Polyphenols Coordinated with Cu (II) in an Aqueous System Build Ion-Channel Coatings on Hair Surfaces
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Materials
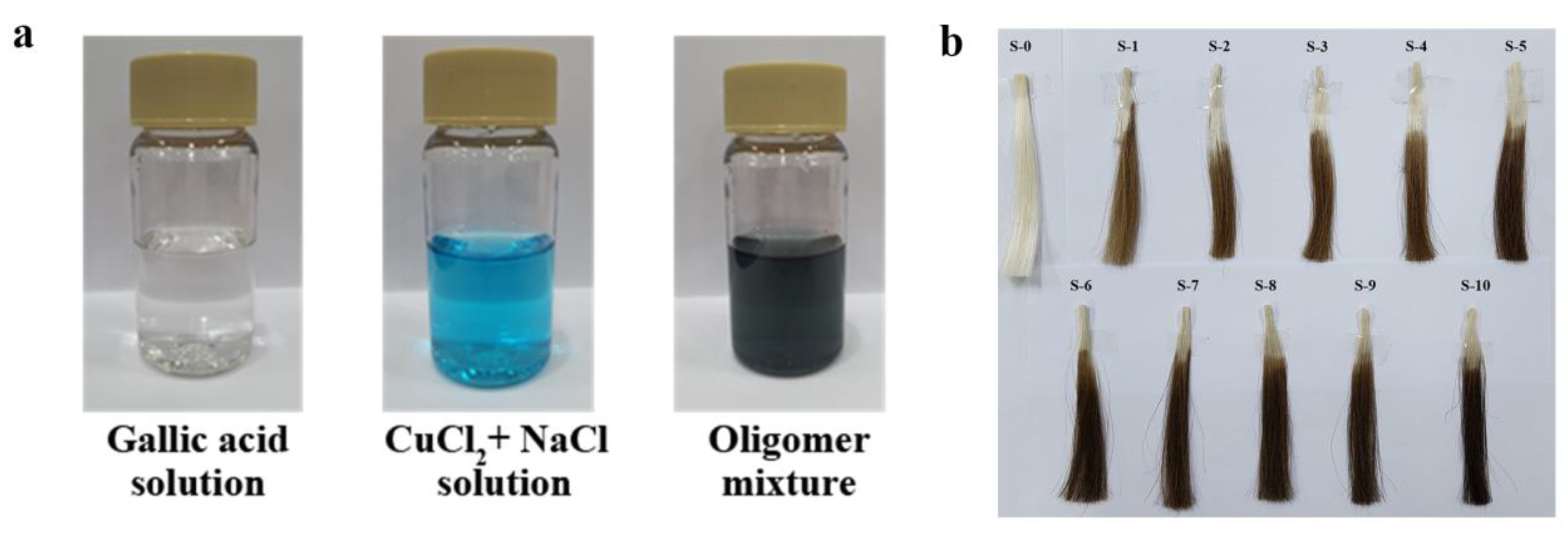
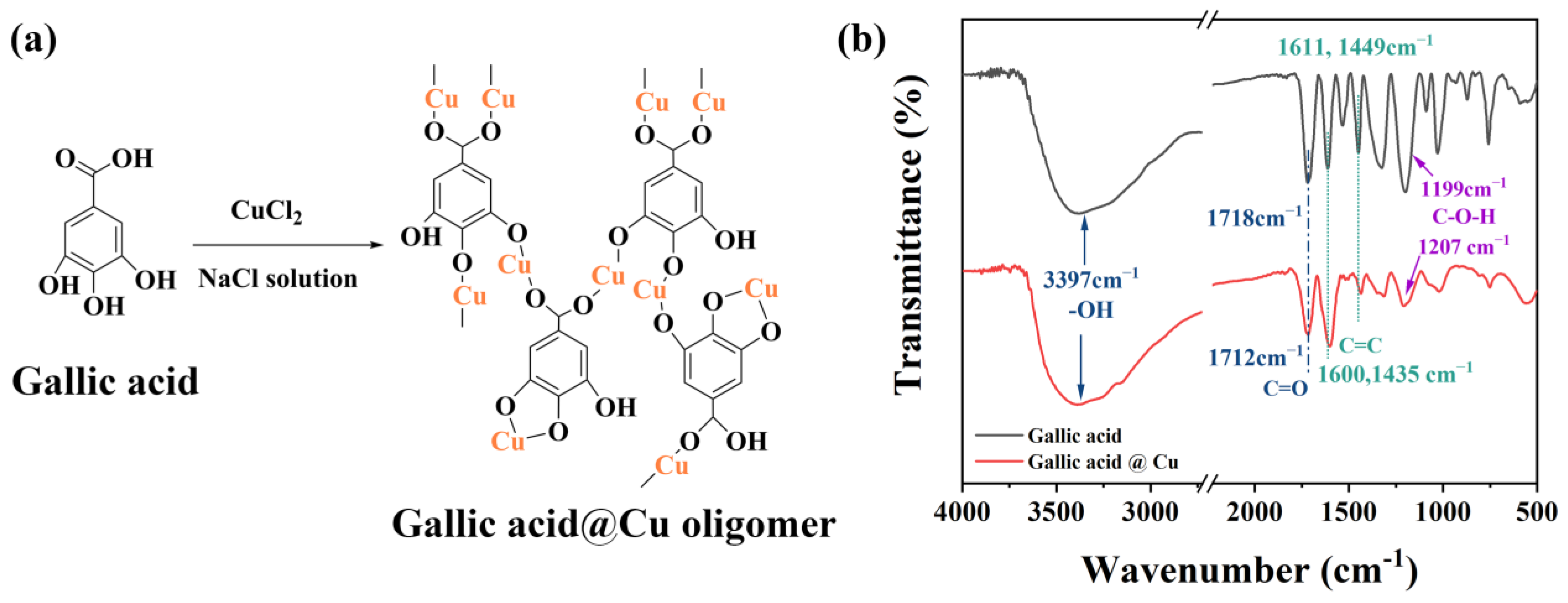
2.2. Synthesis of Gallic Acid and Pyrogallol Oligomer
2.3. Hair-Dyeing Process
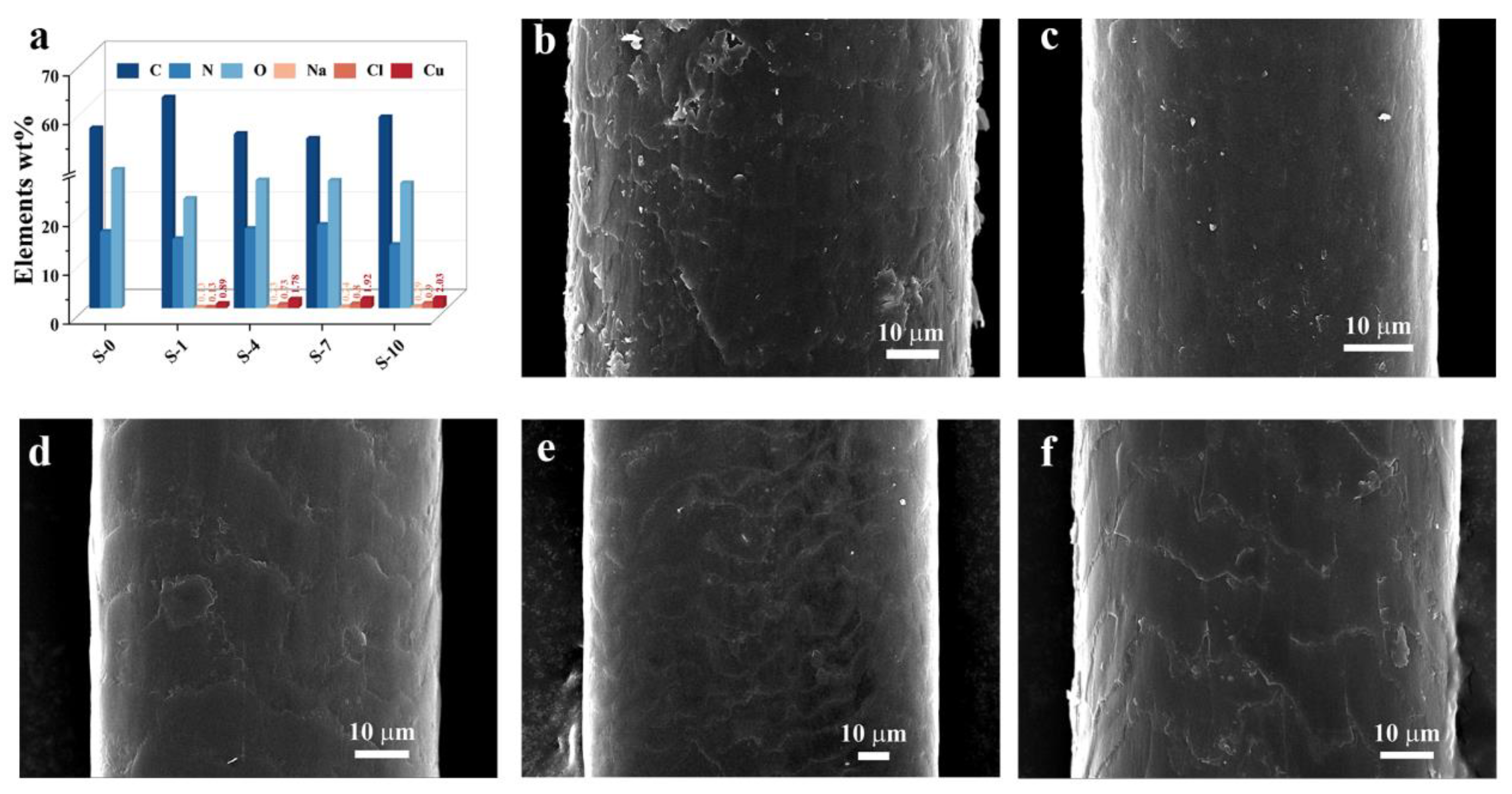
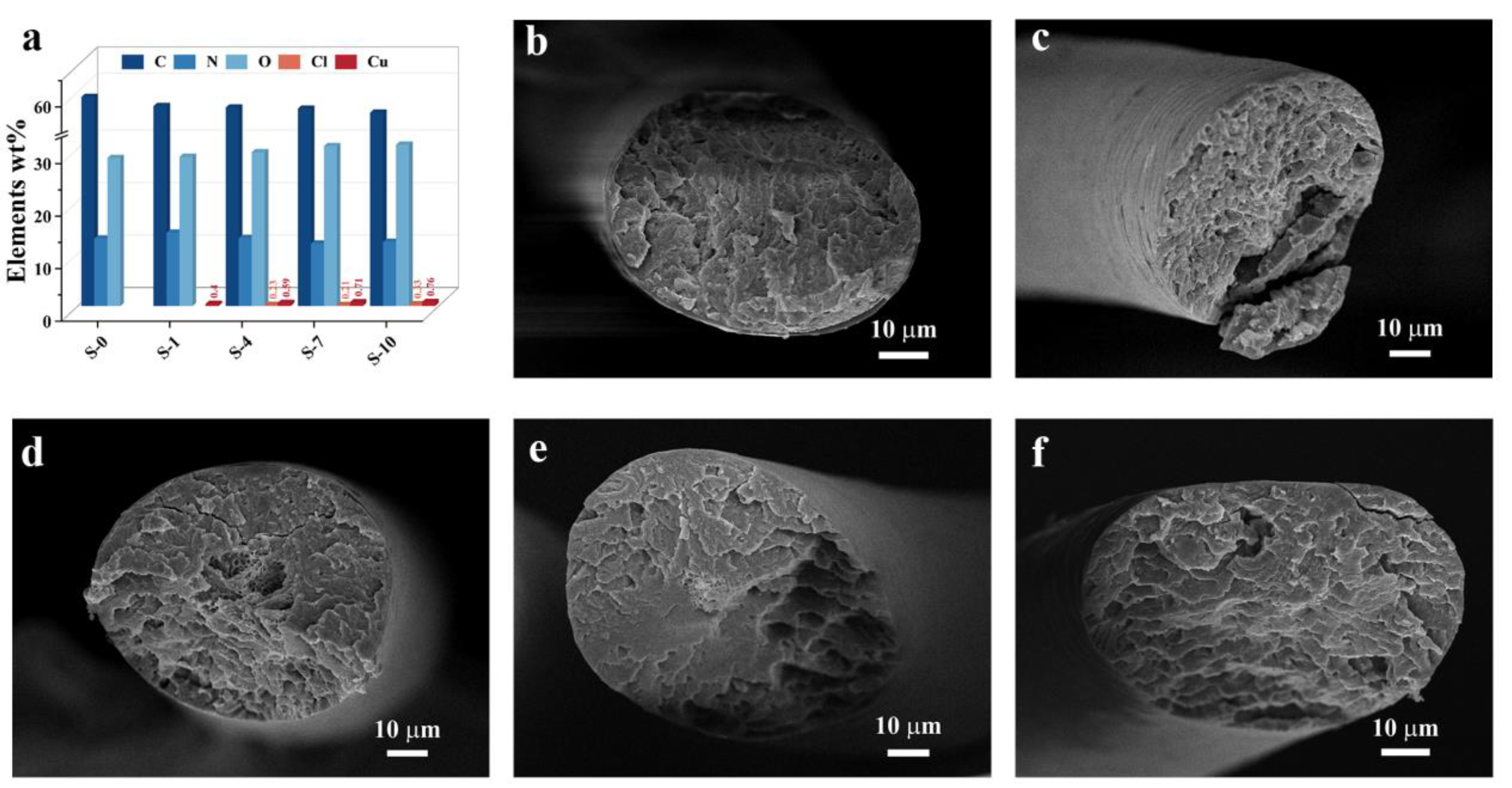
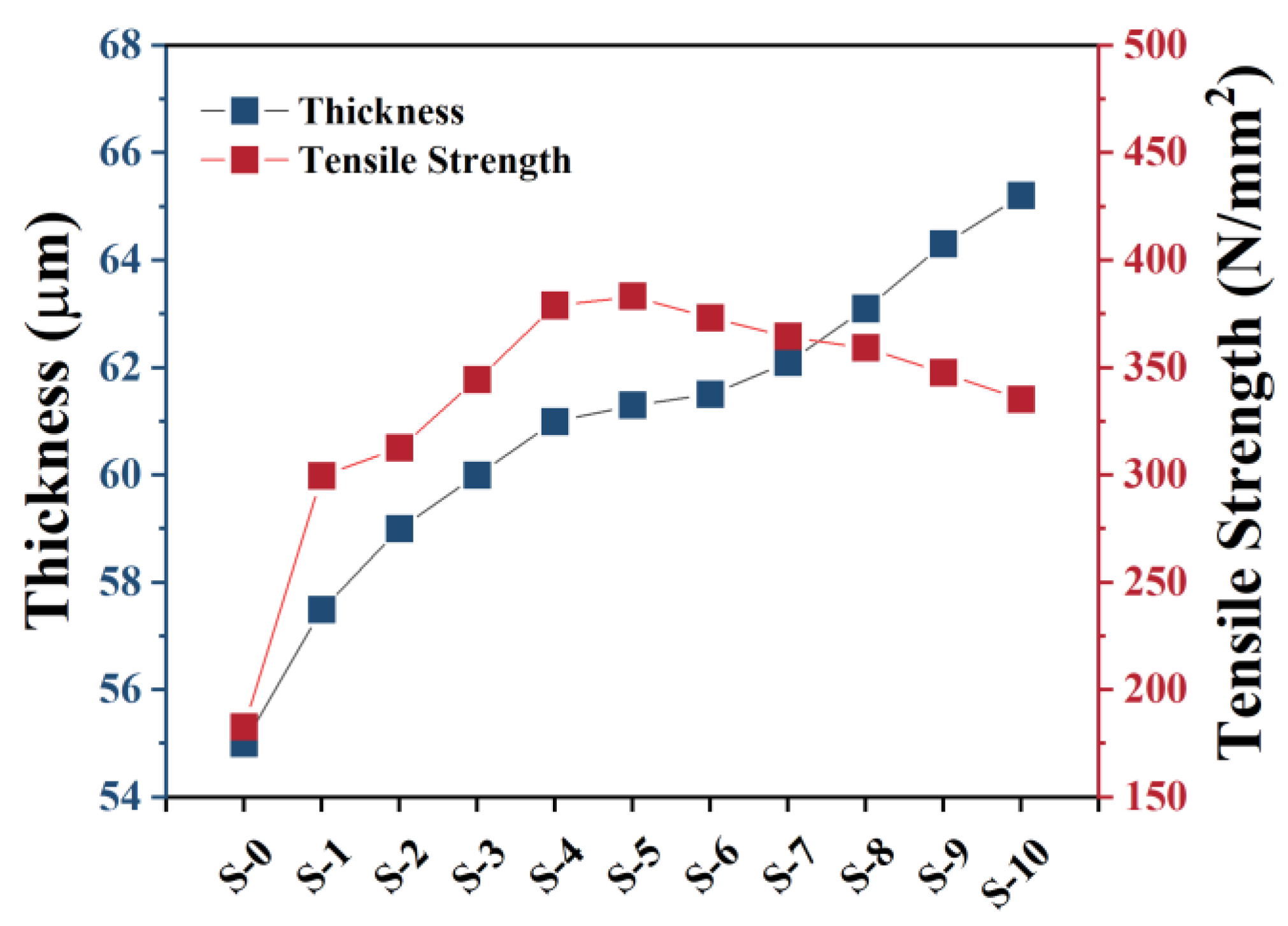
2.4. Characteristics of Dyed Hair
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rust, R.C.; Schlatter, H. Hair Dyes. In Cosmetic Dermatology; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2022; pp. 309–319. ISBN 9781119676881. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, A.; Moinuddin, A.A.; Allarakha, S.; Fatima, S.; Ali, S.A.; Habib, S. Risk of Carcinogenicity Associated with Synthetic Hair Dyeing Formulations: A Biochemical View on Action Mechanisms, Genetic Variation and Prevention. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2022, 37, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Da França, S.A.; Dario, M.F.; Esteves, V.B.; Baby, A.R.; Velasco, M.V.R. Types of Hair Dye and Their Mechanisms of Action. Cosmetics 2015, 2, 110–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra-Tapia, A.; Gonzalez-Guerra, E. Hair Cosmetics: Dyes. Actas Dermo-Sifiliográficas (Engl. Ed.) 2014, 105, 833–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coimbra, S.C.; Sousa-Oliveira, I.; Ferreira-Faria, I.; Peixoto, D.; Pereira-Silva, M.; Mathur, A.; Pawar, K.D.; Raza, F.; Mazzola, P.G.; Mascarenhas-Melo, F. Safety Assessment of Nanomaterials in Cosmetics: Focus on Dermal and Hair Dyes Products. