Use of ZnAl-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) to Extend the Service Life of Reinforced Concrete
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Synthesis of ZnAl-NO3 and ZnAl-NO2 LDHs
2.2. Structure and Morphology of the ZnAl LDH
2.3. Stability of ZnAl LDH in Aqueous Solution
2.4. Ion Exchange in Aqueous Solution
2.5. Effect of ZnAl LDH on the Corrosion of Steel in Aqueous Solutions
2.6. Cement Pastes and Mortars Preparation
2.7. Chloride Sensors inside Mortars
2.8. Impact of ZnAl LDH on the Corrosion of Steel Rebars in Mortars
3. Results and Discussion
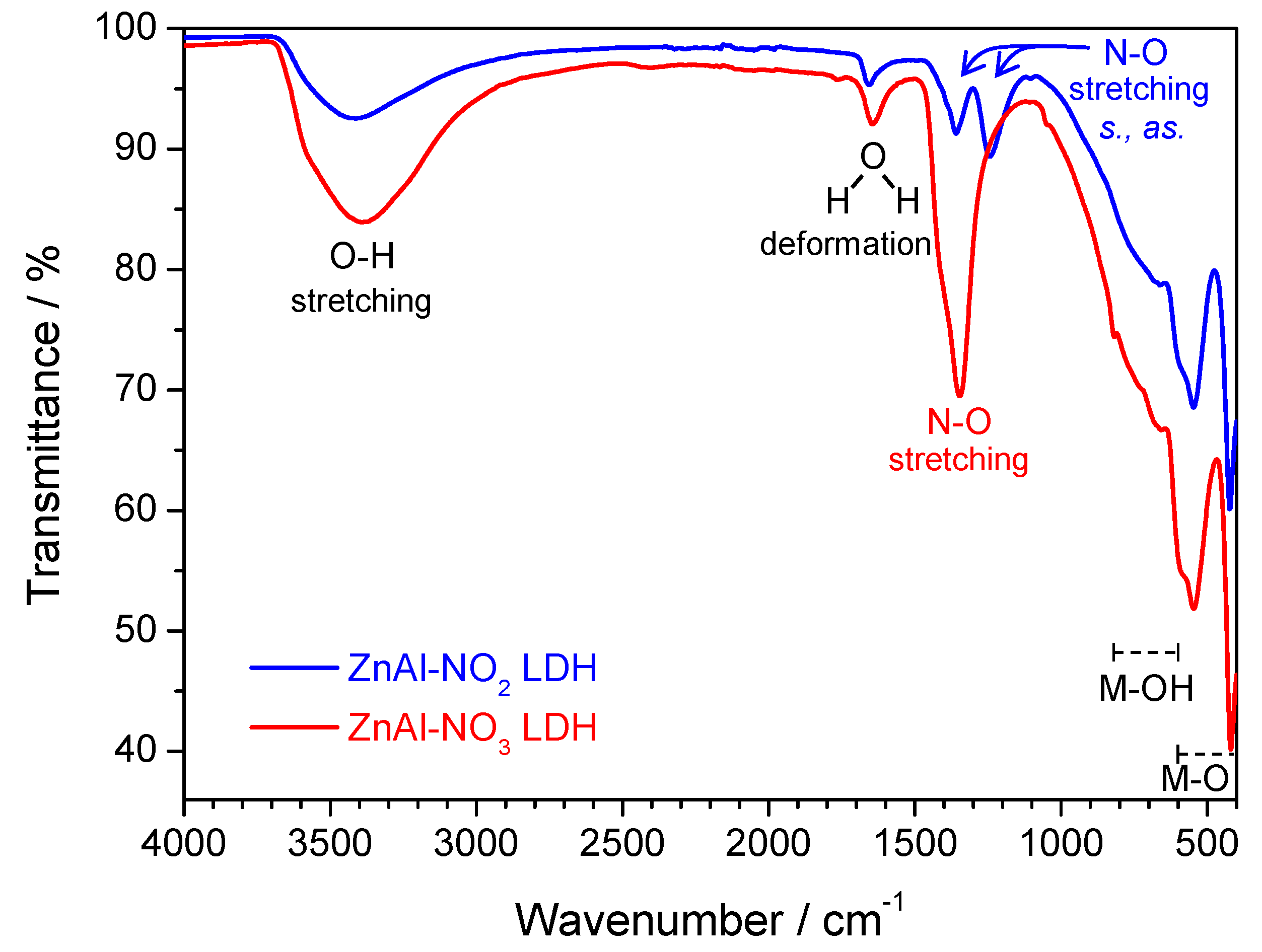
3.1. Structure and Morphology of the Synthesized ZnAl LDHs
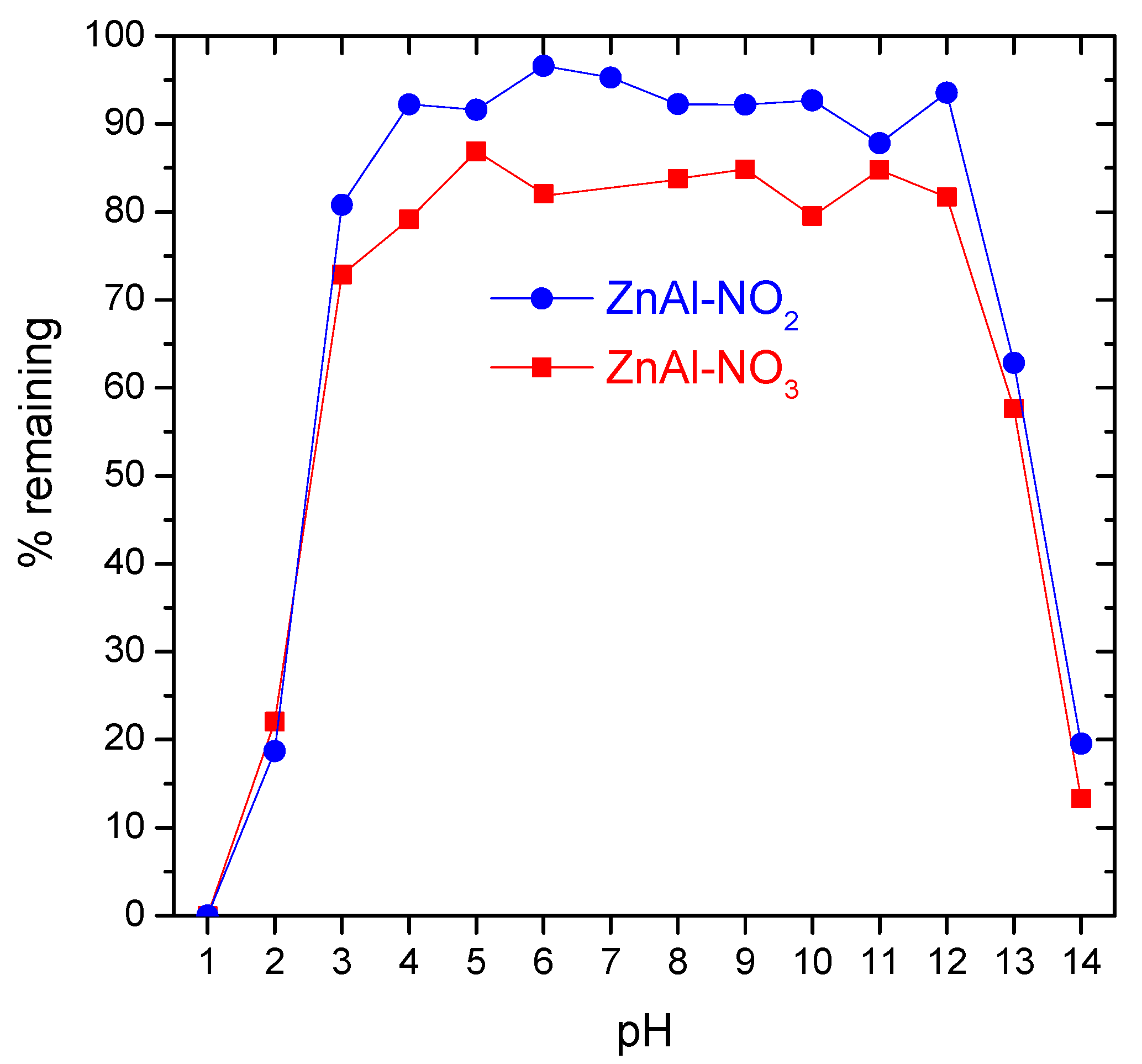
3.2. Stability of ZnAl LDH in Aqueous Solution
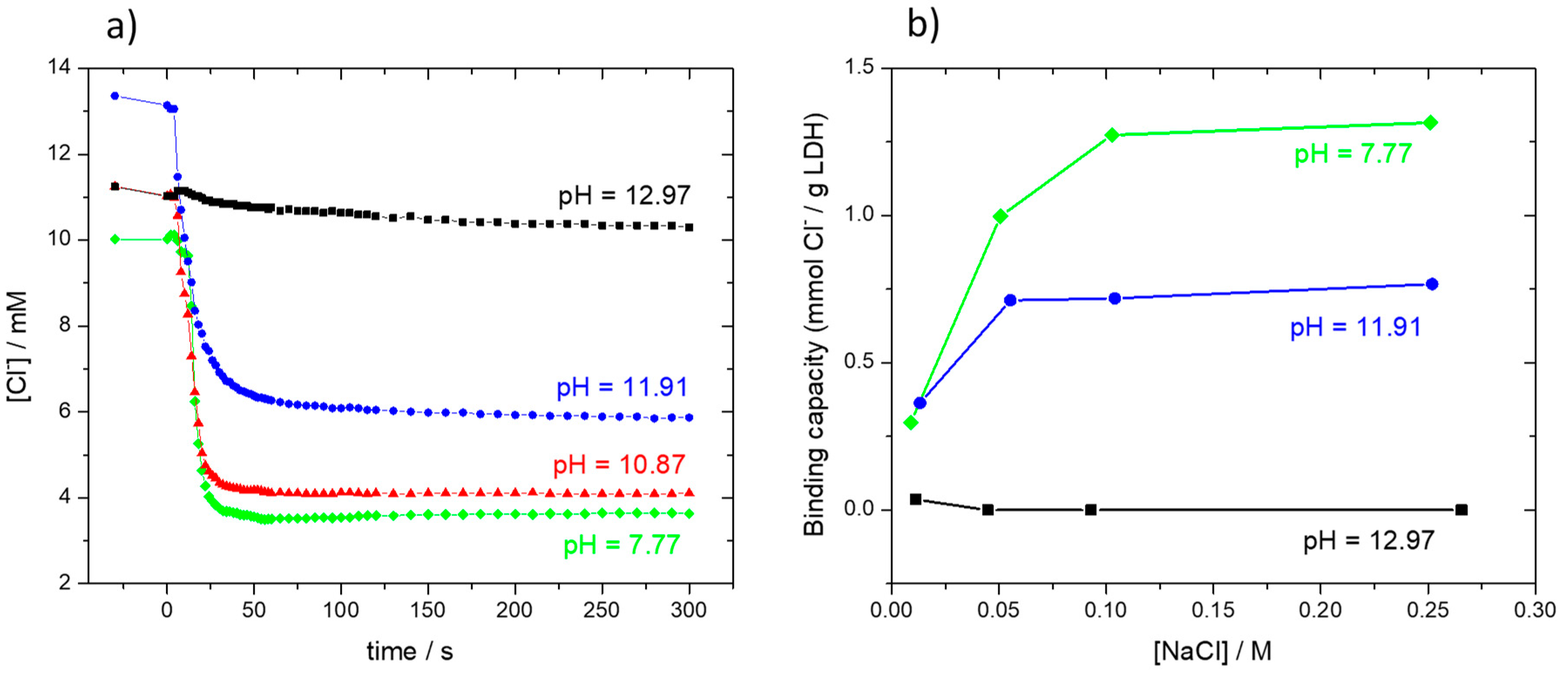
3.3. The Capacity of ZnAl LDH for Capturing Chloride Ions
3.4. Effect of ZnAl LDH on the Corrosion of Steel in Aqueous Solution
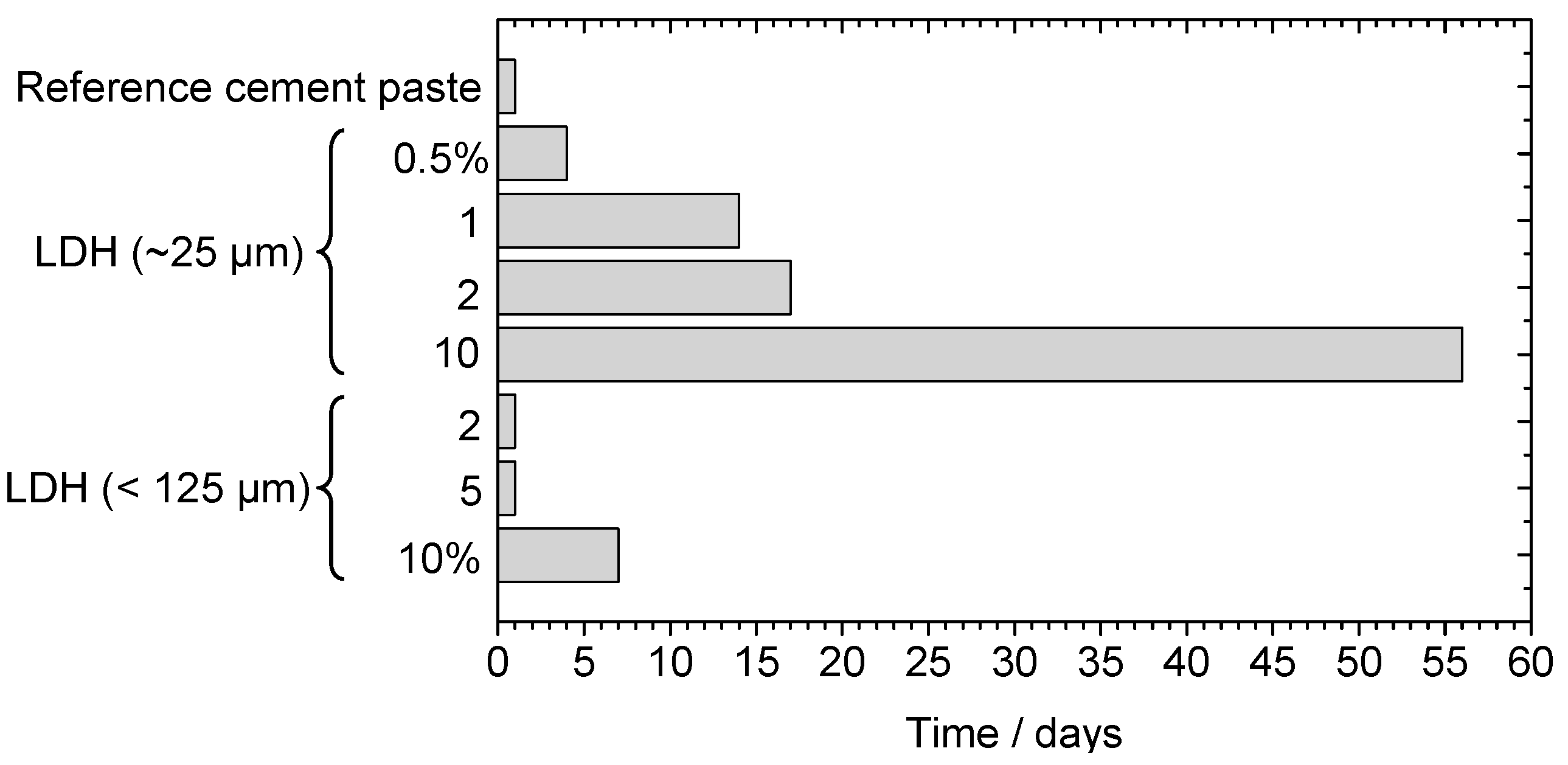
3.5. Influence of ZnAl LDH on the Hardening of Cement Paste
3.6. Impact of ZnAl LDH on the Corrosion of Steel Rebars in Mortars
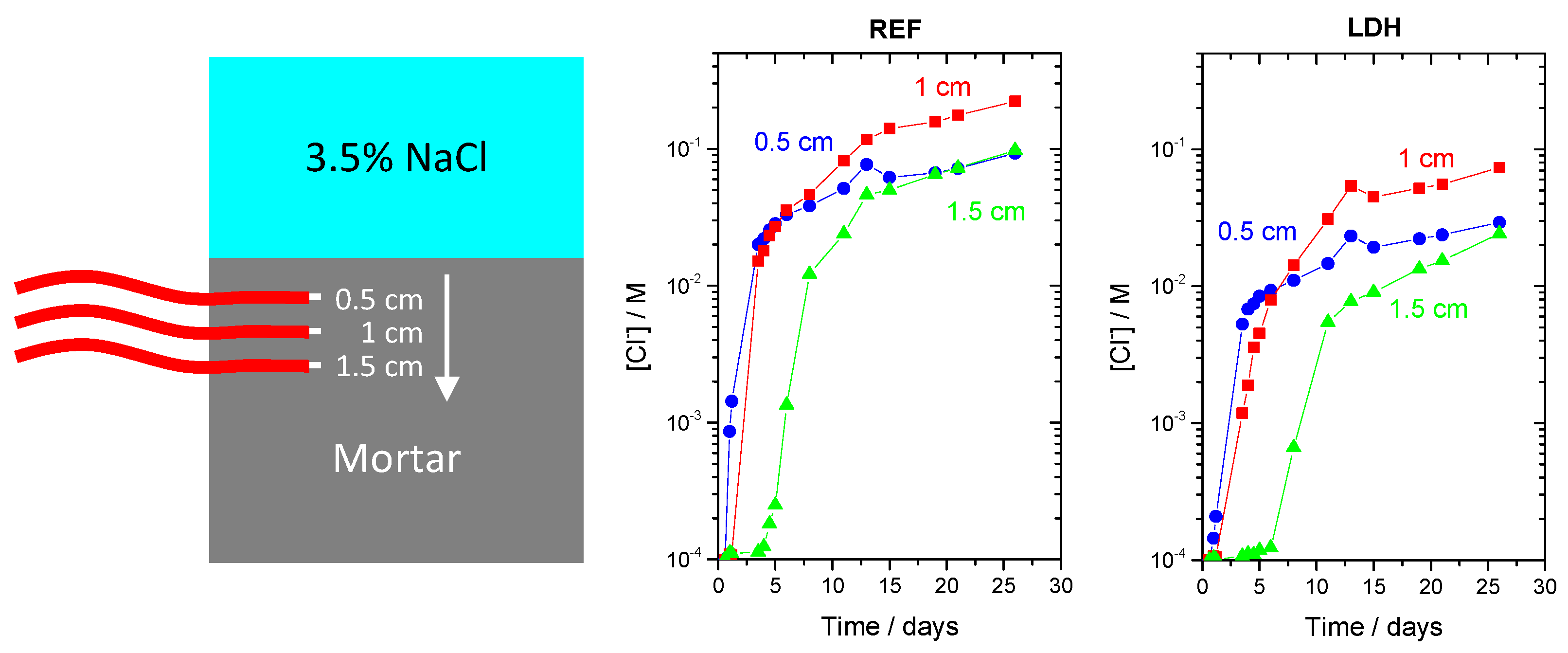
3.6.1. Chloride Sensors inside Mortar
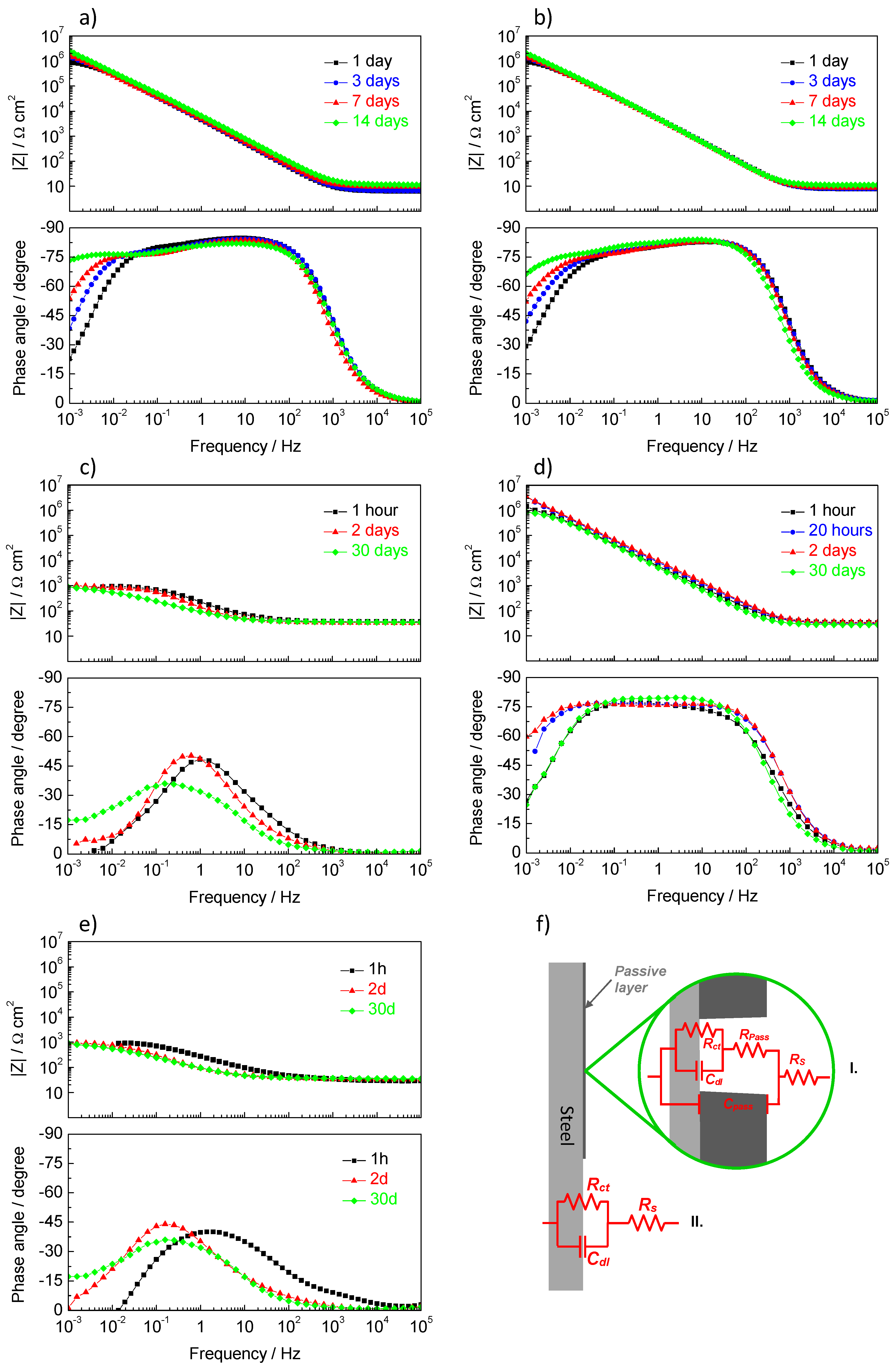
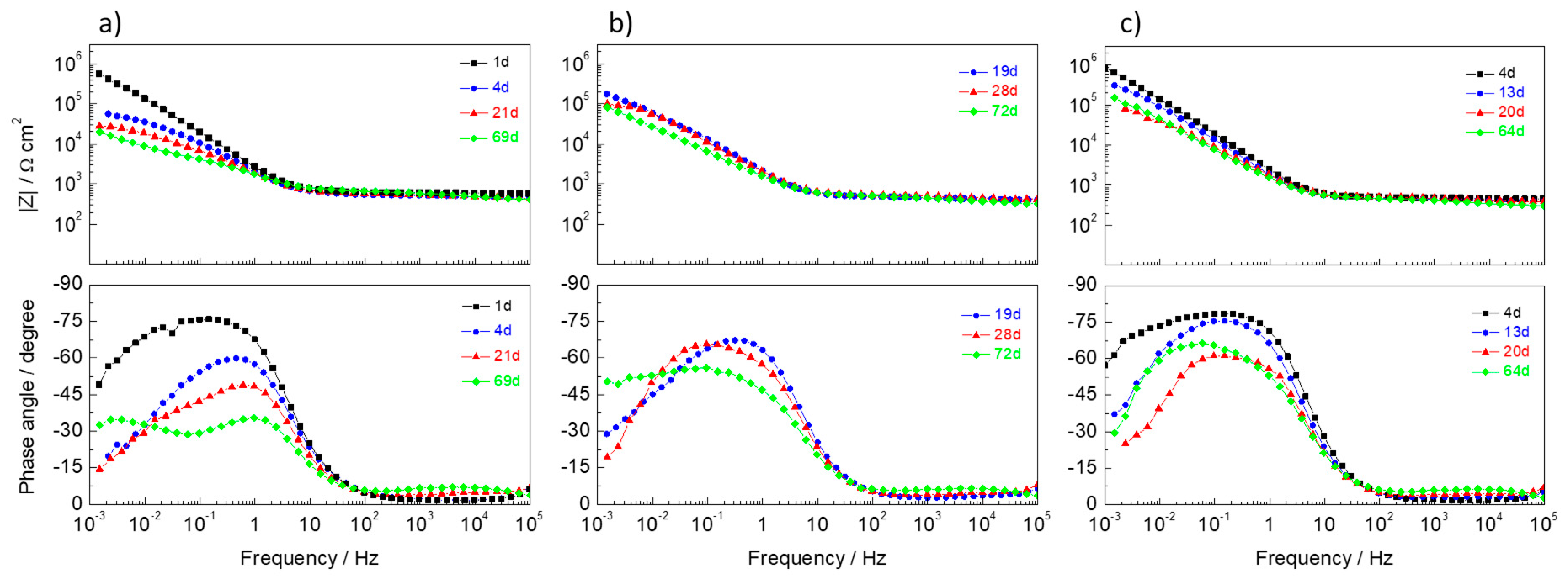
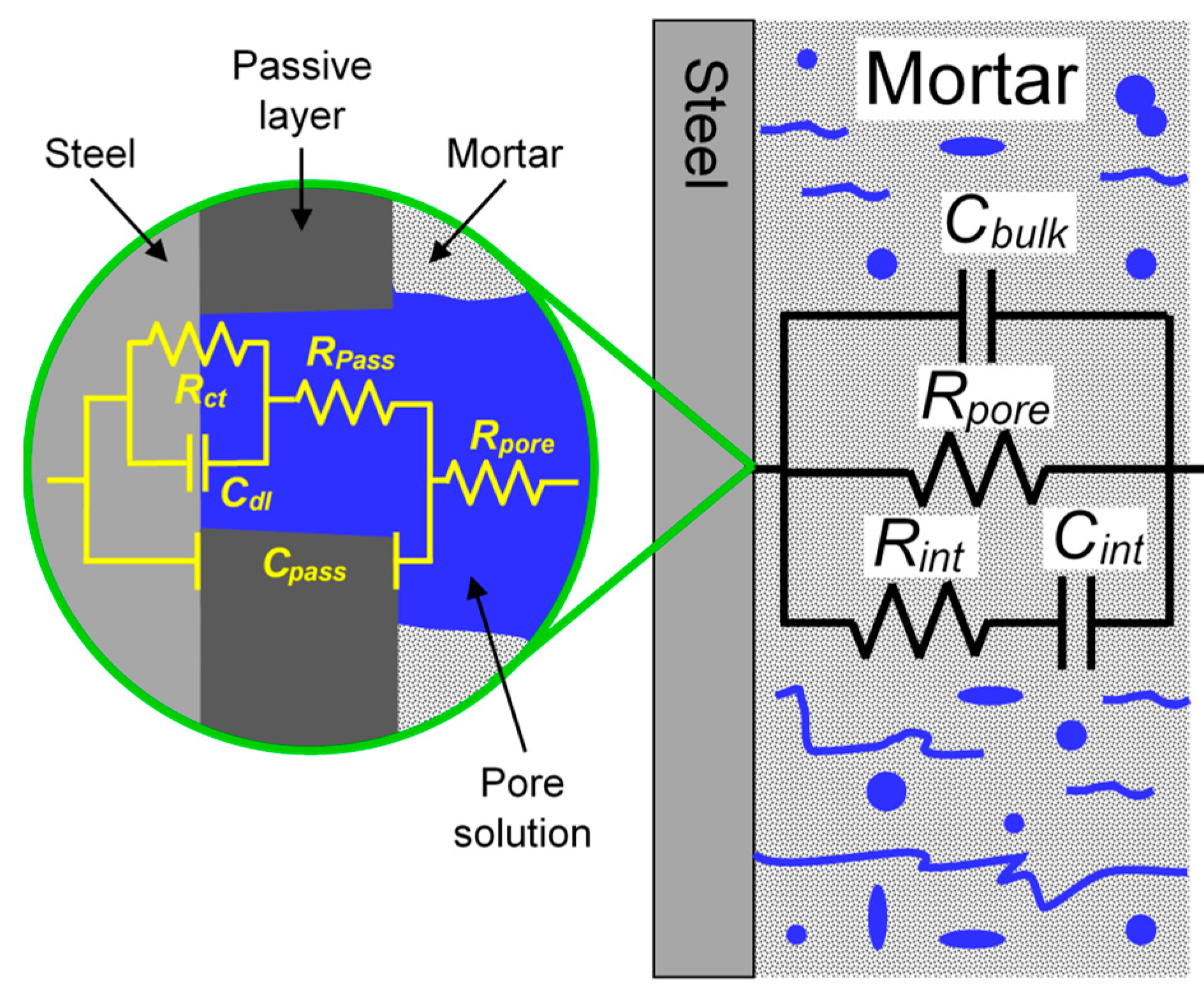
3.6.2. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy
3.7. Final Remarks
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Darwin, D.; Dolan, C.W.; Nilson, A.H. Design of Concrete Structures, 15th ed.; McGraw-Hill: New York, NY, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Bertolini, L.; Elsener, B.; Pedeferri, P.; Redaelli, E.; Polder, R. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete, Prevention, Diagnosis, Repair, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA: Weinheim, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Broomfield, J.P. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete, Understanding, Investigation and Repair, 2nd ed.; Taylor and Francis: London, UK; New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Poursaee, A. Corrosion of Steel in Concrete Structures; Woodhead Publishing: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Angst, U.; Elsener, B.; Larsen, C.K.; Vennesland, Ø. Critical chloride content in reinforced concrete—A review. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1122–1138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsener, B.; Zurich, E. Corrosion of Reinforcement in Concrete: Mechanisms, Monitoring, Inhibitors and Rehabilitation Techniques, EFC38; Raupach, M., Elsener, B., Polder, R., Mietz, J., Eds.; Woodhead Publishing Ltd.: Cambridge, UK, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Elsener, B. Corrosion Inhibitors for Steel in Concrete: State of the Art Report, EFC3; Maney Publishing: London, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, X.; Evans, D.G. Layered Double Hydroxides; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Rives, V. (Ed.) Layered Double Hydroxides: Present and Future; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Cavani, F.; Trifiro, F.; Vaccari, A. Hydrotalcite-type anionic clays: Preparation, properties and applications. Catal. Today 1991, 11, 173–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Li, F.; Evans, D.G.; Duan, X. Catalytic Applications of Layered Double Hydroxides: Recent Advances and Perspectives. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 7040–7066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedim, J.; Kuznetsova, A.; Salak, A.N.; Montemor, F.; Snihirova, D.; Pilz, M.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Zn–Al layered double hydroxides as chloride nanotraps in active protective coatings. Corros. Sci. 2012, 55, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedim, J.; Poznyak, S.K.; Kuznetsova, A.; Raps, D.; Hack, T.; Zheludkevich, M.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Enhancement of Active Corrosion Protection via Combination of Inhibitor-Loaded Nanocontainers. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 1528–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchheit, R.G.; Guan, H.; Mahajanam, S.; Wong, F. Active corrosion protection and corrosion sensing in chromate-free organic coatings. Progr. Org. Coat. 2003, 47, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tedim, J.; Zheludkevich, M.L.; Salak, A.N.; Lisenkov, A.; Ferreira, M.G.S. Nanostructured LDH-container layer with active protection functionality. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15464–15470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatematsu, H.; Sasaki, T. Repair materials system for chloride-induced corrosion of reinforcing bars. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2003, 25, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raki, L.; Beaudoin, J.J.; Mitchell, L. Layered double hydroxide-like materials: Nanocomposites for use in concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 1717–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Chen, Z.; Zhang, B.; Yu, J.; Zhang, F.; Evans, D.G. Facile preparation of pure CaAl-layered double hydroxides and their application as a hardening accelerator in concrete. Chem. Eng. J. 2009, 155, 881–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raki, L.; Alizadeh, A.R. Hydration of cement systems in the presence of novel LDH nanocomposite. Am. Concr. Inst. 2016, 312, 104–115. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Controlling the reaction kinetics of sodium carbonate-activated slag cements using calcined layered double hydroxides. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 81, 24–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, L.; Guo, J.; Tian, J.; Xu, Y.; Hu, M.; Wang, M.; Fan, J. Preparation of Ca/Al-layered double hydroxide and the influence of their structure on early strength of cement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 184, 203–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, W.; Gao, X. The effect of layered double hydroxides on the concrete resistance of chloride-ion penetration. Key Eng. Mat. 2012, 509, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kayali, O.; Khan, M.S.H.; Sharfuddin Ahmed, M. The role of hydrotalcite in chloride binding and corrosion protection in concretes with ground granulated blast furnace slag. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2012, 34, 936–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Shui, Z.; Chen, G. Influence of LDHs on chloride ion binding in cementitious materials. Key Eng. Mat. 2014, 599, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fischer, H.; Polder, R. Modified hydrotalcites as a new emerging class of smart additive of reinforced concrete for anticorrosion applications: A literature review. Mater. Corros. 2013, 64, 1066–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fischer, H.; Polder, R. Synthesis and characterization of modified hydrotalcites and their ion exchange characteristics in chloride-rich simulated concrete pore solution. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2014, 47, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Moon, J.; Bae, S.; Duan, X.; Giannelis, E.P.; Monteiro, P.M. Chloride adsorption by calcined layered double hydroxides in hardened Portland cement paste. Mater. Chem. Phys. 2014, 145, 376–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fischer, H.; Polder, R. Laboratory investigation of the influence of two types of modified hydrotalcites on chloride ingress into cement mortar. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2015, 58, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.S.H.; Kayali, O.; Troitzsch, U. Chloride binding capacity of hydrotalcite and the competition with carbonates in ground granulated blast furnace slag concrete. Mater. Struct. 2016, 49, 4609–4619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Fischer, H.; Cerezo, J.; Mol, J.M.C.; Polder, R. Modified hydrotalcites for improved corrosion protection of reinforcing steel in concrete—Preparation, characterization, and assessment in alkaline chloride solution. Mater. Corros. 2016, 67, 721–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Polder, R.; Mol, J.M.C. Modified hydrotalcites as chloride scavengers and inhibitor release agents for improved corrosion protection of reinforced concrete. Heron 2017, 62, 61–83. [Google Scholar]
