Influence of Fragment Size on the Time and Temperature of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Lamination Decomposition in the Photovoltaic Module Recycling Process
Abstract
:1. Introduction
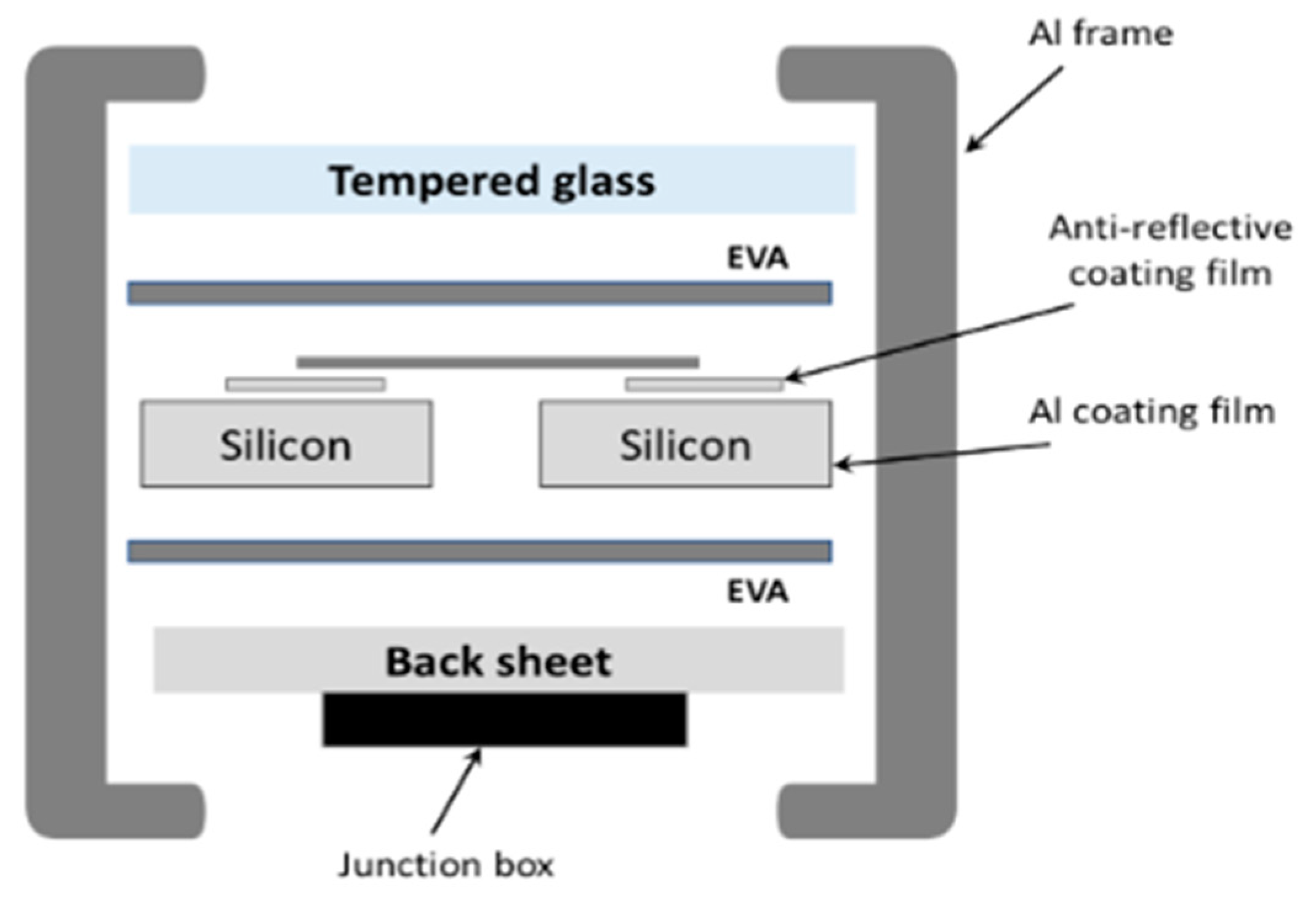
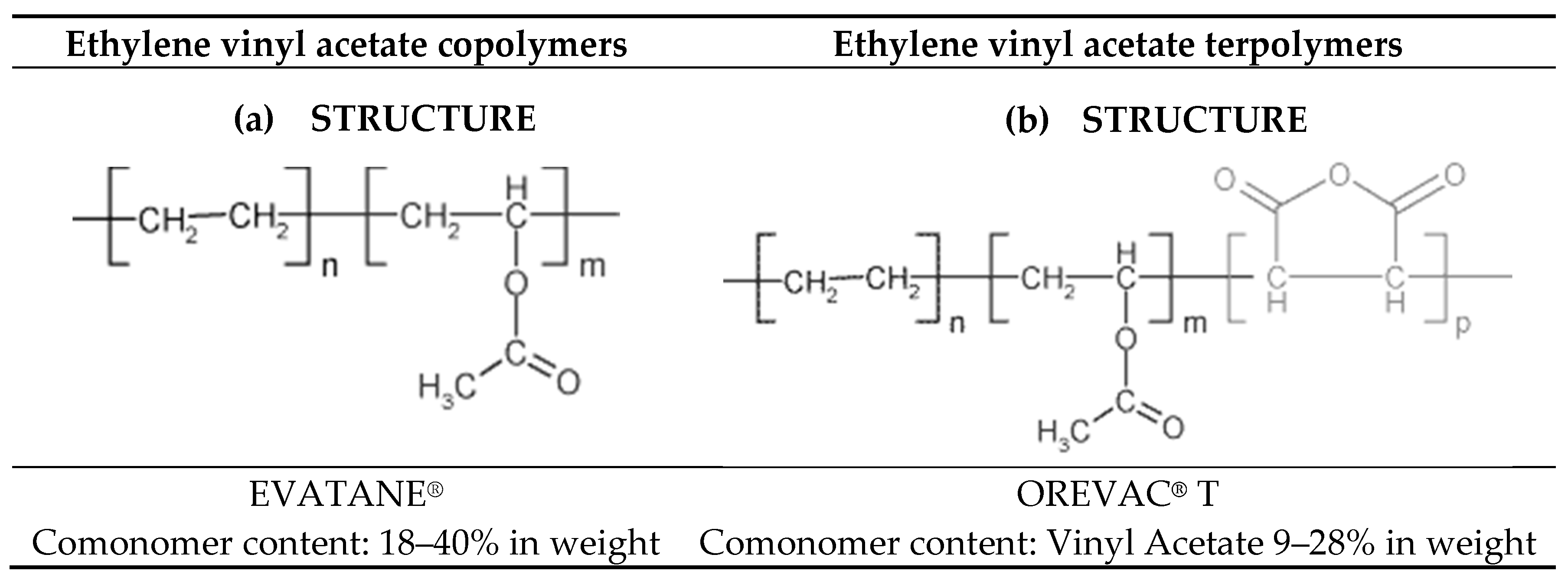
2. Material Description
3. Experimental
3.1. Materials
3.2. Thermal Treatment
4. Results and Discussion
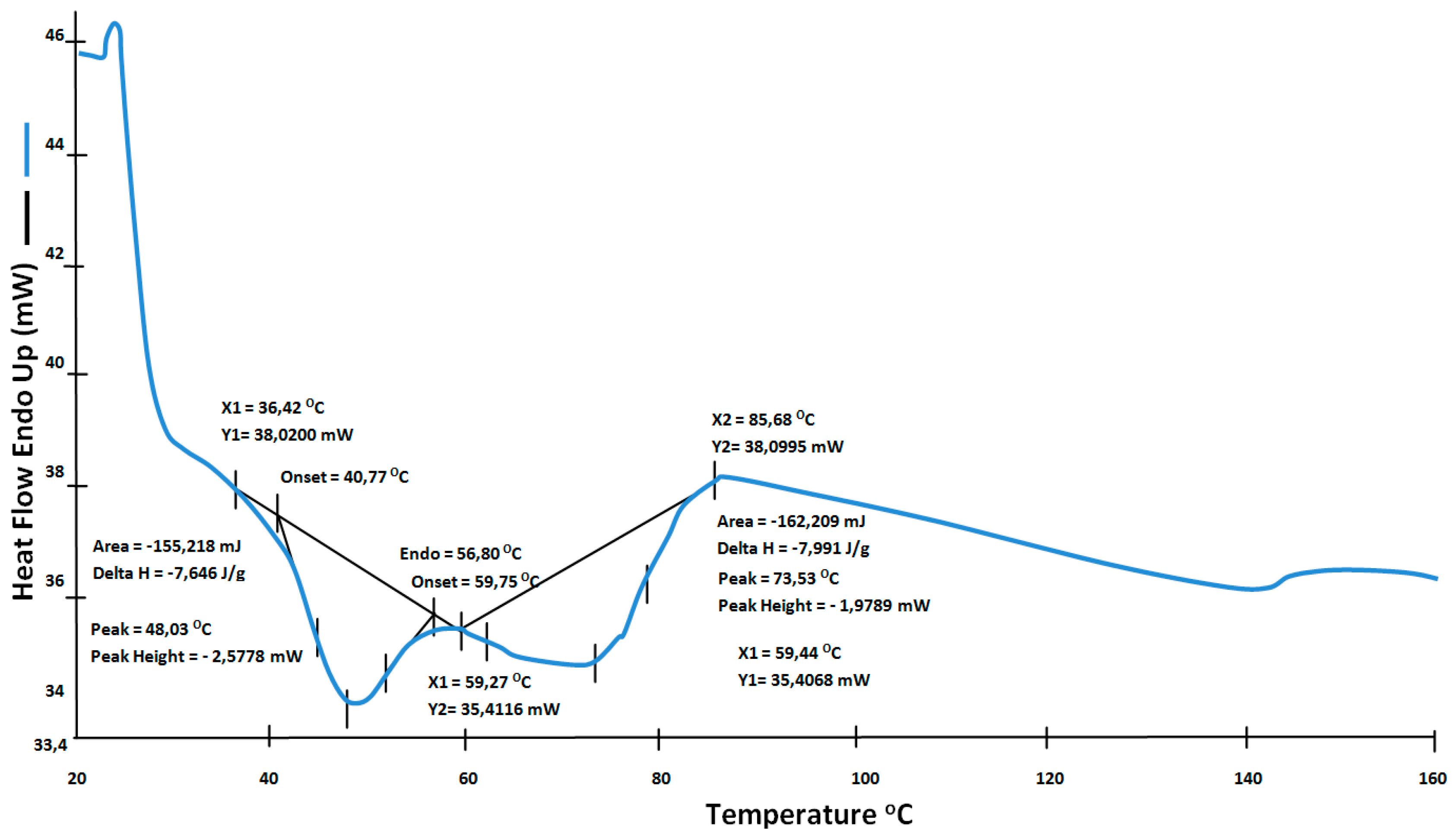
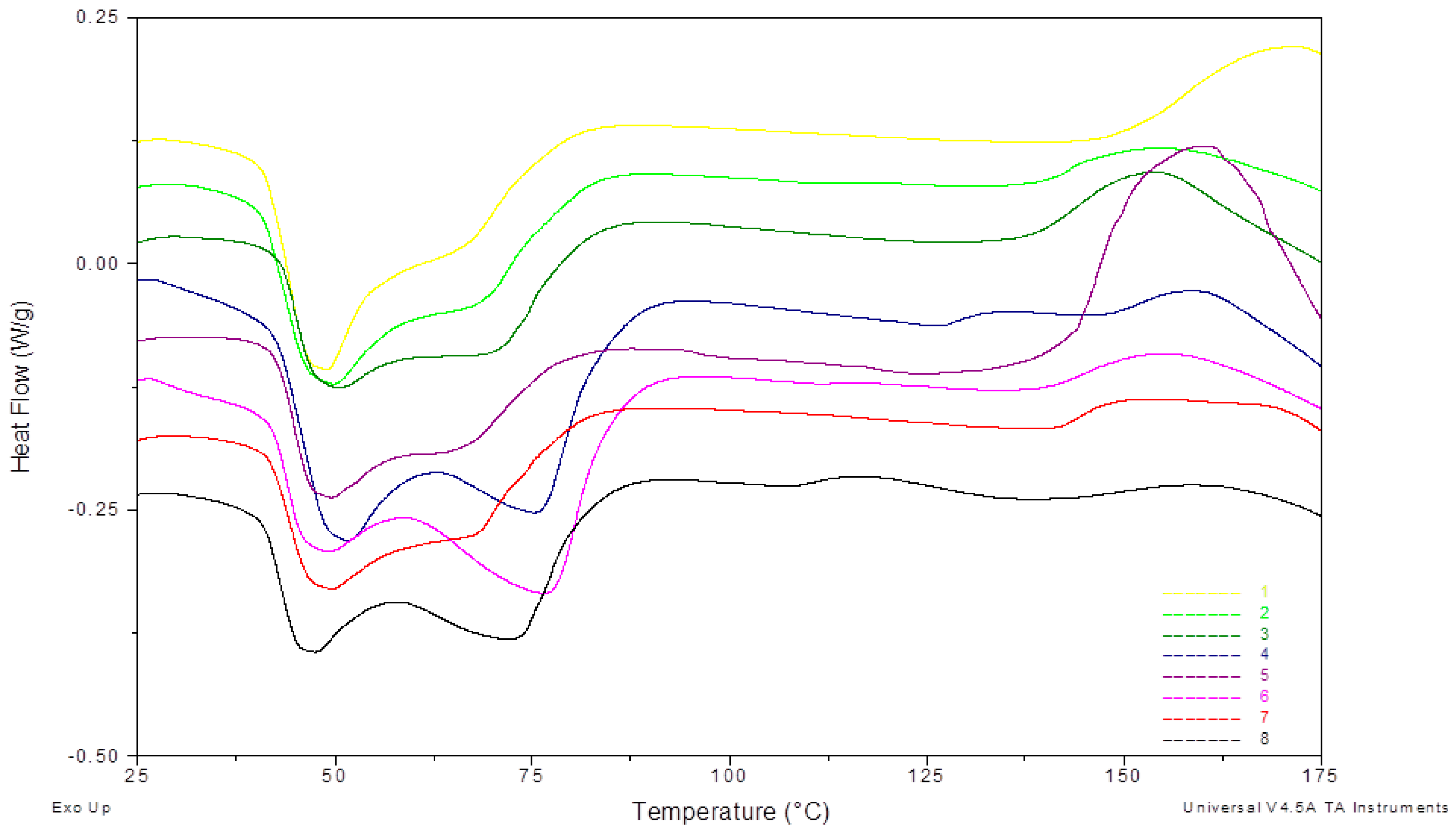
4.1. Material Characteristics
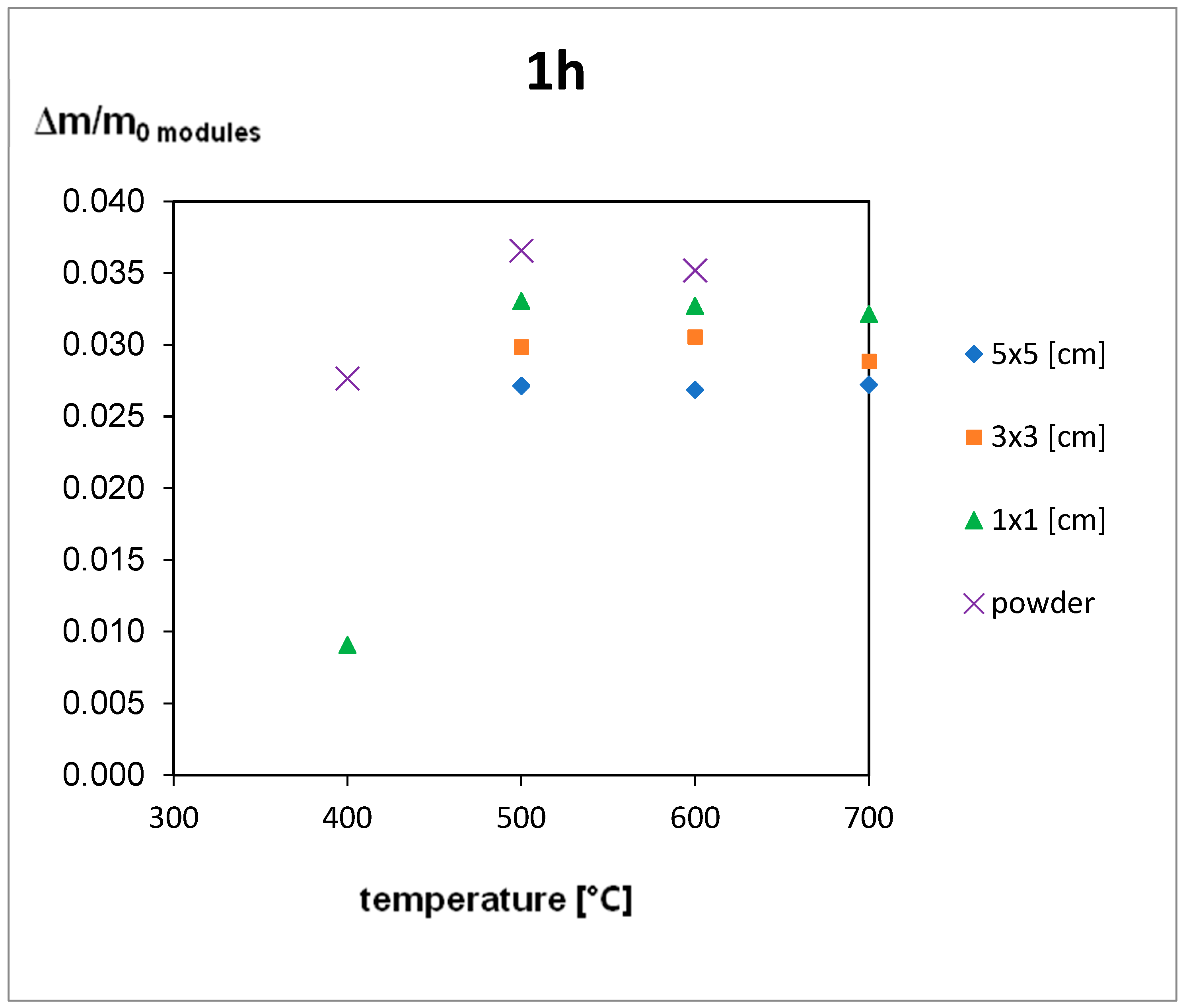
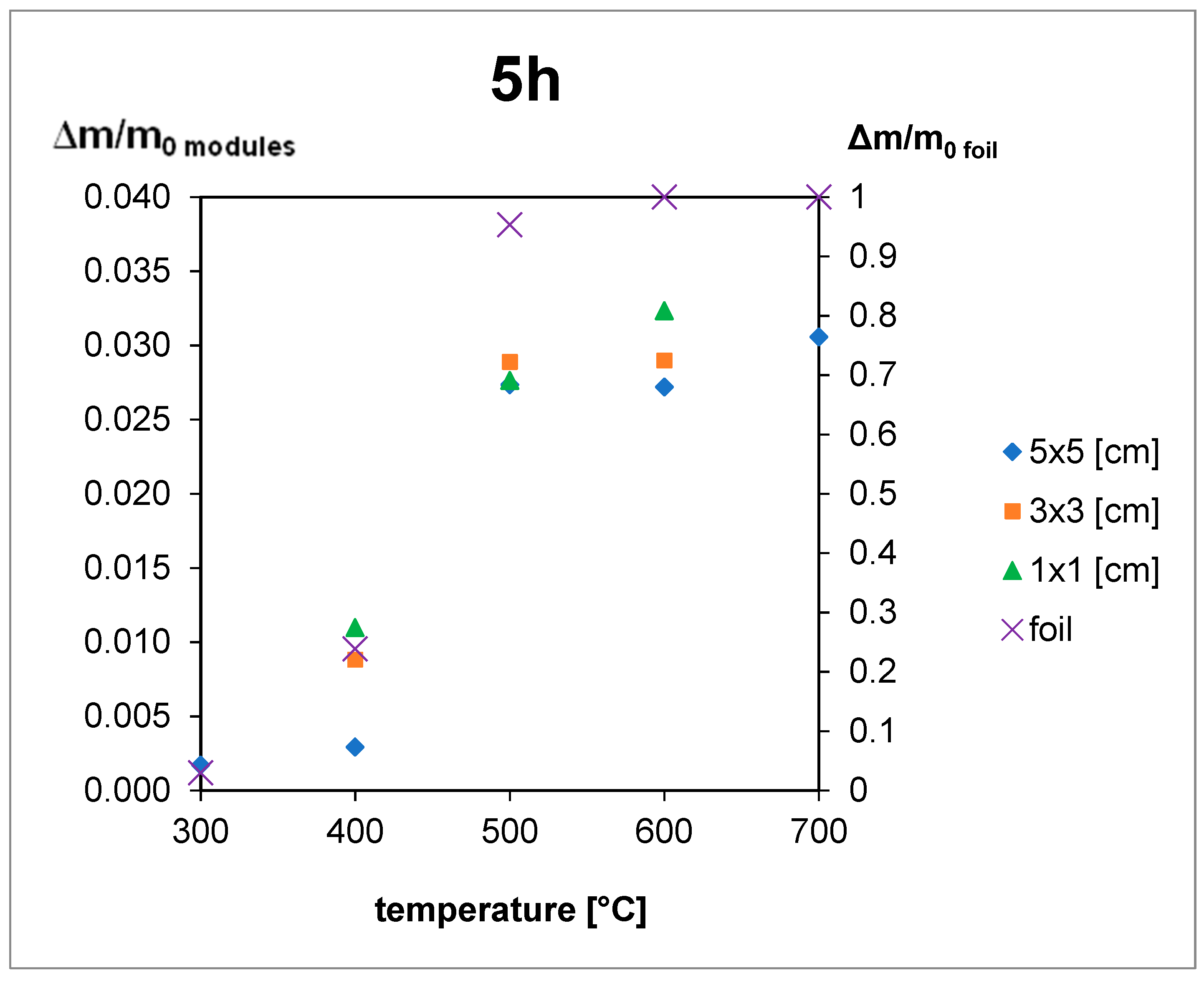
4.2. Thermal Treatment
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E. Recycling and Reuse Treatment Technologies for Photovoltaic Cells and Modules—A Review. Recycling: Processes, Costs and Benefits; Nova Science Publishers: New York, NY, USA, 2011; pp. 205–221. [Google Scholar]
