Influence of Monomer Ratios on Molecular Weight Properties and Dispersing Effectiveness in Polycarboxylate Superplasticizers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Preparation of 52IPEG Series PCE Polymers
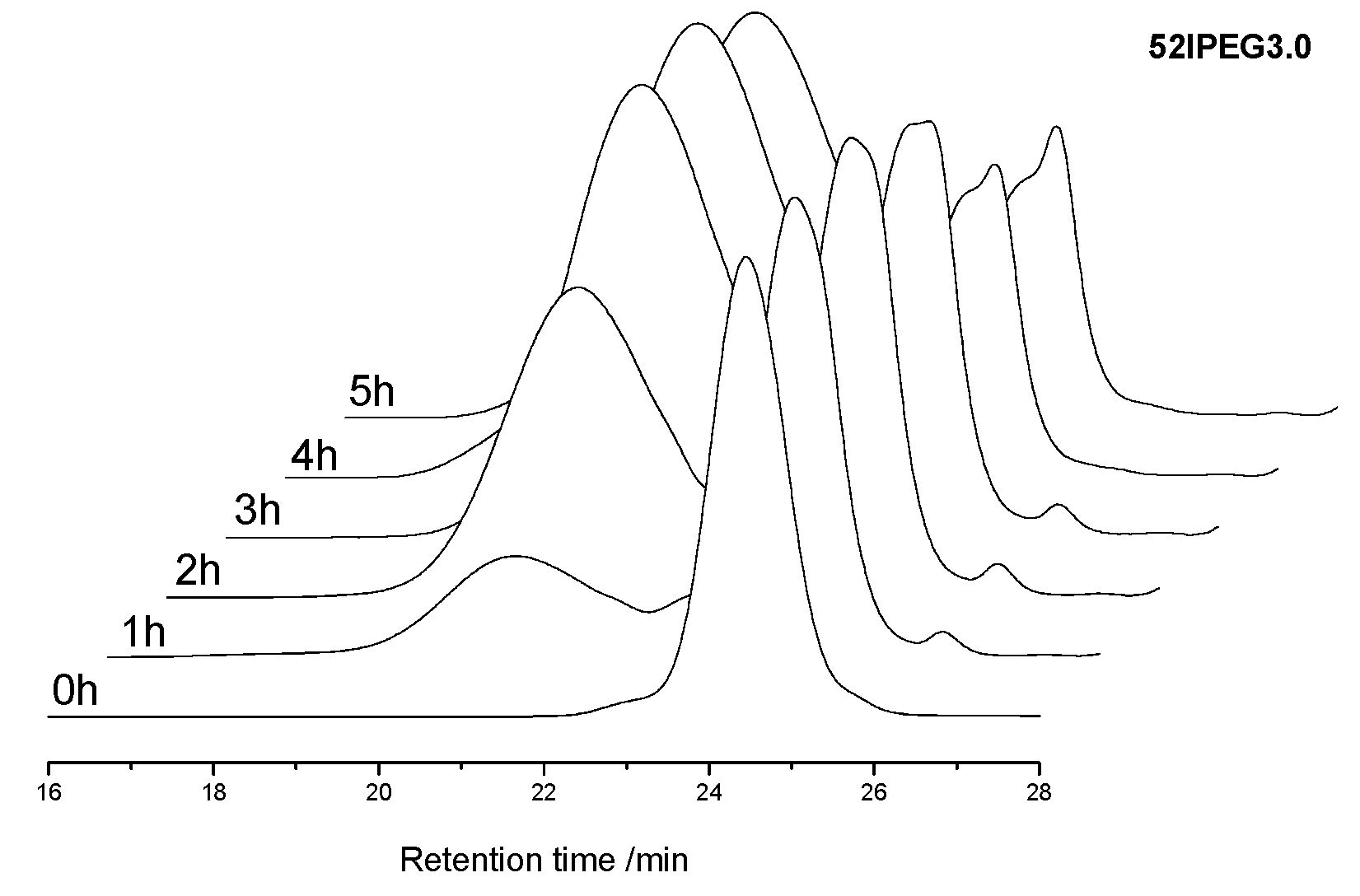
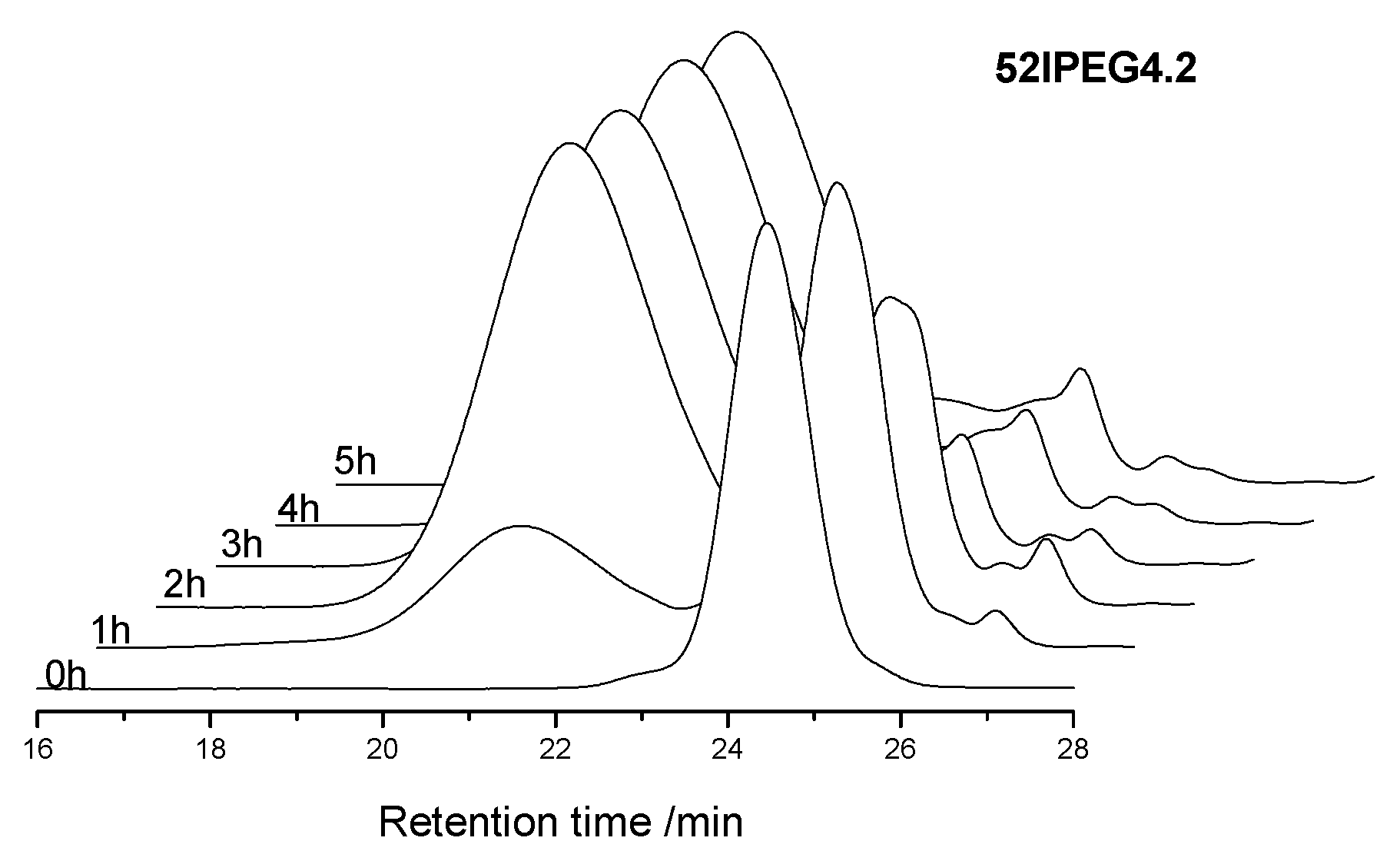
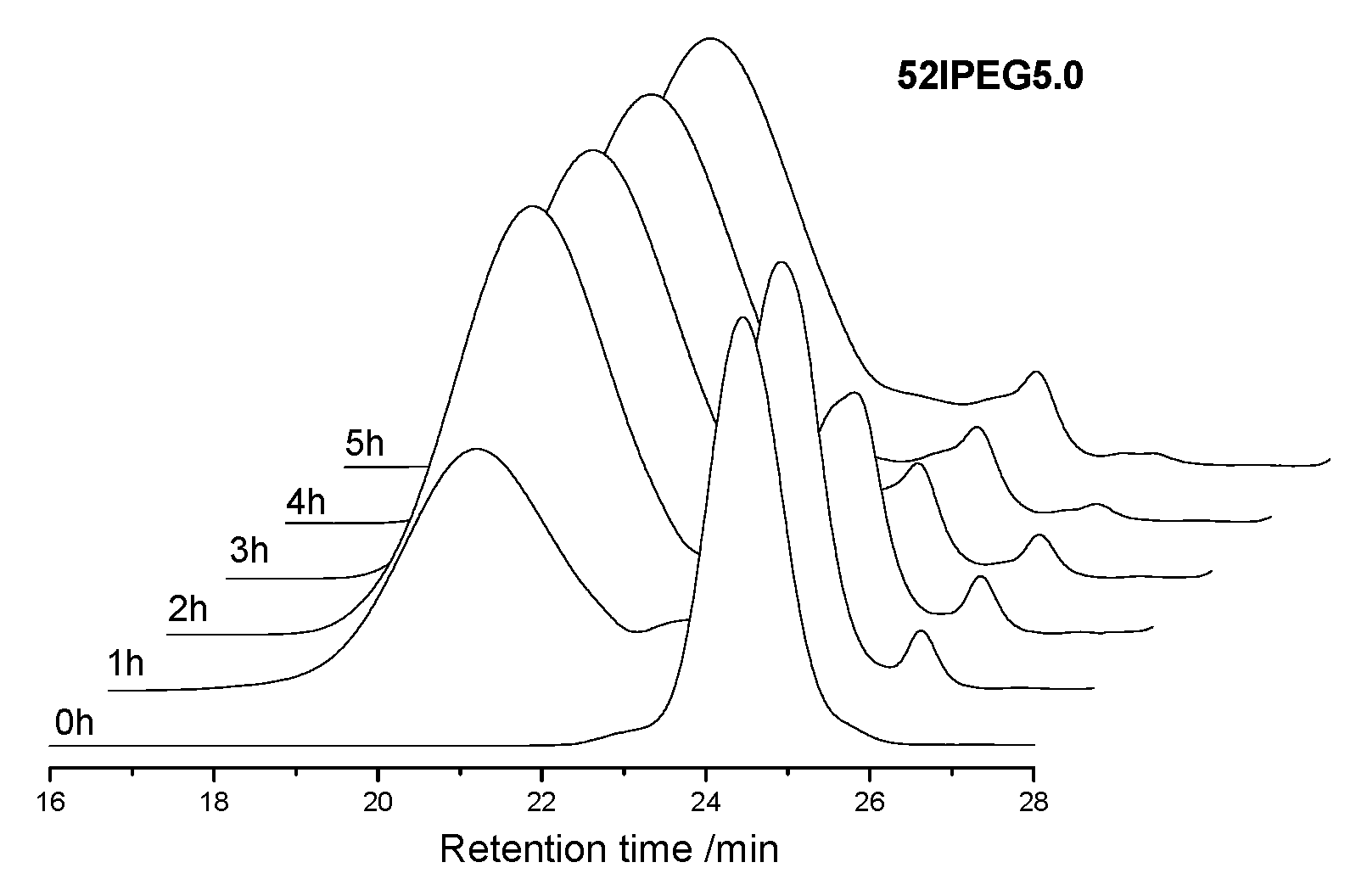
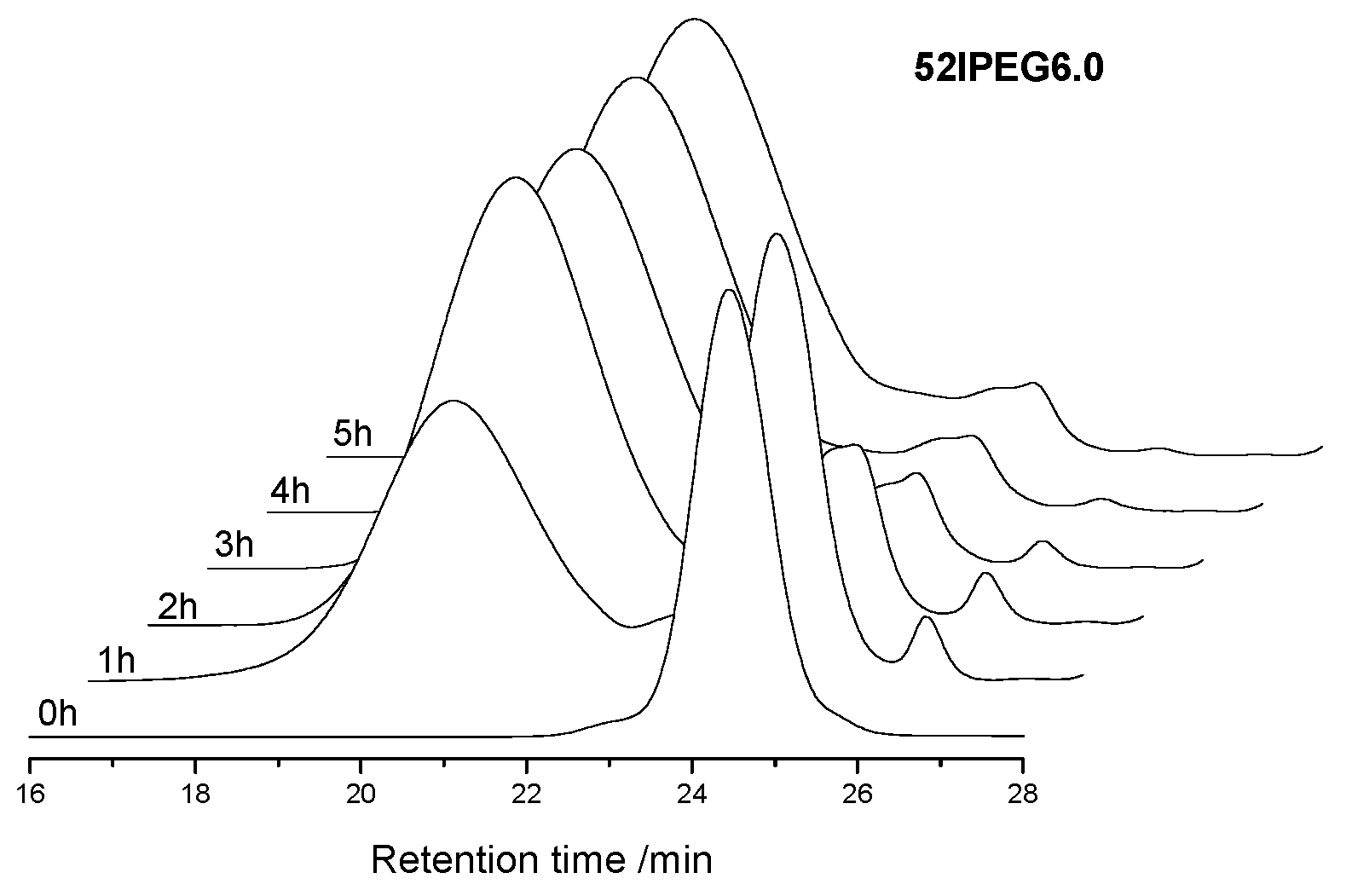
2.2.2. Size Exclusion Chromatography
2.2.3. Fluidity of Cement Paste
3. Results
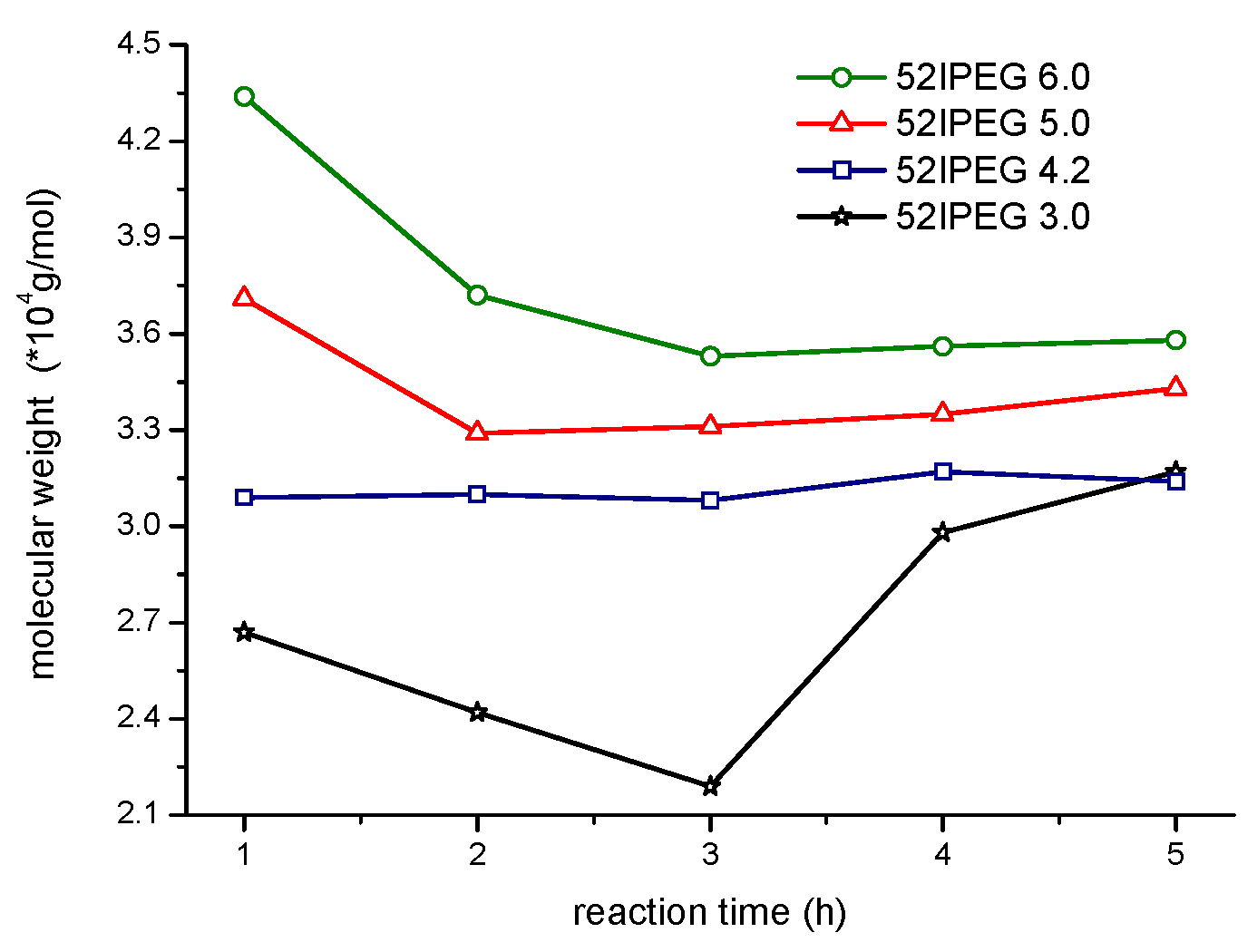
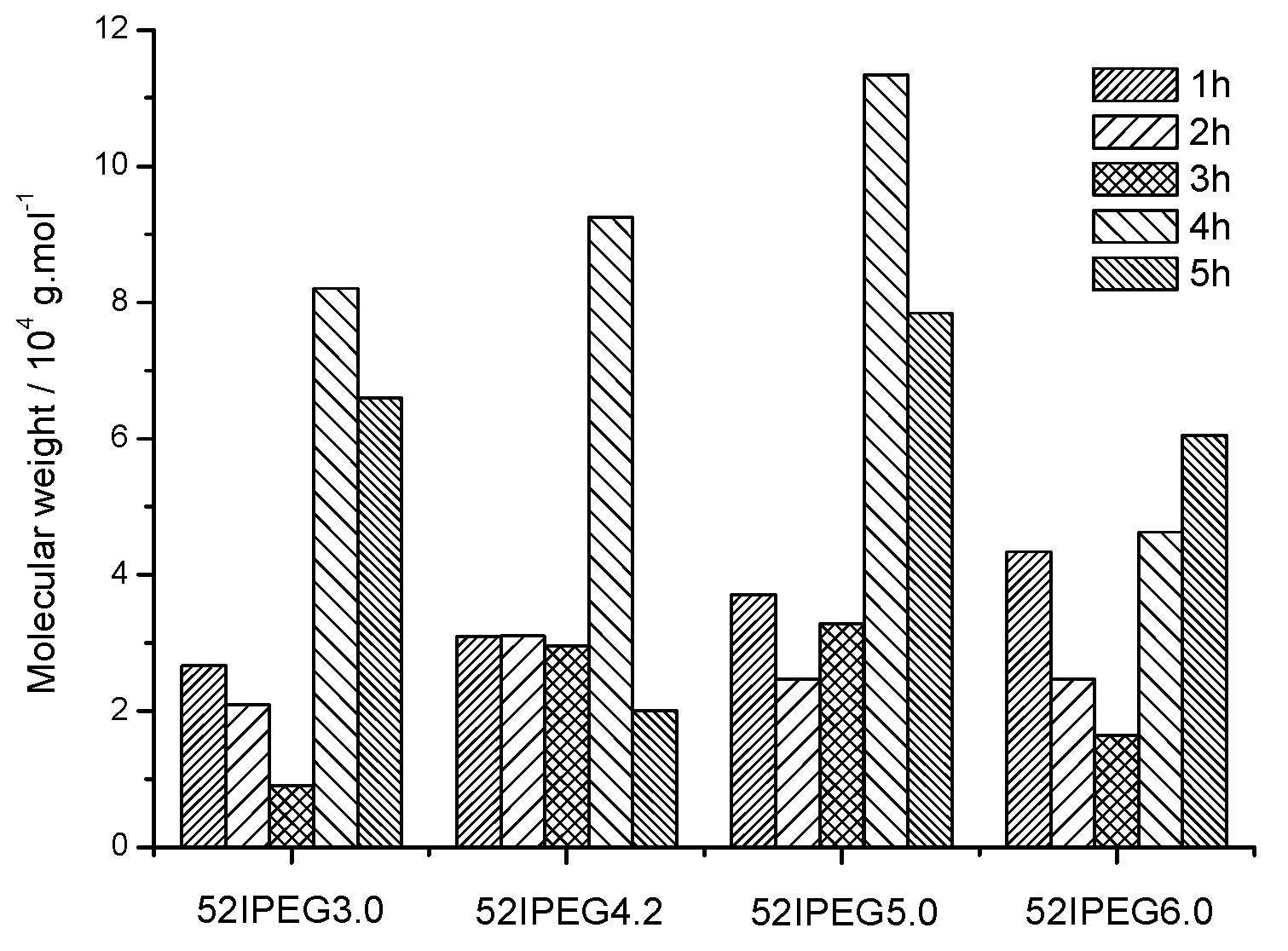
3.1. Molecular Properties over Time
3.2. Molecular Properties Comparision
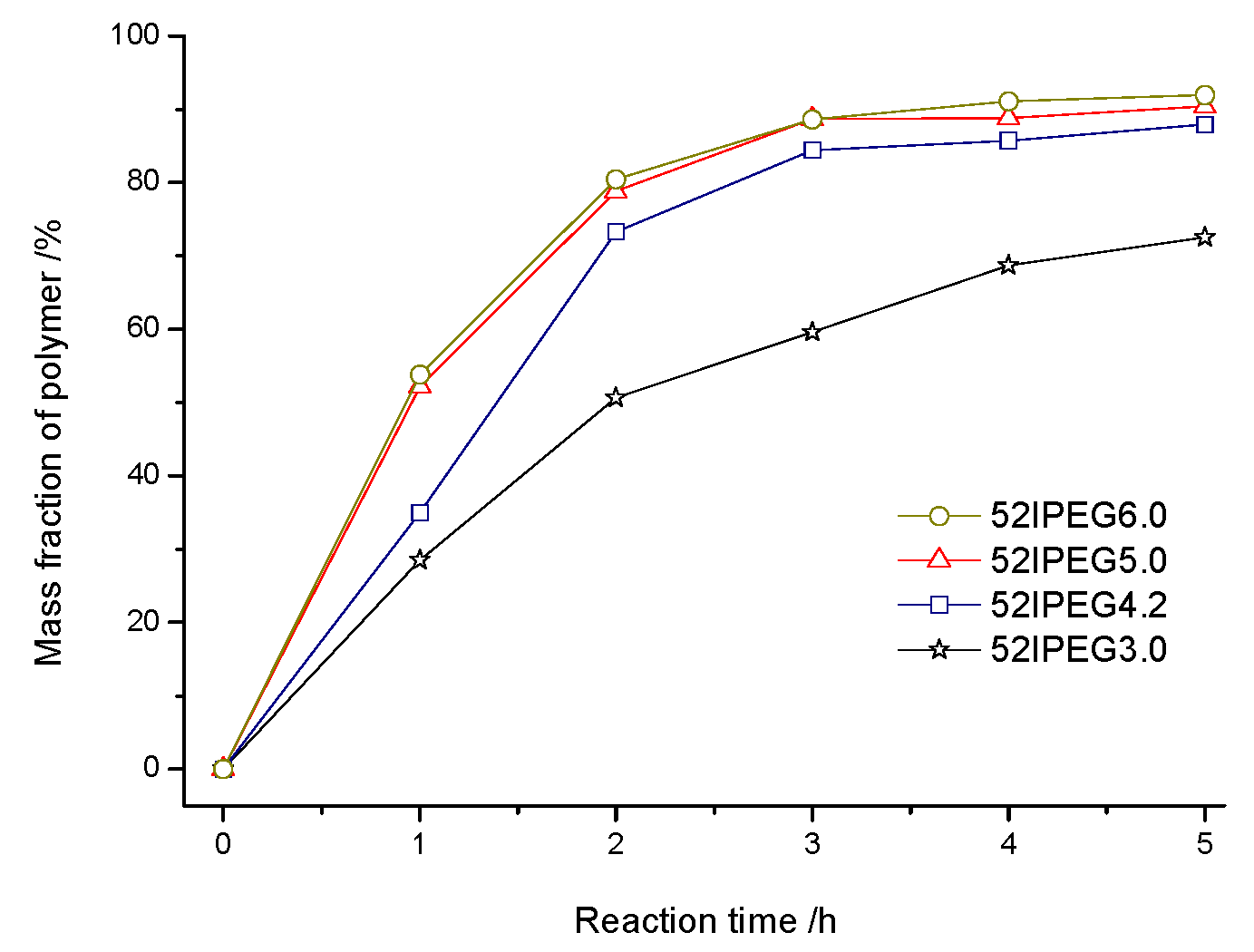
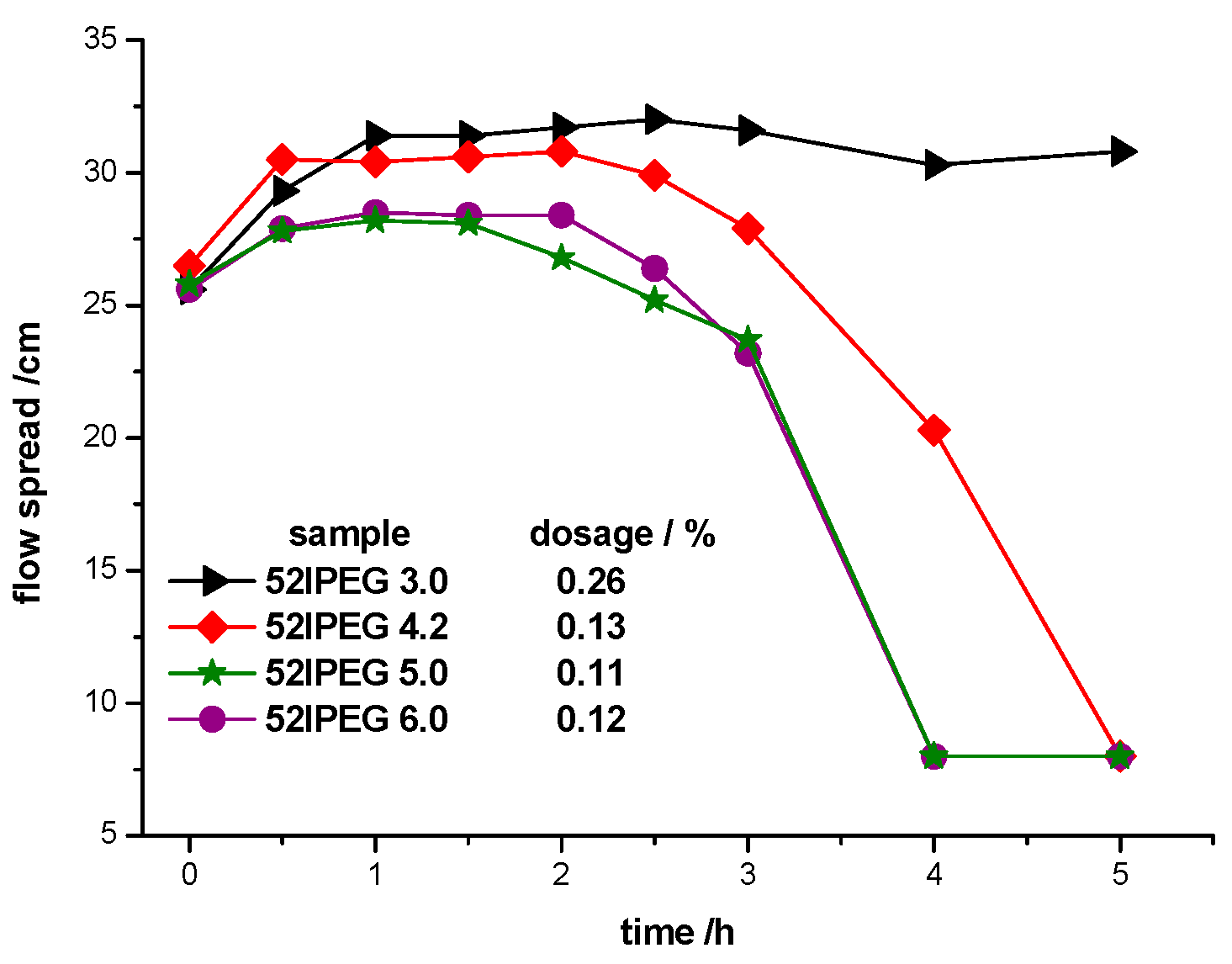
3.3. Dispersing Effectiveness of 52IPEGs
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Feneuil, B.; Pitois, O.; Roussel, N. Effect of surfactants on the yield stress of cement paste. Cem. Concr. Res. 2017, 100, 32–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, X.M.; Hou, S.S.; Shi, Z.H. Influences of functional monomers on performance of polycarboxylate superplasticizers. J. Build. Mater. 