Lean Wrought Magnesium Alloys
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Terms and Definitions
3. Basic Aspects of Alloy Development
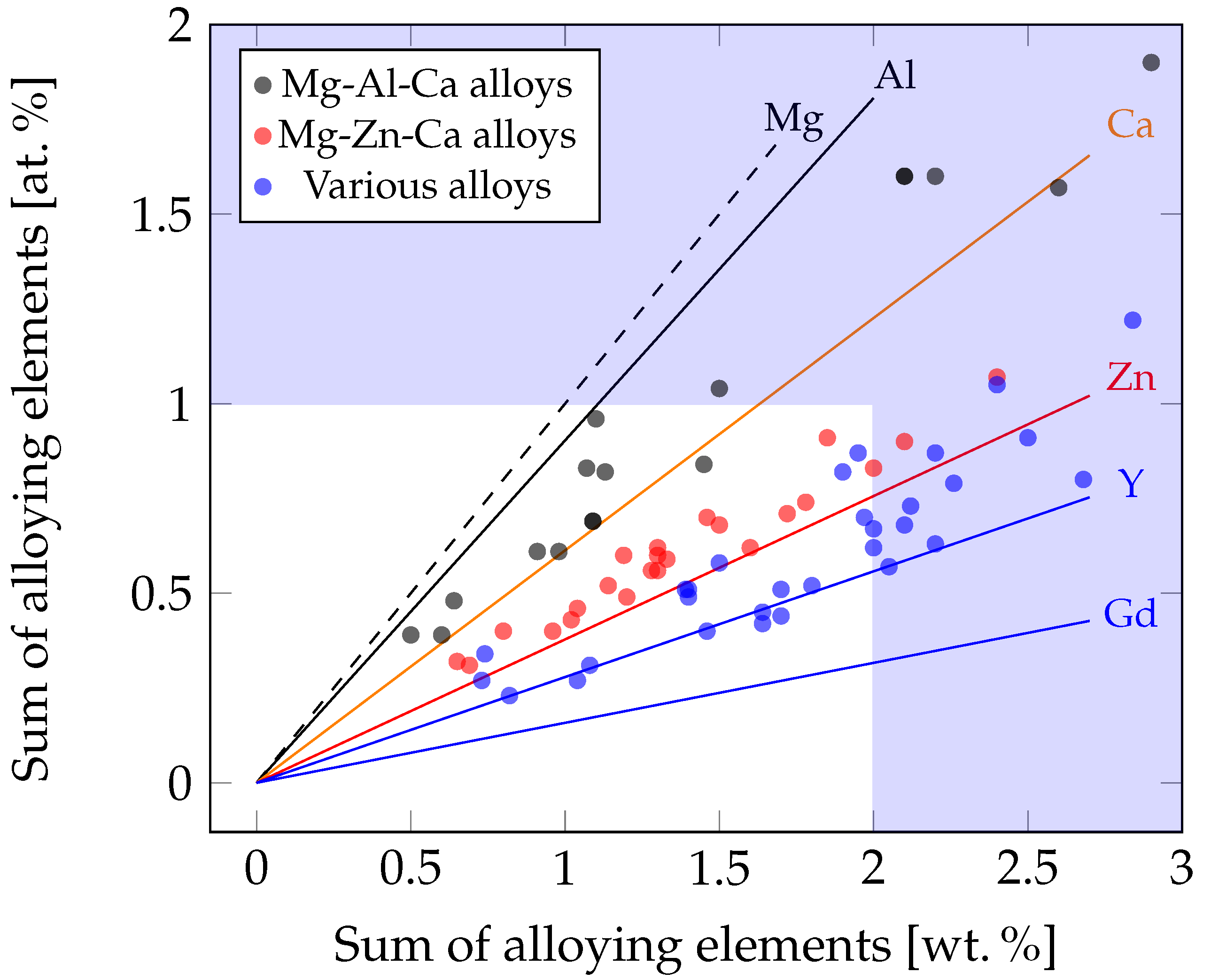
4. Mg Alloys with a Low Alloying Content
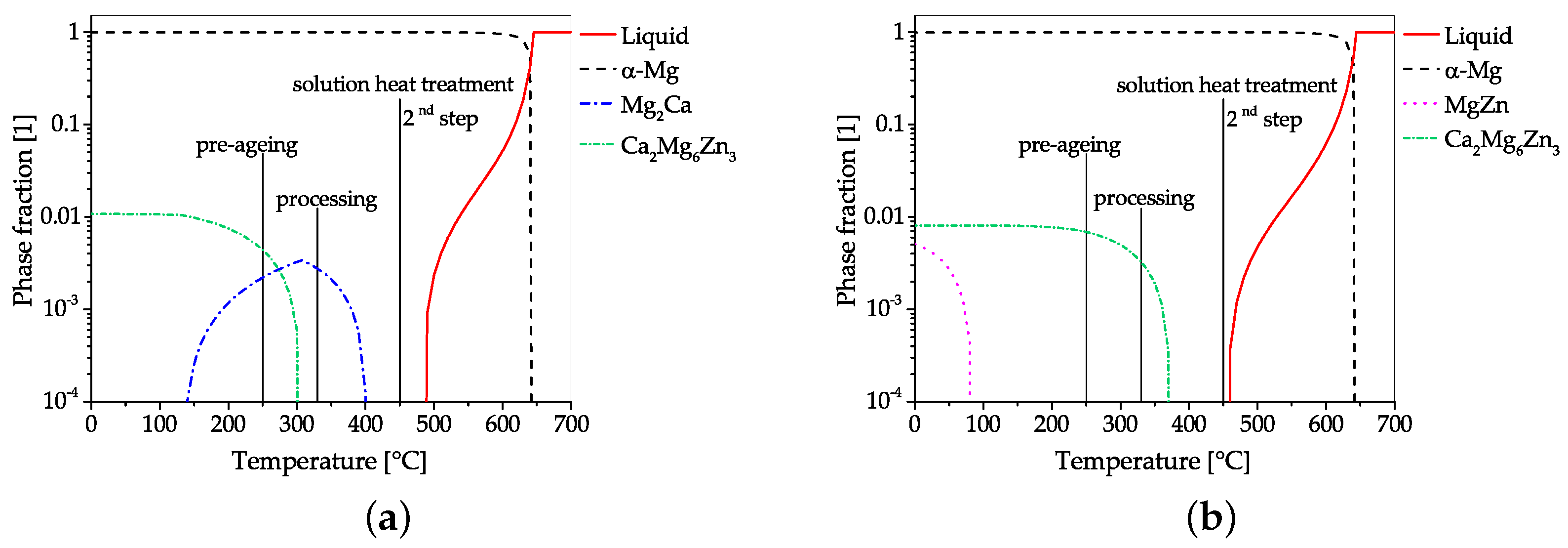
4.1. Alloys Containing Aluminum and Calcium
4.2. Alloys Containing Zinc and Calcium
4.3. Alloys Containing Various Alloying Elements
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CRSS | critical resolved shear stress | SPD | severe plastic deformation |
| ECAP | equal channel angular pressing | UCS | ultimate compressive strength |
| G.P.- zone | Guinier-Preston zone | UTS | ultimate tensile strength |
| HPT | high pressure torsion | YS | tensile yield strength |
| HSLA | High Strength Low Alloyed | YSc | compressive yield strength |
| I.E.-value | Erichsen Index | ||
| IMP | intermetallic particle/phase | elongation to failure | |
| LPSO | long period stacking order | d | grain diameter |
| MAF | multi axial forging | k | Hall Petch slope |
| MM | mischmetal | frictional stress | |
| RE/REE | rare earth elements | at.% | atomic percent |
| RT | room temperature | wt.% | weight percent |
Appendix A. Additional Information
Appendix A.1. Sources for Literature Research
Appendix A.2. CALPHAD Calculations
Appendix B. Alloy Overview
| Alloy | Source | ∑ Elements | Mg | Al | Zn | Ca | Mn | Si | ∑ REE | Sn | Zr | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-Ca | Mg-0.1Al-0.5Ca | [26,48] | 0.60 (0.39) | Bal | 0.10 (0.09) | 0.50 (0.30) | ||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.2Ca | [26,48] | 0.50 (0.39) | Bal | 0.30 (0.27) | 0.20 (0.12) | |||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.2Ca-0.5Mn | [9,40] | 0.98 (0.61) | Bal | 0.30 (0.27) | 0.21 (0.13) | 0.47 (0.21) | ||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca | [70] | 0.64 (0.48) | Bal | 0.32 (0.29) | 0.32 (0.19) | |||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.2Mn | [70] | 0.91 (0.61) | Bal | 0.33 (0.30) | 0.34 (0.20) | 0.24 (0.11) | ||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | [70,71] | 1.09 (0.69) | Bal | 0.34 (0.31) | 0.32 (0.19) | 0.43 (0.19) | ||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.8Mn | [70] | 1.45 (0.84) | Bal | 0.30 (0.27) | 0.31 (0.19) | 0.84 (0.37) | ||||||
| Mg-0.6Al-0.3Ca-0.3Mn | [23,72] | 1.13 (0.82) | Bal | 0.60 (0.54) | 0.28 (0.17) | 0.25 (0.11) | ||||||
| Mg-0.6Al-0.5Ca | [10] | 1.07 (0.83) | Bal | 0.61 (0.55) | 0.46 (0.28) | |||||||
| Mg-0.7Al-0.3Ca-0.5Mn | [73] | 1.50 (1.04) | Bal | 0.68 (0.62) | 0.32 (0.20) | 0.50 (0.22) | ||||||
| Mg-1.0Al-0.1Ca | [24] | 1.10 (0.96) | Bal | 1.00 (0.90) | 0.10 (0.06) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Al-1.0Zn-0.1Ca-0.5Mn | [58] | 2.60 (1.57) | Bal | 1.00 (0.91) | 1.00 (0.38) | 0.10 (0.06) | 0.50 (0.22) | |||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.3Zn-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | [75] | 2.20 (1.60) | Bal | 1.20 (1.10) | 0.30 (0.10) | 0.30 (0.20) | 0.40 (0.20) | |||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.5Ca-0.4Mn | [74] | 2.10 (1.60) | Bal | 1.20 (1.10) | 0.50 (0.30) | 0.40 (0.20) | ||||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.8Zn-0.5Ca-0.4Mn | [74] | 2.90 (1.90) | Bal | 1.20 (1.10) | 0.80 (0.30) | 0.50 (0.30) | 0.40 (0.20) | |||||
| Mg-1.3Al-0.3Ca-0.5Mn | [71] | 2.10 (1.60) | Bal | 1.31 (1.19) | 0.33 (0.20) | 0.46 (0.21) | ||||||
| Mg-2.7Al-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | [71] | 3.51 (2.88) | Bal | 2.73 (2.48) | 0.34 (0.20) | 0.44 (0.20) | ||||||
| Mg-Zn-Ca | Mg-0.2Zn-0.3Ca-0.1Mn | [84,85] | 0.65 (0.32) | Bal | 0.21 (0.08) | 0.30 (0.18) | 0.14 (0.06) | |||||
| Mg-0.3Zn-0.5Ca | [77] | 0.80 (0.40) | Bal | 0.30 (0.10) | 0.50 (0.30) | |||||||
| Mg-0.8Ca-0.37Zr | [50] | 1.19 (0.60) | Bal | 0.82 (0.50) | 0.37 (0.10) | |||||||
| Mg-0.8Ca-0.37Zr-0.3Zn | [50] | 1.46 (0.70) | Bal | 0.27 (0.10) | 0.82 (0.50) | 0.37 (0.10) | ||||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.1Ca-0.1Mn | [28] | 0.69 (0.31) | Bal | 0.02 (0.02) | 0.48 (0.18) | 0.14 (0.09) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.02 (0.02) | ||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ca-0.3Mn | [84] | 1.04 (0.46) | Bal | 0.53 (0.20) | 0.24 (0.15) | 0.27 (0.12) | ||||||
| Mg-0.6Zn-0.6Ca-0.1Zr | [31,32] | 1.30 (0.62) | Bal | 0.60 (0.22) | 0.60 (0.37) | 0.10 (0.03) | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.4Ca-0.1Mn | [84] | 1.14 (0.52) | Bal | 0.71 (0.27) | 0.36 (0.22) | 0.07 (0.03) | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.2Ca | [59] | 1.02 (0.43) | Bal | 0.80 (0.30) | 0.20 (0.12) | 0.02 (0.01) | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.2Ca | [20,78,79,80] | 0.96 (0.40) | Bal | 0.80 (0.30) | 0.16 (0.10) | |||||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.5Ca | [77] | 1.30 (0.60) | Bal | 0.80 (0.30) | 0.50 (0.30) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.2Ca | [41,60] | 1.20 (0.49) | Bal | 1.00 (0.37) | 0.20 (0.12) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.3Ca | [19] | 1.30 (0.56) | Bal | 1.00 (0.37) | 0.30 (0.18) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.3Ca | [28] | 1.33 (0.59) | Bal | 0.02 (0.02) | 0.96 (0.36) | 0.29 (0.18) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.03 (0.03) | ||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.3Ca | [86] | 1.28 (0.56) | Bal | 0.96 (0.36) | 0.32 (0.20) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.5Ca | [42,60] | 1.50 (0.68) | Bal | 1.00 (0.37) | 0.50 (0.31) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.9Ca | [81] | 1.85 (0.91) | Bal | 0.95 (0.36) | 0.90 (0.55) | |||||||
| Mg-1.2Zn-0.4Ca-0.2Zr | [82] | 1.78 (0.74) | Bal | 1.21 (0.45) | 0.39 (0.24) | 0.18 (0.05) | ||||||
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr-0.4Ca | [83] | 2.00 (0.83) | Bal | 1.40 (0.53) | 0.40 (0.25) | 0.10 (0.02) | 0.10 (0.03) | |||||
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr-0.8Ca | [83] | 2.40 (1.07) | Bal | 1.40 (0.53) | 0.80 (0.49) | 0.10 (0.02) | 0.10 (0.03) | |||||
| Mg-1.5Zn-0.1Ca | [58] | 1.60 (0.62) | Bal | 1.50 (0.56) | 0.10 (0.06) | |||||||
| Mg-1.5Zn-0.2Ca | [86] | 1.72 (0.71) | Bal | 1.48 (0.56) | 0.24 (0.15) | |||||||
| Mg-1.6Zn-0.5Ca | [77] | 2.10 (0.90) | Bal | 1.60 (0.60) | 0.50 (0.30) | |||||||
| Mg-2.6Zn-0.5Ca | [77] | 3.10 (1.30) | Bal | 2.60 (1.00) | 0.50 (0.30) | |||||||
| Various | Mg-1.0Mn-1.0Nd | [98,99] | 2.00 (0.62) | Bal | 1.00 (0.45) | 1.00 (0.17) | ||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.1Er | [97] | 1.90 (0.82) | Bal | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.10 (0.01) | |||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.1Er-0.1Al | [97] | 1.95 (0.87) | Bal | 0.05 (0.05) | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.10 (0.01) | ||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.4Er | [97] | 2.20 (0.87) | Bal | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.40 (0.06) | |||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.4Er-0.2Al | [97] | 2.40 (1.05) | Bal | 0.20 (0.18) | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.40 (0.06) | ||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.7Er | [97] | 2.50 (0.91) | Bal | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.70 (0.10) | |||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.7Er-0.3Al | [97] | 2.84 (1.22) | Bal | 0.34 (0.31) | 1.80 (0.81) | 0.70 (0.10) | ||||||
