Flexible Memory Device Composed of Metal-Oxide and Two-Dimensional Material (SnO2/WTe2) Exhibiting Stable Resistive Switching
Abstract
:1. Introduction
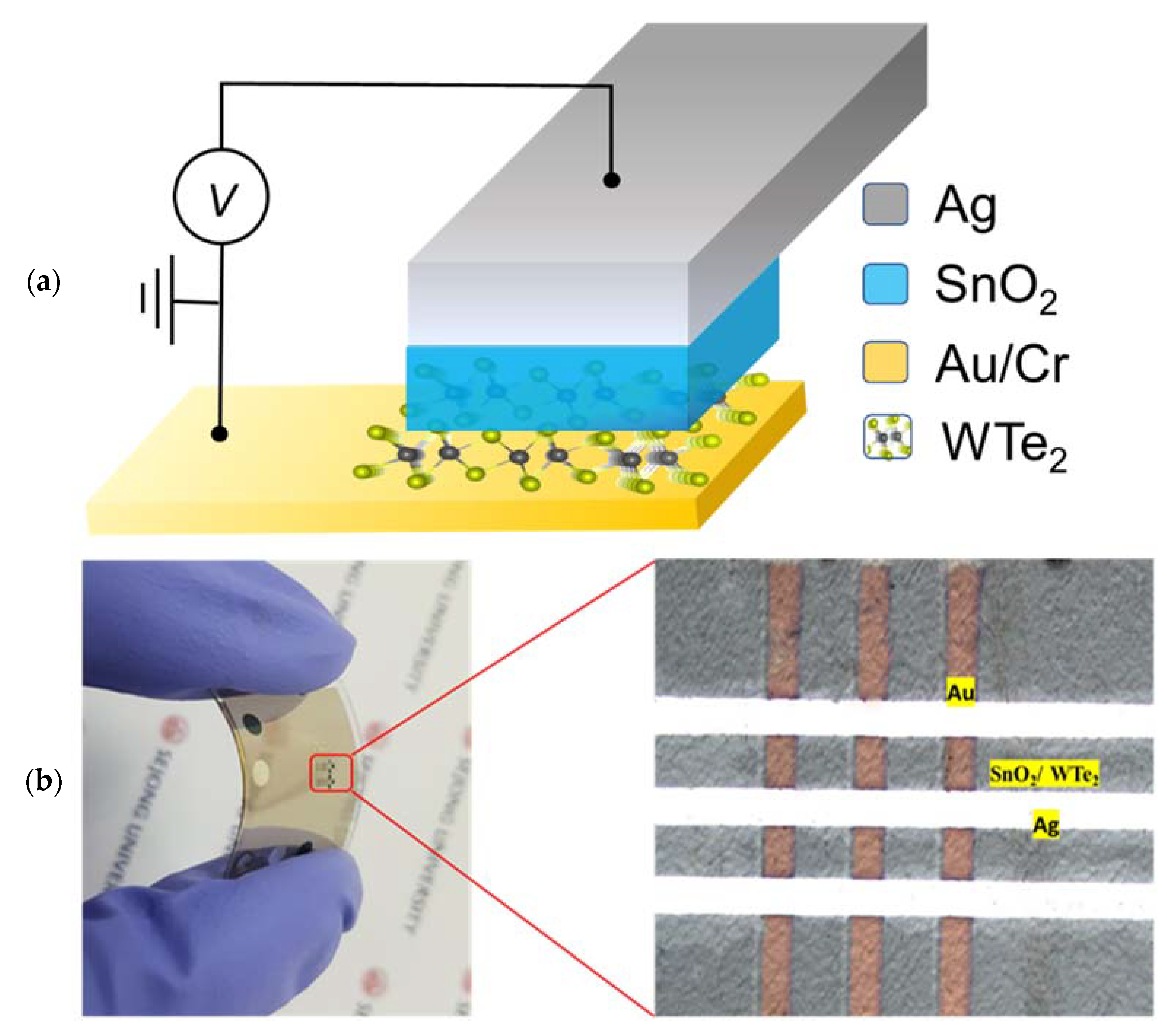
2. Experimental Details
Device Fabrication and Characterizations
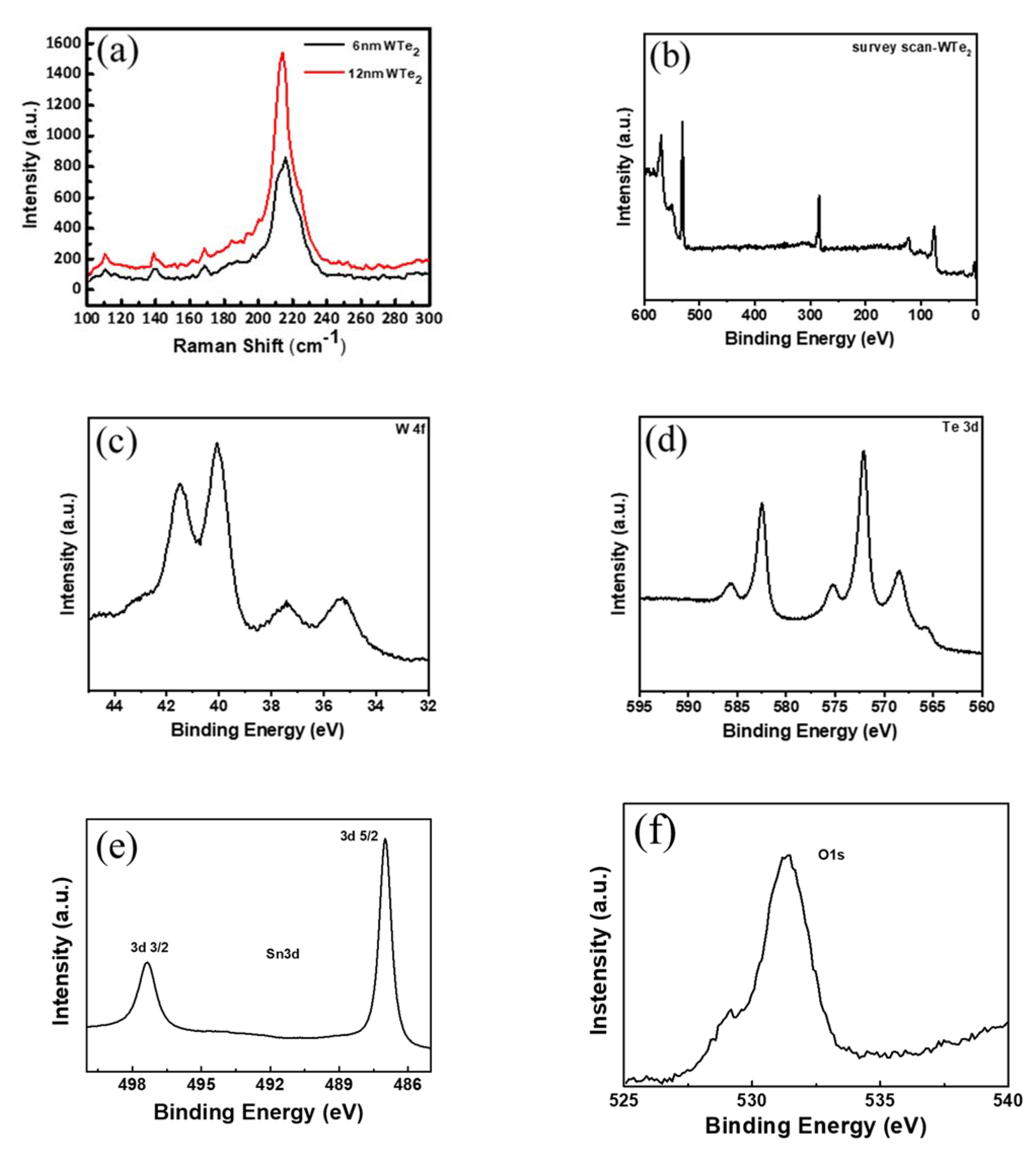
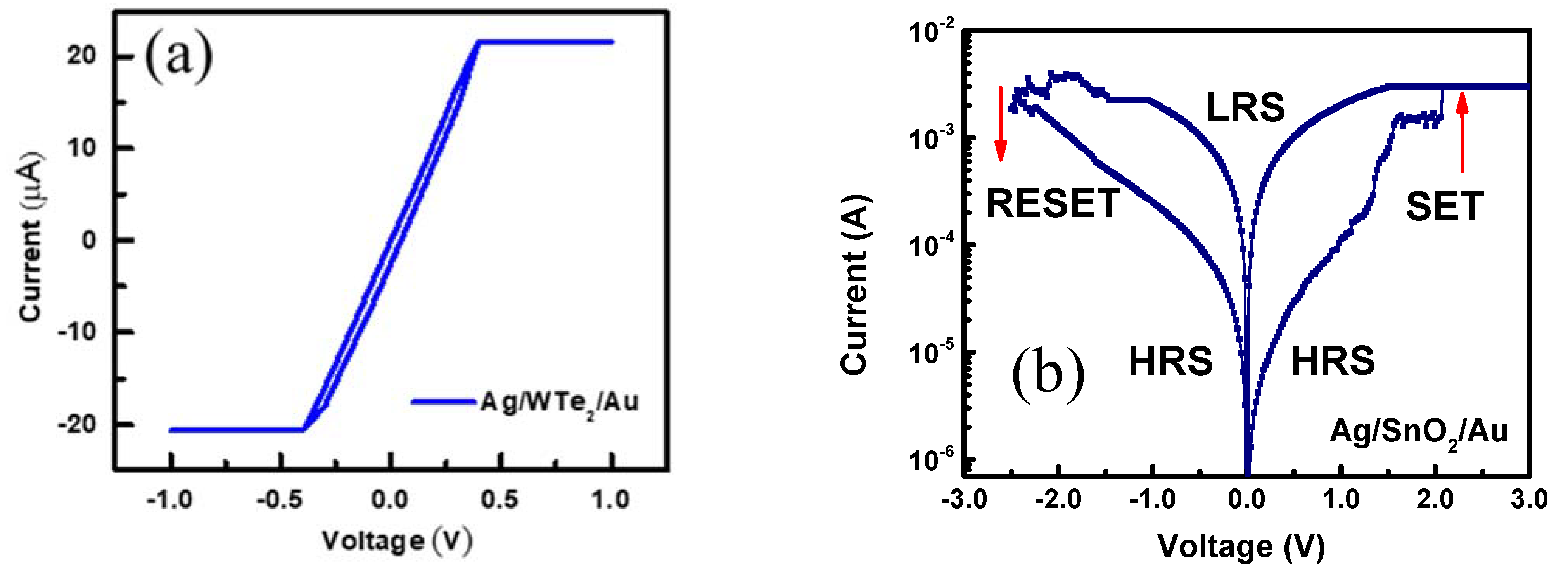
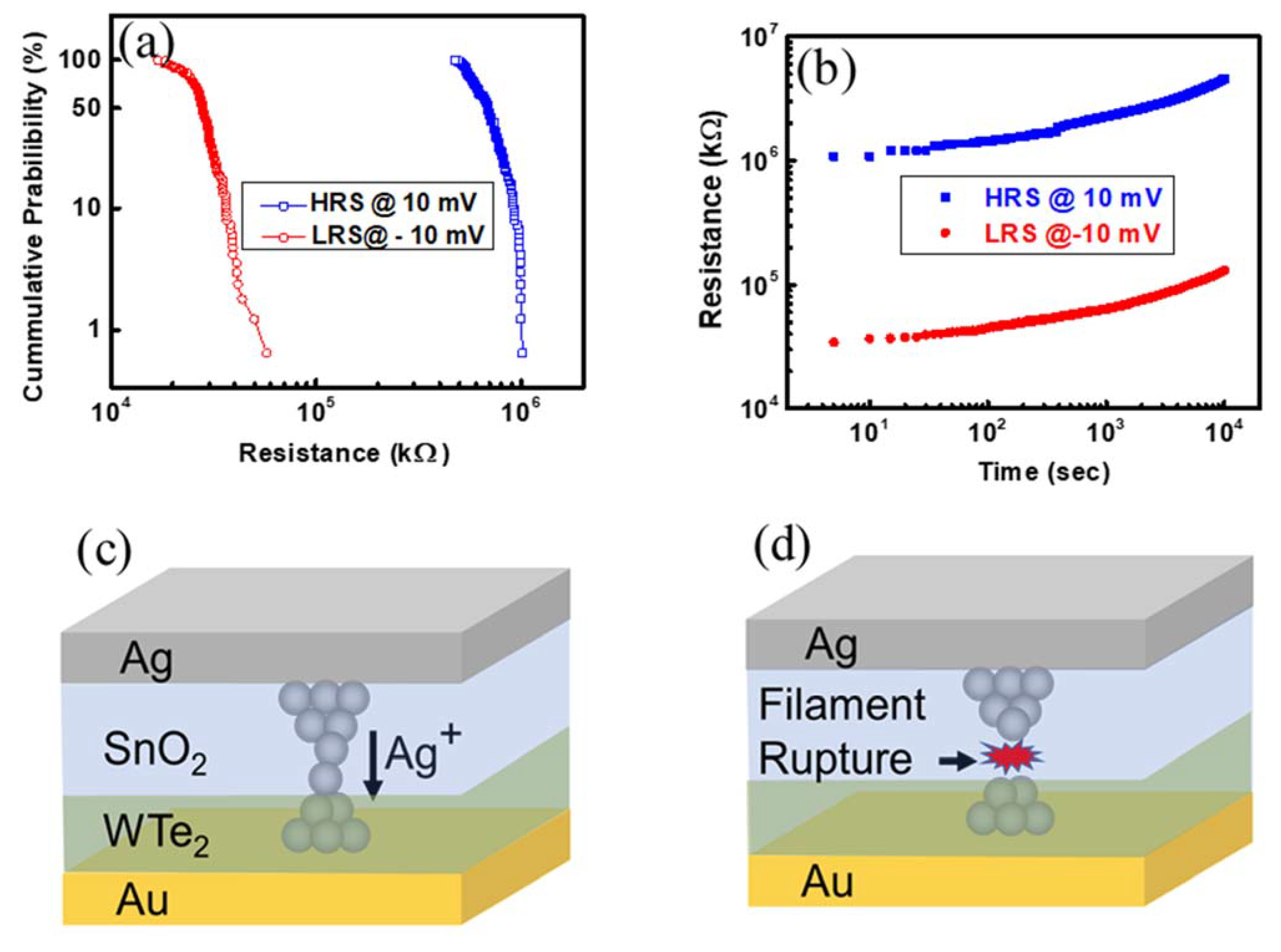
3. Results and Discussions
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nagareddy, V.K.; Barnes, M.D.; Zipoli, F.; Lai, K.T.; Alexeev, A.M.; Craciun, M.F.; Wright, C.D. Multilevel ultrafast flexible nanoscale nonvolatile hybrid graphene oxide–titanium oxide memories. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 3010–3021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Mauri, A.; Bortolossi, A.; Novielli, G.; Sacco, R. 3D finite element modeling and simulation of industrial semiconductor devices including impact ionization. J. Math. Ind. 2015, 5, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Waser, R.; Aono, M. Nanoionics-based resistive switching memories. Nanosci. Technol. Collect. Rev. Nat. J. 2010, 158–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, D.S.; Thomas, R.; Katiyar, R.; Scott, J.; Kohlstedt, H.; Petraru, A.; Hwang, C.S. Emerging memories: Resistive switching mechanisms and current status. Rep. Prog. Phys. 2012, 75, 076502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgeer, G.; Abbas, H.; Kim, D.Y.; Eom, J.; Choi, C. Synaptic Characteristics of an Ultrathin Hexagonal Boron Nitride ( h-BN) Diffusive Memristor. Phys. Status Solidi (RRL)-Rapid Res. Lett. 2021, 15, 2000473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaba, S.; Sheridan, P.; Zhou, J.; Choi, S.; Lu, W. Stochastic memristive devices for computing and neuromorphic applications. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 5872–5878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yang, J.J.; Strukov, D.B.; Stewart, D.R. Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, F.; Gao, S.; Chen, C.; Song, C.; Zeng, F. Recent progress in resistive random access memories: Materials, switching mechanisms, and performance. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2014, 83, 1–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wright, C.D.; Liu, Y.; Kohary, K.I.; Aziz, M.M.; Hicken, R.J. Arithmetic and biologically-inspired computing using phase-change materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3408–3413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xu, J.; Xie, D.; Feng, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, X.; Peng, P.; Fu, D.; Qian, H.; Ren, T.-l.; Liu, L. Scaling-down characteristics of nanoscale diamond-like carbon based resistive switching memories. Carbon 2014, 75, 255–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santini, C.A.; Sebastian, A.; Marchiori, C.; Jonnalagadda, V.P.; Dellmann, L.; Koelmans, W.W.; Rossell, M.D.; Rossel, C.P.; Eleftheriou, E. Oxygenated amorphous carbon for resistive memory applications. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 8600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, H.Y.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, J.W.; Hwang, J.O.; Kim, J.-E.; Lee, J.Y.; Yoon, T.H.; Cho, B.J.; Kim, S.O.; Ruoff, R.S. Graphene oxide thin films for flexible nonvolatile memory applications. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4381–4386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuge, F.; Hu, B.; He, C.; Zhou, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, R.-W. Mechanism of nonvolatile resistive switching in graphene oxide thin films. Carbon 2011, 49, 3796–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ki Hong, S.; Eun Kim, J.; Kim, S.O.; Jin Cho, B. Analysis on switching mechanism of graphene oxide resistive memory device. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 044506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hong, S.K.; Kim, J.E.; Kim, S.O.; Choi, S.-Y.; Cho, B.J. Flexible resistive switching memory device based on graphene oxide. IEEE Electron Device Lett. 2010, 31, 1005–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, H.; Abbas, Y.; Hassan, G.; Sokolov, A.S.; Jeon, Y.-R.; Ku, B.; Kang, C.J.; Choi, C. The coexistence of threshold and memory switching characteristics of ALD HfO2 memristor synaptic arrays for energy-efficient neuromorphic computing. Nanoscale 2020, 12, 14120–14134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, K.; Tay, R.Y.; Nguyen, V.C.; Wang, J.; Cai, G.; Chen, T.; Teo, E.H.T.; Lee, P.S. Hexagonal Boron Nitride Thin Film for Flexible Resistive Memory Applications. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2016, 26, 2176–2184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgeer, G.; Afzal, A.M.; Nazir, G.; Sarwar, N. p-GeSe/n-ReS2 Heterojunction Rectifier Exhibiting A Fast Photoresponse with Ultra-High Frequency-Switching Applications. Adv. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 8, 2100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usman, M.; Muhammad, Z.; Dastgeer, G.; Zawadzka, N.; Niu, Y.; Imran, M.; Molas, M.R.; Rui, H. Extended anisotropic phonon dispersion and optical properties of two-dimensional ternary SnSSe. Inorg. Chem. Front. 2021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgeer, G.; Khan, M.F.; Cha, J.; Afzal, A.M.; Min, K.H.; Ko, B.M.; Liu, H.; Hong, S.; Eom, J. Black Phosphorus-IGZO van der Waals Diode with Low-Resistivity Metal Contacts. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 10959–10966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgeer, G.; Khan, M.F.; Nazir, G.; Afzal, A.M.; Aftab, S.; Naqvi, B.A.; Cha, J.; Min, K.-A.; Jamil, Y.; Jung, J.; et al. Temperature-Dependent and Gate-Tunable Rectification in a Black Phosphorus/WS2 van der Waals Heterojunction Diode. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 13150–13157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dastgeer, G.; Shehzad, M.A.; Eom, J. Distinct Detection of Thermally Induced Spin Voltage in Pt/WS2/Ni81Fe19 by the Inverse Spin Hall Effect. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2019, 11, 48533–48539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Zheng, W.; Zhu, Y.; Jin, M.; Lin, Z.; Zhu, R.; Huang, F. Raman Tensor of Layered Td-WTe2. J. Phys. Chem. C 2020, 124, 16596–16603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.C.; Gao, J.; Wang, L. Raman fingerprint for semi-metal WTe2 evolving from bulk to monolayer. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, A.; Li, H.; Huang, R.