Performance Evaluation of the Polyurethane-Based Composites Prepared with Recycled Polymer Concrete Aggregate
Abstract
1. Introduction
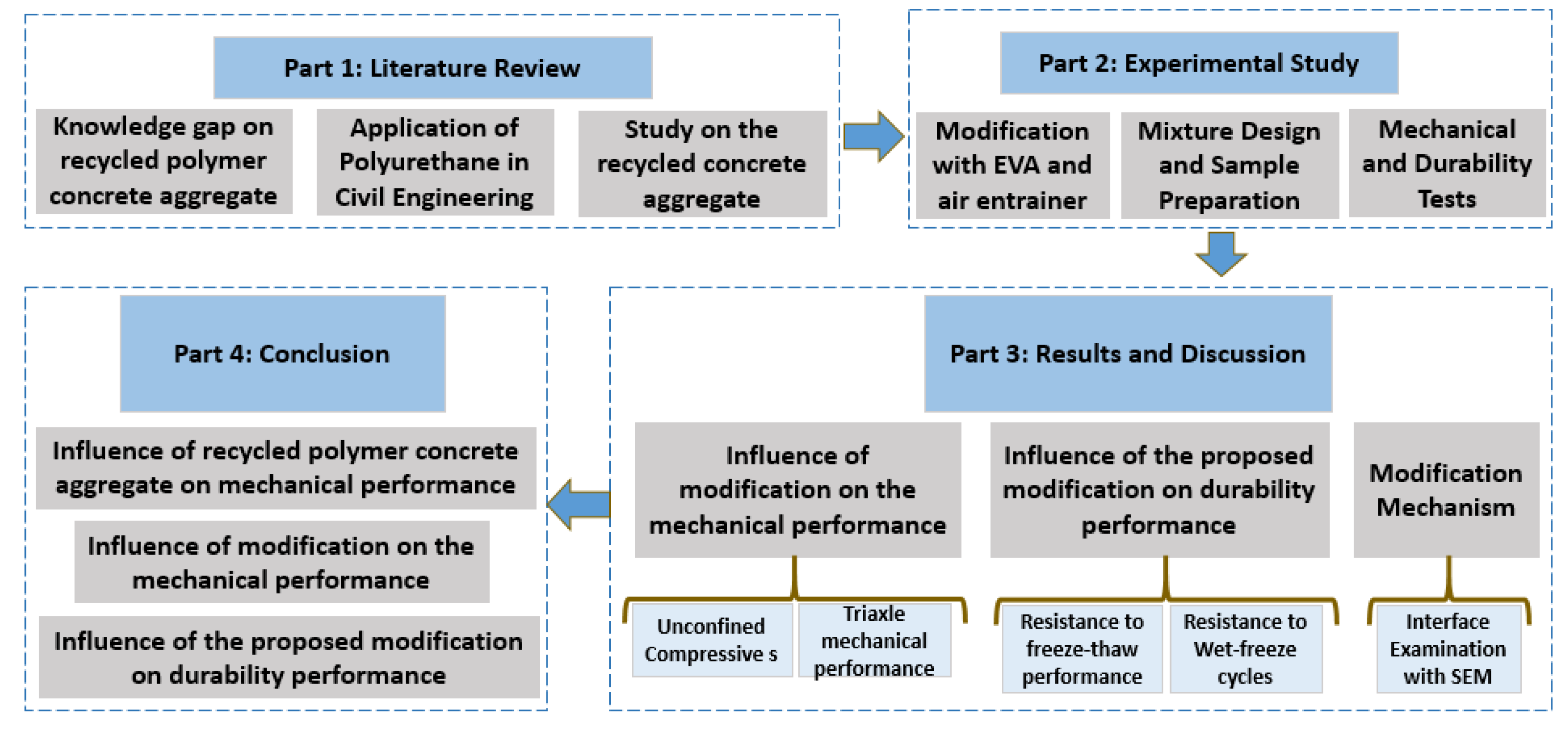
2. Sample Preparation and Experiment
2.1. Preparation and Remolding of the Original Pisha Sandstone/W-OH Composites
2.2. Preparation and Improvement of the Remold Pisha Sandstone /W-OH Composites
2.3. Characterization and Performance Test of the Remolded Pisha/W-OH and Original Pisha/W-OH Composites
2.4. Durability Test of the Pisha Sandstone/W-OH Composites