| Mg-0.3Sn-0.7Y | [101,103,104] | 1.04 (0.27) | Bal | 0.71 (0.20) | 0.33 (0.07) | |||||||
| Mg-0.4Sn-0.7Y-0.6Zn | [104] | 1.70 (0.51) | Bal | 0.64 (0.24) | 0.65 (0.18) | 0.41 (0.09) | ||||||
| Mg-0.5Sn-0.3Mn | [102] | 0.82 (0.23) | Bal | 0.27 (0.12) | 0.55 (0.11) | |||||||
| Mg-0.5Sn-0.3Mn-0.3Y | [102] | 1.08 (0.31) | Bal | 0.27 (0.12) | 0.33 (0.09) | 0.48 (0.10) | ||||||
| Mg-1.1Sn-0.6Zn-0.5Ca | [100] | 2.12 (0.73) | Bal | 0.55 (0.21) | 0.47 (0.29) | 1.10 (0.23) | ||||||
| Mg-1.2Sn-0.5Zn | [100] | 1.64 (0.42) | Bal | 0.48 (0.18) | 1.16 (0.24) | |||||||
| Mg-1.3Sn-0.7Ca | [100] | 1.97 (0.70) | Bal | 0.69 (0.43) | 1.28 (0.27) | |||||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ca | [88] | 0.74 (0.34) | Bal | 0.47 (0.18) | 0.23 (0.14) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | |||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ge | [87,88] | 0.73 (0.27) | Bal | 0.49 (0.18) | 0.03 (0.01) | 0.01 (0.01) | 0.20 (0.07) | |||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-2.2Y | [95] | 2.68 (0.80) | Bal | 0.53 (0.20) | 2.15 (0.60) | |||||||
| Mg-0.6Zn-0.3Zr-0.6Nd | [89] | 1.46 (0.40) | Bal | 0.61 (0.23) | 0.58 (0.10) | 0.27 (0.07) | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.2Zr-0.7Gd | [89] | 1.70 (0.44) | Bal | 0.73 (0.27) | 0.73 (0.11) | 0.24 (0.06) | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.2Zr-0.8Ce | [89] | 1.64 (0.45) | Bal | 0.68 (0.26) | 0.78 (0.14) | 0.18 (0.05) | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.3Zr-0.9MM | [89] | 2.05 (0.57) | Bal | 0.84 (0.32) | 0.88 (0.16) | 0.33 (0.09) | ||||||
| Mg-0.9Zn-0.2Zr-0.7La | [89] | 1.80 (0.52) | Bal | 0.89 (0.34) | 0.69 (0.12) | 0.22 (0.06) | ||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.4Zr | [94] | 1.40 (0.49) | Bal | 1.00 (0.38) | 0.40 (0.11) | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.4Zr-0.8MM | [94] | 2.20 (0.63) | Bal | 1.00 (0.38) | 0.80 (0.14) | 0.40 (0.11) | ||||||
| Mg-1.2Zn-0.2Zr | [82] | 1.39 (0.51) | Bal | 1.22 (0.46) | 0.17 (0.05) | |||||||
| Mg-1.3Zn-0.1Ce | [92] | 1.40 (0.51) | Bal | 1.30 (0.49) | 0.10 (0.02) | |||||||
| Mg-1.3Zn-0.2Ce-0.5Zr | [92] | 2.00 (0.67) | Bal | 1.30 (0.49) | 0.20 (0.04) | 0.50 (0.14) | ||||||
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr | [83] | 1.50 (0.58) | Bal | 1.40 (0.53) | 0.10 (0.02) | |||||||
| Mg-1.6Zn-0.5Gd | [43,90,91] | 2.10 (0.68) | Bal | 1.58 (0.60) | 0.52 (0.08) | |||||||
| Mg-1.8Zn-0.1Nd-0.1Ce-0.05La-0.2Y | [32] | 2.26 (0.79) | Bal | 1.81 (0.68) | 0.45 (0.11) |
Appendix C. Mechanical Properties
| Designation | Explanation |
|---|---|
| F | as-fabricated |
| O | annealed, recrystallized |
| T4 | solution heat treated and naturally aged |
| T5 | artificially aged only |
| T6 | solution heat treated and artificially aged |
| T8 | solution heat treated, cold worked and artificially aged |
| Alloy | k [MPa μm2] | [MPa] | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-0.3Al-0.2Ca-0.5Mn | 208 | 143 | [40] |
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.2Ca * | 72 | 121 | [41] |
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.3Ca | 241 | 47 | [28] |
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.5Ca * | 236 | 37 | [42] |
| Mg-1.6Zn-0.5Gd * | 411 | 45 | [43] |
| Alloy | Temper | YS [MPa] | UTS [MPa] | [%] | YSc [MPa] | UCS [MPa] | Source | Process Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mg-Al-Ca | Mg-0.3Al-0.2Ca-0.5Mn | as-extr. | 170 | 15.5 | [9] | cast, hom. at 500 C for 24 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 500 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | ||||
| T5 | 207 | 12.5 | [9] | as above, aged at 200 C for 7 h | ||||||
| as-extr. | 206 | 29 | [40] | cast, extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 350 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | ||||||
| as-extr. | 177 | [40] | cast, extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 500 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | |||||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.2Mn | as-extr. | 136 ± 2 | 203 ± 2 | 29 ± 2 | [70] | cast, hom. at 450 C for 1 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (indirect w/o lubricant, 1:20) at 400 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | ||||
| T6 | 188 | 247 | 27 | [70] | as above, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q., aged at 200 C | |||||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | as-extr. | 166 ± 1 | 220 ± 1 | 24 | [70] | cast, hom. at 450 C for 1 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (indirect w/o lubricant, 1:20) at 400 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | ||||
| T6 | 220 ± 2 | 264 | 22 ± 2 | [70] | as above, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q., aged at 200 C | |||||
| T4/s.h.t. | 159 ± 3 | 228 ± 1 | 29 ± 1 | 119 ± 5 | 405 ± 4 | [71] | cast, hom. at 500 C for 1 h, extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 275 C with a die-exit speed of 24 m min, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q. | |||
| T5 | 230 ± 5 | 262 ± 3 | 26 ± 1 | 165 ± 2 | 434 ± 1 | [71] | as above, aged at 200 C for 8 h | |||
| Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca-0.8Mn | as-extr. | 190 ± 3 | 229 ± 1 | 24 ± 3 | [70] | cast, hom. at 450 C for 1 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (indirect w/o lubricant, 1:20) at 400 C with a die-exit speed of 60 m min | ||||
| T6 | 199 ± 1 | 243 | 22 ± 3 | [70] | as above, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q., aged at 200 C | |||||
| Mg-0.6Al-0.3Ca-0.3Mn | as-extr. | 165 ± 7.8 | 232 ± 2.7 | 14 ± 0.3 | [23,72] | cast, hom. at 480 C for 6 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (direct, 1:25) at 450 C with a die-exit speed of range 0.75 to 3.75 m min | ||||
| T5 | 236 ± 2.1 | 265 ± 1.9 | 7 ± 11.0 | [23,72] | as above, aged at 200 C | |||||
| T4/s.h.t. | 156 ± 0.1 | 225 ± 5.3 | 9 ± 2.5 | [23,72] | extruded as above, s.h.t. (510 C for 10 min) and w.q. | |||||
| T6 | 253 ± 0.2 | 277 ± 4.2 | 8 ± 2.9 | [23,72] | as above, aged at 200 C | |||||
| Mg-0.6Al-0.5Ca | as-extr. | 182 | 250 | 19.4 | [10] | cast, hom. at 400 C for 24 h, extr. (direct, 1:28) at 400 C with speed of 2 mm s | ||||
| Mg-0.7Al-0.3Ca-0.5Mn | as-cast | 35 ± 1.0 | 106 ± 1.2 | 5.9 ± 0.1 | [73] | cast in steel mold | ||||
| as-extr. | 316 ± 6.0 | 327 ± 2.3 | 4.3 ± 0.5 | [73] | cast, hom. at 500 C for 4 h, extr. (1:12) at 350 C with ram-speed of 0.1 mm s | |||||
| T4 | 162 ± 1.2 | 247 ± 1.9 | 25.4 ± 0.8 | [73] | as above, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) | |||||
| T6 | 248 ± 1.5 | 288 ± 3.0 | 21.0 ± 0.4 | [73] | as above, aged at 200 C for 16 h | |||||
| Mg-1.0Al-0.1Ca | rolled, O, TD | 220 | ~20 | [24] | cast, hot rolled at 430 C to SI50% thickness, annealed at 450 C for 0.25 h, w.q. | |||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.3Zn-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | T4/s.h.t. | ~125 | ~220 | ~30 | [75] | cast, hom. at 300 C for 4 h followed by 500 C for 6 h and w.q., rolling at various conditions, s.h.t. at 450 C for 1 h | ||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.5Ca-0.4Mn | T4 | 145 | 229 | 28 | [74] | cast, hom. at 300 C for 4 h followed by 450 C for 6 h and w.q., rolling at 300 C (from range 10 to 5 mm, 4 passes), subsequent rolling at 100 C (from range 5 to 1 mm, 6 passes, reheated to 450 C for 5 min, solutionized at 450 C for 1 h | ||||