- Ke, X.; Bernal, S.A.; Provis, J.L. Uptake of chloride and carbonate by Mg-Al and Ca-Al layered double hydroxides in simulated pore solutions of alkali-activated slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Lu, S.; Yao, Y. Layered double hydroxides precursor as chloride inhibitor: Synthesis, characterization, assessment of chloride adsorption performance. Materials 2018, 11, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, Z.Y.; Yu, Q.L.; Brouwers, H.J.H. Relationship between the particle size and dosage of LDHs and concrete resistance against chloride ingress. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 105, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Song, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Jiang, L.; Mei, Y.; Chen, P. Chloride removal and corrosion inhibitions of nitrate, nitrite intercalated MgAl layered double hydroxides on steel in saturated calcium hydroxide solution. Appl. Clay Sci. 2018, 163, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machner, A.; Zajac, M.; Ben Haha, M.; Kjellsen, K.O.; Geiker, M.R.; De Weerdt, K. Chloride-binding capacity of hydrotalcite in cement pastes containing dolomite and metakaolin. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 107, 163–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Yu, R.; Wang, X.; Chen, J.; Shui, Z. Evaluation and optimization of ultra-high-performance concrete (UHPC) subjected to harsh ocean environment: Towards an application of layered double hydroxides (LDHs). Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 51–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, B.; Zuo, J.; Dong, B.; Xing, F.; Luo, C. Study on the affinity sequence between inhibitor ions and chloride ions in MgAl layer double hydroxides and their effects on corrosion protection for carbon steel. Appl. Clay Sci. 2019, 180, 105–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Zhu, Q.; Su, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, A.; Xing, Z. Preparation of MgAlFe-LDHs as a deicer corrosion inhibitor to reduce corrosion of chloride ions in deicing salts. Ecotoxicol. Env. Saf. 2019, 174, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, C.W.; Jung, H.Y.; Kwon, J.H.; Jang, B.K.; Kim, J.H. Use of calcium aluminum–layered double hydroxide to control chloride ion penetration of cement-based materials. J. Struct. Integr. Maint. 2019, 4, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Chen, X.; Chen, W. Research on the carbonation of cement paste modified with layered double hydroxides. Appl. Mech. Mater. 