Effect of Er on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Aluminum Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
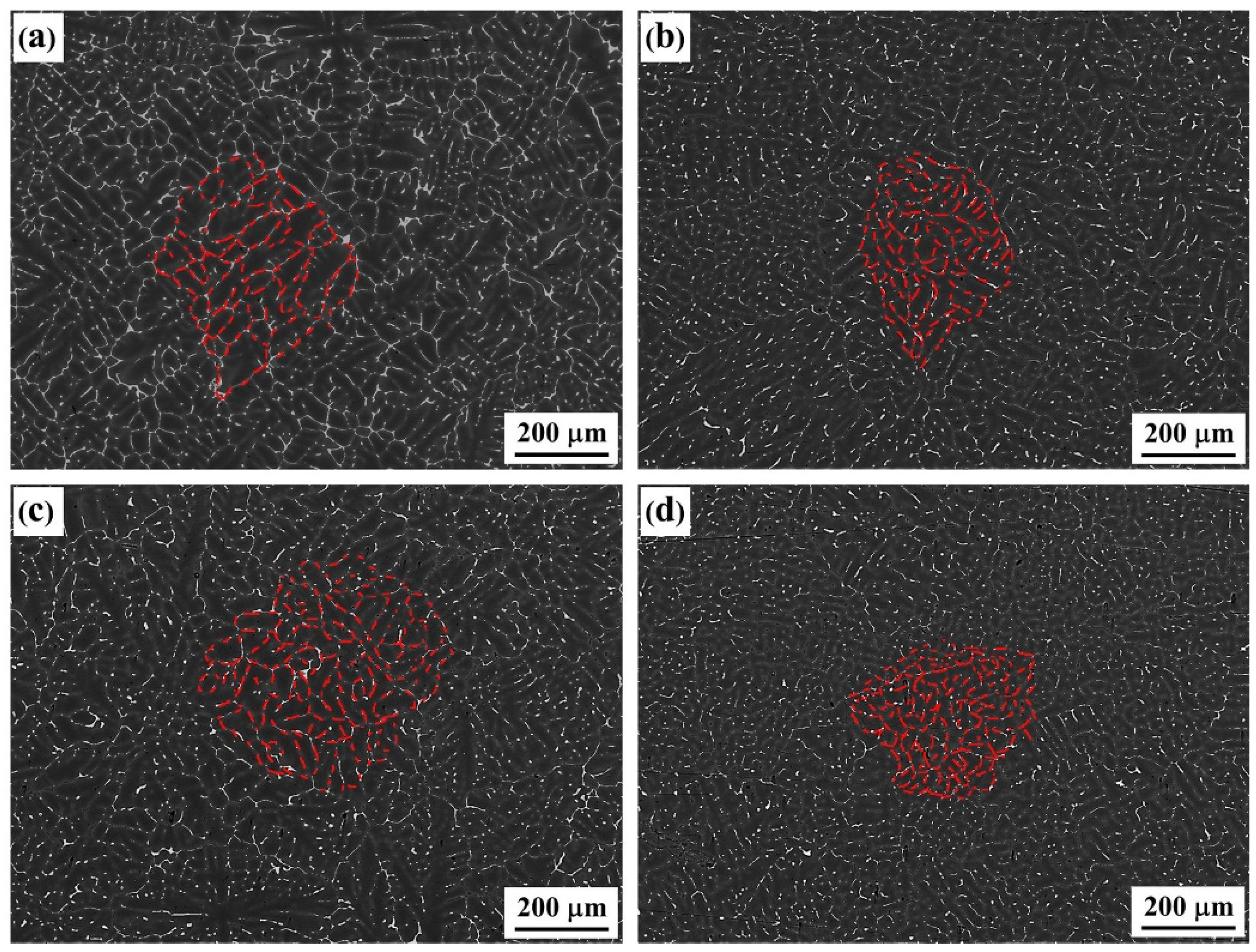
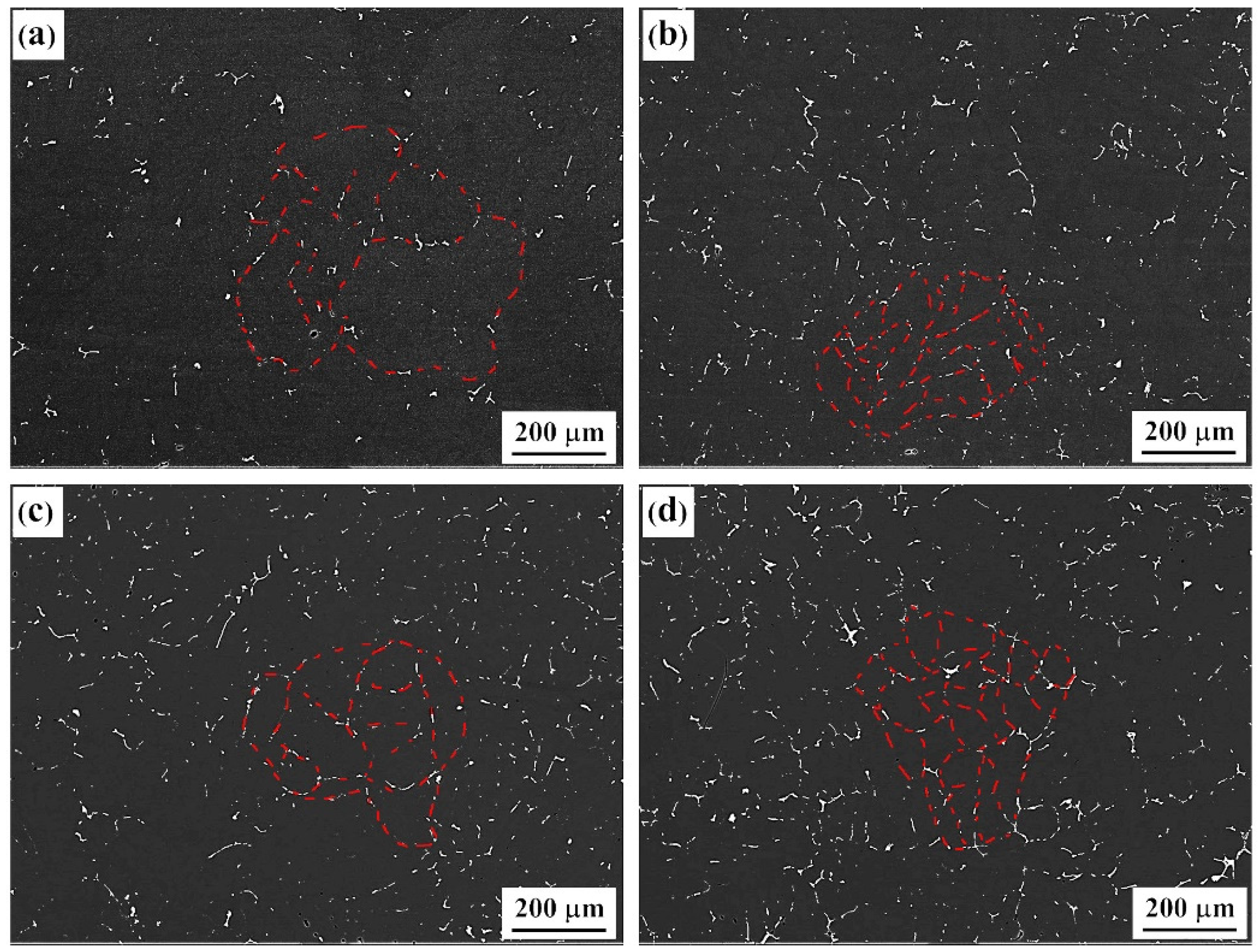
3.1. As-Cast and Solid Solution-State Microstructural Characteristics of Alloy
