Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass Based on the Steady-State Method
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experiment
2.1. Experimental Raw Materials
2.2. Sample Preparation
2.3. Analysis Instruments
2.4. Analysis Instruments
2.5. The L9(34) Orthogonal Experiment Results
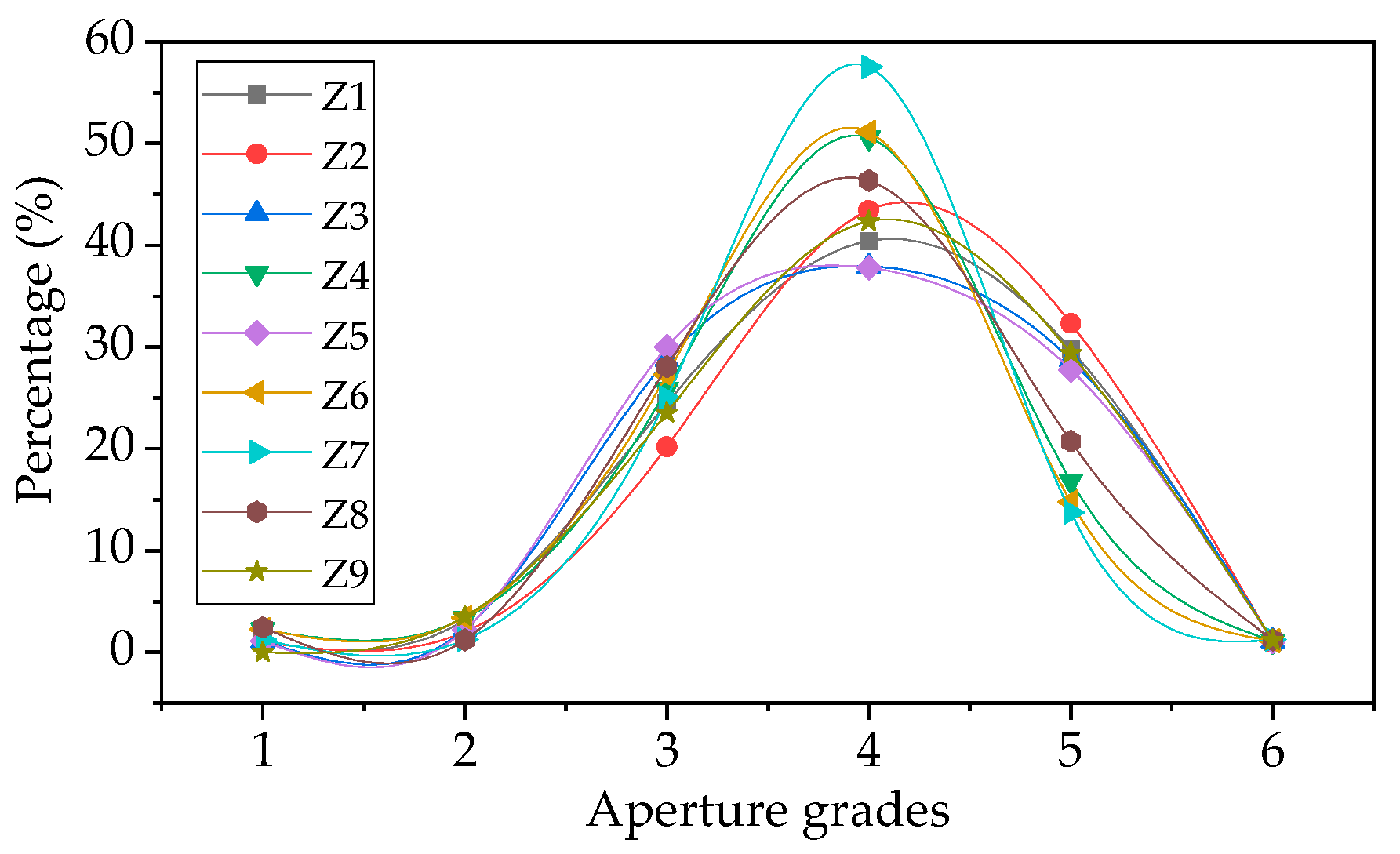
