Influence of Phosphorus Slag on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortars
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
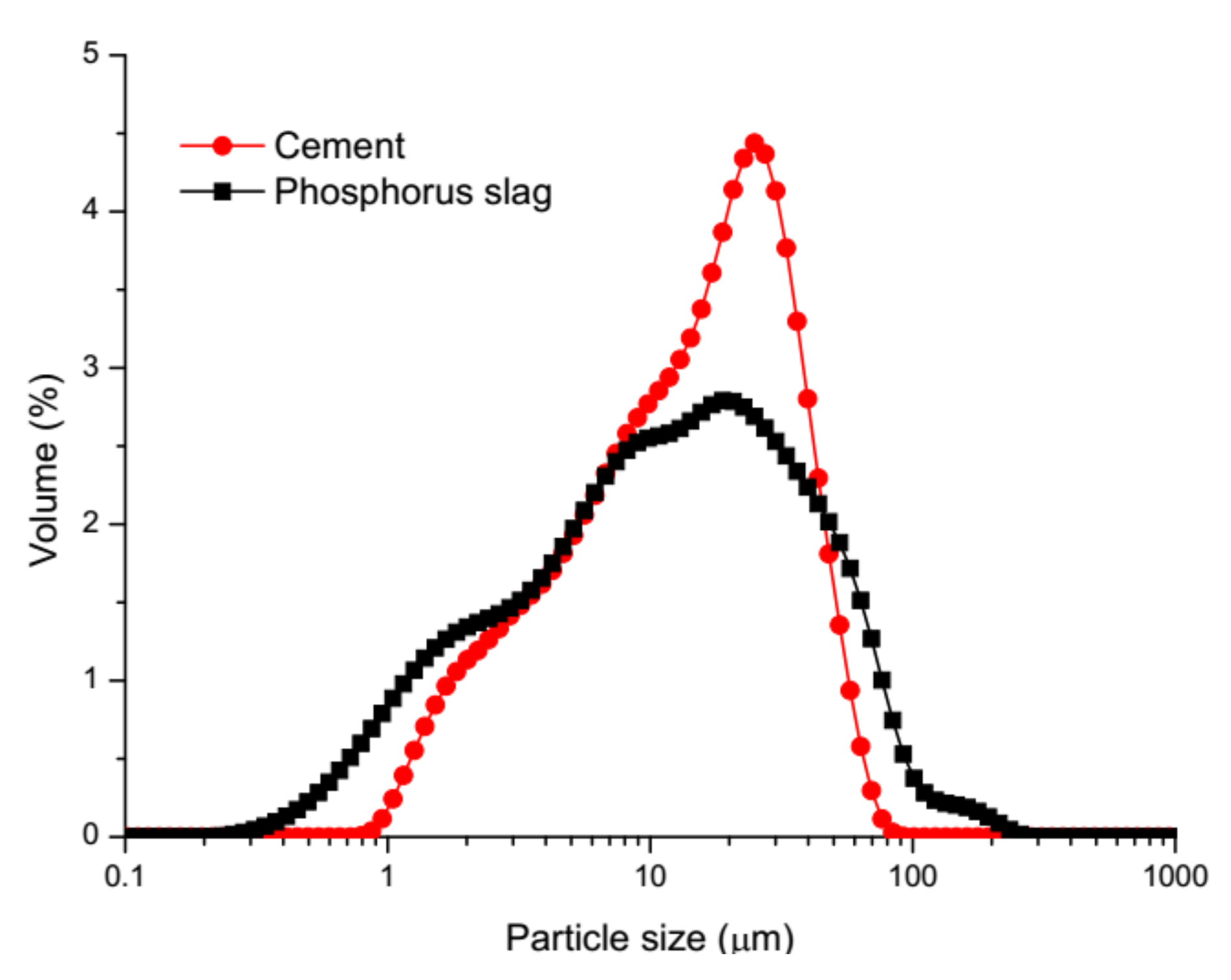
2.1. Materials and Mix Proportions
2.2. Performance of Cement Pastes and Fresh Mortars
2.3. Compressive Strength
2.4. Resistance to Carbonation
2.5. Activation of Phosphorus Slag
2.6. Microstructure Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
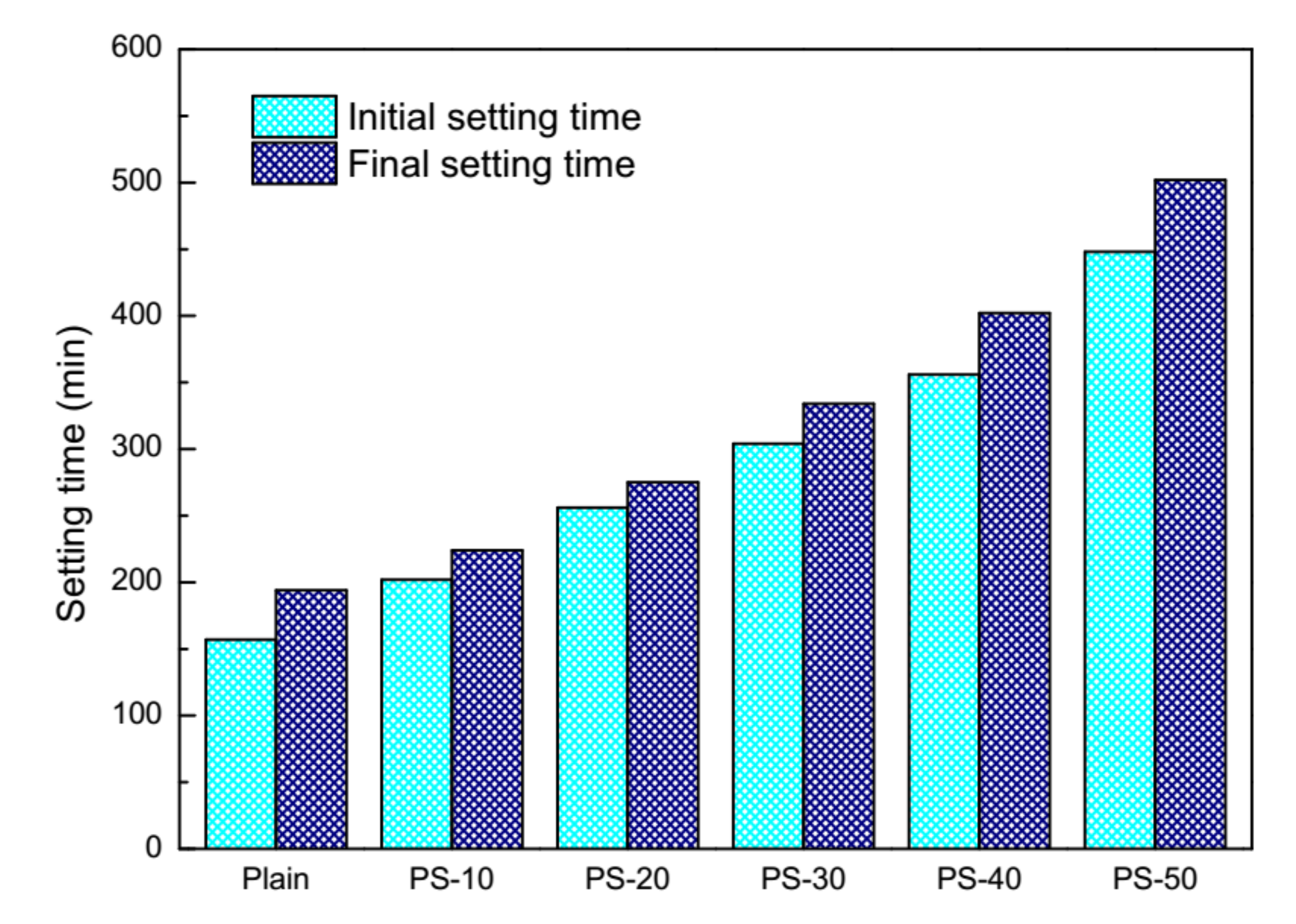
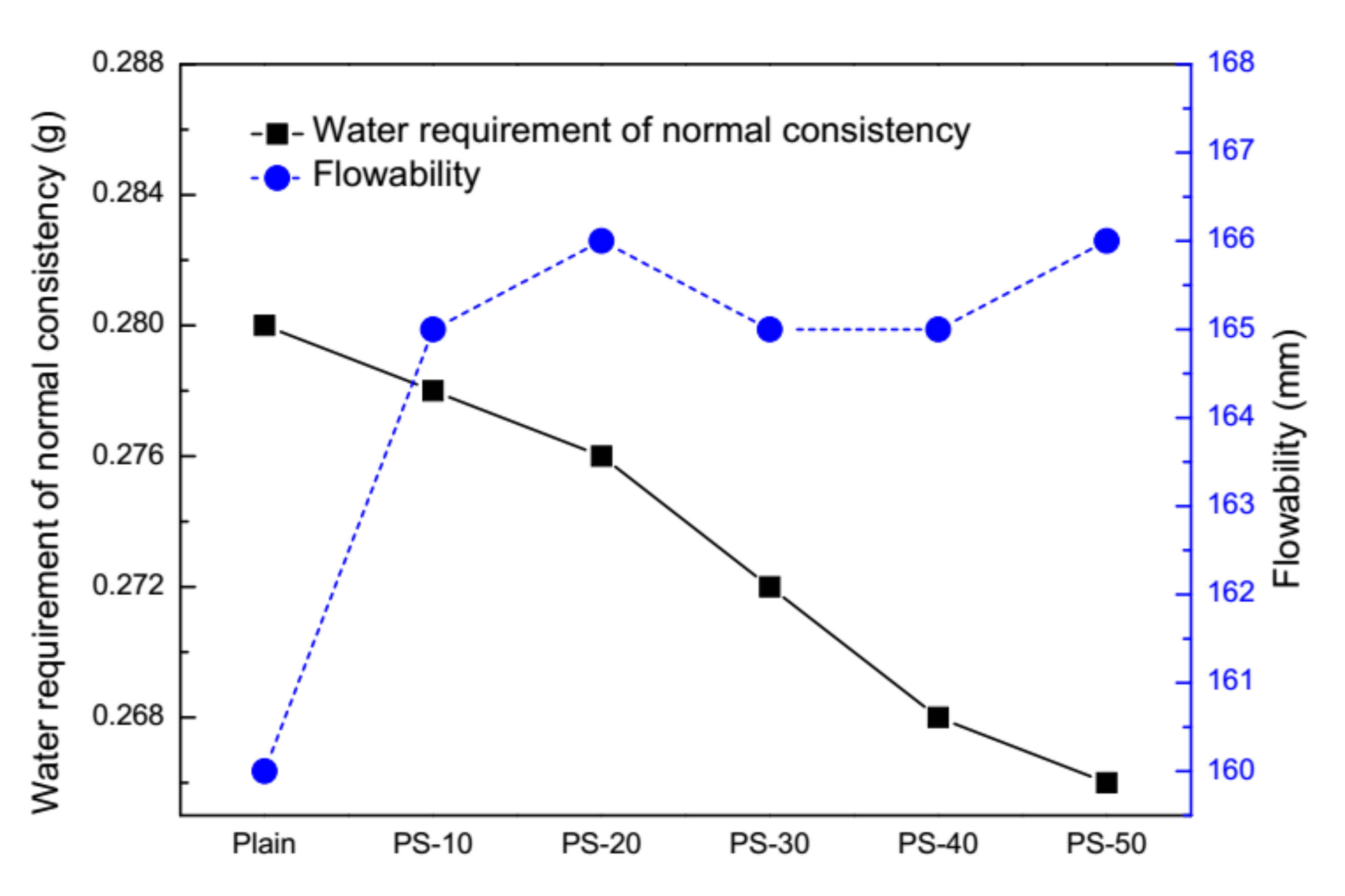
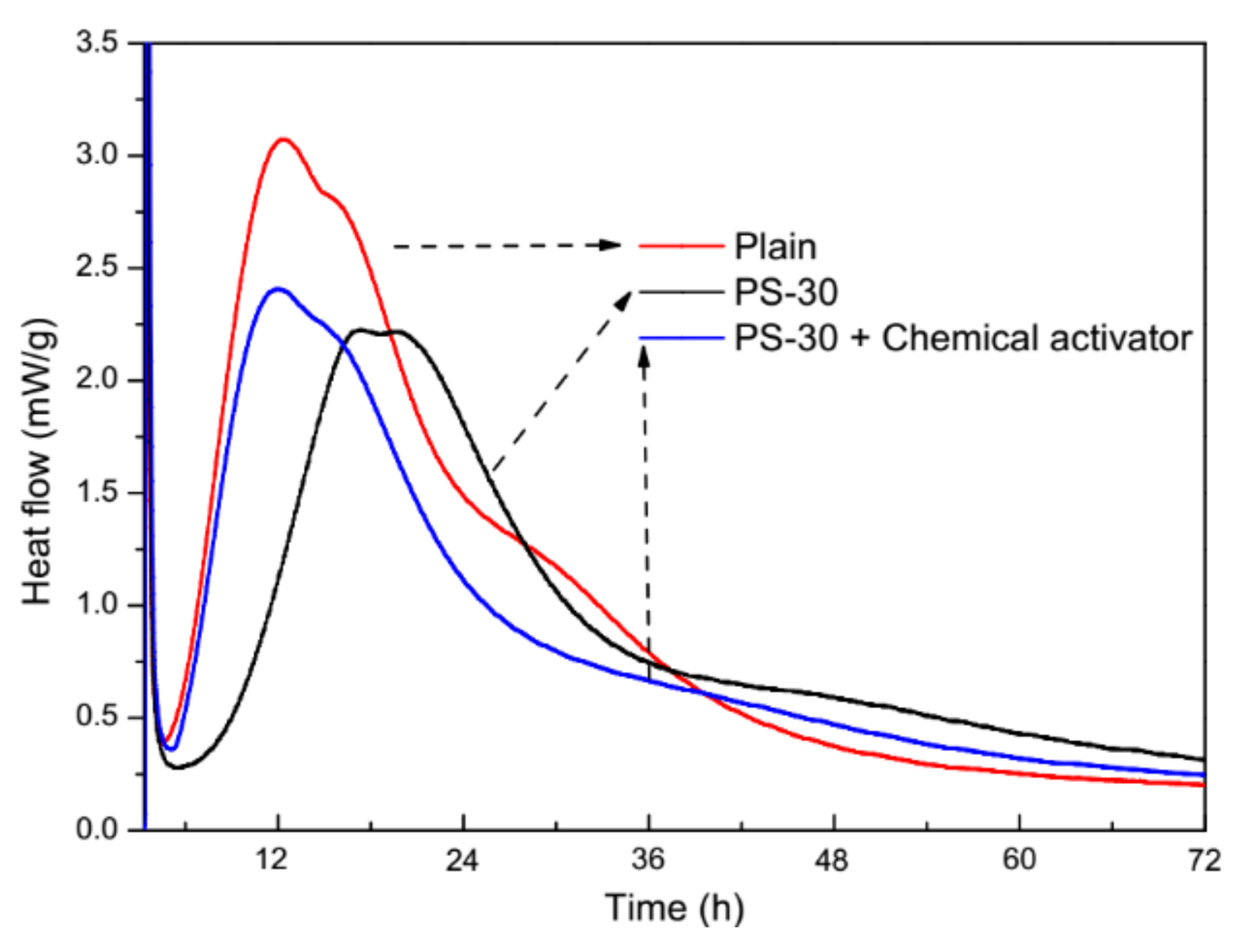
3.1. Behavior of Cement Pastes and Fresh Mortars
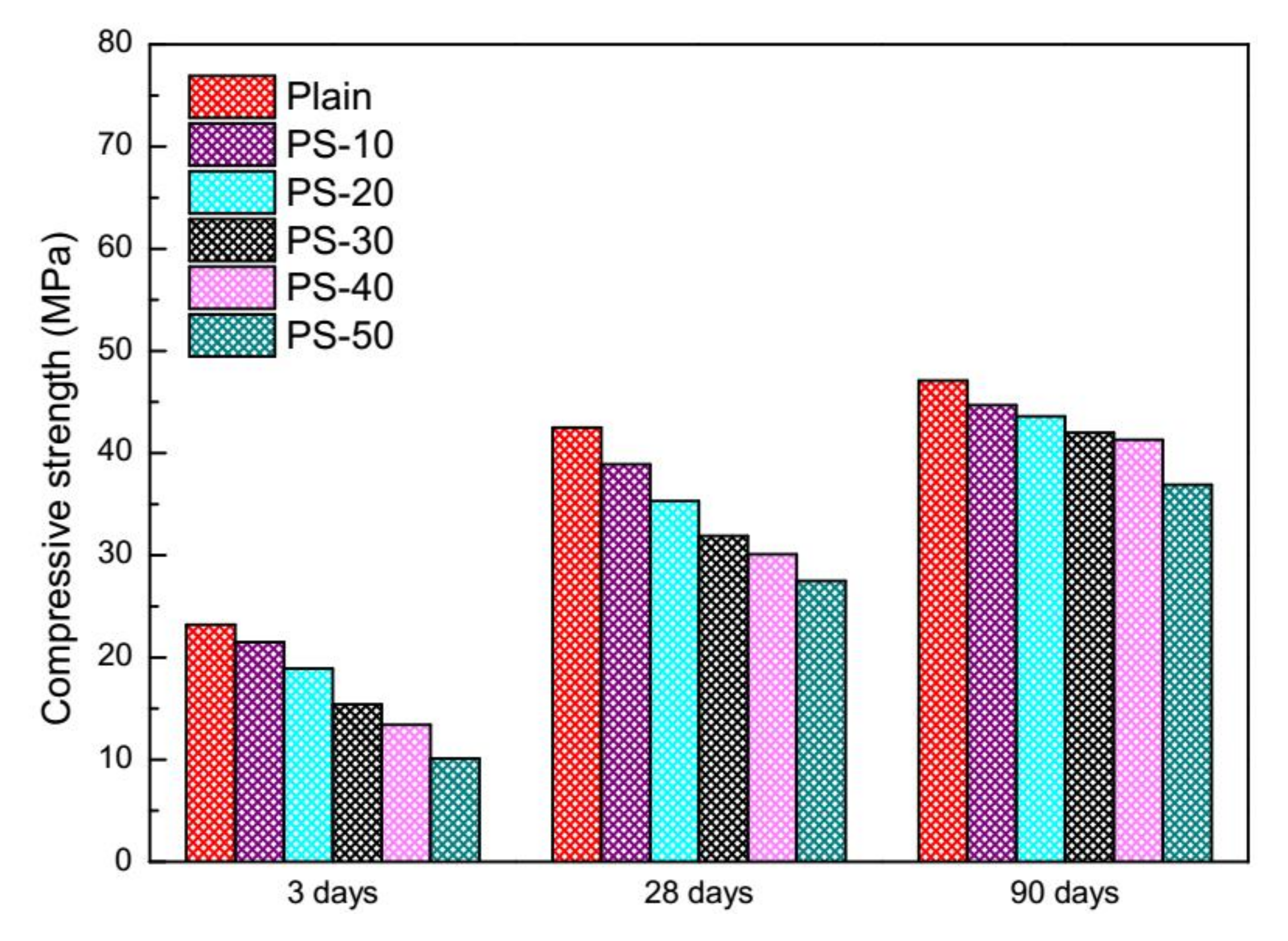
3.2. Compressive Strength
3.3. Carbonation Depth
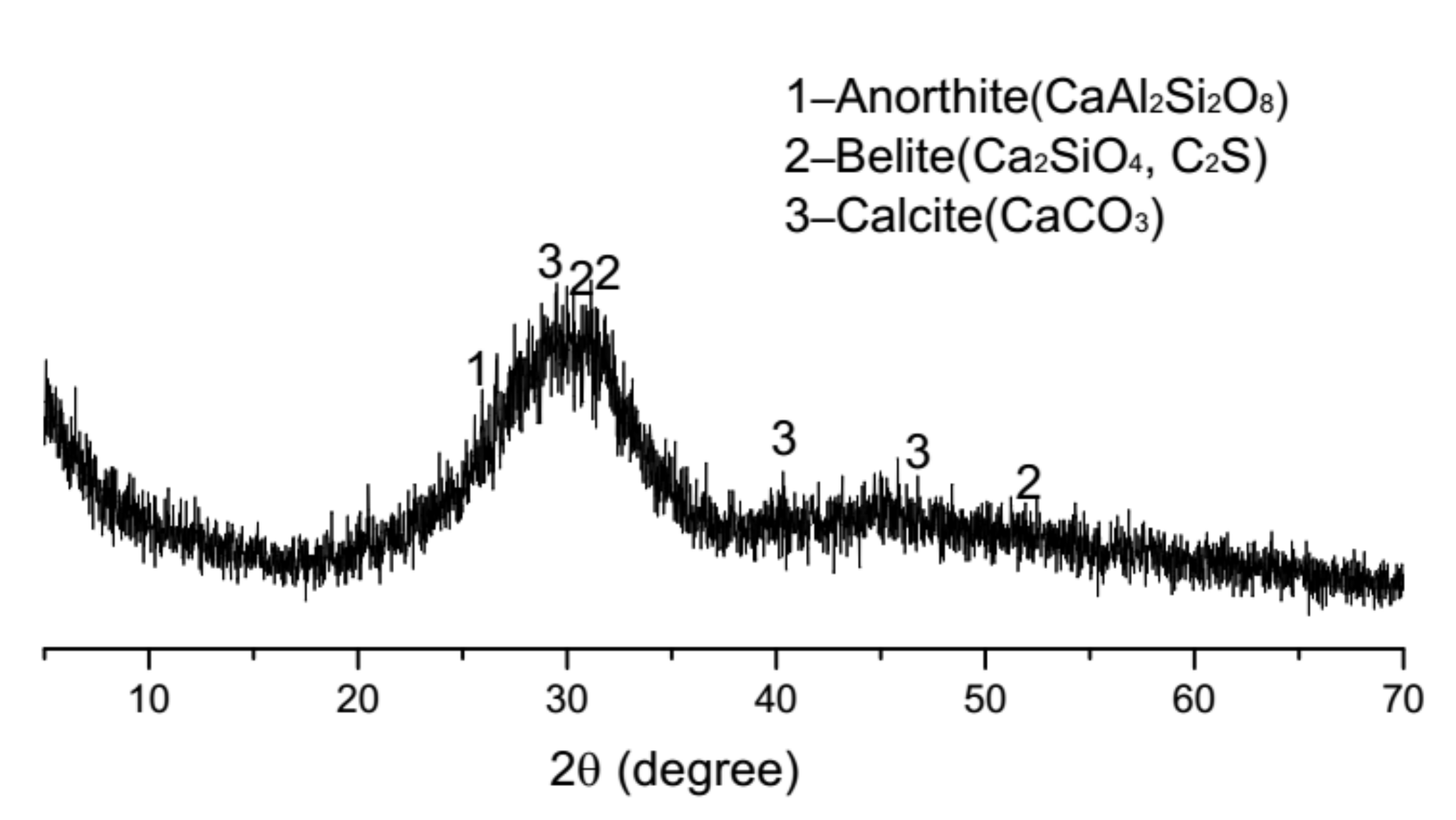
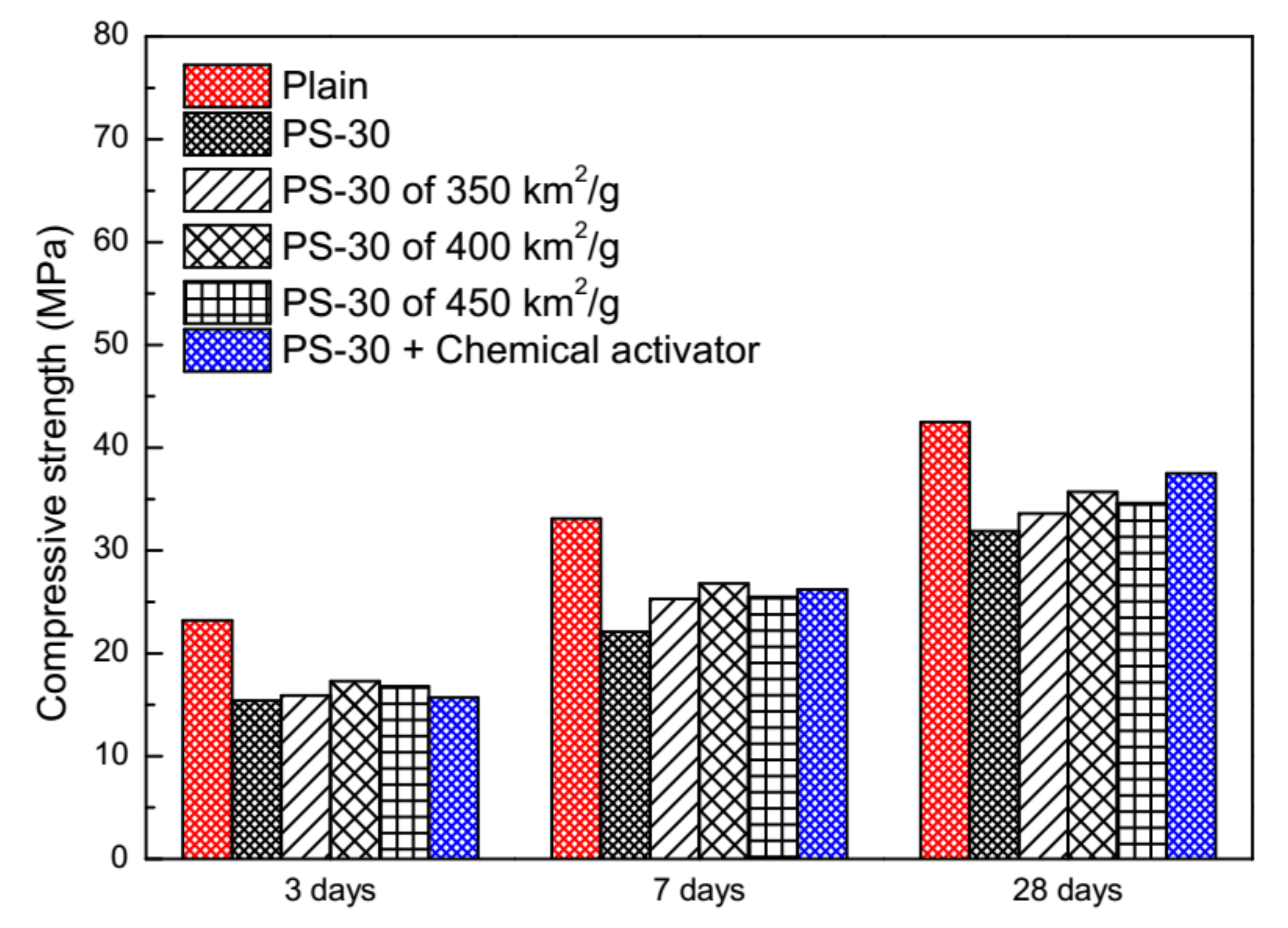
3.4. Physical and Chemical Activation
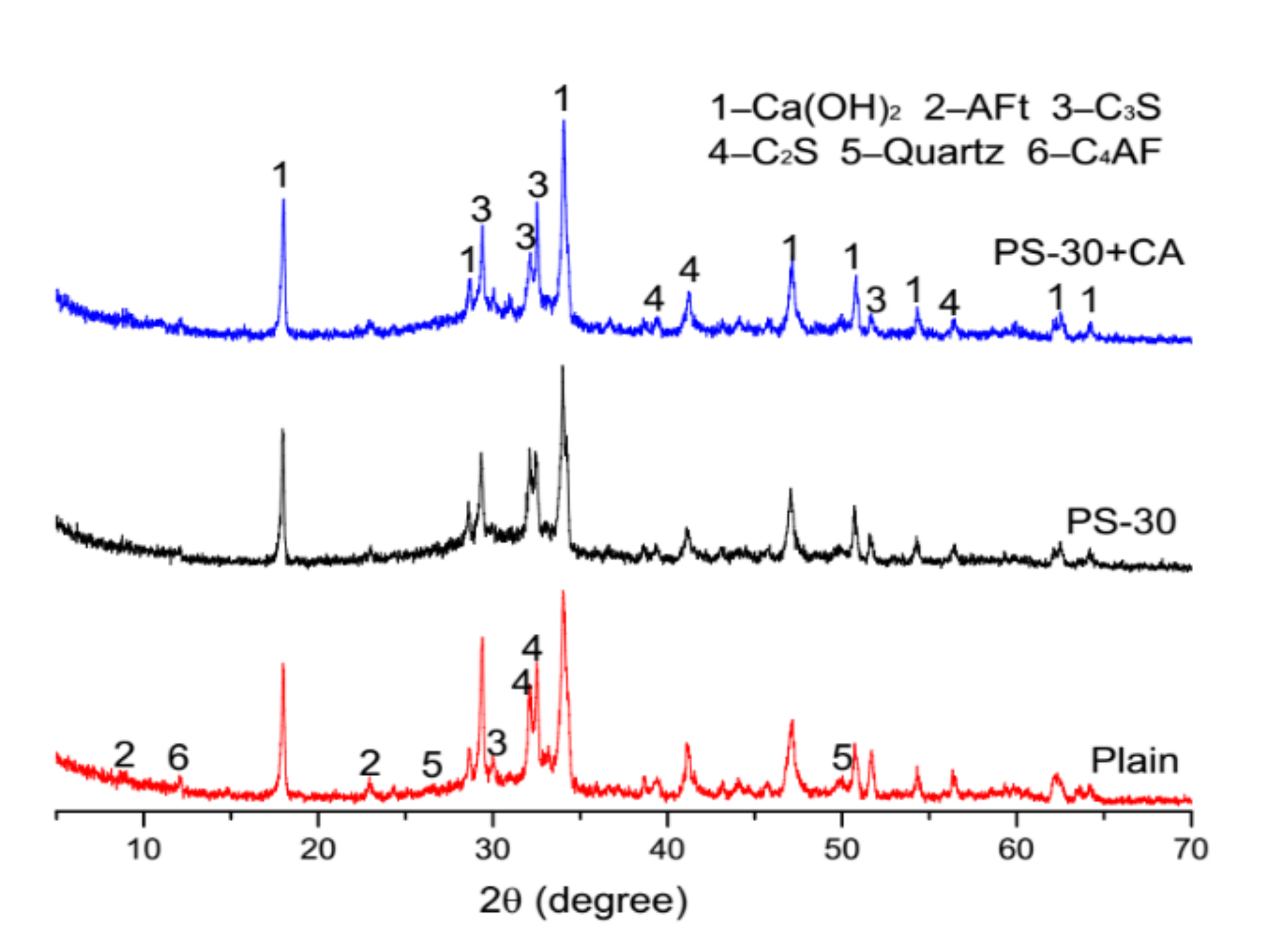
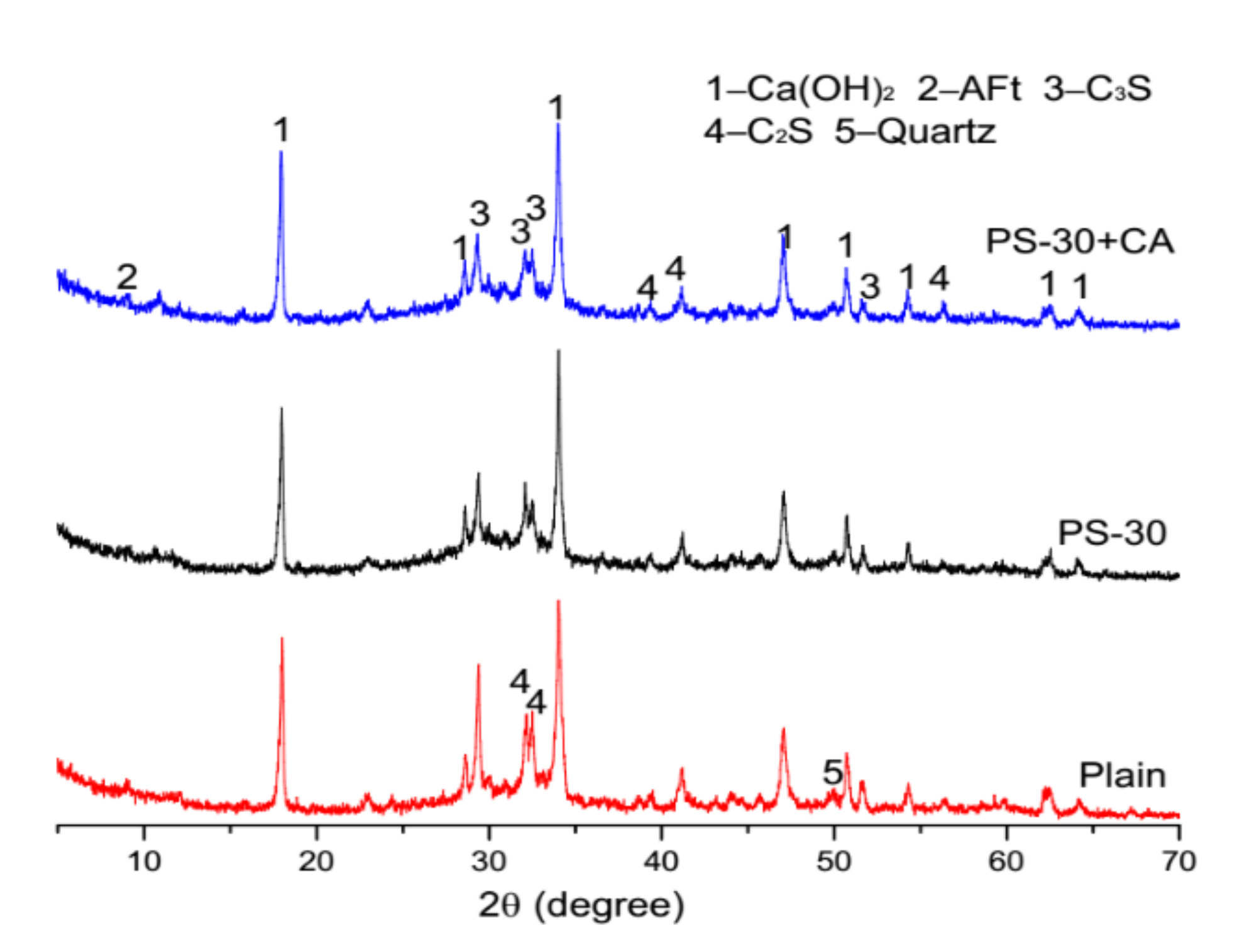
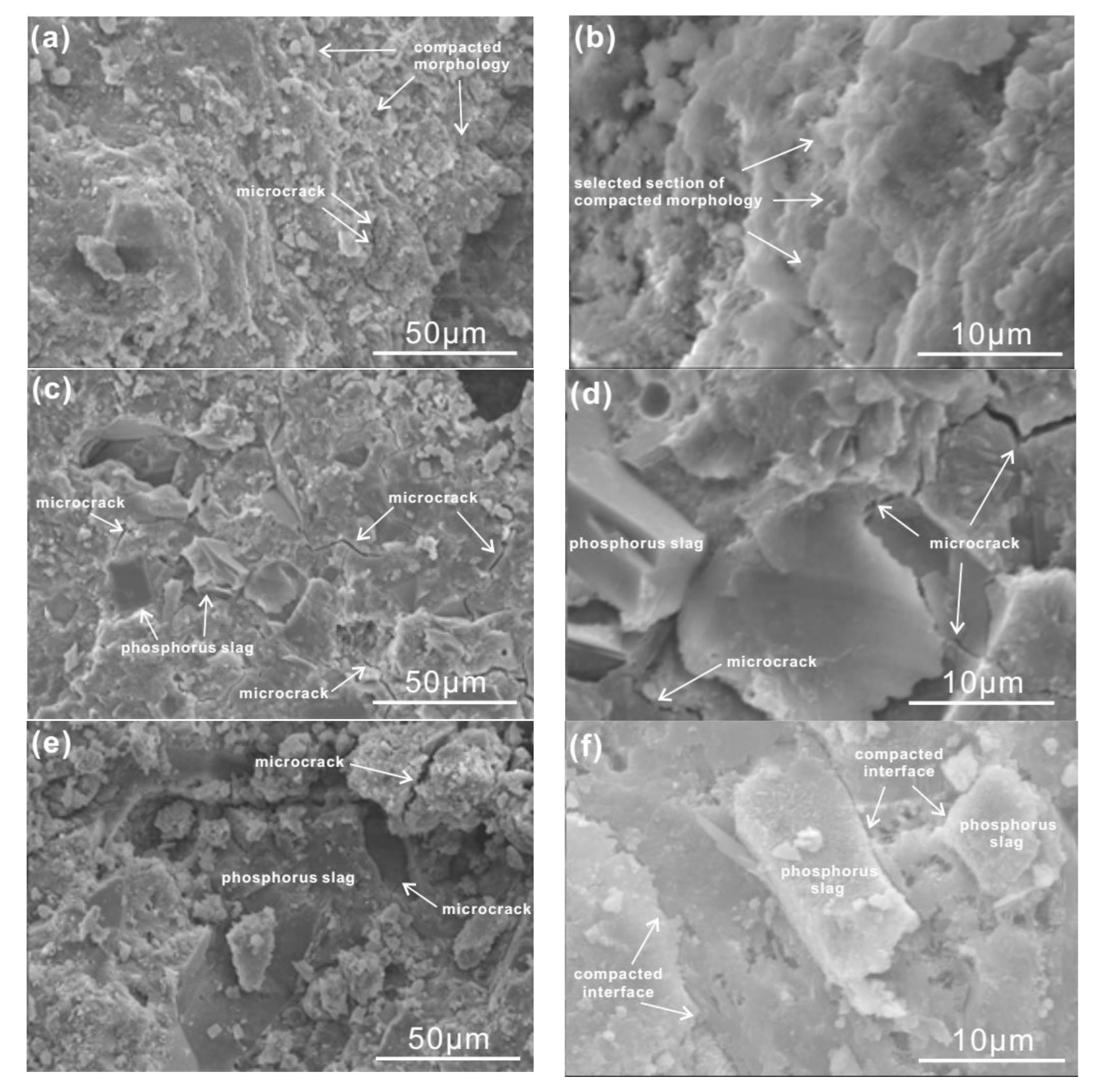
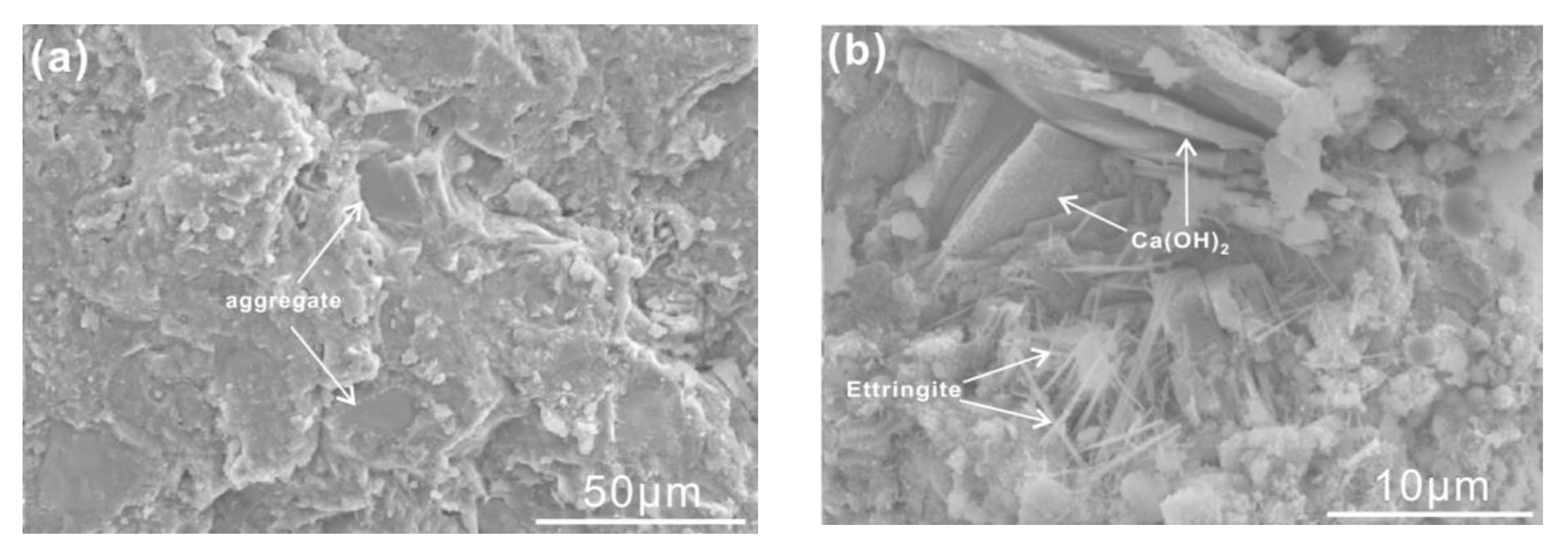
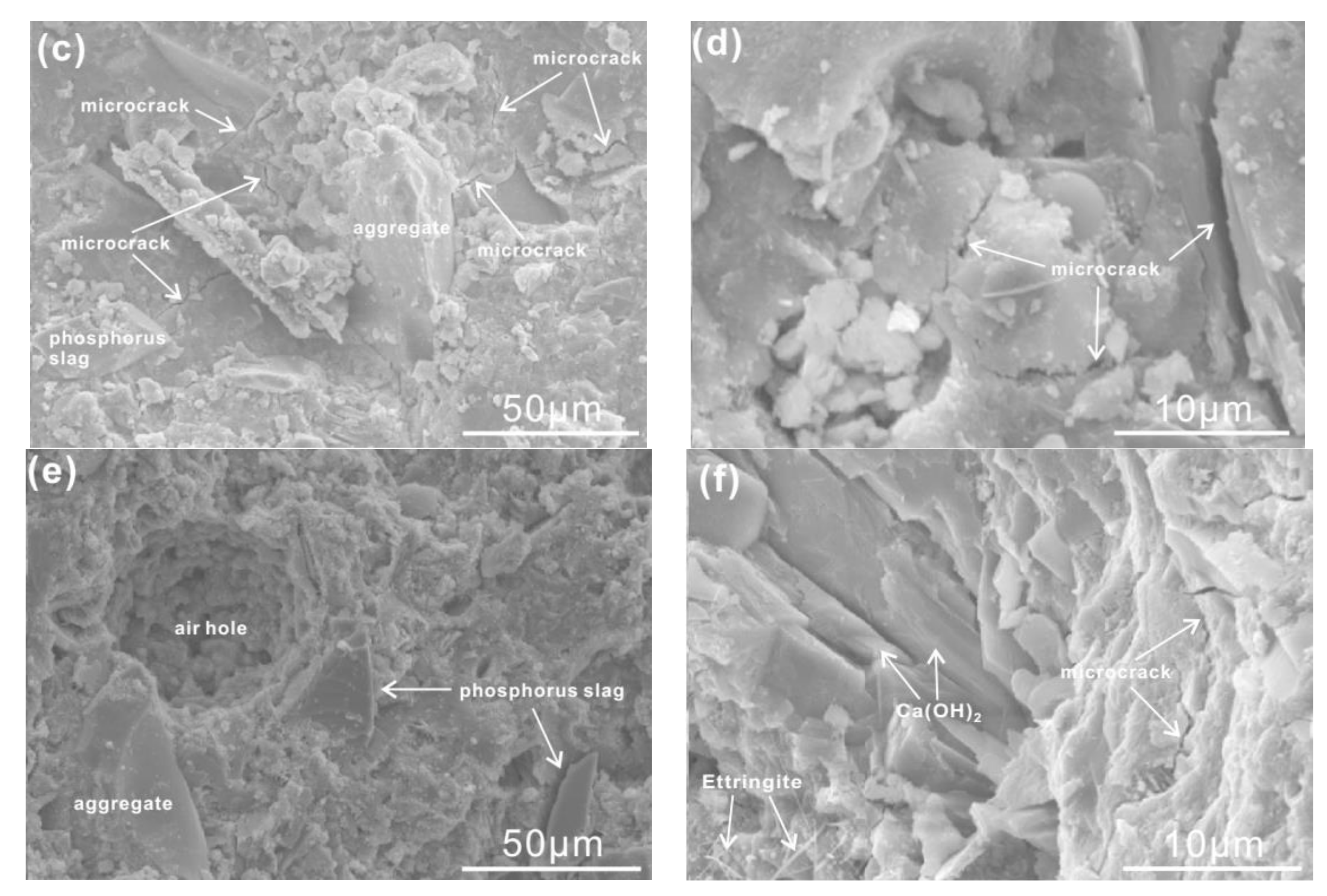
3.5. Microstructure Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, Y.; Chen, J.N.; Mol, A.P.J.; Ayres, R.U. Comparative analysis of phosphorus use within national and local economies in China. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2007, 51, 454–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.H.; Xie, X.L. Utilization of phosphate fertilizer industry waste for belite—Ferroaluminate cement production. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 38, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yan, Y.; Hu, Z.H. Utilization of phosphogypsum for the preparation of non-autoclaved aerated concrete. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 44, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, W.G.; Liu, Z.X.; He, X.Q.; Liu, Q.L. Mixture ratio of phosphogypsum in backfilling. Min. Technol. 2013, 122, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, G.Z.; Wu, A.X.; Wang, Y.M.; Li, J.Q. Effect of lime on properties of filling cementitious material prepared by hemihydrate phosphogypsum. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2020, 48, 86–93. [Google Scholar]
- Li, F.L.; Qian, J.S.; Ni, X.Q.; Zhang, C.; Lin, Z. Effect of fast-firing on dehydrated phase composition and cementitious property of phosphogypsum. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 43, 579–584. [Google Scholar]