- Klugmann-Radziemska, E. Recycling of Photovoltaic Solar Cells and Modules—The State Of Art; Lambert Academic Publishing: Riga, Latvia, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Urashima, N.; Izumina, M.; Arita, A.; Matsumoto, K. Research & development on recycling technology of photovoltaic power generation systems—Social system for PV recycling. In Proceedings of the 3rd World Conference on Photovoltaic Energy Conversion, Osaka, Japan, 11–18 May 2003; pp. 1985–1987. [Google Scholar]
- Eberspacher, C.; Fthenakis, V.M. Disposal and Recycling of end-of-Life PV Modules. In Proceedings of the 26th Photovoltiac Special Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 29 September–3 October 1997; pp. 1067–1072. [Google Scholar]
- Fthenakis, V.M. Overview of potential hazards. In Practical Handbook of Photovoltaics: Fundamentals and Applications; Markvart, T., Castaner, L., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Müller, A.; Röver, I.; Wambach, K.; von Ramin-Marro, D.W. Recovery of high value material of different photovoltaic technologies. In Proceedings of the 22nd European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Milan, Italy, 3–5 Septemeber 2007; pp. 2613–2616. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, S.; Yoo, S.; Lee, J.; Boo, B.; Ryu, H. Experimental investigations for recycling of silicon and glass from waste photovoltaic modules. Renew. Energy 2012, 47, 152–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marwede, M.; Berger, W.; Schlummer, M.; Mäurer, A.; Reller, A. Recycling paths for thin-film chalcogenide photovoltaic waste—Current feasible processes. Renew. Energy 2013, 55, 220–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Held, M. Life cycle assessment of CdTe module recycling. In Proceedings of the 24th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference, Hamburg, Germany, 21–25 September 2009; pp. 2370–2375. [Google Scholar]
- Bohland, J.R.; Anisimov, I.I.; Dapkus, T. Economic recycling of CdTe photovoltaic modules. In Proceedings of the 26th Photovoltiac Special Conference, Anaheim, CA, USA, 29 September–3 October 1997; pp. 355–358. [Google Scholar]
