Comparison of the Biological Behavior and Topographical Surface Assessment of a Minimally Invasive Dental Implant and a Standard Implant: An In Vitro Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Surface Properties Characterization
2.1.1. Studied Implants
2.1.2. SEM-EDX Analysis
2.1.3. AFM and Profilometer Surface Roughness Measurement
2.1.4. Wettability Measurement
2.2. Biological Assessment
2.2.1. Cell Culture
2.2.2. Cytotoxicity
2.2.3. Metabolic Activity
2.2.4. Cells Morphology, Colonization, and Adhesion Using Confocal and SEM Imaging
2.2.5. ALP Quantification
2.2.6. Alizarin Red S
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Surfaces Properties Characterization
3.1.1. SEM-EDX Analysis
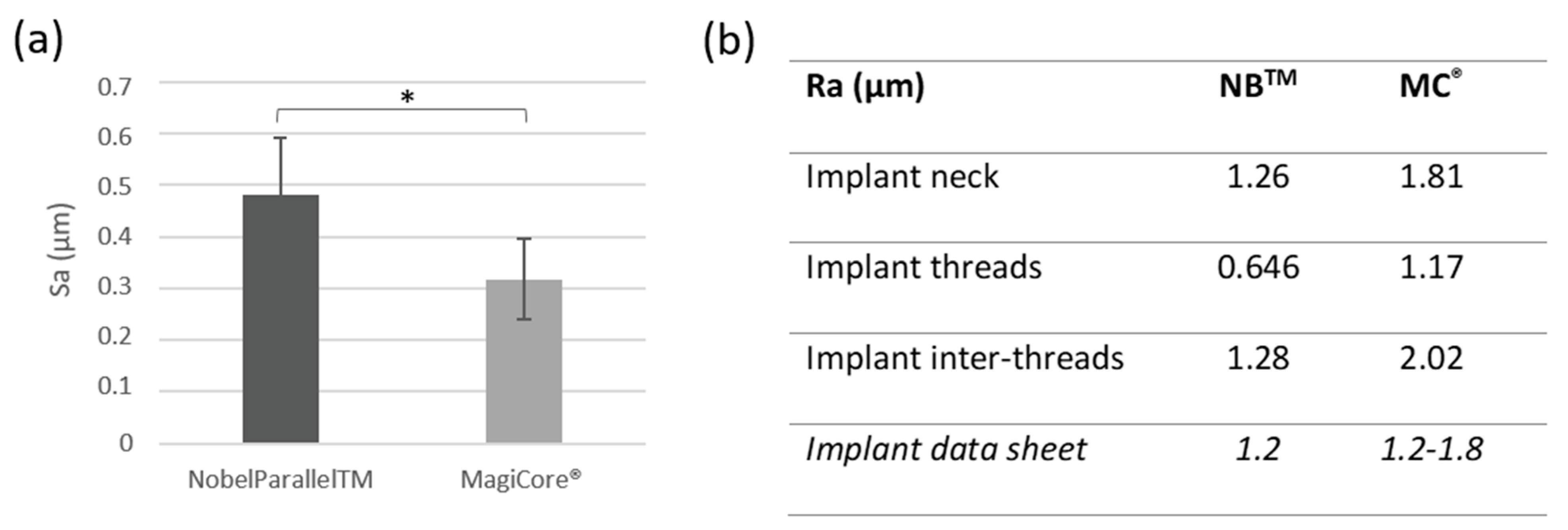
3.1.2. Surface Roughness
3.1.3. Wettability Measurement
3.2. Biological Assessment
3.2.1. Cytotoxicity
3.2.2. Metabolic Activity
3.2.3. Cell Morphology, Colonization, and Adhesion Using Confocal and SEM Imaging
