Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cements in the Augmentation of Sheep Vertebrae—An Ex Vivo Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation of Bone Cements
2.2. Cement Injection
2.3. High-Resolution Micro-CT and Analysis
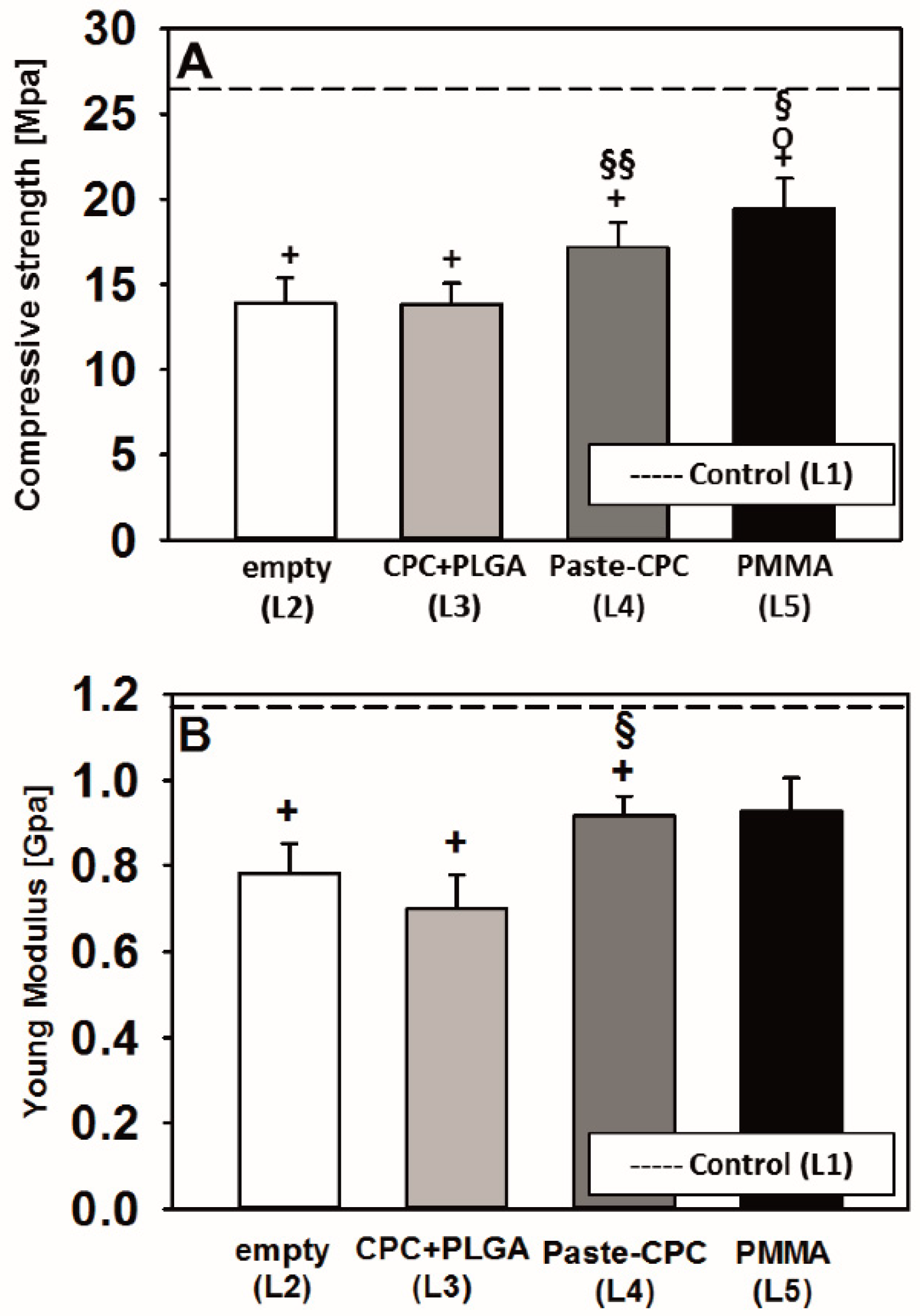
2.4. Biomechanical Testing (Compressive Strength)
2.5. Histology
2.6. Statistical Analyses
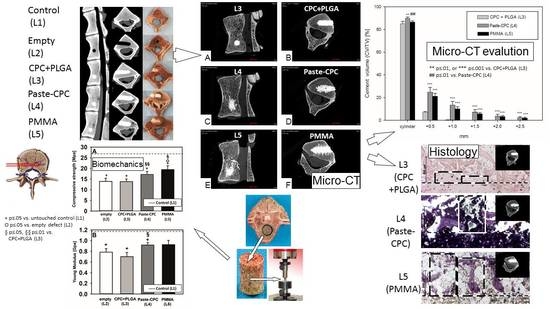
3. Results
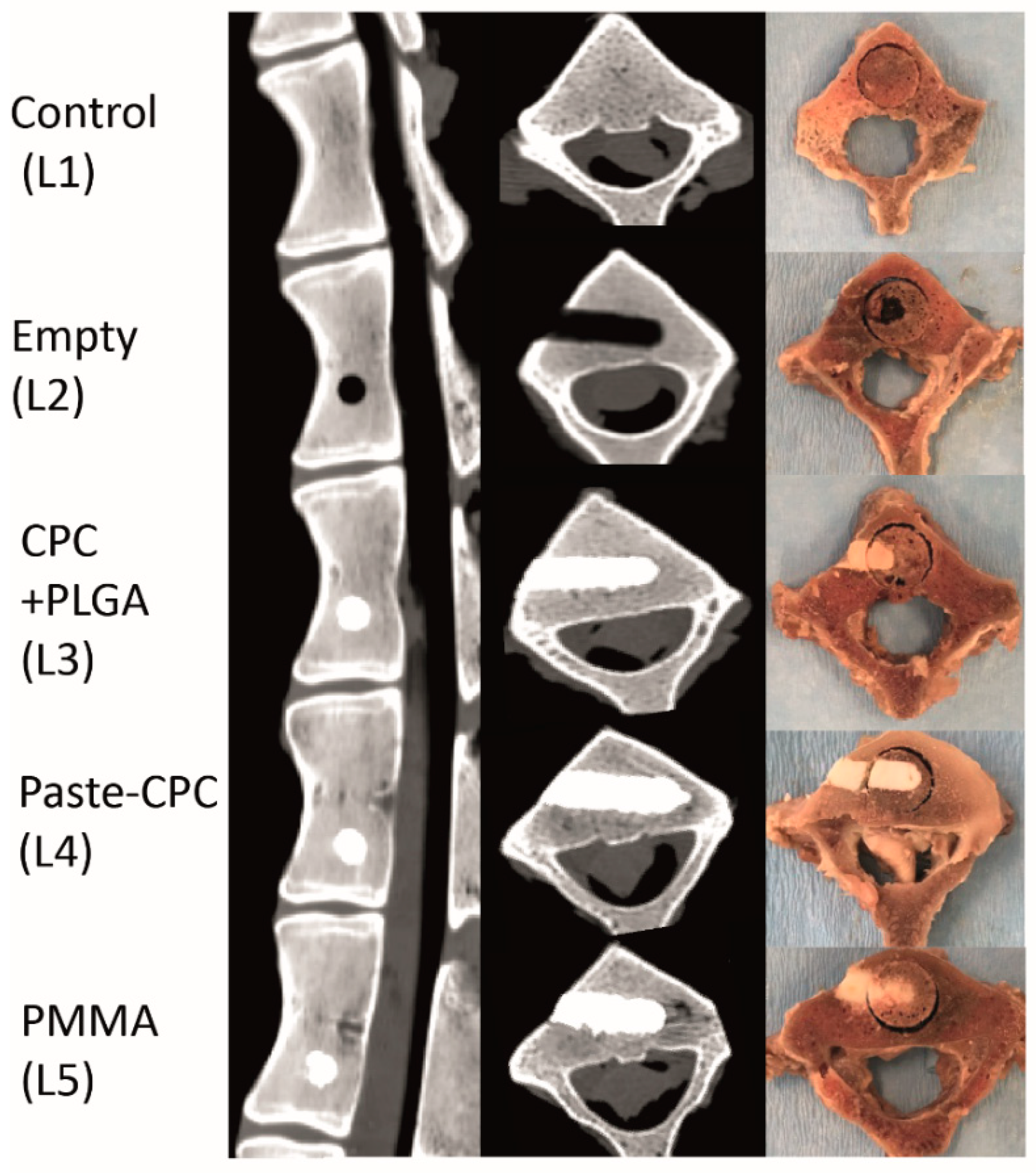
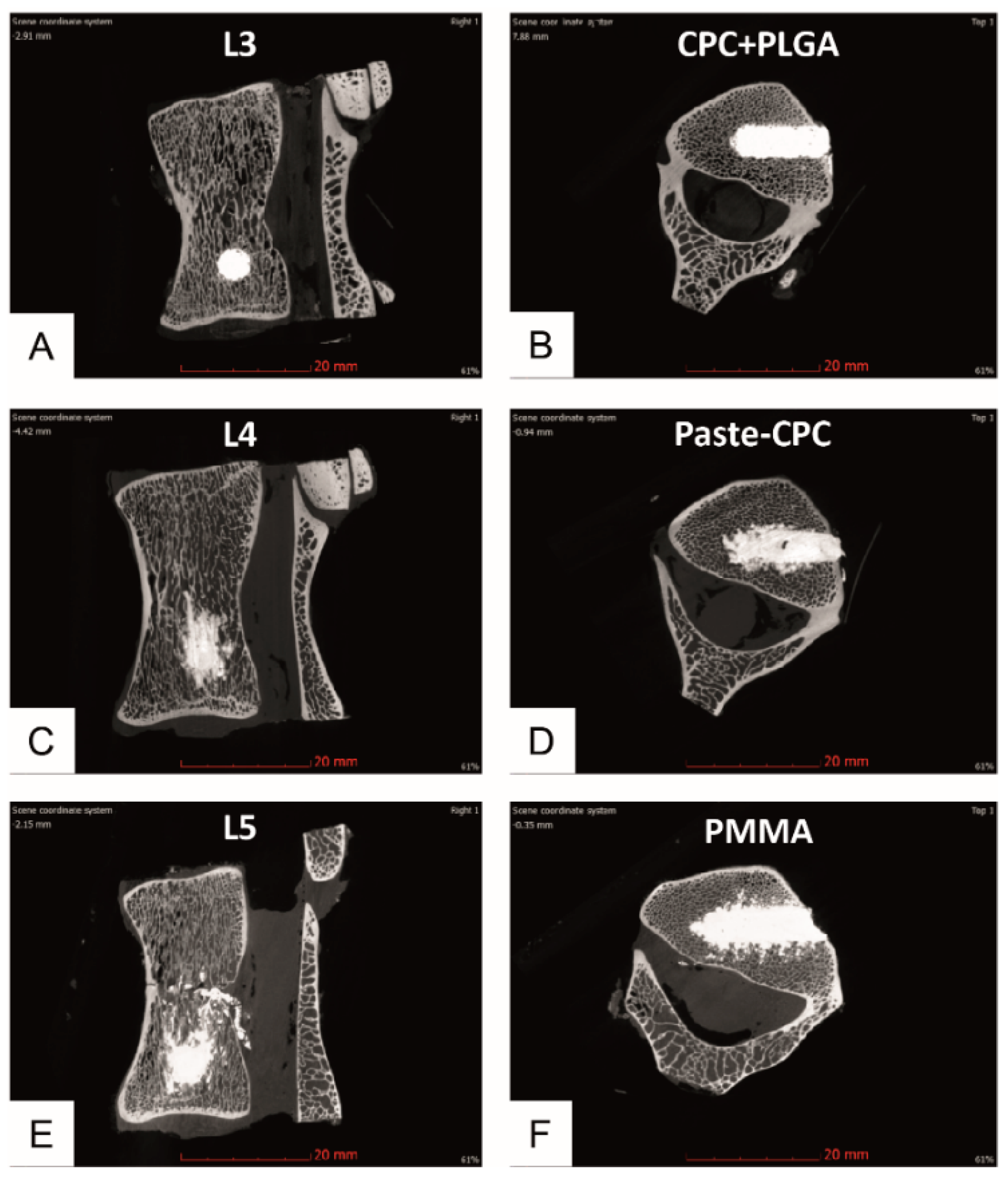
3.1. Micro-CT Analyses
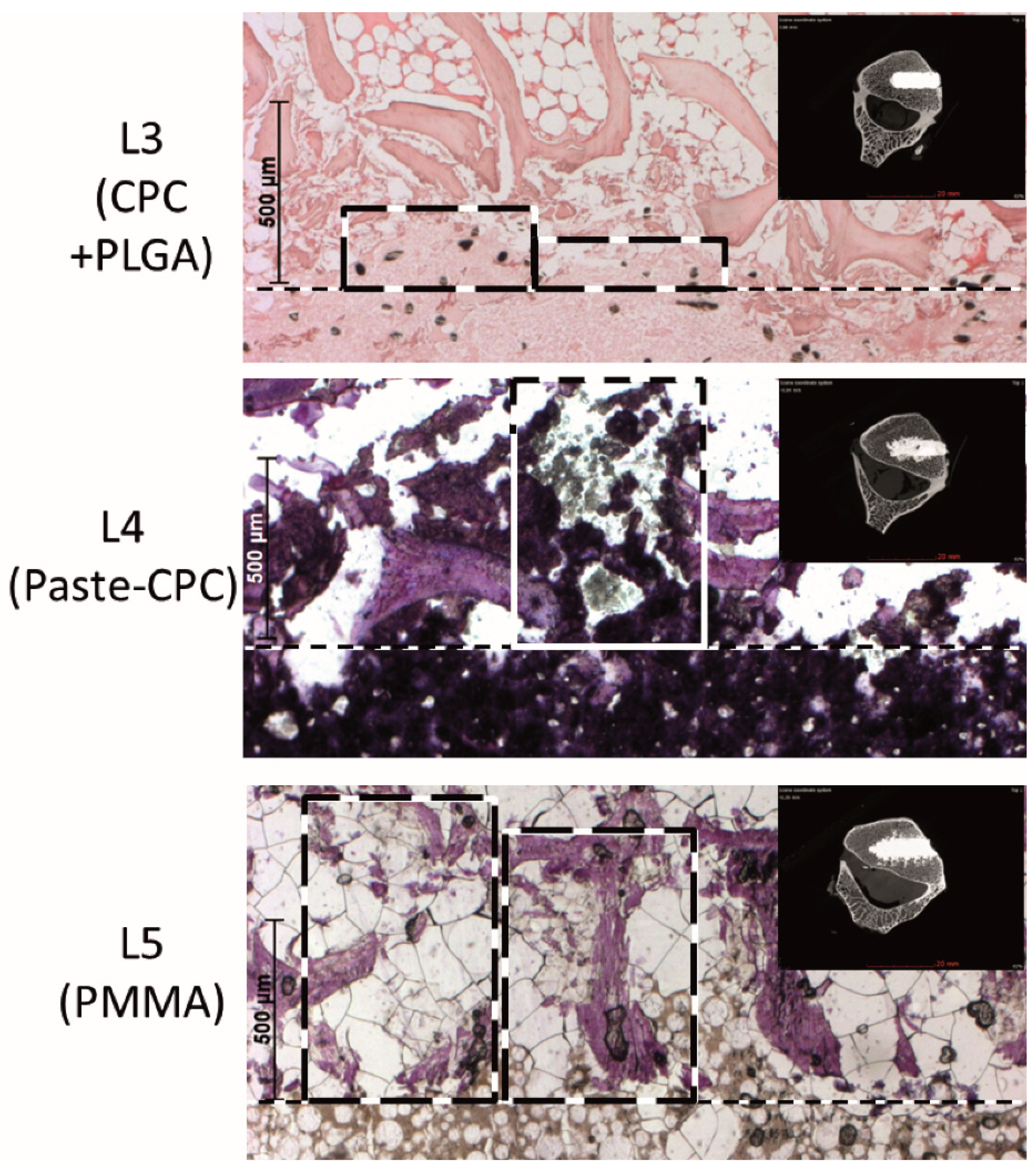
3.2. Histology
3.3. Biomechanical Testing
4. Discussion
4.1. Extrusion Patterns of Conventional CPC (+ PLGA Fibers) and Oil-Based Paste-CPC
4.2. Possible Extrusion Mechanisms
4.3. Biomechanical Considerations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hulme, P.A.; Krebs, J.; Ferguson, S.J.; Berlemann, U. Vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: A systematic review of 69 clinical studies. Spine 2006, 31, 1983–2001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Epstein, N.E. A Comparison of Kyphoplasty, Vertebroplasty, or Non-Surgical Treatment of Traumatic/Atraumatic Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fractures: A Short Review. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Cheng, J.; Yin, J.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, C.; Hao, D. Therapeutic effect of kyphoplasty and balloon vertebroplasty on osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Medicine 2019, 98, e17810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deb, S. A review of improvements in acrylic bone cements. J. Biomater. Appl. 1999, 14, 16–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grados, F.; Depriester, C.; Cayrolle, G.; Hardy, N.; Deramond, H.; Fardellone, P. Long-term observations of vertebral osteoporotic fractures treated by percutaneous vertebroplasty. Rheumatology 2000, 39, 1410–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Chen, W.J.; Kao, Y.H.; Yang, S.C.; Yu, S.W.; Tu, Y.K.; Chung, K.C. Impact