Understanding the Influence of a Bifunctional Polyethylene Glycol Derivative in Protein Corona Formation around Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Nanoparticle Synthesis
2.2. Nanoparticle Characterization
2.3. Nanoparticle Incubation with Plasma
2.4. Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
2.5. Liquid Chromatography and Mass Spectrometry Analysis
2.6. Data Analysis: MS/MS Ion Search and Peptide Identification
2.7. Cell Culture
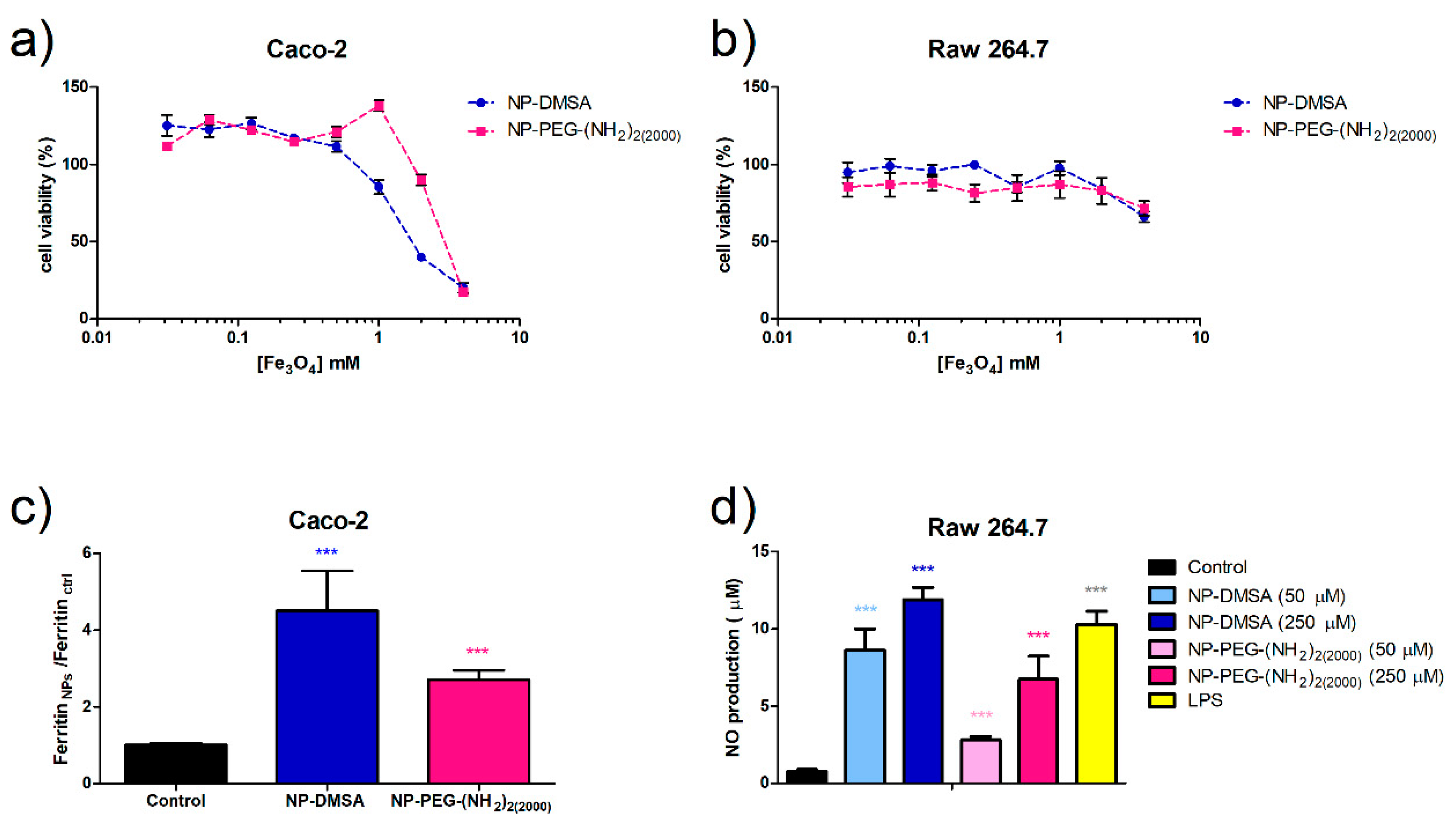
2.8. Cytotoxicity Assay (MTT)
2.9. Iron Uptake
2.10. Nitric Oxide Production
3. Results
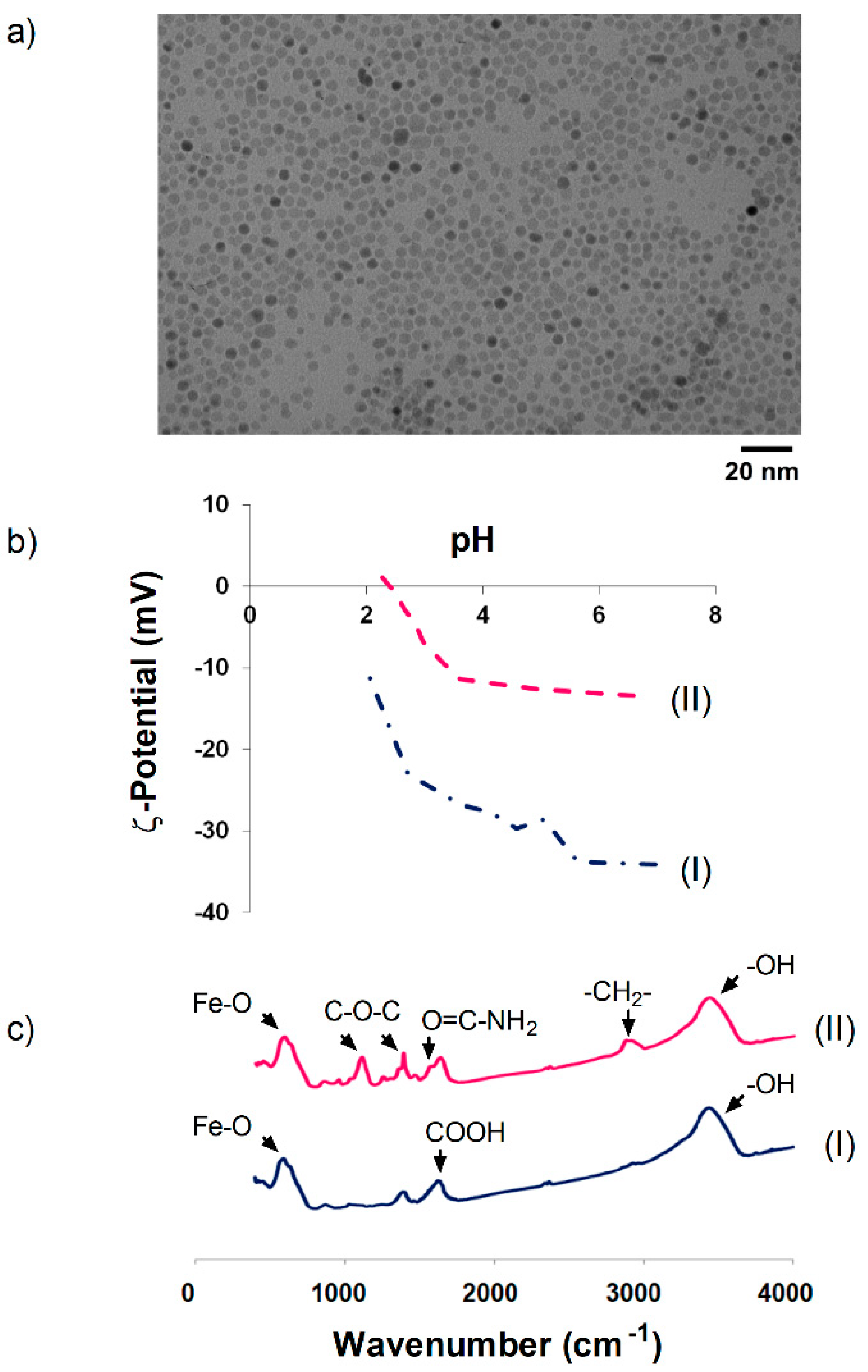
3.1. Synthesis and Characterization of DMSA and PEG-Coated Nanoparticles
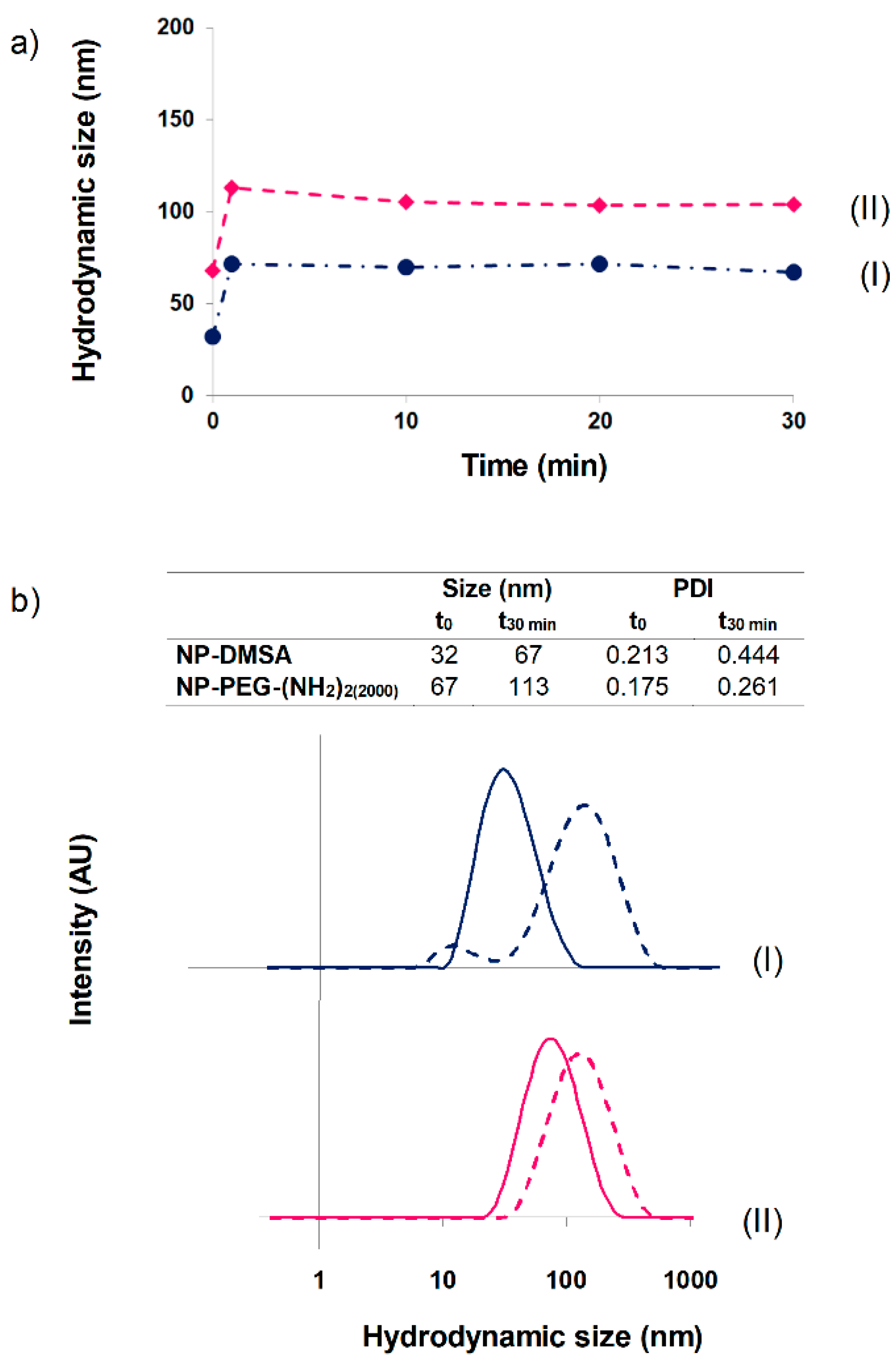
3.2. Monitoring Protein Corona Formation
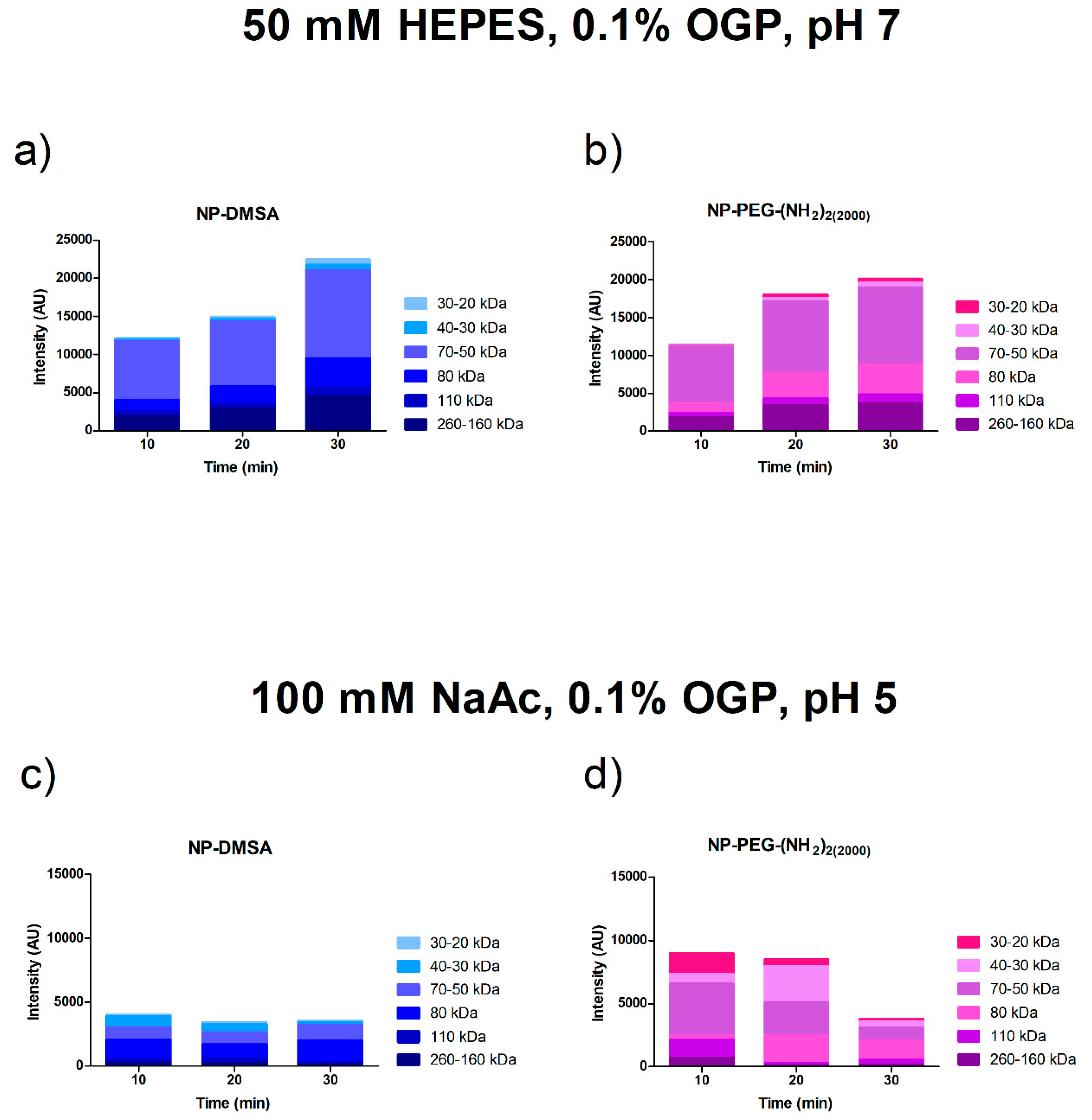
3.3. Protein Corona Characterization by Electrophoresis SDS-PAGE
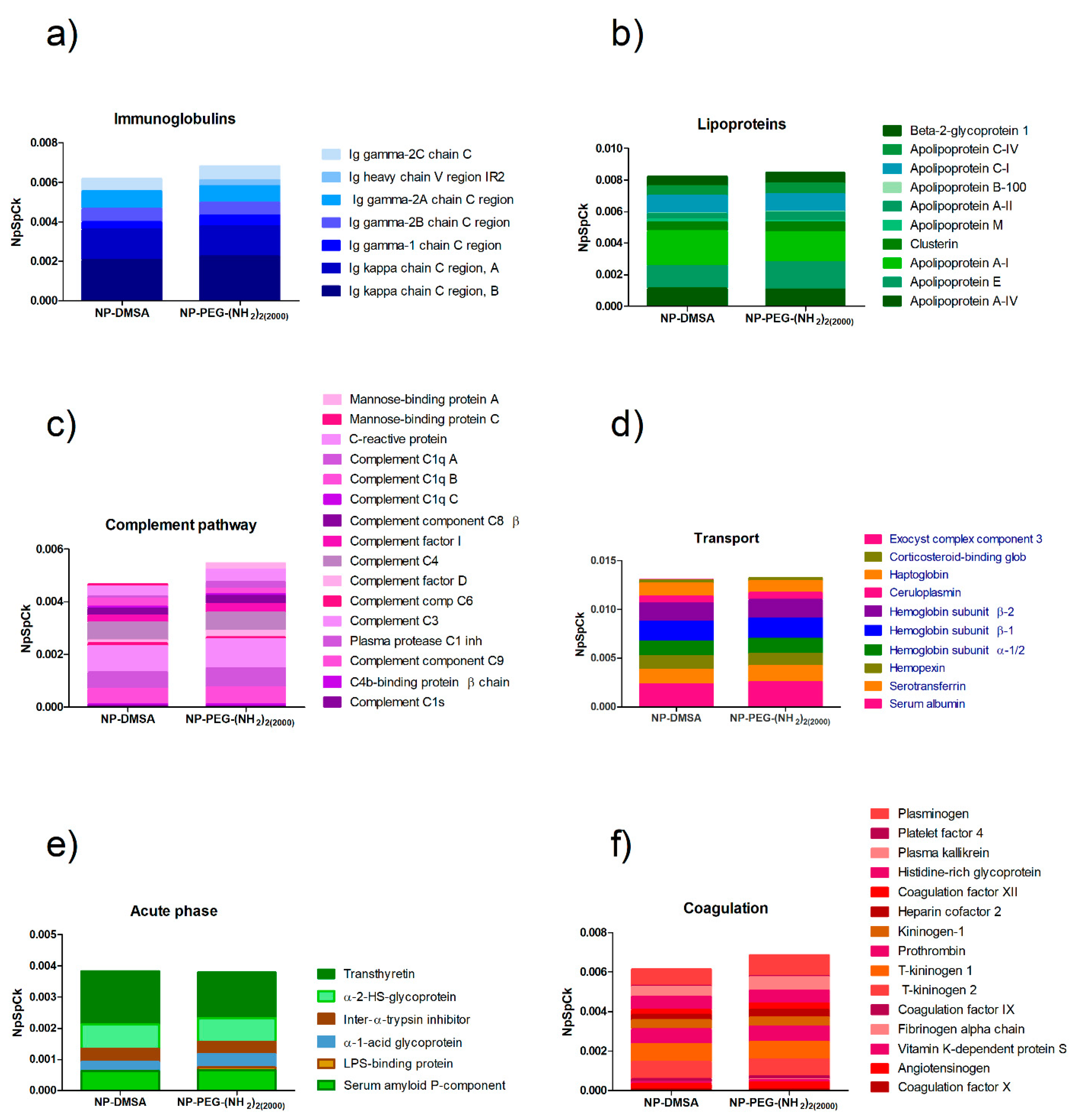
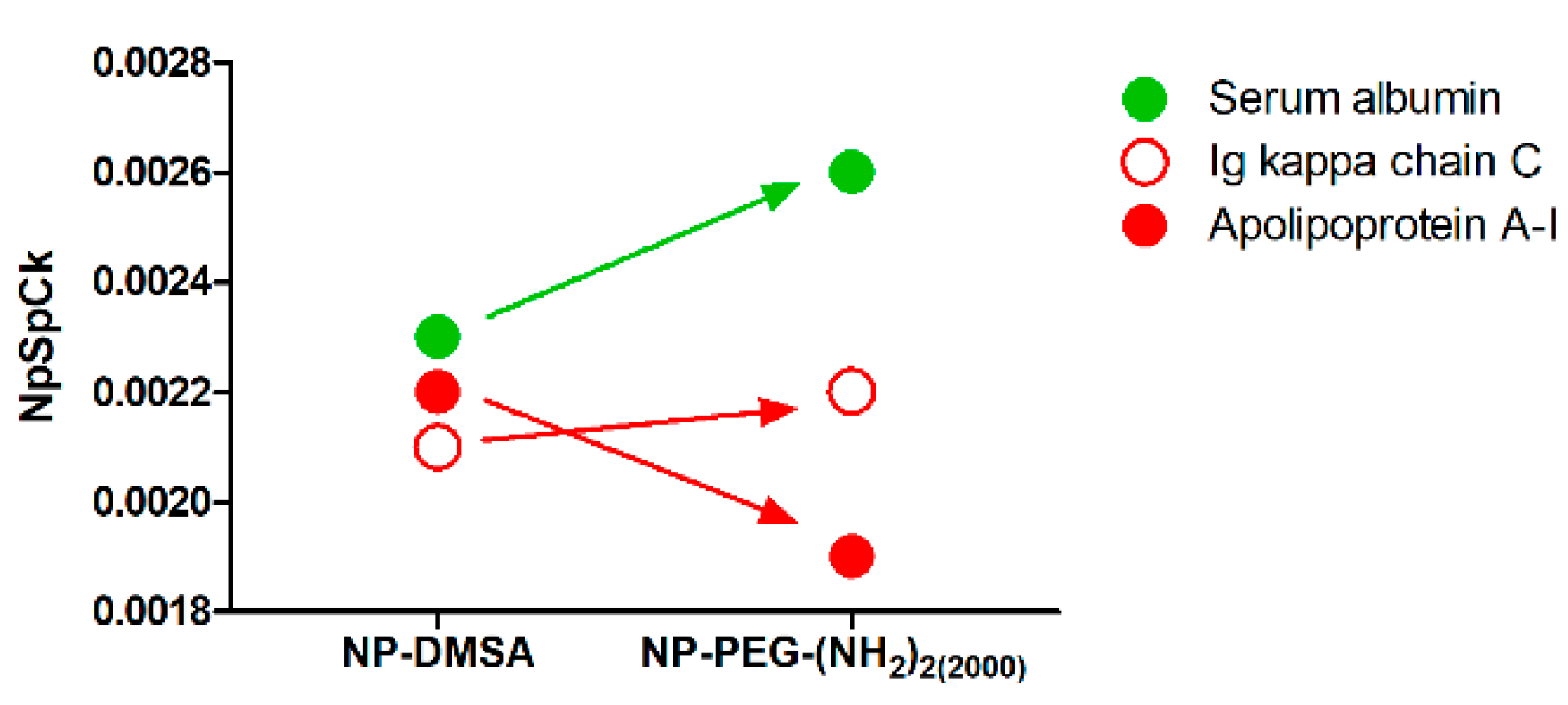
3.4. Protein Corona Characterization by Mass Spectrometry
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Clinicaltrials.gov. Available online: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/results?term=iron+oxide+nanoparticles (accessed on 6 February 2019).
- Magro, M.; Baratella, D.; Bonaiuto, E.; de A. Roger, J.; Vianello, F. New Perspectives on Biomedical Applications of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Curr. Med. Chem. 2018, 25, 540–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arias, L.; Pelim Pessan, J.; Miranda Vieira, A.; Toito de Lima, T.; Botazzo Delbem, A.; Monteiro, D. Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Applications: A Perspective on Synthesis, Drugs, Antimicrobial Activity, and Toxicity. Antibiotics 2018, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veronese, F.M.; Pasut, G. PEGylation, Successful Approach to Drug Delivery. Drug Discov. Today 2005, 10, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkachenko, A.G.; Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Coleman, D.; Ryan, J.; Glomm, W.R.; Shipton, M.K.; Franzen, S.; Feldheim, D.L. Cellular Trajectories of Peptide-Modified Gold Particle Complexes: Comparison of Nuclear Localization Signals and Peptide Transduction Domains. Bioconjug. Chem. 2004, 15, 482–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, L.L. Actively-Targeted LTVSPWY Peptide-Modified Magnetic Nanoparticles for Tumor Imaging. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 3981–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Illés, E.; Szekeres, M.; Tóth, I.Y.; Szabó, Á.; Iván, B.; Turcu, R.; Vékás, L.; Zupkó, I.; Jaics, G.; Tombácz, E. Multifunctional PEG-Carboxylate Copolymer Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Biomedical Application. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2018, 451, 710–720. [Google Scholar]
