Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length
Abstract
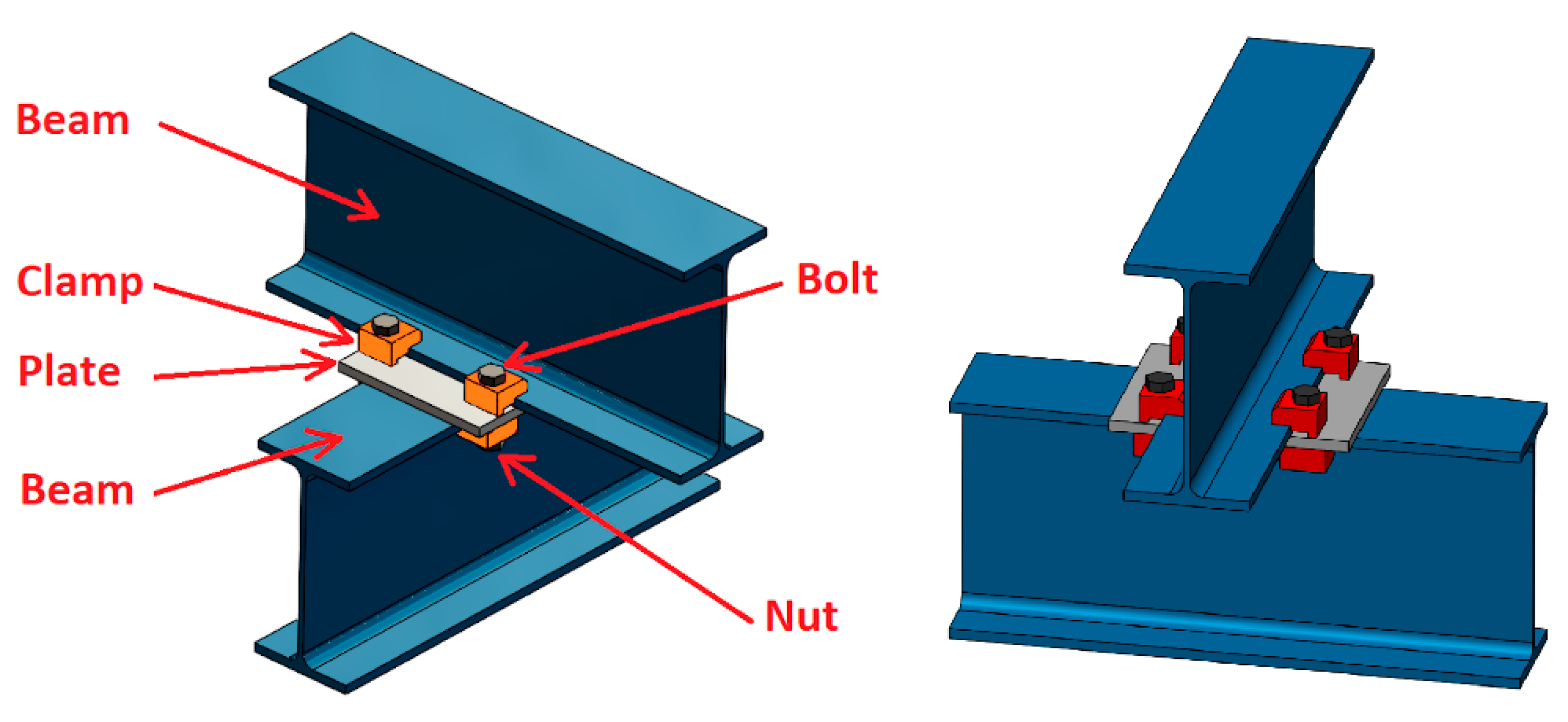
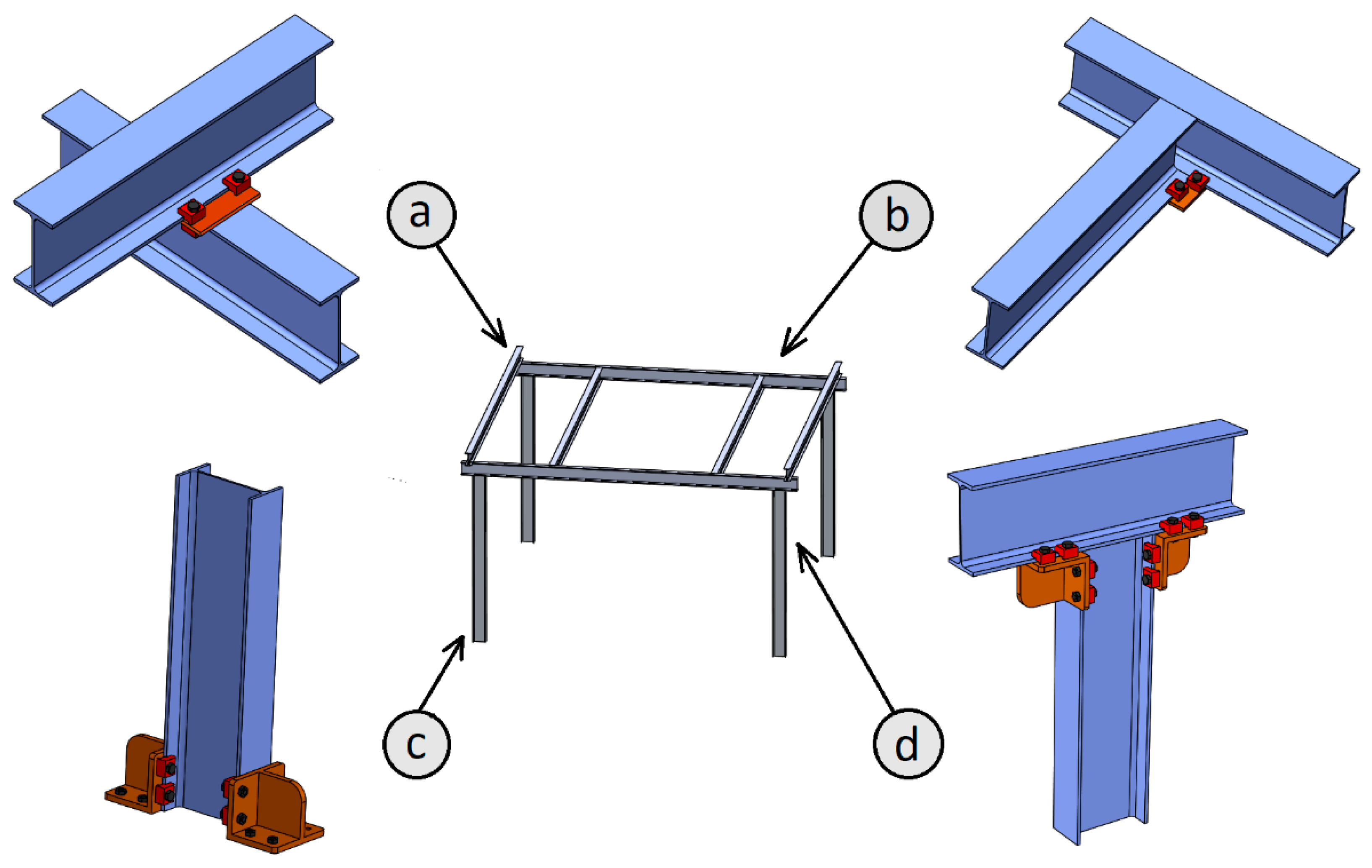
:1. Introduction
2. Proposed Analytical Method
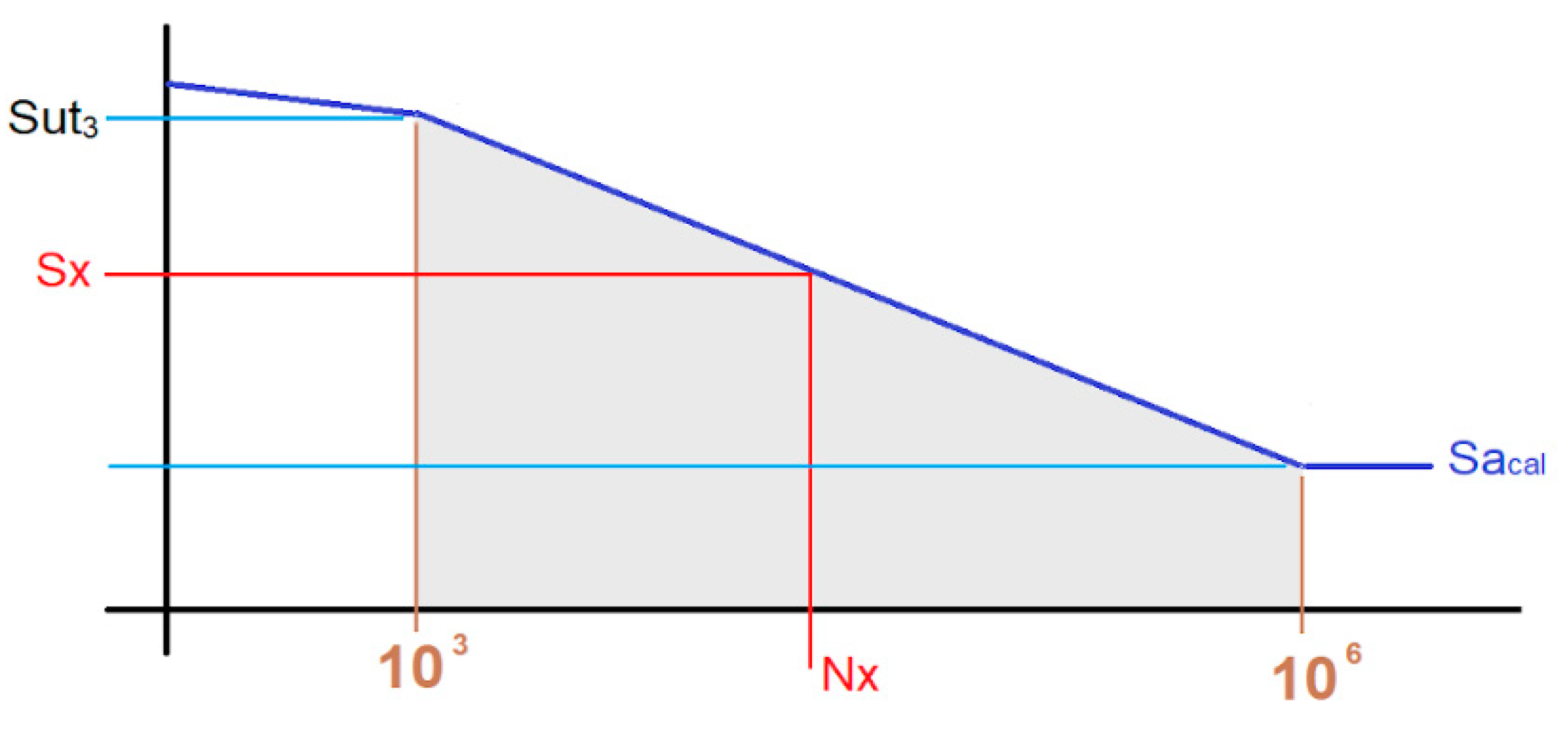
2.1. Calculation of the Theoretical Value of the Bolt Fatigue Limit
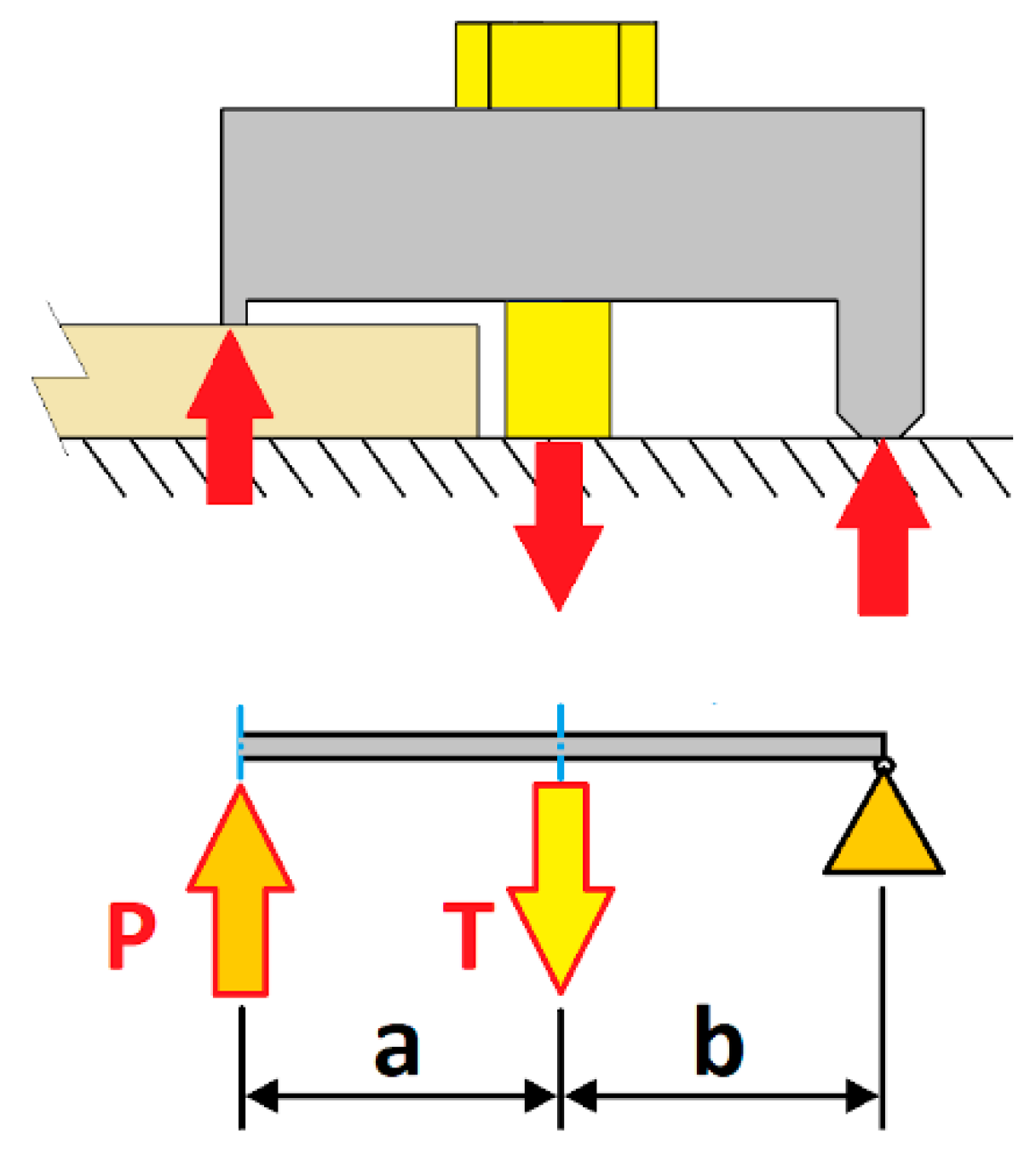