of cement leakage into disks on the development of adjacent vertebral compression fractures. J. Spinal. Disord. Tech. 2010, 23, 35–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, G. Injectable bone cements for use in vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: State-of-the-art review. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2006, 76, 456–468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zou, J. Filling materials used in kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for vertebral compression fracture: A literature review. Artif. Cells Blood Substit. Immobil. Biotechnol. 2011, 39, 87–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, W.; Schnitzler, V.; Tancret, F.; Bouler, J.M. Calcium phosphate cements for bone substitution: Chemistry, handling and mechanical properties. Acta Biomater. 2014, 10, 1035–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenz, S.; Kunisch, E.; Muhlstadt, M.; Bohm, A.; Kopsch, V.; Bossert, J.; Kinne, R.W.; Jandt, K.D. Enhanced mechanical properties of a novel, injectable, fiber-reinforced brushite cement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2014, 39, 328–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenz, S.; Hennig, M.; Muhlstadt, M.; Kunisch, E.; Bungartz, M.; Brinkmann, O.; Bossert, J.; Kinne, R.W.; Jandt, K.D. Effects of oxygen plasma treatment on interfacial shear strength and post-peak residual strength of a PLGA fiber-reinforced brushite cement. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2016, 57, 347–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bungartz, M.; Maenz, S.; Kunisch, E.; Horbert, V.; Xin, L.; Gunnella, F.; Mika, J.; Borowski, J.; Bischoff, S.; Schubert, H.; et al. First-time systematic postoperative clinical assessment of a minimally invasive approach for lumbar ventrolateral vertebroplasty in the large animal model sheep. Spine J. 2016, 16, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maenz, S.; Brinkmann, O.; Kunisch, E.; Horbert, V.; Gunnella, F.; Bischoff, S.; Schubert, H.; Sachse, A.; Xin, L.; Gunster, J.; et al. Enhanced bone formation in sheep vertebral bodies after minimally invasive treatment with a novel, PLGA fiber-reinforced brushite cement. Spine J. 2017, 17, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peersman, G.; Laskin, R.; Davis, J.; Peterson, M.G.; Richart, T. Prolonged operative time correlates with increased infection rate after total knee arthroplasty. HSS J. 2006, 2, 70–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Aberg, J.; Brisby, H.; Henriksson, H.B.; Lindahl, A.; Thomsen, P.; Engqvist, H. Premixed acidic calcium phosphate cement: Characterization of strength and microstructure. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2010, 93, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinemann, S.; Rossler, S.; Lemm, M.; Ruhnow, M.; Nies, B. Properties of injectable ready-to-use calcium phosphate cement based on water-immiscible liquid. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 6199–6207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, L.; Bungartz, M.; Maenz, S.; Horbert, V.; Hennig, M.; Illerhaus, B.; Gunster, J.; Bossert, J.; Bischoff, S.; Borowski, J.; et al. Decreased extrusion of calcium phosphate cement versus high viscosity PMMA cement into spongious bone marrow-an ex vivo and in vivo study in sheep vertebrae. Spine J. 2016, 16, 1468–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maenz, S. Entwicklung eines faserverstärkten, Brushit-bildenden Calciumphosphat-Zementes zur minimal-invasiven Behandlung von Knochendefekten. Ph.D. Thesis, Friedrich-Schiller-Universität Jena, Jena, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Turner, R.T.; Maran, A.; Lotinun, S.; Hefferan, T.; Evans, G.L.; Zhang, M.; Sibonga, J.D. Animal models for osteoporosis. Rev. Endocr. Metab. Disord. 