2.6. Aperture Structure Analysis
3. Numerical model
3.1. Conditional Assumptions
3.2. Model Establishment and Grid Generation
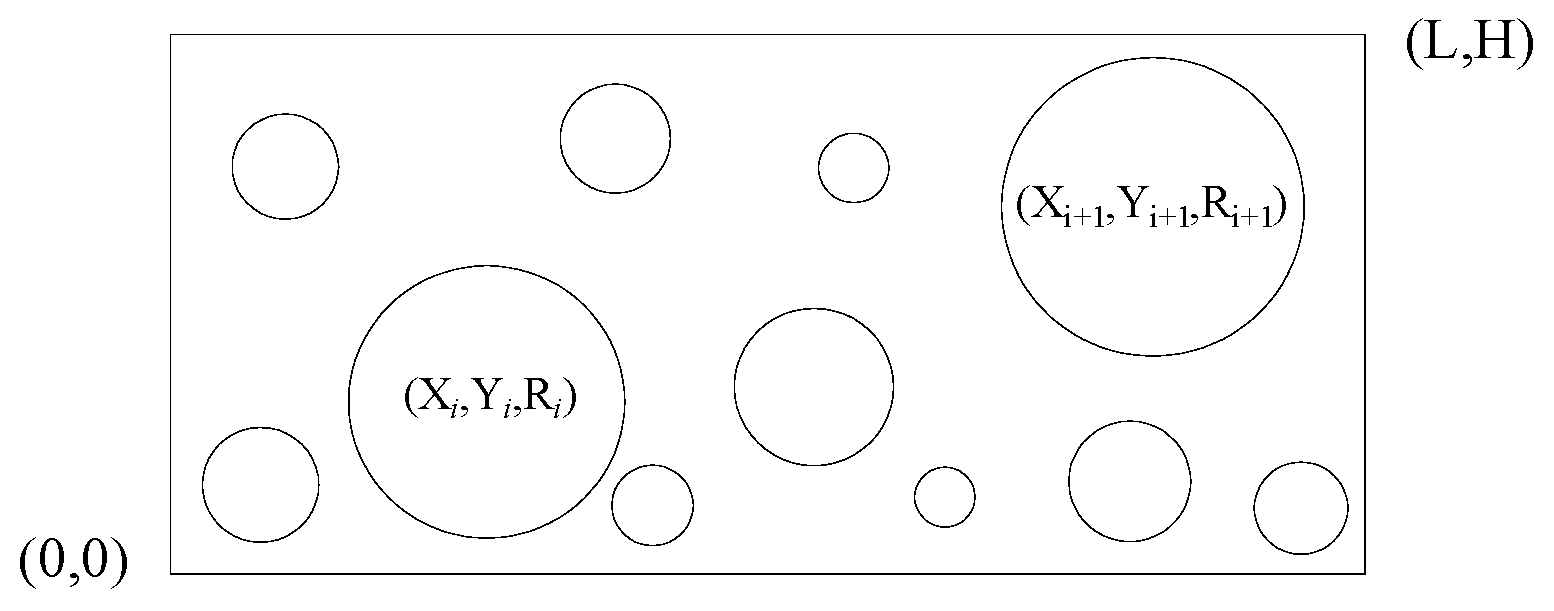
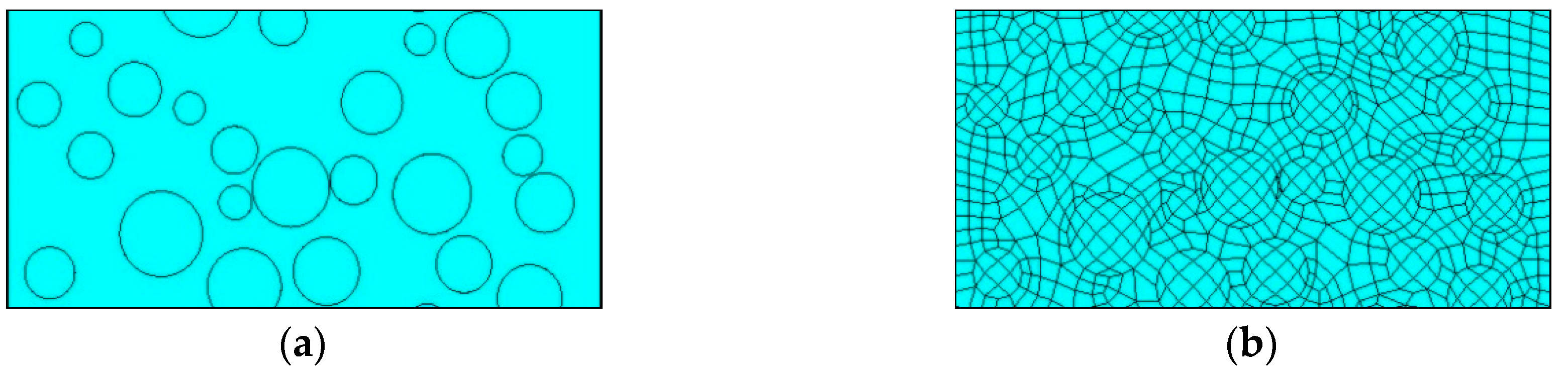
3.2.1. The Establishment of a Geometric Model
- First bullet Determine the coordinates (, ) and radius Ri of the number i aperture by generating a random number.
