Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater with High Concentration of Sulfide
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Specimen and Solution
2.2. Immersion Test
2.3. Electrochemical Measurement
2.4. Surface Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Weight Loss Experiment
3.2. Potentiodynamic Polarization Measurements
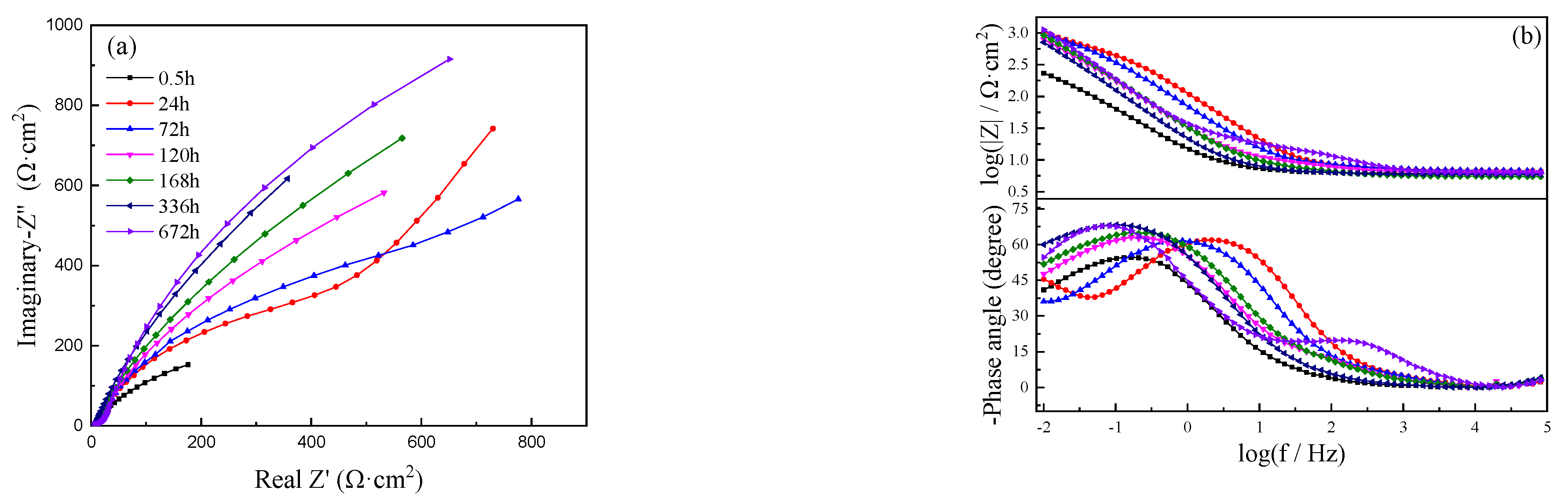
3.3. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.4. Morphology Analysis
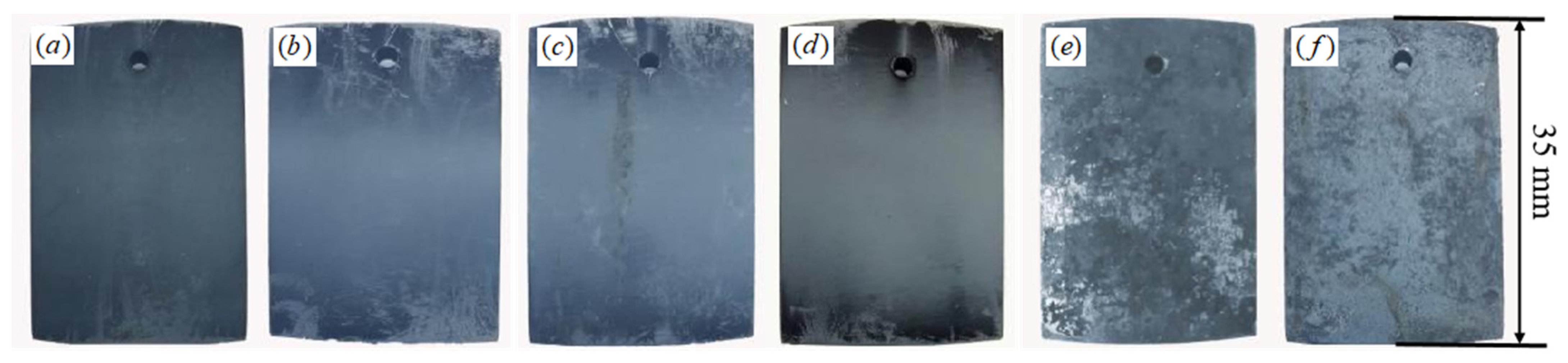
3.4.1. Macroscopic Morphology
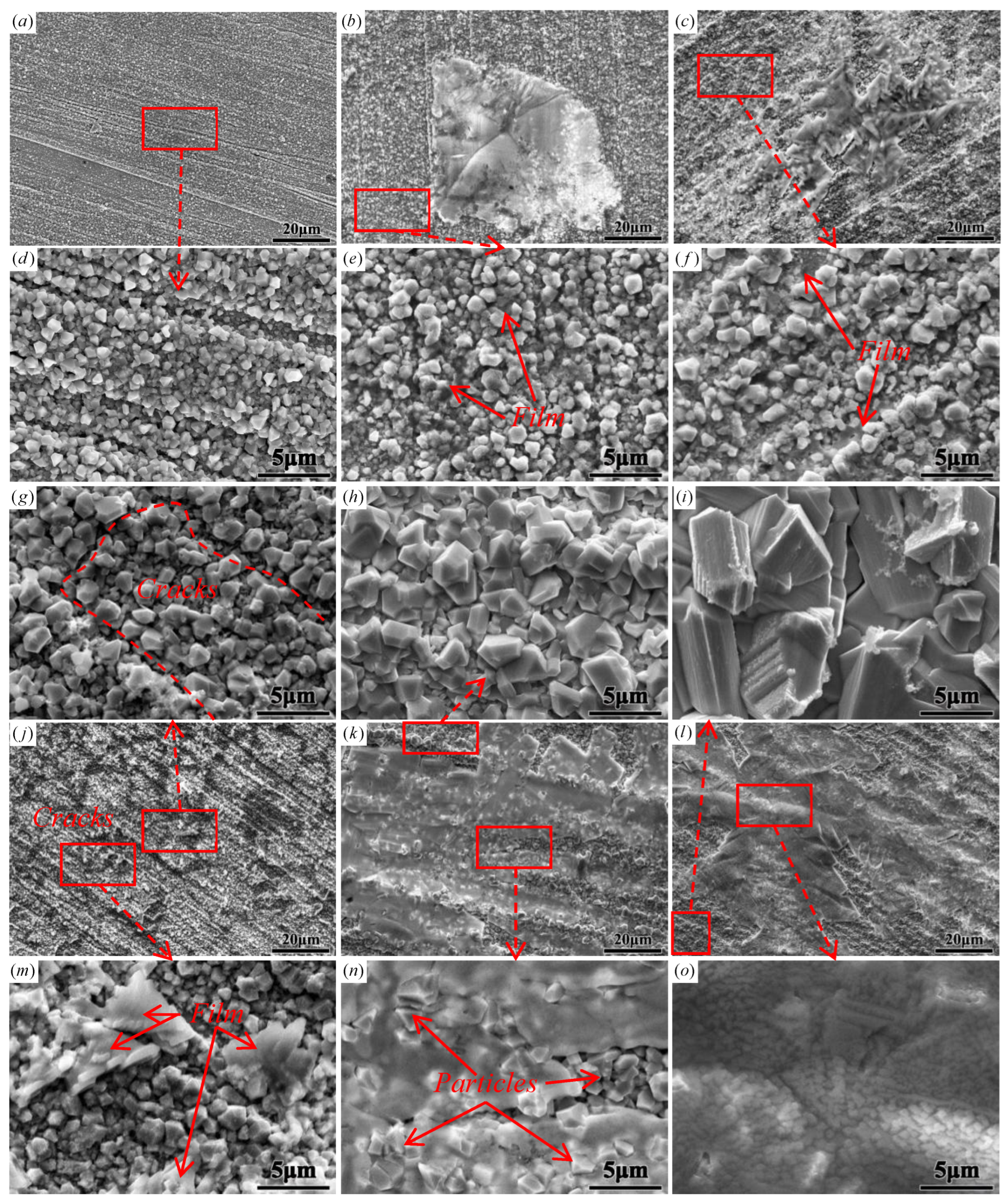
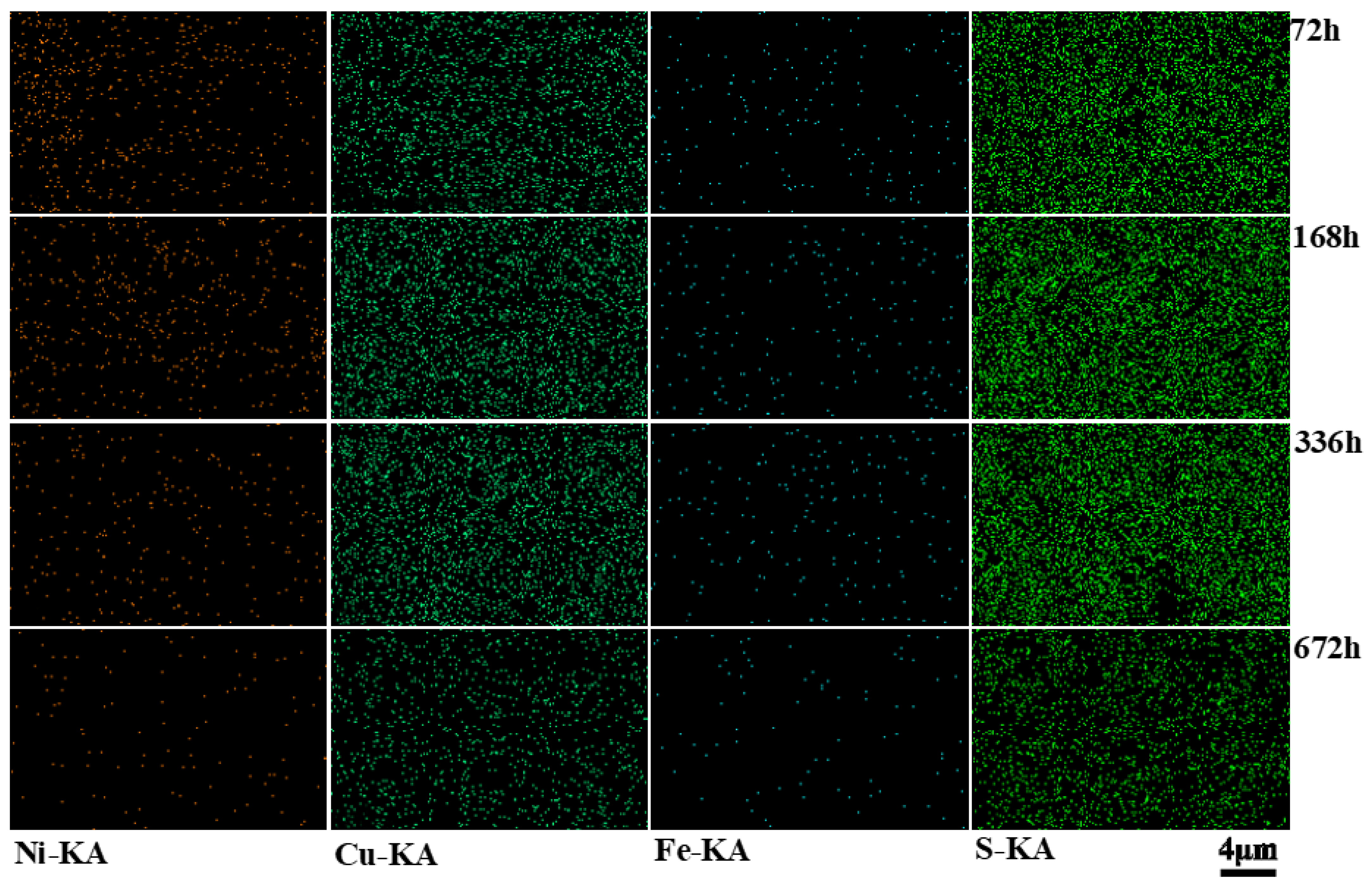
3.4.2. SEM Analysis
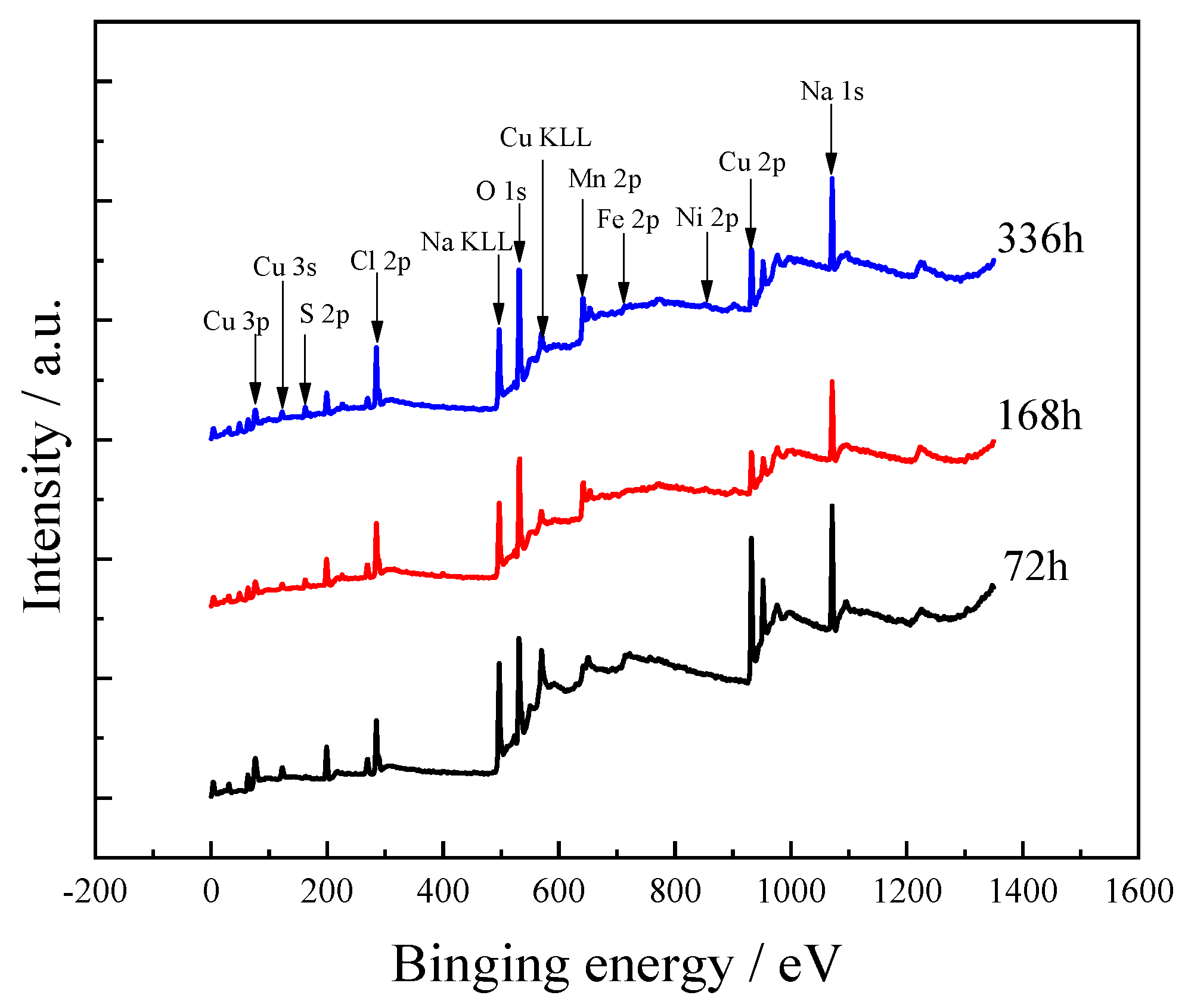
3.5. XPS Analysis
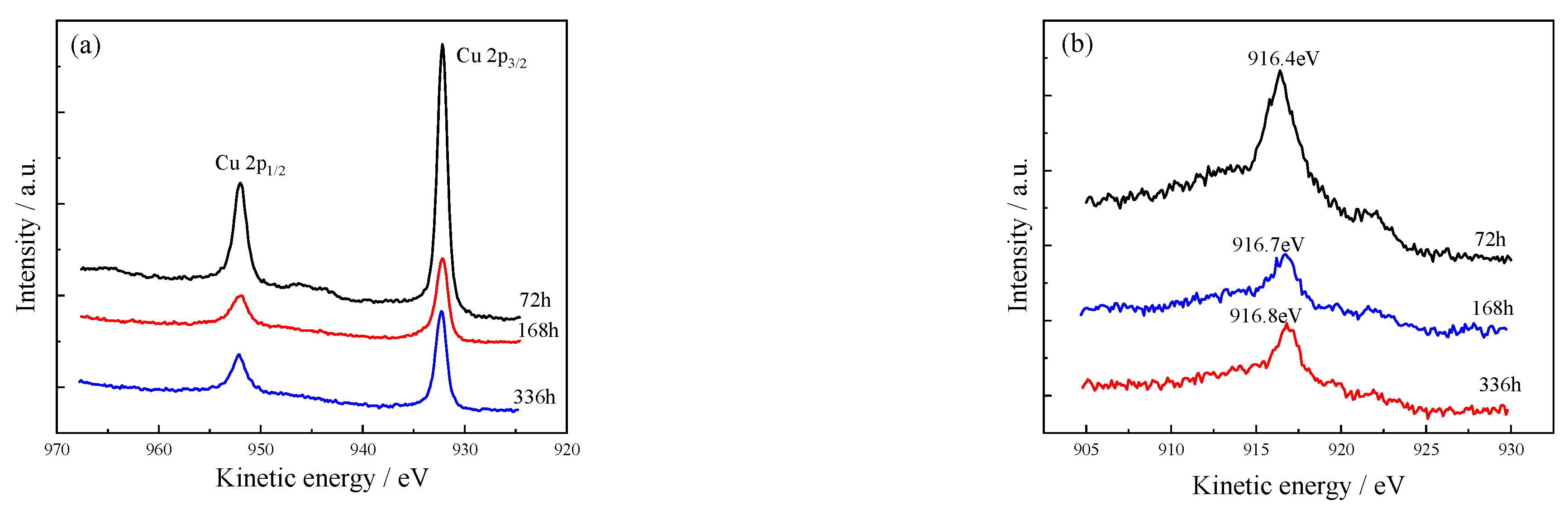
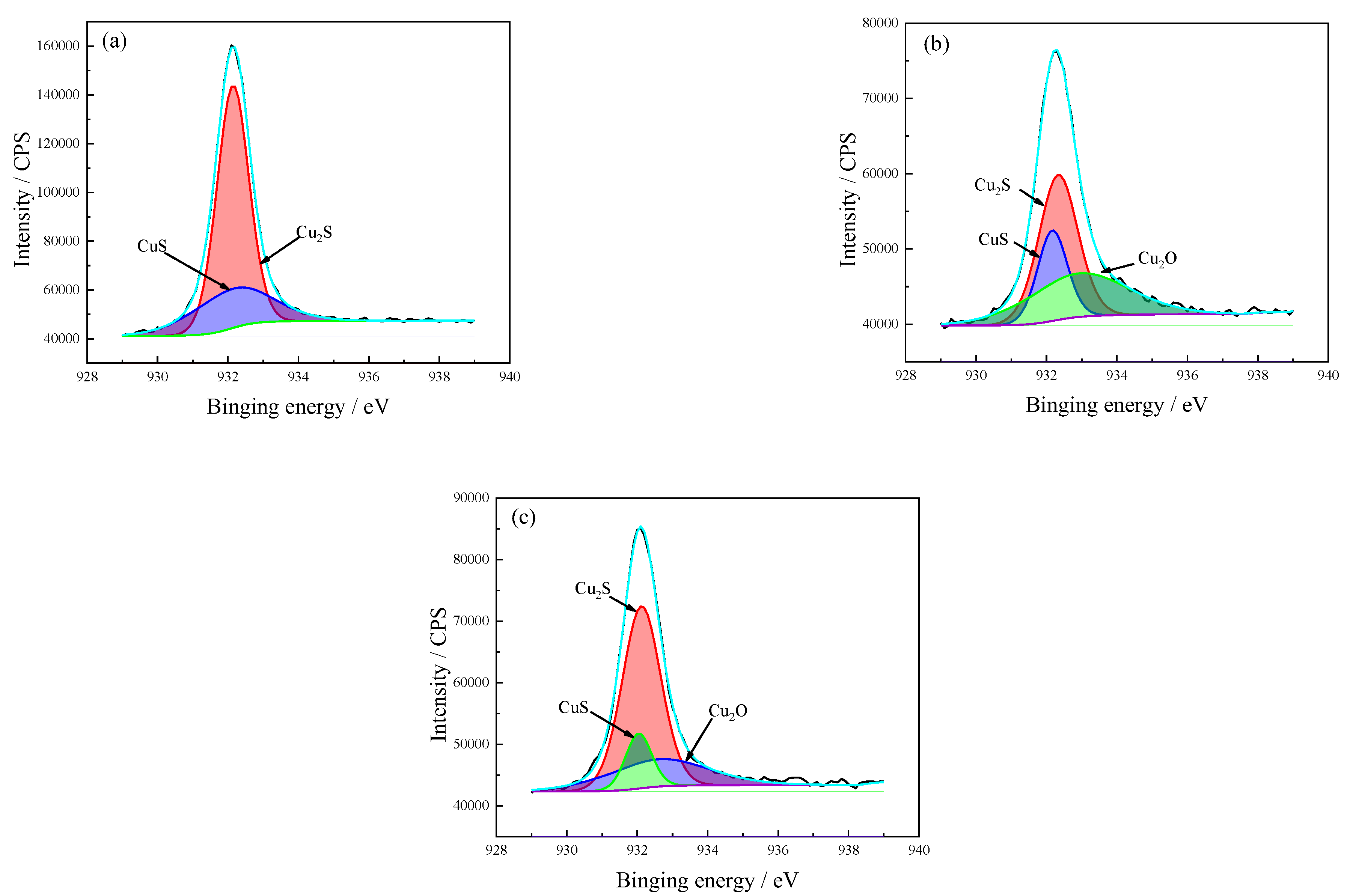
3.5.1. Cu Spectrum
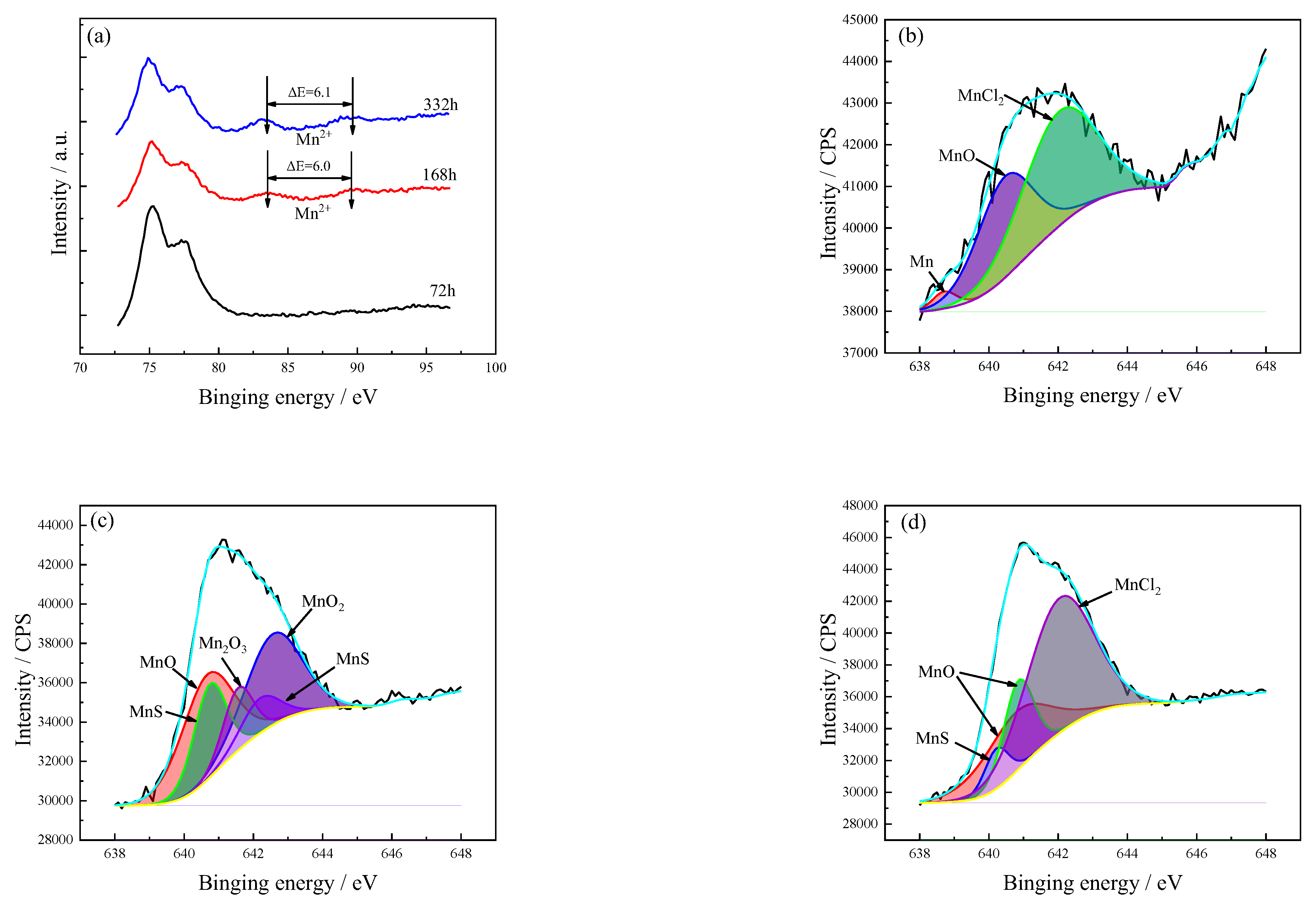
3.5.2. Mn Spectrum
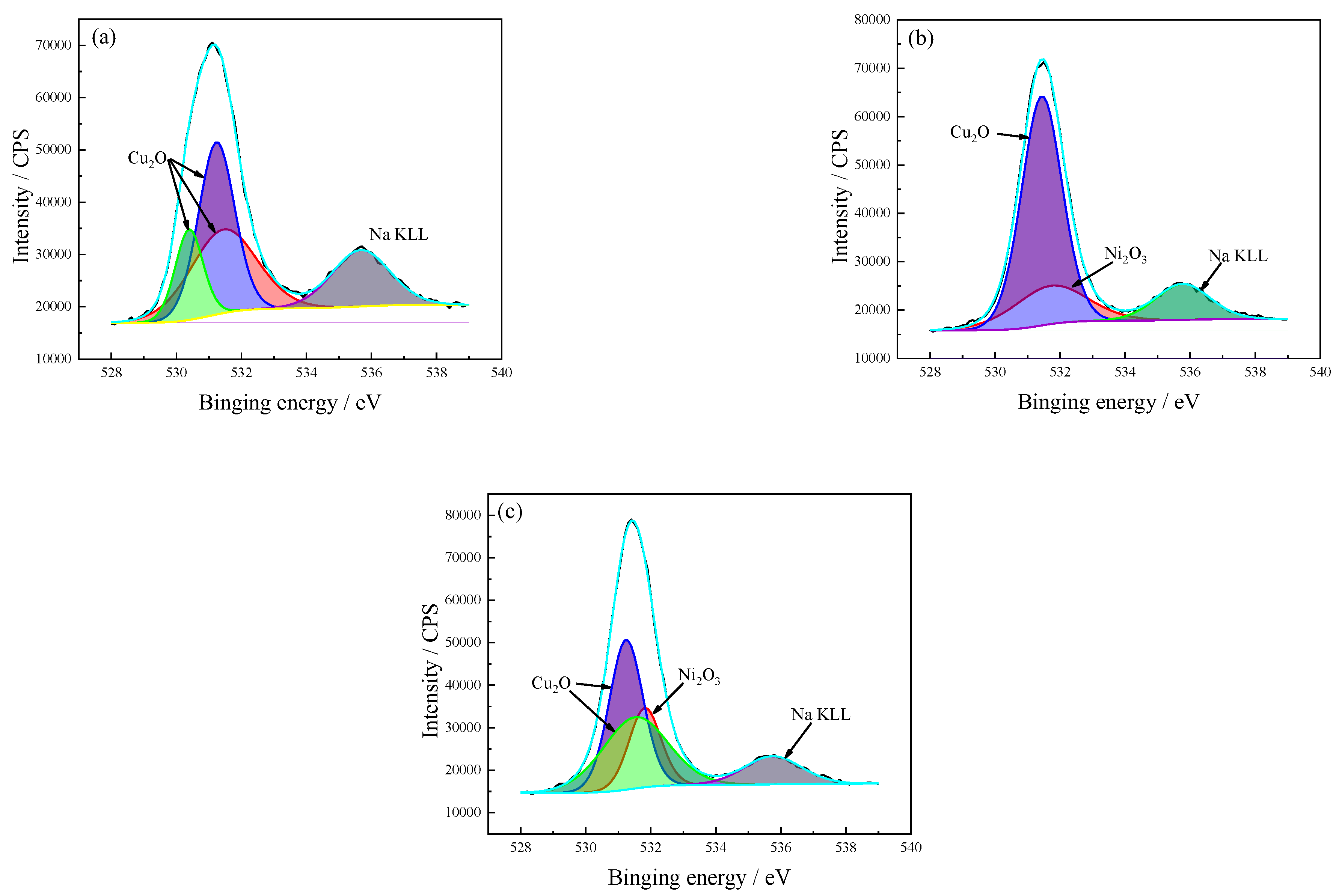
3.5.3. O Spectrum
3.5.4. S Spectrum
3.6. XRD Analysis
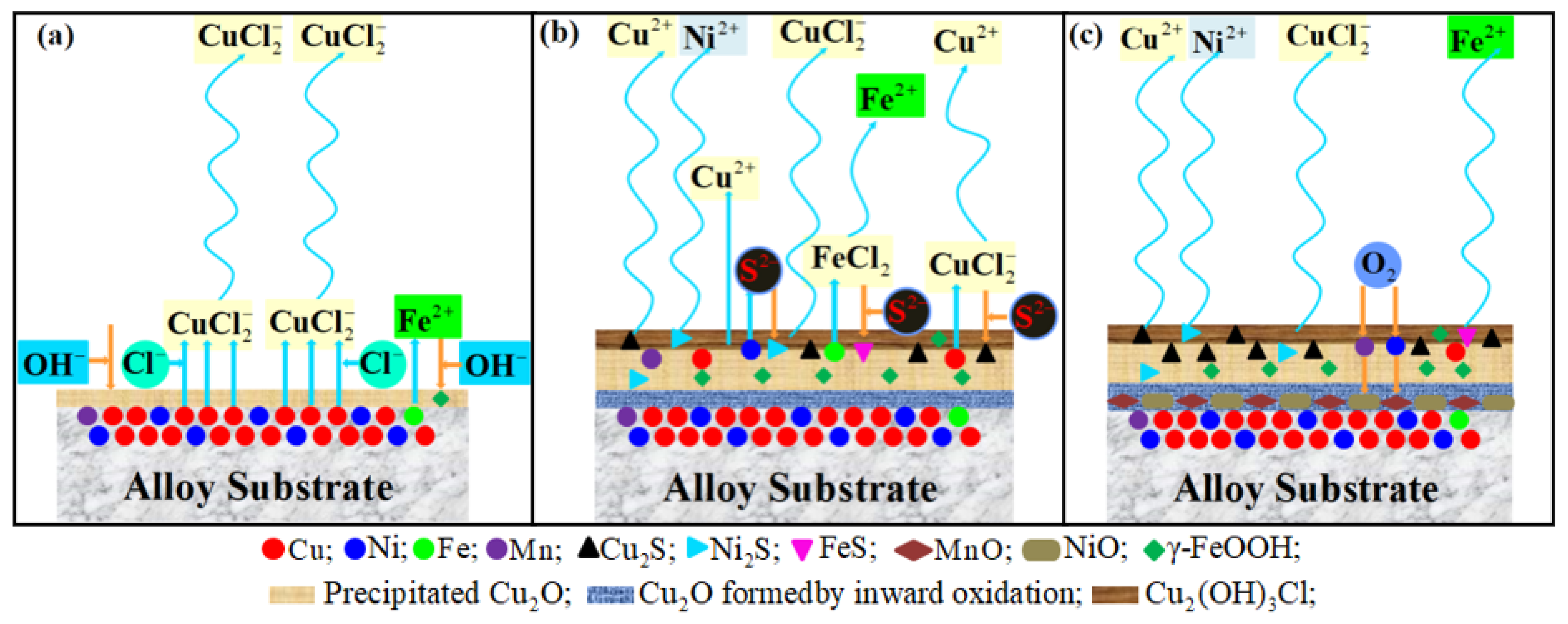
4. Corrosion Mechanism
4.1. Cu Reaction Mechanism
4.2. Fe Reaction Mechanism
4.3. Ni Reaction Mechanism
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ma, A.L.; Jiang, S.L.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ke, W. Corrosion product film formed on the 90/10 copper-nickel tube in natural seawater: Composition/structure and formation mechanism. Corros. Sci. 2015, 91, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, M.; Yang, B.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Yao, J.; Gao, L. Research progress and prospect on erosion-corrosion of Cu-Ni alloy pipe in seawater. J. Chin. Soc. Corros. Prot. 2016, 36, 513–521. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, M. Effect of uniform corrosion on mechanical behavior of E690 high-strength steel lattice corrugated panel in marine environment: A finite element analysis. Mater. Res. Express 2021, 8, 066510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Wang, H.; En-Hou, F.; Wang, G.; Huang, H. Corrosion Behavior of Cupronickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater in the Presence of Sulfate-Reducing Bacteria. Acta Metall. Sin. (Engl. Lett.) 2017, 30, 1201–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Sayed, S.; Ashour, E.; Youssef, G. Effect of sulfide ions on the corrosion behaviour of Al–brass and Cu10Ni alloys in salt water. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2003, 78, 825–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, K.C.; Rao, B.V.A. Mitigation of microbially influenced corrosion of Cu–Ni (90/10) alloy in a seawater environment. Res. Chem. Intermed. 2016, 42, 5807–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, J.; Zhang, Y.X.; Xue, Y.N. Recent Advances in Corrosion Research of Biomedical NiTi Shape Memory Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2021, 50, 4165–4173. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, J.; Qin, Z.; Martino, T.; Guo, M.; Shoesmith, D. Copper transport and sulphide sequestration during copper corrosion in anaerobic aqueous sulphide solutions. Corros. Sci. 2017, 131, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, B.V.A.; Kumar, K.C. 5-(3-Aminophenyl)tetrazole—A new corrosion inhibitor for Cu–Ni (90/10) alloy in seawater and sulphide containing seawater. Arab. J. Chem. 2017, 10, S2245–S2259. [Google Scholar]
- Radovanović, M.B.; Antonijević, M.M. Protection of copper surface in acidic chloride solution by non-toxic thiadiazole derivative. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2016, 31, 369–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nady, H.; El-Rabiei, M.; Samy, M. Corrosion behavior and electrochemical properties of carbon steel, commercial pure titanium, copper and copper–aluminum–nickel alloy in 3.5% sodium chloride containing sulfide ions. Egypt. J. Pet. 2017, 26, 79–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jandaghi, M.R.; Saboori, A.; Khalaj, G.; Shiran, M.K.G. Microstructural Evolutions and its Impact on the Corrosion Behaviour of Explosively Welded Al/Cu Bimetal. Metals 2020, 10, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, Y.-X. Analysis of the Influence of Sulfur on the Hot Tensile Fracture of C71500 Cu-Ni Alloy. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2021, 30, 312–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.-B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.-X.; Zhou, X.-D. Dynamic Recovery and Recrystallization Behaviors of C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy Under Hot Deformation. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2020, 29, 7678–7692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.-B.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.-X. Effect of annealing time on grain boundary characteristics of C71500 cupronickel alloy tubes with different deformation. Mater. Charact. 2020, 169, 110603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F.; Sun, H. Processing Map of C71500 Copper-nickel Alloy and Application in Production Practice. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Sci. Ed. 2020, 35, 1104–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Tang, D.; Li, D.; Liu, M.; Zhou, X. Six Different Mathematical Models to Predict the Hot Deformation Behavior of C71500 Cupronickel Alloy. Rare Met. Mater. Eng. 2020, 49, 4129–4141. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Wu, H.; Liu, M.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, F. Corrosion Behavior of High Strength C71500 Cu-Ni Alloy Pipe in Simulated High Sulfide Polluted Seawater at Different Temperatures. Int. J. Electrochem. Sci. 2021, 16, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchers, R.E. Long-term immersion corrosion of steels in seawaters with elevated nutrient concentration. Corros. Sci. 2014, 81, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimoto, M.; Muto, I.; Sugawara, Y.; Hara, N. Role of Cerium Ions for Improving Pitting Corrosion Resistance of Sulfide Inclusions in Stainless Steels. ECS Meet. Abstr. 2017, 698–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiahosseini, S.R.; Baygi, S.J.M.; Khalaj, G.; Khoshakhlagh, A.; Samadipour, R. A Study on Structural, Corrosion, and Sensitization Behavior of Ultrafine and Coarse Grain 316 Stainless Steel Processed by Multiaxial Forging and Heat Treatment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 27, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezuber, H.M.; al Shater, A. Influence of environmental parameters on the corrosion behavior of 90/10 cupronickel tubes in 3.5% NaCl. Desalination Water Treat. 2016, 57, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Liu, R.; Liu, L.; Cui, Y.; Oguzie, E.E.; Wang, F. Effect of hydrostatic pressure on the galvanic corrosion of 90/10 Cu-Ni alloy coupled to Ti6Al4V alloy. Corros. Sci. 2020, 163, 108242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Yue, P.; Li, J. Corrosion Behavior and Durability of Low-Alloy Steel Rebars in Marine Environment. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2016, 25, 4967–4979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Cheng, X.; Li, X.; Zhou, C.; Tan, H. Effect of carbonation on the electrochemical behavior of corrosion resistance low alloy steel rebars in cement extract solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M. Finite element analysis of pitting corrosion on mechanical behavior of E690 steel panel. Anti-Corrosion Methods Mater. 2022, 69, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Z.; Li, Z.; Zhu, A.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, J.; Zhu, Y. Surface characterization and corrosion behavior of a novel gold-imitation copper alloy with high tarnish resistance in salt spray environment. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, N.D. Role of Zinc in Enhancing the Corrosion Resistance of Mg-5Ca Alloys. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2015, 163, C76–C84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, T.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Lou, W. Accelerated Corrosion Behavior of B10 Cu-Ni Alloy in Seawater. J. Mater. Eng. 2017, 45, 31–37. [Google Scholar]
- Patil, A.P.; Tupkary, R.H. Corrosion resistance of new copper alloy containing 29Zn, 10Ni and up to 5Mn vis-a-vis Cu-10Ni in sulphide polluted synthetic seawater. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2009, 62, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deroubaix, G.; Marcus, P. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy analysis of copper and zinc oxides and sulphides. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 18, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galtayries, A.; Bonnelle, J.-P. XPS and ISS studies on the interaction of H2S with polycrystalline Cu, Cu2O and CuO surfaces. Surf. Interface Anal. 2010, 23, 171–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.N.; Xu, N.; Bao, Y.F.; Jiang, Y.F.; Qiao, Y.X. Corrosion Behavior of Cu40Zn in Sulfide-Polluted 3.5% NaCl Solution. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2017, 26, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.P.; Tupkary, R.H. Development of single-phased copper alloy for seawater applications: As a cost-effective substitute for Cu-10Ni alloy. Trans. Indian Inst. Met. 2008, 61, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Li, J. In-Situ Raman Characterization of Initial Corrosion Behavior of Copper in Neutral 3.5% (wt.) NaCl Solution. Materials 2019, 12, 2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.P.; Rodrigues, J.A.; Da Fonseca, I.T.E. Copper corrosion in buffered and non-buffered synthetic seawater: A comparative study. J. Solid State Electrochem. 2004, 8, 260–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kear, G.; Barker, B.D.; Stokes, K.; Walsh, F.C. Electrochemical Corrosion Behaviour of 90–10 Cu–Ni Alloy in Chloride-Based Electrolytes. J. Appl. Electrochem. 2004, 34, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Chen, W.; Zhang, Y.; Qun, H.; Ming, L.; Nian, L.; Li, B. Investigation of the inhibition effect of trithiocyanuric acid on corrosion of copper in 3.0 wt.% NaCl. Corros. Sci. 2013, 66, 308–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonora, P.L.; Rossi, S.; Benedetti, L.; Draghetti, M. Improved Sacrificial Anode for the Protection of Off-Shore Structures. Dev. Mar. Corros. 1998, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Sanchez, S.R.; Berlouis, L.E.; Schiffrin, D.J. Difference reflectance spectroscopy of anodic films on copper and copper base alloys. J. Electroanal. Chem. Interfacial Electrochem. 1991, 307, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, S.A.; Radford, G.J.W.; Tuck, C.D.S.; Barker, B.D. Corrosion and Galvanic Compatibility Studies of a High-Strength Copper-Nickel Alloy. Corrosion 2002, 58, 57–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bech-Nielsen, G.; Jaskula, M.; Chorkendorff, I.; Larsen, J. The initial behaviour of freshly etched copper in moderately acid, aerated chloride solutions. Electrochim. Acta 2003, 47, 4279–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Hajji, J.; Reda, M. The corrosion of copper-nickel alloys in sulfide-polluted seawater: The effect of sulfide concentration. Corros. Sci. 1993, 34, 163–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alkharafi, F.M.; Nazeer, A.A.; Abdullah, R.M.; Galal, A. Effect of Sulfide-Containing Solutions on the Corrosion of Cu-Ni Alloys; Electrochemical and Surface Studies. In Proceedings of the ECS & SMEQ Joint International Meeting, Cancun, Mexico, 5–9 October 2014; Volume 64, p. 121. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kharafi, F.M.; Abdel-Nazeer, A.; Abdullah, R.M.; Galal, A. Effect of Sulfide-Containing Solutions on the Corrosion of Cu-Ni Alloys; Electrochemical and Surface Studies. ECS Trans. 2015, 64, 121–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vazquez, M.; De Sanchez, S.R. Influence of sulphide ions on the cathodic behaviour of copper in 0.1 M borax solution. J. Appl. Electrochem. 1998, 28, 1383–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanoni, R.; Gusmano, G.; Montesperelli, G.; Traversa, E. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy Investigation of Corrosion Behavior of ASTM C71640 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Seawater. Corrosion 1992, 48, 404–410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burleigh, T.D.; Waldeck, D.H. Effect of Alloying on the Resistance of Cu-10% Ni Alloys to Seawater Impingement. Corrosion 1999, 55, 800–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.H.; Wei, Y.; Shao, C.Y.; Shi, Y.J.; Xue, W.; Zhu, J.F. Study on Corrosion Behavior of the 304 Stainless Steel in the Heavy Oil with High Salt, High Sulfur and High Acid Value. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2013, 252, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, R.L. Raman spectroscopy of selected copper minerals of significance in corrosion. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2003, 59, 1195–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Efird, K.D. Potential-pH Diagrams for 90-10 and 70-30 Cu-Ni in Sea Water. Corrosion 2013, 31, 77–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Time (h) | βa (mV/dec) | βc (mV/dec) | icorr (μA/cm2) | Ecorr (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 337 ± 12 | −541 ± 16 | 27.4 ± 10 | −877 ± 25 |
| 24 | 15 ± 7 | −18 ± 5 | 2.72 ± 0.5 | −899 ± 8 |
| 72 | 33 ± 5 | −41 ± 4 | 1.7 ± 0.3 | −758 ± 7 |
| 120 | 54 ± 4 | −30 ± 3 | 1.3 ± 0.2 | −902 ± 8 |
| 168 | 40 ± 5 | −23 ± 3 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | −773 ± 6 |
| 336 | 42 ± 3 | −23 ± 2 | 0.8 ± 0.1 | −929 ± 7 |
