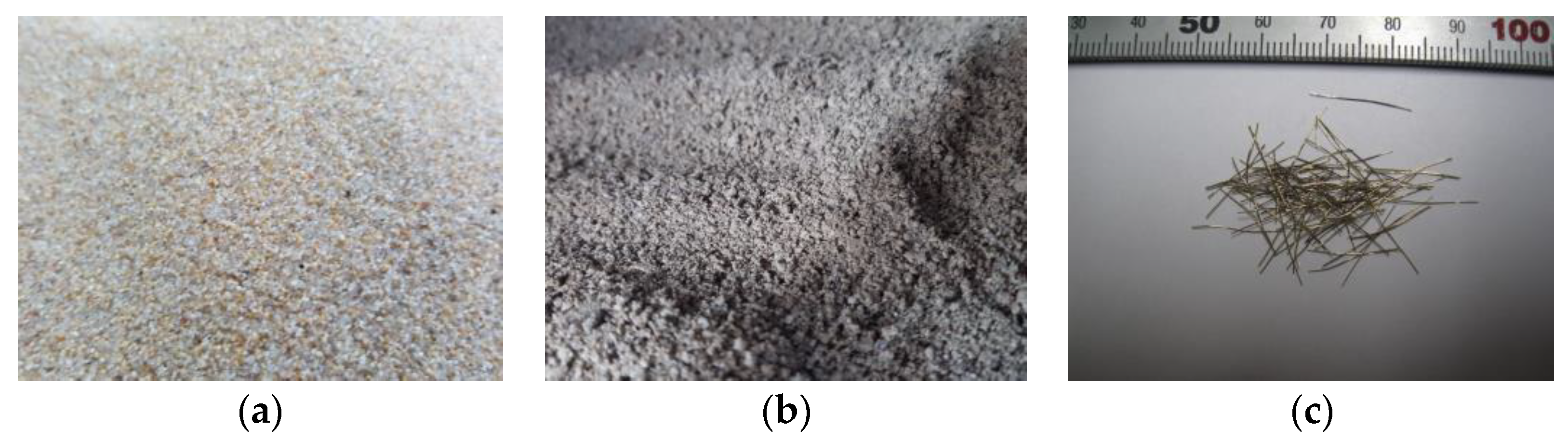
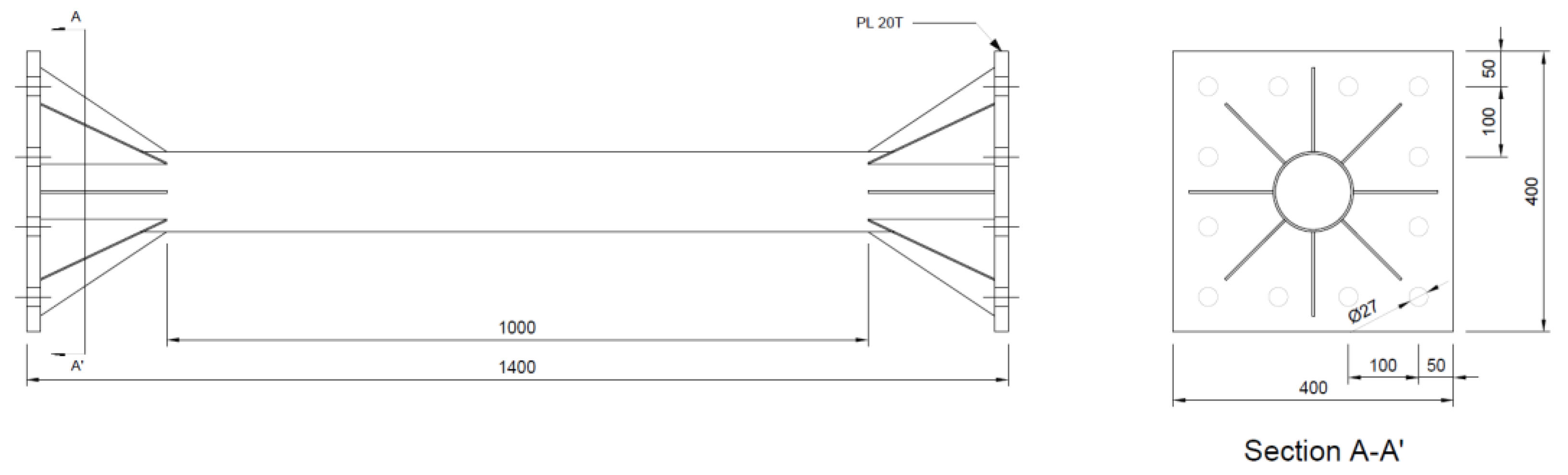

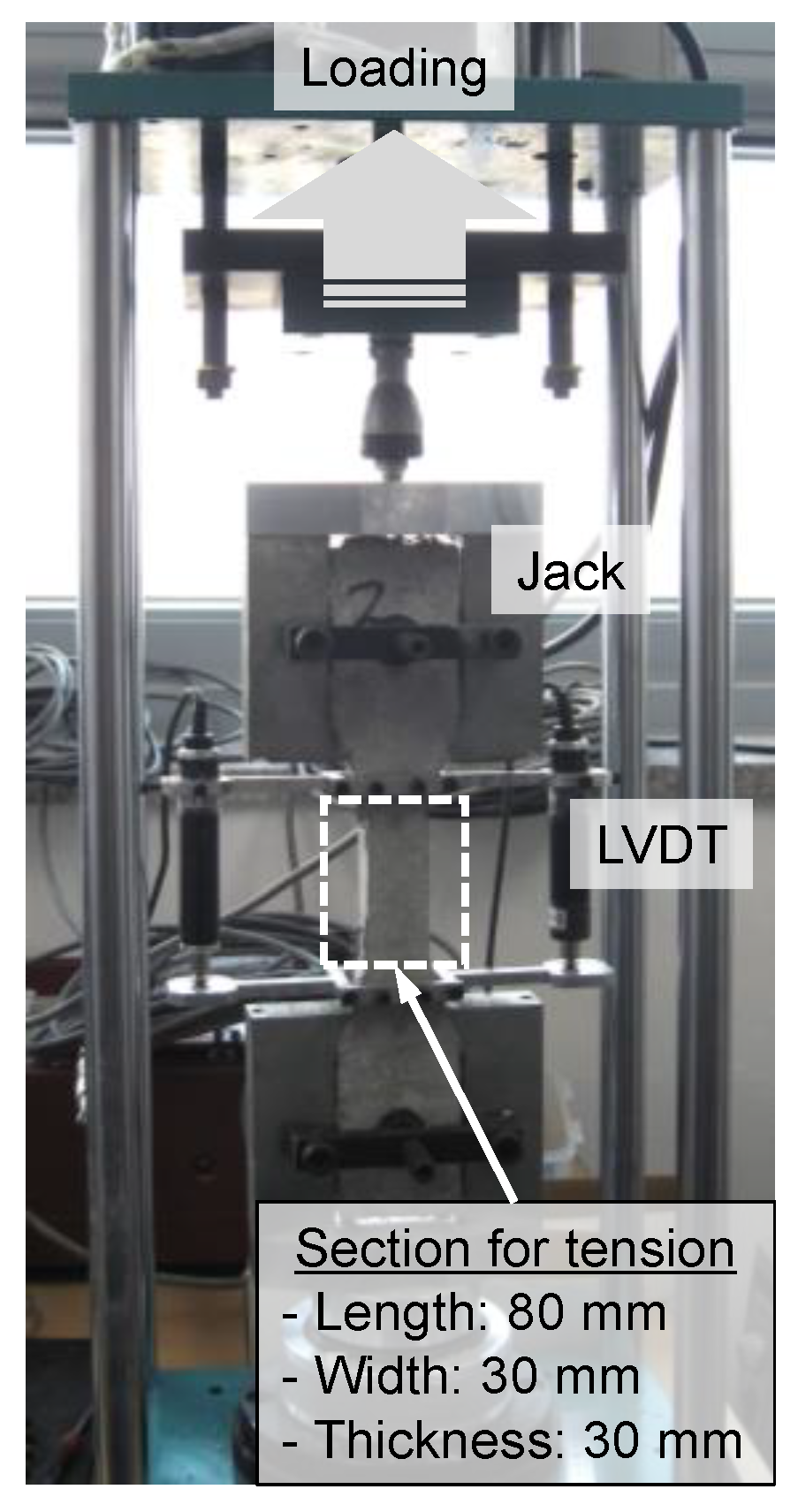
| Specimen | Steel Tube | Mixture | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| L 1 (mm) | D 2 (mm) | t 3 (mm) | L/D | D/t | ||
| STC STF STFR | 1000 | 114.3 | 3.2 | 8.75 | 25.4 | OPC OPCF F25S50F |
| Mix | W/B (%) | Weight (kg) * | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W 1 | C 2 | FA 3 | NS 4 | RS 5 | SF 6 | SP 7 | ||
| OPC | 0.40 | 323 | 807 | - | 1090 | - | - | 0.16 |
| OPCF | 323 | 807 | - | 1090 | - | 20.12 | 0.81 | |
| F25S50F | 323 | 605 | 202 | 545 | 545 | 20.12 | 0.81 | |
| Parameter | Type I Portland Cement | Class F Fly Ash |
|---|---|---|
| SiO2 (%) | 33.44 | 50.72 |
| Al2O3 (%) | 15.03 | 20.73 |
| Fe2O3 (%) | 0.57 | 6.37 |