- Hua, S.D.; Zhang, L.L.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, M.J.; Guo, D.P.; Tong, F.; Zhao, Y.H. Study on physical and chemical properties of high magnesium nickel slag-phosphogypsum composite cementitious materials in different particle sizes. J. Adv. Concr. Technol. 2020, 18, 129–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.S.; Zhao, B.; Wang, X.M.; Zhang, Q.L.; Wang, L. Cemented backfilling performance of yellow phosphorus slag. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2010, 17, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukhamedzhanova, M.T.; Irkakhodzhaeva, A.P. Low-temperature porcelain body using phosphorus slag. Glass Ceram. 1990, 47, 107–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.P.; Ma, L.P.; Huang, X.F.; Tang, J.X.; Yang, J.; Yang, J. Effect of different amounts of slag on the crystallization behavior of glass-ceramics produced by natural cooling yellow phosphorus slag. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 87696–87702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.L.; Dong, F.Q.; Luo, Y.J.; Huang, L.L.; Zhang, B.S. Preparation of spherical calcium carbonate from phosphorus slag. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2010, 38, 1268–1273. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Shu, Z.; Hu, X.H.; Wang, Y.X. Direct utilization of liquid slag from phosphorus-smelting furnace to prepare cast stone as decorative building material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2010, 24, 811–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, G.P.; Bai, S.Y.; Ju, S.J.; Huang, T. Laboratory evaluation on recycling waste phosphorus slag as the mineral filler in hot-mix asphalt. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 846–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, Y.P.; Zhang, B.; Yan, Y.; Chen, H.X.; Xiong, R.; Geng, J.G. Effects of phosphorus slag powder and polyester fiber on performance characteristics of asphalt binders and resultant mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 141, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.S.; Xue, Q.; Wang, P.; Li, Z.Z.; Du, Y.J. Solidification/stabilization of lead-contaminated soil using cement and waste phosphorus slag. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy 2015, 34, 957–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, C.J.; Qian, J.S. High performance cementing materials from industrial slags-a review. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2000, 29, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Shen, J.J.; Mao, L.X.; Wu, X.Q. The influence of admixtures on the properties of phosphorous slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2000, 30, 1169–1173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.X.; Shen, J.J.; Chen, L.; Wu, X.Q. The influence of fast-setting/early-strength agent on high phosphorous slag content cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 2001, 31, 119–124. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.X.; Chen, L.; Xu, Z.Z.; Luo, Z.M. A blended cement containing blast furnace slag and phosphorous slag. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2002, 17, 62–65. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, Q.; Wu, Y. The influence of steel slag on phosphorus slag cement. Key Eng. Mater. 2012, 509, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, L.Y.; Huang, S.M.; Shen, W. Characteristics of hydration, setting and hardening of clinker with phosphorus slag as mineralizing agent. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 1996, 24, 132–136. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, B.G.; Mu, S.; Jian, S.W.; Yu, M.L. Effect of phosphorus slag composite mineralizer on burnability of portland cement raw meals. Bull. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 26, 80–83. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Fang, K.H.; Yang, H.Q.; Peng, H. Hydration kinetics of phosphorus slag-cement paste. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2011, 26, 142–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, J.H.; Deng, M.; Wang, A.G.; Xie, L.L. Influence of the cement fineness on strengths of cement pastes containing high phosphorus slag. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2015, 27, 04015047. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.Y.; Ye, Q.; Yang, J.; Dai, F.; Su, Y.; Wang, Y.B.; Strnadel, B. Physico-chemical characteristics of wet-milled ultrafne-granulated phosphorus slag as a supplementary cementitious material. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol. Mater. Sci. Ed. 2018, 33, 625–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.Q.; Wang, Q.; Yang, J. Hydration mechanisms of composite binders containing phosphorus slag at different temperatures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 147, 720–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.M.; Fang, K.H.; Shi, Y. Effects of phosphorus slag on hydration properties and pore structure of cement paste. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2007, 35, 109–113. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, Y.; Li, J.Z.; Liu, D.M. Fractal theory used in pore structure of cement-based materials incorporated phosphorus slag. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 405–406, 384–389. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.M.; Fang, K.H.; Yang, H.S. Research on the strengthening effect of phosphorus slag powder on cement-based materials. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 405–406, 356–360. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, K.T.; Yang, H.Q.; Dong, Y. Study on the influence of admixture on chemical shrinkage of cement based materials. Key Eng. Mater. 2009, 405–406, 226–233. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, C.J.; Li, Y.Y. Investigation on some factors affecting the characteristics of alkali-phosphorous slag cement. Cem. Concr. Res. 1989, 19, 527–533. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, F.Z.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, D.W.; Wang, J.X.; Huang, T.Y.; Wang, D.M. Reaction kinetics and kinetics models of alkali activated phosphorus slag. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 237, 117728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Kani, E.N.; Sanchez, A.P.; Fernandez-Jimenez, A. Rheology of activated phosphorus slag with lime and alkaline salts. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 113, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodloorad, H.; Allahverdi, A. Efflorescence formation and control in alkali-activated phosphorus slag cement. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2016, 14, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Mahinroosta, M.; Pilehvar, S. A temperature—Age model for prediction of compressive strength of chemically activated high phosphorus slag content cement. Int. J. Civ. Eng. 2017, 15, 839–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehdizadeh, H.; Kani, E.N. Modeling the influence of chemical composition on compressive strength behavior of alkali-activated phosphorus slag cement using statistical design. Can. J. Civ. Eng. 2018, 45, 1073–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maghsoodloorad, H.; Khalili, H.; Allahverdi, A. Alkali-activated phosphorous slag performance under different curing conditions: Compressive strength, hydration products, and microstructure. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2018, 30, 04017253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Abadi, M.M.B.R.; Anwar Hossain, K.M.; Lachemi, M. Resistance of chemically-activated high phosphorous slag content cement against freeze—Thaw cycles. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 103, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Abadi, M.M.B.R. Resistance of chemically activated high phosphorous slag content cement against frost-salt attack. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2014, 98, 18–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allahverdi, A.; Akhondi, M.; Mahinroosta, M. Superior sodium sulfate resistance of a chemically activated phosphorus slag—Based composite cement. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2017, 29, 04016231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Z.Q.; Zhou, X.T.; Jia, Q.M.; Zhou, Y.K.; Liu, S.Q.; Zhang, Z.S. Solidification/immobilization of calcium arsenate waste using phosphorous slag based geopolymers. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2015, 43, 699–704. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, X.; Zeng, L.; Fang, K.H. Anti-crack performance of phosphorus slag concrete. Wuhan Univ. J. Nat. Sci. 2009, 14, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J. Research on the Cementitious Characteristics of Phosphorus Slag Powder and Properties of C50 T-Shaped Beam Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, L.; Guo, F.X.; Lin, Y.Q.; Yang, H.M.; Tang, S.W. Comparison between the effects of phosphorous slag and fly ash on the C-S-H structure, long-term hydration heat and volume deformation of cement-based materials. Constr. Build. Mater. 2020, 250, 118807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, P.W.; Lu, X.L.; Yang, C.X.; Li, X.Y.; Shi, N.N.; Jin, S.C. Microstructure and pore structure of concrete mixed with superfine phosphorous slag and superplasticizer. Constr. Build. Mater. 2008, 22, 837–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. Comparison between the effects of superfine steel slag and superfine phosphorus slag on the long-term performances and durability of concrete. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2017, 128, 1251–1263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.R. Effect of Mineral Admixture on Performance of Sleeper Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Southwest University of Science and Technology, Mianyang, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F. Properties of Phosphorus Slag Powder Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- He, D.L.; Shi, Y.; Luo, T.L.; Wu, T.; Luo, X.D.; Zhu, J.H. Mechanical and durability properties of self-compacting concrete made with fly ash microbeads and phosphorous slag powder. J. Adhes. Sci. Technol. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.J. Effect of Phosphorus Slag Additive on Performance of Concrete. Master’s Thesis, Chongqing University, Chongqing, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Fang, Y.H.; Xuan, W.; Wang, R.; Pang, E.B. Mechanical properties and durability of alkali activated phosphorus slag fly ash cement concrete. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2009, 37, 1235–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Vafaei, M.; Allahverdi, A. Strength development and acid resistance of geopolymer based on waste clay brick powder and phosphorous slag. Struc. Concr. 2019, 20, 1596–1606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.Z.; Zhang, J.; Liu, J.Y.; Ke, J.; Wang, F.Z. Properties and microstructure of reactive powder concrete having a high content of phosphorous slag powder and silica fume. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 482–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Cao, K.; Wang, C.; Zhu, A.; Wang, X.; Shang, C. Temperature and age effects on mechanical behaviour of phosphorus slag-based concrete. Adv. Cem. Res. 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.Q.; Rao, M.J.; Yang, H.Q.; Li, J.Z.; Shi, Y. Study on microstructures and macro-properties in cement-based materials adding phosphorous slag. Mater. Res. Innov. 2015, 19, 122–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Z.X.; Wang, D.Q. Influence of high-volume electric furnace nickel slag and phosphorous slag on the properties of massive concrete. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2018, 131, 873–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.K.; Zha, J.; Shen, W.G. Design, preparation and property of phosphorus slag road base material. Acta Sci. Natur. Univ. Sunyatseni 2007, 46, 159–160. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.M.; Zhao, G.R.; Zhang, G.F. Research progress on microstructure of polymer cement concrete. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 42, 653–660. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.M.; Zhao, G.R.; Zhang, G.F. Mechanism on water retention and thickening of cellulose ethers in fresh mortars. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2017, 45, 1190–1196. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, P.M.; Zhao, G.R.; Zhang, G.F. Mechanism of redispersible polymer powder in cement mortar. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2018, 46, 256–262. [Google Scholar]
- Li, N.; Xu, L.L.; Wang, R.; Li, L.; Wang, P.M. Experimental study of calcium sulfoaluminate cement-based self-leveling compound exposed to various temperatures and moisture conditions: Hydration mechanism and mortar properties. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 108, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, Y.L.; Pel, L.; Sun, Z.P. The microstructure development during bleeding of cement paste: An NMR study. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 125, 105866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pu, X.C. The evaluation system of pozzolanic activity in high strength concrete and high performance concrete. Concrete 1998, 6, 13–23. [Google Scholar]
- Shah, V.; Scrivener, K.; Bhattacharjee, B.; Bishnoi, S. Changes in microstructure characteristics of cement paste on carbonation. Cem. Concr. Res. 2018, 109, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Weerdt, K.; Plusquellec, G.; Belda Revert, A.; Geiker, M.R.; Lothenbach, B. Effect of carbonation on the pore solution of mortar. Cem. Concr. Res. 2019, 118, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.B.; Xu, H.X.; Xu, D.Y.; Du, P.; Zhou, Z.H.; Yuan, L.W.; Cheng, X. Accelerated carbonation of hardened cement pastes: Influence of porosity. Constr. Build. Mater. 