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Compressive Performance Test of the Original Pisha Stone/W-OH Composites Un
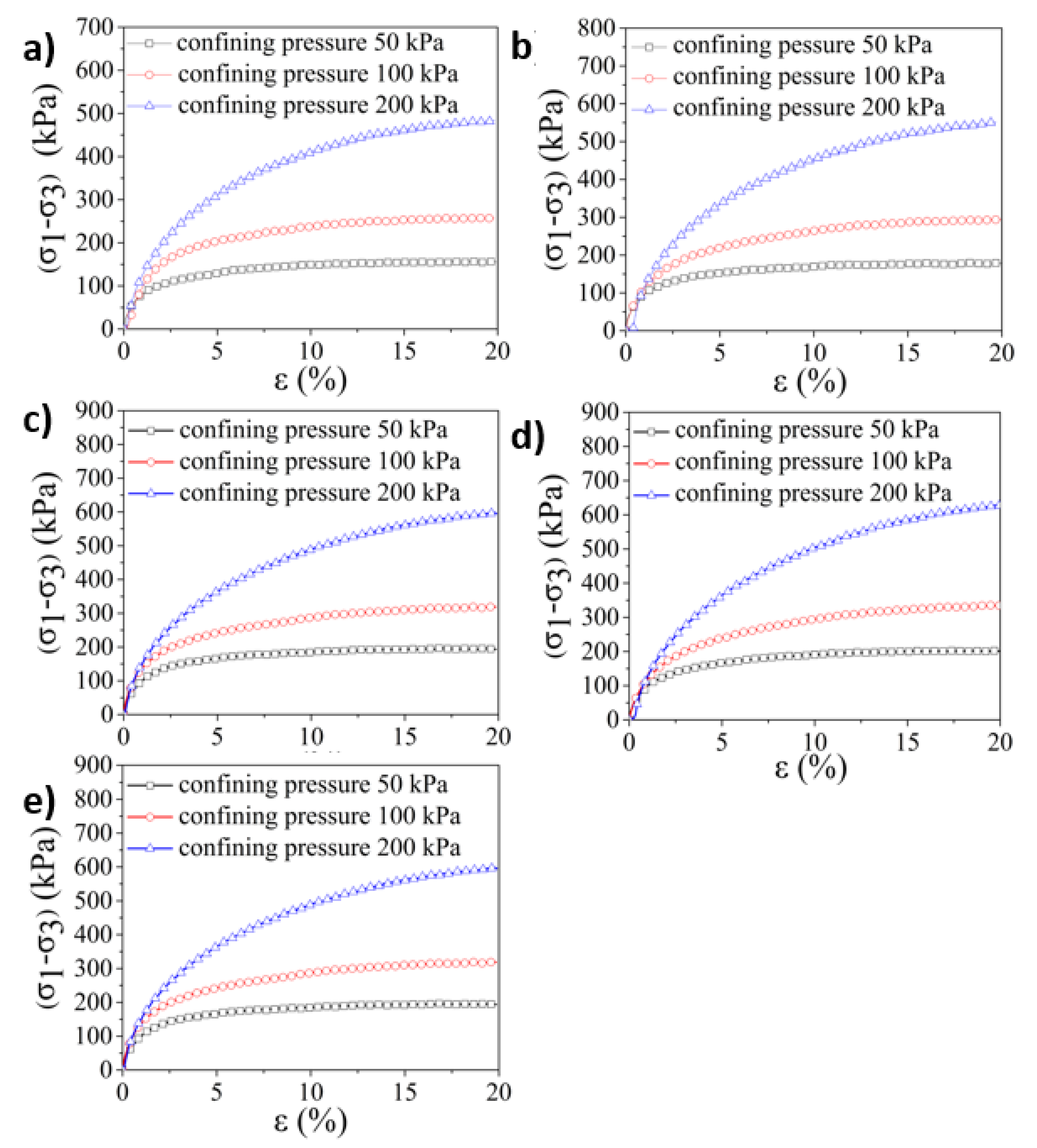
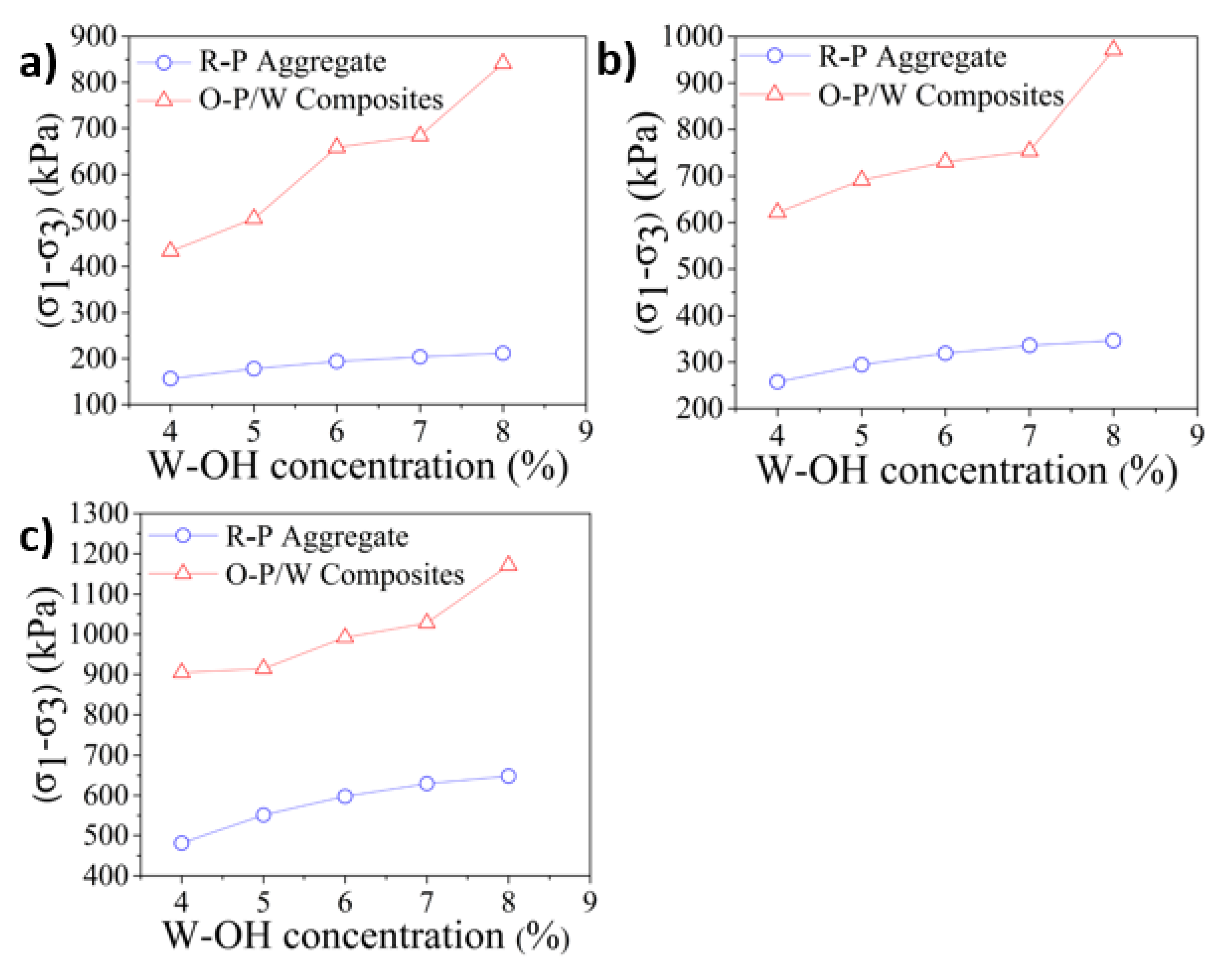
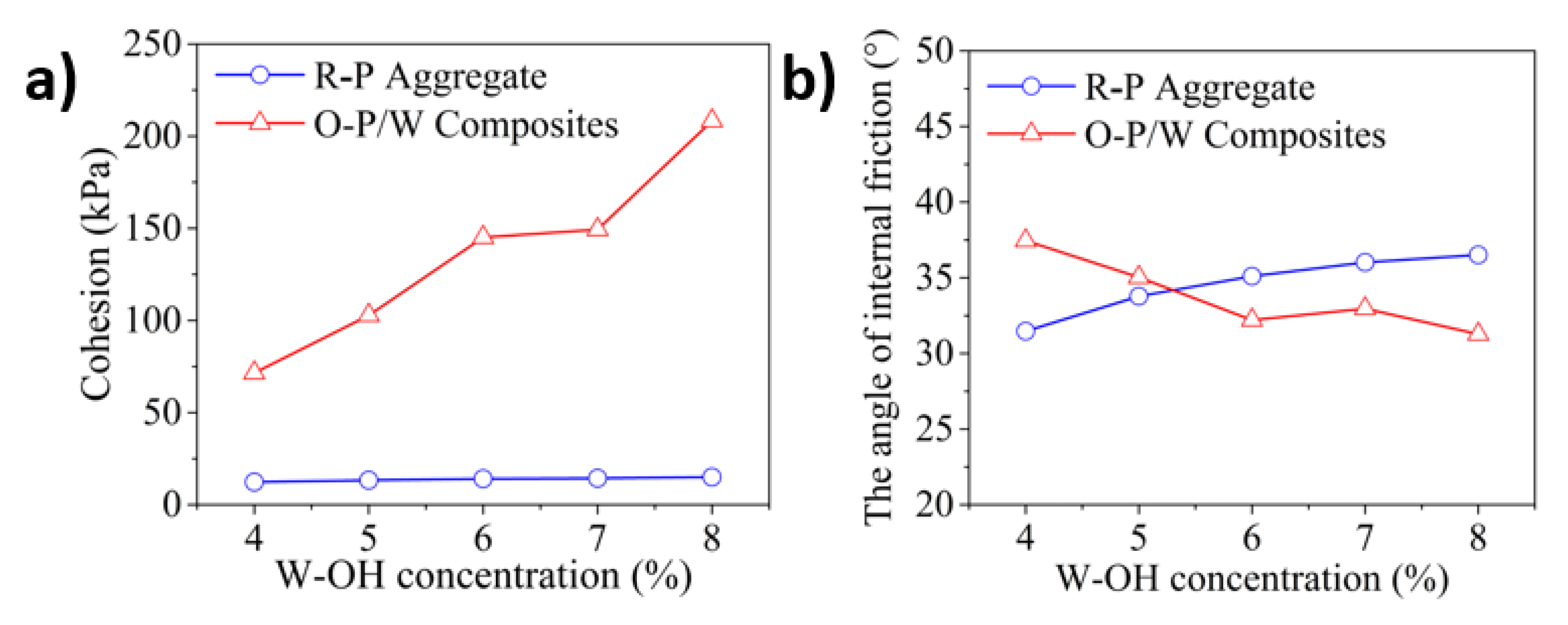
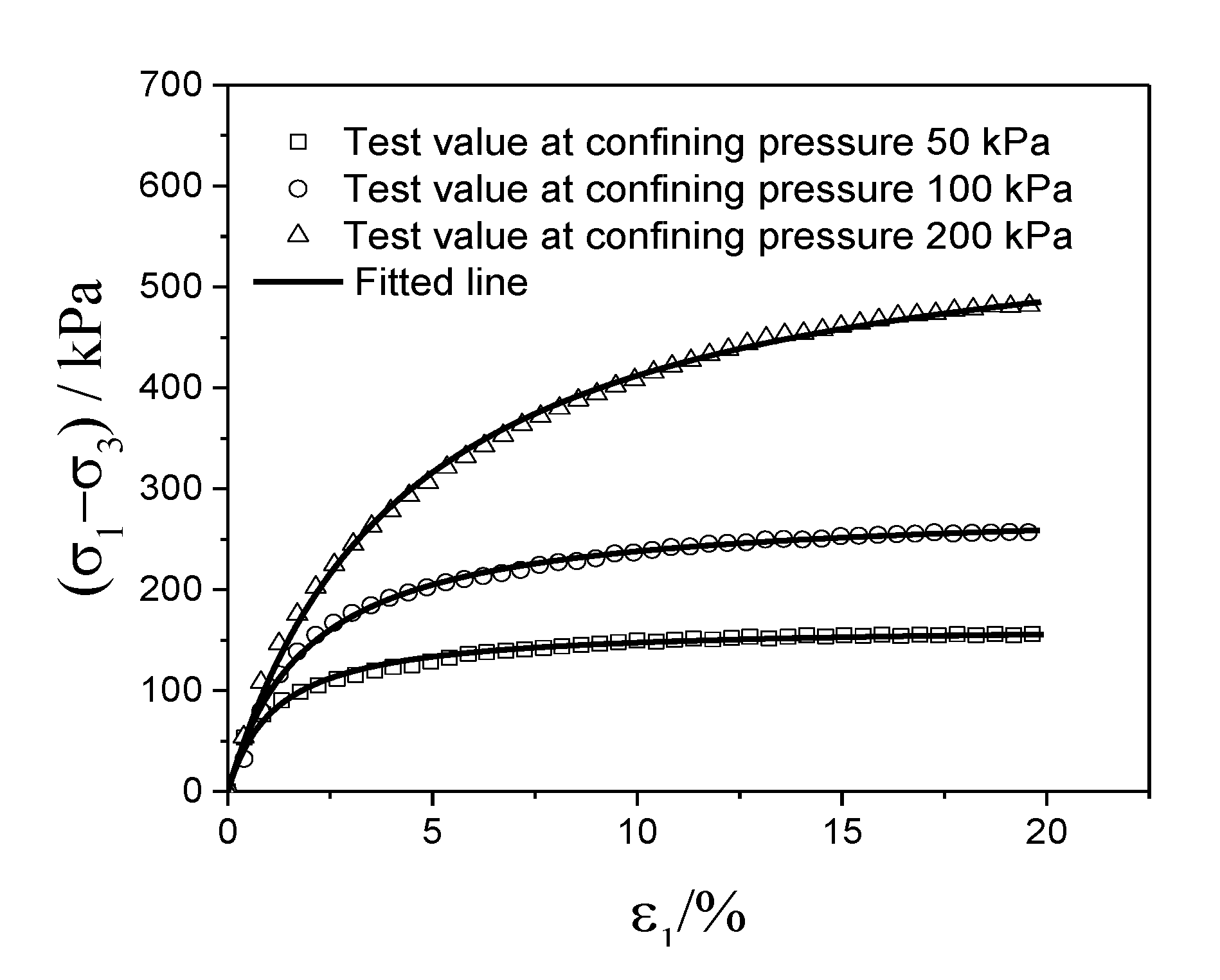
3.2. Triaxle Mechanical Performance of the Induration Prepared with Polyurethane and Remolded Pisha Sandstone
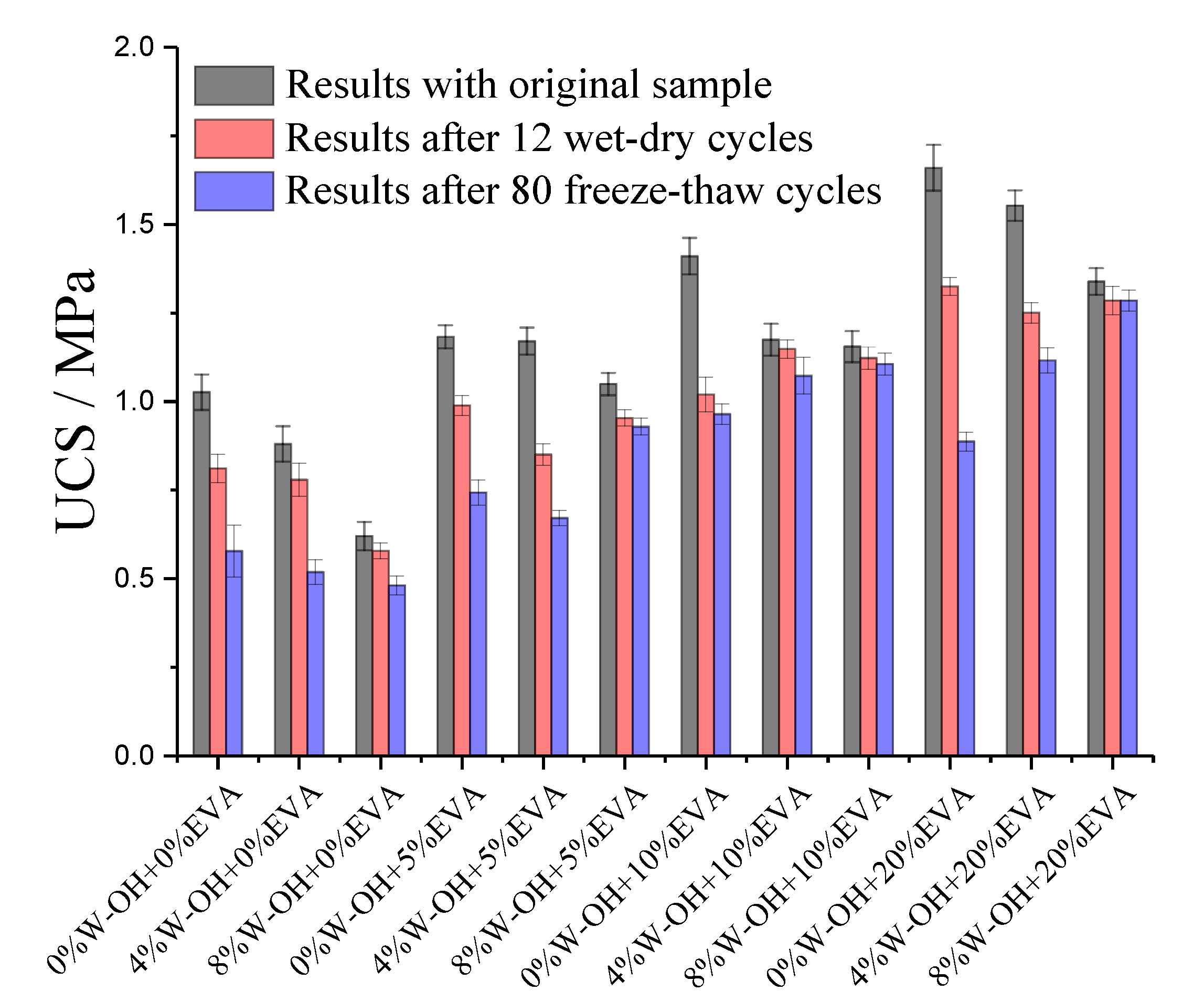
3.3. Mechanical and Durability Examination of the Composites Prepared with Remolded Pisha Sandstone and EVA Modified W-OH Material
3.4. Constitutive Analysis for the Remolded Pisha Sandstone Composites
3.5. Morphology Characterization of the Original/Remolded Pisha Sandstone and Pisha/W-OH Composites
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- The remained polyurethane material on the surface of the remolded sandstone aggregate can enhance its internal friction. The samples with a higher amount of remained polyurethane can have higher compressive strength under the triaxle test.
