The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Surface Properties
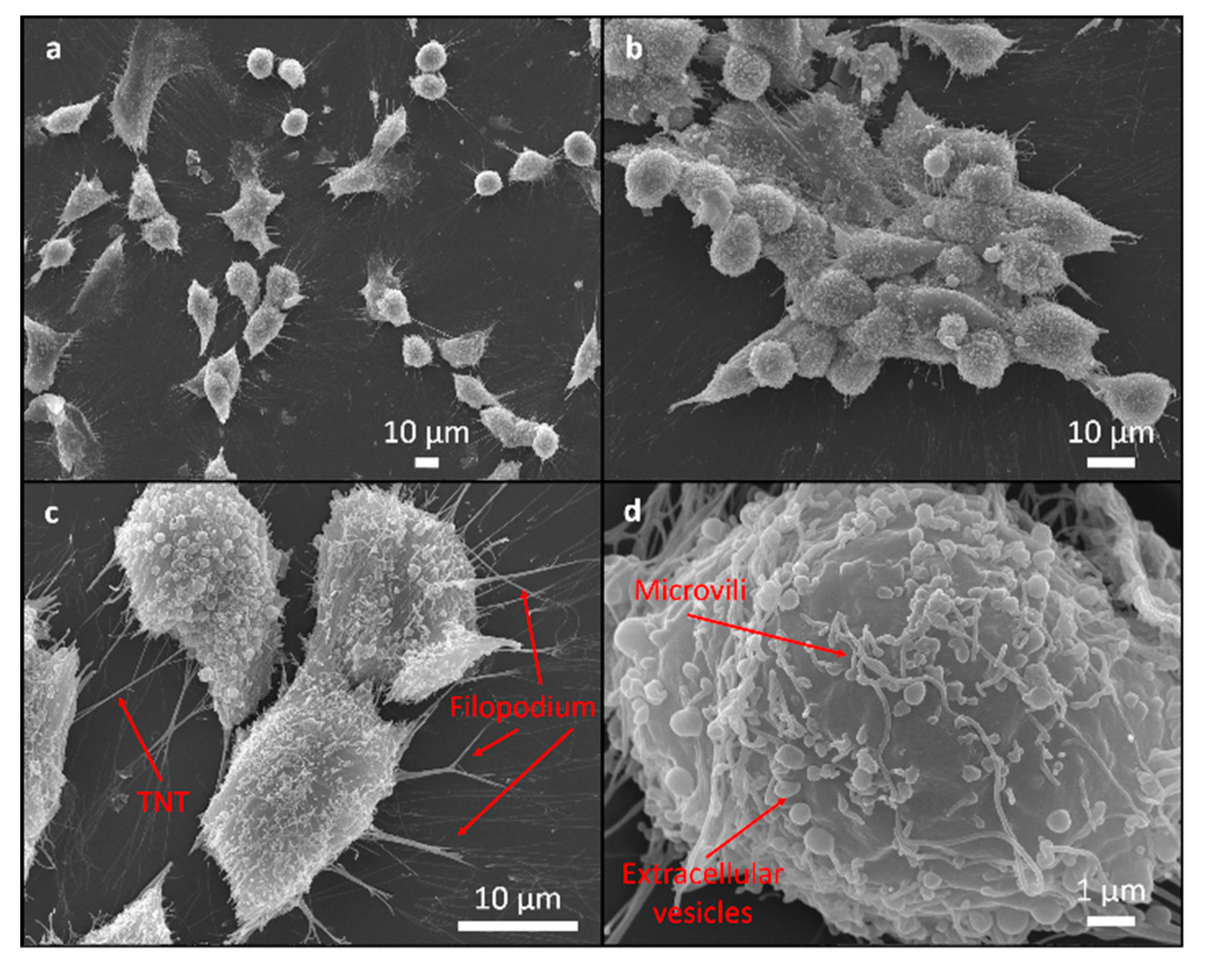
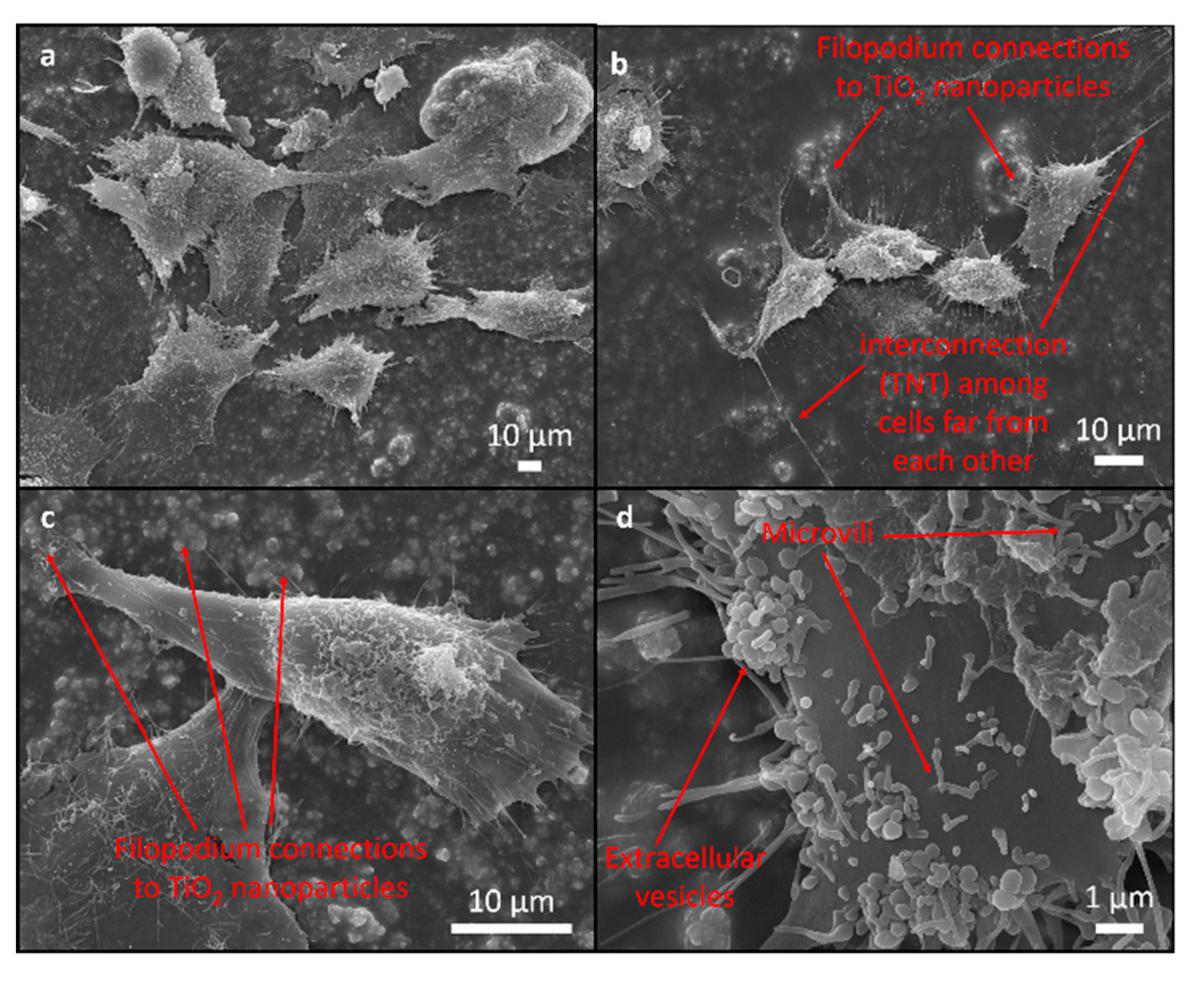
3.2. Biocompatibility Evaluation
3.3. Antibacterial Properties
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dowling, D.P.; Miller, I.S.; Ardhaoui, M.; Gallagher, W.M. Effect of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Adhesion of Osteosarcoma Cells on Plasma-modified Polystyrene. J. Biomater. Appl. 2011, 26, 327–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biggs, M.J.P.; Richards, R.G.; Gadegaard, N.; Wilkinson, C.D.W.; Dalby, M.J. The effects of nanoscale pits on primary human osteoblast adhesion formation and cellular spreading. J. Mater. Sci. Med. 2007, 18, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Junkar, I.; Kulkarni, M.; Drasler, B.; Rugelj, N.; Recek, N.; Drobne, D.; Kovac, J.; Humpolicek, P.; Iglic, A.; Mozetic, M. Enhanced biocompatibility of TiO2 surfaces by highly reactive plasma. J. Phys. D-Appl. Phys. 2016, 49, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenko, M.; Godec, M.; Kocijan, A.; Rudolf, R.; Dolinar, D.; Ovsenik, M.; Gorensek, M.; Zaplotnik, R.; Mozetic, M. A new route to biocompatible Nitinol based on a rapid treatment with H gaseous plasma. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2019, 473, 976–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.Y.; Hansen, J.C.; Siedlecki, C.A.; Hengstebeck, R.W.; Cheng, J.; Winograd, N.; Donahue, H.J. Osteoblast adhesion on poly(L-lactic acid)/polystyrene demixed thin film blends: Effect of nanotopography, surface chemistry, and wettability. Biomacromolecules 2005, 6, 3319–3327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, A.Y.; Guo, C. Direct femtosecond laser surface nano/microstructuring and its applications. Laser Photonics Rev. 2013, 7, 385–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselme, K. Osteoblast adhesion on biomaterials. Biomaterials 2000, 21, 667–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, C.A.; Vaughan, T.J.; Voisin, M.C.; Brennan, M.A.; Layrolle, P.; McNamara, L.M. Cell morphology and focal adhesion location alters internal cell stress. J. Soc. Interface 2014, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papenburg, B.J.; Rodrigues, E.D.; Wessling, M. Stamatialis, Insights into the role of material surface topography and wettability on cell-material interactions. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 4377–4388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lourenco, B.N.; Marchioli, G.; Song, W.; Reis, R.L.; Van Blitterswijk, C.A.; Karperien, M.; Van Apeldoorn, A.; Mano, J.F. Wettability Influences Cell Behavior on Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Different Topographies. Biointerphases 2012, 7, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.Y.; Kim, E.