Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control
Abstract
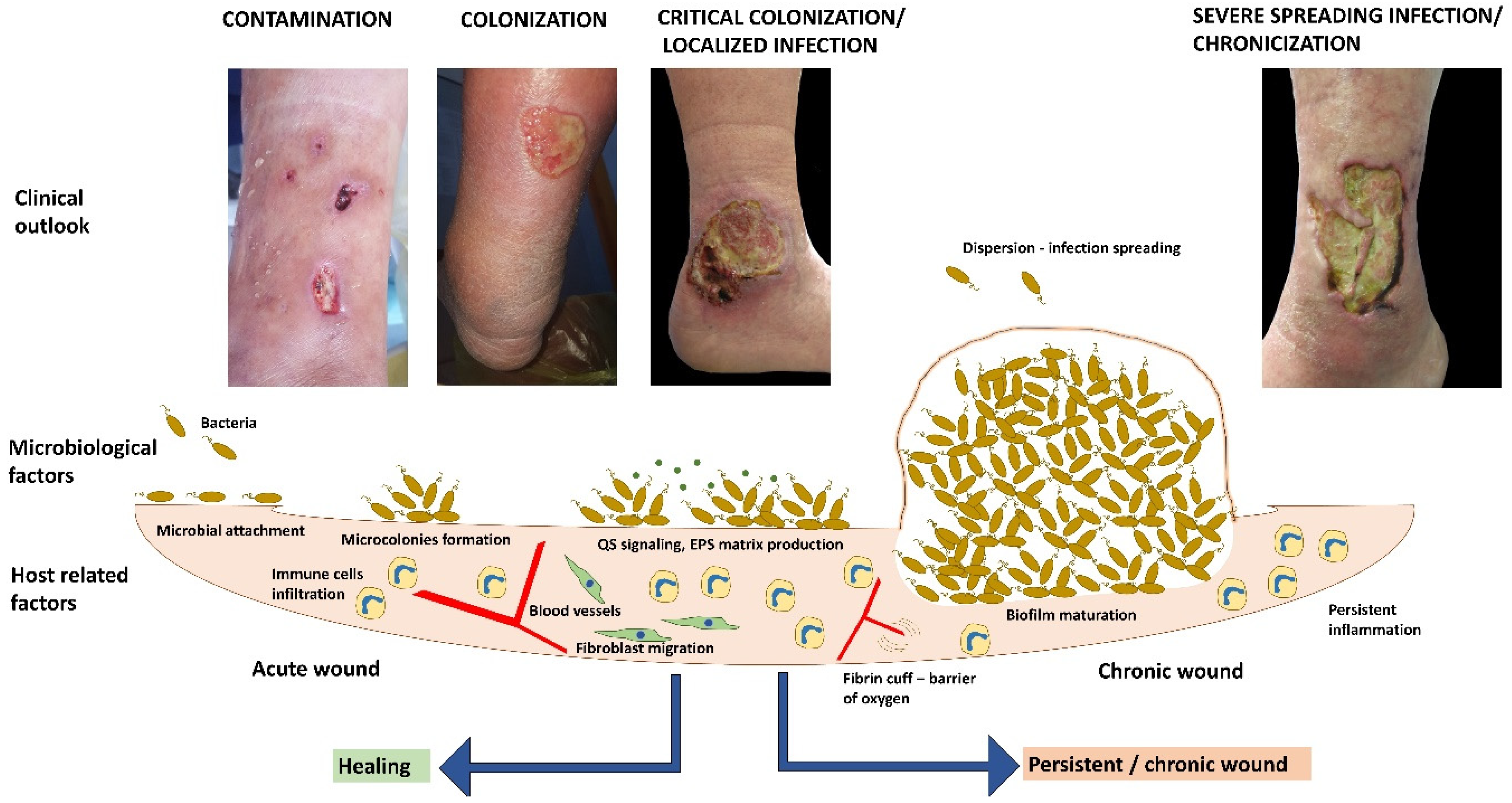
1. Introduction
2. Current Wound Therapy
3. Nanomaterials in Wound Healing
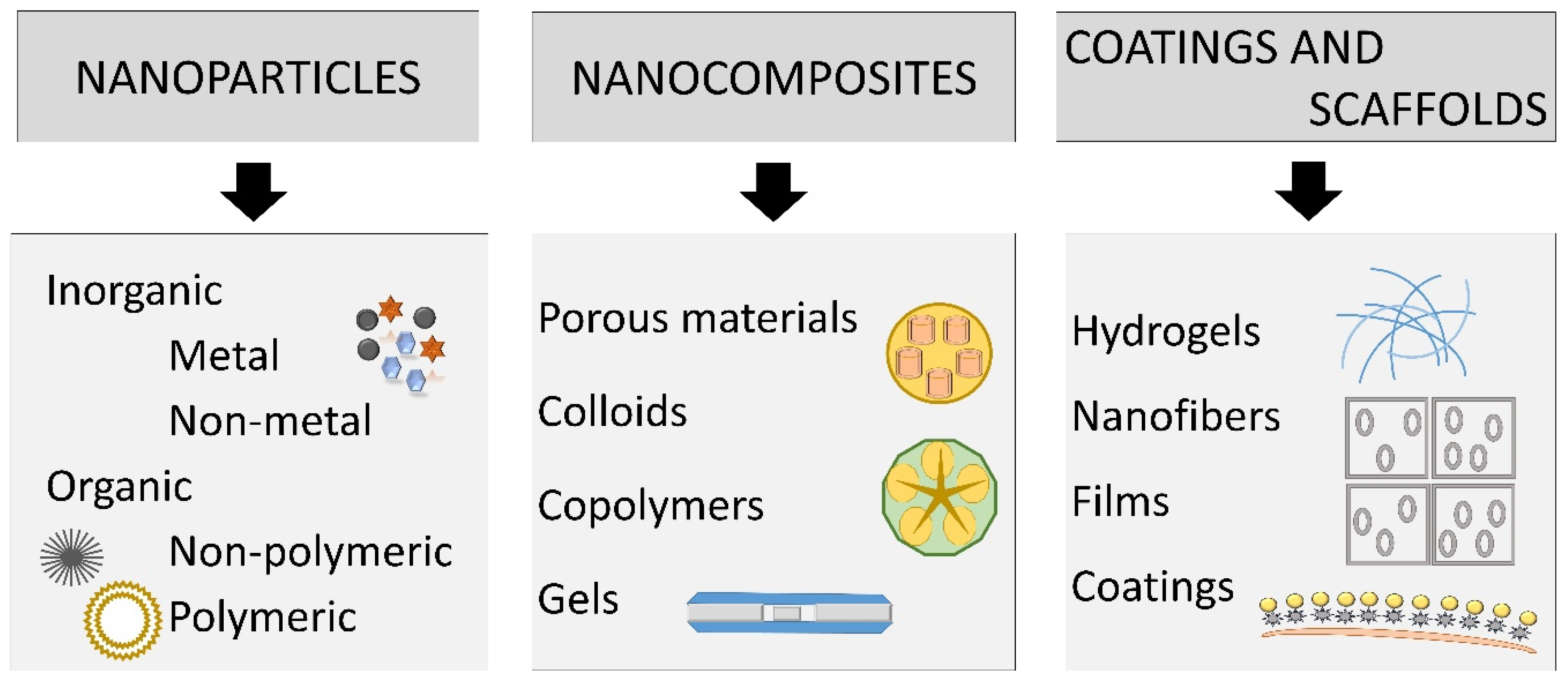
3.1. Definition and Classification
3.2. Nanoparticles
3.2.1. Silver Nanoparticles
3.2.2. Gold Nanoparticles
3.2.3. Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
3.3. Nanocomposites or Composite Nanoparticles
Nano-Carriers for Wound Healing
3.4. Coatings and Scaffolds
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; Chen, J.; Kirsner, R. Pathophysiology of acute wound healing. Clin. Dermatol. 2007, 25, 9–18. [Google Scholar]
- Negut, I.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M. Treatment Strategies for Infected Wounds. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.M.; Holban, A.M.; Giurcăneanu, C.Ă.L.I.N.; Popa, L.G.; Buzea, M.; Filipov, M.; Lazăr, V.E.R.O.N.I.C.A.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Popa, M.I. Identification and phenotypic characterization of the most frequent bacterial etiologies in chronic skin ulcers. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2014, 55, 1401–1408. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.M.; Holban, A.M.; Giurcaneanu, C.; Popa, L.G.; Oanea, R.M.; Lazar, V.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Popa, M.; Popa, M.I. Microbial biofilms: Impact on the pathogenesis of periodontitis, cystic fibrosis, chronic wounds and medical device-related infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 15, 1552–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malone, M.; Johani, K.; Jensen, S.; Gosbell, I.; Dickson, H.; Hu, H.; Vickery, K. Next Generation DNA Sequencing of Tissues from Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcers. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.M.; Preda, M.; Lungu, I.; Gestal, M.C.; Popa, M.I.; Holban, A.M. Nanocoatings for Chronic Wound Repair-Modulation of Microbial Colonization and Biofilm Formation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications. ACS Cent. Sci. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, M.C.; Nanchahal, J. Advances in the modulation of cutaneous wound healing and scarring. BioDrugs 2005, 19, 363–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedman, N.D.; Temkin, E.; Carmeli, Y. The negative impact of antibiotic resistance. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2016, 22, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arafa, M.G.; El-Kased, R.F. Thermoresponsive gels containing gold nanoparticles as smart antibacterial and wound healing agents. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 13674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoiby, N.; Bjarnsholt, T.; Moser, C.; Bassi, G.; Coenye, T.; Donelli, G.; Hall-Stoodley, L.; Hola, V.; Imbert, C.; Kirketerp-Møller, K.; et al. ESCMID guideline for the diagnosis and treatment of biofilm infections 2014. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2015, 21, S1–S25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mihai, M.M.; Giurcãneanu, C.; Popa, L.G.; Nitipir, C.; Popa, M.I. Controversies and challenges of chronic wound infection diagnosis and treatment. Mod. Med. 2015, 22, 375–381. [Google Scholar]