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, J.C.; da Silva, B.F.; Morales, D.A.; Umbuzeiro, G.D.A.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Assessment of the Compounds Formed by Oxidative Reaction between P-Toluenediamine and p-Aminophenol in Hair Dyeing Processes: Detection, Mutagenic and Toxicological Properties. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 795, 148806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, T.N.; Szymczyk, M.; Freeman, H.S. In Situ Chelation of Monoazo Dyes in Human Hair Keratin Fibers Using Environmentally Benign Metal Ions. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2021, 4, 6195–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Wang, J.F.; Wang, Y. Influence of Cosmetic Hair Treatments on Hair of Methamphetamine Abuser: Bleaching, Perming and Coloring. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 222, 112542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, V.; Panicker, A.G.; Indrakumar, S.; Chatterjee, K. Comparative Study of Keratin Extraction from Human Hair. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 133, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cesarini, J.P. Hair Melanin and Hair Color. In Hair and Hair Diseases; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1990; pp. 165–197. [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa, N.; Tanizawa, Y.; Tanaka, S.; Horiguchi, Y.; Asakura, T. Structural Change of Keratin Protein in Human Hair by Permanent Waving Treatment. Polymer 1998, 39, 3835–3840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, M.; Li, Y.; Allen, M.C.; Deheyn, D.D.; Yue, X.; Zhao, J.; Gianneschi, N.C.; Shawkey, M.D.; Dhinojwala, A. Bio-Inspired Structural Colors Produced via Self-Assembly of Synthetic Melanin Nanoparticles. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 5454–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Battistella, C.; Mccallum, N.C.; Gnanasekaran, K.; Zhou, X.; Caponetti, V.; Montalti, M.; Gianneschi, N.C. Mimicking Natural Human Hair Pigmentation with Synthetic Melanin. ACS Cent. Sci. 2020, 6, 1179–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarna, T.; Burke, J.M.; Korytowski, W.; Rózanowska, M.; Skumatz, C.M.B.; Zarȩba, A.; Zarȩba, M. Loss of Melanin from Human RPE with Aging: Possible Role of Melanin Photooxidation. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Souza, J.C.; Machini, W.B.S.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Human Hair Keratin Direct Electrochemistry and In Situ Interaction with P-Toluenediamine and P-Aminophenol Hair Dye Precursors Using a Keratin Electrochemical Biosensor. ChemElectroChem 2020, 7, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, G.T.; de Souza, J.C.; Silva, J.P.; Pividori, M.I.; Zanoni, M.V.B. Determination of Temporary Dye Basic Red 51 in Commercial Hair Dye, River Water and Wastewater from Hairdressing Salon Using Graphite-Epoxy Composite Electrode Modified with Magnetic Nanoparticles. Microchem. J. 2020, 159, 105485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Souza, J.C.; Zanoni, M.V.B.; Oliveira-Brett, A.M. Genotoxic Permanent Hair Dye Precursors P-Aminophenol and p-Toluenediamine Electrochemical Oxidation Mechanisms and Evaluation in Biological Fluids. J. Electroanal. Chem. 2020, 857, 113509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, A.; Fischer, K. Oxidative Transformation Processes and Products of Para-Phenylenediamine (PPD) and Para-Toluenediamine (PTD)—A Review. Environ. Sci. Eur. 2015, 27, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-Y.; Lin, Y.