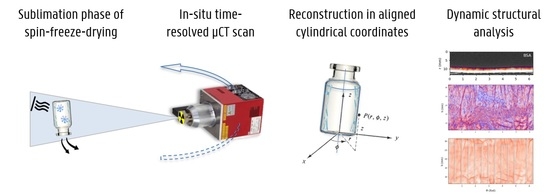
In-Situ X-ray Imaging Of Sublimating Spin-Frozen Solutions
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Spin-Freezing Materials and Method
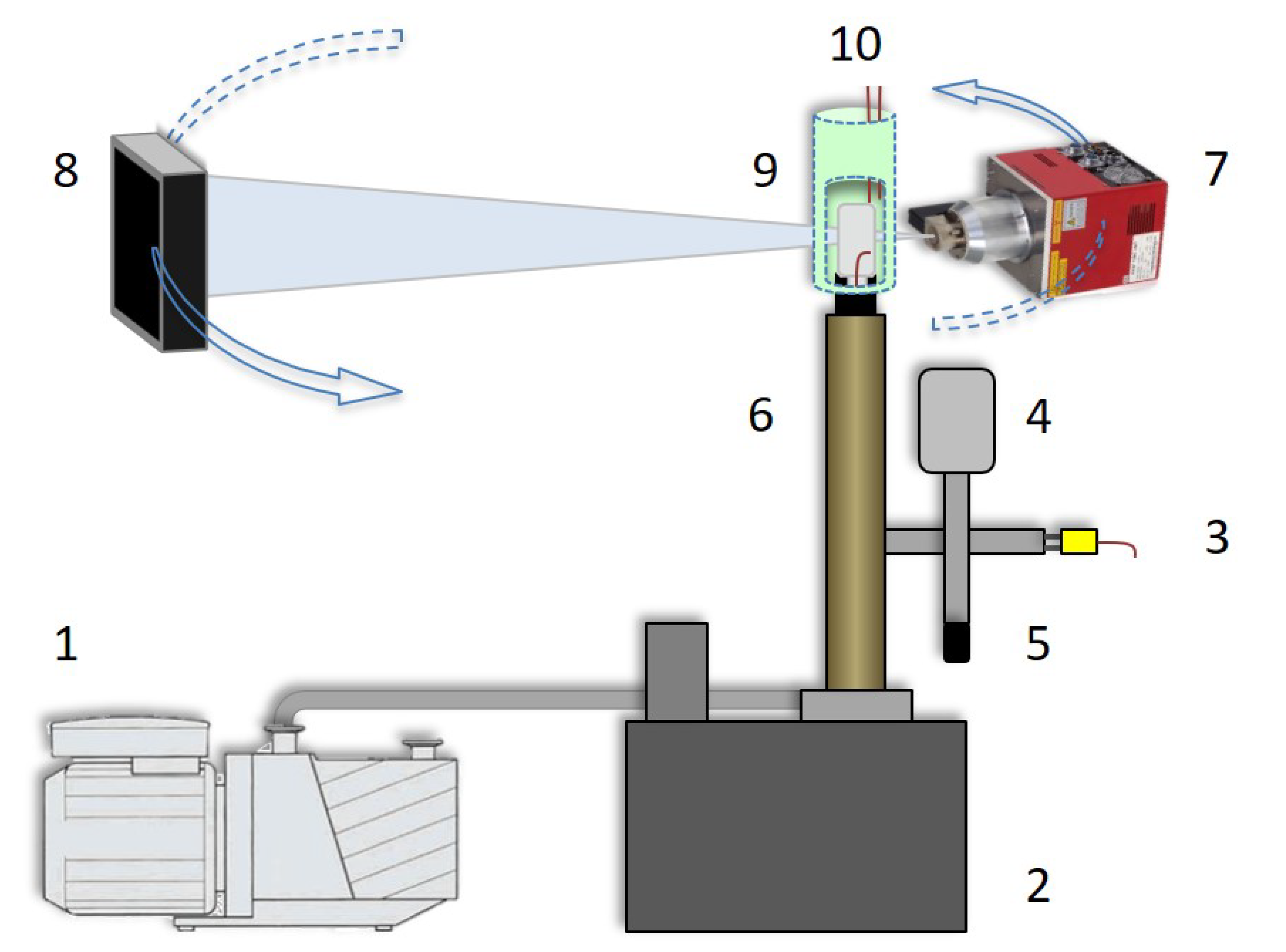
2.2. Micro-CT Setup
2.3. Freeze-Drying Peripheral Equipment
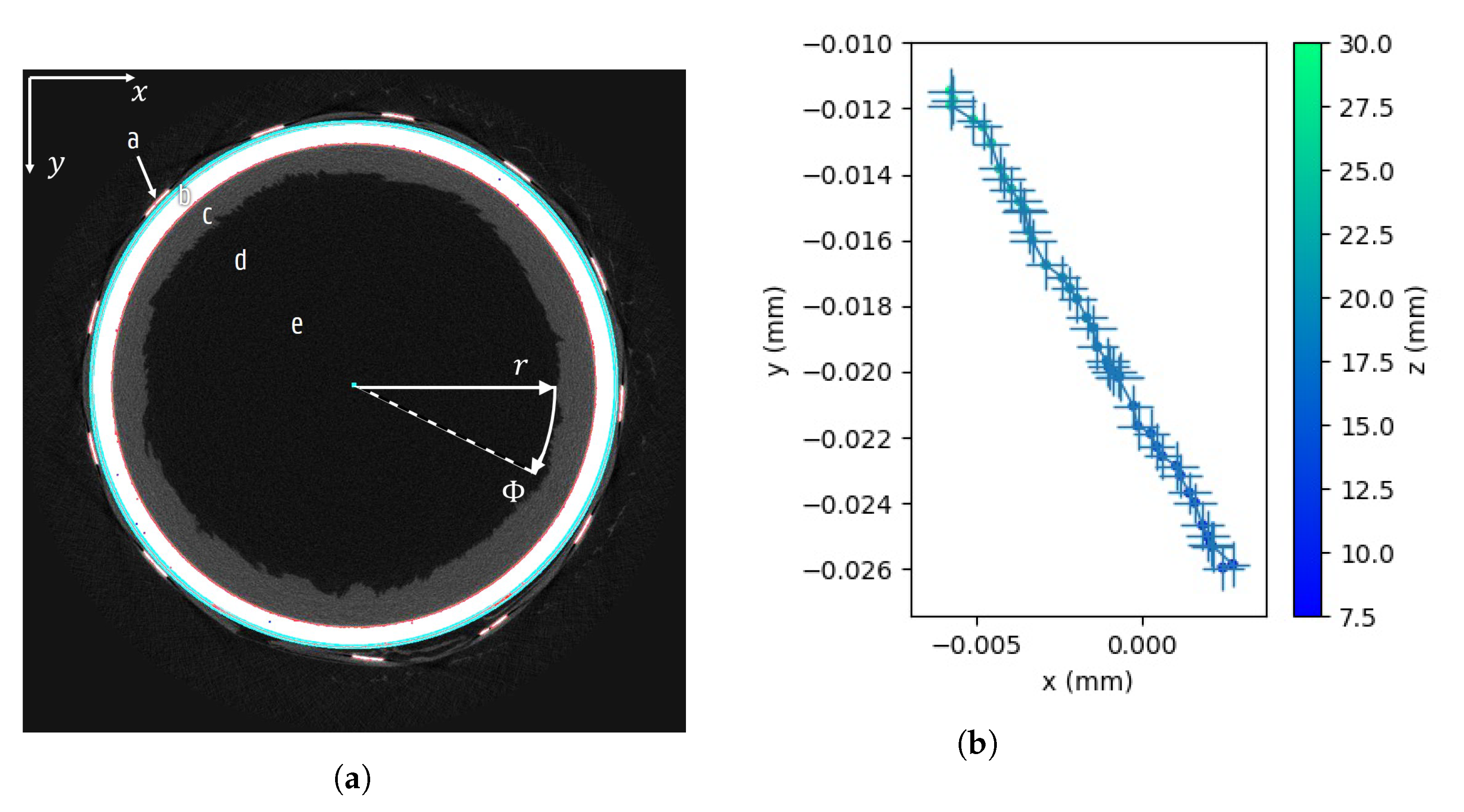
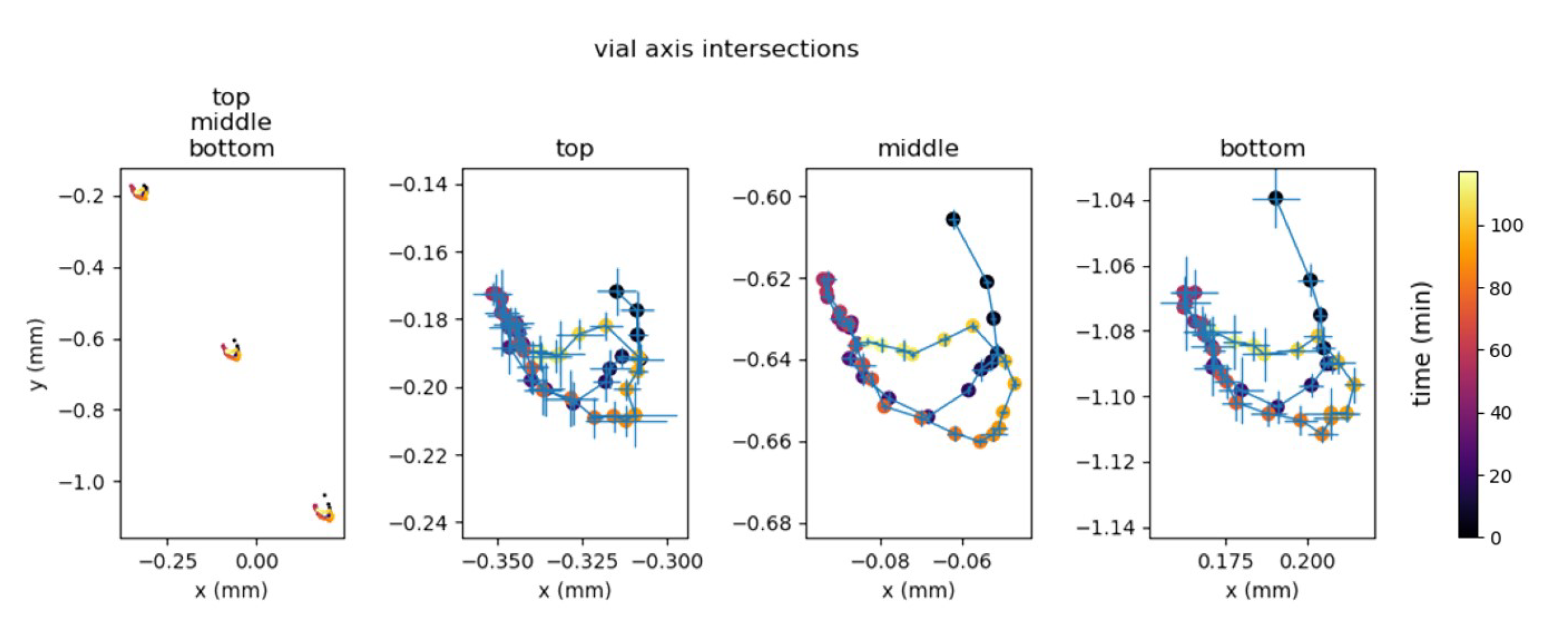
2.4. Cylindrical Vial Pose Estimation
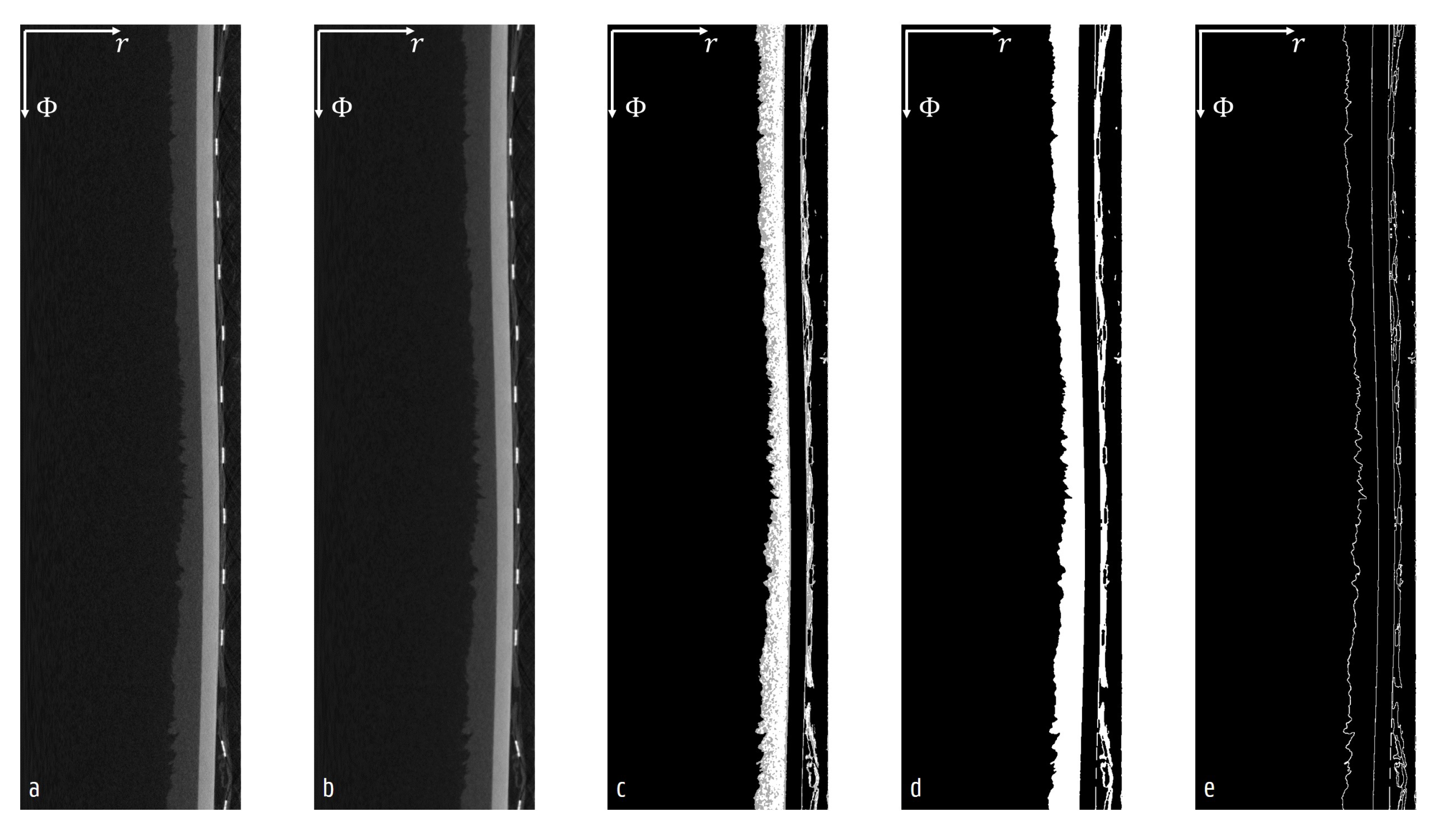
2.5. Cylindrical CT Reconstruction and Image Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Pose Estimation Stability
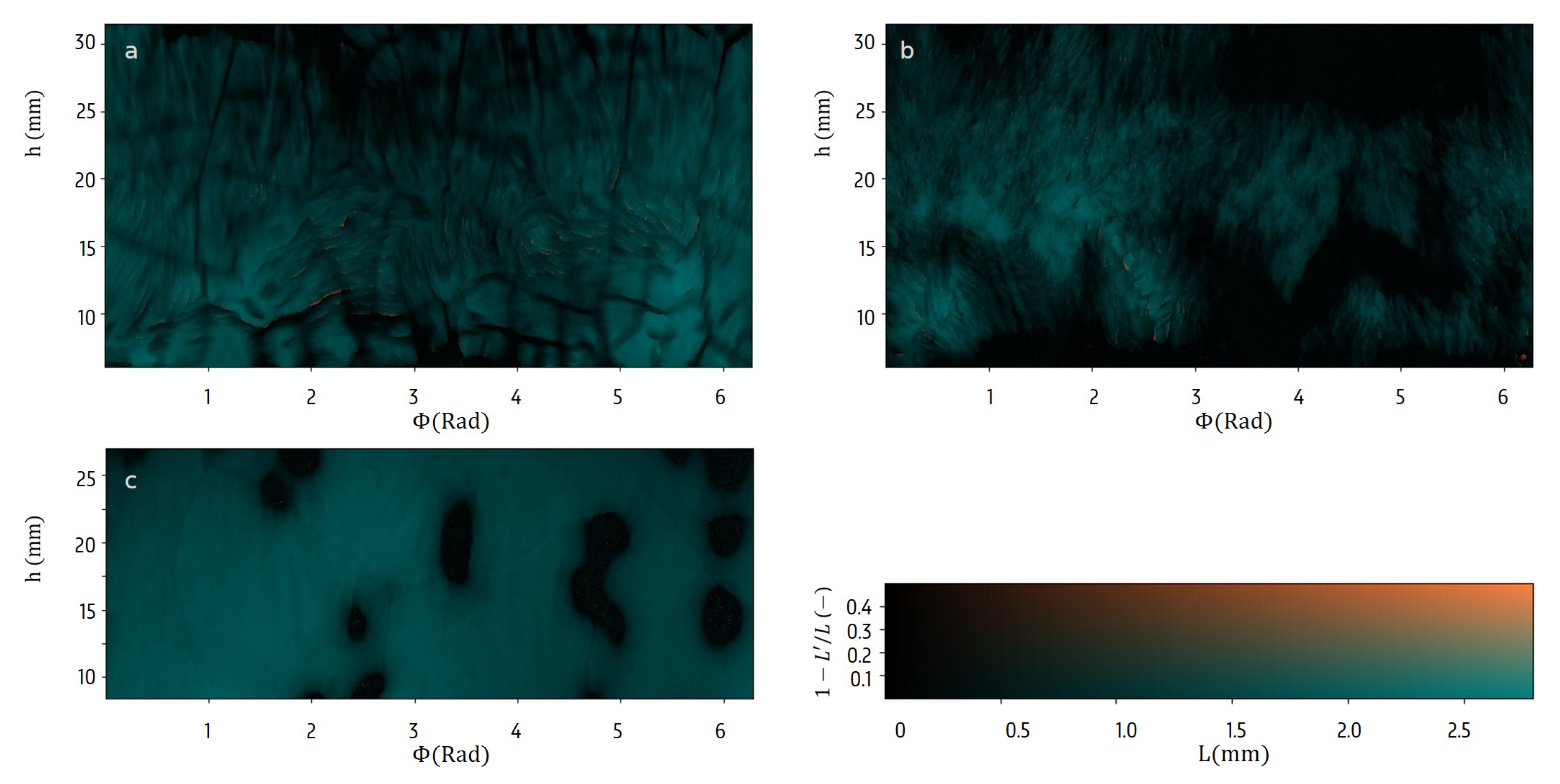
3.2. Surface Characteristics
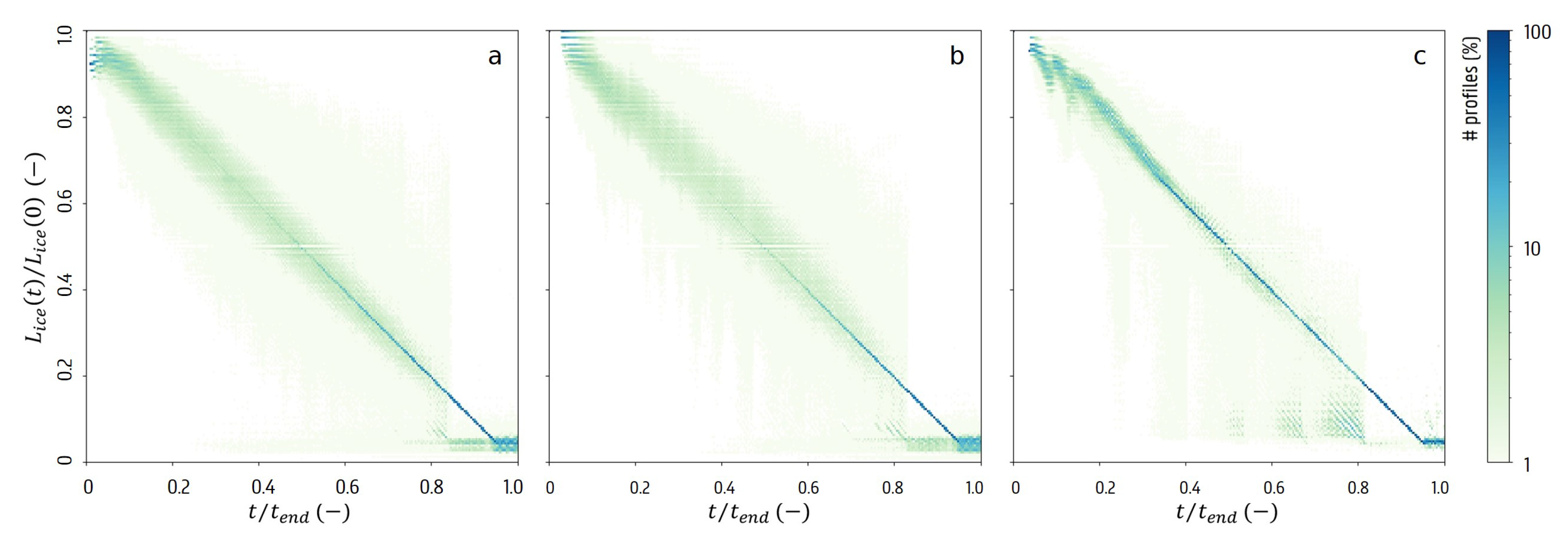
3.3. Sublimation Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Geometrical Sources of Errors
4.2. Motion Artefacts
4.3. Imaging the Dry Layer
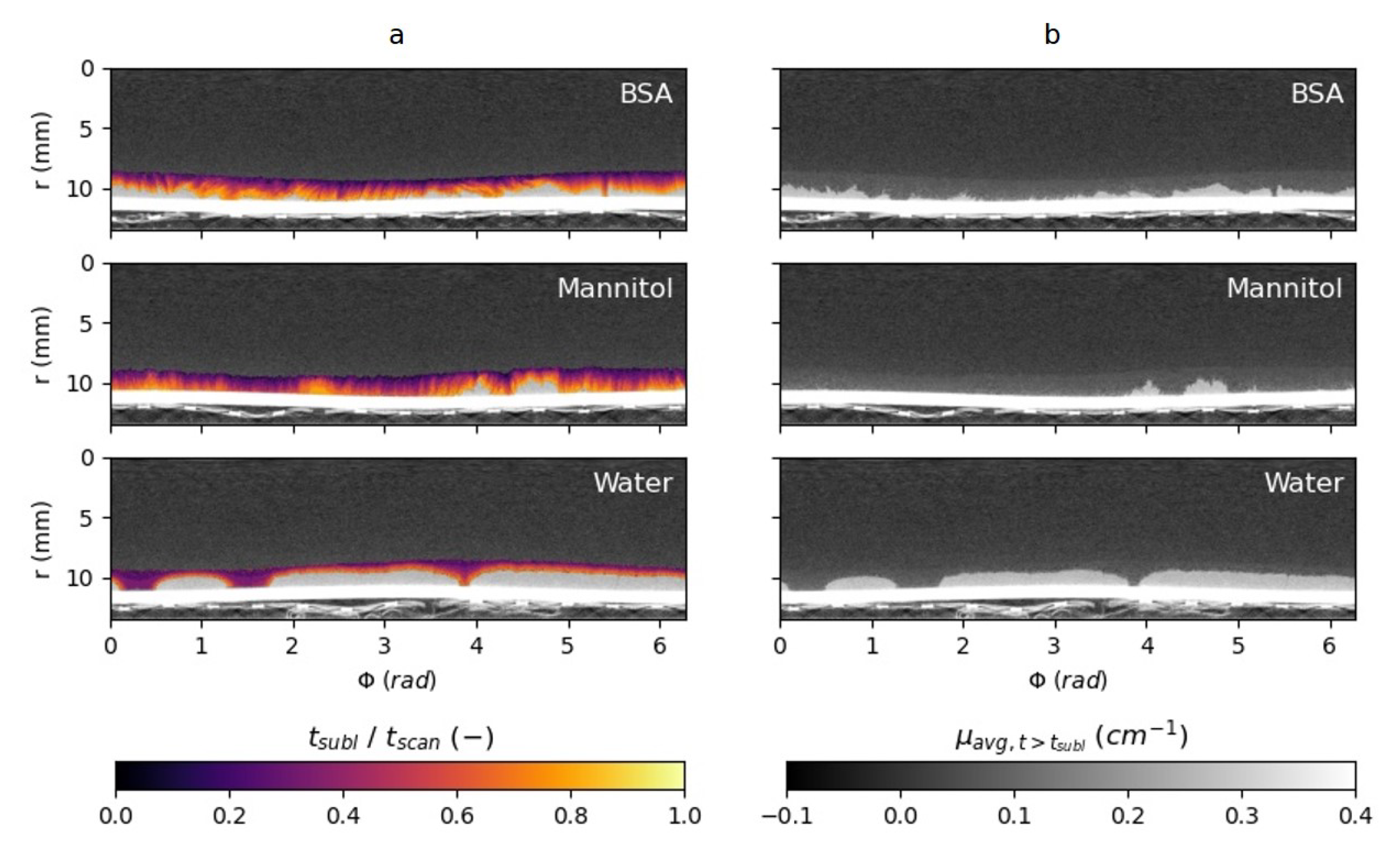
4.4. Chemical Influence on the Sublimation
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nail, S.; Jiang, S.; Chongprasert, S.; Knopp, S. Development and Manufacture of Protein Pharmaceuticals. In Fundamentals of Freeze-Drying. Pharmaceutical Biotechnology; Steve, L.N., Michael, J.A., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2002; Volume 14. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, X.; Pikal, M. Design of freeze-drying processes for pharmaceuticals: Practical advice. Pharm. Res. 2004, 21, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pikal, M.J. Freeze-drying of proteins: Process, formulation, and stability. In Formulation and Delivery of Proteins and Peptides; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 1994; pp. 120–133. [Google Scholar]
- Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.T.F.; De Meyer, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Van Herck, S.; Corver, J.; Nopens, I.; Vanhoorne, V.; De Geest, B.G.; et al. The relevance of shear, sedimentation and diffusion during spin freezing, as potential first step of a continuous freeze-drying process for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 539, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Meyer, L.; Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.T.F.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; Nopens, I.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. Modelling the primary drying step for the determination of the optimal dynamic heating pad temperature in a continuous pharmaceutical freeze-drying process for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2017, 532, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; De Meyer, L.; Vervaet, C.; De Beer, T. Thermal Imaging as a Noncontact Inline Process Analytical Tool for Product Temperature Monitoring during Continuous Freeze-Drying of Unit Doses. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 13591–13599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brouckaert, D.; De Meyer, L.; Vanbillemont, B.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Lammens, J.; Mortier, S.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; Nopens, I.; De Beer, T. Potential of near-infrared chemical imaging as process analytical technology tool for continuous freeze-drying. Anal. Chem. 2018, 90, 4354–4362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Meyer, L.; Van Bockstal, P.J.; Corver, J.; Vervaet, C.; Remon, J.; De Beer, T. Evaluation of spin freezing versus conventional freezing as part of a continuous pharmaceutical freeze-drying concept for unit doses. Int. J. Pharm. 2015, 496, 75–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maire, E.; Withers, P.J. Quantitative X-ray tomography. Int. Mater. Rev. 2014, 59, 1–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnudde, V.; Boone, M.N. High-resolution X-ray computed tomography in geosciences: A review of the current technology and applications. Earth Sci. Rev. 2013, 123, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, A.; Yadroitsev, I.; Yadroitsava, I.; Le Roux, S.G. X-ray microcomputed tomography in additive manufacturing: A review of the current technology and applications. 3D Print. Addit. Manuf. 2018, 5, 227–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, S.; Ott, H.; Klapp, S.A.; Schwing, A.; Neiteler, R.; Brussee, N.; Makurat, A.; Leu, L.; Enzmann, F.; Schwarz, J.O. Real-time 3D imaging of Haines jumps in porous media flow. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 3755–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bultreys, T.; Boone, M.A.; Boone, M.N.; Schryver, T.D.; Masschaele, B.; Loo, D.V.; Hoorebeke, L.V.; Cnudde, V. Real-time visualization of Haines jumps in sandstone with laboratory-based microcomputed tomography. Water Resour. Res. 2015, 51, 8668–8676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.R.; Brun, F.; O’shaughnessy, C.; Mancini, L.; Fife, J.L.; Rivers, M. A four-dimensional X-ray tomographic microscopy study of bubble growth in basaltic foam. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marone, F.; Schlepütz, C.M.; Marti, S.; Fusseis, F.; Velásquez-Parra, A.; Griffa, M.; Jiménez-Martínez, J.; Dobson, K.J.; Stampanoni, M. Time resolved in situ X-ray tomographic microscopy unraveling dynamic processes in geologic systems. Front. Earth Sci. 2020, 7, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gioumouxouzis, C.I.; Katsamenis, O.L.; Bouropoulos, N.; Fatouros, D.G. 3D printed oral solid dosage forms containing hydrochlorothiazide for controlled drug delivery. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2017, 40, 164–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Kock, T.; Boone, M.A.; De Schryver, T.; Van Stappen, J.; Derluyn, H.; Masschaele, B.; De Schutter, G.; Cnudde, V. A pore-scale study of fracture dynamics in rock using X-ray micro-CT under ambient freeze–thaw cycling. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 2867–2874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, M.J.; Simonsen, T.J.; Martín-Vega, D. The ‘dance’of life: Visualizing metamorphosis during pupation in the blow fly Calliphora vicina by X-ray video imaging and micro-computed tomography. R. Soc. Open Sci. 2017, 4, 160699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, T.; Garwood, R.J.; Simonsen, T.J.; Bradley, R.S.; Withers, P.J. Metamorphosis revealed: Time-lapse three-dimensional imaging inside a living chrysalis. J. R. Soc. Interface 2013, 10, 20130304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, T.; Dierick, M.; Heyndrickx, M.; Van Stappen, J.; Boone, M.A.