2.2. Calculation of the Load Experienced by the Bolt
2.3. Calculation of the Maximum Allowable Alternating Stress in the Bolt
2.4. Calculation of the Bolt’s Useful Life
3. Materials and Experimental Methods
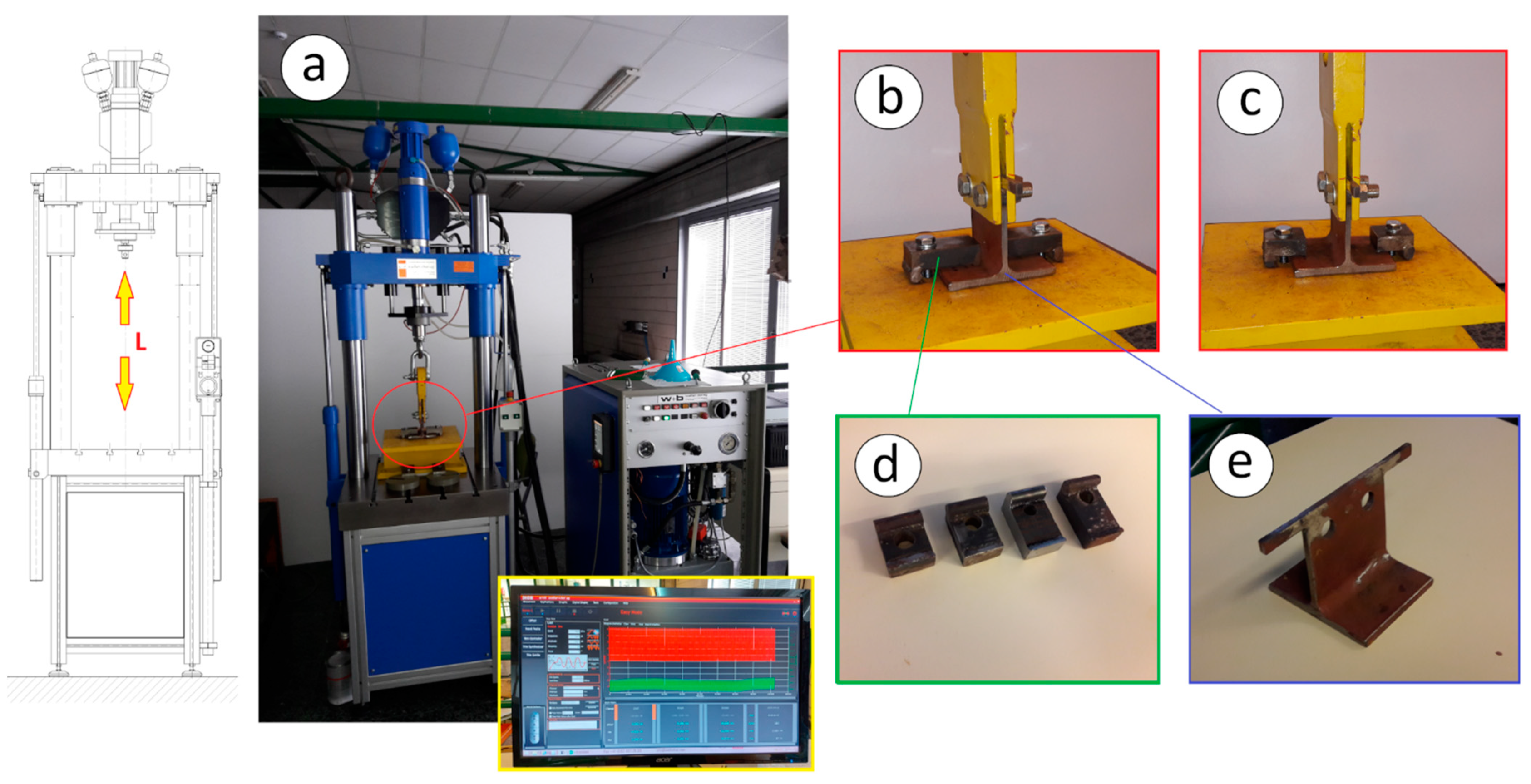
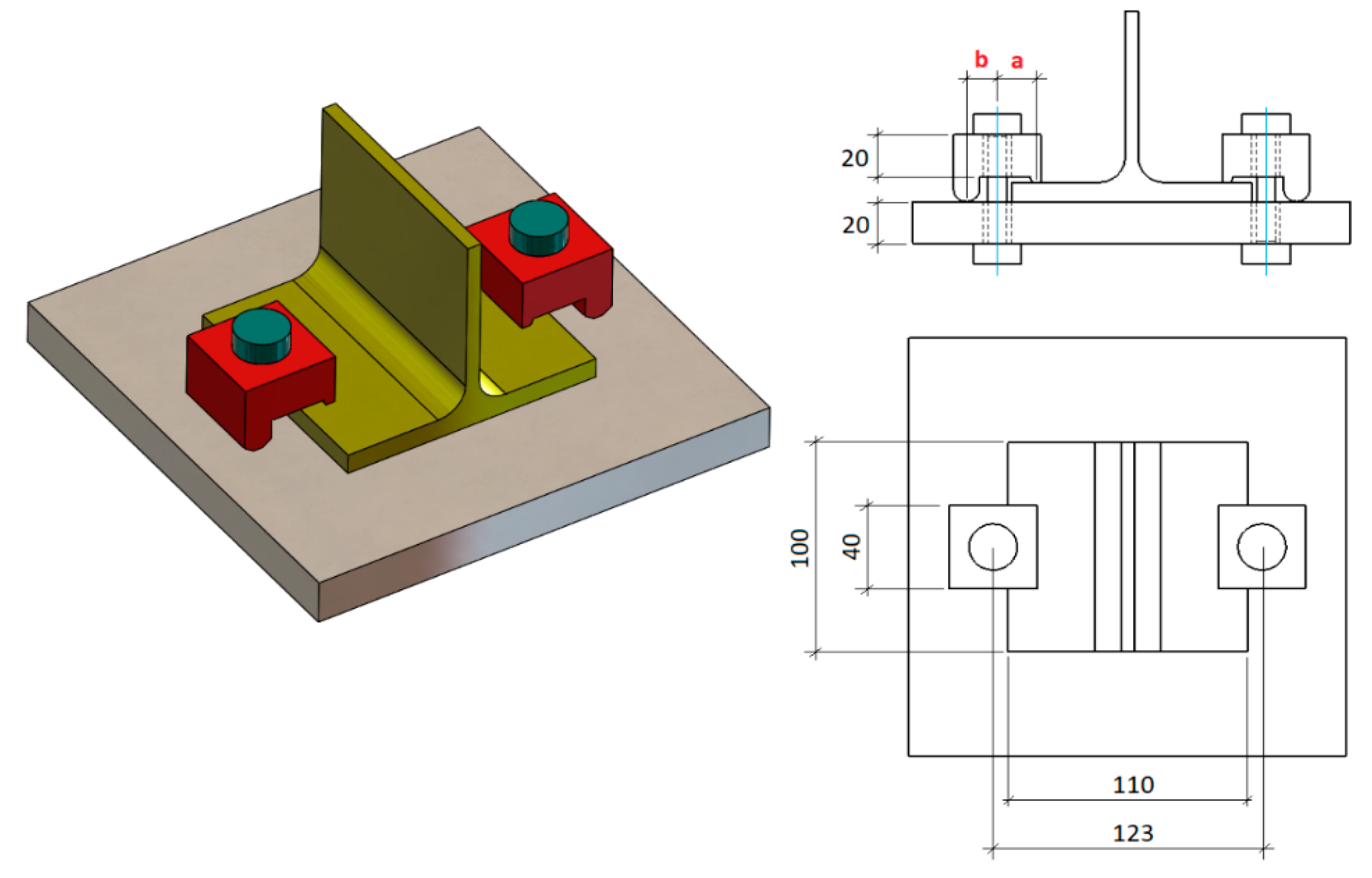
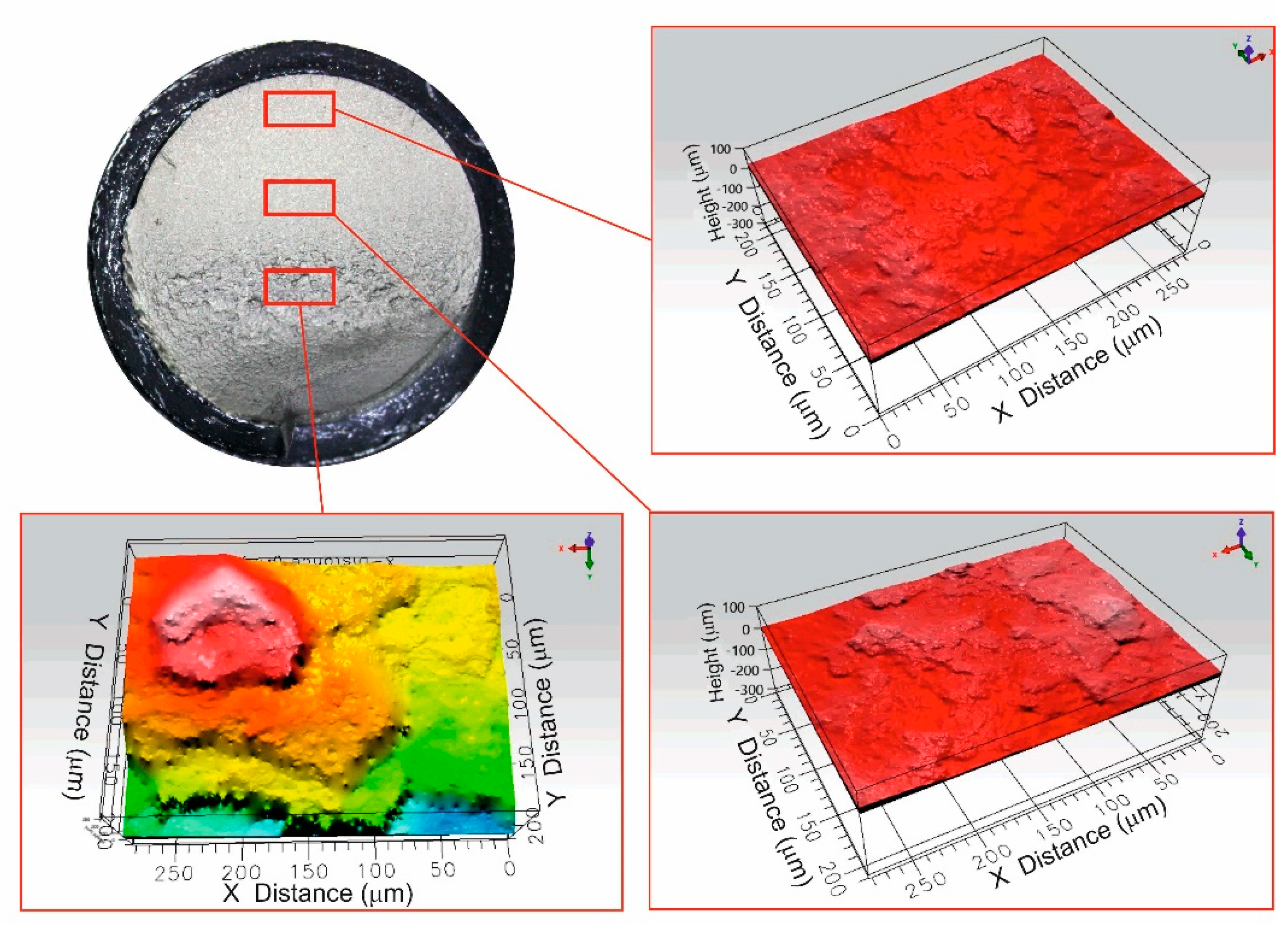
3.1. Laboratory Test