- (2)
- The remained polyurethane material can reduce the unconfined compressive strength of the polyurethane composites containing remolded aggregate. The reduction is caused by the poor bonding between the remained polyurethane on the remolded aggregate surface and the new polyurethane material. The strength loss can be partially compensated with a higher concentration of polyurethane solution.
- (3)
- The modification with EVA can fully compensate for the strength loss of the polyurethane-based composites due to the applied remolded sandstone aggregate.
- (4)
- The EVA content can enhance the resistance to both freeze-thaw and wet-dry resistance of the polyurethane-based composites. The optimized EVA content based on mechanical and durability performance is 10m% based on the polyurethane content.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tavira, J.; Jiménez, J.R.; Ayuso, J.; Sierra, M.J.; Ledesma, F.E. Functional and structural parameters of a paved road section constructed with mixed recycled aggregates from non-selected construction and demolition waste with excavation soil. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Dai, Q.; Si, R.; Sun, X.; Lu, C. Evaluation of properties and performance of rubber-modified concrete for recycling of waste scrap tire. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 148, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brantley, A.S.; Townsend, T.G. Leaching of pollutants from reclaimed asphalt pavement. Environ. Eng. Sci. 1999, 16, 105–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkó, Z.; Szijártó, A.; Nemes, R. Cellular concrete waste as an economical alternative to traditional supplementary cementitious materials. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2019, 138, 947–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Zollinger, D.; Grasley, Z. Economic input-output life cycle assessment of concrete pavement containing recycled concrete aggregate. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 225, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyurkó, Z.; Jankus, B.; Fenyvesi, O.; Nemes, R. Sustainable applications for utilization the construction waste of aerated concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 230, 430–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Zollinger, D.; Huang, K. Performance evaluation of jointed plain concrete pavement made with portland cement concrete containing reclaimed asphalt pavement. Road Mater. Pavement Design 2019, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.; Mirsayar, M.; Mukhopadhyay, A.; Zollinger, D. Characterization of two-parameter fracture properties of portland cement concrete containing reclaimed asphalt pavement aggregates by semicircular bending specimens. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2019, 95, 56–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Hu, J.; Dai, Q. A critical review on the performance of portland cement concrete with recycled organic components. J. Clean. Prod. 2018, 188, 92–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvín, A.P.; Ayuso, J.; Agrela, F.; Barbudo, A.; Jiménez, J.R. Analysis of leaching procedures for environmental risk assessment of recycled aggregate use in unpaved roads. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaboki, H.R.; Ghalehnovi, M.; Karimipour, A.; de Brito, J. Experimental study on the flexural behaviour and ductility ratio of steel fibres coarse recycled aggregate concrete beams. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 186, 400–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaboki, H.R.; Ghalehnovi, M.; Karimipour, A.; de Brito, J.; Khatibinia, M. Shear behaviour of concrete beams with recycled aggregate and steel fibres. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 204, 809–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ledesma, E.F.; Jiménez, J.R.; Fernández, J.M.; Galvín, A.P.; Agrela, F.; Barbudo, A. Properties of masonry mortars manufactured with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 289–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.R.; Ayuso, J.; López, M.; Fernández, J.M.; de Brito, J. Use of fine recycled aggregates from ceramic waste in masonry mortar manufacturing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 40, 679–690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Xiao, J.; Shen, L. Damage assessment for seismic response of recycled concrete filled steel tube columns. Earthq. Eng. Eng. Vib. 2016, 15, 607–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saikia, N.; de Brito, J. Use of plastic waste as aggregate in cement mortar and concrete preparation: A review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 34, 385–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somarathna, H.M.C.C.; Raman, S.N.; Mohotti, D.; Mutalib, A.A.; Badri, K.H. The use of polyurethane for structural and infrastructural engineering applications: A state-of-the-art review. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 995–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, X.; Liang, Z.; Wei, J.; Wang, C.; Zhou, X.; Wu, Z. Preparation of hydrophilic reactive polyurethane and its application of anti-water erodibility in ecological restoration. J. Polym. Eng. 2019, 39, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Karsani, K.S.M.; Al-Muntasheri, G.A.; Hussein, I.A. Polymer systems for water shutoff and profile modification: A review over the last decade. SPE J. 2014, 19, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; He, M.; Huang, Z.; Wu, Z. Long-tern field test and numerical simulation of foamed polyurethane insulation on concrete dam in severely cold region. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 212, 618–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; van Tittelboom, K.; de Belie, N.; Verstraete, W. Use of silica gel or polyurethane immobilized bacteria for self-healing concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 26, 532–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akkoyun, M.; Akkoyun, S. Blast furnace slag or fly ash filled rigid polyurethane composite foams: A comprehensive investigation. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2019, 136, 47433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Shuai, B.; Zhang, X.; Yu, H.; Zhang, H.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, C.; Guan, X. Fabrication and performance of a polyurethane hybrid composite with waste red mud. Polym. Compos. 2019, 40, 2424–2431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junco, C.; Rodríguez, A.; Calderón, V.; Muñoz-Rupérez, C.; Gutiérrez-González, S. Fatigue durability test of mortars incorporating polyurethane foam wastes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 190, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Ma, X.; Wang, H.; Xie, P.; Huang, W. Experimental study on anti-icing and deicing performance of polyurethane concrete as road surface layer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 598–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Renken, L.; Li, T.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Oeser, M. Experimental study on the polyurethane-bound pervious mixtures in the application of permeable pavements. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 202, 838–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Liu, P.; Wang, Y.; Faßbender, S.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M. Development of a sustainable pervious pavement material using recycled ceramic aggregate and bio-based polyurethane binder. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 220, 1052–1060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.-J.; Su, Q.; Cheng, Y.-M.; Liu, B.; Liu, T. Improved performance of the subgrade bed under the slab track of high-speed railway using polyurethane adhesive. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 208, 710–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Choi, J.-I.; Kim, S.-K.; Lee, B.-K.; Hwang, J.-S.; Lee, B.Y. Damping and mechanical properties of composite composed of polyurethane matrix and preplaced aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 145, 68–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.S.; Choi, J.-I.; Park, S.E.; Hwang, J.-S.; Lee, B.Y. Damping property of prepacked concrete incorporating coarse aggregates coated with polyurethane. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 93, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junco, C.; Gadea, J.; Rodríguez, A.; Gutiérrez-González, S.; Calderón, V. Durability of lightweight masonry mortars made with white recycled polyurethane foam. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2012, 34, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, S.; Shang, W.; Qi, X.; Dong, S.; Zhang, Z. New polyurethane modified coating for maintenance of asphalt pavement potholes in winter-rainy condition. Prog. Org. Coat. 2019, 133, 368–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linag, Z.; Wu, Z.; Noori, M.; Yang, C.; Yao, W. A new ecological control method for Pisha sandstone based on hydrophilic polyurethane. J. Arid Land 2017, 9, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Feng, Q.; Deng, L.; Noori, M. Durability of the Pisha Sandstone Consolidation Body Solidified by Hydraulic Polyurethane in Simulated UV Tests. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2018, 27, 5882–5890. [Google Scholar]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C.; Noori, M.; Wu, X.; Ge, H.; Iwashita, K.; Yao, W.; Xiao, P. A Comprehensive Method of Erosion Resistance and Growth Promotion for Pisha Sandstone. Int. J. 2018, 14, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, C.; de Brito, J.; Gil, V.; Sainz-Aja, J.A.; Cimentada, A. Multiple recycled aggregate properties analysed by X-ray microtomography. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 166, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S. Interfacial Transition Zone Composition and Bonding in Cementitious Materials with Asphalt-Coated Particles. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, Champaign, IL, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Bonding in cementitious materials with asphalt-coated particles: Part II–Cement-asphalt chemical interactions. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 182–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brand, A.S.; Roesler, J.R. Bonding in cementitious materials with asphalt-coated particles: Part I–The interfacial transition zone. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 130, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matias, D.; de Brito, J.; Rosa, A.; Pedro, D. Mechanical properties of concrete produced with recycled coarse aggregates–Influence of the use of superplasticizers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, P.; Evangelista, L.; de Brito, J. The effect of superplasticisers on the workability and compressive strength of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 28, 722–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, L.; Tam, V.W.; Li, H. The state of the art regarding the long-term properties of recycled aggregate concrete. Struct. Concr. 2014, 15, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Luo, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Y.; Xiao, J. A review of life cycle assessment of recycled aggregate concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 209, 115–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaidachatorn, K.; Suebsuk, J.; Horpibulsuk, S.; Arulrajah, A. Extended water/cement ratio law for cement mortar containing recycled asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 196, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cartuxo, F.; de Brito, J.; Evangelista, L.; Jiménez, J.R.; Ledesma, E.F. Rheological behaviour of concrete made with fine recycled concrete aggregates–Influence of the superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 89, 36–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.H.; Li, Q.; Cao, Z.Y.; Tian, W.Y. The deterioration law of recycled concrete under the combined effects of freeze-thaw and sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 200, 344–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuyan, M.; Mardani-Aghabaglou, A.; Ramyar, K. Freeze–thaw resistance, mechanical and transport properties of self-consolidating concrete incorporating coarse recycled concrete aggregate. Mater. Des. 2014, 53, 983–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yildirim, S.T.; Meyer, C.; Herfellner, S. Effects of internal curing on the strength, drying shrinkage and freeze–thaw resistance of concrete containing recycled concrete aggregates. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 91, 288–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Q.H.; Cao, Z.Y.; Guan, X.; Li, Q.; Liu, X.L. Damage to recycled concrete with different aggregate substitution rates from the coupled action of freeze-thaw cycles and sulfate attack. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 221, 74–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, B.; Li, W.; Tang, Z.; Tam, V.W.Y.; Sun, Z. Durability of recycled aggregate concrete under coupling mechanical loading and freeze-thaw cycle in salt-solution. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 163, 840–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Liu, K.; Zou, C.; Wang, J. Eccentric compressive behavior of recycled aggregate concrete columns after freezing and thawing cycles. Adv. Struct. Eng. 2018, 21, 2299–2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Alam, M.S.; Zou, C. Seismic fragility analysis of deteriorating recycled aggregate concrete bridge columns subjected to freeze-thaw cycles. Eng. Struct. 2019, 187, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Yan, J.; Zou, C.; Wu, H. Cyclic stress-strain model for air-entrained recycled aggregate concrete after freezing-and-thawing cycles. ACI Struct. J. 2018, 115, 711–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Šeps, K.; Fládr, J.; Broukalová, I. Resistance of Recycled Aggregate Concrete to Freeze-thaw and Deicing Salts. Procedia Eng. 2016, 151, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, A.; Coventry, K.; Bacon, J. Freeze/thaw durability of concrete with recycled demolition aggregate compared to virgin aggregate concrete. J. Clean. Prod. 2011, 19, 272–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolay, P.K.; Sulaiman, S.O.; Kumar, S. Freeze-Thaw Durability of Concrete with Natural and Recycled Concrete Aggregates Using Air-Entraining Admixture. Adv. Civ. Eng. Mater. 2018, 7, 328–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gokce, A.; Nagataki, S.; Saeki, T.; Hisada, M. Freezing and thawing resistance of air-entrained concrete incorporating recycled coarse aggregate: The role of air content in demolished concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2004, 34, 799–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Moon, J.-H.; Shim, J.W.; Sim, J.; Lee, H.-G.; Zi, G. Durability properties of a concrete with waste glass sludge exposed to freeze-and-thaw condition and de-icing salt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 66, 398–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnam, Y.; Bentz, D.; Hampton, A.; Weiss, W.J. Acoustic Emission and Low-Temperature Calorimetry Study of Freeze and Thaw Behavior in Cementitious Materials Exposed to Sodium Chloride Salt. Transp. Res. Rec. 2014, 2441, 81–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, G.; Zhu, C.; Liu, C.; Liu, H. Chloride Ion Invasive Behavior of Recycled Aggregate Concrete under Coupling Flexural Loading and Wetting-Drying Cycles. KSCE J. Civ. Eng. 2019, 23, 4454–4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Shen, D. Evaluation of the damage process of recycled aggregate concrete under sulfate attack and wetting-drying cycles. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 138, 254–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Ji, T.; Liu, H. Performance evolution of the interfacial transition zone (ITZ) in recycled aggregate concrete under external sulfate attacks and dry-wet cycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 229, 116938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, A.K.; Sarker, P.K. Durability of Mortar Incorporating Ferronickel Slag Aggregate and Supplementary Cementitious Materials Subjected to Wet–Dry Cycles. Int. J. Concr. Struct. Mater. 2018, 12, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, B.; Gao, J.; Chen, F.; Shen, D. Chloride penetration into recycled aggregate concrete subjected to wetting–drying cycles and flexural loading. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 174, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenauer, M.; GerhardAbozari, E.; Hocker, H. Chemical stability of a polyurethane-based stone-protecting agent under artificial weathering. Angew. Makromol. Chem. 1997, 246, 169–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carmona-Quiroga, P.M.; Jacobs, R.M.; Martínez-Ramírez, S.; Viles, H.A. Durability of anti-graffiti coatings on stone: Natural vs accelerated weathering. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0172347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Yao, W.; Noori, M.; Yang, C.; Xiao, P.; Leng, Y.; Deng, L. Pisha sandstone: Causes, processes and erosion options for its control and prospects. Int. Soil Water Conserv. Res. 2018, 7, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Wu, Z.; Noori, M.; Deng, L. Effect of simulated corrosion environment on mechanical performances of sand fixation by hydrophilic Polyurethane. Feb-Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2017, 26, 5797. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, W.; Hu, C.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Z.; Huang, T. Flexural and Shear Bond Performance of Polyurethane-Mortar Interface under Micro-and Macroscale. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2019, 31, 04019105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y. Preservation Property and Decay Kinetic of Polyurethane Immobilized Nitrifying Bacteria Pellets. J. Geosci. Environ. Prot. 2018, 6, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Standard for soil test method; Ministry of Water Resources of the PRC: Beijing, China, 1999.