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Boone, M.N. Motion compensated micro-CT reconstruction for in-situ analysis of dynamic processes. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Odstrcil, M.; Holler, M.; Raabe, J.; Sepe, A.; Sheng, X.; Vignolini, S.; Schroer, C.G.; Guizar-Sicairos, M. Ab initio nonrigid X-ray nanotomography. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 2600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Moreno, F.; Kamm, P.H.; Neu, T.R.; Bülk, F.; Mokso, R.; Schlepütz, C.M.; Stampanoni, M.; Banhart, J. Using X-ray tomoscopy to explore the dynamics of foaming metal. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, S.M.; Schwyn, D.A.; Mokso, R.; Wicklein, M.; Müller, T.; Doube, M.; Stampanoni, M.; Krapp, H.G.; Taylor, G.K. In Vivo Time-Resolved Microtomography Reveals the Mechanics of the Blowfly Flight Motor. PLoS Biol. 2014, 12, e1001823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bultreys, T.; Boone, M.A.; Boone, M.N.; Schryver, T.D.; Masschaele, B.; Hoorebeke, L.V.; Cnudde, V. Fast laboratory-based micro-computed tomography for pore-scale research: Illustrative experiments and perspectives on the future. Adv. Water Resour. 2016, 95, 341–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Schryver, T.; Boone, M.A.; De Kock, T.; Duquenne, B.; Christaki, M.; Masschaele, B.; Dierick, M.; Boone, M.N.; Van Hoorebeke, L. A Compact Low Cost Cooling Stage for Lab Based X-ray Micro-CT Setups. In AIP Conference Proceedings; AIP Publishing LLC: College Park, MD, USA, 2016; Volume 1696, p. 020018. [Google Scholar]
