Shelf Life Prediction of Picric Acid via Model-Based Kinetic Analysis of Its Thermal Decomposition
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
| Differential Scanning Calorimeter | Temperature (°C) | Exposure Time (min) |
| 200–230 | 25–180 | |
| Dry Bath Heater | Temperature (°C) | Exposure Time |
| 140 | 1 week and 5 weeks | |
| 90 | 6 months |
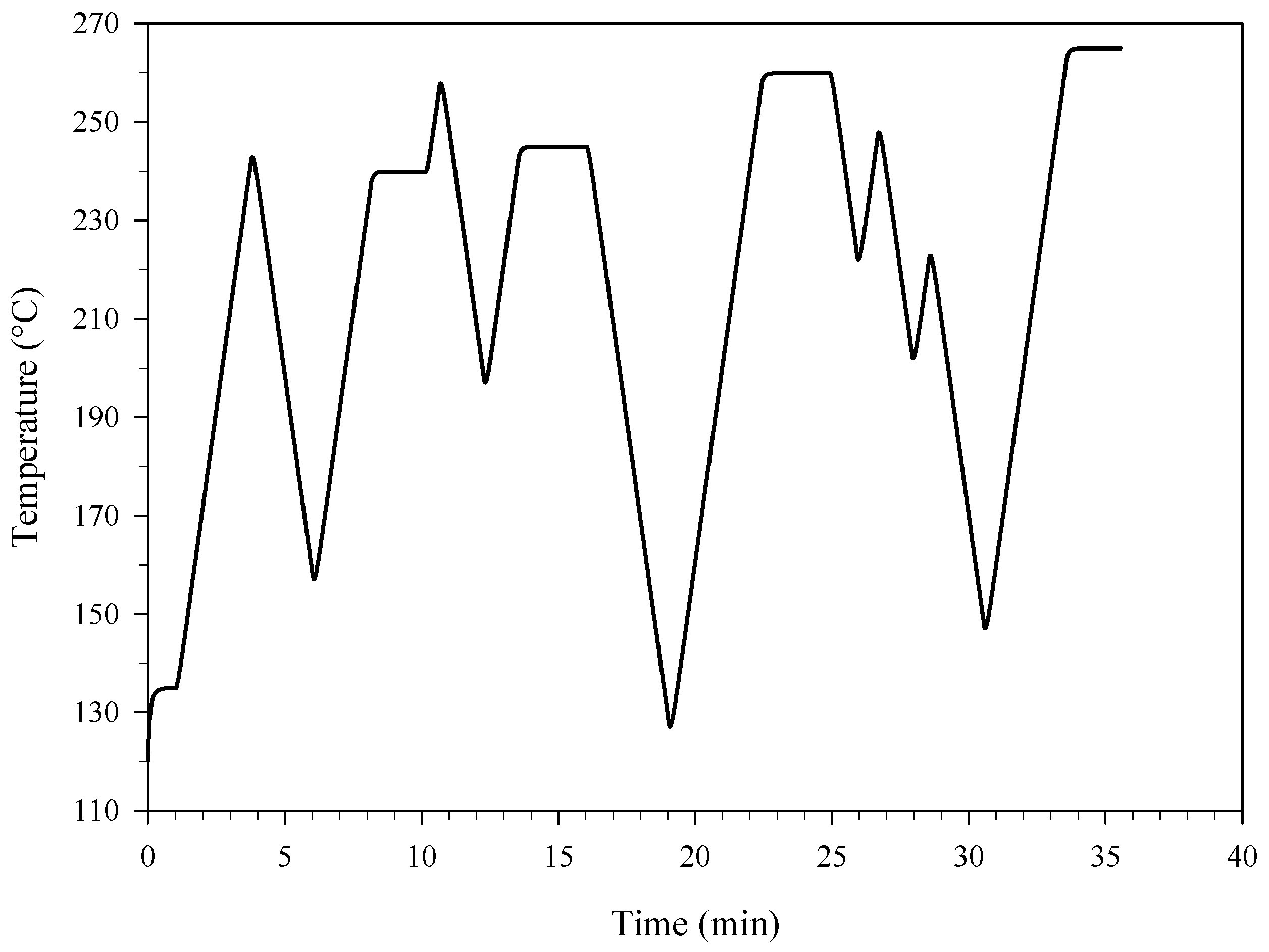
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Estimation and Validation of the Kinetics of Thermal Decomposition of Picric Acid (PA)
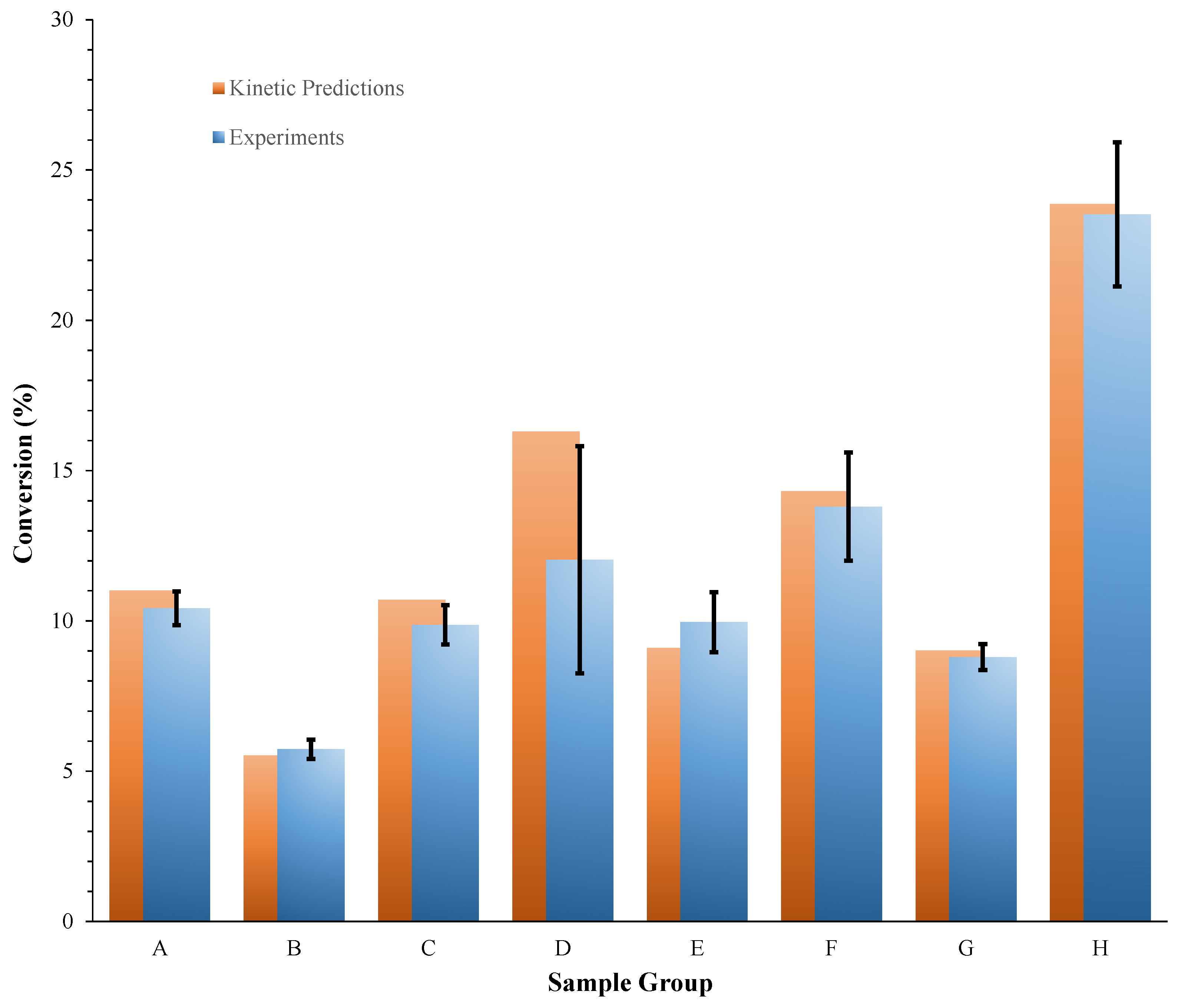
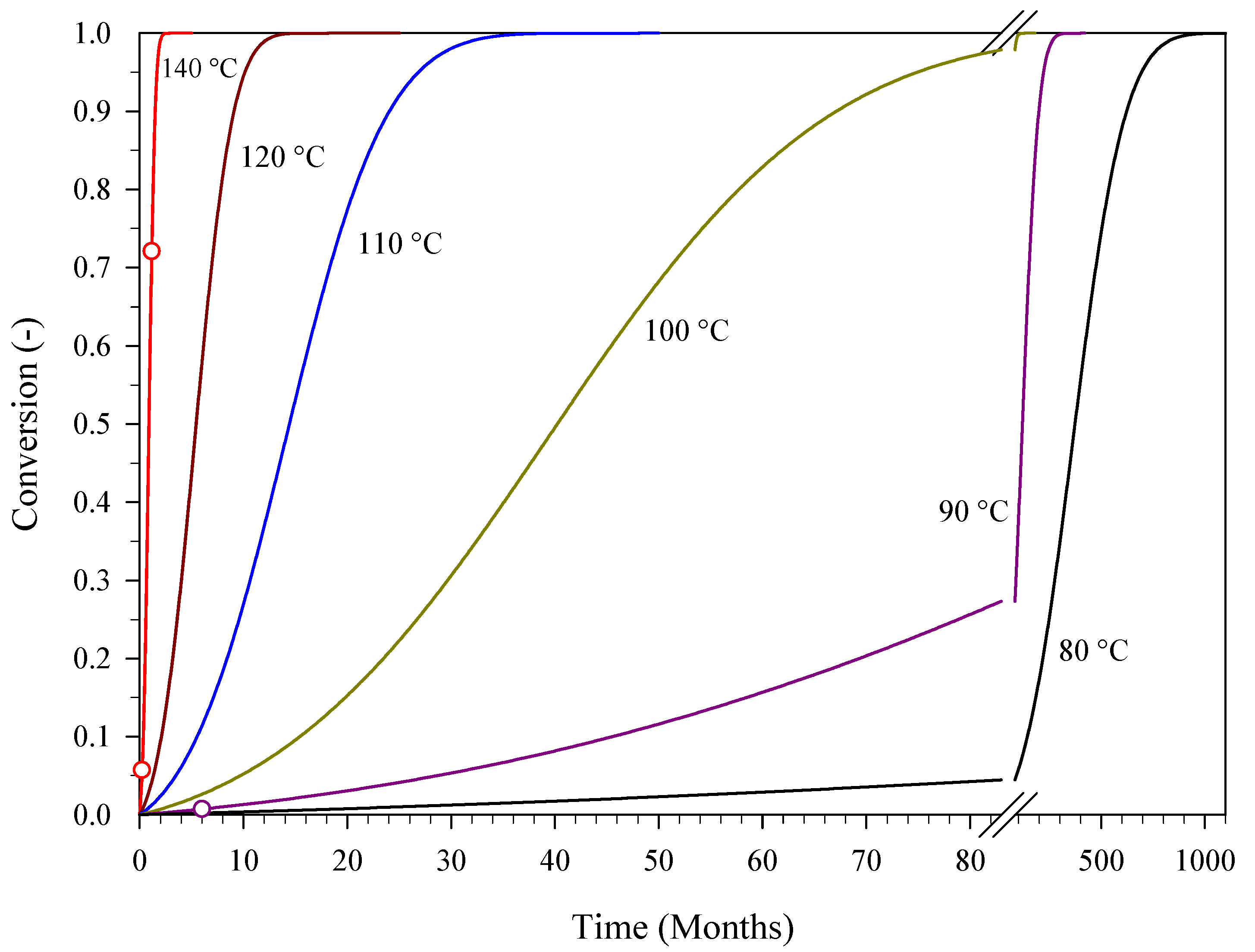
3.2. Kinetic Predictions for Aged PA
| Sample Group | ID | mPA (mg) * | T (°C) | Exposure Time (min) | (%) | (%) | σ (%) | (%) | ε (Equation (6)) (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A | 1 | 5.5 | 200 | 180 | 10.8 | 10.4 | 0.6 | 11.0 | −5.3 |
| 2 | 2.1 | 10.7 | |||||||