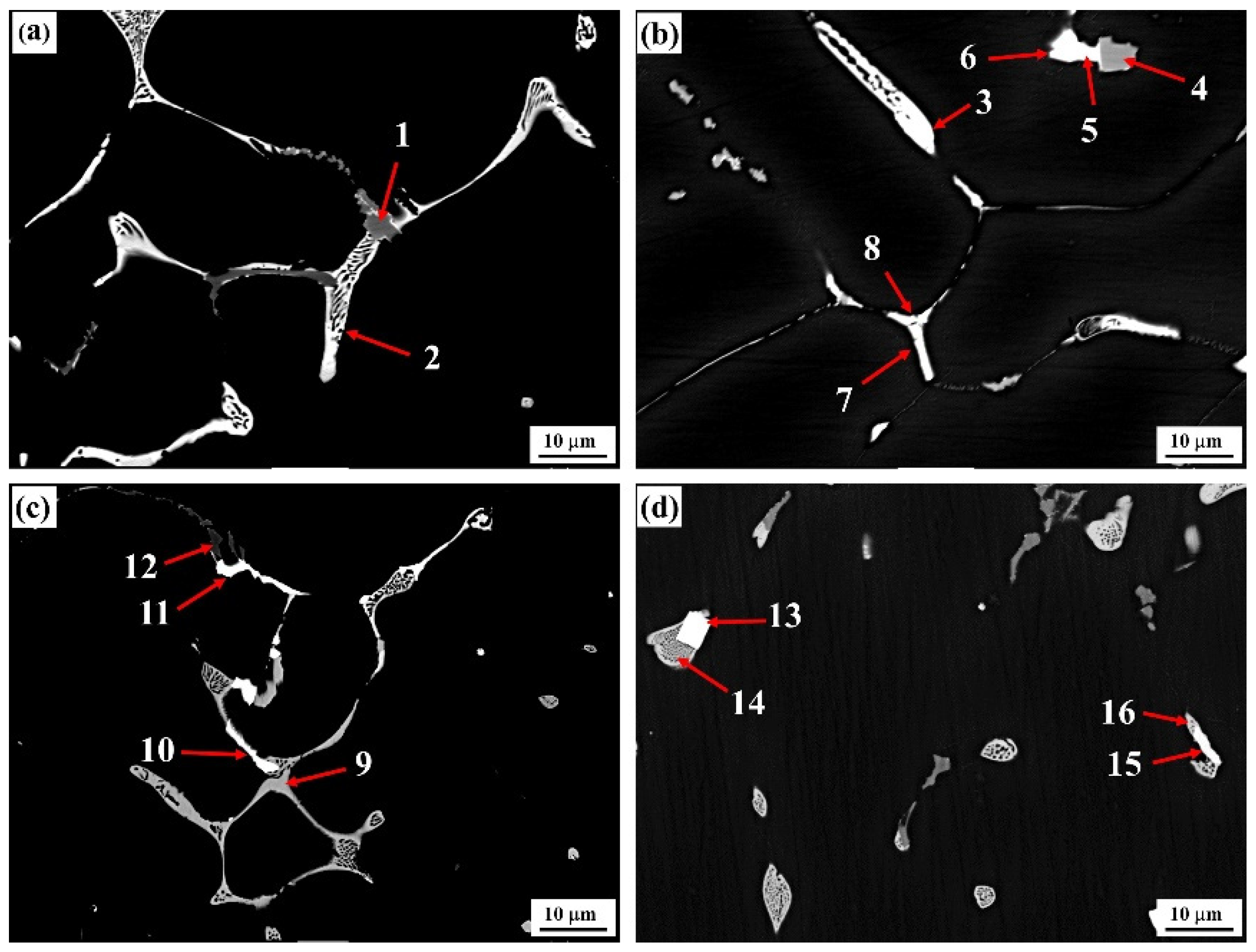
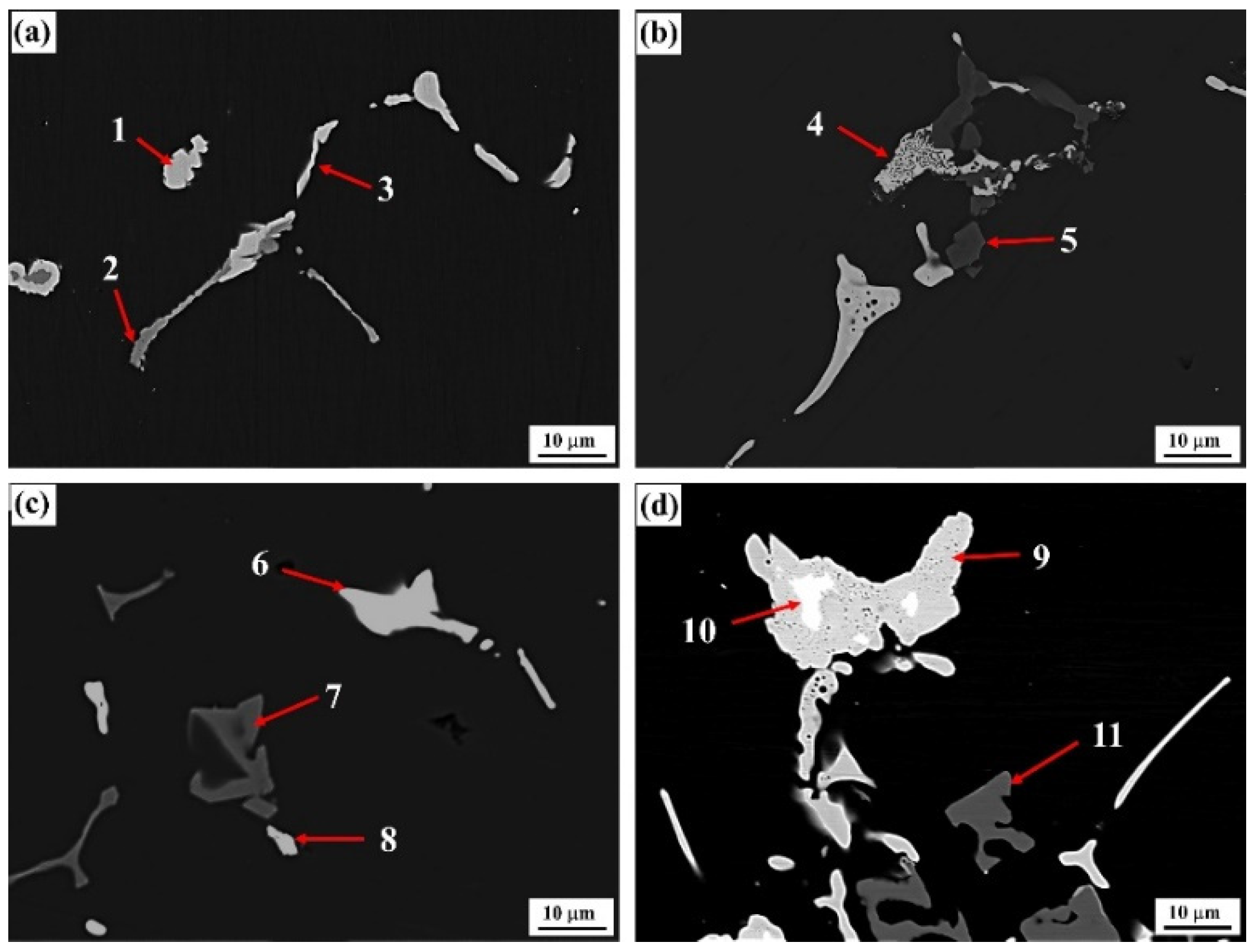
3.2. Types of Evolution Characteristics of Second Phases at the Grain Boundary
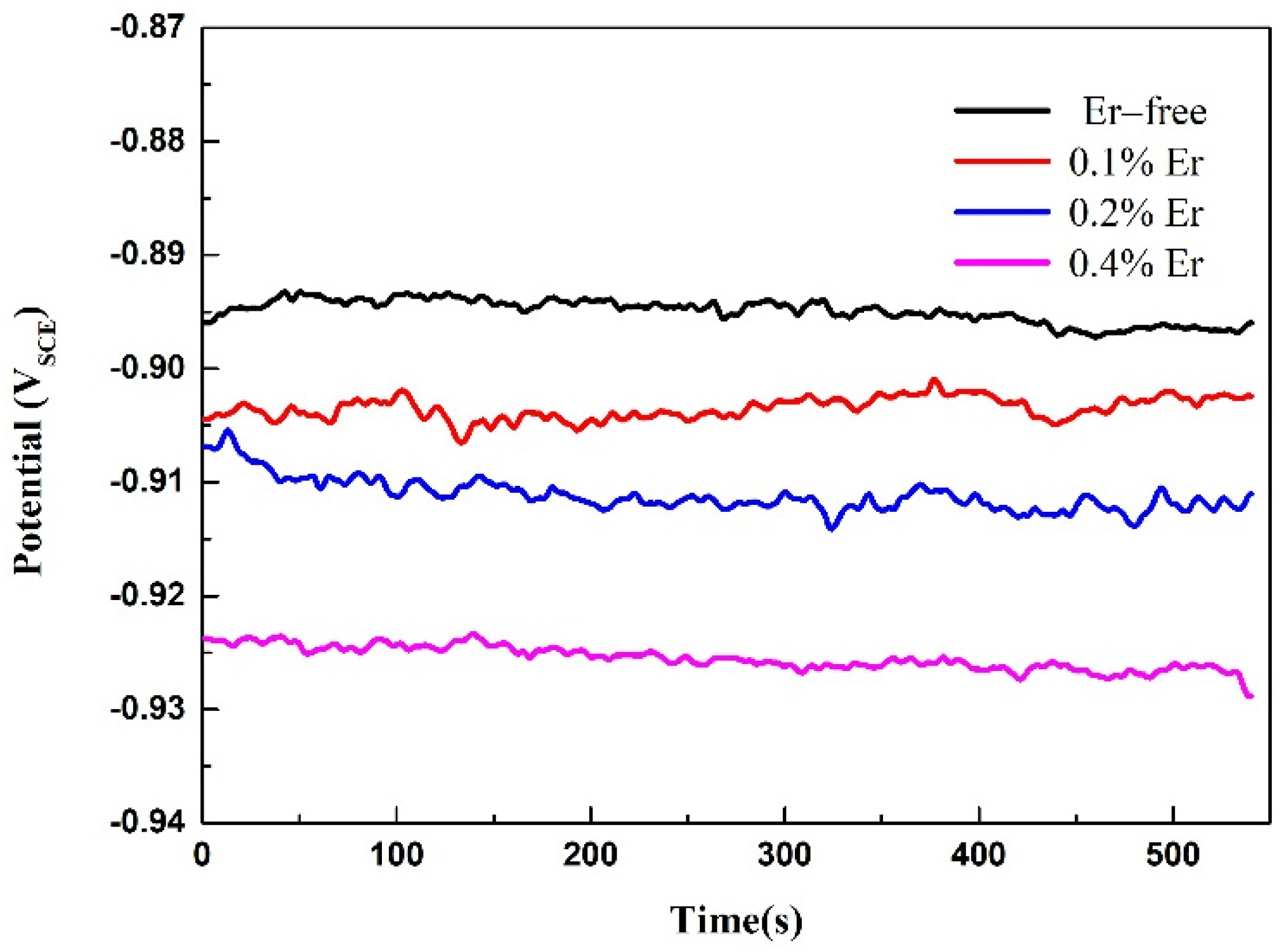
3.3. Corrosion Resistance
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- As the Er content (0–0.4%) increased in the Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr alloy, the types of second phases formed by Er control the microstructure; the dendrite arms and grains size were first refined, then coarsened and refined again.
- (2)
- The interaction between Cu and Er can form the ternary Al8Cu4Er phase in the Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr alloy; however, when the Er content increased, the primary Al3Er phase was formed in the center of the Al8Cu4Er phase, which showed an interactive and competitive growth relation with the Al8Cu4Er phase.