- Dilnawaz, F.; Singh, A.; Mohanty, C.S.S.K. Dual Drug Loaded Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Targeted Cancer Therapy. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3694–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Na, H.; Song, I.; Hyeon, T. Inorganic Nanoparticles for MRI Contrast Agents. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2133–2148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, S.D.; Walkey, C.; Jennings, T.; Fischer, H.C.; Chan, W.C.W. Mediating Tumor Targeting Efficiency of Nanoparticles through Design. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1909–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaConte, L.E.; Nitin, N.; Zurkiya, O.; Caruntu, D.; O’Connor, C.J.; Hu, X.; Bao, G. Coating Thickness of Magnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Affects R2 Relaxivity. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2007, 26, 1634–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wattendorf, U.; Merkle, H. PEGylation as a Tool for the Biomedical Engineering of Surface Modified Microparticles. J. Pharm. Sci. 2008, 97, 4655–4669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.W.; Hua, M.Y.; Liu, H.L.; Huang, C.Y.; Wei, K.C. Potential of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery. Nanotechnol. Sci. Appl. 2012, 5, 73–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gustafson, H.H.; Holt-casper, D.; Grainger, D.W.; City, S.L.; City, S.L.; Chemistry, P.; City, S.L. Nanoparticle Uptake: The Phagocyte Problem. Nano Today 2016, 10, 487–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cedervall, T.; Lynch, I.; Lindman, S.; Berggård, T.; Thulin, E.; Nilsson, H.; Dawson, K.A.; Linse, S. Understanding the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona Using Methods to Quantify Exchange Rates and Affinities of Proteins for Nanoparticles. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 2050–2055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Åberg, C.; Salvati, A.; Dawson, K.A. Biomolecular Coronas Provide the Biological Identity of Nanosized Materials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 779–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, S.; Loo, J.; Wong, D. Human Body Fluid Proteome Analysis. Proteomics 2006, 6, 6326–6353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fountoulakis, M.; Juranville, J.; Jiang, L.; Avila, D.; Röder, D.; Jakob, P.; Berndt, P.; Evers, S.; Langen, H. Depletion of the High-Abundance Plasma Proteins. Amino Acids 2004, 27, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milani, S.; Bombelli, F.B.; Pitek, A.S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J.; Baldelli Bombelli, F.; Pitek, A.S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J. Reversible versus Irreversible Binding of Transferrin to Polystyrene Nanoparticles: Soft and Hard Corona. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 2532–2541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V. Time Evolution of the Nanoparticle Protein Corona. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 3623–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Patri, A.K.; Zheng, J.; Clogston, J.D.; Ayub, N.; Aggarwal, P.; Neun, B.W.; Hall, J.B.; McNeil, S.E. Interaction of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles with Human Blood: Effects on Particle Size and Analysis of Plasma Protein Binding Profiles. Nanomedicine 2009, 5, 106–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; Neun, B.W.; Man, S.; Ye, X.; Hansen, M.; Patri, A.K.; Crist, R.M.; McNeil, S.E. Protein Corona Composition Does Not Accurately Predict Hematocompatibility of Colloidal Gold Nanoparticles. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2014, 10, 1453–1463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casals, E.; Pfaller, T.; Duschl, A.; Oostingh, G.J.; Puntes, V.F. Hardening of the Nanoparticle-Protein Corona in Metal (Au, Ag) and Oxide (Fe3O4, CoO, and CeO2) Nanoparticles. Small 2011, 7, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durán, N.; Silveira, C.P.; Durán, M.; Martinez, D.S.T. Silver Nanoparticle Protein Corona and Toxicity: A Mini-Review. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2015, 13, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Wan, S.; Baldelli-Bombelli, F.; Mahon, E.; Dawson, K.A. Comparisons of Nanoparticle Protein Corona Complexes Isolated with Different Methods. Nano Life 2013, 3, 1343004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Cedervall, T.; Dawson, K.A. Nanoparticle Size and Surface Properties Determine the Protein Corona with Possible Implications for Biological Impacts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 14265–14270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundqvist, M.; Stigler, J.; Cedervall, T.; Bergga, T.; Flanagan, M.B.; Lynch, I.; Elia, G.; Dawson, K. The Evolution of the Protein Corona around Nanoparticles: A Test Study. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7503–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczyk, D.; Baldelli-Bombelli, F.; Monopoli, M.P.; Lynch, I.; Dawson, K.A. What the Cell “Sees” in Bionanoscience. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 5761–5768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monopoli, M.P.; Walczyk, D.; Campbell, A.; Elia, G.; Lynch, I.; Bombelli, F.; Dawson, K.A. Physical-Chemical Aspects of Protein Corona: Relevance to in Vitro and in Vivo Biological Impacts of Nanoparticles. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2011, 133, 2525–2534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tenzer, S.; Docter, D.; Rosfa, S.; Wlodarski, A.; Kuharev, J.; Rekik, A.; Knauer, S.K.; Bantz, C.; Nawroth, T.; Bier, C.; et al. Nanoparticle Size Is a Critical Physicochemical Determinant of the Human Blood Plasma Corona: A Comprehensive Quantitative Proteomic Analysis. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7155–7167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z.Z.J.; Mortimer, G.; Schiller, T.; Musumeci, A.; Martin, D.; Minchin, R.F.R. Differential Plasma Protein Binding to Metal Oxide Nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 455101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Sánchez-Martín, M.; Busquets, M. Nanoparticles in Magnetic Resonance Imaging: From Simple to Dual Contrast Agents. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1727–1741. [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi, M.; Sahraian, M.A.; Shokrgozar, M.A.; Laurent, S. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles: Promises for Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2011, 2, 118–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Behzadi, S.; Serpooshan, V.; Sakhtianchi, R.; Müller, B.; Landfester, K.; Crespy, D.; Mahmoudi, M. Protein Corona Change the Drug Release Profile of Nanocarriers: The“Overlooked” Factor at the Nanobio Interface. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2014, 123, 143–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakulkhu, U.; Mahmoudi, M.; Maurizi, L.; Coullerez, G.; Hofmann-Amtenbrink, M.; Vries, M.; Motazacker, M.; Rezaee, F.; Hofmann, H. Significance of Surface Charge and Shell Material of Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticle (SPION) Based Core/Shell Nanoparticles on the Composition of the Protein Corona. Biomater. Sci. 2015, 3, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolosnjaj-Tabi, J.; Javed, Y.; Lartigue, L.; Volatron, J.; Elgrabli, D.; Marangon, I.; Pugliese, G.; Caron, B.; Figuerola, A.; Luciani, N.; et al. The One Year Fate of Iron Oxide Coated Gold Nanoparticles in Mice. ACS Nano 2015, 9, 7925–7939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepien, G.; Moros, M.; Pérez-Hernández, M.; Monge, M.; Gutiérrez, L.; Fratila, R.; Las Heras, M.; Menao Guillén, S.; Puente Lanzarote, J.; Solans, C.; et al. Effect of Surface Chemistry and Associated Protein Corona on the Long-Term Biodegradation of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles In Vivo. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfacesd Mater. Interfaces 2018, 10, 4548–4560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haynes, P.; Miller, I.; Aebersold, R.; Gemeiner, M.; Eberini, I.; Lovati, M.R.; Manzoni, C.; Vignati, M.; Gianazza, E. Proteins of Rat Serum: I. Establishing a Reference Two-Dimensional Electrophoresis Map by Immunodetection and Microbore High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Electrospray Mass Spectrometry. Electrophoresis 1998, 19, 1484–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Salas, G.; Calero, M.; Hernández, Y.; Villanueva, A.; Herranz, F.