2001, 2, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, H.J.; Kettler, A.; Wenger, K.H.; Claes, L.E. Anatomy of the sheep spine and its comparison to the human spine. Anat. Rec. 1997, 247, 542–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eggli, S.; Schlapfer, F.; Angst, M.; Witschger, P.; Aebi, M. Biomechanical testing of three newly developed transpedicular multisegmental fixation systems. Eur. Spine J. 1992, 1, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurwitz, G.S.; Dawson, J.M.; McNamara, M.J.; Federspiel, C.F.; Spengler, D.M. Biomechanical analysis of three surgical approaches for lumbar burst fractures using short-segment instrumentation. Spine 1993, 18, 977–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee for Advanced Therapies, E.M.E.A. Reflection Paper on In-Vitro Cultured Chondocyte Containing Products for Cartilage Repair of the Knee; EMEA: London, UK, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Edmonston, S.J.; Singer, K.P.; Day, R.E.; Breidahl, P.D.; Price, R.I. Formalin fixation effects on vertebral bone density and failure mechanics: An stuy of human and sheep vertebrae. Eur. Spine J. 1994, 1, 175–179. [Google Scholar]
- Baroud, G.; Crookshank, M.; Bohner, M. High-viscosity cement significantly enhances uniformity of cement filling in vertebroplasty: An experimental model and study on cement leakage. Spine 2006, 31, 2562–2568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohner, M.; Gasser, B.; Baroud, G.; Heini, P. Theoretical and experimental model to describe the injection of a polymethylmethacrylate cement into a porous structure. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 2721–2730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryu, K.S.; Park, C.K.; Kim, M.C.; Kang, J.K. Dose-dependent epidural leakage of polymethylmethacrylate after percutaneous vertebroplasty in patients with osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures. J. Neurosurg. 