- If the aperture does not overlap with the boundary, and it does not overlap with the aperture generated previously either, then calculate the temporary variable .
- Compare the cumulative aperture area and the total area of apertures . If , stop generating the apertures.
3.2.2. Define Material Properties
3.2.3. Cell Selection and Meshing
3.3. Boundary Conditions
4. Results and Discussion
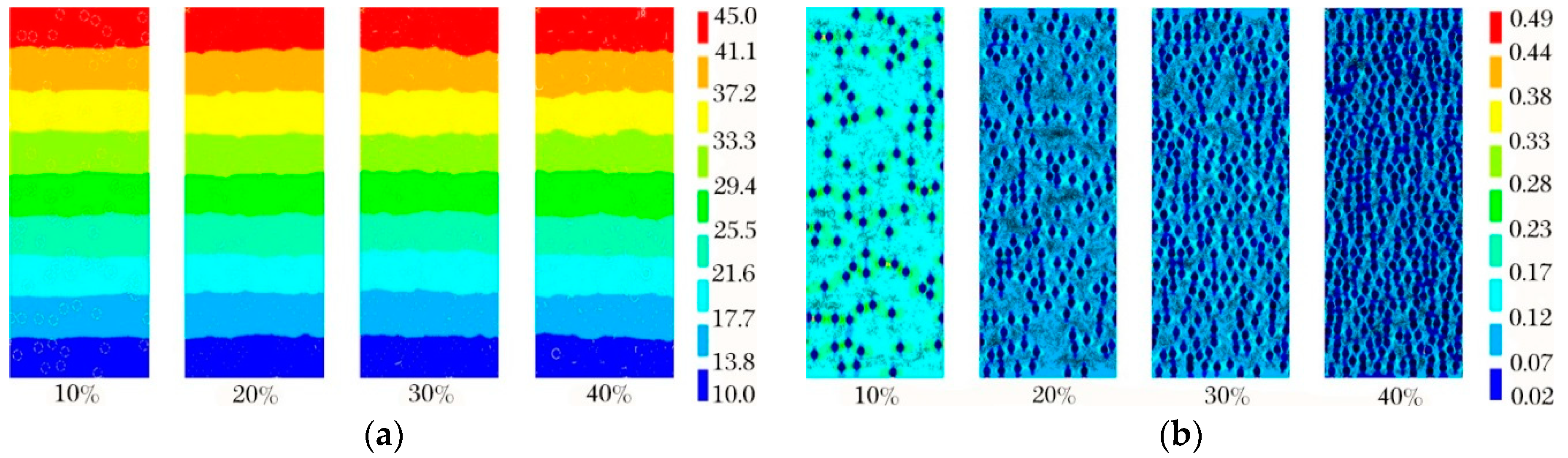
4.1. Model Validation
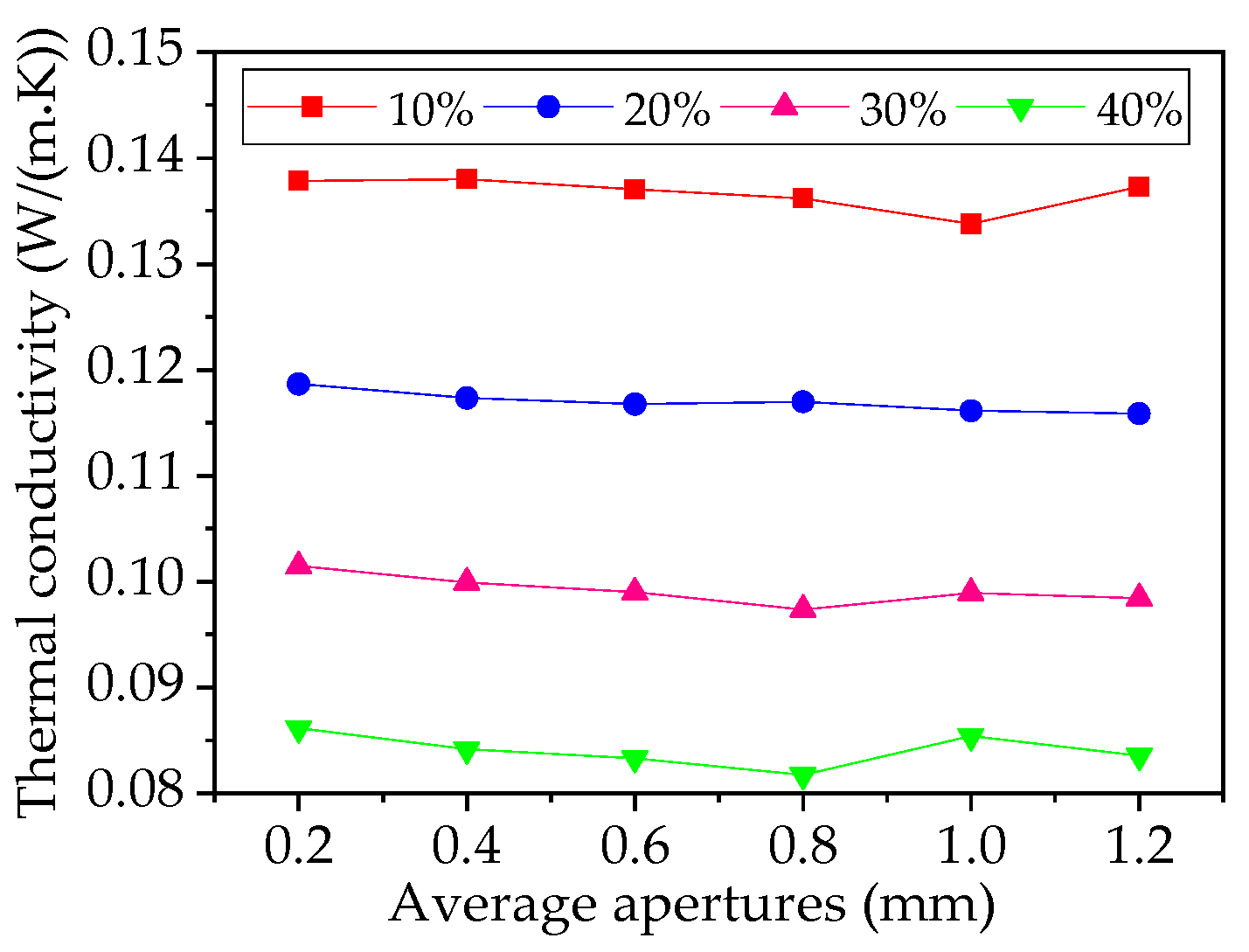
4.2. Effect of Aperture on Thermal Conductivity Performance of Foam Glass
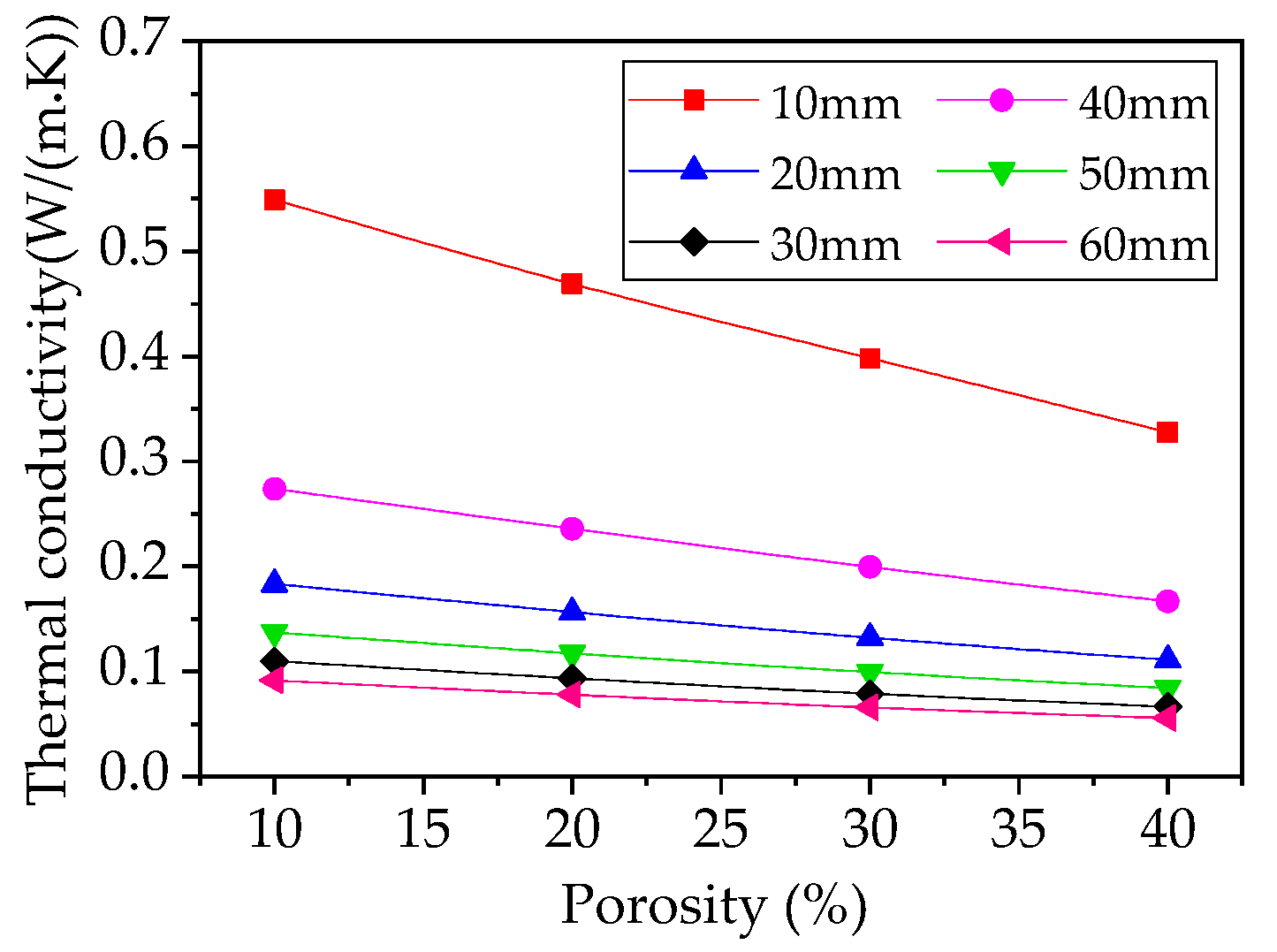
4.3. Effect of Thickness on Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass
4.4. Effects of Porosity on Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Baidzhanov, D.O.; Nuguzhinov, Z.S.; Fedorchenko, V.I.; Kropachev, P.A.; Rakhimov, A.M.; Divak, L.A. Thermal Insulation Material Based on Local Technogenic Raw Material. Glass Ceram. 2017, 73, 427–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Luo, Z.; Lu, A. Preparation of sintered foam glass with high fly ash content. Mater. Lett. 2011, 65, 3555–3558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, J.; Petersen, R.R.; Yue, Y. Influence of the glass-calcium carbonate mixture’s characteristics on the foaming process and the properties of the foam glass. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 34, 1591–1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, R.R.; König, J.; Yue, Y. The viscosity window of the silicate glass foam production. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2017, 456, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamri, Y.; Benzerga, R.; Ayadi, A.; Le Gendre, L.; Aicha, E.A. Synthesis and characterization of foam glass composites for electromagnetic absorption application. Mater. Res. Express. 2019, 6, 035201. [Google Scholar]