-H.; Shih, C.-J.; Chen, Y.-L. Determination of Phenylenediamines in Hair Colors Derivatizated with 5-(4, 6-Dichlorotriazinyl)Aminofluorescein via Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography. J. Food Drug Anal. 2019, 27, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamann, D.; Yazar, K.; Hamann, C.R.; Thyssen, J.P.; Lidén, C. P-Phenylenediamine and Other Allergens in Hair Dye Products in the United States: A Consumer Exposure Study. Contact Dermat. 2014, 70, 213–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warsi, M.S.; Habib, S.; Talha, M.; Mir, A.R.; Alam, K.; Ali, A. Characterization of Human Serum Albumin Modified by Hair Dye Component, 4-Chloro-1, 2-Phenylenediamine: Role in Protein Aggregation, Redox Biology and Cytotoxicity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 331, 115731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, Y.; Li, Y.; Ma, F.; Zhang, M.; Chen, X.; Ye, B.-C. Ratiometric Electrochemical Sensing Platform Based on N-Doped MOF-Derived CoNi/C for the Determination of p-Phenylenediamine in Hair Dyes. Microchim. Acta 2023, 190, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, L.; Michailidou, F.; Gahlon, H.L.; Zeng, W. Hair Dye Ingredients and Potential Health Risks from Exposure to Hair Dyeing. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2022, 35, 901–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Liu, B.; Li, W.; Lin, T.; Yang, H.; Pei, Y.; Gong, Z. Highly Selective and Sensitive Fluorescence Determination of M-Phenylenediamine. Microchem. J. 