2002, 96, 56–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klazen, C.A.; Lohle, P.N.; de Vries, J.; Jansen, F.H.; Tielbeek, A.V.; Blonk, M.C.; Venmans, A.; van Rooij, W.J.; Schoemaker, M.C.; Juttmann, J.R.; et al. Vertebroplasty versus conservative treatment in acute osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures (Vertos II): An open-label randomised trial. Lancet 2010, 376, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Phillips, F.M.; Todd Wetzel, F.; Lieberman, I.; Campbell-Hupp, M. An in vivo comparison of the potential for extravertebral cement leak after vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Spine 2002, 27, 2173–2178, discussion 2178–2179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.J.; Yang, H.L.; Shi, Y.X.; Jiang, W.M.; Chen, L. Pulmonary cement embolism associated with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty: A systematic review. Orthop. Surg. 2012, 4, 182–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choe, D.H.; Marom, E.M.; Ahrar, K.; Truong, M.T.; Madewell, J.E. Pulmonary embolism of polymethyl methacrylate during percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2004, 183, 1097–1102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, J.S.; Kim, Y.J.; Choi, B.W.; Kim, T.H.; Choe, K.O. MDCT of pulmonary embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2005, 184, 1364–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duran, C.; Sirvanci, M.; Aydogan, M.; Ozturk, E.; Ozturk, C.; Akman, C. Pulmonary cement embolism: A complication of percutaneous vertebroplasty. Acta Radiol. 2007, 48, 854–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeom, J.S.; Kim, W.J.; Choy, W.S.; Lee, C.K.; Chang, B.S.; Kang, J.W. Leakage of cement in percutaneous transpedicular vertebroplasty for painful osteoporotic compression fractures. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 2003, 85, 83–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Groen, R.J.; du Toit, D.F.; Phillips, F.M.; Hoogland, P.V.; Kuizenga, K.; Coppes, M.H.; Muller, C.J.; Grobbelaar, M.; Mattyssen, J. Anatomical and pathological considerations in percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: A reappraisal of the vertebral venous system. Spine 