- Mori, H.M.; Kawanami, H.; Kawahata, H.; Aoki, M. Wound healing potential of lavender oil by acceleration of granulation and wound contraction through induction of TGF-beta in a rat model. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 16, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orchard, A.; van Vuuren, S. Commercial Essential Oils as Potential Antimicrobials to Treat Skin Diseases. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 2017, 4517971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jamil, B.; Abbasi, R.; Abbasi, S.; Khan, S.U.; Ihsan, A.; Javed, S.; Bokhari, H.; Imran, M. Encapsulation of Cardamom Essential Oil in Chitosan Nano-composites: In-vitro Efficacy on Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens and Cytotoxicity Studies. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, P.T.; Lakshmanan, V.-K.; Anilkumar, T.; Ramya, C.; Reshmi, P.; Unnikrishnan, A.; Nair, S.V.; Jayakumar, R. Flexible and microporous chitosan hydrogel/nano ZnO composite bandages for wound dressing: In vitro and in vivo evaluation. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 2618–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niska, K.; Zielinska, E.; Radomski, M.W.; Inkielewicz-Stepniak, I. Metal nanoparticles in dermatology and cosmetology: Interactions with human skin cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2018, 295, 38–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.C.; Lin, S.; Wang, P.C.; Sridhar, R. Techniques for physicochemical characterization of nanomaterials. Biotechnol. Adv. 2014, 32, 711–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, M. Nanogeometry: Beyond drug delivery. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 131–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- George, S.; Lin, S.; Ji, Z.; Thomas, C.R.; Li, L.; Mecklenburg, M.; Meng, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xia, T.; et al. Surface defects on plate-shaped silver nanoparticles contribute to its hazard potential in a fish gill cell line and zebrafish embryos. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 3745–3759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumar, V.; Samal, S.K.; Mohanty, S.; Nayak, S.K. Recent advancements in biopolymer and metal nanoparticle-based materials in diabetic wound healing management. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 122, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Szmyd, R.; Goralczyk, A.G.; Skalniak, L.; Cierniak, A.; Lipert, B.; Filon, F.L.; Crosera, M.; Borowczyk, J.; Laczna, E.; Drukala, J.; et al. Effect of silver nanoparticles on human primary keratinocytes. Biol. Chem. 2013, 394, 113–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Adibhesami, M. The Effect of Silver Nanoparticles on Wounds Contaminated with Pseudomonas aeruginosa in Mice: An Experimental Study. Iran. J. Pharm. Res. 2017, 16, 661–669. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pal, S.; Nisi, R.; Stoppa, M.; Licciulli, A. Silver-Functionalized Bacterial Cellulose as Antibacterial Membrane for Wound-Healing Applications. ACS Omega 2017, 2, 3632–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radulescu, M.; Andronescu, E.; Dolete, G.; Popescu, R.C.; Fufă, O.; Chifiriuc, M.C.; Mogoantă, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Mogoșanu, G.D.; Grumezescu, A.M.; et al. Silver Nanocoatings for Reducing the Exogenous Microbial Colonization of Wound Dressings. Materials 2016, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, M.M.; Bai, J.; Shao, D.; Qiu, J.; Li, M.; Zheng, X.; Xiao, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chang, Z.-M.; Chen, L.; et al. Antibacterial and biodegradable tissue nano-adhesives for rapid wound closure. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5849–5863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boroumand, Z.; Golmakani, N.; Boroumand, S. Clinical trials on silver nanoparticles for wound healing. Nanomed. J. 2018, 5, 186–191. [Google Scholar]