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Wang, L.; Chen, F.; Ren, W.; Lu, S.; et al. Observation of band bending in WTe2 after surface oxidation. Surf. Sci. 2022, 716, 121956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-H.; Silva, E.C.; Calderin, L.; Nguyen, M.A.T.; Hollander, M.J.; Bersch, B.; Mallouk, T.E.; Robinson, J.A. Tungsten Ditelluride: A layered semimetal. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bäumer, C.; Dittmann, R. 20-Redox-based memristive metal-oxide devices. In Metal Oxide-Based Thin Film Structures; Pryds, N., Esposito, V., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 489–522. [Google Scholar]
- Carlos, E.; Branquinho, R.; Martins, R.; Kiazadeh, A.; Fortunato, E. Recent Progress in Solution-Based Metal Oxide Resistive Switching Devices. Adv. Mater. 2021, 33, 2004328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulloni, V.; Lorenzelli, L.; Margesin, B.; Barbato, M.; Meneghesso, G. Temperature as an accelerating factor for lifetime estimation of RF-MEMS switches. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 160, 63–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, D.J.J.; Dananjaya, P.A.; Hong, X.L.; Shum, D.P.; Lew, W.S. Conduction Mechanisms on High Retention Annealed MgO-based Resistive Switching Memory Devices. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 14774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, M.; Ziegler, M.; Kolberg, L.; Soni, R.; Dirkmann, S.; Mussenbrock, T.; Kohlstedt, H. A double barrier memristive device. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ali, A.; Abbas, Y.; Abbas, H.; Jeon, Y.