| 3 | 4.3 | 9.8 | |||||||
| B | 1 | 3.2 | 210 | 60 | 5.6 | 5.7 | 0.3 | 5.5 | 3.9 |
| 2 | 4.0 | 5.5 | |||||||
| 3 | 4.2 | 6.1 | |||||||
| C | 1 | 2.4 | 210 | 90 | 9.3 | 9.9 | 0.6 | 10.7 | −7.7 |
| 2 | 2.2 | 10.6 | |||||||
| 3 | 2.4 | 9.8 | |||||||
| D | 1 | 2.3 | 210 | 120 | 14.7 14.0 14.9 | 14.5 | 0.5 | 16.3 | −10.8 |
| 2 | 2.1 | ||||||||
| 3 | 2.2 | ||||||||
| E | 1 | 2.3 | 220 | 45 | 10.5 | 10.0 | 1.0 | 9.1 | 9.5 |
| 2 | 6.2 | 8.8 | |||||||
| 3 | 3.2 | 10.6 | |||||||
| F | 1 | 3.2 | 220 | 60 | 15.8 | 13.8 | 1.8 | 14.3 | −3.6 |
| 2 | 2.5 | 13.3 | |||||||
| 3 | 3.7 | 12.4 | |||||||
| G | 1 | 4.9 | 230 | 25 | 9.2 | 8.8 | 0.4 | 9.0 | −2.3 |
| 2 | 3.1 | 8.4 | |||||||
| 3 | 2.8 | 8.8 | |||||||
| H | 1 | 2.1 | 230 | 45 | 22.5 | 23.5 | 2.4 | 23.9 | −1.4 |
| 2 | 8.0 | 26.3 | |||||||
| 3 | 3.4 | 21.8 |
| Temperature (°C) | 70 | 60 | 50 | 40 | 30 | 20 |
| Shelf Life (years) * | 40 | 144 | 564 | 2411 | 11,287 | 58,800 |
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Manelis, G.B.; Nazin, G.M.; Rubtsov, Yu.I.; Strunin, V.A. Thermal Decomposition and Combustion of Explosives and Propellants, 1st ed.; Taylor & Francis: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Vogelsanger, B. Chemical stability, compatibility and shelf life of explosives. Chimia 2004, 58, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AOP-48—Edition 2—Explosives, Nitrocellulose-Based Propellants, Stability Test Procedures and Requirements Using Stabilizer Depletion. Allied Ordnance Publication (AOP), 2008. NATO/PFP Unclassified. Available online: https://www.msiac.nato.int/sites/default/files/media/SurveyonInServiceSurveillanceandStabilityTests/aop-48_edn02_explosives_nitrocellulose_based_propellants_stability_test_procedures_and_requirements_using_stabilizer_depletion_-e.pdf (accessed on 18 September 2022).