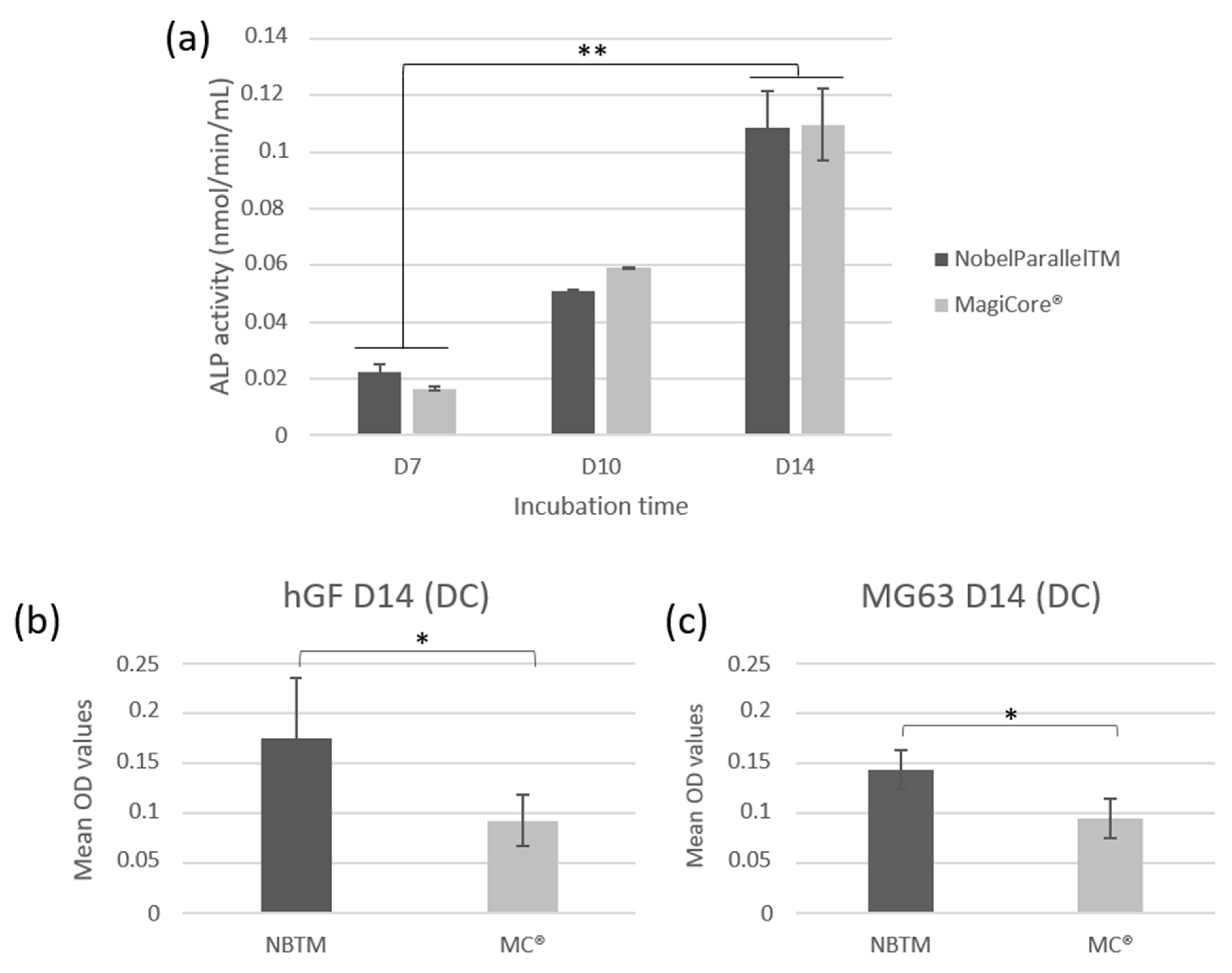
3.2.4. Quantitative Assay of ALP Activity
3.2.5. Alizarin Red S Staining—Mineralization
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Moraschini, V.; Poubel, L.A.; da Ferreira, C.V.F.; dos Barboza, E.S.P. Evaluation of Survival and Success Rates of Dental Implants Reported in Longitudinal Studies with a Follow-up Period of at Least 10 Years: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 44, 377–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elani, H.W.; Starr, J.R.; Da Silva, J.D.; Gallucci, G.O. Trends in Dental Implant Use in the U.S., 1999–2016, and Projections to 2026. J. Dent. Res. 2018, 97, 1424–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucintel, Insight That Matter. (Opportunities in the Dental Implants and Prosthetic Market: Growth Trends, Forecast and Competitive Analysis). Available online: https://www.lucintel.com/dental-implant-prosthetic-market.aspx (accessed on 24 August 2022).