- (3)
- The Al8Cu4Er and Al3Er phases enhanced the corrosion resistance of the alloy by changing the potential difference between the grain boundary phases and the matrix; however, higher Er content lead to the coarsening of the Er-containing phase, which inhibited the further improvement of the corrosion performance of the alloy.
- (4)
- To enhance the corrosion resistance of the alloy, it is important to control the interaction between the Al8Cu4Er phase and Cu during its formation and growth process. In the future, by studying the effect of Cu enrichment and redistribution on the Al8Cu4Er phase, a finely dispersed Er-containing rare earth phase can be obtained, thereby improving the corrosion performance of the alloy.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jin, R.Z.; Hou, L.G.; Shi, J.T.; Hua, C.; Zhang, J.S. Improvement of Mechanical Properties and Corrosion Resistance by Deformation Induced Precipitation in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu Alloy. Mater. Sci. Forum 2017, 898, 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Marlaud, T.; Malki, B.; Henon, C.; Deschamps, A.; Baroux, B. Relationship between alloy composition, microstructure and exfoliation corrosion in Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloys. Corros. Sci. 2011, 53, 3139–3149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, J.C.; Starke, E.A., Jr. Progress in structural materials for aerospace systems. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 5775–5799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Q.; Frankel, G.S. Effect of Cu Content on Corrosion Behavior of 7xxx Series Aluminum Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2004, 151, B271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Hyer, H.; Chang, J.; Mehta, A.; Huynh, T.; Yang, Y.; Sohn, Y. Microstructure, mechanical performance, and corrosion behavior of additively manufactured aluminum alloy 5083 with 0.7 and 1.0wt.% Zr addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 823, 141679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Liu, T.; He, C.; Ding, J.; Liu, E.; Shi, C.; Li, J.; Zhao, N. Evolution of microstructure and properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr alloy during aging treatment. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 658, 946–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, H.; Liang, H.; Yang, W.D.; Liu, B.X.; Li, T.S.; Yao, G.C. Study of Effect of Ce-Rich Mixed Rare Earth on Corrosivity of New 5XXX Series Aluminium Alloys. Adv. Mater. Res. 2011, 314–316, 1449–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senkov, O.N.; Shagiev, M.R.; Senkova, S.V.; Miracle, D.B. Precipitation of Al3(Sc,Zr) particles in an Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr alloy during conventional solution heat treatment and its effect on tensile properties. Acta Mater. 