- Dubois, C.; Perreault, F. Shelf life prediction of propellants using a reaction severity index. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2002, 27, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benhammada, A.; Trache, D. Thermal decomposition of energetic materials using TG-FTIR and TG-MS: A state-of-the-art review. Appl. Spectrosc. Rev. 2020, 55, 724–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z. Review and prospect of thermal analysis technology applied to study thermal properties of energetic materials. FirePhysChem 2021, 1, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EL-Sayed, S.A. Review of thermal decomposition, kinetics parameters and evolved gases during pyrolysis of energetic materials using different techniques. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2022, 161, 105364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnham, A.K.; Dinh, L.N. A comparison of isoconversional and model-fitting approaches to kinetic parameter estimation and application predictions. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2007, 89, 479–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cheng, Y. Investigation on the thermal stability of nitroguanidine by TG/DSC-MS-FTIR and multivariate non-linear regression. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2010, 100, 949–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harter, A.G.; Klapötke, T.M.; Lechner, J.T.; Stierstorfer, J. Kinetic predictions concerning the long-term stability of TKX-50 and other common explosives using the NETZSCH Kinetics Neo software. Propellants Explos. Pyrotech. 2022, 47, e202200031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Ambekar, A.; Yoh, J.J. Toward understanding the aging effect of energetic materials via advanced isoconversional decomposition kinetics. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 133, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.P.; Back, M.H. Kinetic studies of the thermal decomposition of nitroguanidine using accelerating rate calorimetry. Thermochim. Acta 1988, 127, 89–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brill, T.B.; James, K.J. Kinetics