2004, 29, 1465–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z.X.; Liu, D.; Wan, S.Y.; Sang, H.X.; Lei, W. Staged-injection procedure to prevent cement leakage during vertebroplasty: An in vitro study. J. Surg. Res. 2010, 164, e253–e256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galovich, L.A.; Perez-Higueras, A.; Altonaga, J.R.; Orden, J.M.; Barba, M.L.; Morillo, M.T. Biomechanical, histological and histomorphometric analyses of calcium phosphate cement compared to PMMA for vertebral augmentation in a validated animal model. Eur. Spine J. 2011, 20 (Suppl. 3), 376–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loeffel, M.; Ferguson, S.J.; Nolte, L.P.; Kowal, J.H. Vertebroplasty: Experimental characterization of polymethylmethacrylate bone cement spreading as a function of viscosity, bone porosity, and flow rate. Spine 2008, 33, 1352–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohamed, R.; Silbermann, C.; Ahmari, A.; Bohner, M.; Becker, S.; Baroud, G. Cement filling control and bone marrow removal in vertebral body augmentation by unipedicular aspiration technique: An experimental study using leakage model. Spine 2010, 35, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Togawa, D.; Bauer, T.W.; Lieberman, I.H.; Takikawa, S. Histologic evaluation of human vertebral bodies after vertebral augmentation with polymethyl methacrylate. Spine 2003, 28, 1521–1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belkoff, S.M.; Molloy, S. Temperature measurement during polymerization of polymethylmethacrylate cement used for vertebroplasty. Spine 2003, 28, 1555–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwenhuijse, M.J.; Van Erkel, A.R.; Dijkstra, P.D. Cement leakage in percutaneous vertebroplasty for osteoporotic vertebral compression fractures: Identification of risk factors. Spine J. 2011, 11, 839–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Zamparo, E.; Kronen, P.W.; Kampf, K.; Makara, M.; Steffen, T.; von Rechenberg, B. Bone augmentation for cancellous bone- development of a new animal model. BMC Musculoskelet. Disord. 