Facile Microemulsion Synthesis of Vanadium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles to Analyze the Compositional, Optical, and Electronic Properties
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Experimental Work
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Structural Analysis
3.2. X-ray Absorption Near Edge Spectroscopy (XANES)
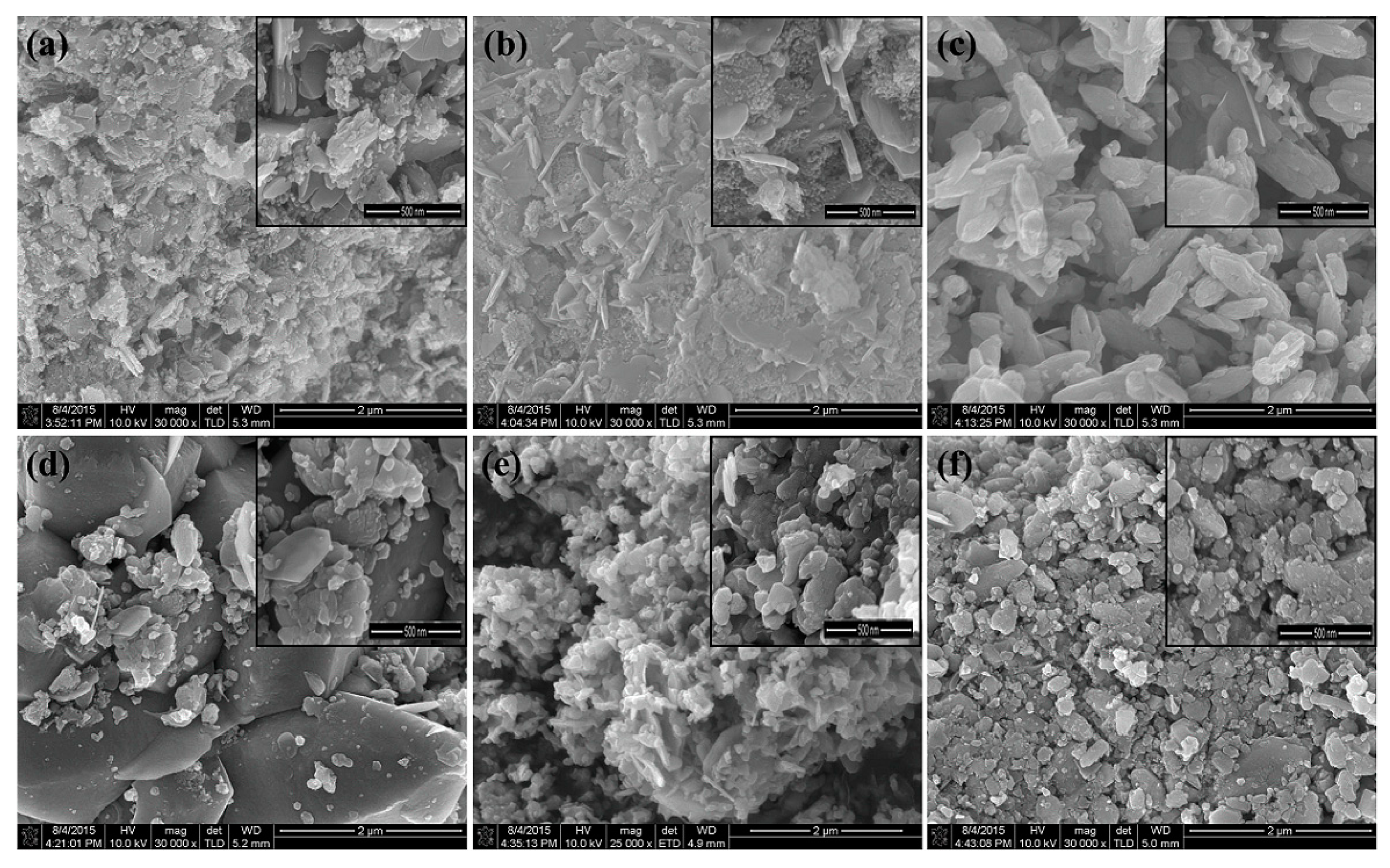
3.3. SEM Analysis
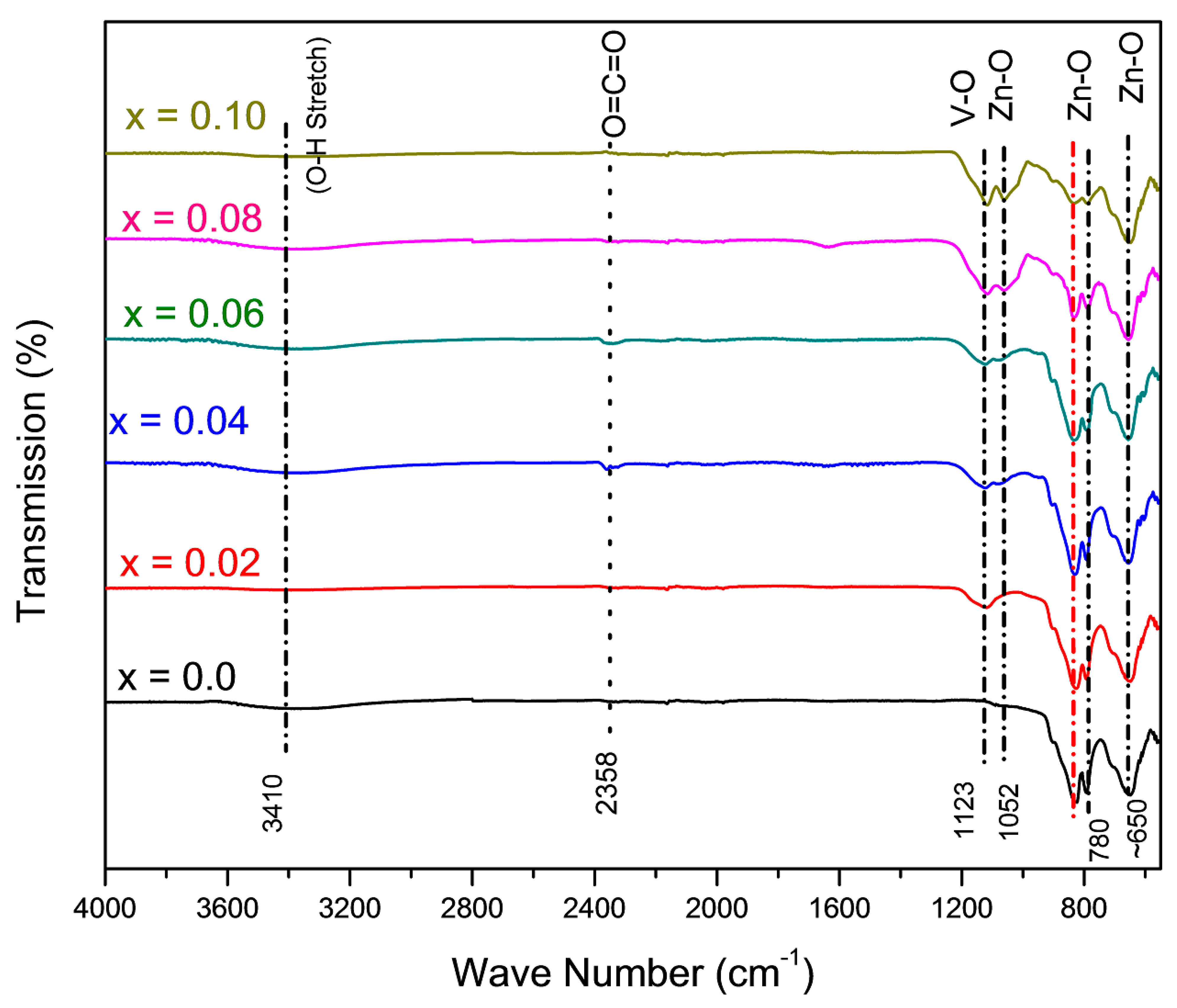
3.4. FTIR Analysis
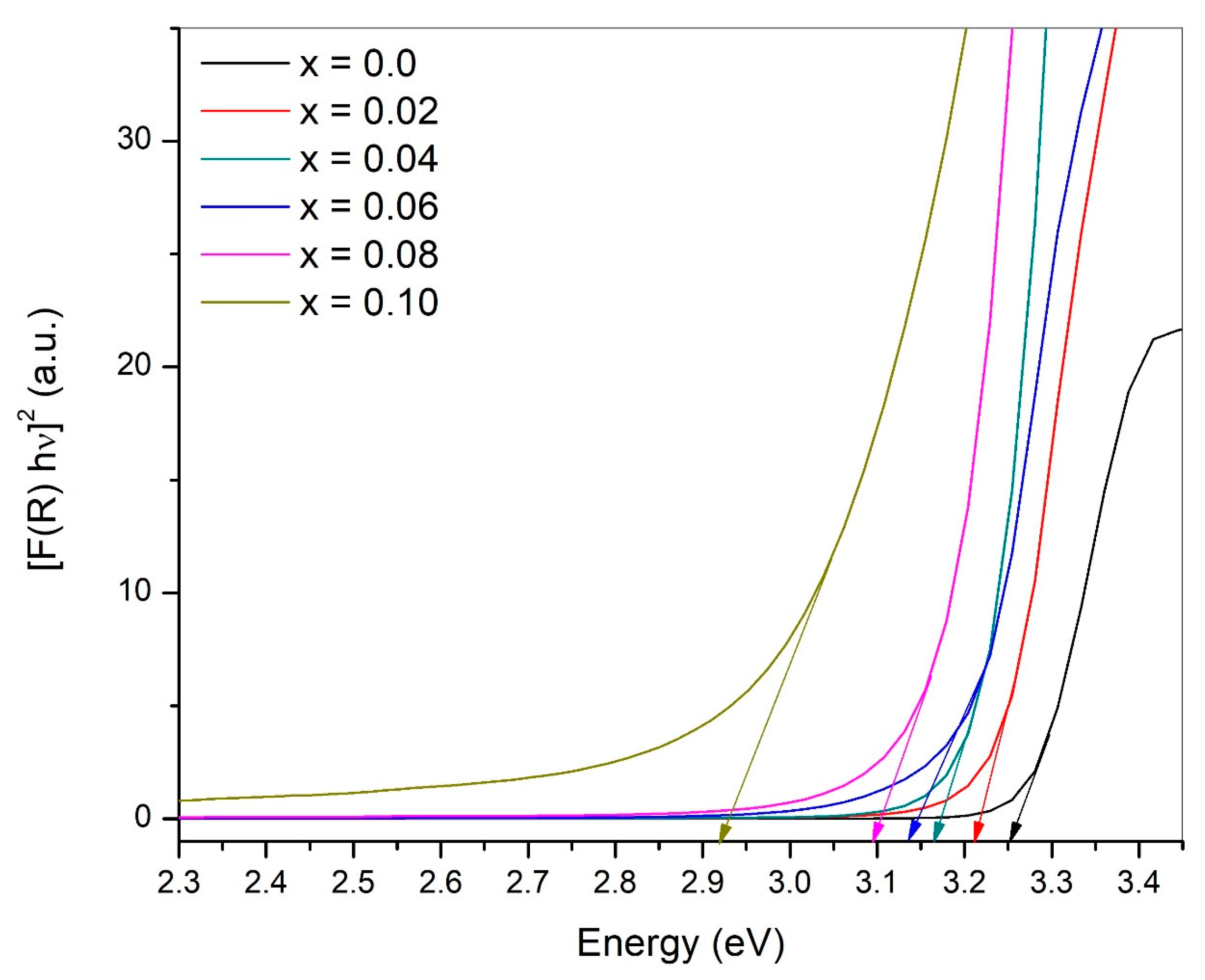
3.5. Optical Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.S.; Park, W.I.; Lee, C.H.; Yi, G.C. ZnO nanorod biosensor for highly sensitive detection of specific protein binding. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2006, 49, 1635. [Google Scholar]
- Acosta-Humánez, F.; Pitalúa, R.C.; Almanza, O. Electron paramagnetic resonance in Zn1−xCoxO. J. Magn. Magn. Mater 2013, 329, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilyas, U.; Tan, T.; Lee, P.; Ramanujan, R.; Li, F.; Zhang, S.; Chen, R.; Sun, H.; Rawat, R. Enhanced ferromagnetic response in ZnO: Mn thin films by tailoring composition and defect concentration. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2013, 344, 171–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, A.; Sun, X.; Wang, J.; Lei, Y.; Cai, X.; Li, C.; Dong, Z.; Huang, W. Enzymatic glucose biosensor based on ZnO nanorod array grown by hydrothermal decomposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 123902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Li, S.; Zhuang, J.; Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Li, H.; Liu, Z.; Han, Y.; Jiang, X.; Zhang, P. Improved selective acetone sensing properties of Co-doped ZnO nanofibers by electrospinning. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2011, 155, 782–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, S.K.; Saha, S.; Ramirez-Vick, J.E.; Gupta, V.; Bhansali, S.; Singh, S.P. Recent advances in ZnO nanostructures and thin films for biosensor applications: Review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 737, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Q.; Hein, S.; Misra, R. New generation of chitosan-encapsulated ZnO quantum dots loaded with drug: Synthesis, characterization and in vitro drug delivery response. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2732–2739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, J.; Wu, M.; Kai, G.; Wang, F.; Cao, H.; Yu, X. ZnO-ZnS QDs interfacial heterostructure for drug and food delivery application: Enhancement of the binding affinities of flavonoid aglycones to bovine serum albumin. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2011, 7, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorfman, A.; Kumar, N.; Hahm, J.-I. Nanoscale ZnO-Enhanced Fluorescence Detection of Protein Interactions. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 2685–2690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Lim, C.; Fu, S.; Tok, A.; Lau, H.; Boey, F.; Zeng, X. Surface modifications of ZnO quantum dots for bio-imaging. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 215604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, T.; Sung, J.; Shim, W.; Moon, H.; Cho, J.; Jo, Y.; Lee, W.; Kim, B. Synthesis and magnetic properties of single-crystalline Mn/Fe-doped and Co-doped ZnS nanowires and nanobelts. J. Phys. Chem. C 2009, 113, 5352–5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, M.G.B. Breast cancer treatment by nanophotolysis Approach. Results Phys. 2018, 9, 982–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, D.; Zhang, Z.; Fu, J.; Xu, Y.; Qi, J.; Xue, D. Room temperature ferromagnetism of pure ZnO nanoparticles. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 113928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Kim, Y.; Koo, B.; Gautam, S.; Chae, K.; Kumar, R.; Lee, C. Room temperature ferromagnetism in chemically synthesized ZnO rods. Mater. Lett. 2009, 63, 194–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Yu, K.; Peng, D.; Zhang, Z.; Zhu, Z. Field emission and room temperature ferromagnetism properties of triangle-like ZnO nanosheets. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 256, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapilashrami, M.; Xu, J.; Biswas, A.; Tamaki, T.; Sharma, P.; Rao, K.V.; Belova, L. Coexistence of ultraviolet photo-response and room-temperature ferromagnetism in polycrystalline ZnO thin films. Mater. Lett. 2010, 64, 1291–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Dorpe, P.; Motsnyi, V.F.; Nijboer, M.; Goovaerts, E.; Safarov, V.I.; Das, J.; Van Roy, W.; Borghs, G.; De Boeck, J. Highly efficient room temperature spin injection in a metal-insulator-semiconductor light-emitting diode. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 42, L502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.-T.; Wang, C.-Y.; Tang, J.; Nie, T.; Jiang, W.; Chu, C.-P.; Arafin, S.; He, L.; Afsal, M.; Chen, L.-J. Electric-field control of ferromagnetism in Mn-doped ZnO nanowires. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1823–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, J.; Wang, C.-Y.; Chang, L.-T.; Fan, Y.; Nie, T.; Chan, M.; Jiang, W.; Chen, Y.-T.; Yang, H.-J.; Tuan, H.-Y. Electrical spin injection and detection in Mn5Ge3/Ge/Mn5Ge3 nanowire transistors. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4036–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bibes, M.; Barthelemy, A. Oxide spintronics. IEEE Trans. Electron Dev. 2007, 54, 1003–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furdyna, J.K. Diluted magnetic semiconductors. J. Appl. Phys. 1988, 64, R29–R64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerjee, P.; Lee, W.-J.; Bae, K.-R.; Lee, S.B.; Rubloff, G.W. Structural, electrical, and optical properties of atomic layer deposition Al-doped ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 2010, 108, 043504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Shao, Q.; Leung, C.; Ruotolo, A. Non-volatile, reversible switching of the magnetic moment in Mn-doped ZnO films. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 17C301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Treharne, R.; Hutchings, K.; Lamb, D.; Irvine, S.; Lane, D.; Durose, K. Combinatorial optimization of Al-doped ZnO films for thin-film photovoltaics. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2012, 45, 335102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Fan, F.; Xu, C.; Lin, S.; Wei, M.; Duan, X.; Wang, Z.L. ZnO nanotube-based dye-sensitized solar cell and its application in self-powered devices. Nanotechnology 2010, 21, 405203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Yan, M. Effect of oxygen deficiency on room temperature ferromagnetism in Co doped ZnO. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2012, 100, 202401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadam, P.; Agashe, C.; Mahamuni, S. Al-doped ZnO nanocrystals. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 104, 3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lo, S.-S.; Huang, D.; Tu, C.H.; Hou, C.-H.; Chen, C.-C. Raman scattering and band-gap variations of Al-doped ZnO nanoparticles synthesized by a chemical colloid process. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2009, 42, 095420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gondoni, P.; Ghidelli, M.; Di Fonzo, F.; Carminati, M.; Russo, V.; Bassi, A.L.; Casari, C. Structure-dependent optical and electrical transport properties of nanostructured Al-doped ZnO. Nanotechnology 2012, 23, 365706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klingshirn, C.; Fallert, J.; Zhou, H.; Sartor, J.; Thiele, C.; Maier-Flaig, F.; Schneider, D.; Kalt, H. 65 years of ZnO research–old and very recent results. Phys. Status Solidi (B) 2010, 247, 1424–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thota, S.; Dutta, T.; Kumar, J. On the sol–gel synthesis and thermal, structural, and magnetic studies of transition metal (Ni, Co, Mn) containing ZnO powders. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 2006, 18, 2473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Ghoul, J.; Barthou, C.; El Mir, L. Synthesis, structural and optical properties of nanocrystalline vanadium doped zinc oxide aerogel. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2012, 44, 1910–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murtaza, G.; Ahmad, R.; Rashid, M.; Hassan, M.; Hussnain, A.; Khan, M.A.; ul Haq, M.E.; Shafique, M.; Riaz, S. Structural and magnetic studies on Zr doped ZnO diluted magnetic semiconductor. Curr. Appl. Phys. 2014, 14, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruan, H.; Fang, L.; Li, D.; Saleem, M.; Qin, G.; Kong, C. Effect of dopant concentration on the structural, electrical and optical properties of Mn-doped ZnO films. Thin Solid Films 2011, 519, 5078–5081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagesh, K.S. Stabilization of V 4 State in Vanadium Compounds. Vivechan-IJR 2010, 1, 10–17. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, S.; Li, Y.; Ma, Q.; Liu, L.; Xu, X.; Niu, P.; Li, Y.; Niu, S.; Li, H. Infrared absorption spectrum studies of the VO defect in fast-neutron-irradiated Czochralski silicon. J. Cryst. Growth 2005, 280, 60–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Begum, N.J.; Ravichandran, K. Effect of source material on the transparent conducting properties of sprayed ZnO: Al thin films for solar cell applications. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 2013, 74, 841–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, Z.; Wu, S. Synthesis, characterization and gas sensing properties of undoped and Co-doped γ-Fe2O3-based gas sensors. Mater. Lett. 2006, 60, 952–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, R.; Kumar, A.; Chaudhary, R.P. Structural and photocatalytic studies of Mn doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Spectrochim. Acta Part A Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2012, 98, 256–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ankudinov, A.; Ravel, B.; Rehr, J.; Conradson, S. Real-space multiple-scattering calculation and interpretation of x-ray-absorption near-edge structure. Phys. Rev. B 1998, 58, 7565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crozier, E.; Rehr, J.; Ingalls, R. Amorphous and Liquid Systems; John Wiley & Sons: New York, NY, USA, 1988; Volume 92, p. 373. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Laan, G.; Kirkman, I. The 2p absorption spectra of 3d transition metal compounds in tetrahedral and octahedral symmetry. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 1992, 4, 4189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goering, E.; Müller, O.; Klemm, M.; DenBoer, M.; Horn, S. Angle dependent soft-X-ray absorption spectroscopy of V2O5. Philos. Mag. B 1997, 75, 229–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rehr, J.J.; Albers, R. Theoretical approaches to x-ray absorption fine structure. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2000, 72, 621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perales-Perez, O.; Parra-Palomino, A.; Singhal, R.; Voyles, P.; Zhu, Y.; Jia, W.; Tomar, M. Evidence of ferromagnetism in Zn1− xMxO (M= Ni, Cu) nanocrystals for spintronics. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 315606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habibi, M.H.; Karimi, B. Application of impregnation combustion method for fabrication of nanostructure CuO/ZnO composite oxide: XRD, FESEM, DRS and FTIR study. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2014, 20, 1566–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, A.J.; Kokila, M.; Nagabhushana, H.; Chakradhar, R.; Shivakumara, C.; Rao, J.; Nagabhushana, B. Structural, optical and EPR studies on ZnO: Cu nanopowders prepared via low temperature solution combustion synthesis. J. Alloys Compd. 