| T6 | 196 | 256 | 27 | [74] | as above, aged at 200 C for 1 h | |||||
| Mg-1.2Al-0.8Zn-0.5Ca-0.4Mn | T4 | 144 | 242 | 32 | [74] | cast, hom. at 300 C for 4 h followed by 450 C for 6 h and w.q., rolling at 300 C (from range 10 to 5 mm, 4 passes), subsequent rolling at 100 C (from range 5 to 1 mm, 6 passes, reheated to 450 C for 5 min, solutionized at 450 C for 1 h | ||||
| T6 | 204 | 263 | 27 | [74] | as above, aged at 200 C for 1 h | |||||
| Mg-1.3Al-0.3Ca-0.5Mn | T4/s.h.t. | 187 ± 1 | 267 ± 2 | 18 ± 1 | 138 ± 3 | 448 ± 6 | [71] | cast, hom. at 500 C for 1 h, extr. to round bars (indirect w/o lubricant, 1:20) at 275 C with a die-exit speed of 24 m min, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q. | ||
| T5 | 287 ± 2 | 306 ± 1 | 20 ± 2 | 194 ± 1 | 472 ± 3 | [71] | as above, aged at 200 C for 0.5 h | |||
| Mg-2.7Al-0.3Ca-0.4Mn | T4/s.h.t. | 188 ± 1 | 267 ± 2 | 18 ± 1 | 121 ± 5 | 398 ± 4 | [71] | cast, hom. at 500 C for 1 h, extr. to round bars (indirect w/o lubricant, 1:20) at 275 C with a die-exit speed of 24 m min, s.h.t. (500 C for 10 min) and w.q. | ||
| T5 | 240 ± 2 | 283 ± 1 | 18 ± 1 | 149 ± 1 | 427 ± 3 | [71] | as above, aged at 200 C for 0.5 h | |||
| Mg-Zn-Ca | Mg-0.2Zn-0.3Ca-0.1Mn | hom. | 36 | 134 | 7.3 | [85] | cast, cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h and 450 C for 12 h, w.q. | |||
| as-extr. | 307 | 20.6 | [85] | as above, extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 300 C with a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min | ||||||
| as-extr. | 164 | 30 | [85] | as above, extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 350 C with a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Ca-0.37Zr | rolled, O, RD | 133 | 196 | 14 | [50] |  | cast, hom. at 300 C for 12 h w.q., rolled at 450 C from range 5 to 1 mm thickness in 4 passes using cold rollers, reheating for 6 min between passes, annealed at 400 C for 0.5 h | |||
| rolled, O, TD | 126 | 191 | 9 | [50] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 130 | 189 | 10 | [50] | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Ca-0.37Zr-0.3Zn | rolled, O, RD | 134 | 205 | 29 | [50] |  | cast, hom. at 300 C for 12 h w.q., rolled at 450 C from range 5 to 1 mm thickness in 4 passes using cold rollers, reheating for 6 min between passes, annealed at 400 C for 0.5 h | |||
| rolled, O, TD | 104 | 198 | 34 | [50] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 110 | 200 | 32 | [50] | ||||||
| rolled, T6 | 166 | 220 | 26 | [50] | as above, aged in oil at 200 C for 1 h | |||||
| rolled, T8 | 201 | 226 | 20 | [50] | as above, deformed to 0.015 plastic strain, aged in oil at 200 C for 1 h | |||||
| Mg-0.6Zn-0.6Ca-0.1Zr | as-rolled, RD | 255 ± 2 | 276 ± 2 | 8 | [31,32] |  | Twin-rolled cast (5.3 mm), rolled at range 370 to 400 C in 7 passes, with intermediate heating for 0.25 h to a thickness of 1.8 mm, cooled at air | |||
| as-rolled, TD | 200 ± 2 | 265 ± 2 | 23 | [31,32] | ||||||
| as-rolled, 45 | 217 ± 3 | 255 ± 2 | 19 | [31,32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, RD | 174 ± 3 | 239 ± 3 | 25 | [31,32] |  | as above, annealed at 370 C for 0.5 h | ||||
| rolled, O, TD | 135 ± 2 | 226 ± 2 | 31 | [31,32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 152 ± 3 | 232 ± 2 | 27 | [31,32] | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.4Ca-0.1Mn | as-extr. | 108 | 220 | 37.0 | [84] | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h and 450 C for 12 h, w.q., extr. to round bars (indirect, 1:20) at 300 C with a die-exit speed of 6 m min | ||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.2Ca | rolled, O, RD | 92.5 ± 2.5 | 182.5 ± 0.5 | 24 ± 1 | [80] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 24 h, rolled (450 C) from range 5 to 1 mm in 8 passes, annealed at 400 C for 0.5 h | |||
| rolled, O, TD | 61 ± 1 | 186.5 ± 2 | 30.5 ± 0.5 | [80] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 68.5 ± 0.5 | 185 ± 2 | 32 ± 1 | [80] | ||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.2Ca | as-cast | 125 | 8 | [41] | cast, hom. at 430 C for 22 h and w.q. | |||||
| SPD | 225 | 16 | [41] | as above, preheated to pressing temp. for 0.3 h, ECAP (120, 6mm min) for 2 passes at each temp. 400, 350 and 300 C | ||||||
| SPD | 263.7 | [41] | ECAP as above, subseq. HPT (6GPa) for 0.5 revolutions at RT | |||||||
| SPD | 283.3 | [41] | ECAP as above, subseq. HPT (6GPa) for 1 revolution at RT | |||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.3Ca | as-extr. | 238 | 265 | 31 | 205 | [28] | cast, hom. at 350 C for 12 h and 450 C for 8 h, cooled with pressurized air, aged at 250 C for 0.5 h, heated to extr. temp. (300 C) and held for 0.5 h, indirectly extr. to round bars (1:25) using a RAM speed of 0.5 mm s, cooled with pressurized air | |||
| as-extr. | 184 | 240 | 32 | 162 | [28] | as above, heated to extr. temp. (325 C) and held for 0.5 h, indirectly extr. to round bars (1:25) using a RAM speed of 0.5 mm s, cooled with pressurized air | ||||
| as-extr. | 247 | 268 | 20 | 184 | [28] | as above, heated to extr. temp. (325 C) and held for 0.5 h, directly extr. to round bars (1:25) using a RAM speed of 0.5 mm s, cooled with pressurized air | ||||
| as-extr. | 140 | 226 | 25 | 119 | [28] | as above, heated to extr. temp. (400 C) and held for 0.5 h, directly extr. to round bars (1:25) using a RAM speed of 0.5 mm s, cooled with pressurized air | ||||
| as-extr. | 240 | 255 | 27 | 205 | 245 | [19] | as above, indirectly extr. to round bars (1:25) at 300 C using a RAM speed of 0.15 mm s | |||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.5Ca | as-cast | 55 ± 2 | 120 ± 5 | 5 ± 0.5 | [42] | cast in steel mold | ||||
| as-extr. | 297 ± 2 | 300 ± 5 | 8 ± 1 | [42] | cast, hom. at 400 C for 10 h, extr. (1:16) at 310 C, using an extr. speed of 4 mm s | |||||
| as-extr. | 197 ± 3 | 256 ± 5 | 17 ± 1.5 | [42] | as above, extr. (1:16) at 330 C, using an extr. speed of 4 mm s | |||||
| as-extr. | 120 ± 3 | 200 ± 5 | 40 ± 3 | [42] | as above, extr. (1:16) at 350 C, using an extr. speed of 4 mm s | |||||
| as-extr. | 105 ± 3 | 205 ± 5 | 44 ± 3 | [42] | as above, extr. (1:16) at 370 C, using an extr. speed of 4 mm s | |||||
| as-extr. | 99 ± 3 | 201 ± 4 | 36 ± 2 | [42] | as above, extr. (1:16) at 400 C, using an extr. speed of 4 mm s | |||||
| as-extr. | 105 | 210 | 44 | [60] | cast, extr. (1:16) at 350 C, using an extr. speed of 2 mm s | |||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.9Ca | rolled, T4 | 154.9 | 234.3 | 12.3 | [81] | cast, hom. at 440 C for 1 h and w.q., hot rolled with 5 passes at 300 C to a overall reduction of 50%, intermediate reheating between the passes at 300 C for 0.3 h, annealing at 440 C for 0.5 h and w.q. | ||||
| Mg-1.2Zn-0.4Ca-0.2Zr | rolled, O, RD | 229.6 ± 2.8 | 264.0 ± 2.2 | 24.7 ± 2.4 | [82] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 4 h w.q., machined, rolled at 300 C (5 passes, with intermediate annealing, total reduction 72%), subseq. annealed at 300 C for 0.5 h | |||