and mechanisms of thermal decomposition of nitroaromatic explosives. Chem. Rev. 1993, 93, 2667–2692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, G.T.; Brems, B.A.; Wight, C.A. Autocatalytic thermal decomposition kinetics of TNT. Thermochim. Acta 2002, 388, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchirico, R. Model selection and parameters estimation in kinetic thermal evaluations using semiempirical models. AIChE J. 2012, 58, 1869–1879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchirico, R. On the use of the generalized autocatalytic models: The thermal decomposition of 3,5-dinitro-4-methylbenzoic acid. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 1300–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llópiz, J.; Romero, M.M.; Jerez, A.; Laureiro, Y. Generalization of the Kissinger equation for several kinetic models. Thermochim. Acta 1995, 256, 205–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kossoy, A.; Hofelich, T. Methodology and software for assessing reactivity ratings of chemical systems. Process Saf. Prog. 2003, 22, 235–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchirico, R.; Lisi, L.; Di Sarli, V. The combined effect of ambient conditions and diluting salt on the degradation of picric acid: An in situ DRIFT study. Materials 2022, 15, 6029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
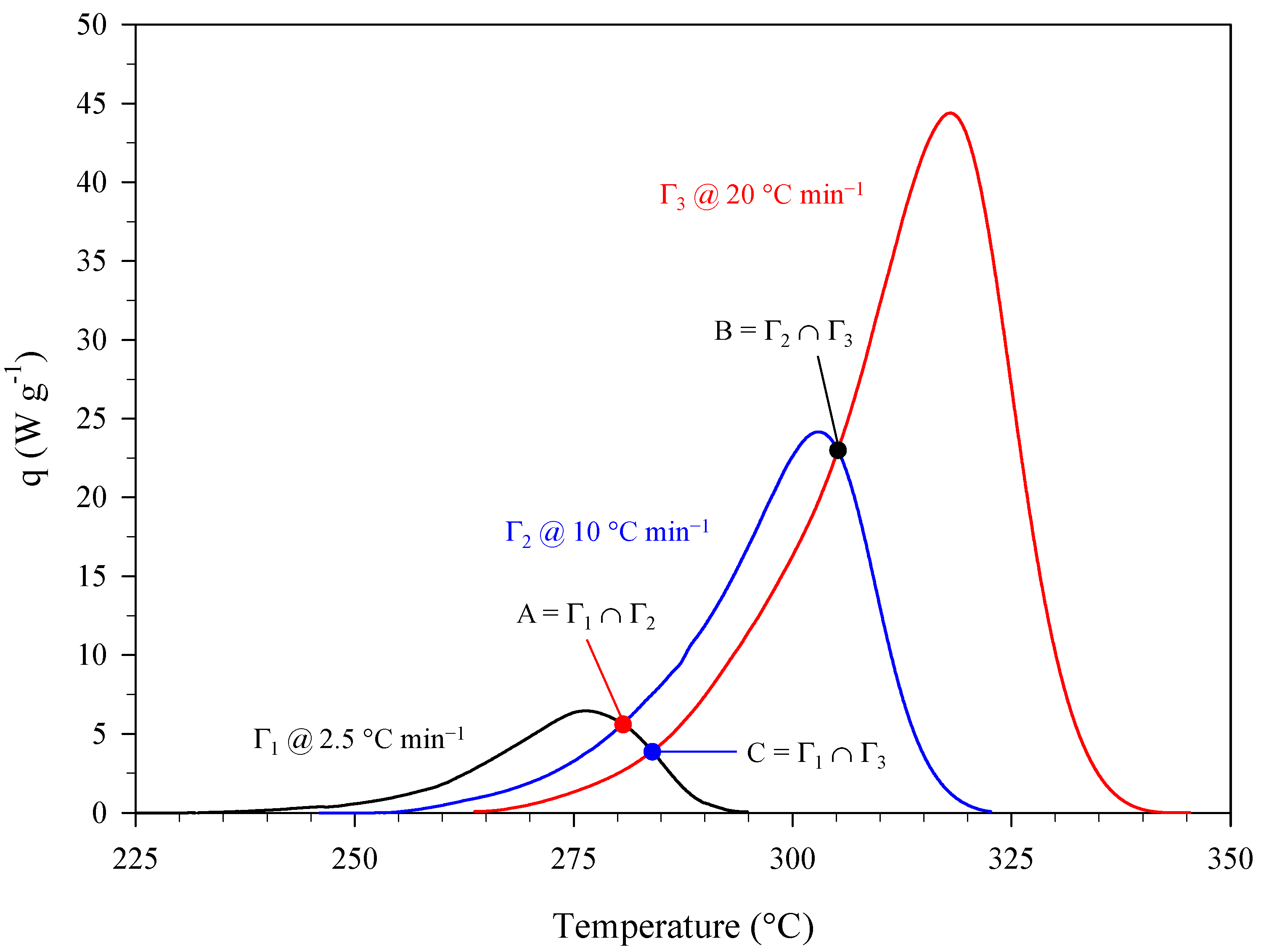
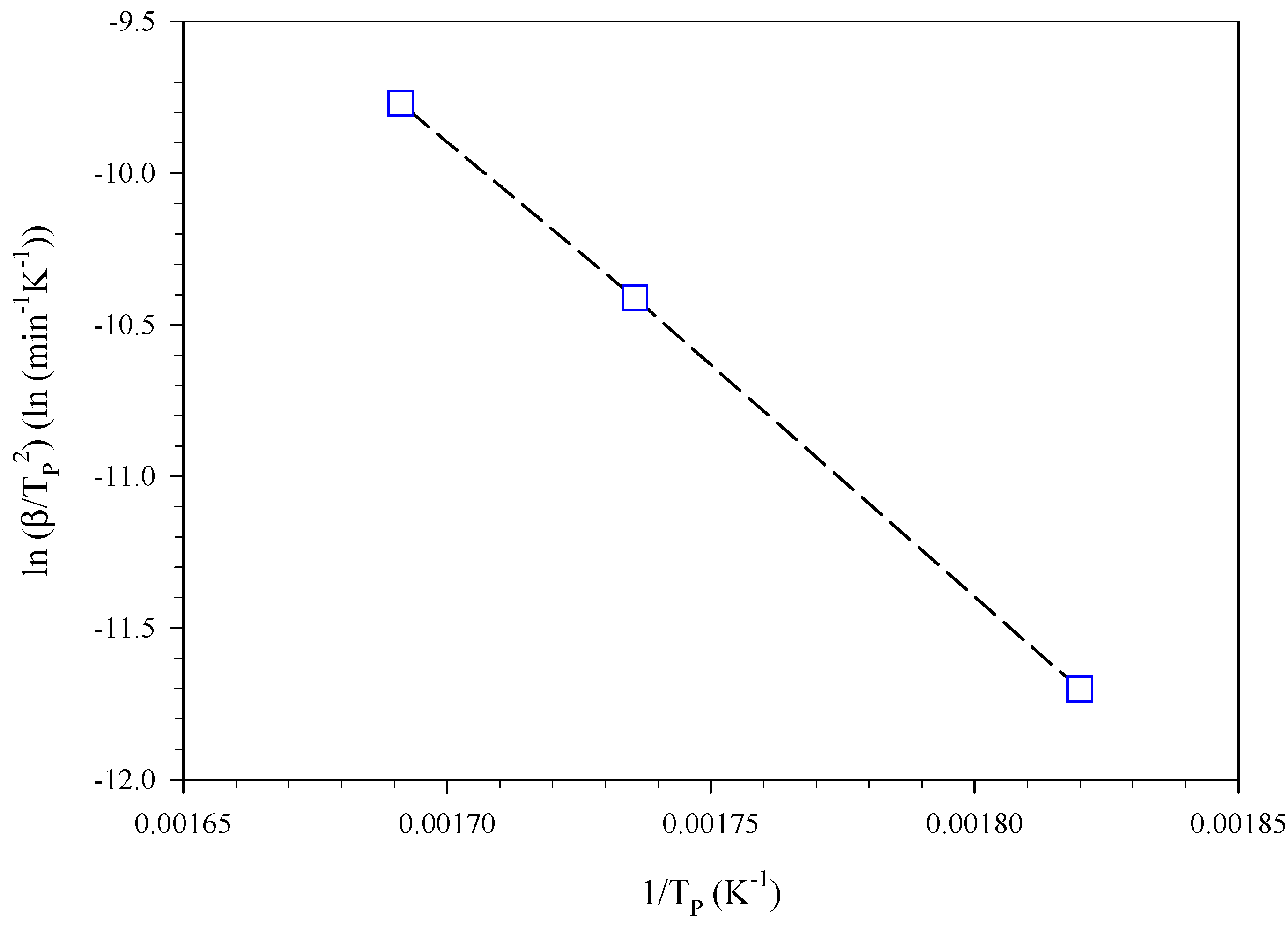
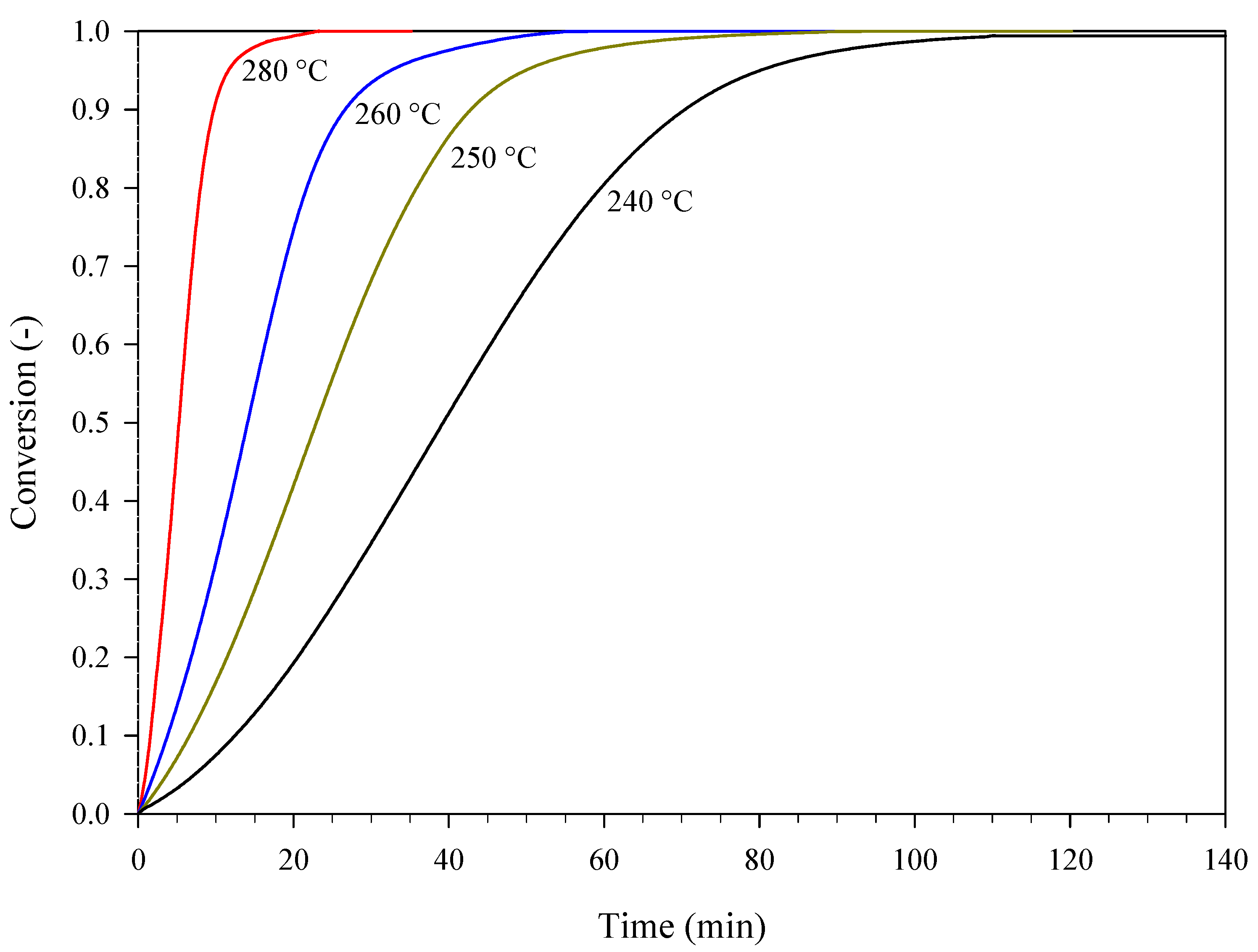
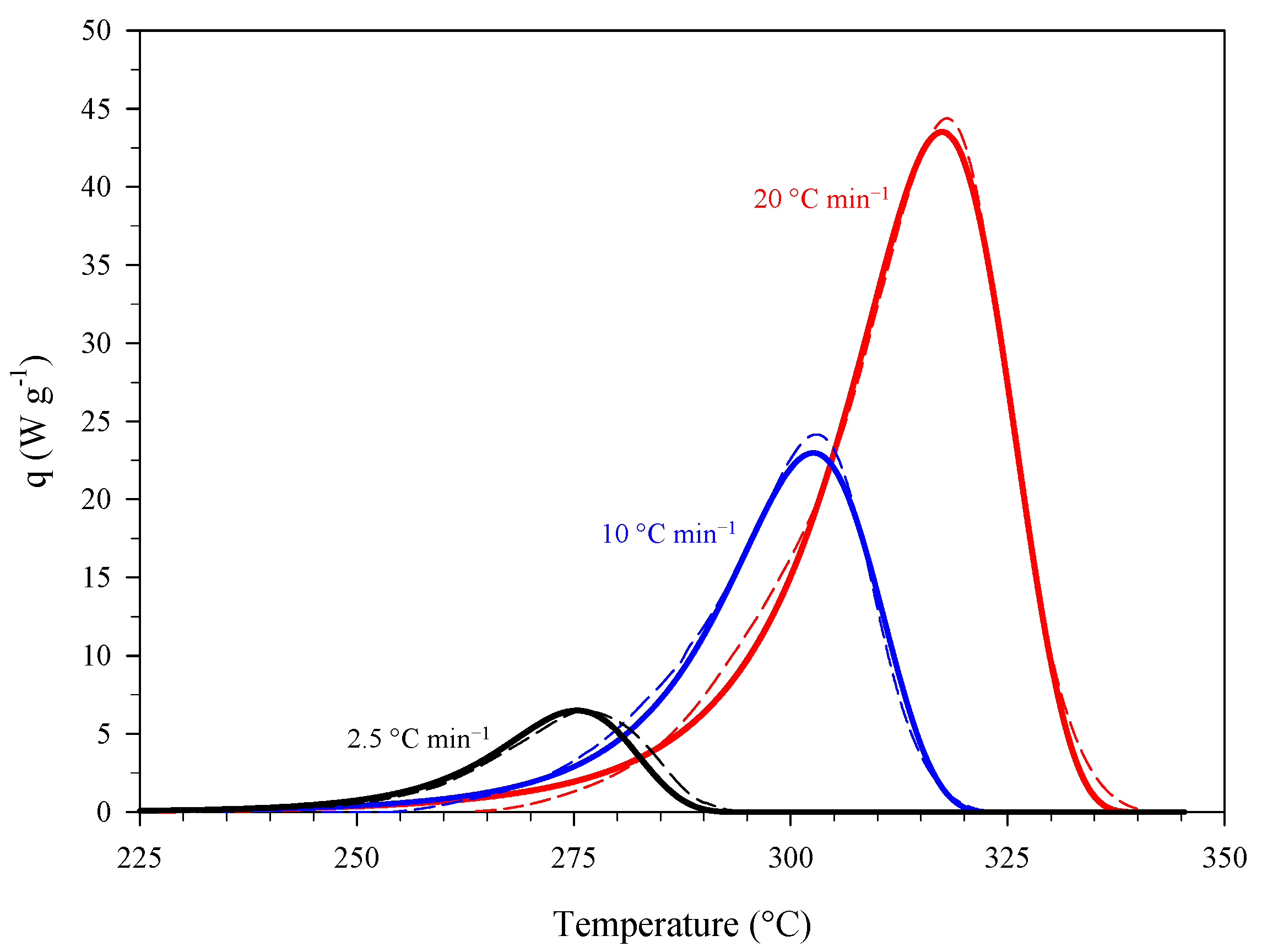
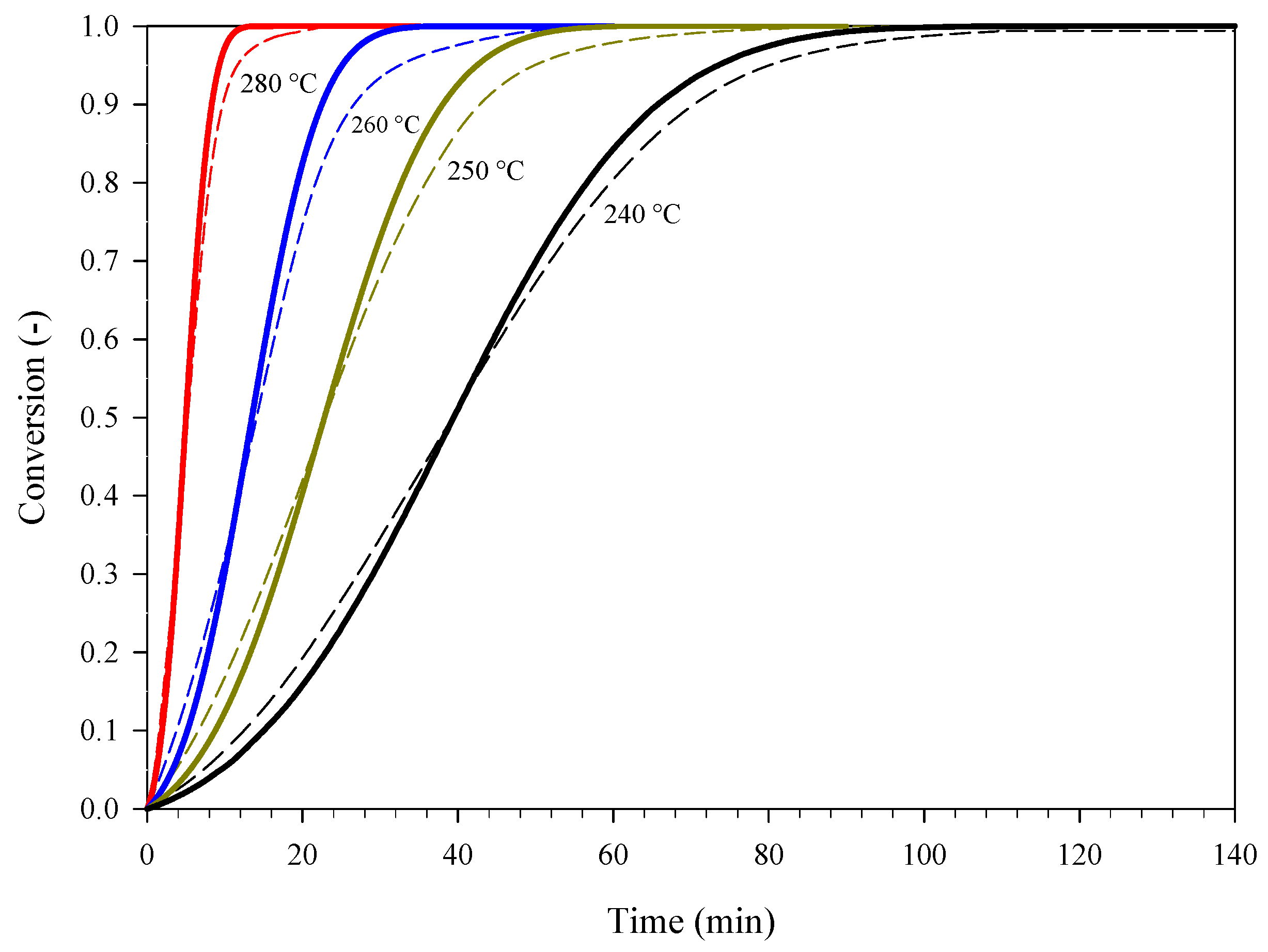

| Estimation | Dynamic Conditions, Heating Rate (°C min−1) |
| 2.5; 10; 20 | |
| Validation | Isothermal Conditions, Temperature (°C) |
| 240; 250; 260; 280 | |
| Dynamic Conditions, Heating Rate (°C min−1) | |
| 40 |
| (min−1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| 1.98 × 1011 | 125,174 | 0.49 | 0.79 |
| (min−1) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean Value | 1.52 × 1011 | 121,991 | 0.055 | 0.850 | 0.828 |
| 95% Confidence Interval | 3.09 × 1010 | 1043 | 0.012 | 0.079 | 0.037 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sanchirico, R.; Santonocito, M.L.; Di Sarli, V.; Lisi, L. Shelf Life Prediction of Picric Acid via Model-Based Kinetic Analysis of Its Thermal Decomposition. Materials 2022, 15, 8899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248899
Sanchirico R, Santonocito ML, Di Sarli V, Lisi L. Shelf Life Prediction of Picric Acid via Model-Based Kinetic Analysis of Its Thermal Decomposition. Materials. 2022; 15(24):8899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248899
Chicago/Turabian StyleSanchirico, Roberto, Marco Luca Santonocito, Valeria Di Sarli, and Luciana Lisi. 2022. "Shelf Life Prediction of Picric Acid via Model-Based Kinetic Analysis of Its Thermal Decomposition" Materials 15, no. 24: 8899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248899
APA StyleSanchirico, R., Santonocito, M. L., Di Sarli, V., & Lisi, L. (2022). Shelf Life Prediction of Picric Acid via Model-Based Kinetic Analysis of Its Thermal Decomposition. Materials, 15(24), 8899. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15248899








