In Situ Formation of Ti47Cu38Zr7.5Fe2.5Sn2Si1Nb2 Amorphous Coating by Laser Surface Remelting
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
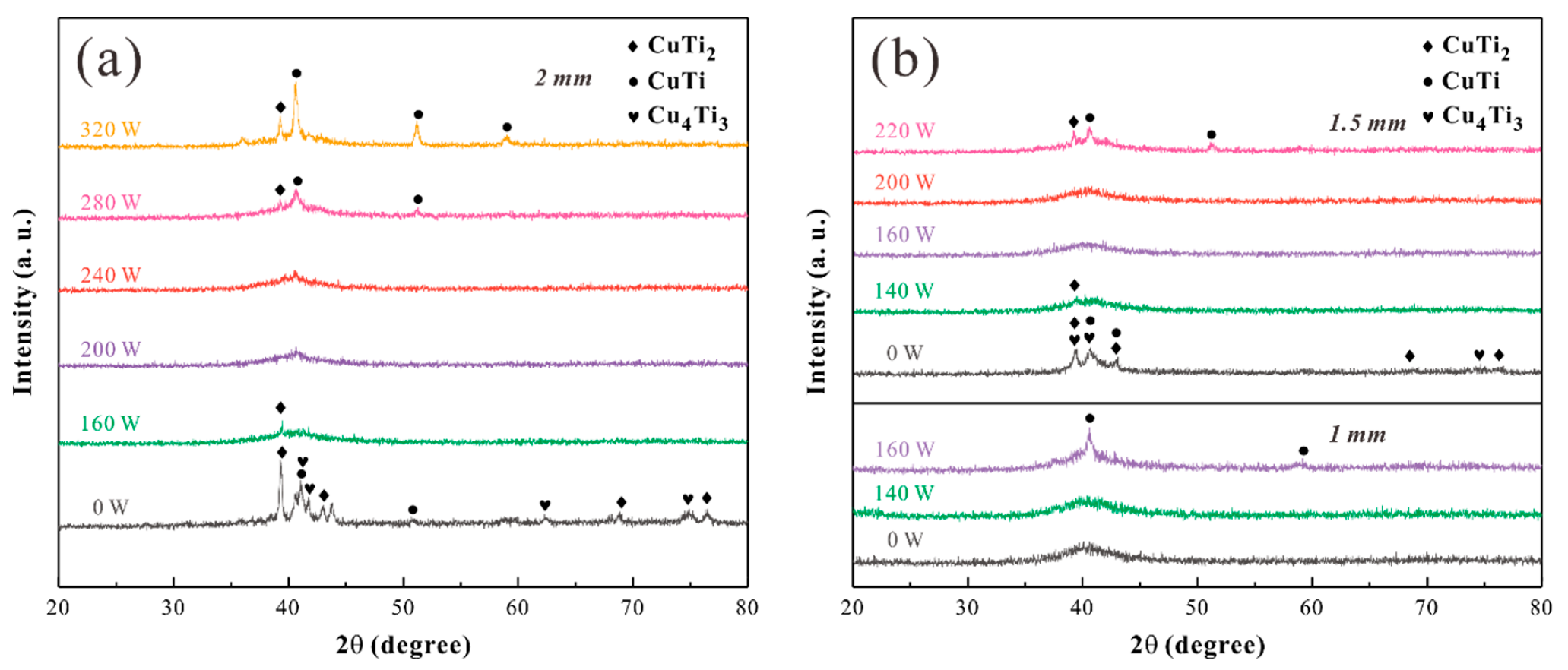
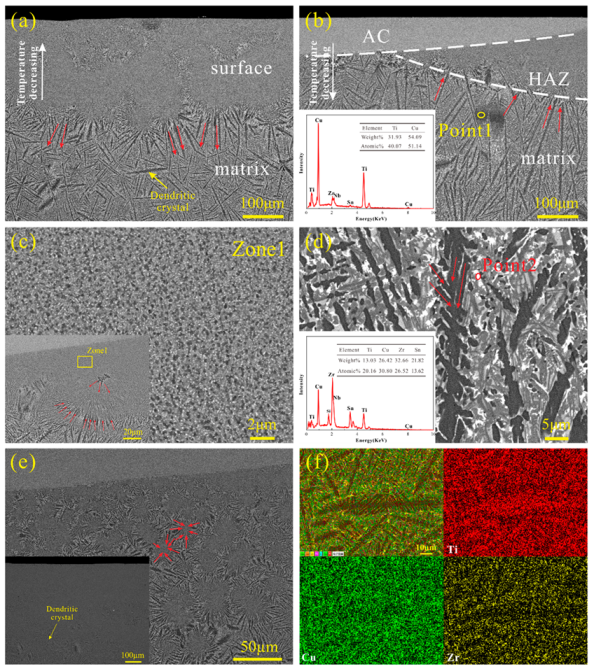
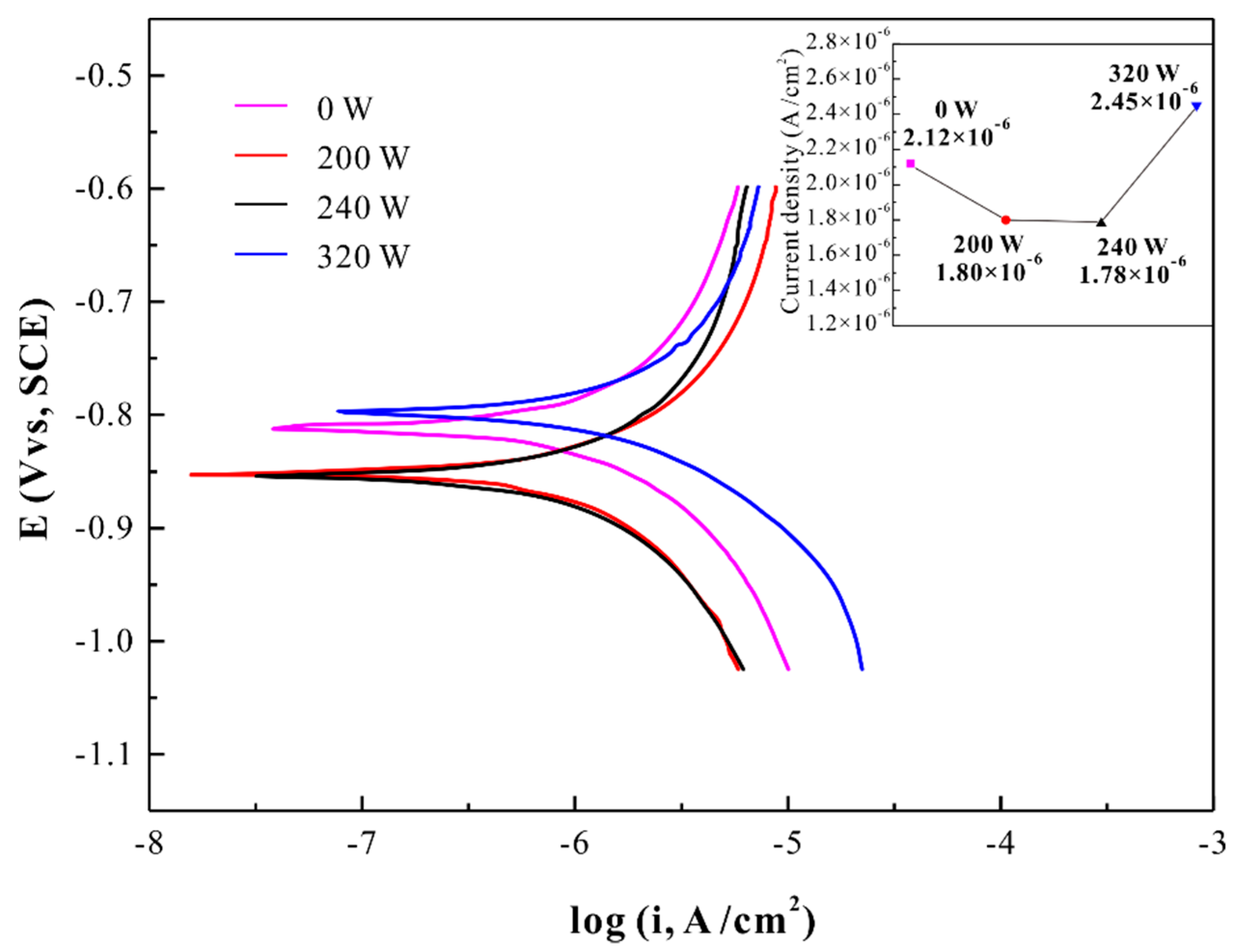
3. Results and Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geetha, M.; Singh, A.K.; Asokamani, R.; Gogia, A.K. Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—A review. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2009, 54, 397–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A. Stabilization of metallic supercooled liquid and bulk amorphous alloys. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 279–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. A brief overview of bulk metallic glasses. Npg Asia Mater. 2011, 3, 82–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WWang, H.; Dong, C.; Shek, C.H. Bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2004, 44, 45–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Thouas, G.A. Metallic implant biomaterials. Mater. Sci. Eng. R 2015, 87, 1–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanawa, T. Research and development of metals for medical devices based on clinical needs. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2012, 13, 064102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Wu, Y.D.; Si, J.J.; Cai, Y.H.; Chen, X.H.; Hui, X.D. Novel Ti-based bulk metallic glasses with superior plastic yielding strength and corrosion resistance. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2015, 642, 297–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Liu, M.; Song, J.; Deng, C.; Deng, C. Microstructure and corrosion behavior of Fe-based amorphous coating prepared by HVOF. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 721, 506–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, G.; Qu, L.; Lu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Qin, Z.; Lu, X. Corrosion resistance improvement of 45 steel by Fe-based amorphous coating. Vacuum 2018, 153, 39–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, Q.; Yang, B.; Chen, Y.M.; Liu, H.D.; Ren, F. Grain size dependence of the radiation tolerances of nano-amorphous Ti-Si-N composite coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 466, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yang, H.; Gao, J.; Yang, Y. Microstructure detection of Mg-Zi-Ti-Si amorphous composite coating prepared by SMAT. Mater. Charact. 2018, 135, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Li, X.; Xing, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Y. A novel non-skid composite coating with higher corrosion resistance. Ceram. Int. 2017, 43, 15095–15106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, L.; Wu, H.; Zheng, Z.; Guan, H.; Pan, H.; Guo, N.; Song, B. Microstructural characterization and hardness variation of pure Ti surface-treated by pulsed laser. J. Alloy. Compd. 2018, 741, 116–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.Y.; Zhao, W.; Li, G.; Liu, R.P. Microstructural evolution and mechanical properties of Ti–Zr beta titanium alloy after laser surface remelting. J. Alloy. Compd. 2014, 583, 43–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.S.; Han, X.L.; Song, K.K.; Tian, Y.H.; Peng, C.X.; Wang, L.; Sun, B.A.; Wang, G.; Kaban, I.; Eckert, J. Local melting to design strong and plastically deformable bulk metallic glass composites. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 42518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Pang, S.; Li, H.; Hu, Q.; Chen, B.; Zhang, T. Formation and properties of Ti-based Ti–Zr–Cu–Fe–Sn–Si bulk metallic glasses with different (Ti + Zr)/Cu ratios for biomedical application. Intermetallics 2016, 72, 36–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.; Liu, Y.; Li, H.; Sun, L.; Li, Y.; Zhang, T. New Ti-based Ti–Cu–Zr–Fe–Sn–Si–Ag bulk metallic glass for biomedical applications. J. Alloy. Compd. 2015, 625, 323–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Fan, X.D.; Wang, F.L.; Qi, H.N.; Yue, Y.