2021, 167, 106283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, G.; Dancik, Y.; Sinha, A.; Kyaw, H.M.; Srinivas, R.; Dawson, T.L.; Bigliardi, M.; Bigliardi, P.; Pastorin, G. Development of Novel Alternative Hair Dyes to Hazardous Para-Phenylenediamine. J. Hazard. Mater. 2021, 402, 123712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampathkumar, K.; Yesudas, S. Hair Dye Poisoning and the Developing World. J. Emerg.Trauma Shock 2009, 2, 129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sileika, T.S.; Barrett, D.G.; Zhang, R.; Lau, K.H.A.; Messersmith, P.B. Colorless Multifunctional Coatings Inspired by Polyphenols Found in Tea, Chocolate, and Wine. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2013, 52, 10766–10770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geng, H.; Dai, Q.; Sun, H.; Zhuang, L.; Song, A.; Caruso, F.; Hao, J.; Cui, J. Injectable and Sprayable Polyphenol-Based Hydrogels for Controlling Hemostasis. ACS Appl. Bio. Mater. 2020, 3, 1258–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.-F.; Wei, Z.-F.; Jiang, J.-J.; Peng, J.-Q.; He, Q.-T.; Xu, W.-Y.; Liu, H.-M. Microemulsion of Cinnamon Essential Oil Formulated with Tea Polyphenols, Gallic Acid, and Tween 80: Antimicrobial Properties, Stability and Mechanism of Action. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panwar, V.; Dey, B.; Sheikh, J.N.; Dutta, T. Thermostable Bacterial Laccase for Sustainable Dyeing Using Plant Phenols. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 18168–18180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, D.