2012, 174–177, 706–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Chen, W.; Ma, J.; Shui, Z. Influence of layered double hydroxides on microstructure and carbonation resistance of sulphoaluminate cement concrete. Const. Build. Mat. 2013, 48, 601–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Dong, S.; Zheng, D.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Du, R.; Song, G.; Lin, C. Multifunctional inhibition based on layered double hydroxides to comprehensively control corrosion of carbon steel in concrete. Corros. Sci. 2017, 126, 166–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shui, Z.H.; Yu, R.; Chen, Y.X.; Duan, P.; Ma, J.T.; Wang, X.P. Improvement of concrete carbonation resistance based on a structure modified Layered Double Hydroxides (LDHs): Experiments and mechanism analysis. Const. Build. Mat. 2018, 176, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, P.; Yan, C.; Zhou, W. Effects of calcined layered double hydroxides on carbonation of concrete containing fly ash. Const. Build. Mat. 2018, 160, 725–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wu, B.; Luo, C.; Dong, B.; Xing, F. Preparation of MgAl layered double hydroxides intercalated with nitrite ions and corrosion protection of steel bars in simulated carbonated concrete pore solution. Corros. Sci. 2019, 152, 120–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Duan, P.; Ren, D.; Zhou, W. Effects of layered double hydroxides incorporation on carbonation resistance of cementitious materials. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2019, 8, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Dong, S.; Zhang, F.; Lin, J.; Wang, C.; Lin, C. A composite corrosion inhibitor of MgAl layered double hydroxides co-intercalated with hydroxide and organic anions for carbon steel in simulated carbonated concrete pore solutions. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, C3106–C3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Xu, J.; Jiang, L.; Tan, Q. Enhancing corrosion resistance of epoxy coating on steel reinforcement by aminobenzoate intercalated layered double hydroxides. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 134, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Nie, S.; Li, H.; Dai, Y.; Pang, L.; Li, C.; Zhang, A. Field evaluation of LDHs effect on the aging resistance of asphalt concrete after four years of road service. Const. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 192–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Dong, C.; Wang, G.; Cheng, X.; Li, X. Zn-Al-NO2 layered double hydroxide as a controlled-release corrosion inhibitor for steel reinforcements. Mater. Lett. 2019, 236, 517–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Y.; Zheng, D.; Luo, J.; Zhang, F.; Dong, S.; Pan, J.; Lin, C. Insight into the fabrication of ZnAl layered double hydroxides intercalated with organic anions and their corrosion protection of steel reinforced concrete. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2019, 166, C617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prevot, V.; Forano, C.; Besse, J.P.; Abraham, F. Syntheses and Thermal and Chemical Behaviors of Tartrate and Succinate Intercalated Zn3Al and Zn2Cr Layered Double Hydroxides. Inorg. Chem. 1998, 37, 4293–4301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvão, T.L.P.; Neves, C.S.; Caetano, A.P.F.; Maia, F.; Mata, D.; Malheiro, E.; Ferreira, M.J.; Bastos, A.C.; Salak, A.N.; Gomes, J.R.B.; et al. Control of crystallite and particle size in the synthesis of layered double hydroxides: Macromolecular insights and a complementary modeling tool. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2016, 468, 86–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S. Anion-exchange properties of hydrotalcite-like compounds. Clays Clay Miner. 1983, 31, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Shui, Z.; Chen, W.; Chen, G. Chloride binding of synthetic Ca–Al–NO3 LDHs in hardened cement paste. Const. Build. Mater. 2015, 93, 1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddi, B.A.J. Why is saline so acidic (and does it really matter?). Int. J. Med. Sci. 2013, 10, 747–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, F.M.M.; Hering, J.G. Principles and Applications of Aquatic Chemistry; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 1993; p. 157. [Google Scholar]
- Orazem, M.E.; Tribollet, B. Electrochemical Impedance Spectroscopy, 2nd ed.; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Brug, G.J.; van den Eeden, A.L.G.; Sluyters-Rehbach, M.; Sluyters, J.H. The analysis of electrode impedances complicated by the presence of a constant phase element. J. Electroanal. Chem. 1984, 176, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, P.; Bensted, J. Structure and Performance of Cement; Jawed, I., Skalny, J., Young, J.F., Barnes, P., Eds.; Applied Science Publishers: Barking, UK, 1983; p. 237. [Google Scholar]
- Stephan, D.; Maleki, H.; Knöfel, D.; Eber, B.; Härdtl, R. Influence of Cr, Ni, and Zn on the properties of pure clinker phases: Part, I. C3S. Cem. Concr. Res. 1999, 29, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asavapisit, S.; Fowler, G.; Cheeseman, C.R. Solution chemistry during cement hydration in the presence of metal hydroxide wastes. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trezza, M.A. Hydration study of ordinary Portland cement in the presence of zinc ions. Mater. Res. 2007, 10, 331–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrade, C.; Dıez, J.M.; Alonso, C. Mathematical modeling of a concrete surface “skin effect” on diffusion in chloride contaminated media. Adv. Cem. Bas. Mater. 