2011, 509, 5349–5355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Mai, L.Q.; Peng, J.F.; Xu, Q.; Zhu, Q.Y. FTIR study of vanadium oxide nanotubes from lamellar structure. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 2625–2627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senthilkumaar, S.; Rajendran, K.; Banerjee, S.; Chini, T.; Sengodan, V. Influence of Mn doping on the microstructure and optical property of ZnO. Mater. Sci. Semicond. Process. 2008, 11, 6–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hapke, B. Theory of Reflectance and Emittance Spectroscopy; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Song, C.; Wang, X.; Zeng, F.; Pan, F. Cr-substitution-induced ferroelectric and improved piezoelectric properties of Zn1−xCrxO films. J. Appl. Phys. 2008, 103, 074107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
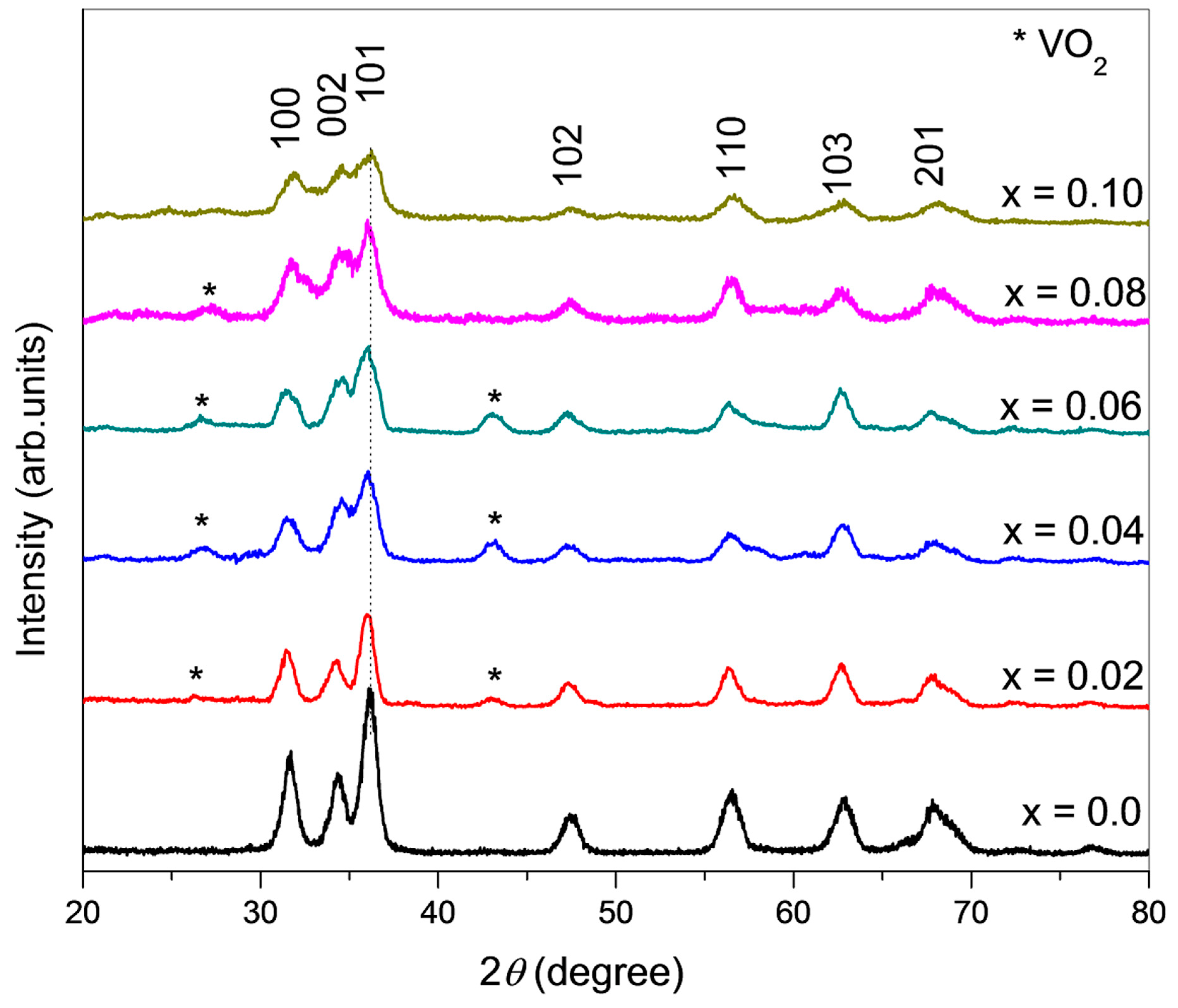
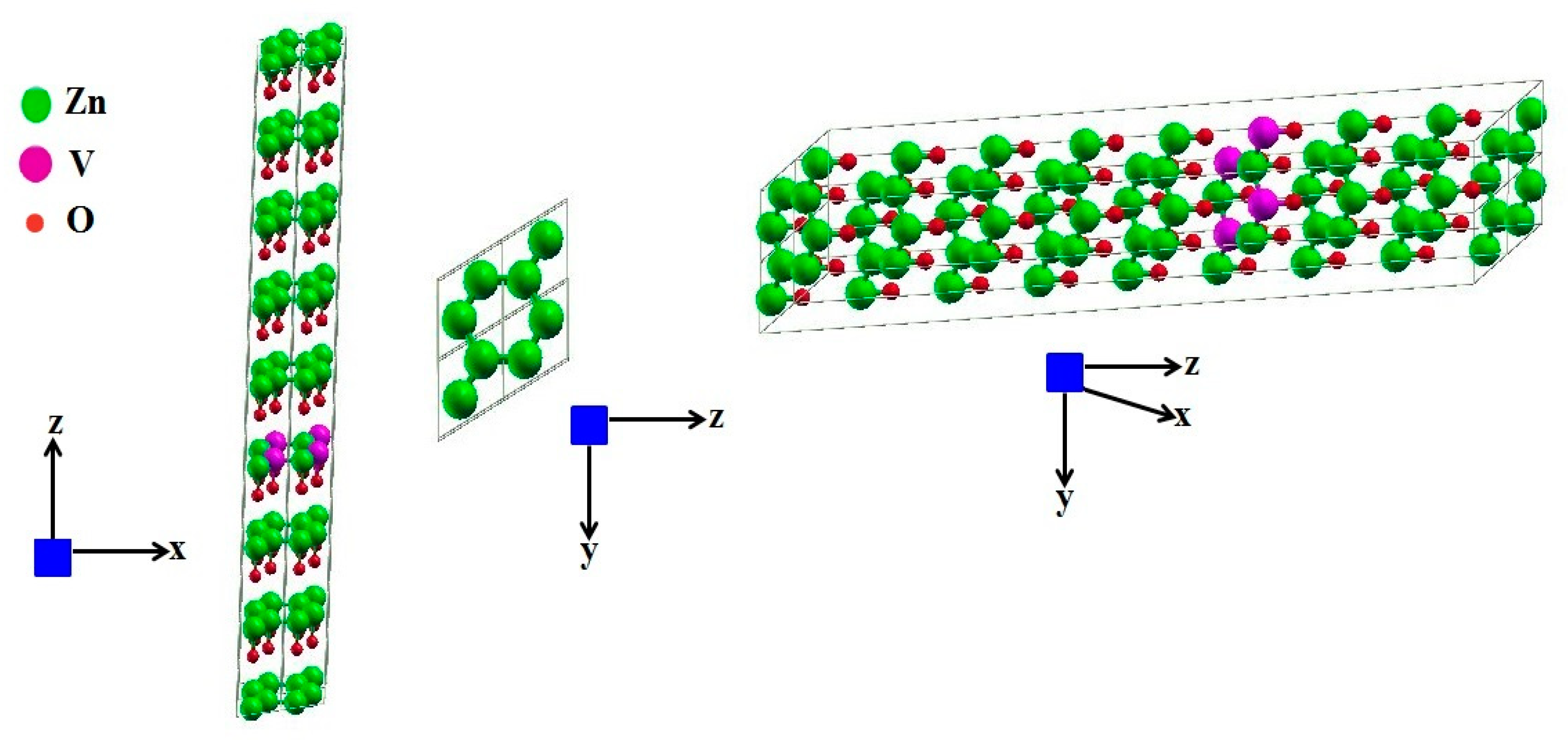
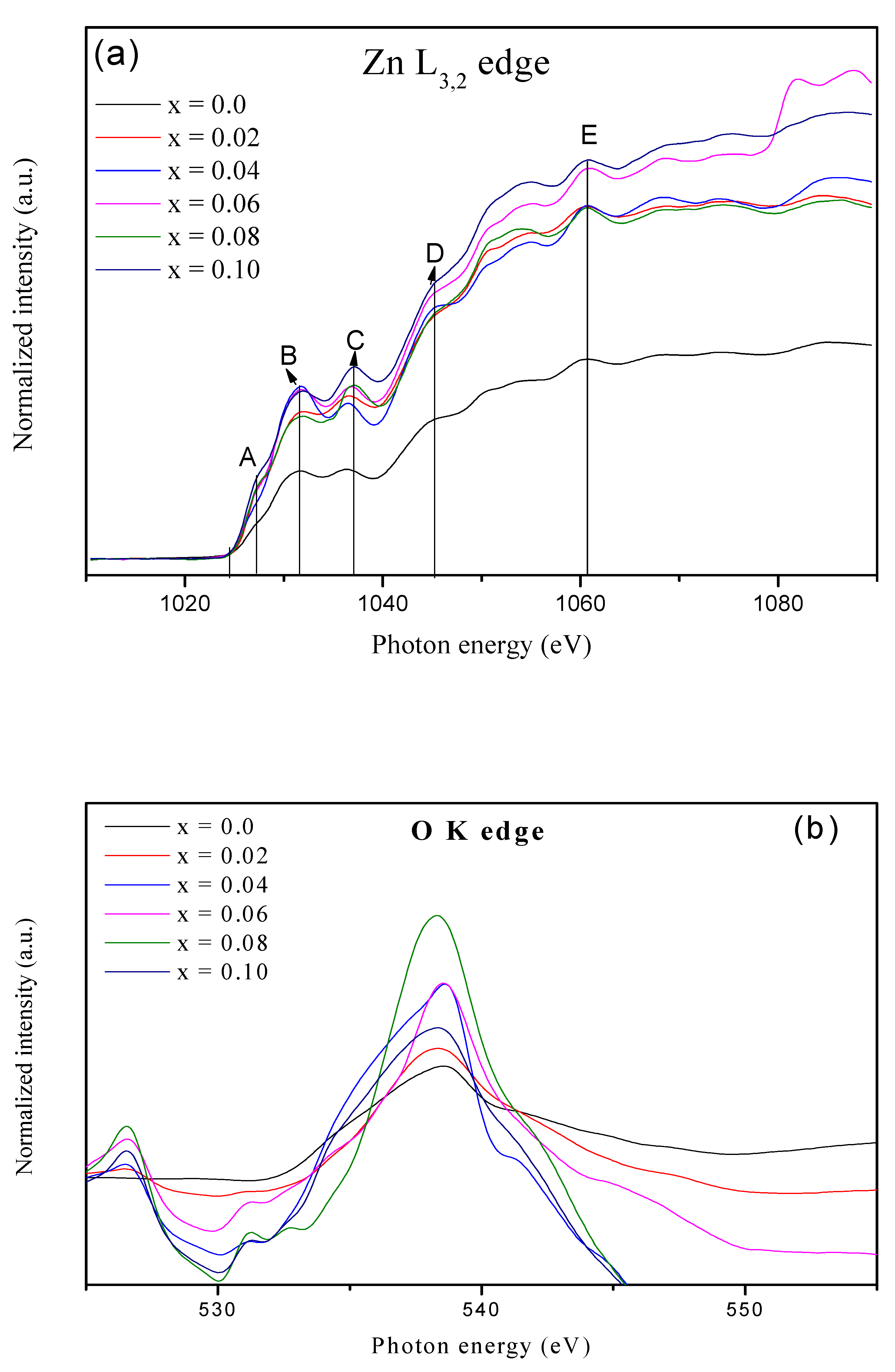
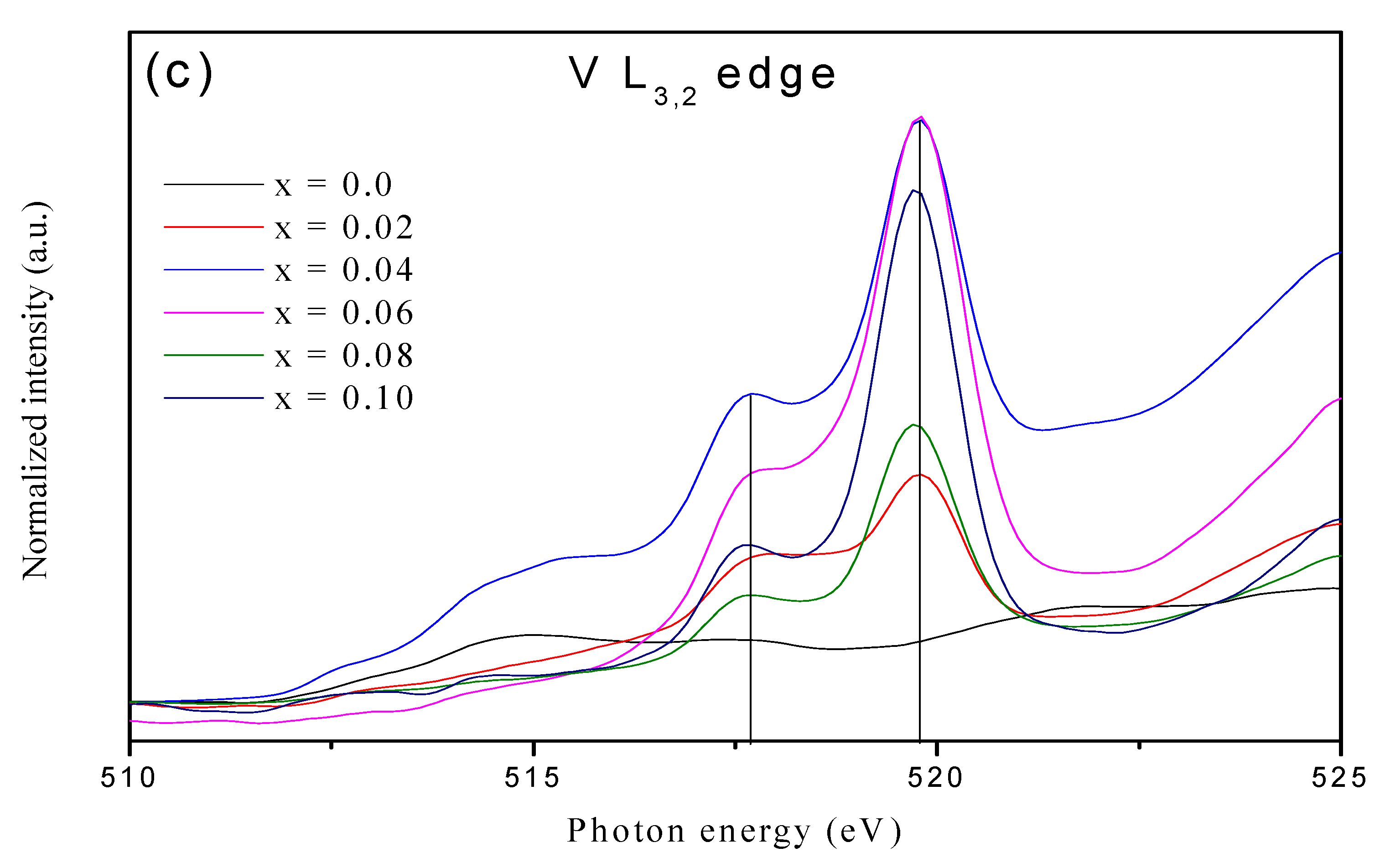
| Samples | Pure ZnO | 2% V Doped | 4% V Doped | 6% V Doped | 8% V Doped | 10% V Doped |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a (Å) | 3.257 | 3.277 | 3.283 | 3.291 | 3.25 | 3.24 |
| c(Å) | 5.20 | 5.23 | 5.24 | 5.24 | 5.20 | 5.19 |
| c/a | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.60 | 1.59 | 1.60 | 1.60 |
| Cell volume (Å)3 | 47.8 | 48.6 | 48.9 | 49.1 | 47.6 | 47.2 |
| Bond length | 2.603 | 2.615 | 2.620 | 2.673 | 2.6 | 2.56 |
| Crystallite Size (nm) | 22 | 19 | 15 | 11 | 19 | 20 |
| Volume of crystallite | 484 | 324 | 225 | 121 | 361 | 400 |
| Number of unit cell | 10 | 7 | 5 | 2 | 7 | 8 |
| Sample | a = b (Å) | c (Å) | Residual Factors | Values |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ZnO(pure) | 3.251 | 5.21 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 13.27 30.51 41.196 9.62 |
| ZnO 2% | 3.254 | 5.22 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 14.86 17.25 21.72 2.1 |