| rolled, O, 45 | 290.8 ± 2.7 | 247.3 ± 0.2 | 32.3 ± 1.5 | [82] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 171.3 ± 2.2 | 248.9 ± 2.5 | 27.5 ± 1.8 | [82] | ||||||
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr | extr., O | 200 ± 7 | 250 ± 5 | 15.3 ± 0.3 | 150 ± 6 | 441 ± 3 | [83] |  | cast, pre-heated at 340 C, extr. (direct) to round bars at 300 C, air cooled, annealed at 300 C for 0.5 h | |
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr-0.4Ca | extr., O | 171 ± 2 | 243 ± 1 | 14.6 ± 0.0 | 148 ± 1 | 432 ± 6 | [83] | |||
| Mg-1.4Zn-0.1MM-0.1Zr-0.8Ca | extr., O | 174 ± 1 | 243 ± 1 | 15 ± 1.1 | 149 ± 2 | 410 ± 4 | [83] | |||
| Various | Mg-1.8Mn-0.1Er | extr., O | 173 | 255 | 7 | [97] |  | cast, hom. at 450 C for 4 h air-cooled, machined, pre-heated to 450 C for 1 h, extr. to round bars (1:25) air-cooled, annealed at 390 C for 1 h | ||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.4Er | extr., O | 224 | 276 | [97] | ||||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.7Er | extr., O | 228 | 275 | 12.5 | [97] | |||||
| Mg-1.8Mn-0.7Er-0.3Al | extr., O | 19 | [97] | |||||||
| Mg-0.3Sn-0.7Y | as-extr., ED | 99.1 ± 1.0 | 264.2 ± 2.0 | 32.7 ± 0.2 | [101] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, extr. (1:51) at 400 C, using a RAM speed of 3 mm s to sheets | |||
| as-extr., 45 | 115.3 ± 0.5 | 226.8 ± 1.0 | 25.8 ± 0.3 | [101] | ||||||
| as-extr., TD | 124.9 ± 1.0 | 236.7 ± 1.0 | 24.7 ± 0.2 | [101] | ||||||
| as-extr., ED | 90.9 ± 0.8 | 191.9 ± 1.3 | 39.7 ± 0.3 | [103,104] | ||||||
| as-extr., 45 | 115.4 ± 1.1 | 182.5 ± 1.2 | 28.3 ± 0.3 | [103,104] | ||||||
| as-extr., TD | 119.6 ± 1.2 | 182.5 ± 1.2 | 28.3 ± 0.3 | [103,104] | ||||||
| rolled, T4, RD | 110.5 ± 1.3 | 199.5 ± 0.8 | 29.7 ± 0.3 | [103] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, hot rolled with a mat. temp. of 400 C and roll temp. of 160 C, mat. reheated for 0.3 h after each pass, rolled to a sheet thickness of 1 mm with reductions of 20%, subseq. annealed at 400 C for 1 h and w.q. | ||||
| rolled, T4, 45 | 109.9 ± 1.4 | 187.6 ± 0.7 | 34.7 ± 0.5 | [103] | ||||||
| rolled, T4, TD | 133.1 ± 0.9 | 184.5 ± 1.3 | 31.2 ± 0.1 | [103] | ||||||
| Mg-0.4Sn-0.7Y-0.6Zn | as-extr., ED | 188.4 ± 2.5 | 251.1 ± 1.4 | 33.1 ± 0.4 | [104] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, extr. (1:51) at 400 C, using a RAM speed of 3 mm s to sheets | |||
| as-extr., 45 | 130.3 ± 3.8 | 221.8 ± 1.9 | 47.2 ± 0.1 | [104] | ||||||
| as-extr., TD | 124.3 ± 2.0 | 231.4 ± 1.3 | 39.1 ± 0.2 | [104] | ||||||
| Mg-0.5Sn-0.3Mn | as-extr., ED | 130 | 239 | 10.4 | [102] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 10 h air-cooled, machined, extr. to sheets at 400 C with an extr. speed of 1.2 m min | |||
| as-extr., 45 | 137 | 251 | 10 | [102] | ||||||
| as-extr., TD | 157 | 266 | 8.5 | [102] | ||||||
| Mg-0.5Sn-0.3Mn-0.3Y | as-extr., ED | 141 | 288 | 30.3 | [102] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 10 h air-cooled, machined, extr. to sheets at 400 C with an extr. speed of 1.2 m min | |||
| as-extr., 45 | 170 | 286 | 28.1 | [102] | ||||||
| as-extr., TD | 188 | 302 | 28 | [102] | ||||||
| Mg-1.1Sn-0.6Zn-0.5Ca | as-extr., ED | 104.2 ± 1.8 | 311.9 ± 2.4 | 30.5 ± 1.4 | [100] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, extr. (1:32) at 400 C, using a RAM speed of 1 mm s to sheets with a thickness of 3 mm | |||
| as-extr., TD | 188.9 ± 2.5 | 295.6 ± 3.4 | 12.9 ± 0.4 | [100] | ||||||
| Mg-1.2Sn-0.5Zn | as-extr., ED | 129.4 ± 2.4 | 260.9 ± 2.7 | 17.6 ± 0.9 | [100] | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, extr. (1:32) at 400 C, using a RAM speed of 1 mm s to sheets with a thickness of 3 mm | ||||
| as-extr., TD | 153.1 ± 1.2 | 262.1 ± 1.9 | 14.3 ± 0.6 | [100] | ||||||
| Mg-1.3Sn-0.7Ca | as-extr., ED | 137.8 ± 3.2 | 264.8 ± 3.2 | 17.3 ± 1.1 | [100] | cast, hom. at 400 C for 12 h, extr. (1:32) at 400 C, using a RAM speed of 1 mm s to sheets with a thickness of 3 mm | ||||
| as-extr., TD | 209.3 ± 3.5 | 293.7 ± 3.2 | 10.3 ± 0.5 | [100] | ||||||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ca | as-extr. | 119 ± 2 | 224 ± 1 | 25 ± 2 | 93 ± 1 | 331 ± 3 | [88] | cast, hom. at 370 C for 24 h and quenched in warm water, preheated to 375 C for 1 h, indirectly extr. (1:25) at 375 C, using an extr. speed of 2.2 mm s to round bars | ||
| Mg-0.5Zn-0.2Ge | as-extr. | 171 ± 2 | 249 ± 2 | 10 ± 1 | 75 ± 1 | 367 ± 6 | [88] | cast, hom. at 320 C for 24 h and quenched in warm water, preheated to 375 C for 1 h, indirectly extr. (1:25) at 375 C, using an extr. speed of 2.2 mm s to round bars | ||
| Mg-0.6Zn-0.3Zr-0.6Nd | rolled, O, RD | 111 | 243 | 27.58 | [89] |  | cast, hom. at 450 C for 12 h and w.q., hot rolled at 400 C from range 8 to 2 mm at a reduction of range 15 to 20% per pass, intermediate reheating between the passes at 400 C for 10 min, subseq. w.q., annealing at 440 C for 1 h | |||
| rolled, O, 45 | 101 | 234 | 27.95 | [89] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 84 | 238 | 28.61 | [89] | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.2Zr-0.8Ce | rolled, O, RD | 131 | 234 | 16.86 | [89] | |||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 110 | 237 | 22.96 | [89] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 115 | 222 | 12.61 | [89] | ||||||
| Mg-0.7Zn-0.2Zr-0.7Gd | rolled, O, RD | 88 | 229 | 29.33 | [89] | |||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 78 | 227 | 29.93 | [89] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 66 | 233 | 32.19 | [89] | ||||||
| Mg-0.8Zn-0.3Zr-0.9MM | rolled, O, RD | 131 | 233 | 18.95 | [89] | |||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 108 | 243 | 25.27 | [89] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 99 | 247 | 24.86 | [89] | ||||||
| Mg-0.9Zn-0.2Zr-0.7La | rolled, O, RD | 123 | 241 | 22.75 | [89] | |||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 108 | 240 | 24.78 | [89] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 96 | 243 | 25.34 | [89] | ||||||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.4Zr | as-extr. | 237 | 271 | 24 | 165 | 436 | [93] | cast, hom. at 350 C for 15 h, extr. to round bars (indir., 1:30) at 300 C, using a speed of 1 m min | ||
| as-extr. | 196 | 248 | 19 | 96 | 370 | [93] | as above, using a speed of 5 m min | |||
| as-extr. | 188 | 245 | 21 | 101 | 366 | [93] | as above, using a speed of 10 m min | |||
| Mg-1.0Zn-0.4Zr-0.8MM | as-extr. | 296 | 299 | 18 | 184 | 434 | [93] | cast, hom. at 350 C for 15 h, extr. to round bars (indir., 1:30) at 300 C, using a speed of 1 m min | ||
| as-extr. | 221 | 260 | 21 | 156 | 381 | [93] | as above, using a speed of 5 m min | |||
| as-extr. | 201 | 251 | 19 | 142 | 369 | [93] | as above, using a speed of 10 m min | |||
| Mg-1.2Zn-0.2Zr | rolled, O, RD | 211.6 ± 2.3 | 247.4 ± 2.7 | 19.8 ± 1.6 | [82] |  | cast, hom. at 400 C for 4 h w.q., machined, rolled at 300 C (5 passes, with intermediate annealing, total reduction 72%), subseq. annealed at 300 C for 0.5 h | |||
| rolled, O, 45 | 204.3 ± 0.5 | 242.6 ± 1.6 | 25.9 ± 1.3 | [82] | ||||||
| rolled, O, TD | 203.1 ± 2.5 | 243.5 ± 3.4 | 21.2 ± 0.8 | [82] | ||||||
| Mg-1.3Zn-0.1Ce | as-extr. | 206 ± 1 | 261 ± 3 | 20.1 ± 0.4 | 124 ± 2 | 410 ± 7 | [92] | cast, extr. to round bars (indir., 1:30) at 300 C, using a speed of 1 m min | ||