- Fong, J.; Wood, F.; Fowler, B. A silver coated dressing reduces the incidence of early burn wound cellulitis and associated costs of inpatient treatment: Comparative patient care audits. Burns 2005, 31, 562–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Xia, D.; Huang, G.; Jing, H.; Wang, Y.; Gu, H. Concentration effect of gold nanoparticles on proliferation of keratinocytes. Colloids Surf. B Biointerfaces 2010, 81, 406–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marza, S.; Magyari, K. Skin wound regeneration with bioactive glass-gold nanoparticles ointment. Biomed. Mater. 2019, 14, 025011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaure, P.C.; Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Mogoşanu, G.D.; Bălşeanu, T.A.; Stan, M.S.; Dinischiotu, A.; Volceanov, A.; Mogoantă, L. In vitro and in vivo studies of novel fabricated bioactive dressings based on collagen and zinc oxide 3D scaffolds. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 557, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Liu, C.; Yang, D.; Zhang, H.; Xi, Z. Comparative study of cytotoxicity, oxidative stress and genotoxicity induced by four typical nanomaterials: The role of particle size, shape and composition. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2009, 29, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.I.; Behera, S.K.; Paul, P.; Das, B.; Suar, M.; Jayabalan, R.; Fawcett, D.; Poinern, G.E.J.; Tripathy, S.K.; Mishra, A. Biogenic Au@ZnO core-shell nanocomposites kill Staphylococcus aureus without provoking nuclear damage and cytotoxicity in mouse fibroblasts cells under hyperglycemic condition with enhanced wound healing proficiency. Med. Microbiol. Immunol. 2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Han, Y.; Cui, M.; Tey, H.L.; Wang, L.; Xu, C. ZnO nanoparticles as an antimicrobial tissue adhesive for skin wound closure. J. Mater. Chem. B 2017, 5, 4535–4541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arya, G.; Kumari, R.M.; Sharma, N.; Gupta, N.; Kumar, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Nimesh, S. Catalytic, antibacterial and antibiofilm efficacy of biosynthesised silver nanoparticles using Prosopis juliflora leaf extract along with their wound healing potential. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2019, 190, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sood, R.; Chopra, D.S. Optimization of reaction conditions to fabricate Ocimum sanctum synthesized silver nanoparticles and its application to nano-gel systems for burn wounds. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2018, 92, 575–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, H.; Cheng, J.; Yu, K. In situ reduction of silver nanoparticles by gelatin to obtain porous silver nanoparticle/chitosan composites with enhanced antimicrobial and wound-healing activity. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 633–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, F.; Yang, A.; Yu, D.M.; Wang, J.; Gong, X.; Tian, H.X. Bio-synthesis of Barleria gibsoni leaf extract mediated zinc oxide nanoparticles and their formulation gel for wound therapy in nursing care of infants and children. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2018, 189, 267–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shariatinia, Z. Pharmaceutical applications of chitosan. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 2019, 263, 131–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biranje, S.S.; Madiwale, P.V.; Patankar, K.C.; Chhabra, R.; Dandekar-Jain, P.; Adivarekar, R.V. Hemostasis and anti-necrotic activity of wound-healing dressing containing chitosan nanoparticles. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 936–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dan, N.; Dan, W.; Liu, X.; Cong, L. A novel antibacterial acellular porcine dermal matrix cross-linked with oxidized chitosan oligosaccharide and modified by in situ synthesis of silver nanoparticles for wound healing applications. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2019, 94, 1020–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajji, S.; Ben Khedir, S.; Hamza-Mnif, I.; Hamdi, M.; Jedidi, I.; Kallel, R.; Boufi, S.; Nasri, M. Biomedical potential of chitosan-silver nanoparticles with special reference to antioxidant, antibacterial, hemolytic and in vivo cutaneous wound healing effects. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2019, 1863, 241–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holban, A.M.; Grumezescu, V.; Grumezescu, A.M.; Vasile, B.S.; Trusca, R.; Cristescu, R.; Socol, G.; Iordache, F. Antimicrobial nanospheres thin coatings prepared by advanced pulsed laser technique. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2014, 5, 872–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, G.; Jiang, Y.-W.; Jia, H.-R.; Wu, F.-G. Near-infrared light-controllable on-demand antibiotics release using thermo-sensitive hydrogel-based drug reservoir for combating bacterial infection. Biomaterials 2019, 188, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez Martinez, S.P.; Rivera González, T.; Franco Molina, M.; Bollain y Goytia, J.; Martínez Sanmiguel, J.; Zárate Triviño, D.; Rodríguez Padilla, C. A Novel Gold Calreticulin Nanocomposite Based on Chitosan for Wound Healing in a Diabetic Mice Model. Nanomaterials 2019, 9, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Zhan, B.; Zhang, W.; Qin, D.; Xia, G.; Zhang, H.; Peng, M.; Li, S.-A.; Zhang, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Carboxymethyl chitosan nanoparticles loaded with bioactive peptide OH-CATH30 benefit nonscar wound healing. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5771–5786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tayeb, A.H.; Amini, E.; Ghasemi, S.; Tajvidi, M. Cellulose Nanomaterials-Binding Properties and Applications: A Review. Molecules 2018, 23, 2684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Zhang, J.; Yang, G. Present status and applications of bacterial cellulose-based materials for skin tissue repair. Carbohydr. Polym. 2013, 92, 1432–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, A.; Khan, R.; Ul-Islam, M.; Khan, T.; Wahid, F. Bacterial cellulose-zinc oxide nanocomposites as a novel dressing system for burn wounds. Carbohydr. Polym. 2017, 164, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moniri, M.; Moghaddam, A.B.; Azizi, S.; Rahim, R.A.; Zuhainis, S.W.; Navaderi, M.; Mohamad, R. In vitro molecular study of wound healing using biosynthesized bacteria nanocellulose/silver nanocomposite assisted by bioinformatics databases. Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 5097–5112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nurhasni, H.; Cao, J.; Choi, M.; Kim, I.; Lee, B.L.; Jung, Y.; Yoo, J.-W. Nitric oxide-releasing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-polyethylenimine nanoparticles for prolonged nitric oxide release, antibacterial efficacy, and in vivo wound healing activity. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 3065–3080. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Zheng, Y.; Shi, Y.; Zhao, L. pH-responsive calcium alginate hydrogel laden with protamine nanoparticles and hyaluronan oligosaccharide promotes diabetic wound healing by enhancing angiogenesis and antibacterial activity. Drug Deliv. Transl. Res. 2019, 9, 227–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krausz, A.E.; Adler, B.L.; Cabral, V.; Navati, M.; Doerner, J.; Charafeddine, R.A.; Chandra, D.; Liang, H.; Gunther, L.; Clendaniel, A.; et al. Curcumin-encapsulated nanoparticles as innovative antimicrobial and wound healing agent. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2015, 11, 195–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari, S.; Alihosseini, F.; Sorkhabadi, S.M.R.; Bidgoli, S.A.; Mousavi, S.E.; Haghighat, S.; Nasab, A.A.; Kianvash, N. Nanotechnology in Wound Healing; Semisolid Dosage Forms Containing Curcumin-Ampicillin Solid Lipid Nanoparticles, in-Vitro, Ex-Vivo and in-Vivo Characteristics. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 395–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moradi, A.; Kheirollahkhani, Y.; Fatahi, P.; Abdollahifar, M.-A.; Amini, A.; Naserzadeh, P.; Ashtari, K.; Ghoreishi, S.K.; Chien, S.; Rezaei, F.; et al. An improvement in acute wound healing in mice by the combined application of photobiomodulation and curcumin-loaded iron particles. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 34, 779–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Sayed, P.; Kaeppeli, A.; Siriwardena, T.; Darbre, T.; Perron, K.; Jafari, P.; Reymond, J.-L.; Pioletti, D.P.; Applegate, L.A.; Kaeppli, A. Anti-Microbial Dendrimers against Multidrug-Resistant P. aeruginosa Enhance the Angiogenic Effect of Biological Burn-wound Bandages. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haik, J.; Kornhaber, R.; Blal, B.; Harats, M. The Feasibility of a Handheld Electrospinning Device for the Application of Nanofibrous Wound Dressings. Adv. Wound Care 2017, 6, 166–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholipour-Kanani, A.; Bahrami, S.H.; Rabbani, S. Effect of novel blend nanofibrous scaffolds on diabetic wounds healing. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 10, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.H.; Jia, Y.-X.; Qin, C.-C.; Zhan, L.; Yan, X.; Cui, L.; Zhou, Y.; Jiang, X.; Long, Y.-Z. In situ deposition of a personalized nanofibrous dressing via a handy electrospinning device for skin wound care. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3482–3488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, S.Z.; Meng, X.H.; Fan, J.; Yang, L.L.; Wen, Q.L.; Ye, S.J.; Lin, S.; Wang, B.Q.; Chen, L.L.; Wu, J.B.; et al. Acceleration of dermal wound healing by using electrospun curcumin-loaded poly(epsilon-caprolactone)-poly(ethylene glycol)-poly(epsilon-caprolactone) fibrous mats. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. B Appl. Biomater. 2014, 102, 533–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Yu, D.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.; Li, D.; Ding, M. Nanotechnology promotes the full-thickness diabetic wound healing effect of recombinant human epidermal growth factor in diabetic rats. Wound Repair Regen. 2010, 18, 499–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Kang, X.; Jin, L.; Bai, J.; Liu, W.; Wang, Z.; Ji, L. Stimulation of wound healing using bioinspired hydrogels with basic fibroblast growth factor (bFGF). Int. J. Nanomed. 2018, 13, 3897–3906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Yan, C.; Zhang, X.; Shi, D.; Chi, L.; Luo, G.; Deng, J. Antimicrobial peptide modification enhances the gene delivery and bactericidal efficiency of gold nanoparticles for accelerating diabetic wound healing. Biomater. Sci. 2018, 6, 2757–2772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zgheib, C.; Hilton, S.A.; Dewberry, L.C.; Hodges, M.M.; Ghatak, S.; Xu, J.; Singh, S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C.K.; Seal, S.; et al. Use of Cerium Oxide Nanoparticles Conjugated with MicroRNA-146a to Correct the Diabetic Wound Healing Impairment. Lasers Med. Sci. 2019, 228, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moura, J.; Borsheim, E.; Carvalho, E. The Role of MicroRNAs in Diabetic Complications-Special Emphasis on Wound Healing. Genes 2014, 5, 926–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tartarini, D.; Mele, E. Adult Stem Cell Therapies for Wound Healing: Biomaterials and Computational Models. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2015, 3, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Material | Properties | References | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antibacterial | Stimulation of Wound Healing 1 | Prevention of Abnormal Scarring | |||
| Nanoparticles | Silver nanoparticles | + | + | + | [7,21,24,25] |
| Gold nanoparticles | + | + | Unknown | [10,21,30] | |
| Zinc oxide nanoparticles | + | + | Unknown | [7,16,21,33] | |
| Composite nanoparticles Eg. chitosan nanoparticles, nanocellulose | + | + | + | [7,36,37,39,41,42,43,44,45,46,47,49,50] | |
| Nanocarriers | Eg. Nitric oxide-releasing poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid)-polyethylenimine nanoparticles, curcumin loaded super-paramagnetic iron oxide | + | + | Unknown | [51,52,53,54,55] |
| Coatings and Scaffolds | Eg. hydrogel preloaded with bFGF, Hydrogels reinforced with AgNPs | ++ | ++ | Unknown | [63,65,66] |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mihai, M.M.; Dima, M.B.; Dima, B.; Holban, A.M. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials 2019, 12, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132176
Mihai MM, Dima MB, Dima B, Holban AM. Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials. 2019; 12(13):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132176
Chicago/Turabian StyleMihai, Mara Madalina, Monica Beatrice Dima, Bogdan Dima, and Alina Maria Holban. 2019. "Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control" Materials 12, no. 13: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132176
APA StyleMihai, M. M., Dima, M. B., Dima, B., & Holban, A. M. (2019). Nanomaterials for Wound Healing and Infection Control. Materials, 12(13), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12132176