- Fife, J.L.; Rappaz, M.; Pistone, M.; Celcer, T.; Mikuljan, G.; Stampanoni, M. Development of a laser-based heating system for in situ synchrotron-based X-ray tomographic microscopy. J. Synchrotron Radiat. 2012, 19, 352–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez-Tamarit, S.; Solórzano, E.; Mokso, R.; Rodríguez-Pérez, M. In-situ understanding of pore nucleation and growth in polyurethane foams by using real-time synchrotron X-ray tomography. Polymer 2019, 166, 50–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shastry, A.; Palacio-Mancheno, P.E.; Braeckman, K.; Vanheule, S.; Josipovic, I.; Van Assche, F.; Robles, E.; Cnudde, V.; Van Hoorebeke, L.; Boone, M.N. In-situ high resolution dynamic X-ray microtomographic imaging of olive oil removal in kitchen sponges by squeezing and rinsing. Materials 2018, 11, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dierick, M.; Loo, D.V.; Masschaele, B.; den Bulcke, J.V.; Acker, J.V.; Cnudde, V.; Hoorebeke, L.V. Recent micro-CT scanner developments at UGCT. Nucl. Instruments Methods Phys. Res. Sect. B Beam Interact. Mater. Atoms 2014, 324, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewanckele, J.; Boone, M.; Coppens, F.; Van Loo, D.; Merkle, A.P. Innovations in laboratory-based dynamic micro-CT to accelerate in situ research. J. Microsc. 2020, 277, 197–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyndrickx, M.; Boone, M.; De Schryver, T.; Bultreys, T.; Goethals, W.; Verstraete, G.; Vanhoorne, V.; Van Hoorebeke, L. Piecewise linear fitting in dynamic micro-CT. Mater. Charact. 