2019, 225, 159–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.F.; Chen, J.W. The experimental investigation of concrete carbonation depth. Cem. Concr. Res. 2006, 36, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.I.; Lynsdale, C.J. Strength, permeability, and carbonation of high-performance concrete. Cem. Concr. Res. 2002, 32, 123–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monkman, S.; Shao, Y.X. Assessing the carbonation behavior of cementitious materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2006, 18, 768–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sisomphon, K.; Franke, L. Carbonation rates of concretes containing high volume of pozzolanic materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2007, 37, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McPolin, D.O.; Basheer, P.A.M.; Long, A.E. Carbonation and pH in mortars manufactured with supplementary cementitious materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2009, 21, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanjuán, M.Á.; Estévez, E.; Argiz, C.; Del Barrio, D. Effect of curing time on granulated blast-furnace slag cement mortars carbonation. Cem. Concr. Compos. 2018, 90, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuyuki, N.; Koizumi, K. Granularity and surface structure of ground granulated blast-furnace slags. J. Am. Ceram. Soc. 1999, 82, 2188–2192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellmann, F.; Stark, J. Activation of blast furnace slag by a new method. Cem. Concr. Res. 2009, 39, 644–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lothenbach, B.; Scrivener, K.; Hooton, R.D. Supplementary cementitious materials. Cem. Concr. Res. 2011, 41, 1244–1256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Binders | SiO2 | CaO | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | MgO | Na2O | K2O | TiO2 | SO3 | P2O5 | Loss on Ignition |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cement | 20.8 | 61.3 | 6.34 | 3.07 | 1.03 | 0.21 | 0.85 | 0.29 | 2.29 | − | 2.01 |
| PS | 40.8 | 45.7 | 2.57 | 0.41 | 3.32 | 0.38 | 1.01 | 0.22 | 1.56 | 3.91 | 0.52 |
| Sample | Cement | Phosphorus Slag | Sand | Water | Chemical Activator |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 500 | 0 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-10 | 450 | 50 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-20 | 400 | 100 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-30 | 350 | 150 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-40 | 300 | 200 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-50 | 250 | 250 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-30 of 350 km2/g | 350 | 150 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-30 of 400 km2/g | 350 | 150 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-30 of 450 km2/g | 350 | 150 | 1500 | 250 | 0 |