- Gittens, R.A.; Olivares-Navarrete, R.; Cheng, A.; Anderson, D.M.; McLachlan, T.; Stephan, I.; Geis-Gerstorfer, J.; Sandhage, K.H.; Fedorov, A.G.; Rupp, F.; et al. The Roles of Titanium Surface Micro/Nanotopography and Wettability on the Differential Response of Human Osteoblast Lineage Cells. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6268–6277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pommer, B.; Mailath-Pokorny, G.; Haas, R.; Busenlechner, D.; Fürhauser, R.; Watzek, G. Patients’ Preferences towards Minimally Invasive Treatment Alternatives for Implant Rehabilitation of Edentulous Jaws. Eur. J. Oral Implantol. 2014, 7 (Suppl. S2), S91–S109. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Coli, P.; Christiaens, V.; Sennerby, L.; Bruyn, H.D. Reliability of Periodontal Diagnostic Tools for Monitoring Peri-Implant Health and Disease. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 203–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solderer, A.; Al-Jazrawi, A.; Sahrmann, P.; Jung, R.; Attin, T.; Schmidlin, P.R. Removal of Failed Dental Implants Revisited: Questions and Answers. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2019, 5, 712–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brånemark, P.-I.; Chien, S.; Grondahl, H.-G.; Robinson, K. (Eds.) The Osseointegration Book: From Calvarium to Calcaneus; Quintessence Publishing Co, Inc.: Hanover Park, IL, USA, 2005; ISBN 978-1-85097-090-3. [Google Scholar]
- Alhag, M.; Renvert, S.; Polyzois, I.; Claffey, N. Re-Osseointegration on Rough Implant Surfaces Previously Coated with Bacterial Biofilm: An Experimental Study in the Dog. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 2008, 19, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrini, G.; Francetti, L.; Barbaro, B.; del Fabbro, M. Novel Surfaces and Osseointegration in Implant Dentistry. J. Investig. Clin. Dent. 2018, 9, e12349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berglundh, T.; Lindhe, J.; Ericsson, I.; Marinello, C.P.; Liljenberg, B.; Thornsen, P. The Soft Tissue Barrier at Implants and Teeth. Clin. Oral Implant. Res. 1991, 2, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schupbach, P.; Glauser, R. The Defense Architecture of the Human Periimplant Mucosa: A Histological Study. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2007, 97, S15–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tolstunov, L. Dental Implant Success-Failure Analysis: A Concept of Implant Vulnerability. Implant Dent. 2006, 15, 341–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, X.; Xu, A.; Wang, L.; Luo, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Deng, F.; Tang, Z.; Wei, J. Effect of Surface Roughness on Osteogenesis in Vitro and Osseointegration in Vivo of Carbon Fiber-Reinforced Polyetheretherketone-Nanohydroxyapatite Composite. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1425–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K. Osteoblast Adhesion on Biomaterials. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.C.; Jacobs, C.R. Mechanically Induced Osteogenic Lineage Commitment of Stem Cells. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwata, N.; Nozaki, K.; Horiuchi, N.; Yamashita, K.; Tsutsumi, Y.; Miura, H.; Nagai, A. Effects of Controlled Micro-/Nanosurfaces on Osteoblast Proliferation: Micro-/Nanostructured Implant on Osteoblast Proliferation. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2017, 105, 2589–2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jemat, A.; Ghazali, M.J.; Razali, M.; Otsuka, Y. Surface Modifications and Their Effects on Titanium Dental Implants. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 791725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Qi, M.; Sun, X.; Weir, M.D.; Tay, F.R.; Oates, T.W.; Dong, B.