2018, 139, 259–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeuser, C.; Goldbach, P.; Huwyler, J.; Friess, W.; Allmendinger, A. Imaging techniques to characterize cake appearance of freeze-dried products. J. Pharm. Sci. 2018, 107, 2810–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haeuser, C.; Goldbach, P.; Huwyler, J.; Friess, W.; Allmendinger, A. Be Aggressive! Amorphous Excipients Enabling Single-Step Freeze-Drying of Monoclonal Antibody Formulations. Pharmaceutics 2019, 11, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izutsu, K.i.; Yonemochi, E.; Yomota, C.; Goda, Y.; Okuda, H. Studying the morphology of lyophilized protein solids using X-ray micro-CT: Effect of post-freeze annealing and controlled nucleation. AAPS PharmSciTech 2014, 15, 1181–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisano, R.; Barresi, A.A.; Capozzi, L.C.; Novajra, G.; Oddone, I.; Vitale-Brovarone, C. Characterization of the mass transfer of lyophilized products based on X-ray micro-computed tomography images. Dry. Technol. 2017, 35, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanbillemont, B.; Lammens, J.; Goethals, W.; Vervaet, C.; Boone, M.N.; De Beer, T. 4D Micro-Computed X-ray Tomography as a Tool to Determine Critical Process and Product Information of Spin Freeze-Dried Unit Doses. Pharmaceutics 2020, 12, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLaughlin, R.A. Technical Report-Randomized Hough Transform: Improved Ellipse Detection with Comparison; University of Western Australia: Perth, Australia, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- De Schryver, T. Fast Imaging in