- Ventrella, A.; Smeacetto, F.; Salvo, M.; Monica, F. Characterization of new glass coated foam glass insulating tiles by standard tests. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 2012, 21, 2380–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbasi, S.; Mirkazemi, S.M.; Ziaee, A.; Heydari, M.S. The effects of Fe2O3 and Co3O4 on microstructure and properties of foam glass from soda lime waste glasses. Glass Phys. Chem. 2014, 40, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Lee, W.; Park, Y.H. Finite element modeling of tensile deformation behaviors of iron syntactic foam with hollow glass microspheres. Materials 2017, 10, 1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Y.N.; Xu, J.; Su, Z.G.; Ma, N.; Zhang, X.Y.; Xi, X.Q.; Yang, J.-L. Lightweight and high-strength glass foams prepared by a novel green spheres hollowing technique. Ceram. Int. 2016, 42, 2370–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Li, Q.; Yang, T.; Li, Z.; Zhu, Y. Preparation and characterization of glass foams for artificial floating island from waste glass and Li2CO3. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 134, 358–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Sahlani, K.; Taherishargh, M.; Kisi, E.; Fiedler, T. Controlled shrinkage of expanded glass particles in metal syntactic foams. Materials 2017, 10, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hrma, P. Effect of heating rate on glass foaming: Transition to bulk foam. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 2009, 355, 257–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaganov, V.; Popov, M.; Korjakins, A.; Sahmenko, G. Effect of CNT on microstructure and minearological composition of lightweight concrete with granulated foam glass. Procedia Eng. 2017, 172, 1204–1211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bian, J.; Cao, W.; Yang, L.; Xiong, C. Experimental research on the mechanical properties of tailing microcrystalline foam glass. Materials 2018, 11, 2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, K.; Chen, X.; Lu, A. Study of Foam Glass with High Content of Fly Ash Using Calcium Carbonate as Foaming Agent. Mater. Lett. 2012, 79, 263–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Li, G.