3.2. Analysis with the Analytical Model
4. Results and Discussion
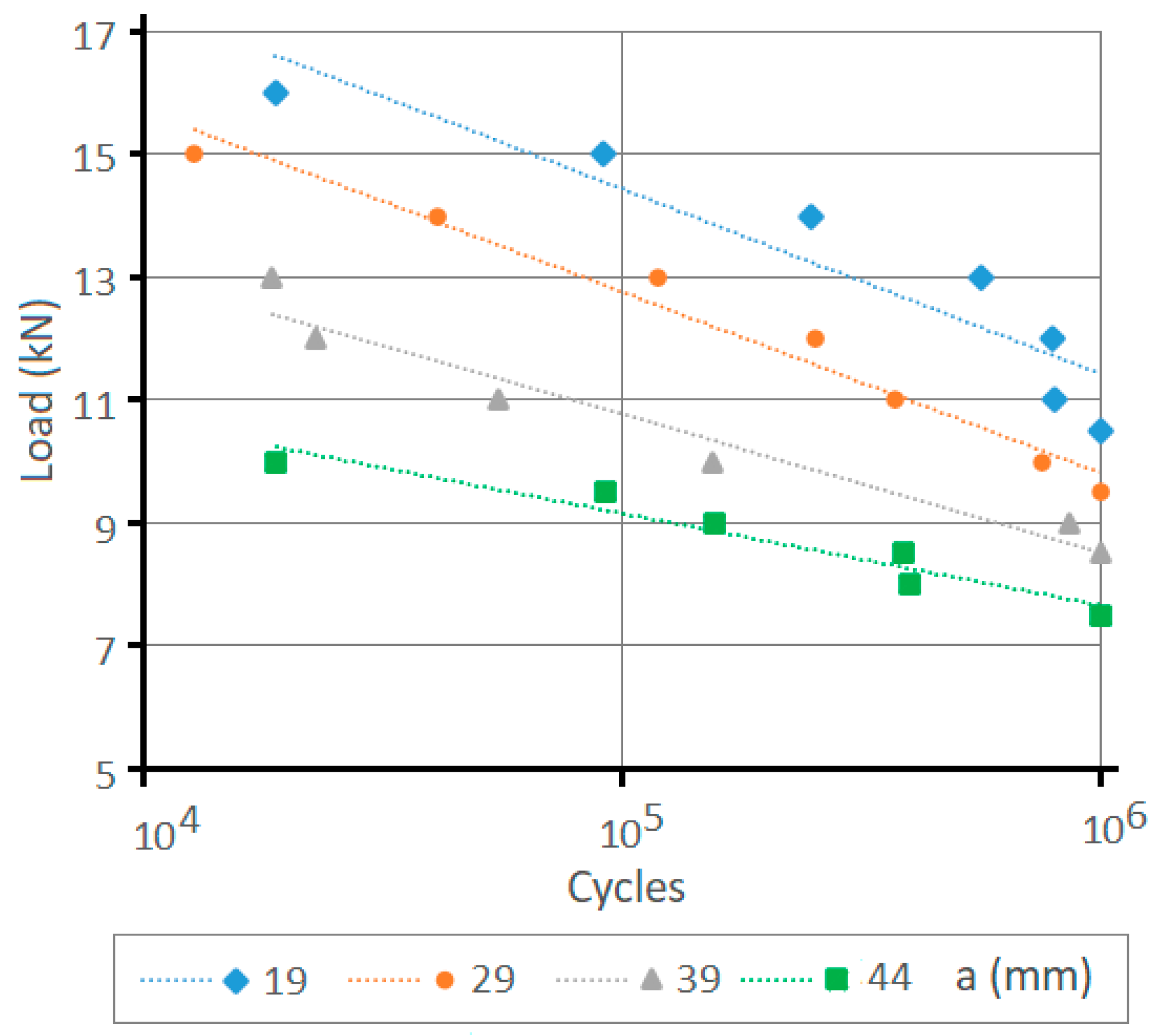
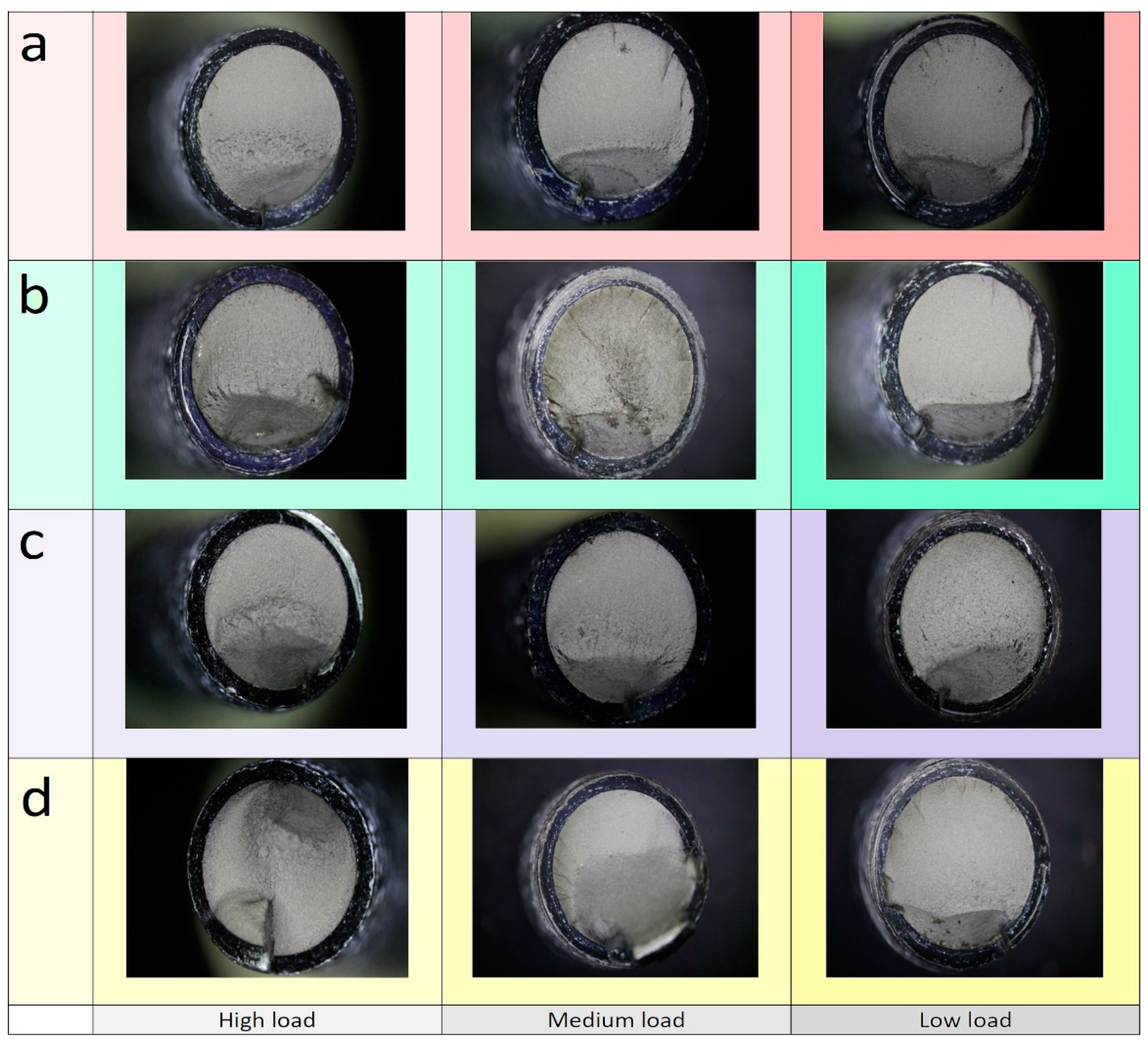
4.1. Results of Experimental Tests
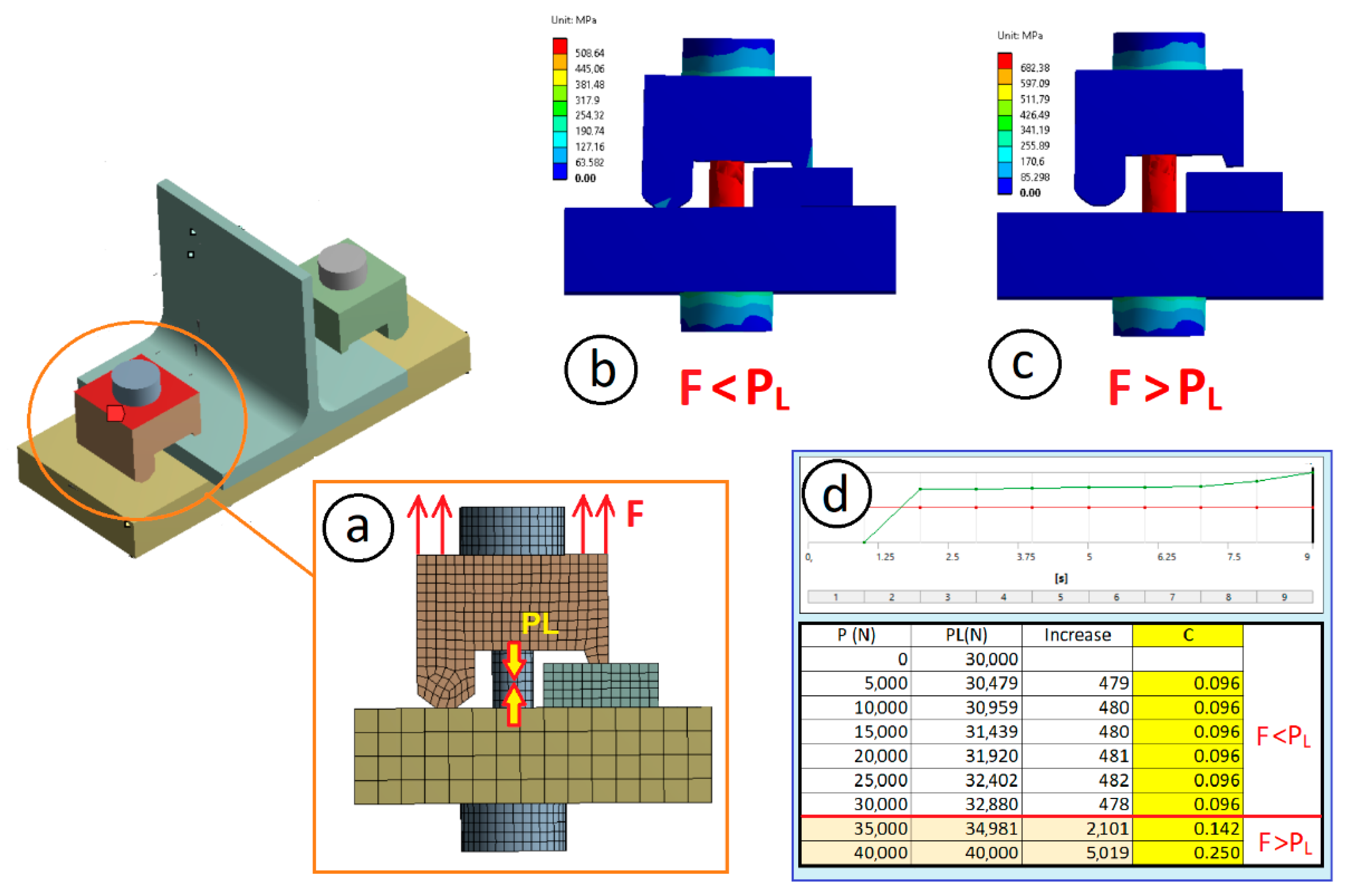
4.2. Analytical Model Results
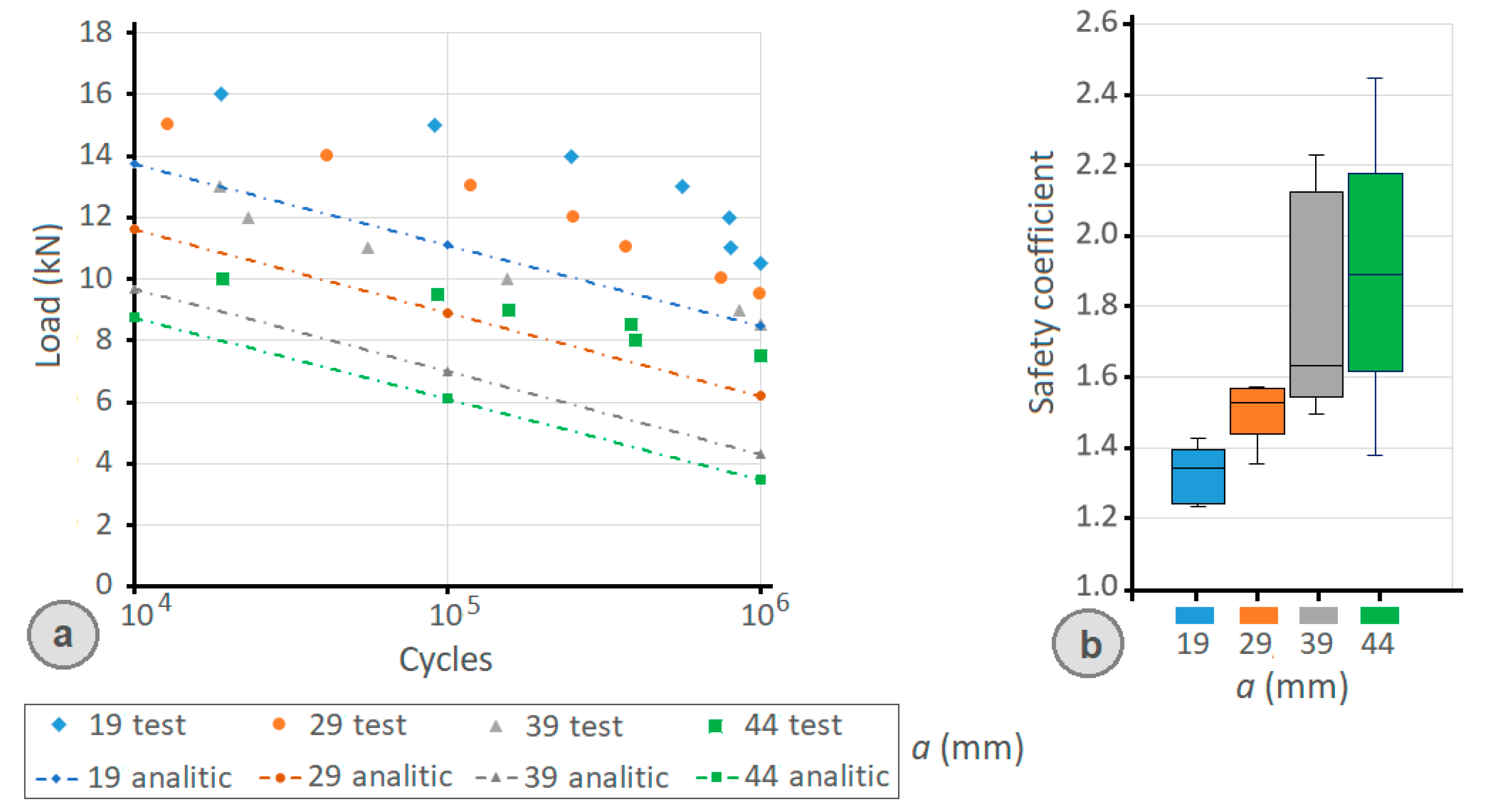
4.3. Comparison of Analytical Model Results and Laboratory Test Results