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Xu, H.H.K. Surface Treatments on Titanium Implants via Nanostructured Ceria for Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory Capabilities. Acta Biomater. 2019, 94, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Bruyn, H.; Christiaens, V.; Doornewaard, R.; Jacobsson, M.; Cosyn, J.; Jacquet, W.; Vervaeke, S. Implant Surface Roughness and Patient Factors on Long-Term Peri-Implant Bone Loss. Periodontol. 2000 2017, 73, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Wennerberg, A. Oral Implant Surfaces: Part 1—Review Focusing on Topographic and Chemical Properties of Different Surfaces and in Vivo Responses to Them. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2004, 17, 536–543. [Google Scholar]
- Doornewaard, R.; Christiaens, V.; de Bruyn, H.; Jacobsson, M.; Cosyn, J.; Vervaeke, S.; Jacquet, W. Long-Term Effect of Surface Roughness and Patients’ Factors on Crestal Bone Loss at Dental Implants. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2017, 19, 372–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz-Sanchez, R.-M.; de-Paz-Carrion, A.; Serrera-Figallo, M.-A.; Torres-Lagares, D.; Barranco, A.; León-Ramos, J.-R.; Gutierrez-Perez, J.-L. In Vitro and In Vivo Study of Titanium Grade IV and Titanium Grade V Implants with Different Surface Treatments. Metals 2020, 10, 449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.-Y.; Kang, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Yeo, I.-S. Control Variable Implants Improve Interpretation of Surface Modification and Implant Design Effects on Early Bone Responses: An In Vivo Study. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2018, 33, 1033–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuereb, M.; Camilleri, J.; Attard, N.J. Systematic Review of Current Dental Implant Coating Materials and Novel Coating Techniques. Int. J. Prosthodont. 2015, 28, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wheelis, S.E.; Montaño-Figueroa, A.G.; Quevedo-Lopez, M.; Rodrigues, D.C. Effects of Titanium Oxide Surface Properties on Bone-Forming and Soft Tissue-Forming Cells. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2018, 20, 838–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Azari, R.; Rezaie, H.R.; Khavandi, A. Effect of Titanium Dioxide Intermediate Layer on Scratch and Corrosion Resistance of Sol–Gel-Derived HA Coating Applied on Ti-6Al-4V Substrate. Prog. Biomater. 2021, 10, 259–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gulati, K.; Moon, H.-J.; Kumar, P.T.S.; Han, P.; Ivanovski, S. Anodized Anisotropic Titanium Surfaces for Enhanced Guidance of Gingival Fibroblasts. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 112, 110860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Becker, W.; Goldstein, M.; Becker, B.E.; Sennerby, L. Minimally Invasive Flapless Implant Surgery: A Prospective Multicenter Study. Clin. Implant Dent. Relat. Res. 2005, 7, s21–s27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeini, E.N.; Atashkadeh, M.; de Bruyn, H.; D’Haese, J. Narrative Review Regarding the Applicability, Accuracy, and Clinical Outcome of Flapless Implant Surgery with or without Computer Guidance. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2020, 22, 454–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zandim-Barcelos, D.L.; de Carvalho, G.G.; Sapata, V.M.; Villar, C.C.; Hämmerle, C.; Romito, G.A. Implant-Based Factor as Possible Risk for Peri-Implantitis. Braz. Oral Res. 2019, 33, e067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wachi, T.; Shuto, T.; Shinohara, Y.; Matono, Y.; Makihira, S. Release of Titanium Ions from an Implant Surface and Their Effect on Cytokine Production Related to Alveolar Bone Resorption. Toxicology 2015, 327, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penmetsa, S.L.D.; Shah, R.; Thomas, R.; Kumar, A.B.T.; Gayatri, P.S.D.; Mehta, D.S. Titanium Particles in Tissues from Peri-Implant Mucositis: An Exfoliative Cytology-Based Pilot Study. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2017, 21, 192–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heise, G.; Black, C.M.; Smith, R.; Morrow, B.R.; Mihalko, W.M. In Vitro Effects of Macrophages on Orthopaedic Implant Alloys and Local Release of Metallic Alloy Components. Bone Joint J. 2020, 102-B, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, K.; Valentine-Thon, E. Hypersensitivity to Titanium: Clinical and Laboratory Evidence. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2006, 27 (Suppl. S1), 31–35. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, X.; Yao, Y.; Tang, W.; Han, D.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, K.; Wang, S.; Meng, Y. Design of Dental Implants at Materials Level: An Overview. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part A 2020, 108, 1634–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willis, J.; Li, S.; Crean, S.J.; Barrak, F.N. Is Titanium Alloy Ti-6Al-4 V Cytotoxic to Gingival Fibroblasts-A Systematic Review. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2021, 7, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5832-3:2021; Implants for Surgery—Metallic Materials—Part 3: Wrought Titanium 6-Aluminium 4-Vanadium Alloy. ISO: Geneva, Switzeland, 2021.
- ISO 10993-5:2009; Biological Evaluation of Medical Devices—Part 5: Tests for in Vitro Cytotoxicity. ISO: Geneva, Switzeland, 2009.
- Velasco-Ortega, E.; Jos, A.; Cameán, A.M.; Pato-Mourelo, J.; Segura-Egea, J.J. In Vitro Evaluation of Cytotoxicity and Genotoxicity of a Commercial Titanium Alloy for Dental Implantology. Mutat. Res. Genet. Toxicol. Environ. Mutagen. 2010, 702, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-J.; Kim, C.-W.; Lim, Y.-J.; Heo, S.-J. Microrough Titanium Surface Affects Biologic Response in MG63 Osteoblast-like Cells. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 2006, 79A, 1023–1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, Y.-H.; Lew, W.-Z.; Lu, E.; Loretz, T.; Lu, L.; Lin, C.-T.; Feng, S.-W. An Evaluation of the Biocompatibility and Osseointegration of Novel Glass Fiber Reinforced Composite Implants: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Dent. Mater. 2018, 34, 470–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukaszewska-Kuska, M.; Wirstlein, P.; Majchrowski, R.; Dorocka-Bobkowska, B. Osteoblastic Cell Behaviour on Modified Titanium Surfaces. Micron 2018, 105, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rottmar, M.; Müller, E.; Guimond-Lischer, S.; Stephan, M.; Berner, S.; Maniura-Weber, K. Assessing the Osteogenic Potential of Zirconia and Titanium Surfaces with an Advanced in Vitro Model. Dent. Mater. 2019, 35, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pires, L.A.; de Meira, C.R.; Tokuhara, C.K.; de Oliveira, F.A.; Dainezi, V.B.; Zardin Graeff, M.S.; Fortulan, C.A.; de Oliveira, R.C.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M.; Borges, A.F.S. Wettability and Pre-Osteoblastic Behavior Evaluations of a Dense Bovine Hydroxyapatite Ceramics. J. Oral Sci. 2020, 62, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guida, L.; Oliva, A.; Basile, M.A.; Giordano, M.; Nastri, L.; Annunziata, M. Human Gingival Fibroblast Functions Are Stimulated by Oxidized Nano-Structured Titanium Surfaces. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 900–907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doll, P.W.; Husari, A.; Ahrens, R.; Spindler, B.; Guber, A.E.; Steinberg, T. Enhancing the Soft-Tissue Integration of Dental Implant Abutments-in Vitro Study to Reveal an Optimized Microgroove Surface Design to Maximize Spreading and Alignment of Human Gingival Fibroblasts. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2021, 109, 1768–1776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jablonská, E.; Horkavcová, D.; Rohanová, D.; Brauer, D.S. A Review of In Vitro Cell Culture Testing Methods for Bioactive Glasses and Other Biomaterials for Hard Tissue Regeneration. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 10941–10953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, K.; Liu, S.; Hu, T.; Razanau, I.; Wu, X.; Ao, H.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Zheng, X. Optimized Nanointerface Engineering of Micro/Nanostructured Titanium Implants to Enhance Cell–Nanotopography Interactions and Osseointegration. ACS Biomater. Sci. Eng. 2020, 6, 969–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, G.; Eggers, B.; Duddeck, D.; Kramer, F.-J.; Bourauel, C.; Jepsen, S.; Deschner, J.; Nokhbehsaim, M. Influence of Cold Atmospheric Plasma on Dental Implant Materials—An In Vitro Analysis. Clin. Oral Invest. 2022, 26, 2949–2963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhan, X.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Tao, A.; Wang, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, C. Comparison of the Osteoblastic Activity of Low Elastic Modulus Ti-24Nb-4Zr-8Sn Alloy and Pure Titanium Modified by Physical and Chemical Methods. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2020, 113, 111018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.-S.; Ji, M.-K.; Jang, W.-H.; Alam, K.; Kim, H.-S.; Cho, H.-S.; Lim, H.-P. Biological Effects of the Novel Mulberry Surface Characterized by Micro/Nanopores and Plasma-Based Graphene Oxide Deposition on Titanium. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 7307–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, B.; Wan, Y.; Liu, C.; Wang, H.; Yu, M.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y. Improved Osseointegration of 3D Printed Ti-6Al-4V Implant with a Hierarchical Micro/Nano Surface Topography: An In Vitro and in Vivo Study. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2021, 118, 111505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maló, P.; de Araújo Nobre, M.; Gonçalves, Y.; Lopes, A.; Ferro, A. Immediate Function of Anodically Oxidized Surface Implants (TiUniteTM) for Fixed Prosthetic Rehabilitation: Retrospective Study with 10 Years of Follow-Up. BioMed Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 2061237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rocci, A.; Martignoni, M.; Gottlow, J. Immediate Loading of Brånemark System® TiUniteTM and Machined-Surface Implants in the Posterior Mandible: A Randomized Open-Ended Clinical Trial. Clin. Implant. Dent. Relat. Res. 2003, 5, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balshi, S.F.; Wolfinger, G.J.; Balshi, T.J. Analysis of 164 Titanium Oxide-Surface Implants in Completely Edentulous Arches for Fixed Prosthesis Anchorage Using the Pterygomaxillary Region. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2005, 20, 946–952. [Google Scholar]
- Marenzi, G.; Impero, F.; Scherillo, F.; Sammartino, J.; Squillace, A.; Spagnuolo, G. Effect of Different Surface Treatments on Titanium Dental Implant Micro-Morphology. Materials 2019, 12, 733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamagami, A.; Yoshihara, Y.; Suwa, F. Mechanical and Histologic Examination of Titanium Alloy Material Treated by Sandblasting and Anodic Oxidization. Int. J. Oral Maxillofac. Implant. 2005, 20, 48–53. [Google Scholar]