-S.; Jeon, G.; Choi, K.Y.; Kim, J.R. Enhanced adhesion of osteoblastic cells on polystyrene films by independent control of surface topography and wettability. Mater. Sci. Eng. C-Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 1689–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yuan, L.; Song, W.; Wu, Z.K.; Li, D. Biocompatible polymer materials: Role of protein-surface interactions. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2008, 33, 1059–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Hays, M.P.; Hardwidge, P.R.; Kim, J. Surface characteristics influencing bacterial adhesion to polymeric substrates. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 14254–14261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wassmann, T.; Kreis, S.; Behr, M.; Buergers, R. The influence of surface texture and wettability on initial bacterial adhesion on titanium and zirconium oxide dental implants. Int. J. Implant Dent. 2017, 3, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, G.; Ciardiello, R.; Commodo, M.; Del Gaudio, P.; Minutolo, P.; Porta, A.; D’Anna, A. TiO2 nanoparticle coatings with advanced antibacterial and hydrophilic properties prepared by flame aerosol synthesis and thermophoretic deposition. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 830–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joost, U.; Juganson, K.; Visnapuu, M.; Mortimer, M.; Kahru, A.; Nommiste, E.; Joost, U.; Kisand, V.; Ivask, A. Photocatalytic antibacterial activity of nano-TiO2 (anatase)-based thin films: Effects on Escherichia coli cells and fatty acids. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B-Biol. 2015, 142, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Falco, G.; Porta, A.; Petrone, A.M.; Del Gaudio, P.; El Hassanin, A.; Commodo, M.; Minutolo, P.; Squillace, A.; D’Anna, A. Antimicrobial activity of flame-synthesized nano-TiO2 coatings. Environ. Sci. 2017, 4, 1095–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jalvo, B.; Faraldos, M.; Bahamonde, A.; Rosal, R. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm efficacy of self-cleaning surfaces functionalized by TiO2 photocatalytic nanoparticles against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas putida. J. Hazard. Mater. 2017, 340, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visai, L.; De Nardo, L.; Punta, C.; Melone, L.; Cigada, A.; Imbriani, M.; Arciola, C.R. Titanium oxide antibacterial surfaces in biomedical devices. Int. J. Artif. Organs 2011, 34, 