- Qiangguo, C.; Shiuhung, L.; Guiping, W. Process-based soil erosion and sediment yield model in a small basin in the hilly loess region. Acta Geogr. Sin. 1996, 51, 108–117. [Google Scholar]
- Belin, P.; Habert, G.; Thiery, M.; Roussel, N. Cement paste content and water absorption of recycled concrete coarse aggregates. Mater. Struct. 2014, 47, 1451–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshibli, K.A.; Batiste, S.N.; Sture, S. Strain localization in sand: Plane strain versus triaxial compression. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2003, 129, 483–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagioia, R.; Nova, R. An experimental and theoretical study of the behaviour of a calcarenite in triaxial compression. Géotechnique 1995, 45, 633–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caravia, L.; Dowson, D.; Fisher, J.; Corkhill, P.; Tighe, B. A comparison of friction in hydrogel and polyurethane materials for cushion-form joints. J. Mater. Sci. 1993, 4, 515–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuhara, K.; Yamanouchi, T.; Hirao, K. Cyclic strength and deformation of normally consolidated clay. Soils Found. 1982, 22, 77–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labuz, J.F.; Zang, A. Mohr–Coulomb failure criterion. Rock Mech. Rock Eng. 2012, 45, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Xiao, J.; Sun, Z. Experimental study on the failure mechanism of recycled concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1050–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weixing, F.; Shaodong, C.; Wanyi, H. Experimental Study on Parameters of Duncan-Chang Model for Beijing Fine Sandy Soil. Chin. J. Rock Mech. Eng. 1999, 18, 327–330. [Google Scholar]