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, G.; Liu, R.P. Effect of Nb content on corrosion behavior of Ti-based bulk metallic glass composites in different solutions. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 471, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weingarten, C.; Buchbinder, D.; Pirch, N.; Meiners, W.; Wissenbach, K.; Poprawe, R. Formation and reduction of hydrogen porosity during selective laser melting of AlSi10Mg. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2015, 221, 112–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, M.; Gu, D.D.; Xi, L.X.; Du, L.; Zhang, H.M.; Zhang, J.Y. Formation of scanning tracks during Selective Laser Melting (SLM) of pure tungsten powder: Morphology, geometric features and forming mechanisms. Int. J. Refract. Met. Hard Mater. 2019, 79, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, J.; Chen, S.; Lin, S.; Gan, J.; Chin, T.; Shun, T.; Tsau, C.; Chang, S. Nanostructured High-Entropy Alloys with Multiple Principal Elements: Novel Alloy Design Concepts and Outcomes. Adv. Eng. Mater. 2004, 6, 299–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, L.S.; Zeng, J.F.; Wang, W.H.; Liu, C.T.; Yang, Y. The dependence of shear modulus on dynamic relaxation and evolution of local structural heterogeneity in a metallic glass. Acta Mater. 2013, 61, 4329–4338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H. The elastic properties, elastic models and elastic perspectives of metallic glasses. Prog. Mater. Sci. 2012, 57, 487–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Z.; Jiao, W.; Wang, W.H.; Bai, H.Y. Flow unit perspective on room temperature homogeneous plastic deformation in metallic glasses. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 045501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turnbull, D.; Cohen, M.H. On the Free-Volume Model of the Liquid-Glass Transition. J. Chem. Phys. 1970, 52, 3038–3041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, S.X.; Nieh, T.G. Direct measurements of shear band propagation in metallic glasses—An overview. Intermetallics 2011, 19, 1968–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuh, C.A.; Nieh, T.G. A nanoindentation study of serrated flow in bulk metallic glasses. Acta Mater. 