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Y.; Su, R.; Qi, W. Colorful Pigments Based on Multicomponent Metal-Phenol Network Nanoparticles for Hair Dyeing. ChemistrySelect 2022, 7, e202203886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, H.R.H.; Hassan, A.I.; Hassan, Y.F.; El-Wekil, M.M. Colorimetric and Fluorimetric (Dual-Mode) Nanoprobe for the Determination of Pyrogallol Based on the Complexation with Copper(II)- and Nitrogen-Doped Carbon Dots. Microchim. Acta 2019, 186, 850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hung, C.H.; Chang, W.T.; Su, W.Y.; Cheng, S.H. Electrochemical Determination of Pyrogallol at Conducting Poly(3,4-Ethylenedioxythiophene) Film-Modified Screen-Printed Carbon Electrodes. Electroanalysis 2014, 26, 2237–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.; Park, E.; Lee, H. Plant-Inspired Pyrogallol-Containing Functional Materials. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1903022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boukamp, P.; Petrussevska, R.T.; Breitkreutz, D.; Hornung, J.; Markham, A.; Fusenig, N.E. Normal Keratinization in a Spontaneously Immortalized Aneuploid Human Keratinocyte Cell Line. J. Cell Biol. 1988, 106, 761–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rocha, J.E.; Guedes, T.T.A.M.; Bezerra, C.F.; Costa, M.D.S.; Campina, F.F.; de Freitas, T.S.; Sousa, A.K.; Souza, C.E.S.; Silva, M.K.N.; Lobo, Y.M.; et al. FTIR Analysis of Pyrogallol and Phytotoxicity-Reductive Effect against Mercury Chloride. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2433–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.J.; Han, S.; Lee, K.B.; Choi, I.S. Biphasic Supramolecular Self-Assembly of Ferric Ions and Tannic Acid across Interfaces for Nanofilm Formation. Adv. Mater. 