1997, 6, 39–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandberg, P.; Tang, L.; Andersen, A. Recurrent studies of chloride ingress in uncracked marine concrete at various exposure times and elevations. Cem. Conc. Res. 1998, 28, 1489–1503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, K.; Orsáková, D.; Müller, A.C.A.; Larsen, C.K.; Pedersen, B.; Geiker, M.R. Towards the understanding of chloride profiles in marine exposed concrete, impact of leaching and moisture content. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 120, 418–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, M.; Merino, P.; Miranda, A.; Novoa, X.R.; Sanchez, I. Impedance spectroscopy study of hardened Portland cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 881–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, L.; Meng, W.; Teng, L.; Khayat, K.H. Effect of steel fibers with galvanized coatings on corrosion of steel bars embedded in UHPC. Compos. Part B Eng. 2019, 177, 107445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| pH | Composition | Time | Rs (Ω cm2) | Y0,pass (F cm−2 sn−1) | npass | Cpass (μF cm−2) | Rpass (Ω cm2) | Y0,dl (F cm−2 sn−1) | ndl | Cdl (μF cm−2) | Rct (Ω cm2) | Χ2/10−4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 13 | Blank | 1d | 6.7 | 3.07 × 10−5 | 0.968 | 23.1 | 50.53 | 6.86 × 10−6 | 0.701 | 0.23 | 1.09 × 106 | 0.83 |
| 3d | 6.9 | 3.55 × 10−5 | 0.946 | 22.1 | 80200 | 9.44 × 10−6 | 0.794 | 8.69 | 2.00 × 106 | 0.37 | ||
| 7d | 9.8 | 3.45 × 10−5 | 0.917 | 16.7 | 81882 | 1.14 × 10−5 | 0.793 | 11.1 | 3.87 × 106 | 0.36 | ||
| 14d | 11.7 | 2.76 × 10−5 | 0.921 | 13.8 | 220140 | 5.95 × 10−6 | 0.740 | 6.52 | 4.27 × 107 | 0.27 | ||
| 0.5% LDH-NO2 | 1d | 8.0 | 3.17 × 10−5 | 0.945 | 19.6 | 19353 | 8.37 × 10−6 | 0.680 | 3.53 | 1.34 × 106 | 0.13 | |
| 3d | 8.2 | 3.16 × 10−5 | 0.950 | 20.4 | 19250 | 8.91 × 10−6 | 0.676 | 3.81 | 2.47 × 106 | 0.25 | ||
| 7d | 8.9 | 3.29 × 10−5 | 0.947 | 20.9 | 28134 | 1.03 × 10−5 | 0.701 | 6.02 | 3.98 × 106 | 0.39 | ||
| 14d | 11.3 | 3.24 × 10−5 | 0.950 | 21.4 | 54358 | 6.03 × 10−6 | 0.650 | 3.32 | 1.80 × 107 | 0.34 | ||
| 6 | Blank | 1h | 37.3 | − | − | − | − | 1.11 × 10−3 | 0.708 | 294 | 1049 | 3.9 |
| 2d | 35.5 | − | − | − | − | 1.84 × 10−3 | 0.750 | 730 | 938 | 8.8 | ||
| 30d | 38.0 | − | − | − | − | 4.00 × 10−3 | 0.600 | 1085 | 500 | 10 | ||
| 0.5% LDH-NO2 | 1h | 33.4 | 2.93 × 10−5 | 0.867 | 10.1 | 5063 | 3.46 × 10−6 | 0.925 | 2.50 | 1.21 × 106 | 4.2 | |
| 20h | 31.2 | 2.20 × 10−5 | 0.870 | 7.41 | 92184 | 2.27 × 10−6 | 0.898 | 1.89 | 5.30 × 106 | 3.4 | ||
| 2d | 34.5 | 1.86 × 10−5 | 0.878 | 6.70 | 67366 | 3.44 × 10−6 | 0.814 | 2.45 | 9.21 × 106 | 1.4 | ||
| 30d | 30.0 | 2.50 × 10−5 | 0.868 | 8.37 | 9089 | 3.40 × 10−6 | 0.915 | 2.46 | 1.30 × 106 | 4 | ||