| CaO (%) | 44.12 | 3.61 |
| Free CaO (%) | 0.82 | - |
| MgO (%) | 3.55 | 1.08 |
| SO3 (%) | 3.45 | 0.54 |
| Ig. loss (%) | 1.27 | 3.04 |
| C3S (%) | 61.24 | - |
| C2S (%) | 12.09 | - |
| C3A (%) | 13.14 | - |
| C4AF (%) | 6.12 | - |
| Blaine (cm2/g) | 3500 | 3990 |
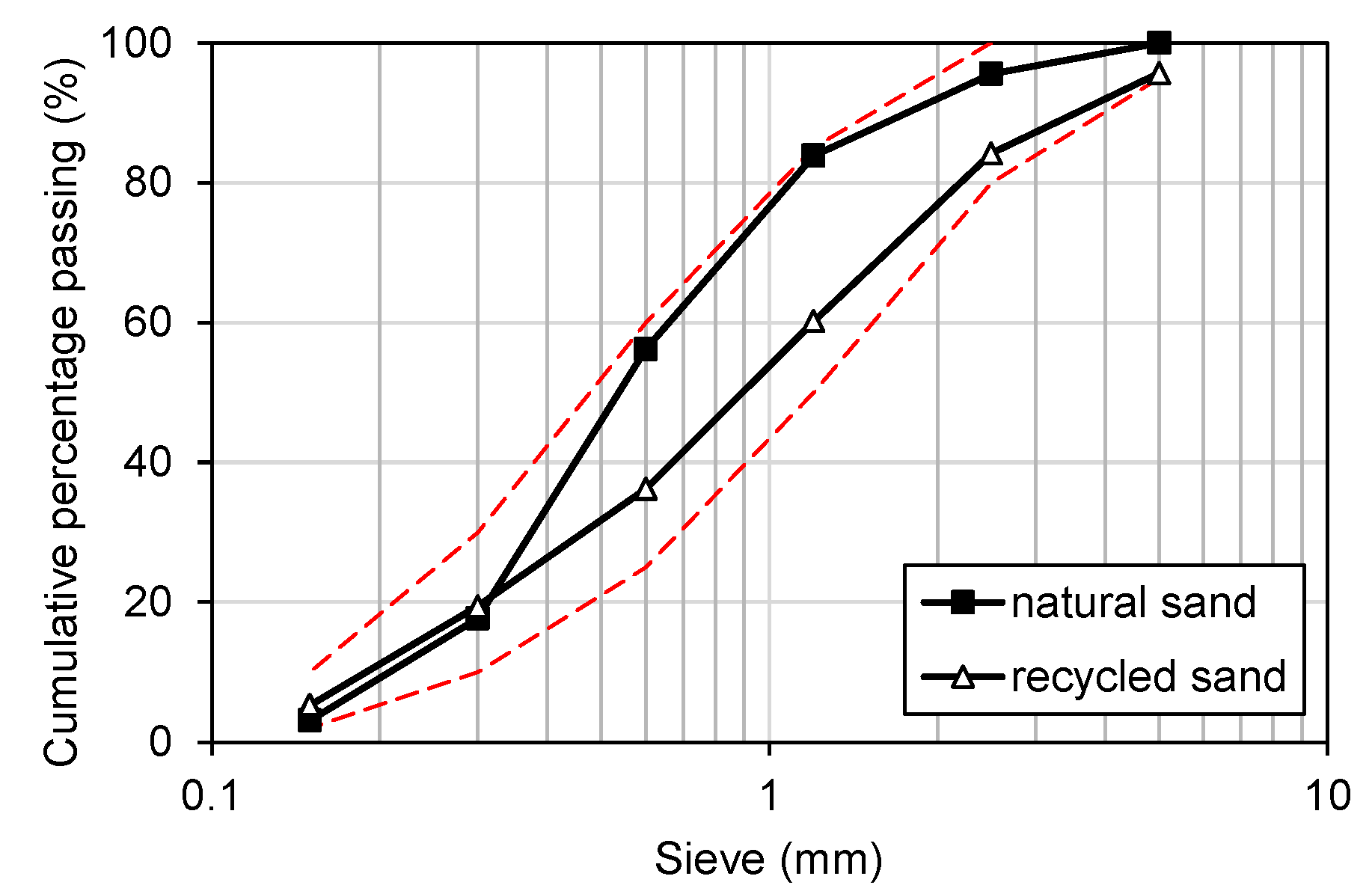
| Type | Density (g/cm3) | Water Absorption (%) | Fineness Modulus |
|---|---|---|---|
| Natural sand | 2.59 | 0.76 | 2.44 |
| Recycled sand | 2.44 | 4.32 | 2.99 |
| Dia. (mm) | Length (mm) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.18–0.23 | 12–14 | 206 | 2580 |
| Mix | Compression | Bending Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength (MPa) | Elastic Modulus (GPa) | Poisson’s Ratio | |||
| OPC | 51.9 | 24.12 | 0.16 | 5.54 | 2.23 |
