Enhanced Switching Reliability of Sol–Gel-Processed Y2O3 RRAM Devices Based on Y2O3 Surface Roughness-Induced Local Electric Field
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
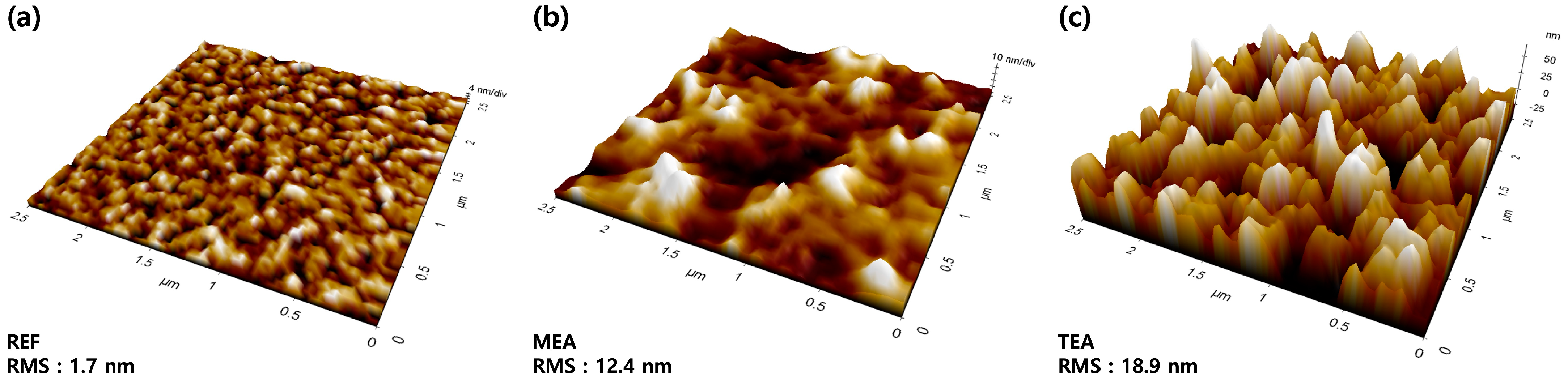
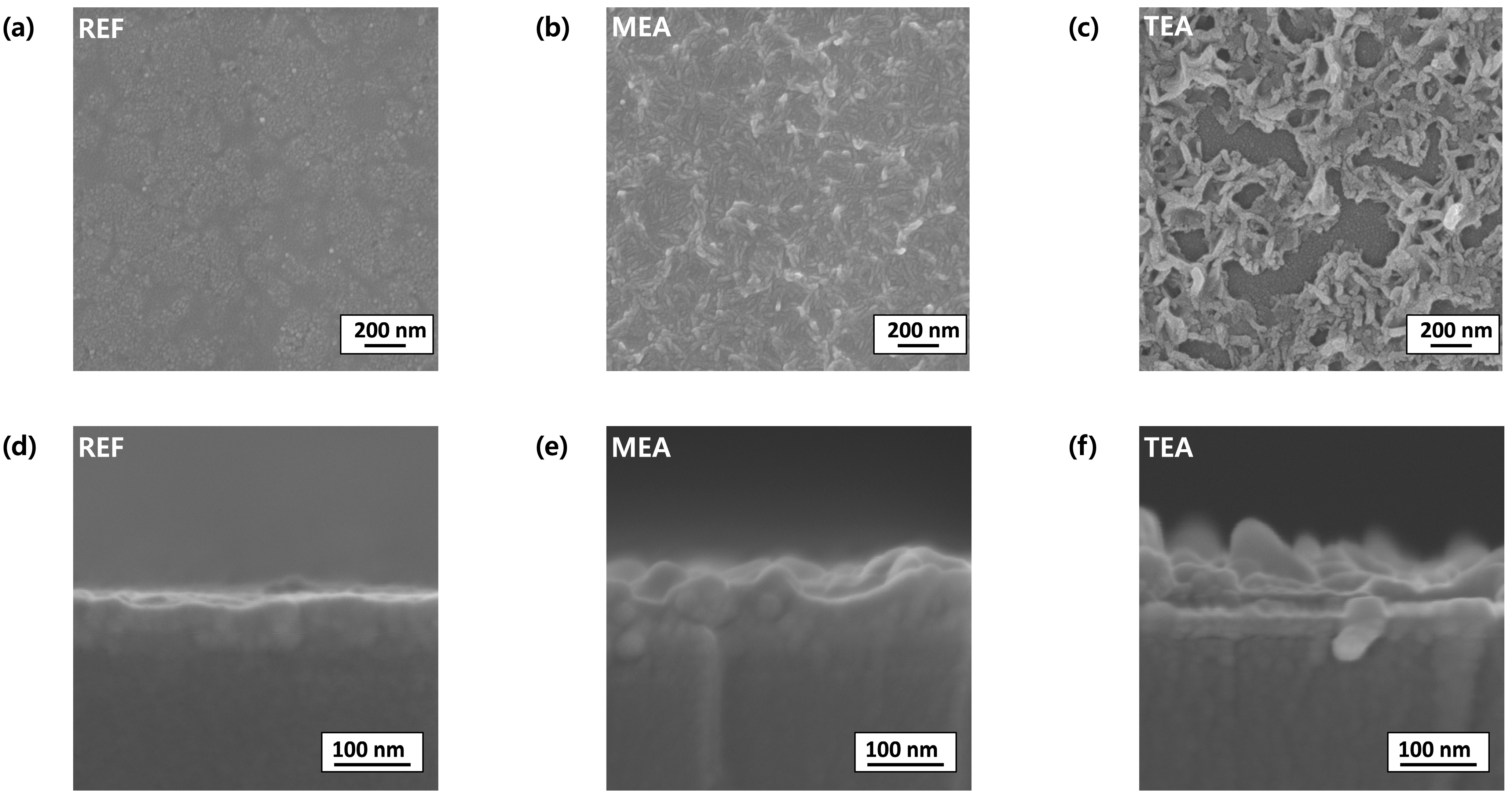
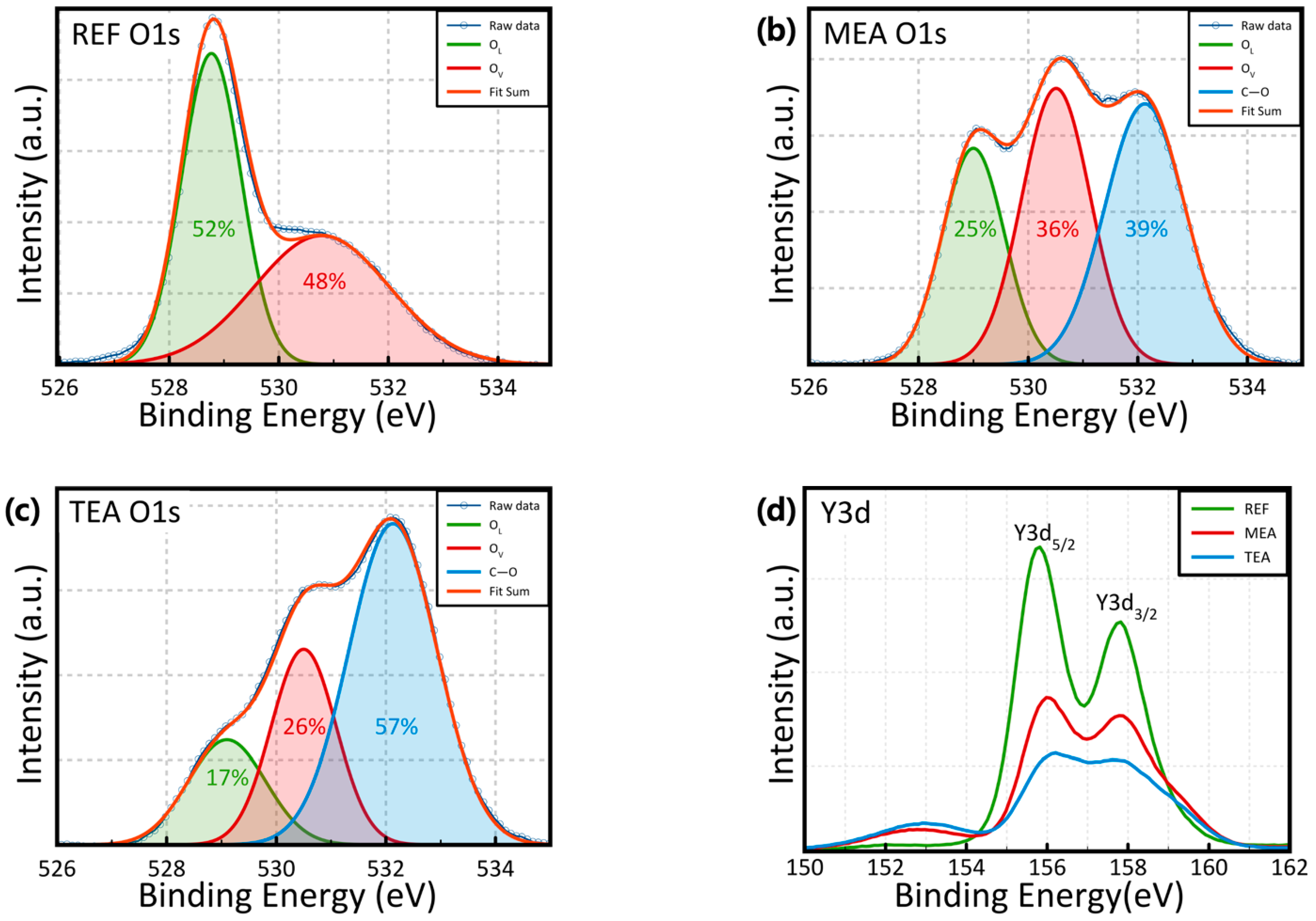
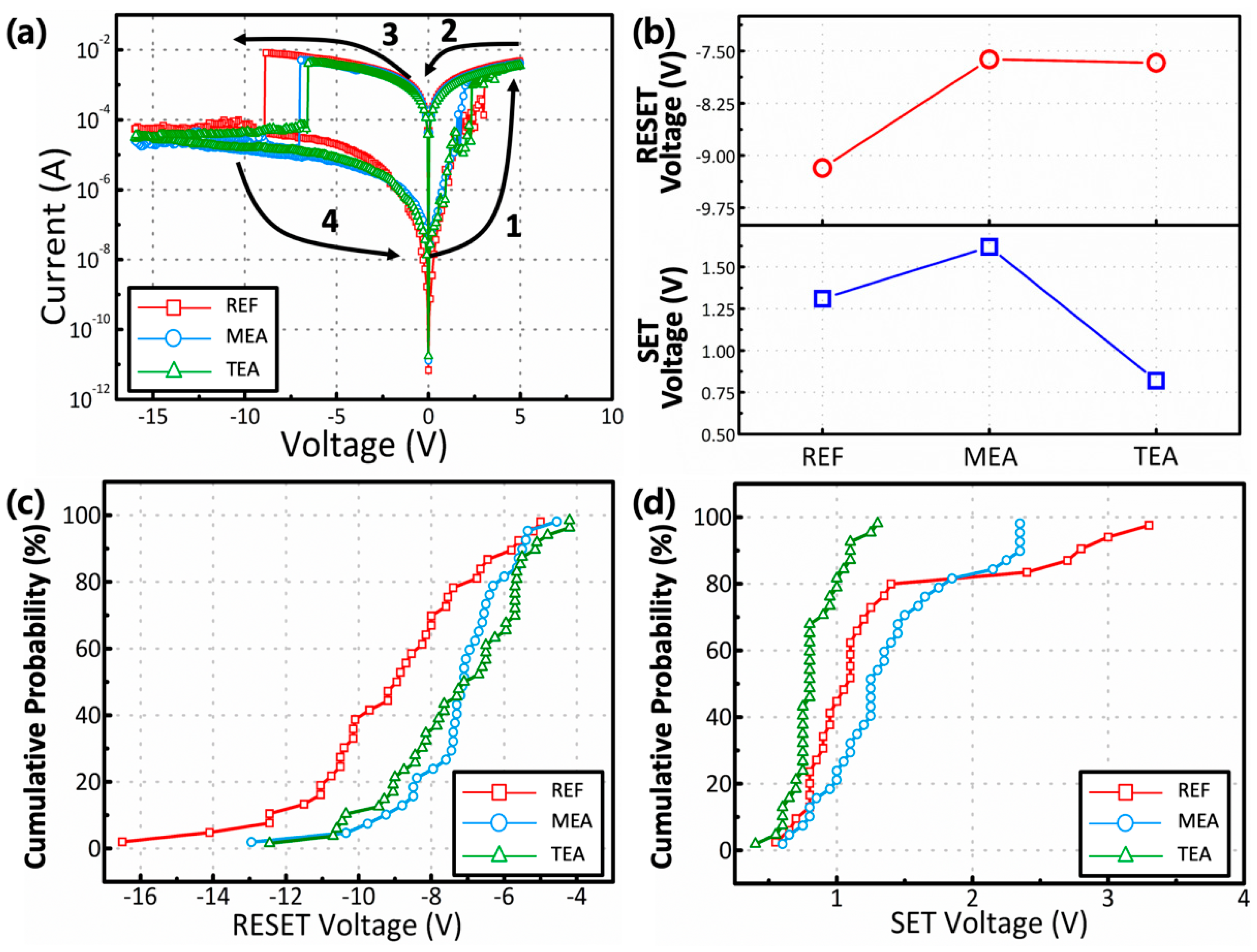
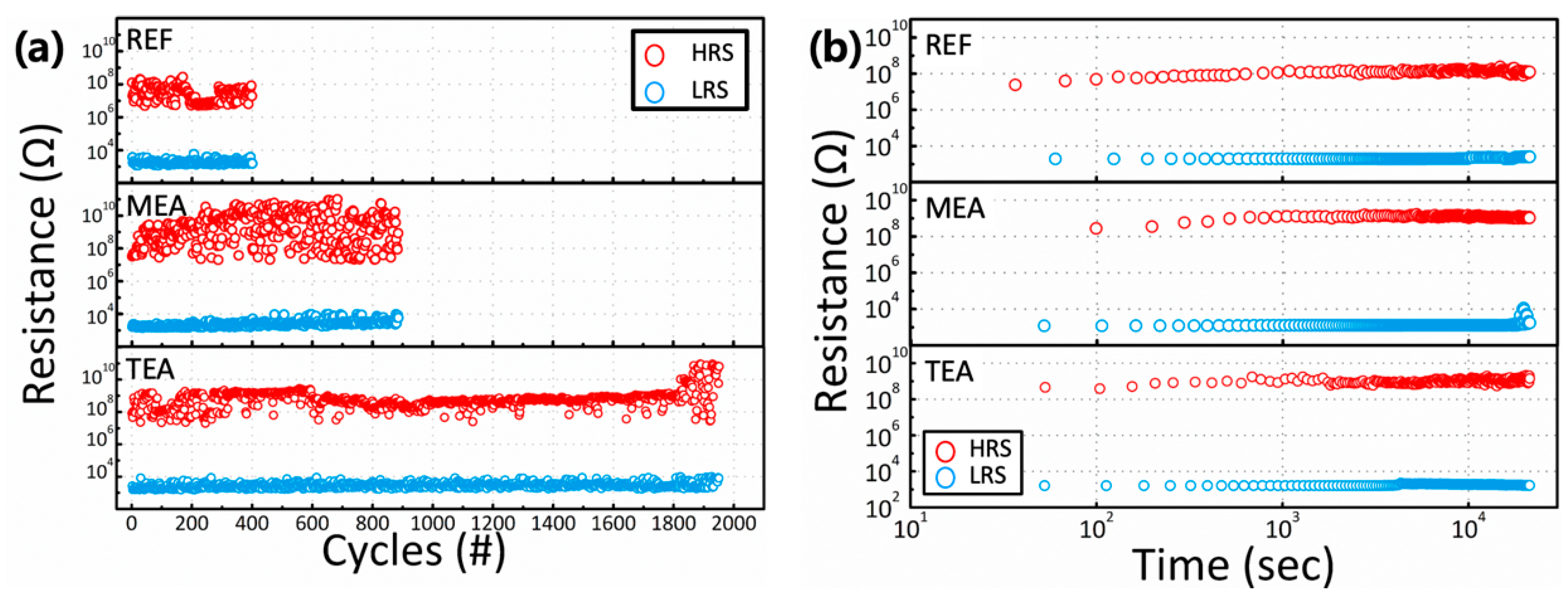
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, Z.; Joshi, S.; Savel’ev, S.E.; Jiang, H.; Midya, R.; Lin, P.; Hu, M.; Ge, N.; Strachan, J.P.; Li, Z.; et al. Memristors with diffusive dynamics as synaptic emulators for neuromorphic computing. Nat. Mater. 2017, 16, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.H.; Wang, Z.; Kim, K.M.; Wu, H.; Ravichandran, V.; Xia, Q.; Hwang, C.S.; Yang, J.J. An artificial nociceptor based on a diffusive memristor. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, D.S.; Hwang, C.S. Nonvolatile Memory Materials for Neuromorphic Intelligent Machines. Adv. Mater. 2018, 30, 1704729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Subramanian, V. Effect of electrode material on resistive switching memory behavior of solution-processed resistive switches: Realization of robust multi-level cell. Thin Solid Films 2017, 625, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.; Chung, S.; Jang, J.; Biaou, C.; Subramanian, V. Solution-processed complementary resistive switching arrays for associative memory. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2017, 64, 4310–4316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.; Kim, T.; Jang, B.; Lee, W.Y.; Song, K.C.; Kim, H.S.; Do, G.Y.; Hwang, S.B.; Chung, S.; Jang, J. Impact of Device Area and Film Thickness on Performance of Sol-gel Processed ZrO2 RRAM. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2018, 39, 668–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, S.; Lee, H.; Lee, W.Y.; Jang, B.; Kwon, H.J.; Kim, K.; Jang, J. Effect of Annealing Environment on the Performance of Sol–Gel-Processed ZrO2 RRAM. Electronics 2019, 8, 947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.; Feng, Y.; Huang, P.; Liu, L.; Kang, J. Low-Power Resistive Switching Characteristic in HfO2/TiOx Bi-Layer Resistive Random-Access Memory. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 14, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piros, E.; Petzold, S.; Zintler, A.; Kaiser, N.; Vogel, T.; Eilhardt, R.; Wenger, C.; Luna, L.M.; Alff, L. Enhanced thermal stability of yttrium oxide-based RRAM devices with inhomogeneous Schottky-barrier. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2020, 177, 013504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petzold, S.; Piros, E.; Sharath, S.U.; Zintler, A.; Hildebrandt, E.; Molina-Luna, L.; Wenger, C.; Alff, L. Gradual reset and set characteristics in yttrium oxide based resistive random access memory. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 075008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiam, S.Y.; Chim, W.K.; Pi, C.; Huan, A.C.H.; Wang, S.J.; Pan, J.S.; Turner, S.; Zhang, J. Band alignment of yttrium oxide on various relaxed and strained semiconductor substrates. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 083702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rushchanskii, K.Z.; Blügel, S.; Ležaić, M. Ab initio phase diagrams of Hf-O, Zr-O and Y-O: A comparative study. Faraday Discuss. 