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Martínez, E.; Barber, D.F.F.; Morales, M.P.P. Short-Chain PEG Molecules Strongly Bound to Magnetic Nanoparticle for MRI Long Circulating Agents. Acta Biomater 2013, 9, 6421–6430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Hernández, Y.; Cabal, C.; González, E.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Martínez, E.; Morales, M.P.P. Biodistribution and Pharmacokinetics of Uniform Magnetite Nanoparticles Chemically Modified with Polyethylene Glycol. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 11400–11408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz, A.; Gutierrez, L.; Cáceres-Velez, P.; Santos, D.; Chaves, S.; Fascineli, M.L.; Garcia, M.P.; Azevedo, R.B.; Morales, M.P. Biotransformation of Magnetic Nanoparticles as a Function of the Coating in a Rat Model. Nanoscale 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, A.G.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Port, M.; Robic, C.; Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Effect of Nanoparticle and Aggregate Size on the Relaxometric Properties of MR Contrast Agents Based on High Quality Magnetite Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. 2009, 113, 7033–7039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salas, G.; Casado, C.; Teran, F.J.; Miranda, R.; Serna, C.J.; Morales, M.P. Controlled Synthesis of Uniform Magnetite Nanocrystals with High-Quality Properties for Biomedical Applications. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 22, 21065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma, S.I.; Marciello, M.; Carvalho, A.; Veintemillas-Verdaguer, S.; Morales, M.P.; Roque, A.C. Effects of Phase Transfer Ligands on Monodisperse Iron Oxide Magnetic Nanoparticles. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2015, 437C, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, D.; Flügge, U.I.; Flugge, U.I. A Method for the Quantitative Recovery of Protein in Dilute Solution in the Presence of Detergents and Lipids. Anal. Biochem. 1984, 138, 141–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Ferrer, D.; Martínez-Bartolomé, S.; Villar, M.; Campillos, M.; Martín-Maroto, F.; Vázquez, J. Statistical Model for Large-Scale Peptide Identification in Databases from Tandem Mass Spectra Using SEQUEST. Anal. Chem. 2004, 76, 6853–6860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcilla, M.; Alpízar, A.; Lombardía, M.; Ramos-Fernandez, A.; Ramos, M.; Albar, J.P. Increased Diversity of the HLA-B40 Ligandome by the Presentation of Peptides Phosphorylated at Their Main Anchor Residue. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2014, 13, 462–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marín-Barba, M.; Gavilán, H.; Gutiérrez, L.; Lozano-Velasco, E.; Rodríguez-Ramiro, I.; Wheeler, G.G.N.; Morris, C.C.J.; Morales, M.M.P.; Ruiz, A. Unravelling the Mechanisms That Determine the Uptake and Metabolism of Magnetic Single and Multicore Nanoparticles in a Xenopus Laevis Model. Nanoscale 2018, 10, 690–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glahn, R.P.; Lee, O.A.; Yeung, A.; Goldman, M.I.; Miller, D.D. Caco-2 Cell Ferritin Formation Predicts Nonradiolabeled Food Iron Availability in an In Vitro Digestion/Caco-2 Cell Culture Model. J. Nutr. 1998, 128, 1555–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roca, A.G.; Marco, J.F.; Morales, M.P.; Serna, C.J. Effect of Nature and Particle Size on Properties of Uniform Magnetite and Maghemite Nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 18577–18584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lattuada, M.; Hatton, T.A. Functionalization of Monodisperse Magnetic Nanoparticles. Langmuir 2007, 23, 2158–2168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, C.; Herrera, A.P.; Rinaldi, C. Colloidal Dispersions of Monodisperse Magnetite Nanoparticles Modified with Poly(Ethylene Glycol). J Colloid Interface Sci 2009, 329, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amici, J.; Celasco, E.; Allia, P.; Tiberto, P.; Sangermano, M. Poly(Ethylene Glycol)-Coated Magnetite Nanoparticles: Preparation and Characterization. Macromol. Chem. Phys. 2011, 212, 411–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amstad, E.; Gillich, T.; Bilecka, I.; Textor, M.; Reimhult, E. Ultrastable Iron Oxide Nanoparticle Colloidal Suspensions Using Dispersants with Catechol-Derived Anchor Groups. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4042–4048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohler, N.; Sun, C.; Fichtenholtz, A.; Gunn, J.; Fang, C.; Zhang, M. Methotrexate-Immobilized Poly(Ethylene Glycol) Magnetic Nanoparticles for MR Imaging and Drug Delivery. Small 2006, 2, 785–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, C.; Du, K.; Fang, C.; Bhattarai, N.; Veiseh, O.; Kievit, F.; Stephen, Z.; Lee, D.; Ellenbogen, R.G.; Ratner, B.; et al. PEG-Mediated Synthesis of Highly Dispersive Multifunctional Superparamagnetic Nanoparticles: Their Physicochemical Properties and Function In Vivo. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2402–2410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walkey, C.D.; Chan, W.C.W. Understanding and Controlling the Interaction of Nanomaterials with Proteins in a Physiological Environment. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 41, 2780–2799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.X.; Hussain, S.M.; Krestin, G.P. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Contrast Agents: Physicochemical Characteristics and Applications in MR Imaging. Eur. Radiol. 2001, 11, 2319–2331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, H.L.; Xu, Y.F.; Qi, X.R.; Maitani, Y.; Nagai, T. Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles Stabilized by Alginate: Pharmacokinetics, Tissue Distribution, and Applications in Detecting Liver Cancers. Int. J. Pharm. 2008, 354, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitek, A.S.; O’Connell, D.; Mahon, E.; Monopoli, M.P.; Francesca Baldelli, F.; Dawson, K.A. Transferrin Coated Nanoparticles: Study of the Bionano Interface in Human Plasma. PLoS ONE 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilanova, O.; Mittag, J.J.; Kelly, P.M.; Milani, S.; Dawson, K.A.; Rädler, J.O.; Franzese, G. Understanding the Kinetics of Protein-Nanoparticle Corona Formation. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 10842–10850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidner, A.; Gräfe, C.; von der Lühe, M.; Remmer, H.; Clement, J.H.; Eberbeck, D.; Ludwig, F.; Müller, R.; Schacher, F.H.; Dutz, S. Preparation of Core-Shell Hybrid Materials by Producing a Protein Corona Around Magnetic Nanoparticles. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2015, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, P.; Hall, J.B.; McLeland, C.B.; Dobrovolskaia, M.A.; McNeil, S.E. Nanoparticle Interaction with Plasma Proteins as It Relates to Particle Biodistribution, Biocompatibility and Therapeutic Efficacy. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2009, 61, 428–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, Y.; Nagasaki, Y. PEGylation Technology in Nanomedicine. Adv. Polym. Sci. 2011, 247, 115–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, I.; Al-Hanbali, O.; Hunter, A.C.; Rutt, K.J.; Andresen, T.L.; Moghimi, S.M. Distinct Polymer Architecture Mediates Switching of Complement Activation Pathways at the Nanosphere-Serum Interface: Implications for Stealth Nanoparticle Engineering. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 6629–6638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gref, R.; Luck, M.; Quellec, P.; Marchand, M.; Dellacherie, E.; Harnisch, S.; Blunk, T.; Muller, R.H. ‘Stealth’ Corona-Core Nanoparticles Surface Modified by Polyethylene Glycol (PEG): Influences of the Corona (PEG Chain Length and Surface Density) and of the Core Composition on Phagocytic Uptake and Plasma Protein Adsorption. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2000, 18, 301–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhoef, J.F.; Anchordoquy, T.J. Questioning the Use of PEGylation for Drug Delivery. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2013, 3, 499–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Kohler, N.; Zhang, M. Surface Modification of Superparamagnetic Magnetite Nanoparticles and Their Intracellular Uptake. Biomaterials 2002, 23, 1553–1561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Xu, C.; Kohler, N.; Hou, Y.; Sun, S. Controlled PEGylation of Monodisperse Fe3O4 Nanoparticles for Reduced Non-Specific Uptake by Macrophage Cells. Adv. Mater. 2007, 19, 3163–3166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, A.; Stellacci, F. Effect of Surface Properties on Nanoparticle-Cell Interactions. Small 2010, 6, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Lookeren Campagne, M.; Wiesmann, C.; Brown, E.J. Macrophage Complement Receptors and Pathogen Clearance. Cell. Microbiol. 2007, 9, 2095–2102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manke, A.; Wang, L.; Rojanasakul, Y. Mechanisms of Nanoparticle-Induced Oxidative Stress and Toxicity. Biomed. Res. Int. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, A.; Ali, L.M.A.M.A.; Cáceres-Vélez, P.R.R.; Cornudella, R.; Gutiérrez, M.; Moreno, J.A.A.; Piñol, R.; Palacio, F.; Fascineli, M.L.L.; Azevedo, R.B.; et al. Hematotoxicity of Magnetite Nanoparticles Coated with Polyethylene Glycol: In Vitro and in Vivo Studies. Toxicol. Res. 2015, 4, 1555–1564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ruiz, A.; Alpízar, A.; Beola, L.; Rubio, C.; Gavilán, H.; Marciello, M.; Rodríguez-Ramiro, I.; Ciordia, S.; Morris, C.J.; Morales, M.d.P. Understanding the Influence of a Bifunctional Polyethylene Glycol Derivative in Protein Corona Formation around Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Materials 2019, 12, 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142218
Ruiz A, Alpízar A, Beola L, Rubio C, Gavilán H, Marciello M, Rodríguez-Ramiro I, Ciordia S, Morris CJ, Morales MdP. Understanding the Influence of a Bifunctional Polyethylene Glycol Derivative in Protein Corona Formation around Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Materials. 2019; 12(14):2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142218
Chicago/Turabian StyleRuiz, Amalia, Adán Alpízar, Lilianne Beola, Carmen Rubio, Helena Gavilán, Marzia Marciello, Ildefonso Rodríguez-Ramiro, Sergio Ciordia, Christopher J. Morris, and María del Puerto Morales. 2019. "Understanding the Influence of a Bifunctional Polyethylene Glycol Derivative in Protein Corona Formation around Iron Oxide Nanoparticles" Materials 12, no. 14: 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142218
APA StyleRuiz, A., Alpízar, A., Beola, L., Rubio, C., Gavilán, H., Marciello, M., Rodríguez-Ramiro, I., Ciordia, S., Morris, C. J., & Morales, M. d. P. (2019). Understanding the Influence of a Bifunctional Polyethylene Glycol Derivative in Protein Corona Formation around Iron Oxide Nanoparticles. Materials, 12(14), 2218. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12142218