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Song, Q. Study on Influence of Fly Ash Content on Properties of Foam Glass. China Ceram. 2017, 53, 58–62. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Song, Q.; Shen, P.; Sun, X. Study on impact of the burning process on fly ash foam glass performance. New Build. Mater. 2016, 43, 88–91. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Qin, Z.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shen, P. Optimization of preparation process and performance analysis of fly ash foam glass. Funct. Mater. 2018, 3, 554–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, S.; Lin, J.; Tang, B. Preparation of glass foams from vitrified municipal solid waste incinerator ash. J. Chin. Ceram. Soc. 2014, 42, 108–112. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Tian, Y.; Lu, P.; Zhang, S.; Cheng, J.; Wu, D. Mechanism of surface depression on foam glass. J. Wuhan Univ. Technol.-Mater. Sci. Ed. 2016, 31, 538–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Feng, K.; Wang, H.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Shi, H. Influence of sintering temperature on the preparation of foam glass-ceramics from high titanium blast furnace slag. J. Sichuan Univ. (Eng. Sci. Ed.) 2014, 46, 192–197. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Feng, K.; Wang, H.; Chen, C.; Zhou, H. Influence of aluminium nitride as a foaming agent on the preparation of foam glass-ceramics from high-titanium blast furnace slag. Int. J. Miner. Metall. Mater. 