- Peterson, G.L. Flow structures in sandstone dikes. Sediment. Geol. 1968, 2, 177–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Huang, X.; Sha, A.; Wang, H.; Chen, J.; Li, C. Improvement of asphalt-aggregate adhesion using plant ash byproduct. Materials 2019, 12, 605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Li, W.; Fan, Y.; Huang, X. An overview of study on recycled aggregate concrete in China (1996–2011). Constr. Build. Mater. 2012, 31, 364–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Chong, L.; Xie, Z. Performance enhancement of recycled concrete aggregate–a review. J. Clean. Prod. 2016, 112, 466–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
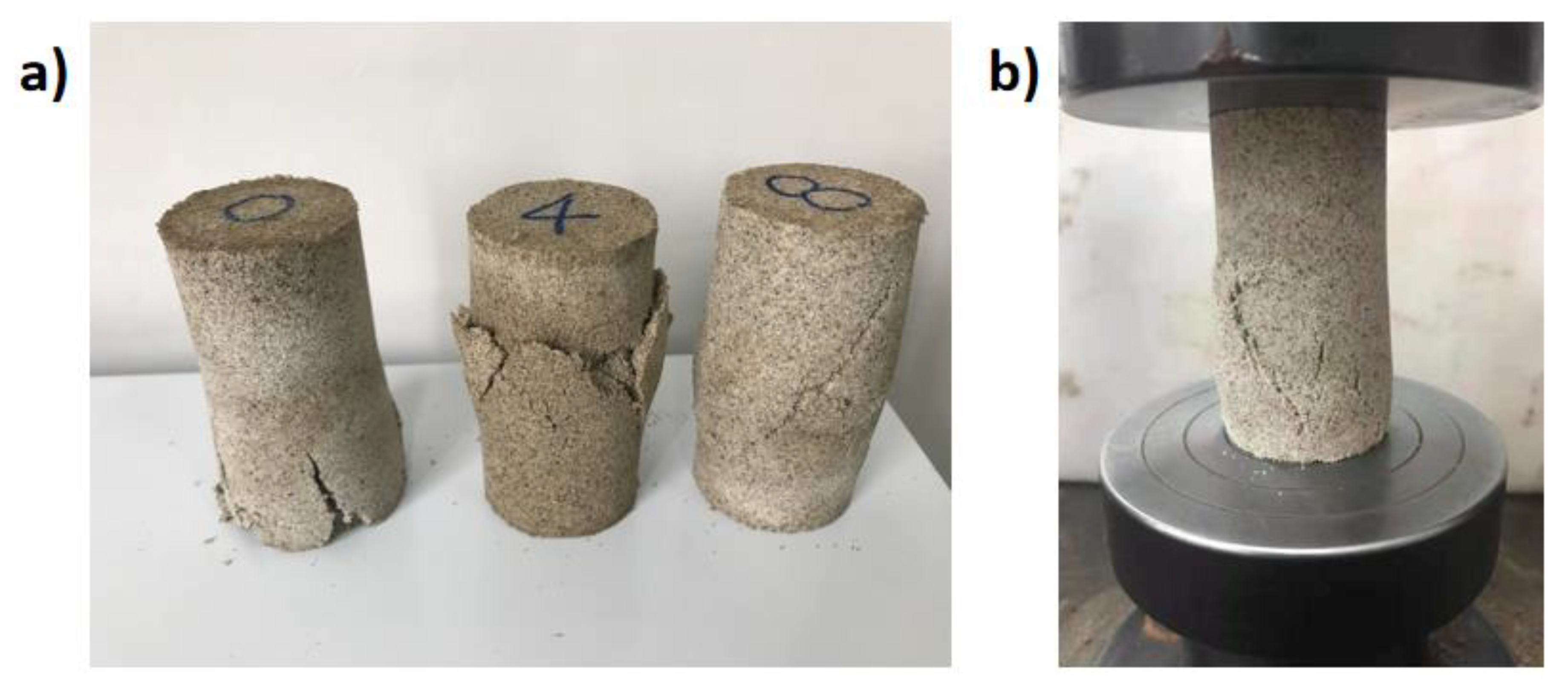
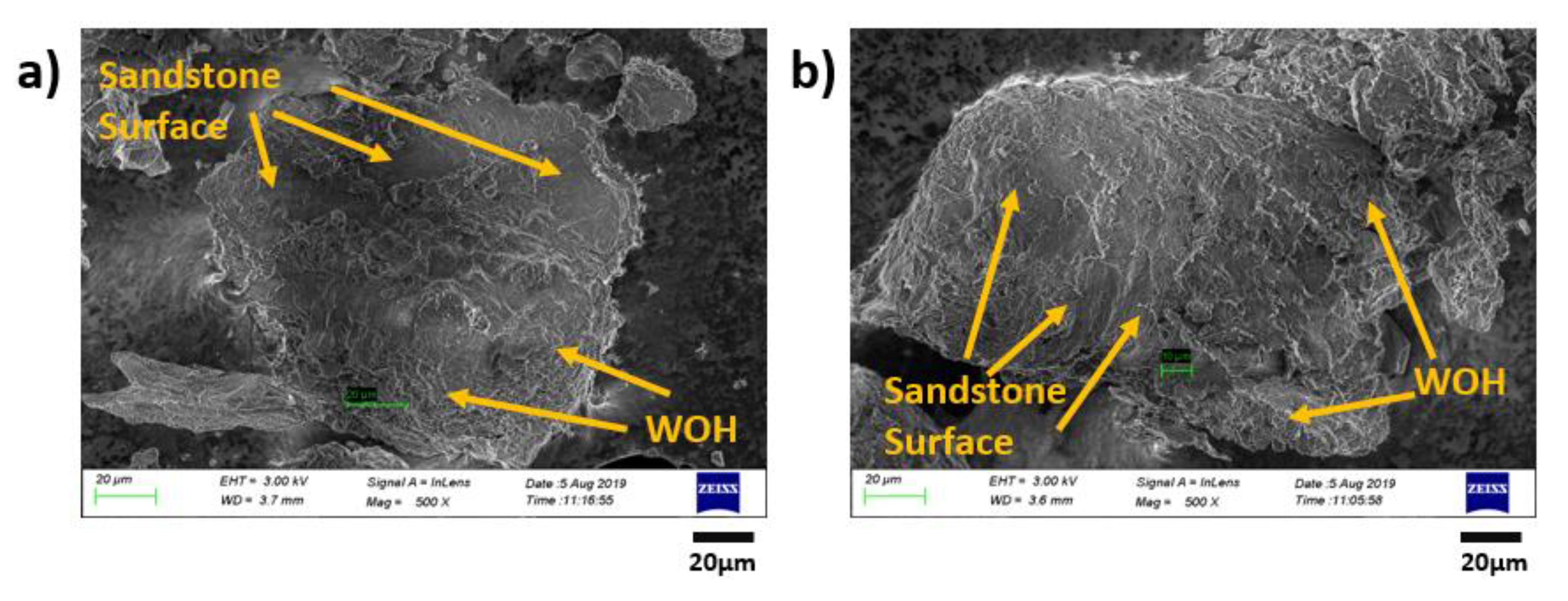
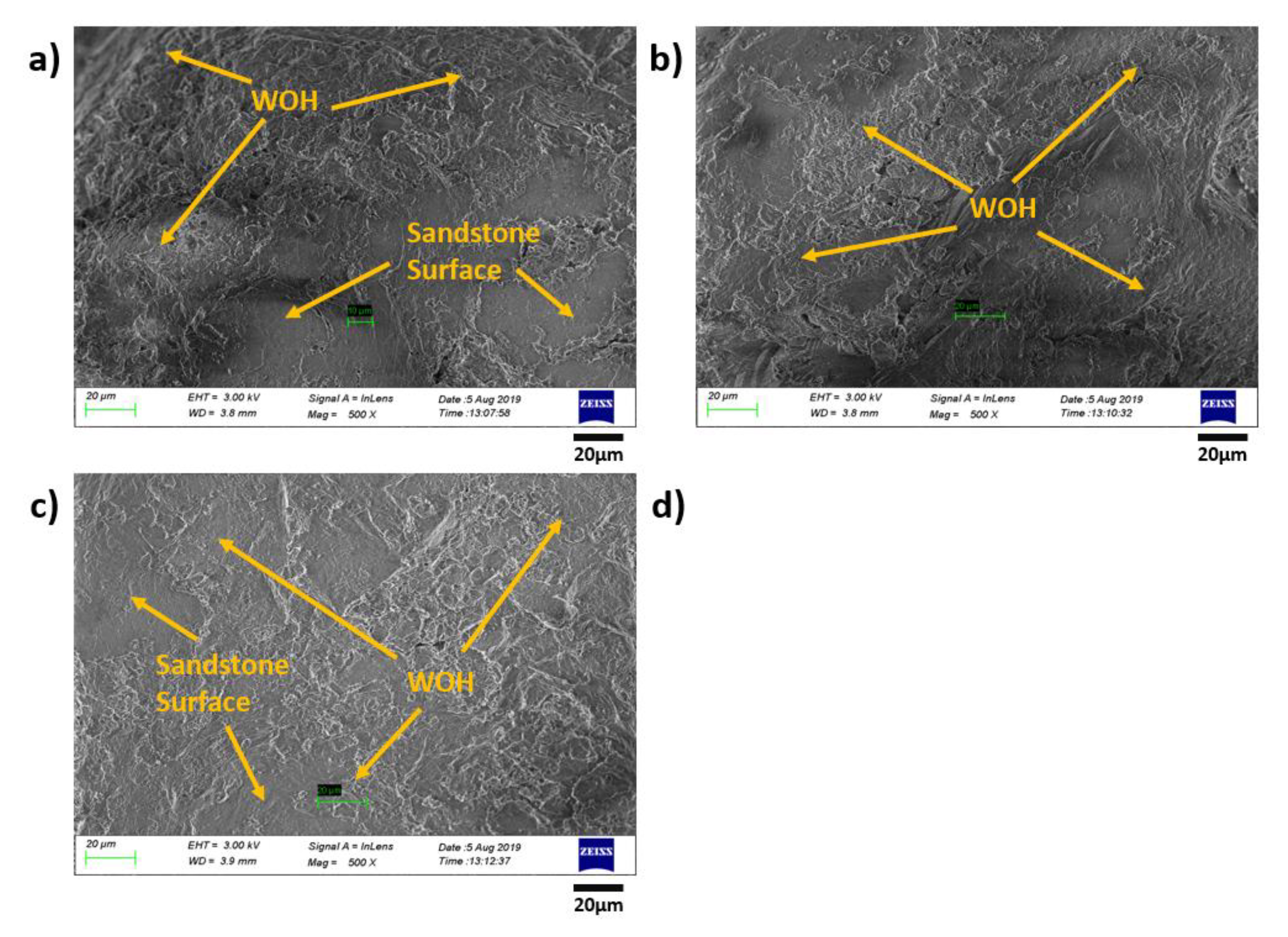

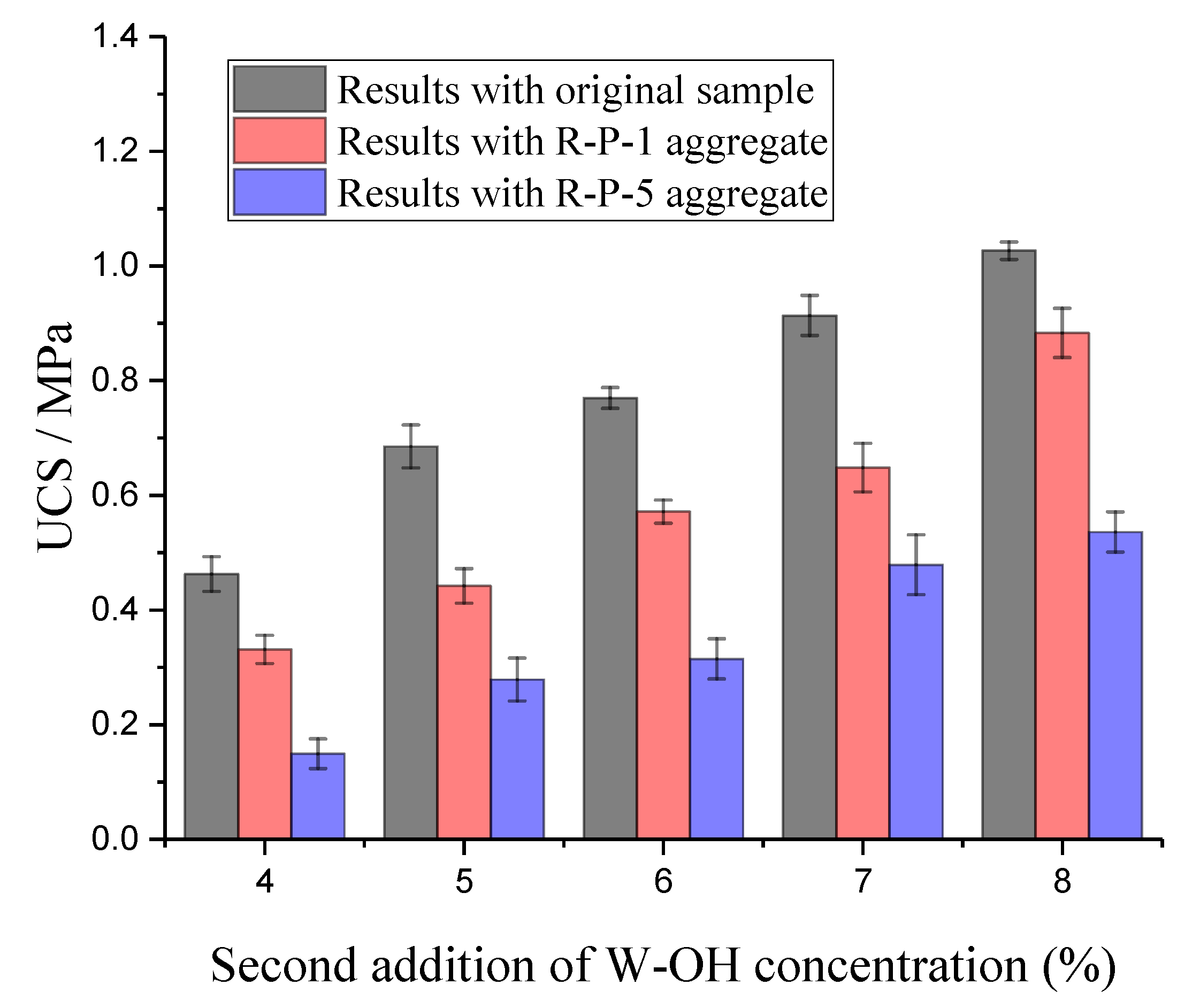





| Sample Type | O-P/W-1 | O-P/W-2 | O-P/W-3 | O-P/W-4 | O-P/W-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aggregate | Original Pisha Sandstone around 2.36 mm | ||||
| W-OH concentration | 4% | 5% | 6% | 7% | 8% |
| Remolded Aggregate Type | R-P-1 | R-P-2 | R-P-3 | R-P-4 | R-P-5 |
| Sample Type | O-P/W-1 | O-P/W-2 | O-P/W-3 | O-P/W-4 | O-P/W-5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Strength (MPa) | 0.47 | 0.69 | 0.76 | 0.91 | 0.10 |
| σ3/kPa | W-OH Concentration/% | a | b | (σ1 − σ3)ult /kPa | (σ1 − σ3)f /kPa | Rf | The Average Value of Rf |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 50 | 4 | 0.00739 | 0.00601 | 166.39 | 153.78 | 0.941 | 0.93 |
| 50 | 5 | 0.00555 | 0.00533 | 187.62 | 175.44 | 0.957 | |
| 50 | 6 | 0.00543 | 0.00484 | 206.61 | 192.23 | 0.940 | |
| 50 | 7 | 0.00624 | 0.00461 | 216.92 | 198.97 | 0.934 | |
| 50 | 8 | 0.00597 | 0.00442 | 226.24 | 207.56 | 0.879 | |