2013, 14, 200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Zhu, X.S.; Zhang, Z.M.; Mao, H.Q.; Geng, D.C.; Zou, J.; Wang, G.L.; Zhang, Z.G.; Wang, J.H.; Chen, L.; Yang, H.L. A novel sheep vertebral bone defect model for injectable bioactive vertebral augmentation materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 2011, 22, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habib, M.; Serhan, H.; Marchek, C.; Baroud, G. Cement leakage and filling pattern study of low viscous vertebroplastic versus high viscous confidence cement. SAS J. 2010, 4, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Aebli, N.; Krebs, J.; Schwenke, D.; Davis, G.; Theis, J.C. Pressurization of vertebral bodies during vertebroplasty causes cardiovascular complications: An experimental study in sheep. Spine 2003, 28, 1513–1519, discussion 1519–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, A.; Bliemel, C.; Zettl, R.; Ruchholtz, S. Management of pulmonary cement embolism after percutaneous vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty: A systematic review of the literature. Eur. Spine J. 2009, 18, 1257–1265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bohner, M. Physical and chemical aspects of calcium phosphates used in spinal surgery. Eur. Spine J. 2001, 10 (Suppl. 2), S114–S121. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Higgins, K.B.; Harten, R.D.; Langrana, N.A.; Reiter, M.F. Biomechanical effects of unipedicular vertebroplasty on intact vertebrae. Spine 2003, 28, 1540–1547, discussion 1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, H.J.; Mehnert, U.; Claes, L.E.; Bierschneider, M.M.; Jaksche, H.; Boszczyk, B.M. Biomechanical evaluation of vertebroplasty and kyphoplasty with polymethyl methacrylate or calcium phosphate cement under cyclic loading. Spine 2006, 31, 2934–2941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomita, S.; Kin, A.; Yazu, M.; Abe, M. Biomechanical evaluation of kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty with calcium phosphate cement in a simulated osteoporotic compression fracture. J. Orthop. Sci. 2003, 8, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blattert, T.R.; Jestaedt, L.; Weckbach, A. Suitability of a calcium phosphate cement in osteoporotic vertebral body fracture augmentation: A controlled, randomized, clinical trial of balloon kyphoplasty comparing calcium phosphate versus polymethylmethacrylate. Spine 2009, 34, 108–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kinne, R.W.; Gunnella, F.; Kunisch, E.; Heinemann, S.; Nies, B.; Maenz, S.; Horbert, V.; Illerhaus, B.; Huber, R.; Firkowska-Boden, I.; et al. Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cements in the Augmentation of Sheep Vertebrae—An Ex Vivo Study. Materials 2021, 14, 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143873
Kinne RW, Gunnella F, Kunisch E, Heinemann S, Nies B, Maenz S, Horbert V, Illerhaus B, Huber R, Firkowska-Boden I, et al. Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cements in the Augmentation of Sheep Vertebrae—An Ex Vivo Study. Materials. 2021; 14(14):3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143873
Chicago/Turabian StyleKinne, Raimund W., Francesca Gunnella, Elke Kunisch, Sascha Heinemann, Berthold Nies, Stefan Maenz, Victoria Horbert, Bernhard Illerhaus, René Huber, Izabela Firkowska-Boden, and et al. 2021. "Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cements in the Augmentation of Sheep Vertebrae—An Ex Vivo Study" Materials 14, no. 14: 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143873
APA StyleKinne, R. W., Gunnella, F., Kunisch, E., Heinemann, S., Nies, B., Maenz, S., Horbert, V., Illerhaus, B., Huber, R., Firkowska-Boden, I., Bossert, J., Jandt, K. D., Sachse, A., Bungartz, M., & Brinkmann, O. (2021). Performance of Calcium Phosphate Cements in the Augmentation of Sheep Vertebrae—An Ex Vivo Study. Materials, 14(14), 3873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143873