2016, 23, 595–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurczyk, K.; Adamek, G.Z.; Kubicka, M.M.; Jakubowicz, J.; Jurczyk, M. Nanostructured titanium-10 wt% 45S5 bioglass-Ag composite foams for medical applications. Materials 2015, 8, 1398–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, Y.J.; Kang, Y.; Lee, Y.C.; Park, Y.; Lee, W. Influence of Partially Debonded Interface on Elasticity of Syntactic Foam: A Numerical Study. Materials 2017, 10, 911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janetti, M.B.; Plaz, T.; Ochs, F.; Klesnil, O.; Feist, W. Thermal conductivity of foam glass gravels: A comparison between experimental data and numerical results. Energy Procedia 2015, 78, 3258–3263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, P.; Qin, Z.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Song, Q.; Zhou, G. Study on effects of sodium carbonate on the properties of fly ash cellular glass. China Ceram. 2017, 53, 46–50. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ochs, F.; Heidemann, W.; Mullersteinhagen, H. Effective thermal conductivity of moistened insulation materials as a function of temperature. Int. J. Heat Mass Transf. 2008, 51, 539–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, J.; Zhou, Y.; Kang, M.; Wang, J. Optimization of process parameters, microstructure, and properties of laser cladding fe-based alloy on 42CrMo steel roller. Materials 2018, 11, 2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Z.; Ma, Y.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Song, Q. Analysis of the main factors affecting the properties of the foam glass based on orthogonal experiment. Non-Metallic Mines 2016, 39, 7–10. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Li, Q.; Cheng, W.; Han, G.; Xuan, L. Optimization of high temperature and pressurized steam modified wood fibers for high-density polyethylene matrix composites using the orthogonal design method. Materials 2016, 9, 847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, S.; Huang, R.; Chi, M.; Hsu, H. Factors affecting the effectiveness of inorganic