| as-extr. | 176 ± 2 | 245 ± 2 | 11.7 ± 2.5 | 81 ± 1 | 361 ± 4 | [92] | as above, using a speed of 10 m min | |||
| as-extr. | 156 ± 2 | 226 ± 2 | 18.1 ± 1.3 | 70 ± 1 | 347 ± 1 | [92] | as above, using a speed of 20 m min | |||
| Mg-1.3Zn-0.2Ce-0.5Zr | as-extr. | 305 ± 3 | 313 ± 3 | 21.0 ± 4.0 | 173 ± 1 | 436 ± 15 | [92] | cast, extr. to round bars (indir., 1:30) at 300 C, using a speed of 1 m min | ||
| as-extr. | 204 ± 1 | 257 ± 1 | 20.3 ± 0.9 | 126 ± 4 | 384 ± 13 | [92] | as above, using a speed of 10 m min | |||
| as-extr. | 209 ± 2 | 259 ± 2 | 22.6 ± 0.5 | 124 ± 1 | 375 ± 3 | [92] | as above, using a speed of 20 m min | |||
| Mg-1.6Zn-0.5Gd | as-extr. | 117 | 213 | 30.1 | [90] | cast, hom. at 480 C for 12 h, indirectly extr. (1:20) at 300 C with a die-exit speed of 6 m min to round bars | ||||
| as-extr. | 283 | 295 | 10 | 154 | [43] | cast, hom. at 480 C for 12 h, indirectly extr. (1:20) at 400 C with a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min to round bars | ||||
| as-extr. | 161 | 233 | 24.7 | 111 | [43] | cast, hom. at 480 C for 12 h, indirectly extr. (1:20) at 350 C with a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min to round bars | ||||
| as-extr. | 254 | 284 | 27.9 | 190 | [43] | cast, hom. at 480 C for 12 h, MDIF at 300 C, w.q., indir. extr. (1:20, 350 C) at a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min to round bars | ||||
| as-extr. | 181 | 248 | 34.8 | 134 | [43] | MDIF as above, w.q., indirectly extr. (1:20) at 400 C with a die-exit speed of 1.2 m min to round bars | ||||
| Mg-1.8Zn-0.1Nd-0.1Ce | as-rolled, RD | 270 ± 2 | 288 ± 2 | 19 | [32] |  | Twin-rolled cast (5.3 mm), rolled at range 370 to 400 C in 7 passes, with intermediate heating for 0.25 h to a thickness of 1.8 mm, cooled at air | |||
| -0.05La-0.2Y | as-rolled, TD | 190 ± 5 | 266 ± 2 | 20 | [32] | |||||
| as-rolled, 45 | 197 ± 3 | 250 ± 2 | 26 | [32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, RD | 181 ± 4 | 244 ± 4 | 33 | [32] |  | as above, annealed at 350 C for 0.5 h | ||||
| rolled, O, TD | 106 ± 3 | 221 ± 4 | 35 | [32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 118 ± 4 | 215 ± 3 | 40 | [32] | ||||||
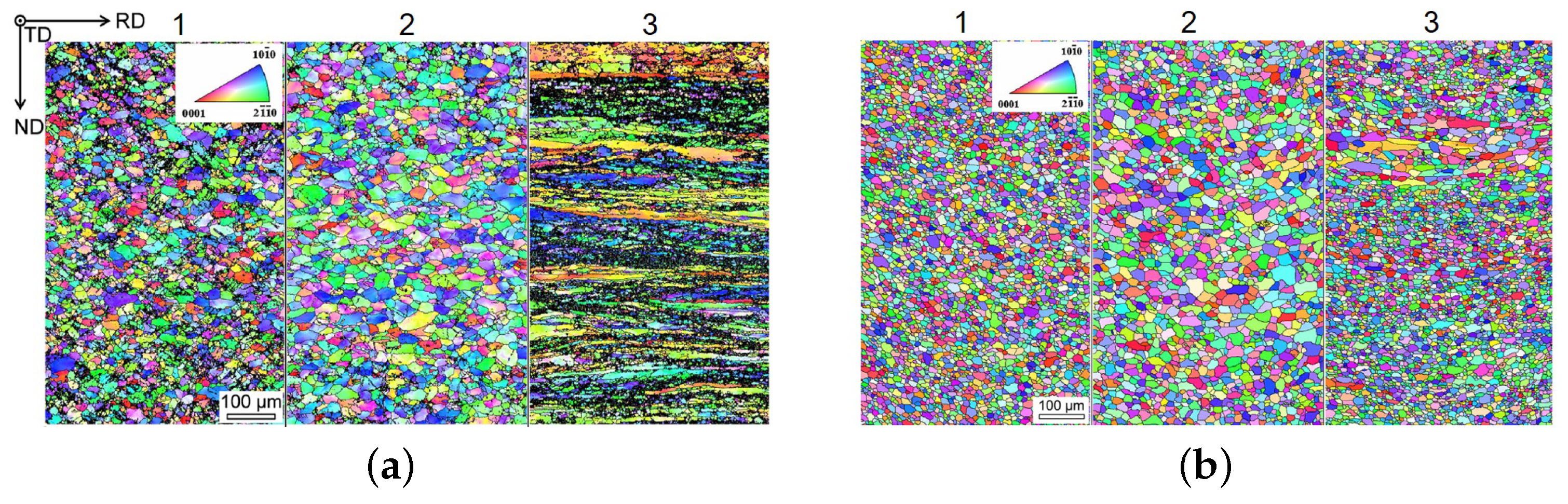
| as-rolled, RD | 298 ± 2 | 320 ± 4 | 16 | [32] |  | Twin-rolled cast (5.3 mm), rolled at range 370 to 400 C in 7 passes, with intermediate heating for 0.25 h to a thickness of 1.8 mm, cooled at air subseq. cold rolled (2 passes, 0.1 true strain) | ||||
| as-rolled, TD | 205 ± 3 | 286 ± 2 | 27 | [32] | ||||||
| as-rolled, 45 | 220 ± 3 | 282 ± 2 | 33 | [32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, RD | 197 ± 3 | 257 ± 2 | 33 | [32] |  | as above, annealed at 350 C for 0.5 h | ||||
| rolled, O, TD | 121 ± 2 | 232 ± 3 | 42 | [32] | ||||||
| rolled, O, 45 | 134 ± 3 | 231 ± 2 | 43 | [32] |
References
- Mordike, B.; Ebert, T. Magnesium: Properties—Applications—Potential. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2001, 302, 37–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kainer, K.U. 40 Years of Magnesium Research—Assessment of Contribution to the Progress in Magnesium Technology. In Proceedings of the 79th Annual IMA World Magnesium Conference, Budapest, Hungary, 15–17 May 2019; International Magnesium Association: Saint Paul, MN, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaily, M.; Svensson, J.; Fajardo, S.; Birbilis, N.; Frankel, G.; Virtanen, S.; Arrabal, R.; Thomas, S.; Johansson, L. Fundamentals and advances in magnesium alloy corrosion. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2017, 89, 92–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Shin, K.; Zeng, Z. Microstructure, Deformation, and Property of Wrought Magnesium Alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2020, 51, 6045–6109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Xiong, X.; Chen, J.; Peng, X.; Chen, D.; Pan, F. Research advances in magnesium and magnesium alloys worldwide in 2020. J. Magnesium Alloys 2021, 9, 705–747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sillekens, W.; Letzig, D. The MagForge project: European Community research on forging of magnesium alloys. In Magnesium: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and Their Applications; Kainer, K.U., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Swiostek, J.; Bober, J.; Blawert, C.; Letzig, D.; Hintze, W.; Kainer, K. Die forging of commercial and modified magnesium alloys. In Magnesium: Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Magnesium Alloys and their Applications; Kainer, K.U., Ed.; Wiley-VCH: Weinheim, Germany, 2007; pp. 344–351. [Google Scholar]
- Gneiger, S. Von der Anforderung zur Anwendung-Modernes Legierungsdesign für Magnesiumbauteile. In Proceedings of the 70. BHT-Freiberger Universitätsforum, Freiberg, Germany, 5–7 June 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nakata, T.; Mezaki, T.; Ajima, R.; Xu, C.; Oh-Ishi, K.; Shimizu, K.; Hanaki, S.; Sasaki, T.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. High-speed extrusion of heat-treatable Mg–Al–Ca–Mn dilute alloy. Scr. Mater. 2015, 101, 28–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Z.; Jiang, B.; Yang, H.; Yang, Q.; Dai, J.; Pan, F. Influence of the Al2Ca phase on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–Al–Ca alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 647, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, M.; Qiao, X.; Wu, K.; Xu, C.; Kamado, S. Effect of Ca/Al ratio on microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg-Al-Ca-Mn alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2017, 682, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, S.; Huang, Y.; Kainer, K.U.; Hort, N. Recent research and developments on wrought magnesium alloys. J. Magnesium Alloys 2017, 5, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Chen, D.; Jin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Yang, Q.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. Strategies for enhancing the room-temperature stretch formability of magnesium alloy sheets: A review. J. Mater. Sci. 2021, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiffl, A.; Schiffl, I.; Hartmann, M.; Brötz, S.; Österreicher, J.; Kühlein, W. Analysis of Impact Factors on Crash Performance of High Strength 6082 Alloys Consider Extrudability and Small Modifications of the Profile Geometry. Mater. Today. Proc. 2019, 10, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Qiao, X.; Zheng, M.; Wu, K.; Xu, S. Development of high-strength, low-cost wrought Mg–2.5 mass% Zn alloy through micro-alloying with Ca and La. Mater. Des. 2015, 85, 549–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basu, I.; Al-Samman, T. Hierarchical twinning induced texture weakening in lean magnesium alloys. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Na, Z.; Zhang, Z.; Jie, D.; Li, J.; Wenjiang, D. Selective oxidation behavior of an ignition-proof Mg-Y-Ca-Ce alloy. J. Rare Earths 2013, 31, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czerwinski, F. Controlling the ignition and flammability of magnesium for aerospace applications. Corros. Sci. 2014, 86, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, J.; Becker, M.; Martinelli, E.; Weinberg, A.M.; Mingler, B.; Kilian, H.; Pogatscher, S.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. High-strength low-alloy (HSLA) Mg–Zn–Ca alloys with excellent biodegradation performance. JOM 2014, 66, 566–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, S.; Bian, M.; Davies, C.; Birbilis, N.; Nie, J. Texture evolution during static recrystallization of cold-rolled magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2016, 105, 479–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, S.; Kanodia, S.; Saha, R.; Bandyopadhyay, T.; Mandal, S. Influence of hard plate hot forging temperature on the microstructure, texture and mechanical properties in a lean Mg–Zn–Al alloy. J. Alloys Compd. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uggowitzer, P.J.; Cihova, M.; Horwatitsch, D.; Hametner, T.; Pogatscher, S.; Klaumünzer, D.; Löffler, J.F. Designkonzepte für niedriglegierte hochfeste Magnesiumlegierungen. In Proceedings of the 9. Ranshofener Leichtmetalltage; LKR-Verlag: Ranshofen, Austria, 2016; pp. 109–118. [Google Scholar]