| 100 | 4 | 0.00683 | 0.00352 | 284.1 | 251.56 | 0.906 | 0.90 |
| 100 | 5 | 0.00677 | 0.00306 | 326.8 | 284.8 | 0.906 | |
| 100 | 6 | 0.00561 | 0.00287 | 348.43 | 308.26 | 0.932 | |
| 100 | 7 | 0.00689 | 0.00266 | 375.94 | 320.58 | 0.874 | |
| 100 | 8 | 0.00792 | 0.00254 | 393.7 | 325.95 | 0.880 | |
| 200 | 4 | 0.00729 | 0.00169 | 591.72 | 459.56 | 0.813 | 0.80 |
| 200 | 5 | 0.00765 | 0.00142 | 704.22 | 518.13 | 0.777 | |
| 200 | 6 | 0.00653 | 0.00135 | 740.74 | 560.12 | 0.807 | |
| 200 | 7 | 0.0074 | 0.00122 | 819.67 | 583.66 | 0.768 | |
| 200 | 8 | 0.00449 | 0.00129 | 775.2 | 629.2 | 0.817 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, W.; Zhao, Z.; Guo, S.; Zhao, Y.; Wu, Z.; Yang, C. Performance Evaluation of the Polyurethane-Based Composites Prepared with Recycled Polymer Concrete Aggregate. Materials 2020, 13, 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030616
Ma W, Zhao Z, Guo S, Zhao Y, Wu Z, Yang C. Performance Evaluation of the Polyurethane-Based Composites Prepared with Recycled Polymer Concrete Aggregate. Materials. 2020; 13(3):616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030616
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Wenbo, Zenggang Zhao, Shuaicheng Guo, Yanbing Zhao, Zhiren Wu, and Caiqian Yang. 2020. "Performance Evaluation of the Polyurethane-Based Composites Prepared with Recycled Polymer Concrete Aggregate" Materials 13, no. 3: 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030616
APA StyleMa, W., Zhao, Z., Guo, S., Zhao, Y., Wu, Z., & Yang, C. (2020). Performance Evaluation of the Polyurethane-Based Composites Prepared with Recycled Polymer Concrete Aggregate. Materials, 13(3), 616. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13030616