5. Conclusions
- -
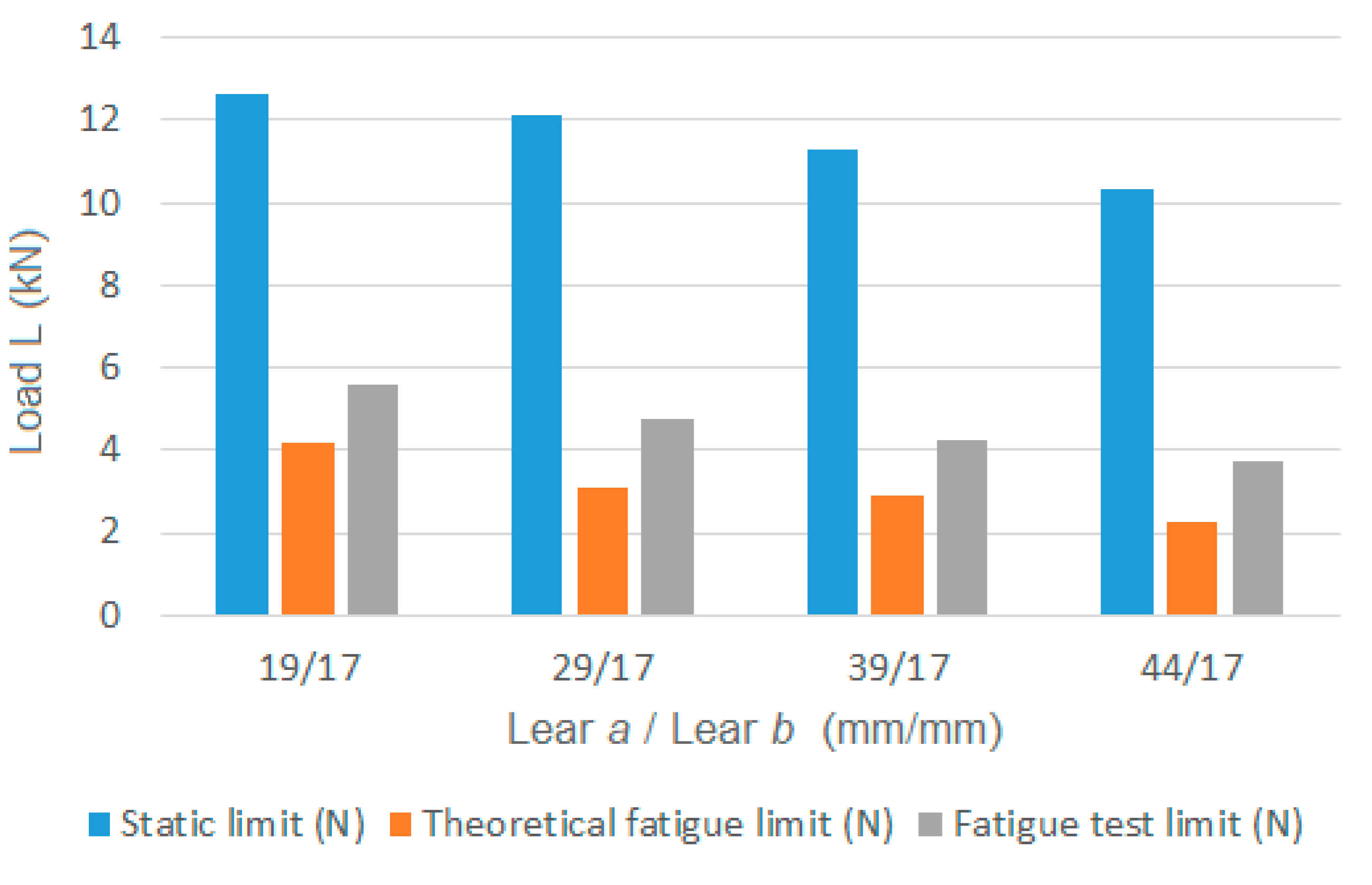
- The data obtained indicate that the joint strength can be reduced to one third when the joint is subjected to fatigue stresses, something that is essential to be considered in structures subjected to dynamic stresses, which can cause fatigue in the joints.
- -
- In this work, an analytical model was proposed and used for a quick analysis of the number of cycles and the fatigue limit of clamped joints and their bolts, according to the size of the clamping levers. The experimental results prove that the maximum allowed fatigue load calculated with the analytical model is always lower than that achieved in the real tests.