2017, 29, 1700784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devi, J.; Yadav, M.; Sharma, S.; Devi, J. Synthesis and Characterization of Co (Ii), Ni (Ii), Cu (Ii), and Zn (Ii) Complexes of Thiosemicarbazones. Molecules 2018, 10, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ejima, H.; Richardson, J.J.; Liang, K.; Best, J.P.; van Koeverden, M.P.; Such, G.K.; Cui, J.; Caruso, F. One-Step Assembly of Coordination Complexes. Science 2013, 341, 154–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jin, L.; Yun, D.; Zhang, W.; Lee, J.; Shin, H.; Kim, D.; Kang, T.-B.; Won, H.-S.; Jang, H.; Kim, W. Polyphenols Coordinated with Cu (II) in an Aqueous System Build Ion-Channel Coatings on Hair Surfaces. Materials 2023, 16, 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041333
Jin L, Yun D, Zhang W, Lee J, Shin H, Kim D, Kang T-B, Won H-S, Jang H, Kim W. Polyphenols Coordinated with Cu (II) in an Aqueous System Build Ion-Channel Coatings on Hair Surfaces. Materials. 2023; 16(4):1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041333
Chicago/Turabian StyleJin, Lei, Daemyoung Yun, Wei Zhang, Jinsung Lee, Hongchul Shin, Donghyuk Kim, Tae-Bong Kang, Hyung-Sik Won, Hohyoun Jang, and Whangi Kim. 2023. "Polyphenols Coordinated with Cu (II) in an Aqueous System Build Ion-Channel Coatings on Hair Surfaces" Materials 16, no. 4: 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041333
APA StyleJin, L., Yun, D., Zhang, W., Lee, J., Shin, H., Kim, D., Kang, T.-B., Won, H.-S., Jang, H., & Kim, W. (2023). Polyphenols Coordinated with Cu (II) in an Aqueous System Build Ion-Channel Coatings on Hair Surfaces. Materials, 16(4), 1333. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma16041333