2008, 56, 3723–3738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Gao, Z.; Bai, Y.; Zhao, P.; Mao, W. Effect of Sc on the Hot Cracking Properties of 7xxx Aluminum Alloy and the Microstructure of Squeeze Castings. Materials 2021, 14, 6881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buranova, Y.; Kulitskiy, V.; Peterlechner, M.; Mogucheva, A.; Kaibyshev, R.; Divinski, S.V.; Wilde, G. Al3(Sc,Zr)-based precipitates in Al–Mg alloy: Effect of severe deformation. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 210–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.C.; Chao, H.; Chen, K.H. Effect of Zr, Er and Cr additions on microstructures and properties of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 610, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anna, K.; Mikhaylovskaya, A.V.; Kotov, A.; Portnoy, V.K. Effect of Homogenization Treatment on Superplastic Properties of Aluminum Based Alloy with Minor Zr and Sc Additions. Defect Diffus. Forum 2018, 385, 84–90. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, M.; Liu, X.; Zhang, Z.; Song, Y.; Bai, L. Effect of Adding Rare Earth Elements Er and Gd on the Corrosion Residual Strength of Magnesium Alloy. Open Phys. 2019, 17, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, J.; Cao, J.; Luo, L.; Guo, S.; Ou, L.; Liu, Z.; Bai, S. Effect of Minor Er Additions on the Microstructures and Mechanical Properties of Cast Al-Cu-Mg-Ag Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.H.; Wiessner, M.; Albu, M.; Wurster, S.; Sartory, B.; Hofer, F.; Schumacher, P. Correlative characterization of primary Al3(Sc,Zr) phase in an Al-Zn-Mg based alloy. Mater. Charact. 2015, 102, 62–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Li, H.; Lai, Y.; Ou, Y.; Li, D. Effects of minor Zr and Er on microstructure and mechanical properties of pure aluminum. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 580, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.F.; Mou, S.Z.; Yang, J.J.; Jin, T.N.; Nie, Z.R.; Yin, Z.M. Effect of trace rare earth element Er on Al-Zn-Mg alloy. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2006, 16, 598–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Jiang, F.; Ai, F.; Yan, H. Effects of rare earth Er additions on microstructure development and mechanical properties of die-cast ADC12 aluminum alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2012, 538, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.N.; Zhou, H.F.; Zhang, X.F. Effects of Al8Cu4Er Phase on Corrosion Behavior of Al–Cu–Mg alloy with Er addition. Acta Metall. Sin. Engl. Lett. 2020, 33, 1379–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, B.; Liu, Z.; Li, Y.; Hou, Y.; Xu, C. Microstructures and fatigue fracture behavior of an Al–Cu–Mg–Ag alloy with addition of rare earth Er. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2010, 527, 1806–1814. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.; Xiong, Y.; Ting, L.I. Effect of Er on Microstructure and Properties of Aluminum Alloy for Vehicle Frame. Dev. Appl. Mater. 2019, 34, 57–62. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Liu, Z.; Ma, F.; Xia, Q. Phase Constitution and Growth Manner at Grain Boundary in Al-Cu-Mg-Ag-Er Alloy. Rare Metal. Mater. Eng. 2008, 37, 1019–1022. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.M.; Xing, T.Y.; Li, G.; Yuan, X.T.; Zhao, Y.T.; Wang, J.J.; Gu, K.X.; Zhang, H. Thermodynamic Condition and Behavior of Precipitates in Al2O3p/7055 Composites with Cryogenic Treatment. Key Eng. Mater. 2014, 575–576, 378–381. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, P.; Chen, S.; Chen, K. Effects of Cu content on microstructure and properties of super-high-strength Al-9.3Zn-2.4Mg-xCu-Zr alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 788, 329–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wang, J.H.; Fu, C.W. Characterization of pitting corrosion of 7A60 aluminum alloy by EN and EIS techniques. Trans. Nonferr. Met. Soc. China 2014, 24, 3907–3916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Bucbbeit, R.G. Electrochemical Characteristics of Intermetallic Phases in Aluminum Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2005, 152, B140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aballe, A.; Bethencourt, M.; Botana, F.J.; Cano, M.J.; Marcos, M. Localized alkaline corrosion of alloy AA5083 in neutral 3.5% NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2001, 43, 1657–1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birbilis, N.; Cavanaugh, M.K.; Buchheit, R.G. Electrochemical behavior and localized corrosion associated with Al7Cu2Fe particles in aluminum alloy 7075-T651. Corros. Sci. 2006, 48, 4202–4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Lin, M.; Yang, G. Effect of Eron Corrosion Behavior of Marine Engineering 5052 Al-alloy. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Protection. 2021, 41, 686–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


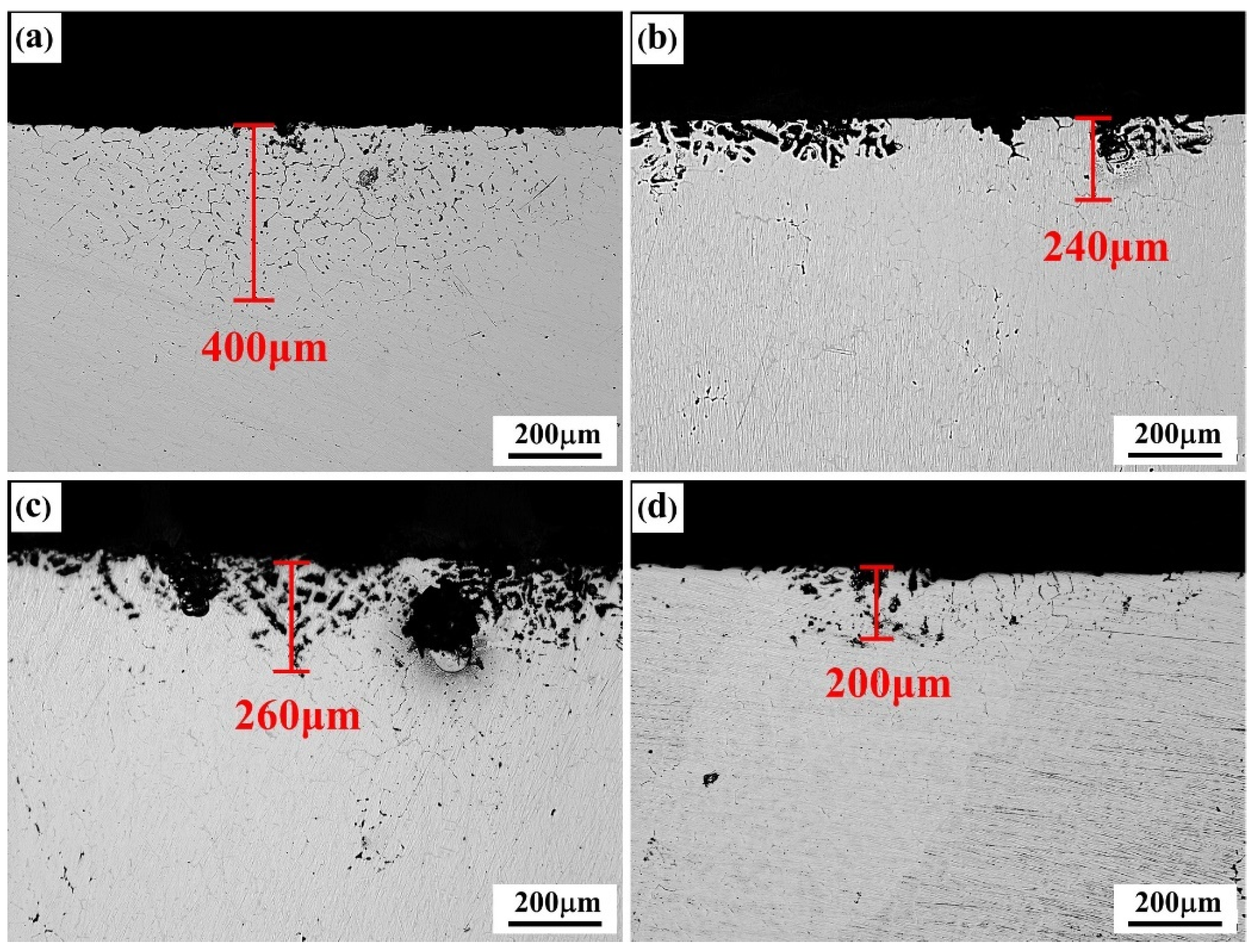
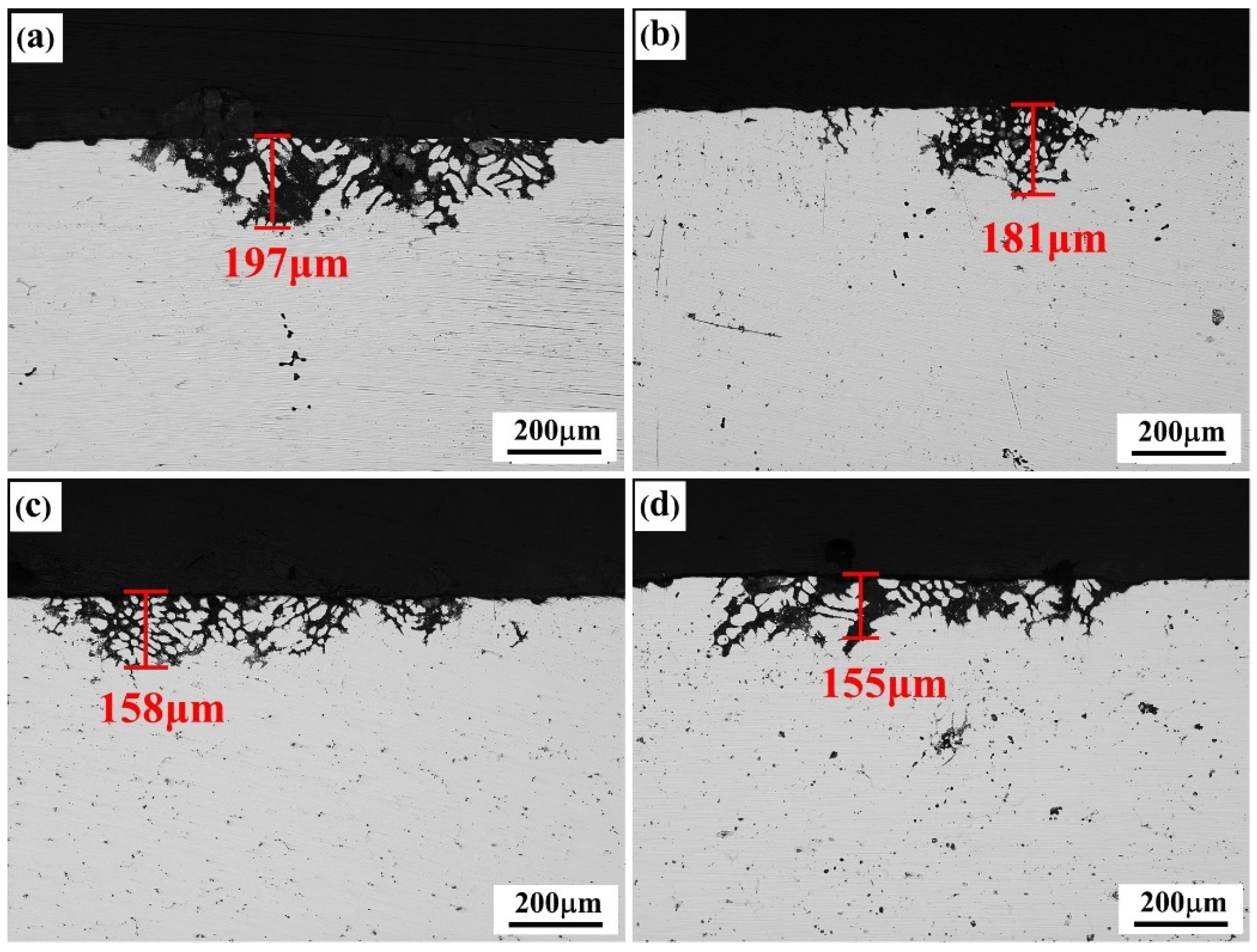

| Alloys | Zn | Mg | Cu | Sc | Zr | Er | Fe | Al |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| #1 | 8.80 | 1.73 | 0.99 | 0.13 | 0.11 | - | 0.11 | Bal. |
| #2 | 8.92 | 1.77 | 1.03 | 0.13 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.13 | Bal. |
| #3 | 8.77 | 1.79 | 1.00 | 0.08 | 0.13 | 0.18 | 0.12 | Bal. |
| #4 | 9.01 | 1.87 | 1.02 | 0.08 | 0.10 | 0.41 | 0.16 | Bal. |
| Alloys | Points | Phase Type | Al | Zn | Mg | Cu | Er | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | Al–Fe | 64.47 | 1.99 | 0.65 | 5.29 | - | 27.57 |