silicate sealer material through multi-quality characteristics. Materials 2013, 6, 1191–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niu, F.S.; Ni, W.; Liang, Y.Y. Numerical simulation of heat conduction in polyfoam-fly ash thermal insulation materials. J. Univ. Sci. Technol. Beijing 2009, 31, 103–107. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, S.; Scheffe, J.R.; Duss, J.; Steinfeld, A. Morphological characterization and effective thermal conductivity of dual-scale reticulated porous structures. Materials 2014, 7, 7173–7195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Tian, Y.; Li, G.; Qin, Z.; Ma, Y. Study on thermal performance of new EPS-basalt fiber hollow fabric insulation board. New Build. Mater. 2018, 45, 145–148. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
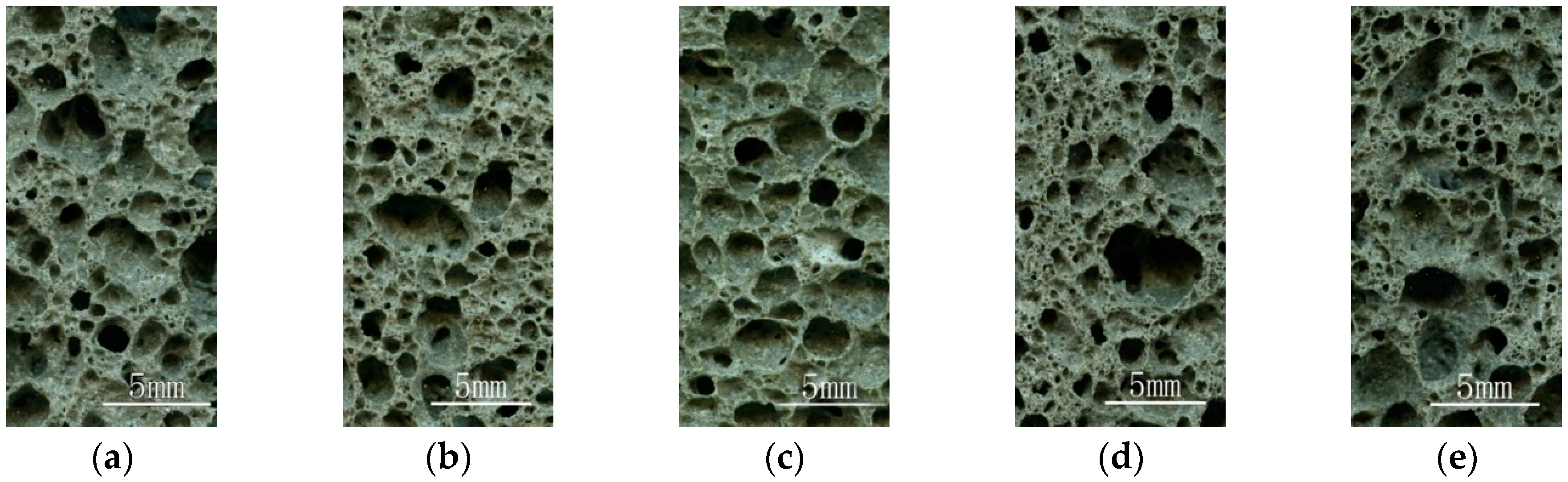

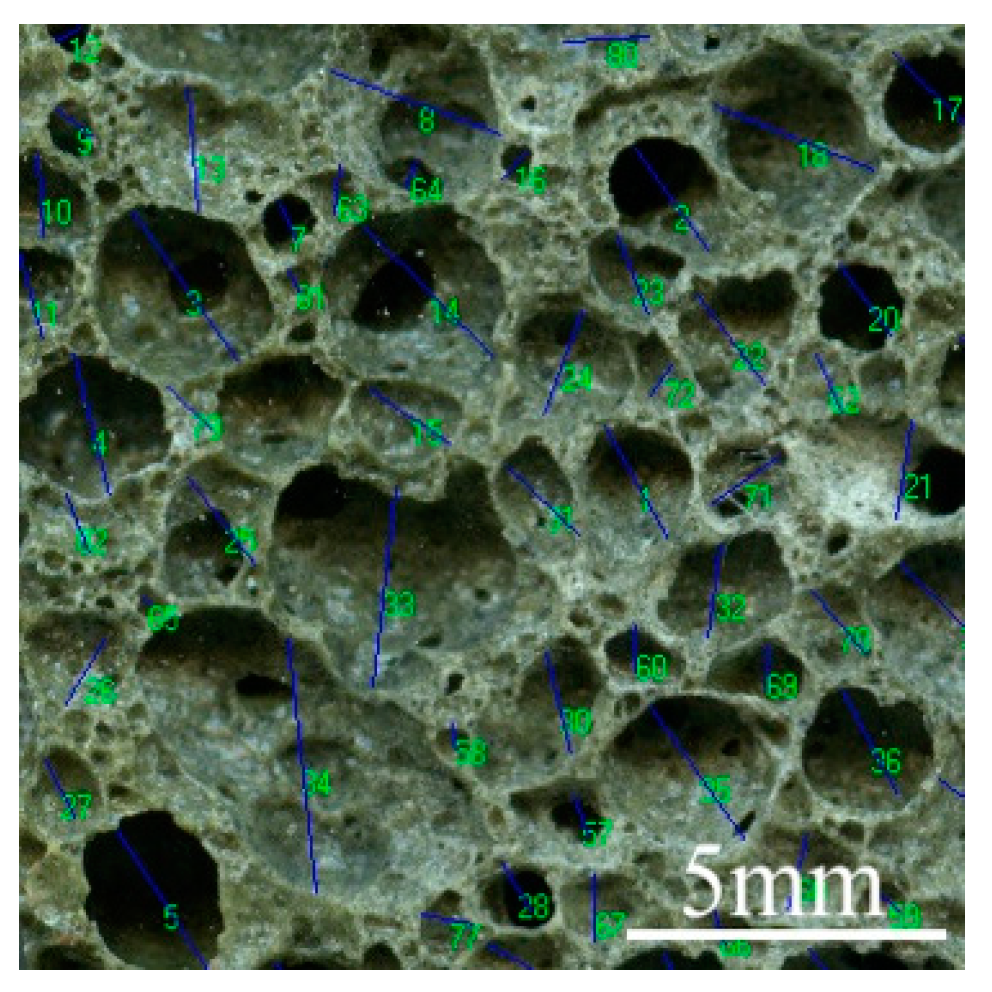


| Designation | Mass Fraction (%) | Fineness (%) | Loss on Ignition (%) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | CaO | MgO | K2O+Na2O | |||
| Fly ash | 59.84 | 30.77 | 3.30 | 1.84 | 2.35 | 1.90 | 4.70 | 4.90 |
| Waste glass | 72.33 | 1.40 | 0.15 | 8.62 | 4.72 | 12.78 | - | - |
| Factors | ω (%) | Foaming Temperature (°C) | Foaming Time (min) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level | Fly Ash | Na2CO3 | |||
| 1 | 20 | 2 | 850 | 20 | |
| 2 | 25 | 4 | 860 | 25 | |
| 3 | 30 | 6 | 870 | 30 | |
| No. | F (%) | C (%) | T (°C) | S (min) | Thermal Conductivity (w/(m·k)) | Porosity (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Z1 | 20 | 2 | 850 | 20 | 0.0587 | 30.54 |
| Z2 | 20 | 4 | 860 | 25 | 0.0569 | 41.29 |
| Z3 | 20 | 6 | 870 | 30 | 0.0545 | 44.29 |
| Z4 | 25 | 2 | 860 | 30 | 0.0671 | 28.64 |
| Z5 | 25 | 4 | 870 | 20 | 0.0570 | 50.94 |
| Z6 | 25 | 6 | 850 | 25 | 0.0608 | 45.67 |
| Z7 | 30 | 2 | 870 | 25 | 0.0656 | 43.00 |
| Z8 | 30 | 4 | 850 | 30 | 0.0675 | 36.69 |
| Z9 | 30 | 6 | 860 | 20 | 0.0703 | 36.67 |