2019, 213, 321–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Mukherjee, S. Realization of synaptic learning and memory functions in Y2O3 based memristive device fabricated by dual ion beam sputtering. Nanotechnology 2018, 29, 055203–055211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.; Lee, C.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, S.H.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, I.M.; Jang, J. Enhanced switching ratio of sol–gel-processed Y2O3 RRAM device by suppressing oxygen vacancy formation at high annealing temperatures. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2022, 37, 015007–105013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Das, M.; Garg, V.; Sengar, B.S.; Htay, M.T.; Kumar, S.; Kranti, A.; Mukherjee, S. Forming-free high- endurance Al/ZnO/Al memristor fabricated by dual ion beam sputtering. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2017, 110, 253509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, H.; Hu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Song, Z. Simultaneously high thermal stability and ultra-fast phase change speed based on samarium-doped antimony thin films. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 31110–31114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Xu, H.Y.; Li, X.H.; Yu, H.; Liu, Y.C.; Zhu, X.J. Synaptic learning and memory functions achieved using oxygen ion migration/diffusion in an amorphous InGaZnO memristor. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2012, 22, 2759–2765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, C.L.; Hou, T.H.; Chen, M.C.; Huang, J.J. Dependence of read margin on pull-up schemes in high-density one selector–one resistor crossbar array. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Y.; Huang, P.; Chen, B.; Yang, X.; Gao, B.; Wang, J.; Zeng, L.; Du, G.; Kang, J. RRAM, Crossbar array with cell selection device: A device and circuit interaction study. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2013, 60, 719–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.; Lee, W.Y.; Kim, H.J.; Bae, J.H.; Kang, I.M.; Lim, D.; Kim, K.; Jang, J. Extremely bias stress stable enhancement mode sol–gel-processed SnO2 thin-film transistors with Y2O3 passivation layers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2021, 559, 149971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niraula, D.; Karpov, V. Comprehensive numerical modeling of filamentary RRAM devices including voltage ramp-rate and cycle-to-cycle variations. J. Appl. Phys. 2018, 124, 174502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, V.G.; Niraula, D.; Karpov, I.V.; Kotlyar, R. Thermodynamics of phase transitions and bipolar filamentary switching in resistive random-access memory. Phys. Rev. Appl. 2018, 8, 024028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waser, R.; Aono, M. Nanoionics-Based Resistive Switching Memories. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 833–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.C.; Pan, F.; Liu, Q.; Liu, M.; Zeng, F. Fully Room- Temperature-Fabricated Nonvolatile Resistive Memory for Ultrafast and High-Density Memory Application. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1636–1643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.H.; Kim, M.; Jang, J.; Lee, K.H.; Jho, J.Y.; Park, J.H. Tip-enhanced electric field-driven efficient charge injection and transport in organic material-based resistive memories. Appl. Mater. Today 2020, 20, 100746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Shin, J.; Lee, D.; Woo, J.; Hwang, H. Improved Switching Variability and Stability by Activating a Single Conductive Filament. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2012, 33, 646–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Park, T.H.; Yoon, K.J.; Seong, W.M.; Jeon, J.W.; Kwon, Y.J.; Kim, Y.; Kwon, D.E.; Kim, G.S.; Ha, T.J.; et al. Fabrication of a Cu-Cone-Shaped Cation Source Inserted Conductive Bridge Random Access Memory and Its Improved Switching Reliability. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019, 29, 1806278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Long, S.; Lv, H.; Wang, W.; Niu, J.; Huo, Z.; Chen, J.; Liu, M. Controllable Growth of Nanoscale Conductive Filaments in Solid- Electrolyte-Based ReRAM by Using a Metal Nanocrystal Covered Bottom Electrode. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6162–6168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, K.Y.; Kim, Y.; Antolinez, F.V.; Ha, J.S.; Lee, S.S.; Park, J.H. Controllable Formation of Nanofilaments in Resistive Memories via Tip-Enhanced Electric Fields. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2016, 2, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, J.; Kang, H.; Chakravarthula, H.C.N.; Subramanian, V. Fully inkjet-printed transparent oxide thin film transistors using a fugitive wettability switch. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2015, 1, 1500086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheideler, W.J.; Jang, J.; Karim, M.A.U.; Kitsomboonloha, R.; Zeumault, Z.; Subramanian, V. Gravure-Printed Sol–Gels on Flexible Glass: A Scalable Route to Additively Patterned Transparent Conductors. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 12679–12687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birnie, D.P. Rational solvent selection strategies to combat striation formation during spin coating of thin films. J. Mater. Res. 2001, 16, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birnie, D.P. A Model for Drying Control Cosolvent Selection for Spin-Coating Uniformity: The Thin Film Limit. Langmuir 2013, 29, 9072–9078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchiyama, H.; Matsui, T.; Kozuka, H. Spontaneous Pattern Formation Induced by Bénard−Marangoni Convection for Sol−Gel-Derived Titania Dip-Coating Films: Effect of Co-solvents with a High Surface Tension and Low Volatility. Langmuir 2015, 31, 12497–12504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houng, B.; Huang, C.L.; Tsai, S.Y. Effect of the pH on the growth and properties of sol–gel derived boron-doped ZnO transparent conducting thin film. J. Cryst. Growth 2007, 307, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, G.; Orlowski, M.K. Correlation between set and reset voltages in resistive RAM cells. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2015, 15, 1124–1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menzel, S.; Waser, R. Analytical analysis of the generic SET and RESET characteristics of electrochemical metallization memory cells. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11003–11010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Laurentis, S.; Nardi, F.; Balatti, S.; Gilmer, D.C.; Ielemini, D. Resistive switching by voltage-driven ion migration in bipolar RRAMdPart II: Modeling. IEEE Trans. Elect. Dev. 2012, 59, 2468–2475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Name (Abbreviation) | Surface Tension (N/m) at 25 °C | Boiling Point (°C) | Vapor Pressure (mm Hg) at 25 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2-methoxyethanol (2-ME) | 42.8 | 124.0 | 9.5 |