2014, 17, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Kirby, G.H.; Lewis, J.A. Comb polymer architecture effects on the rheological property evolution of concentrated cement suspensions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 87, 1643–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalas, F.; Nonat, A.; Pourchet, S. Tailoring the anionic function and the superplasticizers to improve their adsorption. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 67, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Hirsch, C. Impact of zeta potential of early cement hydration phases on superplasticizer adsorption. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 537–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamad, K.; Hanehara, S. Working mechanism of polycarboxylate superplasticizer considering the chemical structure and cement characteristics. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Durban, South Africa, 11–16 May 2003; pp. 538–548. [Google Scholar]
- Zingg, A.; Winnefeld, F.; Holzer, L.; Pakusch, J.; Becker, S.; Gauckler, L. Adsorption of polyelectrolytes and its influence on the rheology, zeta potential, and microstructure of various cement and hydrate phases. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2008, 323, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winnefeld, F.; Becker, S.; Pakusch, J. Effects of the molecular architecture of comb-shaped superplasticizers on their performance in cementitious systems. Cem. Concr. Comp. 2007, 29, 251–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Li, H.Q.; Ilg, M. Amicrostructural analysis of isoprenol ether-based polycarboxylates and the impact of structural motifs on the dispersing effectiveness. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 84, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saka, E.; Kawakam, A.; Daimo, M. Dispersion mechanisms of comb type superplasticizers containing grafted poly(ethylene oxide)chains. Macromol. Symp. 2001, 175, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirby, G.H.; Harris, D.J.; Li, Q.; Lewis, J.A. Poly(acrylic acid)–poly(eth-ylene oxide)comb polymer effects on BaTiO3nano particle suspension stability. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2004, 87, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kjeldsen, A.M.; Flatt, R.J.; Bergström, L. Relating the molecular structure of comb-type superplasticizers to the compression rheology of MgO suspensions. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1231–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchon, D.; Juilland, P.; Gallucc, E. Molecular and submolecular scale effects of comb-copolymers on tri-calcium silicate reactivity: Towardmolecular design. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 100, 817–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuart, M.C.; Scheutjens, J.M.H.M.; Fleer, G.J. Polydispersity effects and the interpretation of polymer adsorption isotherms. J. Polym. Sci. Polym. Phys. 1980, 18, 559–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kauppi, A.; Andersson, K.M.; Bergström, L. Probing the effect of superplasticizer adsorption on the surface forces using the colloidal probe AFM technique. Cem. Concr. Res. 2005, 35, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plank, J.; Sachsenhauser, B.; Reese, J. Experimental determination of the thermodynamic parameters affecting the adsorption behaviour and dispersion effectiveness of PCE superplasticizers. Cem. Concr. Res. 2012, 40, 699–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.Y.A.; Adams, W.J.; Schennach, R. A review of cement- superplasticizer interactions and their models. Adv. Cem. Res. 2000, 12, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.C. The Analysis of Influence of Different Functional Groups on the Hydration of Cement. Ph.D. Thesis, TSinghua University, Beijing, China, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Dalas, F.; Pourchet, S.; Nonat, A.; Rinaldi, D.; Sabio, S.; Mosquet, M. Fluidizing efficiency of comb-like superplasticizers: The effect of the anionic function, the side chain length and the grafting degree. Cem. Concr. Res. 2015, 71, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.M.; Lu, Z.C.; Lu, F. Effect of side chain density of comb-shaped structure on performance of polycarboxylate superplasticizer. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2012, 11, 1570–1575. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.M.; Lu, Z.C.; Lu, F. Effect of backbone length on properties of comb-shaped structure polycarboxylate superplasticizer. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2013, 11, 1534–1539. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, B.L.; Klier, J. Determination of monomer reactivity ratios for copolymerizations of methacrylic acid with poly (ethylene glycol) monomethacrylate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 1998, 68, 1019–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, K.; Ogawa, S.; Hanehara, S. Controlling of the adsorption and dispersing force of polycarboxylate-type superplasticizer by sulfate ion concentration in aqueous phase. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 375–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessaies-Bey, H.; Baumann, R.; Schmitz, M. Organic admixtures and cement particles: Competitive adsorption and its macroscopic rheological consequences. Cem. Concr. Res. 2016, 80, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Schober, I.; Raphael, E.; Plassard, C.; Lesniewska, E. Conformation of adsorbed comb copolymer dispersants. Langmuir 2009, 25, 845–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchikawa, H.; Hanehara, S.; Sawaki, D. The role of steric repulsive force in the dispersion of cement particles in fresh paste prepared with organic admixture. Cem. Concr. Res. 1997, 27, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magarotto, R.; Torresan, I.; Zeminian, N. Influence of the molecular weight of polycarboxylate ether superplasticizers on the rheological properties of fresh cement pastes, mortar and concrete. In Proceedings of the 11th International Congress on the Chemistry of Cement, Durban, South Africa, 11–16 May 2003; pp. 514–526. [Google Scholar]
- Plank, J.; Sachsenhauser, B. Experimental determination of the effective anionic charge density of polycarboxylate superplasticizers in cement pore solution. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flatt, R.J.; Zimmermann, J.; Hampel, C.; Kurz, C.; Schober, I.; Frunz, L.; Plassard, C.; Lesniewska, E. The role of adsorption energy in the sulfate-polycarboxylate competition. In Proceedings of the 9th CANMET/ACI International Conference on Superplasticizers and Other Chemical Admixtures in Concrete, Seville, Spain, 12–16 October 2009; pp. 153–164. [Google Scholar]

| Composition | Results (%) |
|---|---|
| C3S, m | 54.14 |
| C2S, m | 26.63 |
| C3A, c | 3.28 |
| C3A, o | 4.26 |
| C4AF, o | 2.45 |
| Free lime | 0.1 |
| Periclase (MgO) | 0.03 |
| Anhydrite | 2.64 |
| CaSO4 hemihydrate | 1.21 |
| Gypsum | 0.02 |
| Calcite | 3.61 |
| Quartz | 1.16 |
| Arcanite (K2SO4) | 0.46 |
| Sample | Molecular Weight (g/mol) | Mass Fraction (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | 5 h | 1 h | 2 h | 3 h | 4 h | 5 h | |
| 52IPEG3.0 | 26,700 | 20,984 | 9007 | 82,043 | 65,945 | 28.5 | 22.1 | 9.0 | 9.0 | 3.8 |
| 52IPEG4.2 | 30,900 | 31,091 | 29,481 | 92,490 | 20,027 | 35.0 | 38.3 | 11.1 | 1.3 | 2.3 |
| 52IPEG5.0 | 37,103 | 24,681 | 32,900 | 413,429 | 78,419 | 52.2 | 26.7 | 9.8 | 0.14 | 1.6 |
| 52IPEG6.0 | 43,400 | 24,742 | 16,457 | 46,238 | 60,435 | 53.8 | 26.8 | 8.1 | 2.5 | 0.74 |
| Molecular Properties | 52IPEG3.0 | 52IPEG4.2 | 52IPEG5.0 | 52IPEG6.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | low | medium | high | high |
| Side chain density | high | medium | low | low |
| Main chain length | short | medium | long | long |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Yao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Cui, S.; Wang, Y. Influence of Monomer Ratios on Molecular Weight Properties and Dispersing Effectiveness in Polycarboxylate Superplasticizers. Materials 2020, 13, 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13041022
Li H, Yao Y, Wang Z, Cui S, Wang Y. Influence of Monomer Ratios on Molecular Weight Properties and Dispersing Effectiveness in Polycarboxylate Superplasticizers. Materials. 2020; 13(4):1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13041022
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Huiqun, Yan Yao, Ziming Wang, Suping Cui, and Yali Wang. 2020. "Influence of Monomer Ratios on Molecular Weight Properties and Dispersing Effectiveness in Polycarboxylate Superplasticizers" Materials 13, no. 4: 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13041022
APA StyleLi, H., Yao, Y., Wang, Z., Cui, S., & Wang, Y. (2020). Influence of Monomer Ratios on Molecular Weight Properties and Dispersing Effectiveness in Polycarboxylate Superplasticizers. Materials, 13(4), 1022. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13041022