| Sample No. | Z1 | Z2 | Z3 | Z4 | Z5 | Z6 | Z7 | Z8 | Z9 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Aperture number | 1 | D ≥ 3 mm | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 2 | 0 |
| 2 | 2 mm ≤ d < 3 mm | 3 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 3 | |
| 3 | 1 mm ≤ d < 2 mm | 23 | 20 | 25 | 23 | 27 | 24 | 20 | 23 | 20 | |
| 4 | 0.5 mm ≤ d < 1 mm | 38 | 43 | 33 | 45 | 34 | 45 | 46 | 38 | 36 | |
| 5 | 0.1 mm ≤ d < 0.5 mm | 28 | 32 | 25 | 15 | 25 | 13 | 11 | 17 | 25 | |
| 6 | 0.01 mm ≤ d < 0.1 mm | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
| summation | 94 | 99 | 87 | 89 | 90 | 88 | 80 | 82 | 85 | ||
| Average aperture/mm | 0.65 | 0.64 | 0.67 | 0.57 | 0.65 | 0.62 | 0.61 | 0.81 | 0.60 | ||
| Material | Thermal Conductivity Simulated Value (W/(m·K)) | Thermal Conductivity Measured Value (W/(m·K)) | Relative Error (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Foam glass | 0.0612 | 0.0587 | 4.08 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Qin, Z.; Li, G.; Tian, Y.; Ma, Y.; Shen, P. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass Based on the Steady-State Method. Materials 2019, 12, 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010054
Qin Z, Li G, Tian Y, Ma Y, Shen P. Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass Based on the Steady-State Method. Materials. 2019; 12(1):54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010054
Chicago/Turabian StyleQin, Zipeng, Gang Li, Yan Tian, Yuwei Ma, and Pengfei Shen. 2019. "Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass Based on the Steady-State Method" Materials 12, no. 1: 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010054
APA StyleQin, Z., Li, G., Tian, Y., Ma, Y., & Shen, P. (2019). Numerical Simulation of Thermal Conductivity of Foam Glass Based on the Steady-State Method. Materials, 12(1), 54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12010054