929–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conradi, M.; Kocijan, A. Fine-tuning of surface properties of dual-size TiO2 nanoparticle coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2016, 304, 486–491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwok, D.Y.; Neumann, A.W. Contact angle measurement and contact angle interpretation. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1999, 81, 167–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Neumann, A.W. A Reformulation of the Equation of State for Interfacial-Tensions. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 1990, 137, 304–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.Y.; Chen, C.Y.; Chen, W.C. Synthesis and characterization of organic-inorganic hybrid thin films from poly(acrylic) and monodispersed colloidal silica. Polymer 2003, 44, 593–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranella, A.; Barberoglou, M.; Bakogianni, S.; Fotakis, C.; Stratakis, E. Tuning cell adhesion by controlling the roughness and wettability of 3D micro/nano silicon structures. Acta Biomater. 2010, 6, 2711–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chowdhury, A.K.M.R.H.; Tavangar, A.; Tan, B. Venkatakrishnan, Biofunctionalized 3-D Carbon Nano-Network Platform for Enhanced Fibroblast Cell Adhesion. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meldolesi, J. Exosomes and Ectosomes in Intercellular Communication. Curr. Biol. 2018, 28, R435–R444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maas, S.L.N.; Breakefield, X.O.; Weaver, A.M. Extracellular Vesicles: Unique Intercellular Delivery Vehicles. Trends Cell Biol. 2017, 27, 172–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Niel, G.; D’Angelo, G.; Raposo, G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 213–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dupont, M.; Souriant, S.; Lugo-Villarino, G.; Maridonneau-Parini, I.; Vérollet, C. Tunneling Nanotubes: Intimate Communication between Myeloid Cells. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vignais, M.-L.; Caicedo, A.; Brondello, J.-M.; Jorgensen, C. Cell Connections by Tunneling Nanotubes: Effects of Mitochondrial Trafficking on Target Cell Metabolism, Homeostasis, and Response to Therapy. Stem Cells Int. 2017, 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, M.-Y.; Liu, C.-P.; Huang, H.-H.; Lee, S.-W. Both Enhanced Biocompatibility and Antibacterial Activity in Ag-Decorated TiO2 Nanotubes. PLoS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
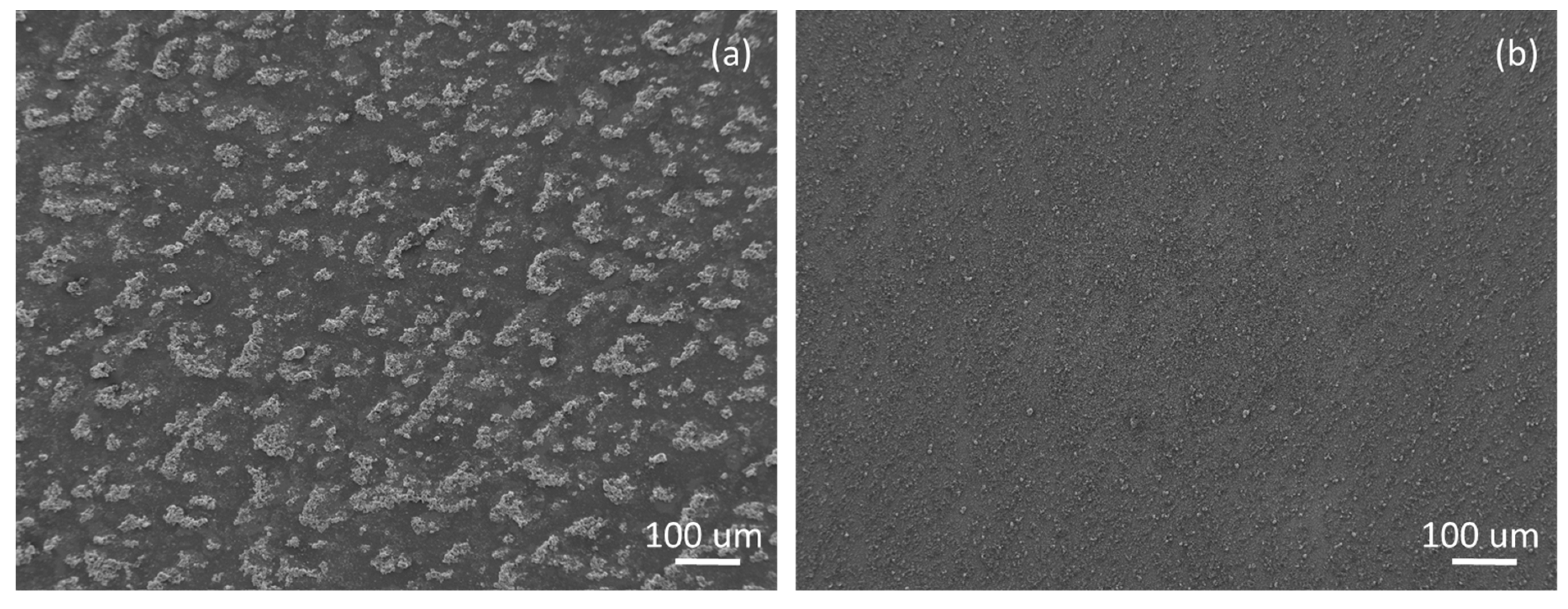
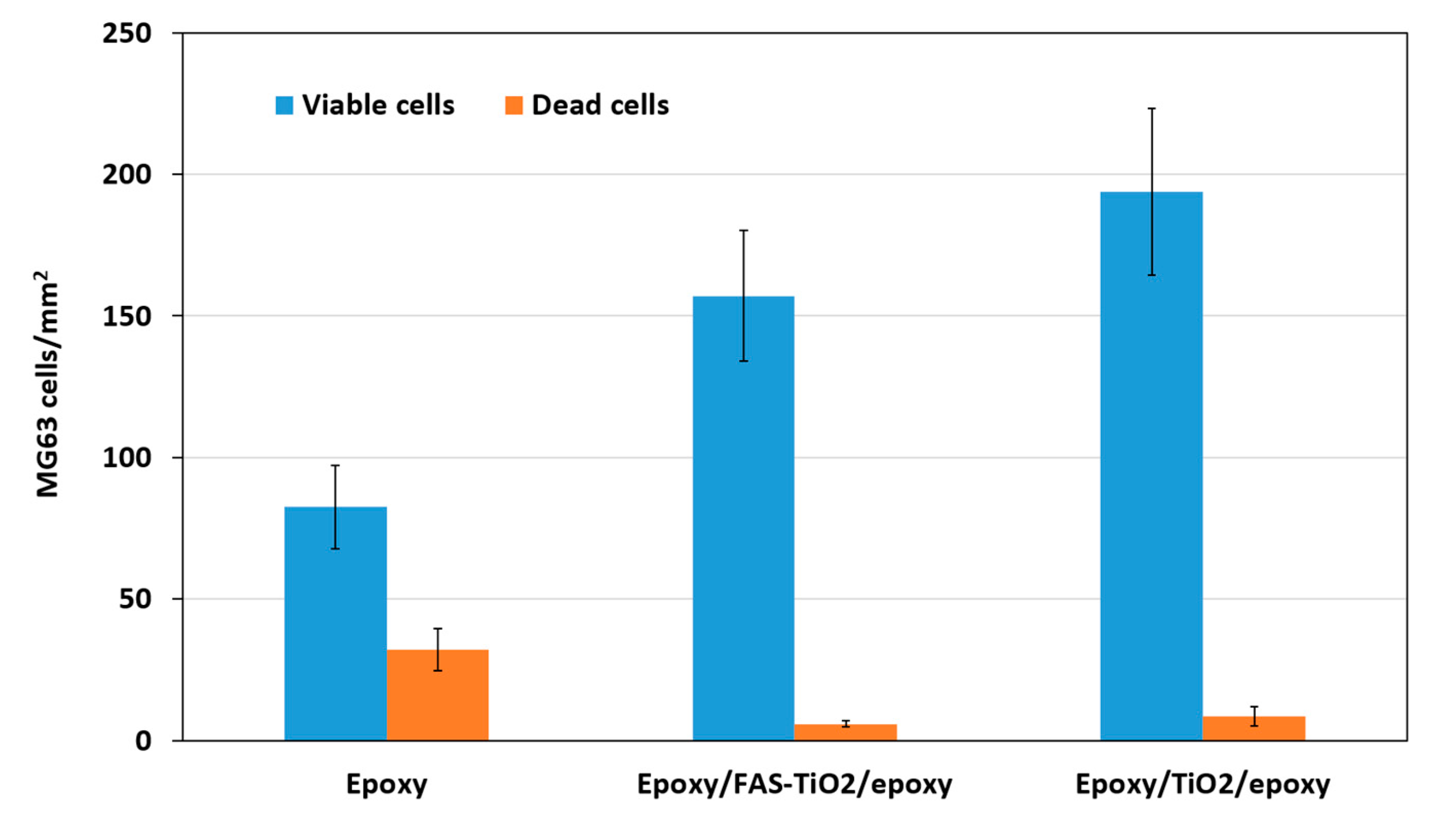
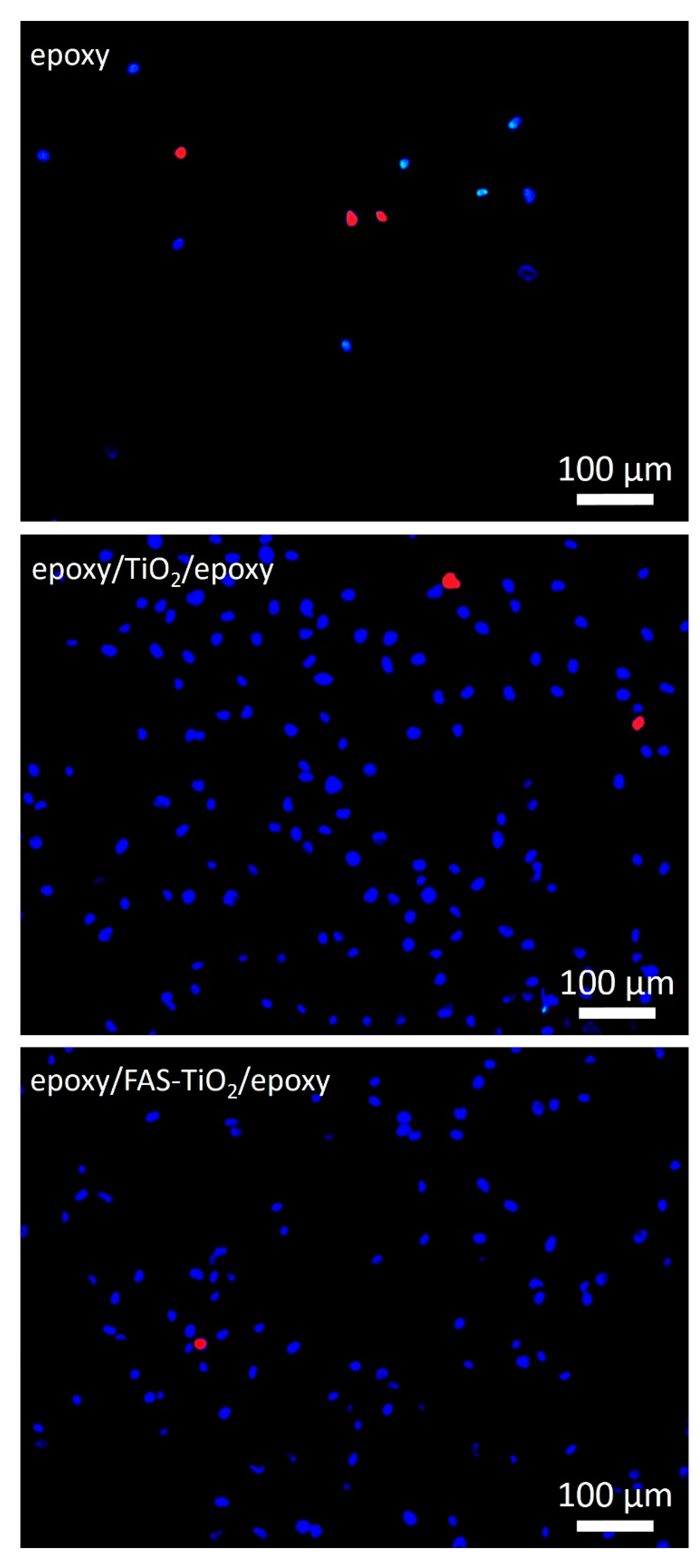

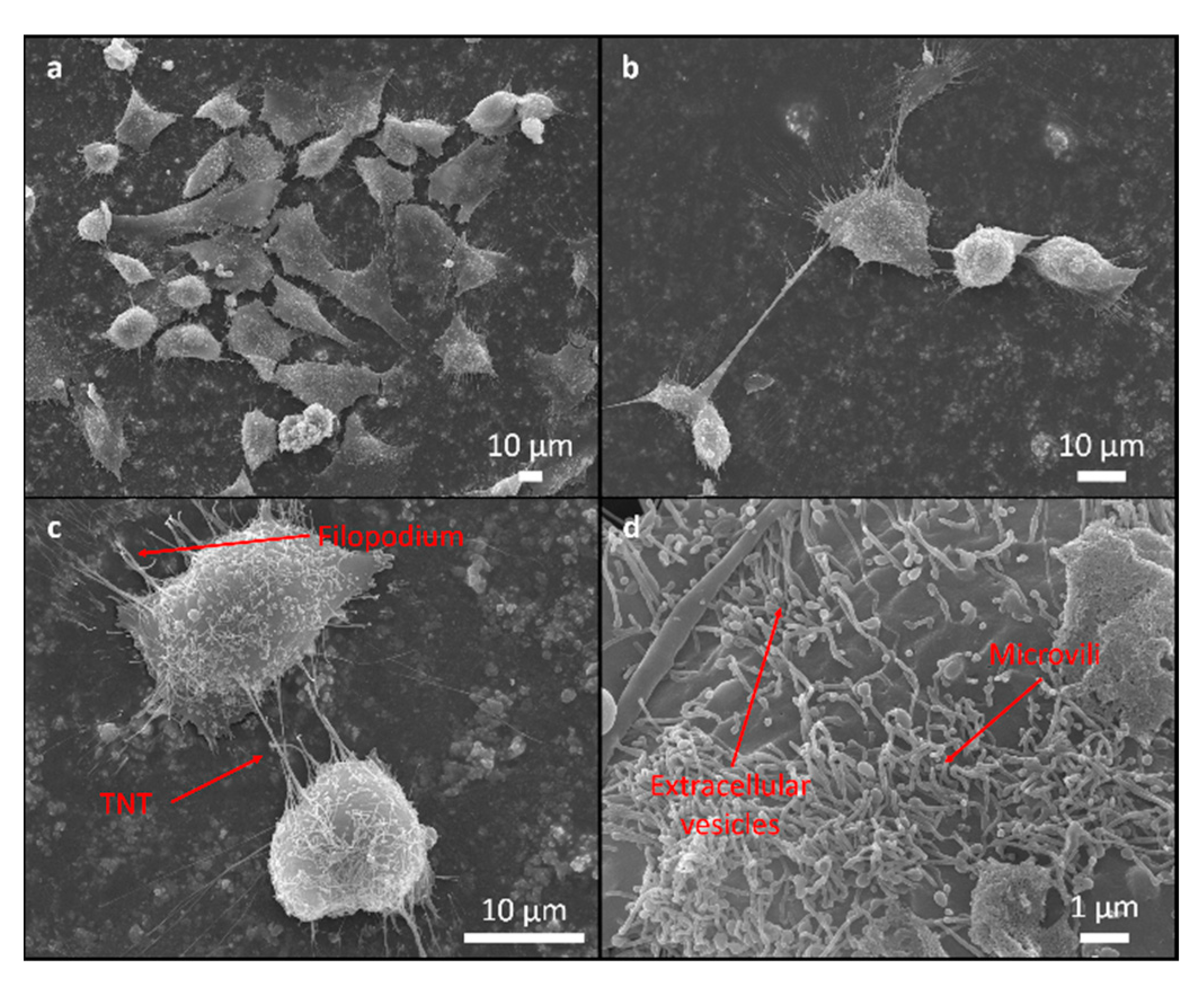
| Coating | θW (o) | γ (mN/m) | Sa (nm) |
|---|---|---|---|