| 2 | T | 41.4 | 29.92 | 20.83 | 7.71 | - | - | |
| b | 3 | Al–Cu–Er | 50.51 | 11.1 | 4.51 | 27.19 | 4.32 | 1.72 |
| 4 | Al–Fe | 67.22 | 1.77 | 0.75 | 3.37 | - | 26.77 | |
| 5 | T | 30.41 | 29.43 | 28.03 | 10.62 | 0.16 | 1.31 | |
| 6 | Al–Cu–Er | 47.97 | 11.33 | 6.72 | 29.03 | 3.02 | 1.52 | |
| 7 | T | 58.04 | 19.82 | 17.75 | 4.36 | - | - | |
| 8 | Al–Cu–Er | 68.65 | 7.34 | 2.78 | 17.34 | 2.41 | 1.05 | |
| c | 9 | T | 26.60 | 33.36 | 31.86 | 7.91 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| 10 | Al–Cu–Er | 48.18 | 9.92 | 2.23 | 32.54 | 4.78 | 1.84 | |
| 11 | Al3Er | 72.68 | 2.41 | 0.53 | 0.54 | 17.03 | 2.69 | |
| 12 | Al–Fe | 66.11 | 1.92 | 0.32 | 3.53 | - | 28.1 | |
| d | 13 | Al3Er | 73.69 | 2.81 | 1.42 | 0.10 | 19.51 | 0.08 |
| 14 | T | 52.13 | 21.41 | 20.50 | 5.52 | 0.35 | 0.08 | |
| 15 | Al–Cu–Er | 55.30 | 9.52 | 1.20 | 26.53 | 6.09 | 1.14 | |
| 16 | T | 48.61 | 25.80 | 20.31 | 4.84 | 0.30 | 0.10 |
| Alloys | Points | Phase Type | Al | Zn | Mg | Cu | Er | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | 1 | Al–Cu–Fe | 71.87 | 1.18 | 0.03 | 16.58 | - | 10.31 |
| 2 | Al–Fe | 76.40 | 1.69 | 0.45 | 2.39 | - | 15.94 | |
| 3 | Al–Cu–Fe | 73.87 | 1.34 | 0.24 | 15.37 | - | 9.11 | |
| b | 4 | Al8Cu4Er | 57.78 | 8.55 | 1.05 | 26.15 | 5.40 | 0.51 |
| 5 | Al–Fe | 78.46 | 2.87 | 2.41 | 0.82 | 0.41 | 12.63 | |
| c | 6 | Al8Cu4Er | 61.77 | 8.86 | 1.59 | 22.09 | 4.68 | 0.54 |
| 7 | Al–Fe | 75.40 | 1.91 | 0.52 | 2.30 | - | 16.58 | |
| 8 | Al8Cu4Er | 59.37 | 8.94 | 1.84 | 24.02 | 4.75 | 0.61 | |
| d | 9 | Al8Cu4Er | 53.24 | 11.37 | 0.08 | 26.44 | 8.05 | 0.11 |
| 10 | Al3Er | 73.03 | 2.08 | 0.31 | 1.14 | 19.87 | 0.04 | |
| 11 | Al–Fe | 75.99 | 2.17 | 1.07 | 2.74 | 0.05 | 17.64 |
| Alloys | Ecorr (VSCE) | icorr (μA/cm2) |
|---|---|---|
| #1 | −0.88 | 8.3 |
| #2 | −0.90 | 5.9 |
| #3 | −0.90 | 5.7 |
| #4 | −0.94 | 3.4 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Xing, Q.; Wu, X.; Zang, J.; Meng, L.; Zhang, X. Effect of Er on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Aluminum Alloys. Materials 2022, 15, 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031040
Xing Q, Wu X, Zang J, Meng L, Zhang X. Effect of Er on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Aluminum Alloys. Materials. 2022; 15(3):1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031040
Chicago/Turabian StyleXing, Qingyuan, Xiaohui Wu, Jinxin Zang, Linggang Meng, and Xingguo Zhang. 2022. "Effect of Er on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Aluminum Alloys" Materials 15, no. 3: 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031040
APA StyleXing, Q., Wu, X., Zang, J., Meng, L., & Zhang, X. (2022). Effect of Er on Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Al–Zn–Mg–Cu–Sc–Zr Aluminum Alloys. Materials, 15(3), 1040. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15031040