| OPCF | 61.4 | 22.49 | 0.16 | 6.39 | 2.62 |
| F25S50F | 53.9 | 16.09 | 0.19 | 6.43 | 2.62 |
| Specimen | Peak Load (kN) | Deflection at Peak Load (mm) | Denting Depth at Peak Load (mm) | Dissipated Energy (kN·m) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Test (1) | AISC (2) | (1)/(2) | by Deflection | by Denting | Total | |||
| STC | 202.42 | 201.20 | 1.01 | 71.10 | 4.05 | 15.939 | 0.872 | 16.811 |
| STF | 207.33 | 201.08 | 1.03 | 82.50 | 6.73 | 17.989 | 1.145 | 19.134 |
| STFR | 203.98 | 201.18 | 1.01 | 79.16 | 9.38 | 18.416 | 1.656 | 20.072 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yun, H.-D.; Park, W.-S.; Jang, Y.-I.; Kim, S.-W. Flexural Behavior Characteristics of Steel Tubes Filled with SFRCCs Incorporating Recycled Materials. Materials 2023, 16, 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051958
Yun H-D, Park W-S, Jang Y-I, Kim S-W. Flexural Behavior Characteristics of Steel Tubes Filled with SFRCCs Incorporating Recycled Materials. Materials. 2023; 16(5):1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051958
Chicago/Turabian StyleYun, Hyun-Do, Wan-Shin Park, Young-Il Jang, and Sun-Woo Kim. 2023. "Flexural Behavior Characteristics of Steel Tubes Filled with SFRCCs Incorporating Recycled Materials" Materials 16, no. 5: 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051958
APA StyleYun, H.-D., Park, W.-S., Jang, Y.-I., & Kim, S.-W. (2023). Flexural Behavior Characteristics of Steel Tubes Filled with SFRCCs Incorporating Recycled Materials. Materials, 16(5), 1958. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16051958