- Esposito, M.; Ardebili, Y.; Worthington, H.V. Interventions for Replacing Missing Teeth: Different Types of Dental Implants. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 7, CD003815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henningsen, A.; Smeets, R.; Hartjen, P.; Heinrich, O.; Heuberger, R.; Heiland, M.; Precht, C.; Cacaci, C. Photofunctionalization and Non-Thermal Plasma Activation of Titanium Surfaces. Clin. Oral Invest. 2018, 22, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabel, K.; Kohal, R.-J.; Steinberg, T.; Tomakidi, P.; Rolauffs, B.; Adolfsson, E.; Palmero, P.; Fürderer, T.; Altmann, B. Controlling Osteoblast Morphology and Proliferation via Surface Micro-Topographies of Implant Biomaterials. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 12810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.G.; Hill, E.W.; Bayat, A. Designing Implant Surface Topography for Improved Biocompatibility. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2013, 10, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuzaka, K.; Frank Walboomers, X.; Yoshinari, M.; Inoue, T.; Jansen, J.A. The Attachment and Growth Behavior of Osteoblast-like Cells on Microtextured Surfaces. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2711–2719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.-D.; Kim, W.-J.; Kim, S.; Ku, Y.; Ryoo, H.-M. Surface Topography of Titanium Affects Their Osteogenic Potential through DNA Methylation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albrektsson, T.; Brånemark, P.I.; Hansson, H.A.; Lindström, J. Osseointegrated Titanium Implants. Requirements for Ensuring a Long-Lasting, Direct Bone-to-Implant Anchorage in Man. Acta Orthop. Scand. 1981, 52, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almas, K.; Smith, S.; Kutkut, A. What Is the Best Micro and Macro Dental Implant Topography? Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 63, 447–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]






| IMPLANTS | NOBELPARALLELTM | MAGICORE® |
|---|---|---|
| DIMENSION | 4.3 × 10 mm | 4.5 × 11 mm + 5 mm (neck) |
| SURFACES TREATMENTS GRADE (COMPOSITION) | Anodic oxidation, thick TiO2 layer Tubules, curved angles Grade IV (pure titanium): no other alloys, only titanium | Sandblasting with calcium phosphate apatitite particles Abrasive: 40 (400 µm)–80 (177 µm) mesh. Sharp angles and summits Grade V (Ti6Al4V): titanium alloy, containing aluminum and vanadium |
| THREADS DEPTH | 0.25 mm | 0.9 mm |
| THREADS WIDTH | 0.4 mm | 0.25 mm |
| INTER-THREADS LENGTH | 0.6 mm | 1.2 mm |
| Ti (%) | Al (%) | V (%) | O (%) | P (%) | C (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NOBELPARALLELTM | 28.38 | - | - | 65.24 | 4.03 | 2.34 |
| MAGICORE® | 47.67 | 5.30 | 0.86 | 19.42 | - | 26.74 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Attik, N.; Phantarasmy, M.; Abouelleil, H.; Chevalier, C.; Barraco, A.; Grosgogeat, B.; Lafon, A. Comparison of the Biological Behavior and Topographical Surface Assessment of a Minimally Invasive Dental Implant and a Standard Implant: An In Vitro Study. Materials 2022, 15, 7540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217540
Attik N, Phantarasmy M, Abouelleil H, Chevalier C, Barraco A, Grosgogeat B, Lafon A. Comparison of the Biological Behavior and Topographical Surface Assessment of a Minimally Invasive Dental Implant and a Standard Implant: An In Vitro Study. Materials. 2022; 15(21):7540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217540
Chicago/Turabian StyleAttik, Nina, Marina Phantarasmy, Hazem Abouelleil, Charlène Chevalier, Aurore Barraco, Brigitte Grosgogeat, and Arnaud Lafon. 2022. "Comparison of the Biological Behavior and Topographical Surface Assessment of a Minimally Invasive Dental Implant and a Standard Implant: An In Vitro Study" Materials 15, no. 21: 7540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217540
APA StyleAttik, N., Phantarasmy, M., Abouelleil, H., Chevalier, C., Barraco, A., Grosgogeat, B., & Lafon, A. (2022). Comparison of the Biological Behavior and Topographical Surface Assessment of a Minimally Invasive Dental Implant and a Standard Implant: An In Vitro Study. Materials, 15(21), 7540. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15217540