- Doi, T.; Tsuda, I.; Unagida, H.; Murata, A.; Sakuta, K.; Kurokawa, K. Experimental study on PV module recycling with organic solvent method. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2001, 67, 397–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campo, M.D.; Dieter, B.; Gegenwart, R.; Beier, J. Process for Recycling CdTe/CdS Thin Film Solar Cell Modules, US Patent 6,572,782 B2, 3 June 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Tammaro, M.; Rimauro, J.; Fiandra, V.; Salluzzo, A. Thermal treatment of waste photovoltaic module for recovery and recycling: Experimental assessment of the presence of metals in the gas emissions and in the ashes. Renew. Energy 2015, 81, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berger, W.; Simon, F.-G.; Weimann, K.; Alsema, E.A. A novel approach for the recycling of thin film photovoltaic modules. Resour. Conserv. Recycl. 2010, 54, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, J.; Yu, S. Review on feasible recycling pathways and technologies of solar photovoltaic modules. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2015, 141, 108–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agroui, K.; Belghachi, A.; Collins, G.; Farenc, J. Quality control of EVA encapsulant in photovoltaic module process and outdoor exposure. Desalination 2007, 209, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agroui, K.; Maallemi, A.; Boumaour, M.; Collins, G.; Salama, M. Thermal stability of slow and fast cure EVA encapsulant material for photovoltaic module manufacturing process. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2006, 90, 2509–2514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, D.; Born, M.; Wambach, K. Pyrolysis of EVA and its application in recycling of photovoltaic modules. J. Environ. Sci. 2004, 16, 889–893. [Google Scholar]