- Cihova, M.; Schäublin, R.; Hauser, L.B.; Gerstl, S.S.; Simson, C.; Uggowitzer, P.; Löffler, J.F. Rational design of a lean magnesium-based alloy with high age-hardening response. Acta Mater. 2018, 158, 214–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandlöbes, S.; Friák, M.; Korte-Kerzel, S.; Pei, Z.; Neugebauer, J.; Raabe, D. A rare-earth free magnesium alloy with improved intrinsic ductility. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Samman, T.; Gottstein, G. Dynamic recrystallization during high temperature deformation of magnesium. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 490, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Kaboli, S.; Kabir, A.S.H.; Jung, I.H.; Yue, S. Effect of dynamic precipitation and twinning on dynamic recrystallization of micro-alloyed Mg–Al–Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 587, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Stanford, N.; Davies, C.H.J.; Nie, J.F.; Birbilis, N. Magnesium extrusion alloys: A review of developments and prospects. Int. Mater. Rev. 2019, 64, 27–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstetter, J.; Rüedi, S.; Baumgartner, I.; Kilian, H.; Mingler, B.; Povoden-Karadeniz, E.; Pogatscher, S.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. Processing and microstructure–property relations of high-strength low-alloy (HSLA) Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. Acta Mater. 2015, 98, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Wang, L.; Zhou, H.; Wang, J.; Shen, Y.; Tu, P.; Zhu, H.; Liu, W.; Jin, P.; Zeng, X. Improving ductility of a Mg alloy via non-basal< a> slip induced by Ca addition. Int. J. Plast 2019, 120, 164–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirth, J. Physical Metallurgy, 4th ed.; Chapter 20-Dislocations; North-Holland: Oxford, UK, 1996; pp. 1831–1875. [Google Scholar]
- Klaumünzer, D.; Hernandez, J.V.; Yi, S.; Letzig, D.; Kim, S.h.; Kim, J.J.; Seo, M.H.; Ahn, K. Magnesium process and alloy development for applications in the automotive industry. In Magnesium Technology 2019; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 15–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Victoria-Hernández, J.; Yi, S.; Klaumünzer, D.; Letzig, D. Comparison of the Mechanical Properties and Forming Behavior of Two Texture-Weakened Mg-Sheet Alloys Produced by Twin Roll Casting. Front. Mater. 2019, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Basu, I.; Chen, M.; Wheeler, J.; Schäublin, R.; Löffler, J. Stacking-fault mediated plasticity and strengthening in lean, rare-earth free magnesium alloys. Acta Mater. 2021, 211, 116877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadorn, J.P.; Hantzsche, K.; Yi, S.; Bohlen, J.; Letzig, D.; Wollmershauser, J.A.; Agnew, S.R. Role of solute in the texture modification during hot deformation of Mg-rare earth alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 1347–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agarwal, R.; Trinkle, D.R. Ab initio magnesium-solute transport database using exact diffusion theory. Acta Mater. 2018, 150, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenberg, N.P.; Gneiger, S.; Weißensteiner, I.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Pogatscher, S. Mg-Alloys for forging applications—A review. Materials 2020, 13, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yuan, W.; Panigrahi, S.; Su, J.Q.; Mishra, R. Influence of grain size and texture on Hall–Petch relationship for a magnesium alloy. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 994–997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Choo, H. Influence of texture on Hall–Petch relationships in an Mg alloy. Acta Mater. 2014, 81, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yu, H.; Xin, Y.; Wang, M.; Liu, Q. Hall-Petch relationship in Mg alloys: A review. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2018, 34, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T.; Mezaki, T.; Xu, C.; Oh-Ishi, K.; Shimizu, K.; Hanaki, S.; Kamado, S. Improving tensile properties of dilute Mg-0.27 Al-0.13 Ca-0.21 Mn (at.%) alloy by low temperature high speed extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2015, 648, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Khudododova, G.; Kulyasova, O.; Islamgaliev, R.; Valiev, R. Microstructure and mechanical properties of the Mg–Zn–Ca biodegradable alloy after severe plastic deformation. In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2019; Volume 672, pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Geng, L.; Huang, L.; Zhang, X.; Dong, C. Enhanced mechanical properties in fine-grained Mg–1.0 Zn–0.5 Ca alloys prepared by extrusion at different temperatures. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 1024–1027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Nakata, T.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.; Kamado, S. Enhancing strength and ductility of Mg-Zn-Gd alloy via slow-speed extrusion combined with pre-forging. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 1214–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Razavi, S.; Foley, D.; Karaman, I.; Hartwig, K.; Duygulu, O.; Kecskes, L.; Mathaudhu, S.; Hammond, V. Effect of grain size on prismatic slip in Mg–3Al–1Zn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2012, 67, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polmear, I. Aluminium Alloys—A Century of Age Hardening. Mater. Forum 2004, 28, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Hono, K.; Mendis, C.; Sasaki, T.; Oh-Ishi, K. Towards the development of heat-treatable high-strength wrought Mg alloys. Scr. Mater. 2010, 63, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.F. Precipitation and hardening in magnesium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2012, 43, 3891–3939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Su, J.; Kaboli, S.; Kabir, A.S.H.; Vo, P.; Jung, I.H.; Yue, S. Precipitation behaviour of micro-alloyed Mg-Al-Ca alloys during heat treatment and hot compression. In Magnesium Technology 2012; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2012; pp. 317–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manohar, P.; Ferry, M.; Chandra, T. Five decades of the Zener equation. ISIJ Int. 1998, 38, 913–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bian, M.Z.; Zeng, Z.R.; Xu, S.W.; Zhu, S.M.; Zhu, Y.M.; Davies, C.H.J.; Birbilis, N.; Nie, J.F. Improving formability of Mg–Ca–Zr sheet alloy by microalloying of Zn. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2016, 18, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, Y.; Fu, X.; Mou, D.; Zhu, Q.; Li, L.; Cui, J. Study on the role of Ca in the grain refinement of Mg–Ca binary alloys. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, S1–S94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Chen, Z.; Yang, W.; Fang, S.; Xu, B. Effect of yttrium, calcium and zirconium on ignition-proof principle and mechanical properties of magnesium alloys. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 74–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Yang, C.; Xu, B. Effect of Ca and Y additions on oxidation behavior of magnesium alloys at high temperatures. J. Rare Earths 2012, 30, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihriban, O.; Pekguleryuz, E.B. Creep resistant magnesium diecasting alloys based on alkaline earth elements. Mater. Trans. JIM 2001, 42, 1258–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, A.A.; Powell, B.R.; Balogh, M.P. Creep and microstructure of magnesium-aluminum-calcium based alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2002, 33, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, A.A. Recent magnesium alloy development for elevated temperature applications. Int. Mater. Rev. 2004, 49, 13–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.; Yin, J. The relation between two ductility mechanisms for Mg alloys revealed by high-throughput simulations. Mater. Des. 2020, 186, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chino, Y.; Ueda, T.; Otomatsu, Y.; Sassa, K.; Huang, X.; Suzuki, K.; Mabuchi, M. Effects of Ca on tensile properties and stretch formability at room temperature in Mg-Zn and Mg-Al alloys. Mater. Trans. JIM 2011, 52, 1477–1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Guan, D.; Liu, X.; Gao, J.; Ma, L.; Wynne, B.P.; Rainforth, W.M. Exploring the mechanism of “Rare Earth” texture evolution in a lean Mg–Zn–Ca alloy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 7152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, Y.; Geng, L.; Lu, C. Effects of calcium on texture and mechanical properties of hot-extruded Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 539, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avedesian, M.M.; Baker, H. (Eds.) ASM Specialty Handbook: Magnesium and Magnesium Alloys; ASM International: Materials Park, OH, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Emley, E.F. Principles of Magnesium Technology; Pergamon Press: Oxford, UK, 1966. [Google Scholar]
- Rokhlin, L.; Dobatkina, T.; Nikitina, N.; Tarytina, I. Calcium-alloyed magnesium alloys. Met. Sci. Heat Treat. 2009, 51, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.P.; Prasad, Y.V.R.K.; Dharmendra, C.; Suresh, K.; Hort, N.; Dieringa, H. Review on Hot Working Behavior and Strength of Calcium-Containing Magnesium Alloys. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2018, 20, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Oh-Ishi, K.; Kamado, S.; Uchida, F.; Homma, T.; Hono, K. High-strength extruded Mg–Al–Ca–Mn alloy. Scr. Mater. 2011, 65, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuoka, S.I.; Miyamoto, S.; Oki, Y.; Nagao, S.; Sano, H. Effects of zinc and manganese contents on extrudability of Mg-Al-Zn alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 2003, 53, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Davies, C.; Barnett, M. Expanding the extrusion limits of wrought magnesium alloys. JOM 2004, 56, 22–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T. Extrusion of magnesium alloys. J. Jpn. Inst. Light Met. 2004, 54, 472–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atwell, D.L.; Barnett, M.R. Extrusion limits of magnesium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38A, 3032–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Nakata, T.; Xu, C.; Matsumoto, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Sasaki, T.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. Optimization of Mn content for high strengths in high-speed extruded Mg-0.3Al-0.3Ca (wt%) dilute alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 673, 443–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakata, T.; Xu, C.; Ajima, R.; Shimizu, K.; Hanaki, S.; Sasaki, T.; Ma, L.; Hono, K.; Kamado, S. Strong and ductile age-hardening Mg-Al-Ca-Mn alloy that can be extruded as fast as aluminum alloys. Acta Mater. 2017, 130, 261–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihova, M.; Schäublin, R.; Gerstl, S.; Hauser, L.; Simson, C.; Papenberg, N.; Gneiger, S.; Schlögl, C.M.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Löffler, J.F. Mikrostruktur-Eigenschafts-Korrelationen in aushärtbaren mageren Mg-Legierungen. In Proceedings of the 10. Ranshofener Leichtmetalltage; LKR-Verlag: Ranshofen, Austria, 2018; pp. 51–61. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X.; Qiao, X.; Li, Z.; Zheng, M. High strength and excellent ductility of dilute Mg-0.68 Al-0.32 Ca-0.50 Mn (wt%) extrusion alloy obtained by T6 treatment. Mater. Charact. 2020, 162, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Sasaki, T.; Suh, B.; Nakata, T.; Kamado, S.; Hono, K. A heat-treatable Mg–Al–Ca–Mn–Zn sheet alloy with good room temperature formability. Scr. Mater. 2017, 138, 151–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, M.; Sasaki, T.; Nakata, T.; Kamado, S.; Hono, K. Effects of rolling conditions on the microstructure and mechanical properties in a Mg–Al–Ca–Mn–Zn alloy sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 730, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, K.P.; Suresh, K.; Prasad, Y.V.R.K.; Dharmendra, C.; Hort, N.; Dieringa, H. High Temperature Strength and Hot Working Technology for As-Cast Mg–1Zn–1Ca (ZX11) Alloy. Metals 2017, 7, 405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh-Ishi, K.; Watanabe, R.; Mendis, C.; Hono, K. Age-hardening response of Mg–0.3 at.% Ca alloys with different Zn contents. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2009, 526, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Bian, M.; Xu, S.; Davies, C.; Birbilis, N.; Nie, J. Annealing strengthening in a dilute Mg–Zn–Ca sheet alloy. Scr. Mater. 2015, 107, 127–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Bian, M.; Xu, S.; Davies, C.; Birbilis, N.; Nie, J. Texture evolution during cold rolling of dilute Mg alloys. Scr. Mater. 2015, 108, 6–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Z.; Bian, M.; Xu, S.; Davies, C.; Birbilis, N.; Nie, J. Effects of dilute additions of Zn and Ca on ductility of magnesium alloy sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 674, 459–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.W.; Suh, B.C.; Shim, M.S.; Bae, J.; Kim, D.H.; Kim, N.J. Texture evolution in Mg-Zn-Ca alloy sheets. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2013, 44, 2950–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xia, N.; Wang, C.; Gao, Y.; Hua, Z.M.; Ma, C.Y.; Du, C.F.