| epoxy | 75 ± 1 | 38.6 ± 0.1 | 50 ± 5 |
| epoxy/TiO2/epoxy | 83 ± 1 | 33.7 ± 0.1 | 320 ± 20 |
| epoxy/FAS-TiO2/epoxy | 120 ± 3 | 11.6 ± 0.1 | 600 ± 30 |
| Coating | Colony Forming Units | θW (°) | γ (mN/m) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| No Wash | After wash | |||
| Epoxy | countless | 97 | 75 ± 1 | 38.6 ± 0.1 |
| Epoxy/TiO2/epoxy | countless | 47 | 83 ± 1 | 33.7 ± 0.1 |
| Epoxy/FAS-TiO2/epoxy | 70 | 7 | 120 ± 3 | 11.6 ± 0.1 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kocijan, A.; Conradi, M.; Hočevar, M. The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Materials 2019, 12, 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111877
Kocijan A, Conradi M, Hočevar M. The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Materials. 2019; 12(11):1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111877
Chicago/Turabian StyleKocijan, Aleksandra, Marjetka Conradi, and Matej Hočevar. 2019. "The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel" Materials 12, no. 11: 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111877
APA StyleKocijan, A., Conradi, M., & Hočevar, M. (2019). The Influence of Surface Wettability and Topography on the Bioactivity of TiO2/Epoxy Coatings on AISI 316L Stainless Steel. Materials, 12(11), 1877. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12111877