- Material Properties. Available online: http://www.matweb.com (accessed on 22 June 2016).
- Stark, W.; Jaunich, M. Investigation of Ethylene/Vinyl Acetate Copolymer (EVA) by thermal analysis DSC and DMA. Polym. Test. 2011, 30, 236–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radziemska, E.; Ostrowski, P.; Janik, H.; Leszkowski, K.; Sielicki, P. The research of physico-chemical properties of EVA copolymer for recycling of photovoltaic modules. ECOpole 2010, 4, 187–192. [Google Scholar]
- Beyler, C.L.; Hirschler, M.M. Thermal Decomposition of Polymers. In SFPE Handbook of Fire Protection Engineering 2; National Fire Protection Association: Quincy, MA, USA, 2002; pp. 110–131. [Google Scholar]

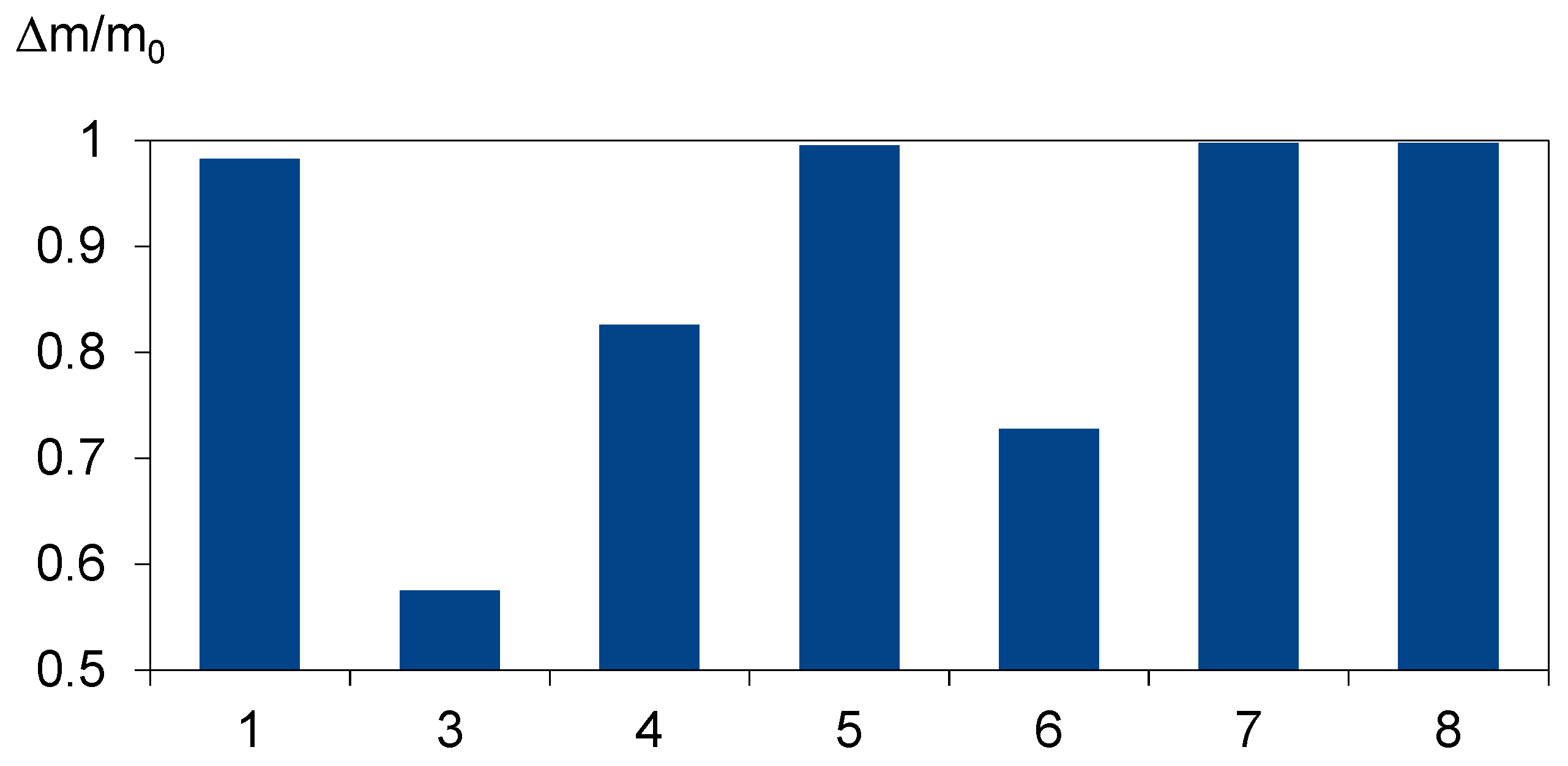
| Solvent | Room Temperature/2 Days | 80 °C/10 min |
|---|---|---|
| Acetone | n | DS |
| Toluene | SW | DS |
| Petroleum benzine | n/SW | DS |
| Isopropanol | n | DS |
| Methyl ethyl/isobutyl ketone | n/SW | DS |