2003, 51, 87–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drozdz, D.; Kulik, T.; Fecht, H.J. Nanoindentation studies of Zr-based bulk metallic glasses. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 441, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.H.; Wang, R.J.; Yang, W.T.; Wei, B.C.; Wen, P.; Zhao, D.Q.; Pan, M.X. Stability of ZrTiCuNiBe bulk metallic glass upon isothermal annealing near the glass transition temperature. J. Mater. Res. 2002, 17, 1385–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Fan, H.; Wang, Y.; Ning, Z.; Liu, F.; Feng, D.; Jin, X.; Shen, J.; Sun, J.; et al. In vitro and in vivo biocompatibility of an Ag-bearing Zr-based bulk metallic glass for potential medical use. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2015, 419, 82–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Guo, Y.; Fan, H.; Shen, J. Synthesis of Fe–Cr–Mo–C–B amorphous coating with high corrosion resistance. Mater. Lett. 2012, 89, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, S.J.; Shek, C.H.; Asami, K.; Inoue, A.; Zhang, T. Formation and corrosion behavior of glassy Ni–Nb–Ti–Zr–Co(–Cu) alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2007, 434–435, 240–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raicheff, R.; Zaprianova, V.; Gattef, E. Effect of structural relaxation on electrochemical corrosion behaviour of amorphous alloys. J. Mater. Sci. Lett. 1997, 16, 1701–1704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, J.-L.; Shao, Y.; Zhao, S.-F.; Lu, S.-Y.; Yang, G.-N.; Chen, S.-Q.; Yao, K.-F. Effects of Cu addition on the glass forming ability and corrosion resistance of Ti-Zr-Be-Ni alloys. J. Alloy. Compd. 2017, 725, 573–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.J.; Zhang, Z.P.; Jin, Z.S.; Sun, W.C.; Xia, C.Q.; Ma, M.Z.; Zhang, X.Y.; Li, G.; Liu, R.P. A study on the corrosion behavior of the in-situ Ti-based bulk metallic glass matrix composites in acid solutions. J. Alloy. Compd. 2019, 782, 927–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