| Ethanolamine (MEA) | 48.3 | 170.0 | 0.4 |
| Triethylamine (TEA) | 22.02 | 88.8 | 57.07 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, D.-W.; Kim, H.-J.; Lee, W.-Y.; Kim, K.; Lee, S.-H.; Bae, J.-H.; Kang, I.-M.; Kim, K.; Jang, J. Enhanced Switching Reliability of Sol–Gel-Processed Y2O3 RRAM Devices Based on Y2O3 Surface Roughness-Induced Local Electric Field. Materials 2022, 15, 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051943
Kim D-W, Kim H-J, Lee W-Y, Kim K, Lee S-H, Bae J-H, Kang I-M, Kim K, Jang J. Enhanced Switching Reliability of Sol–Gel-Processed Y2O3 RRAM Devices Based on Y2O3 Surface Roughness-Induced Local Electric Field. Materials. 2022; 15(5):1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051943
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, Do-Won, Hyeon-Joong Kim, Won-Yong Lee, Kyoungdu Kim, Sin-Hyung Lee, Jin-Hyuk Bae, In-Man Kang, Kwangeun Kim, and Jaewon Jang. 2022. "Enhanced Switching Reliability of Sol–Gel-Processed Y2O3 RRAM Devices Based on Y2O3 Surface Roughness-Induced Local Electric Field" Materials 15, no. 5: 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051943
APA StyleKim, D.-W., Kim, H.-J., Lee, W.-Y., Kim, K., Lee, S.-H., Bae, J.-H., Kang, I.-M., Kim, K., & Jang, J. (2022). Enhanced Switching Reliability of Sol–Gel-Processed Y2O3 RRAM Devices Based on Y2O3 Surface Roughness-Induced Local Electric Field. Materials, 15(5), 1943. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15051943