| 672 | 39 ± 3 | −42 ± 2 | 0.6 ± 0.1 | −873 ± 5 |
| Time, h | Rs, Ω·cm2 | Rt, Ω·cm2 | Qdl | Rf, Ω·cm2 | Qf | W | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n1 | Y0 Ω−1·cm−2·sn | n2 | Y0 Ω−1·cm−2·sn | 10−4·Ω−1·cm−2·s1/2 | ||||
| 0.5 | 6.11 ± 1.81 | 1817 ± 20 | 0.73 ± 0.10 | 459 ± 7 | -- | -- | -- | -- |
| 24 | 6.96 ± 0.55 | 2213 ± 12 | 0.82 ± 0.04 | 485 ± 6 | -- | -- | -- | 43.4 ± 2.4 |
| 72 | 7.17 ± 0.51 | 3454 ± 7 | 0.77 ± 0.04 | 908 ± 6 | -- | -- | -- | 76.4 ± 1.9 |
| 120 | 6.36 ± 0.26 | 5084 ± 8 | 0.69 ± 0.03 | 9 ± 2 | 3069 ± 15 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 2068 ± 18 | -- |
| 168 | 5.53 ± 0.21 | 5134 ± 6 | 0.72 ± 0.02 | 7 ± 1 | 2617 ± 12 | 0.89 ± 0.03 | 2752 ± 11 | -- |
| 336 | 5.98 ± 0.16 | 5950 ± 6 | 0.78 ± 0.01 | 9 ± 1 | 2658 ± 8 | 0.90 ± 0.02 | 3164 ± 9 | -- |
| 672 | 6.17 ± 0.12 | 6619 ± 4 | 0.71 ± 0.01 | 15 ± 1 | 2686 ± 7 | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 3844 ± 10 | -- |
| Exposure Time (h) | O | S | Mn | Fe | Ni | Cu |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 24 | 0.4 | 6.2 | 0.8 | 1.7 | 30.8 | 60.1 |
| 72 | 2.6 | 18.1 | 1.3 | 0.6 | 5.5 | 71.9 |
| 120 | 4.7 | 13.0 | 1.1 | 0.5 | 6.9 | 73.9 |
| 168 | 0.8 | 17.9 | 0.3 | 0.3 | 6.4 | 74.4 |
| 336 | 1.3 | 23.5 | 0.6 | 0.2 | 1.0 | 73.4 |
| 672 | 0.3 | 18.4 | 1.6 | 0.2 | 0.6 | 78.8 |
| Valence | Exposure Time (h) | Proposed Compounds | Binding Energy (eV) | Intensity Area | Atomic (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cu 2p3/2 | 72 | Cu2S | 932.3 | 115,144 | 71.4 |
| CuS | 932.1 | 46,123 | 28.6 | ||
| 168 | Cu2S | 932.3 | 27,119 | 44.3 | |
| CuS | 932.2 | 12,969 | 21.2 | ||
| Cu2O | 932.9 | 21,124 | 34.5 | ||
| 336 | Cu2S | 932.1 | 41,307 | 62.6 | |
| CuS | 932.0 | 8467 | 12.8 | ||
| Cu2O | 932.6 | 16,175 | 24.5 |
| Valence | Exposure Time (h) | Proposed Compounds | Binding Energy (eV) | Intensity Area | Atomic (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mn 2p3/2 | 72 | Mn | 638.7 | 367 | 2.8 |
| MnO | 640.5 | 5061 | 39.0 | ||
| MnO | 640.7 | 10,260 | 32.4 | ||
| 168 | MnS | 640.7 | 5713 | 18.1 | |
| MnS | 642.2 | 2526 | 8.0 | ||
| MnO | 640.8 | 9187 | 23.9 | ||
| MnCl2 | 642.0 | 7557 | 58.2 | ||
| MnO2 | 642.6 | 9584 | 30.3 | ||
| 336 | MnS | 640.2 | 2266 | 5.9 | |
| MnO | 640.9 | 6228 | 16.2 | ||