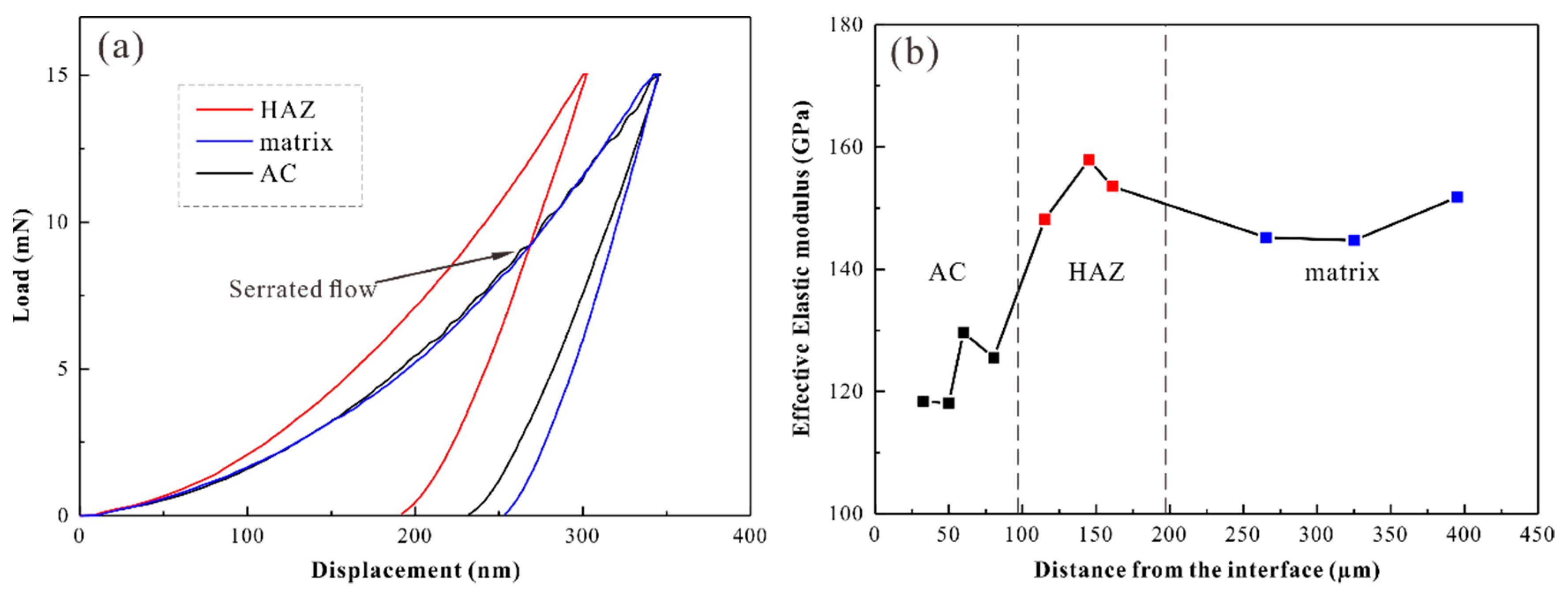
| Test Parameters | HAZ | Matrix | AC |
|---|---|---|---|
| Maximum load (Pmax, mN) | 15 | 15 | 15 |
| Indenter’s Poisson’s ratio | 0.07 | 0.07 | 0.07 |
| Indenter’s elastic modulus (GPa) | 1141 | 1141 | 1141 |
| Contact depth (hc, nm) | 231.93 | 288.88 | 279.59 |
| Contact area (A, nm2) | 1,244,136.48 | 1,878,274.12 | 1,763,841.78 |
| Contact stiffness (S, mN/nm) | 0.1763 | 0.2143 | 0.1753 |
| Nano-hardness (H, GPa) | 12.083 | 7.9951 | 8.5144 |
| Effective Elastic modulus (E*, GPa) | 153.59 | 151.78 | 125.55 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, P.; Meng, L.; Wang, S.; Wang, K.; Sui, Q.; Liu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, L. In Situ Formation of Ti47Cu38Zr7.5Fe2.5Sn2Si1Nb2 Amorphous Coating by Laser Surface Remelting. Materials 2019, 12, 3660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223660
Li P, Meng L, Wang S, Wang K, Sui Q, Liu L, Zhang Y, Yin X, Zhang Q, Wang L. In Situ Formation of Ti47Cu38Zr7.5Fe2.5Sn2Si1Nb2 Amorphous Coating by Laser Surface Remelting. Materials. 2019; 12(22):3660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223660
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Peizhen, Lingtao Meng, Shenghai Wang, Kunlun Wang, Qingxuan Sui, Lingyu Liu, Yuying Zhang, Xiaotian Yin, Qingxia Zhang, and Li Wang. 2019. "In Situ Formation of Ti47Cu38Zr7.5Fe2.5Sn2Si1Nb2 Amorphous Coating by Laser Surface Remelting" Materials 12, no. 22: 3660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223660
APA StyleLi, P., Meng, L., Wang, S., Wang, K., Sui, Q., Liu, L., Zhang, Y., Yin, X., Zhang, Q., & Wang, L. (2019). In Situ Formation of Ti47Cu38Zr7.5Fe2.5Sn2Si1Nb2 Amorphous Coating by Laser Surface Remelting. Materials, 12(22), 3660. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12223660