-R.; Hussain, S.; Naqvi, B.A.; Choi, C.; Jung, J. Dependence of InGaZnO and SnO2 thin film stacking sequence for the resistive switching characteristics of conductive bridge memory devices. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2020, 525, 146390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dastgeer, G.; Afzal, A.M.; Aziz, J.; Hussain, S.; Jaffery, S.H.A.; Kim, D.-k.; Imran, M.; Assiri, M.A. Flexible Memory Device Composed of Metal-Oxide and Two-Dimensional Material (SnO2/WTe2) Exhibiting Stable Resistive Switching. Materials 2021, 14, 7535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247535
Dastgeer G, Afzal AM, Aziz J, Hussain S, Jaffery SHA, Kim D-k, Imran M, Assiri MA. Flexible Memory Device Composed of Metal-Oxide and Two-Dimensional Material (SnO2/WTe2) Exhibiting Stable Resistive Switching. Materials. 2021; 14(24):7535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247535
Chicago/Turabian StyleDastgeer, Ghulam, Amir Muhammad Afzal, Jamal Aziz, Sajjad Hussain, Syed Hassan Abbas Jaffery, Deok-kee Kim, Muhammad Imran, and Mohammed Ali Assiri. 2021. "Flexible Memory Device Composed of Metal-Oxide and Two-Dimensional Material (SnO2/WTe2) Exhibiting Stable Resistive Switching" Materials 14, no. 24: 7535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247535
APA StyleDastgeer, G., Afzal, A. M., Aziz, J., Hussain, S., Jaffery, S. H. A., Kim, D.-k., Imran, M., & Assiri, M. A. (2021). Flexible Memory Device Composed of Metal-Oxide and Two-Dimensional Material (SnO2/WTe2) Exhibiting Stable Resistive Switching. Materials, 14(24), 7535. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14247535