| MnO | 640.8 | 9187 | 23.9 | ||
| MnCl2 | 642.1 | 20,745 | 54.0 |
| Valence | Exposure Time (h) | Proposed Compounds | Binding Energy (eV) | Intensity Area | Atomic (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| O 1s | 72 | Cu2O | 531.5 | 41,584 | 31.5 |
| Cu2O | 531.2 | 47,032 | 35.6 | ||
| Cu2O | 530.4 | 18,914 | 14.3 | ||
| Na KLL | 535.7 | 24,612 | 18.7 | ||
| 168 | Cu2O | 531.4 | 75,394 | 66.1 | |
| Ni2O3 | 531.7 | 22,763 | 20.0 | ||
| Na KLL | 535.8 | 15,830 | 13.9 | ||
| 336 | Cu2O | 531.2 | 46,810 | 36.5 | |
| Cu2O | 531.5 | 43,086 | 33.6 | ||
| Ni2O3 | 531.8 | 23,414 | 18.3 | ||
| Na KLL | 535.8 | 14,872 | 11.6 |
| Valence | Exposure Time (h) | Proposed Compounds | Binding Energy (eV) | Intensity Area | Atomic (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| S 2p | 72 | Cu2S | 161.5 | 254 | 16.8 |
| CuS | 162.1 | 620 | 40.8 | ||
| FeS2 | 162.8 | 150 | 9.9 | ||
| Na2S | 160.9 | 84 | 5.5 | ||
| Na(SO3)2 | 163.2 | 327 | 21.5 | ||
| Na(SO3)2 | 164.0 | 83 | 5.5 | ||
| 168 | Cu2S | 161.9 | 4654 | 58.4 | |
| CuS | 161.6 | 300 | 3.8 | ||
| FeS2 | 162.9 | 1132 | 14.2 | ||
| Na2S | 160.2 | 174 | 2.2 | ||
| Na(SO3)2 | 163.2 | 1713 | 21.5 | ||
| 336 | Cu2S | 161.7 | 1310 | 14.6 | |
| CuS | 162.1 | 2226 | 24.8 | ||
| FeS2 | 162.9 | 2131 | 23.8 | ||
| FeS | 161.5 | 1619 | 18.1 | ||
| Na(SO3)2 | 163.2 | 1673 | 18.7 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gao, X.; Liu, M. Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater with High Concentration of Sulfide. Materials 2022, 15, 8513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238513
Gao X, Liu M. Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater with High Concentration of Sulfide. Materials. 2022; 15(23):8513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238513
Chicago/Turabian StyleGao, Xin, and Ming Liu. 2022. "Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater with High Concentration of Sulfide" Materials 15, no. 23: 8513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238513
APA StyleGao, X., & Liu, M. (2022). Corrosion Behavior of High-Strength C71500 Copper-Nickel Alloy in Simulated Seawater with High Concentration of Sulfide. Materials, 15(23), 8513. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15238513