- -
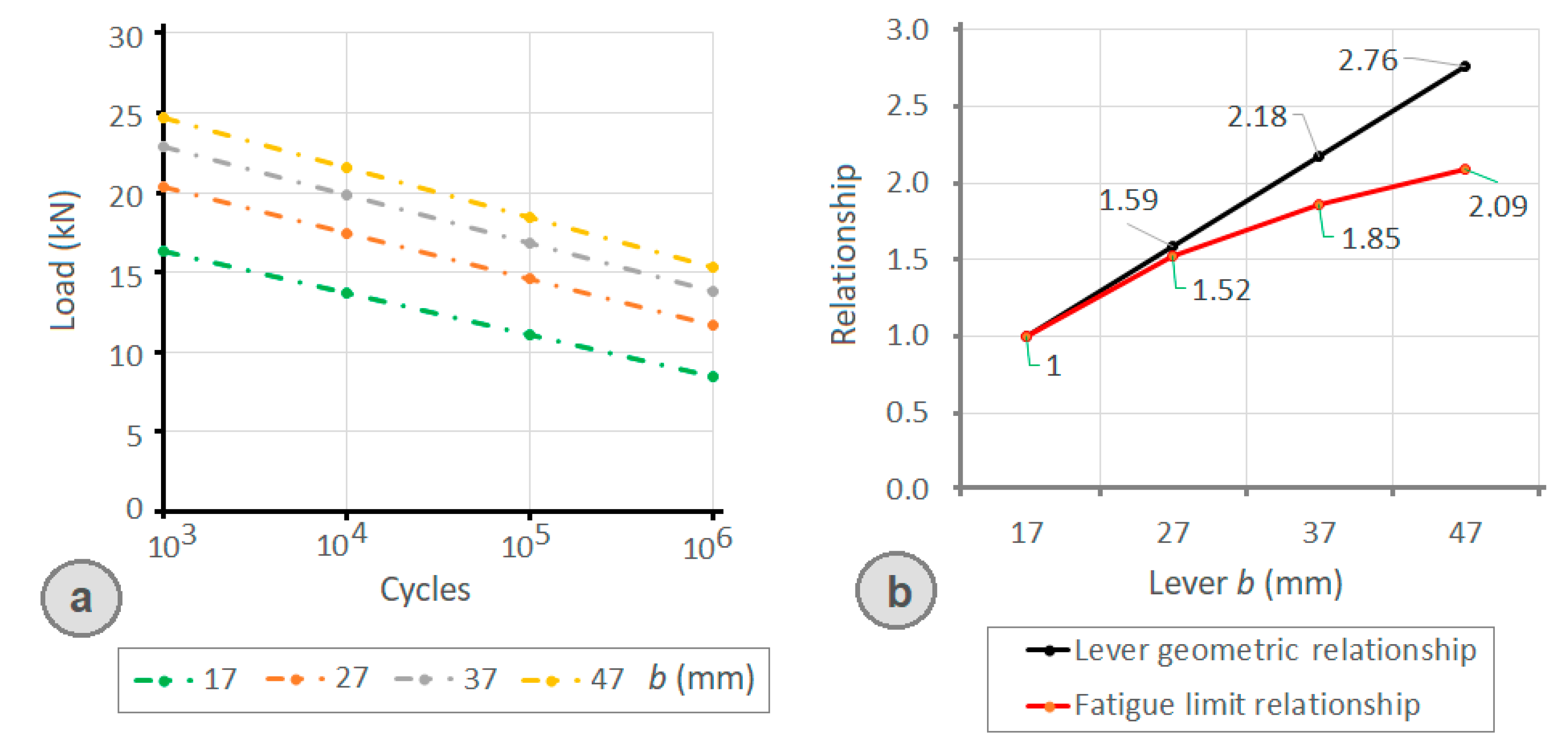
- If the size of the front lever is increased, the fatigue resistance decreases, while for the rear lever, if its size is increased, the fatigue limit of the joint also increases. The combination that provides the greatest fatigue resistance of the clamp joint comprises of the shortest front lever and the longest rear lever.
- -
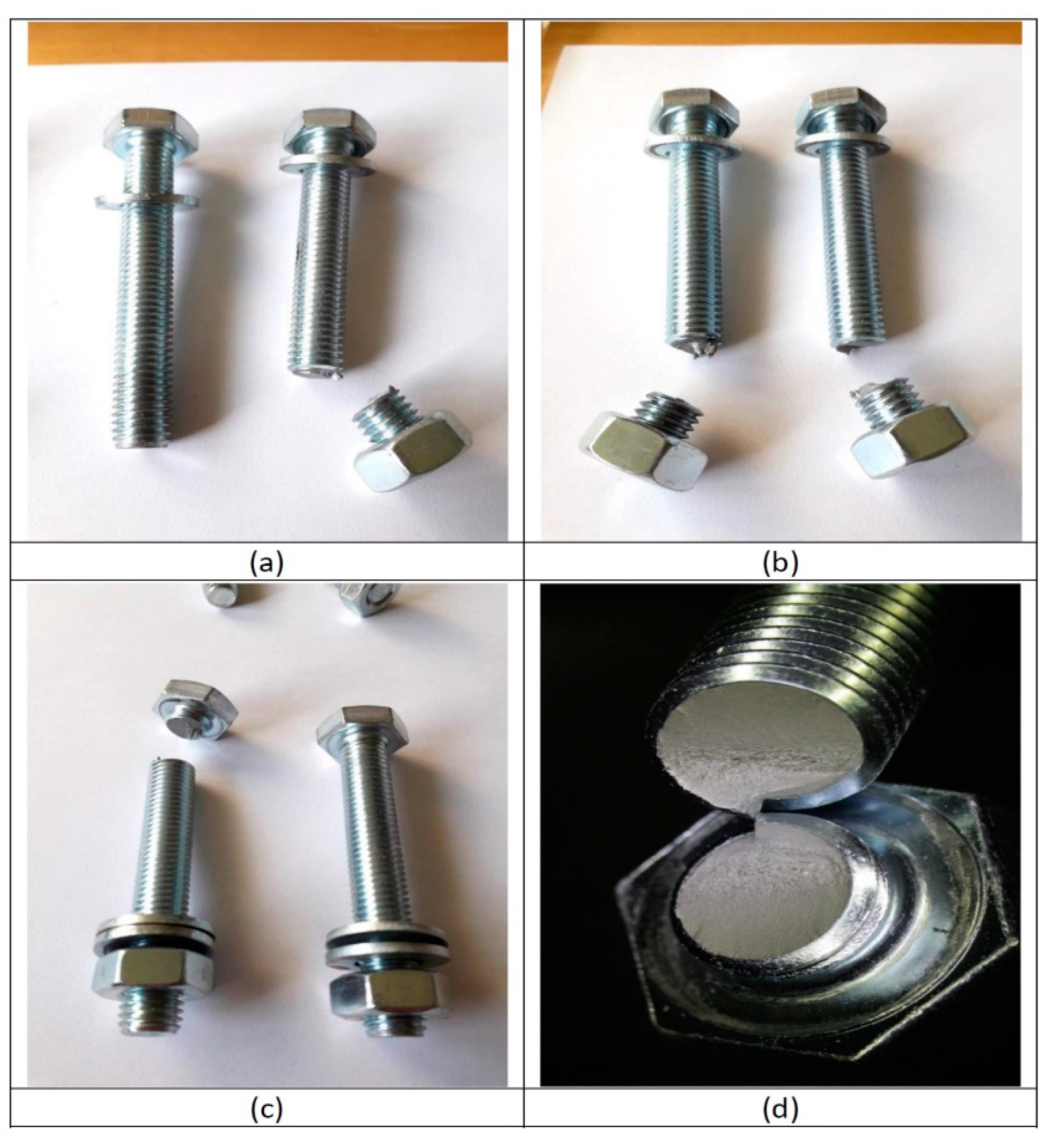
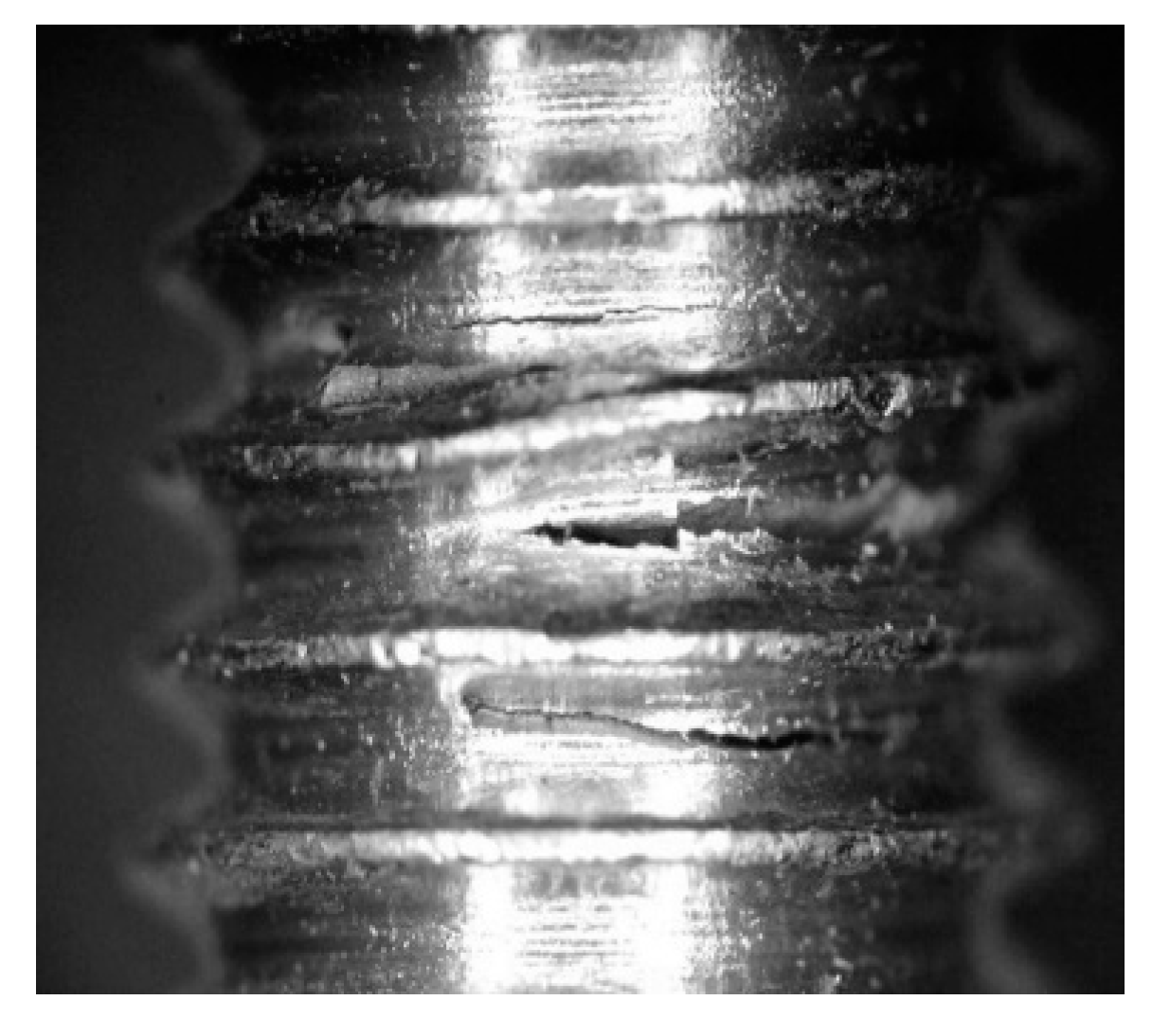
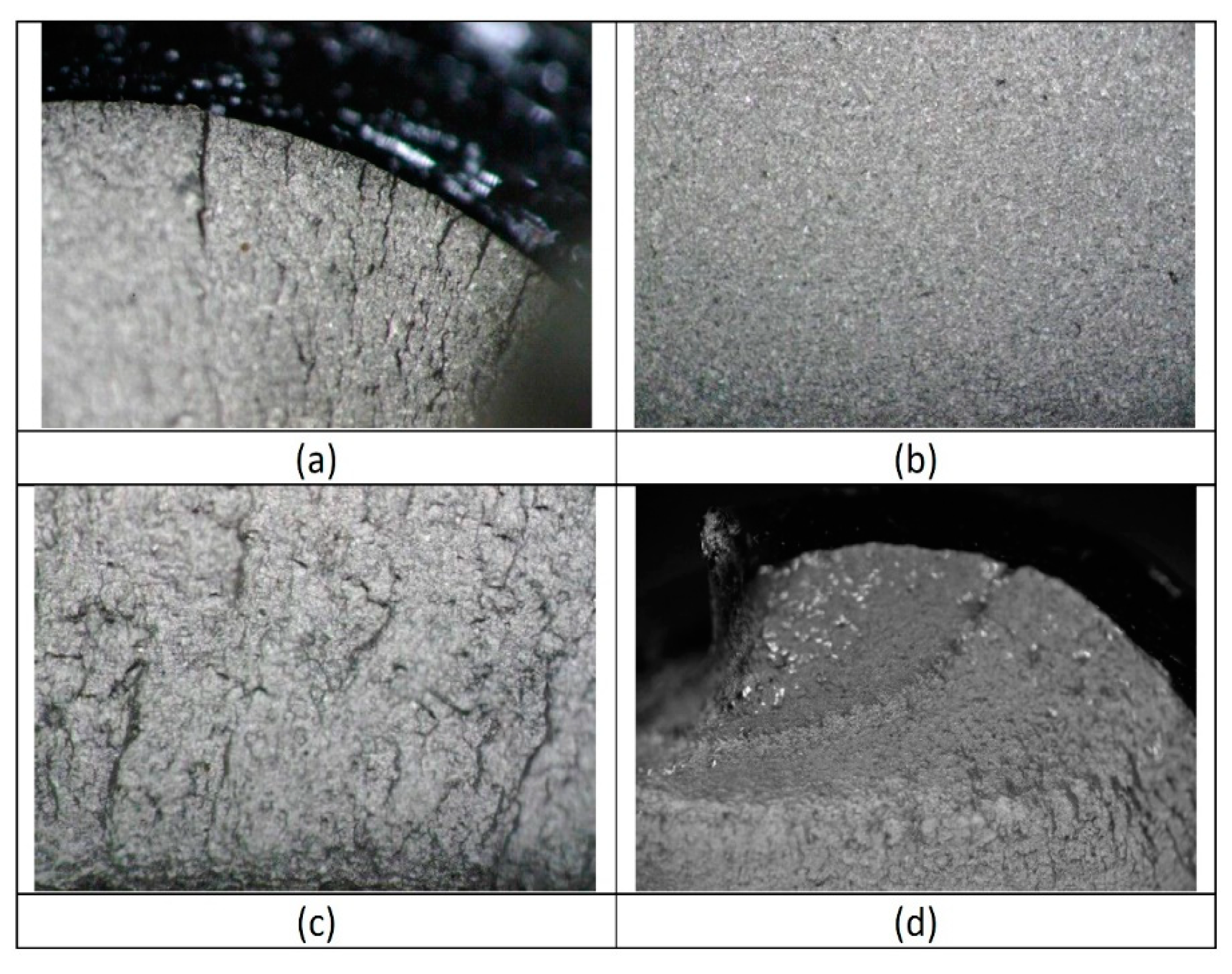
- The experimental tests revealed that 96% of the time the bolt breakage occurred in the lower part, in the bolt–nut union area. The failure of one bolt at the head location was observed in the remaining 4%.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Sisi AE, D.A.; El-Husseiny, O.M.; Matar, E.B.; Sallam HE, D.M.; Salim, H.A. Field-testing and numerical simulation of vantage steel bridge. J. Civ. Struc-Tural Health Monit. 2020, 10, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, F.; Moutinho, C.; Magalhães, F.; Caetano, E.; Cunha, Á. Analysis of dynamic and fatigue effects in an old metallic riveted bridge. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2014, 99, 85–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Riveiro, B.; Conde, B.; Caamaño, J.C. Analytical T-stub model for the analy-sis of clamps in structural metal joints. J. Constr. Steel Res 2017, 130, 138–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehner, P.; Krejsa, M.; Pařenica, P.; Křivý, V.; Brožovský, J. Fatigue damage analysis of a rivet-ed steel overhead crane support truss. Int. J. Fatigue 2019, 128, 105190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindapter. Lindapter International. Available online: www.lindapter.com (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- LNA Solutions. LNA Solutions, Steel Connection Solutions. Available online: www.lnasolutions.com (accessed on 15 October 2021).
- Basta, A.; Serror, M.H.; Marzouk, M. A BIM-based framework for quantitative assessment of steel structure deconstructability. Autom. Constr. 2020, 111, 103064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckelman, M.J.; Brown, C.; Troup, L.N.; Wang, L.; Webster, M.D.; Hajjar, J.F. Life cycle energy and environmental benefits of novel design-for-deconstruction struc-tural systems in steel buildings. Build. Environ. 2018, 143, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabaleiro, M.; Conde, B.; Riveiro, B.; Caamaño, J.C. Analysis of steel connec-tions with girder clamps according to the bolts preload. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 168, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lachowicz, M.B.; Lachowicz, M.M. Influence of Corrosion on Fatigue of the Fastening Bolts. Materials 2021, 14, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Z.X.; Shen, C.J.; Jiang, Z.Q.; Cheng, K.K.; Wang, H.W. Cyclic loading tests of an earthquake-resilient prefabricated steel frame with open-web steel channel beams. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2021, 177, 106477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Du, M.; Yuan, J.; Shi, J.; Yu, S.; Zhang, Y. Parametric Analysis and Stiffness Investigation of Extended End-Plate Connection. Materials 2020, 13, 5133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai-lin, Z.; Ran, L.; Zi-qin, J.; Zhen-yu, Z. Experimental study of earthquake-resilient PBCSC with double flange cover plates. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2018, 143, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Qin, J.; Zhao, D.; Wu, Z. Seismic Behavior of Extended End-Plate Connections Subjected to Cyclic Loading on the Top-Side of the Column. Materials 2020, 13, 3724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reinosa, J.M.; Loureiro, A.; Gutierrez, R.; Lopez, M. Mechanical stiffness prediction of beam-to-column stiffened angle joints. J. Constr. Steel Res. 2020, 168, 105875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartaglia, R.; D’Aniello, M.; Andreini, M.; La Mendola, S. The performance of preloaded bolts in seismically prequalified steel joints in a fire scenario. Materials 2020, 13, 5079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zabojszcza, P.; Radoń, U.; Szaniec, W. Probabilistic Approach to Limit States of a Steel Dome. Materials 2021, 14, 5528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zampieri, P.; Curtarello, A.; Maiorana, E.; Pellegrino, C. A review of the fatigue strength of shear bolted connections. Int. J. Steel Struct. 2019, 19, 1084–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, H.; Hoffmeister, B.; Feldmann, M. Fatigue analysis of welds and bolts in end plate connections of I-girders. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 138, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Cui, X.; Xiao, J.; Lua, J.; Phan, N. A simplified continuum damage mechanics based modeling strategy for cumulative fatigue damage assessment of metallic bolted joints. Int. J. Fatigue 2020, 131, 105302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Nie, X.; Zhang, L.; Yang, F.; Huang, M.; Zhao, T. Test and Finite Element Analysis of a New Type of Double-Limb Double-Plate Connection Joint in Narrow Base Tower. Materials 2021, 14, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norton, R.L. Machine Design: An Integrated Approach, 6th ed.; Pearson: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Budynas, R.G. Shigley’s Mechanical Engineering Design (in Si Units); McGraw Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- The European Union Per Regulation 305/2011: Eurocode 3: Design of Steel Structures—Part 1–8: Design of Joints (EN 1993-1-8:2003); European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2003.