| Tetrahydrofuran | SW/DS | DS |
| Ethylene glycol | n | n |
| Trichloroethylene | SW/DS | DS |
| Glycerine | n | n |
| Ethyl alcohol | n | - |
| SAMPLE NUMBER | AVERAGE THICKNESS [mm] | DENSITY [g/cm3] | LIGHT TRANSMISSION [%] | CROSSLINKING DEGREE [%] | VA CONTENT [wt%] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.4 | nd | Nd | nd | nd |
| 3 | 0.3–0.8 (measured 0.4–0.5) | nd | >91 | >75 | 28–32 |
| 4 | 0.4 | nd | >87 | nd | nd |
| 5 | 0.2–1.1 (measured 0.4–0.5) | 0.95 | 89 | nd | nd |
| 6 | Nd | 0.94 | Nd | nd | 19–22 |
| 7 | 0.46 | 0.96 | 91 | >85 | nd |
| 8 | 0.45–0.5 | 0.96 | >92 | >75 | nd |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuczyńska-Łażewska, A.; Klugmann-Radziemska, E. Influence of Fragment Size on the Time and Temperature of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Lamination Decomposition in the Photovoltaic Module Recycling Process. Materials 2019, 12, 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182857
Kuczyńska-Łażewska A, Klugmann-Radziemska E. Influence of Fragment Size on the Time and Temperature of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Lamination Decomposition in the Photovoltaic Module Recycling Process. Materials. 2019; 12(18):2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182857
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuczyńska-Łażewska, Anna, and Ewa Klugmann-Radziemska. 2019. "Influence of Fragment Size on the Time and Temperature of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Lamination Decomposition in the Photovoltaic Module Recycling Process" Materials 12, no. 18: 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182857
APA StyleKuczyńska-Łażewska, A., & Klugmann-Radziemska, E. (2019). Influence of Fragment Size on the Time and Temperature of Ethylene Vinyl Acetate Lamination Decomposition in the Photovoltaic Module Recycling Process. Materials, 12(18), 2857. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12182857