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.M.; Li, M.X.; Zha, M.; et al. Enhanced ductility of Mg–1Zn–0.2 Zr alloy with dilute Ca addition achieved by activation of non-basal slip and twinning. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2021, 813, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamrani, S.; Fleck, C. Effects of calcium and rare-earth elements on the microstructure and tension–compression yield asymmetry of ZEK100 alloy. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2014, 618, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Nakata, T.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.; Kamado, S. High-speed extrusion of dilute Mg-Zn-Ca-Mn alloys and its effect on microstructure, texture and mechanical properties. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 678, 329–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Nakata, T.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.; Kamado, S. Development of dilute Mg–Zn–Ca–Mn alloy with high performance via extrusion. J. Alloys Compd. 2016, 668, 13–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cihova, M.; Martinelli, E.; Schmutz, P.; Myrissa, A.; Schäublin, R.; Weinberg, A.M.; Uggowitzer, P.; Löffler, J.F. The role of zinc in the biocorrosion behavior of resorbable Mg–Zn–Ca alloys. Acta Biomater. 2019, 100, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Hou, R.; Scharnagl, N.; Bohlen, J.; Zheludkevich, M.L. Microstructural influence on corrosion behavior of MgZnGe alloy in NaCl solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 783, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, P.; Blawert, C.; Hou, R.; Bohlen, J.; Konchakova, N.; Zheludkevich, M.L. A comprehensive comparison of the corrosion performance, fatigue behavior and mechanical properties of micro-alloyed MgZnCa and MgZnGe alloys. Mater. Des. 2020, 185, 108285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Samman, T.; Li, X. Sheet texture modification in magnesium-based alloys by selective rare earth alloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2011, 528, 3809–3822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Nakata, T.; Yan, H.; Chen, R.; Kamado, S. Rare earth texture and improved ductility in a Mg-Zn-Gd alloy after high-speed extrusion. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2016, 667, 233–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, M.; Xu, C.; Yan, H.; Lu, S.; Nakata, T.; Lao, C.; Chen, R.; Kamado, S.; Han, E. Correlation between dynamic recrystallization and formation of rare earth texture in a Mg-Zn-Gd magnesium alloy during extrusion. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 16800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobroň, P.; Chmelík, F.; Parfenenko, K.; Letzig, D.; Bohlen, J. On the Effect of the Extrusion Speed on Microstructure and Plastic Deformation of ZE10 and ZEK100 Magnesium Alloys-an Acoustic Emission Study. Acta Phys. Pol. A 2012, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meza-García, E. Influence of Alloying Elements on the Microstructure and Mechanical Properties of Extruded Mg-Zn Based Alloys. Ph.D. Thesis, Technische Universität Berlin, Berlin, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Meza-García, E.; Bohlen, J.; Yi, S.; Letzig, D.; Kräusel, V.; Landgrebe, D.; Kainer, K. Influence of alloying elements and extrusion process parameter on the recrystallization process of Mg-Zn alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 2015, 2, S19–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, R.; Otsu, M.; Yamasaki, M.; Mayama, T.; Utsunomiya, H.; Kawamura, Y. Application of mixture rule to finite element analysis for forging of cast Mg–Zn–Y alloys with long period stacking ordered structure. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2012, 548, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, E.; He, W.; Du, H.; Yang, K. Microstructure, mechanical properties and corrosion properties of Mg–Zn–Y alloys with low Zn content. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 488, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Yuan, F.; Liu, M.; Pan, F. Microstructure and mechanical properties of Mg–1.8% Mn alloy modified by single Er and composite Er/Al microalloying. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2013, 576, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Manrique, P.; Robson, J.; Pérez-Prado, M. Precipitation strengthening and reversed yield stress asymmetry in Mg alloys containing rare-earth elements: A quantitative study. Acta Mater. 2017, 124, 456–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-Manrique, P.; Herrera-Solaz, V.; Segurado, J.; Llorca, J.; Gálvez, F.; Ruano, O.A.; Yi, S.; Pérez-Prado, M.T. Origin of the reversed yield asymmetry in Mg-rare earth alloys at high temperature. Acta Mater. 2015, 92, 265–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, Y.; Jiang, B.; Song, J.; Liu, B.; Huang, G.; Zhang, D.; Pan, F. Effects of Zn and Ca addition on microstructure and mechanical properties of as-extruded Mg-1.0 Sn alloy sheet. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 82–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Song, J.; Jiang, Z.; Yang, T.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. A micro-alloyed Mg-Sn-Y alloy with high ductility at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 735, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zeng, Y.; Jiang, B.; Yang, Q.; Wan, Y.; Quan, G.; Pan, F. Grain refinement mechanism and improved mechanical properties in Mg–Sn alloy with trace Y addition. J. Alloys Compd. 2020, 820, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Shen, Y.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; Chai, Y.; Song, J.; Yang, T.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. A good balance between ductility and stretch formability of dilute Mg-Sn-Y sheet at room temperature. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2018, 736, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Jiang, B.; Tang, A.; He, C.; Zhang, D.; Song, J.; Yang, T.; Huang, G.; Pan, F. Formation of the elliptical texture and its effect on the mechanical properties and stretch formability of dilute Mg-Sn-Y sheet by Zn addition. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2019, 746, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]






Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Papenberg, N.P.; Gneiger, S.; Uggowitzer, P.J.; Pogatscher, S. Lean Wrought Magnesium Alloys. Materials 2021, 14, 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154282
Papenberg NP, Gneiger S, Uggowitzer PJ, Pogatscher S. Lean Wrought Magnesium Alloys. Materials. 2021; 14(15):4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154282
Chicago/Turabian StylePapenberg, Nikolaus P., Stefan Gneiger, Peter J. Uggowitzer, and Stefan Pogatscher. 2021. "Lean Wrought Magnesium Alloys" Materials 14, no. 15: 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154282
APA StylePapenberg, N. P., Gneiger, S., Uggowitzer, P. J., & Pogatscher, S. (2021). Lean Wrought Magnesium Alloys. Materials, 14(15), 4282. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14154282