Non-Standard X-ray Computed Tomography Geometries. Ph.D. Thesis, Ghent University, Ghent, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Goethals, W.; Heyndrickx, M.; Boone, M. Fast tomographic inspection of cylindrical objects. arXiv 2020, arXiv:eess.IV/2005.11976. [Google Scholar]
- Ogienko, A.; Stoporev, A.; Ogienko, A.; Mel’gunov, M.; Adamova, T.; Yunoshev, A.; Manakov, A.Y.; Boldyreva, E. Discrepancy between thermodynamic and kinetic stabilities of the tert-butanol hydrates and its implication for obtaining pharmaceutical powders by freeze-drying. Chem. Commun. 2019, 55, 4262–4265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Goethals, W.; Vanbillemont, B.; Lammens, J.; De Beer, T.; Vervaet, C.; Boone, M.N. In-Situ X-ray Imaging Of Sublimating Spin-Frozen Solutions. Materials 2020, 13, 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132953
Goethals W, Vanbillemont B, Lammens J, De Beer T, Vervaet C, Boone MN. In-Situ X-ray Imaging Of Sublimating Spin-Frozen Solutions. Materials. 2020; 13(13):2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132953
Chicago/Turabian StyleGoethals, Wannes, Brecht Vanbillemont, Joris Lammens, Thomas De Beer, Chris Vervaet, and Matthieu N. Boone. 2020. "In-Situ X-ray Imaging Of Sublimating Spin-Frozen Solutions" Materials 13, no. 13: 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132953
APA StyleGoethals, W., Vanbillemont, B., Lammens, J., De Beer, T., Vervaet, C., & Boone, M. N. (2020). In-Situ X-ray Imaging Of Sublimating Spin-Frozen Solutions. Materials, 13(13), 2953. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13132953