| ZnO 4% | 3.251 | 5.221 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 12.88 13.05 16.05 1.55 |
| ZnO 6% | 3.253 | 5.21 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 13.99 18.55 22.80 2.65 |
| ZnO 8% | 3.248 | 5.217 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 14.70 21.13 26.7 3.299 |
| ZnO 10% | 3.252 | 5.22 | R expected Rp Rwp GOF | 11.81 17.48 21.69 3.37 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ali, H.S.; Alghamdi, A.S.; Murtaza, G.; Arif, H.S.; Naeem, W.; Farid, G.; Sharif, S.; Ashiq, M.G.B.; Shabbir, S.A. Facile Microemulsion Synthesis of Vanadium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles to Analyze the Compositional, Optical, and Electronic Properties. Materials 2019, 12, 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050821
Ali HS, Alghamdi AS, Murtaza G, Arif HS, Naeem W, Farid G, Sharif S, Ashiq MGB, Shabbir SA. Facile Microemulsion Synthesis of Vanadium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles to Analyze the Compositional, Optical, and Electronic Properties. Materials. 2019; 12(5):821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050821
Chicago/Turabian StyleAli, H. S., Ali S. Alghamdi, G. Murtaza, H. S. Arif, Wasim Naeem, G. Farid, Sadia Sharif, Muhammad Gul Bahar Ashiq, and Syeda Ammara Shabbir. 2019. "Facile Microemulsion Synthesis of Vanadium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles to Analyze the Compositional, Optical, and Electronic Properties" Materials 12, no. 5: 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050821
APA StyleAli, H. S., Alghamdi, A. S., Murtaza, G., Arif, H. S., Naeem, W., Farid, G., Sharif, S., Ashiq, M. G. B., & Shabbir, S. A. (2019). Facile Microemulsion Synthesis of Vanadium-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles to Analyze the Compositional, Optical, and Electronic Properties. Materials, 12(5), 821. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12050821