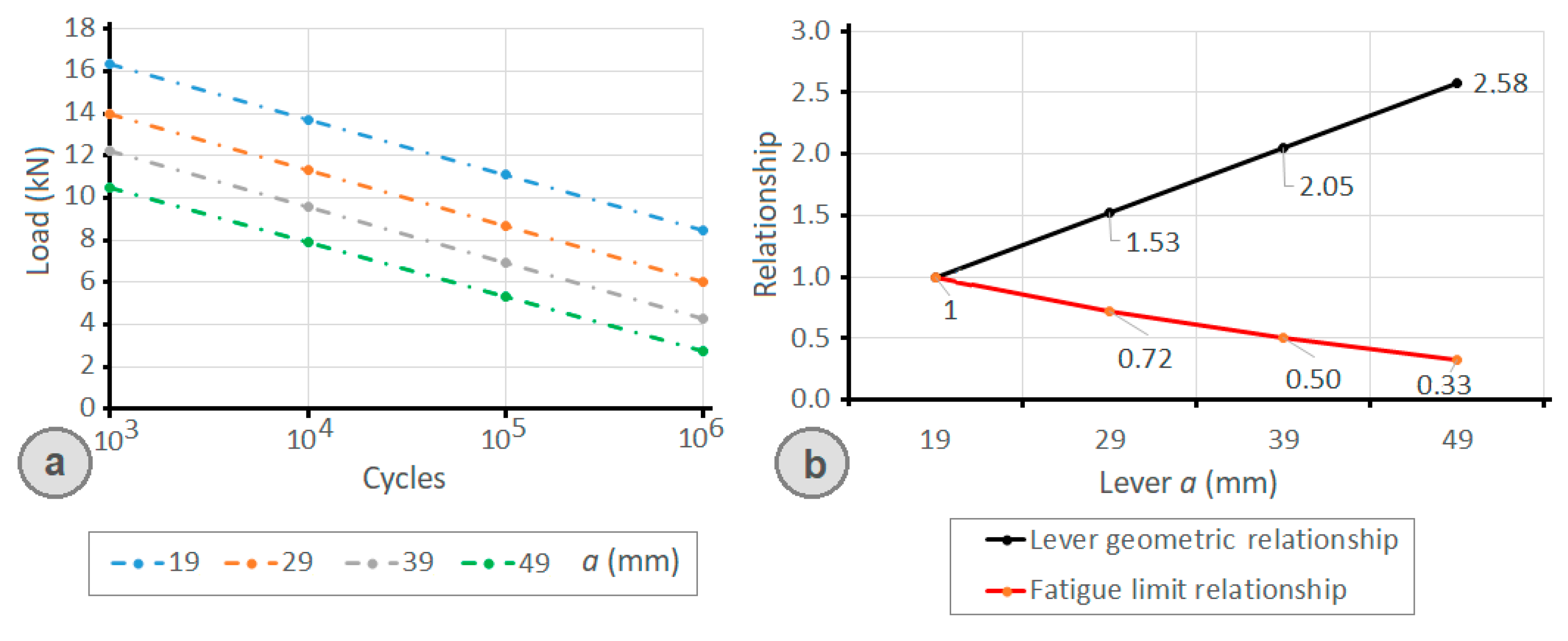
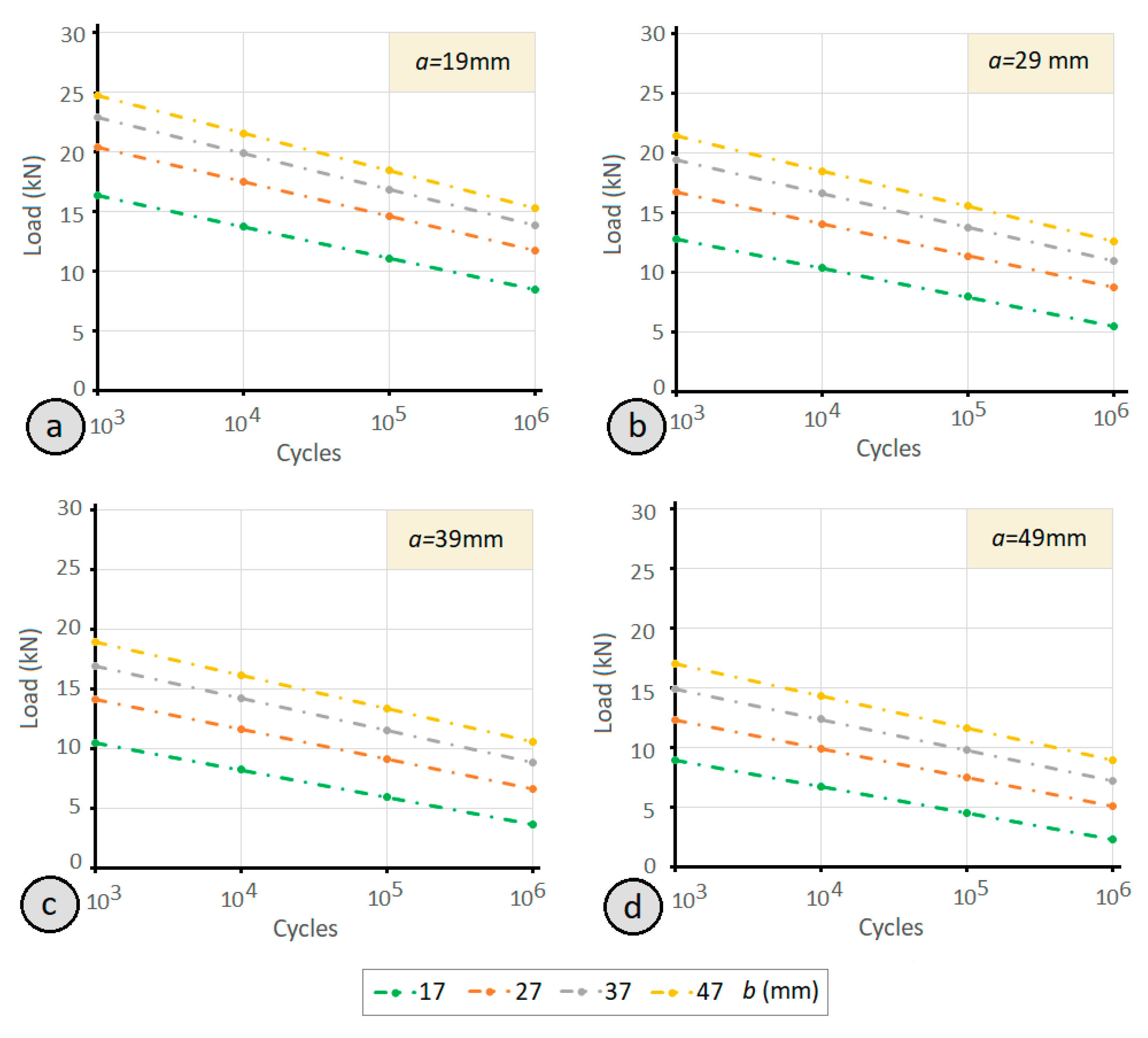
| a/b (mm) | 19/17 | 29/17 | 39/17 | 49/17 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycles | Load L (N) | Load L (N) | Load L (N) | Load L (N) |
| 1000 | 16,367 | 14,014 | 12,255 | 10,503 |
| 10,000 | 13,730 | 11,362 | 9590 | 7923 |
| 100,000 | 11,094 | 8710 | 6925 | 5344 |
| 1,000,000 | 8457 | 6057 | 4261 | 2764 |
| a/b (mm) | 19/17 | 19/27 | 19/37 | 19/47 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cycles | Load L (N) | Load L (N) | Load L (N) | Load L (N) |
| 1000 | 16,367 | 20,344 | 22,900 | 24,682 |
| 10,000 | 13,729 | 17,468 | 19,872 | 21,547 |
| 100,000 | 11,092 | 14,593 | 16,844 | 18,413 |
| 1,000,000 | 8454 | 11,718 | 13,816 | 15,278 |
| a/b | Static Limit (N) | Theoretical Fatigue Limit (N) | Fatigue Test Limit (N) | Relationship (Static/Theoretical Fatigue) | Relationship (Static/Test Fatigue) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 19/17 | 12,665 | 4229 | 5250 | 3.0 | 2.4 |
| 29/17 | 12,120 | 3192 | 4750 | 3.8 | 2.6 |
| 39/17 | 11,269 | 3240 | 4250 | 3.5 | 2.7 |
| 44/17 | 10,345 | 2277 | 3750 | 4.5 | 2.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cabaleiro, M.; Comesaña, R.; González-Gaya, C.; Caamaño, C. Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length. Materials 2021, 14, 7726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247726
Cabaleiro M, Comesaña R, González-Gaya C, Caamaño C. Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length. Materials. 2021; 14(24):7726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247726
Chicago/Turabian StyleCabaleiro, Manuel, Rafael Comesaña, Cristina González-Gaya, and Carlos Caamaño. 2021. "Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length" Materials 14, no. 24: 7726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247726
APA StyleCabaleiro, M., Comesaña, R., González-Gaya, C., & Caamaño, C. (2021). Analytical Model for the Fatigue Analysis of Steel Joints by Clamps According to the Lever Length. Materials, 14(24), 7726. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247726