| PS-30 + Chemical activator | 350 | 150 | 1500 | 250 | 1.5 |
| Sample | Cement | Phosphorus Slag | Water |
|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 500 | 0 | 140 |
| PS-10 | 450 | 50 | 139 |
| PS-20 | 400 | 100 | 138 |
| PS-30 | 350 | 150 | 136 |
| PS-40 | 300 | 200 | 134 |
| PS-50 | 250 | 250 | 134 |
| Sample | FRC (MPa) | FPC (MPa) | K | PP | PH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 0.232 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| PS-10 | 0.239 | 0.007 | 1.030 | 2.9 | 97.1 |
| PS-20 | 0.236 | 0.004 | 1.018 | 1.8 | 98.2 |
| PS-30 | 0.220 | −0.012 | 0.948 | −5.5 | 105.5 |
| PS-40 | 0.223 | −0.009 | 0.963 | −3.9 | 103.9 |
| PS-50 | 0.202 | −0.030 | 0.871 | −14.9 | 114.9 |
| Sample | FRC(MPa) | FPC(MPa) | K | PP | PH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 0.425 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| PS-10 | 0.432 | 0.008 | 0.957 | 1.7 | 104.5 |
| PS-20 | 0.441 | 0.016 | 1.038 | 3.7 | 96.3 |
| PS-30 | 0.456 | 0.031 | 1.072 | 6.7 | 93.3 |
| PS-40 | 0.502 | 0.077 | 1.180 | 15.3 | 84.7 |
| PS-50 | 0.550 | 0.125 | 1.294 | 22.7 | 77.3 |
| Sample | FRC(MPa) | FPC(MPa) | K | PP | PH |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plain | 0.471 | 0.000 | 1.000 | 0.0 | 100.0 |
| PS-10 | 0.497 | 0.026 | 1.054 | 2.4 | 97.6 |
| PS-20 | 0.545 | 0.074 | 1.157 | 6.4 | 93.6 |
| PS-30 | 0.600 | 0.129 | 1.274 | 10.1 | 89.9 |
| PS-40 | 0.688 | 0.217 | 1.461 | 14.9 | 85.1 |
| PS-50 | 0.738 | 0.267 | 1.567 | 17.0 | 83.0 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pang, M.; Sun, Z.; Chen, M.; Lang, J.; Dong, J.; Tian, X.; Sun, J. Influence of Phosphorus Slag on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortars. Materials 2020, 13, 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102390
Pang M, Sun Z, Chen M, Lang J, Dong J, Tian X, Sun J. Influence of Phosphorus Slag on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortars. Materials. 2020; 13(10):2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102390
Chicago/Turabian StylePang, Min, Zhenping Sun, Ming Chen, Jianlei Lang, Jiayan Dong, Xu Tian, and Jiliang Sun. 2020. "Influence of Phosphorus Slag on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortars" Materials 13, no. 10: 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102390
APA StylePang, M., Sun, Z., Chen, M., Lang, J., Dong, J., Tian, X., & Sun, J. (2020). Influence of Phosphorus Slag on Physical and Mechanical Properties of Cement Mortars. Materials, 13(10), 2390. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma13102390