| 0.5% LDH-NO3 | 1h | 32.5 | 3.22 × 10−4 | 0.645 | 16.2 | 23.5 | 6.82 × 10−4 | 0.595 | 40.4 | 1347 | 3 | |
| 2d | 35.0 | 1.84 × 10−3 | 0.681 | 381 | 41.1 | 2.43 × 10−3 | 0.733 | 940 | 925 | 1.4 | ||
| 30d | 35.5 | 1.92 × 10−3 | 0.680 | 382 | 32 | 2.89 × 10−3 | 0.707 | 1063 | 1002 | 8 |
| System | Time | Rpore (Ω cm2) | Y0,pass (F cm−2 sn−1) | npass | Cpass (μF cm−2) | Rpass (Ω cm2) | Y0,dl (F cm−2 sn−1) | ndl | Cdl (μF cm−2) | Rct (Ω cm2) | Χ2/10−4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 1d | 851 | 4.30 × 10−5 | 0.980 | 40.2 | 802721 | − | − | − | − | 2.1 |
| 4d | 518 | 1.19 × 10−4 | 0.810 | 61.6 | 30565 | 1.85 × 10−4 | 0.598 | 409 | 4.22 × 104 | 5 | |
| 21d | 589 | 1.24 × 10−4 | 0.845 | 75.2 | 6515 | 2.50 × 10−4 | 0.636 | 293 | 2.80 × 104 | 0.9 | |
| 69d | 661 | 1.59 × 10−4 | 0.774 | 78.6 | 3860 | 7.73 × 10−4 | 0.615 | 1457 | 4.61 × 104 | 1 | |
| LDH-NO3 | 19d | 468 | 1.07 × 10−4 | 0.854 | 63.9 | 75078 | 2.04 × 10−4 | 0.902 | 260 | 1.21 × 105 | 16 |
| 28d | 524 | 1.22 × 10−4 | 0.790 | 58.2 | 39152 | 2.88 × 10−5 | 0.942 | 28.3 | 8.47 × 104 | 1.8 | |
| 72d | 481 | 1.97 × 10−4 | 0.730 | 81.4 | 15423 | 5.42 ×10−5 | 0.460 | 43.3 | 1.12 × 106 | 2.4 | |
| LDH-NO2 | 4d | 474 | 5.17 × 10−5 | 0.987 | 49.2 | 998436 | − | − | − | − | 2 |
| 13d | 444 | 1.12 × 10−4 | 0.876 | 73.3 | 402510 | − | − | − | − | 3 | |
| 20d | 491 | 1.37 × 10−4 | 0.827 | 77.4 | 17441 | 4.56 × 10−5 | 0.658 | 36.5 | 8.00 × 104 | 0.7 | |
| 64d | 450 | 1.63 × 10−4 | 0.808 | 86.9 | 15241 | 3.40 × 10−6 | 0.936 | 40.2 | 1.79 × 105 | 0.8 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gomes, C.; Mir, Z.; Sampaio, R.; Bastos, A.; Tedim, J.; Maia, F.; Rocha, C.; Ferreira, M. Use of ZnAl-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) to Extend the Service Life of Reinforced Concrete. Materials 2020, 13, 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071769
Gomes C, Mir Z, Sampaio R, Bastos A, Tedim J, Maia F, Rocha C, Ferreira M. Use of ZnAl-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) to Extend the Service Life of Reinforced Concrete. Materials. 2020; 13(7):1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071769
Chicago/Turabian StyleGomes, Celestino, Zahid Mir, Rui Sampaio, Alexandre Bastos, João Tedim, Frederico Maia, Cláudia Rocha, and Mário Ferreira. 2020. "Use of ZnAl-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) to Extend the Service Life of Reinforced Concrete" Materials 13, no. 7: 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071769
APA StyleGomes, C., Mir, Z., Sampaio, R., Bastos, A., Tedim, J., Maia, F., Rocha, C., & Ferreira, M. (2020). Use of ZnAl-Layered Double Hydroxide (LDH) to Extend the Service Life of Reinforced Concrete. Materials, 13(7), 1769. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13071769







