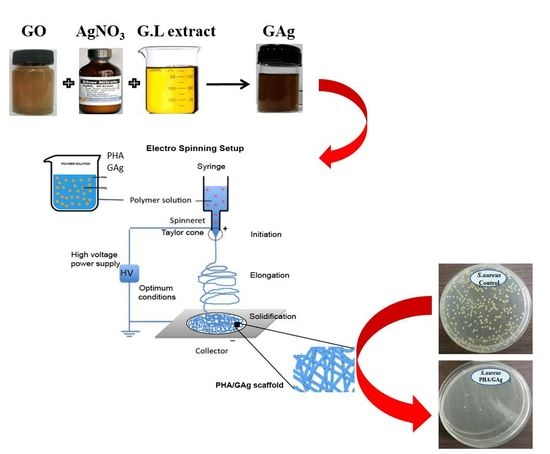
Fabrication and Characterization of an Electrospun PHA/Graphene Silver Nanocomposite Scaffold for Antibacterial Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
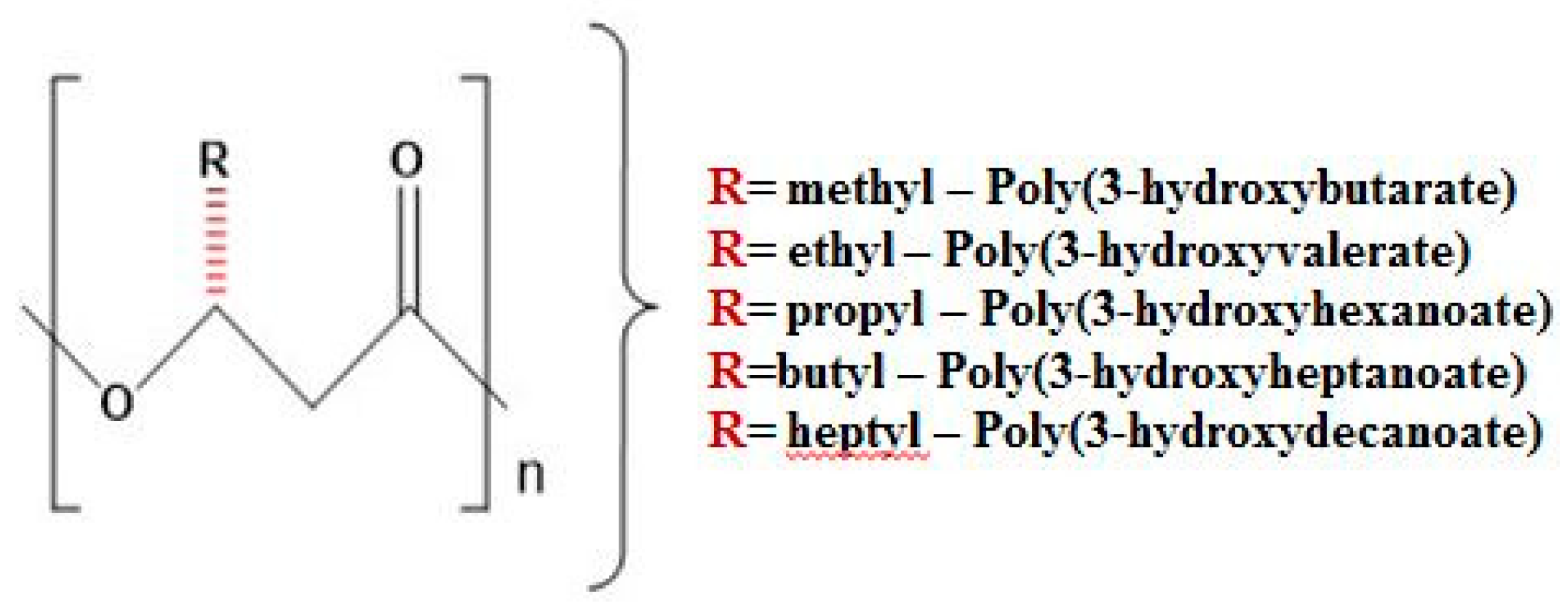
2. Materials and Methods
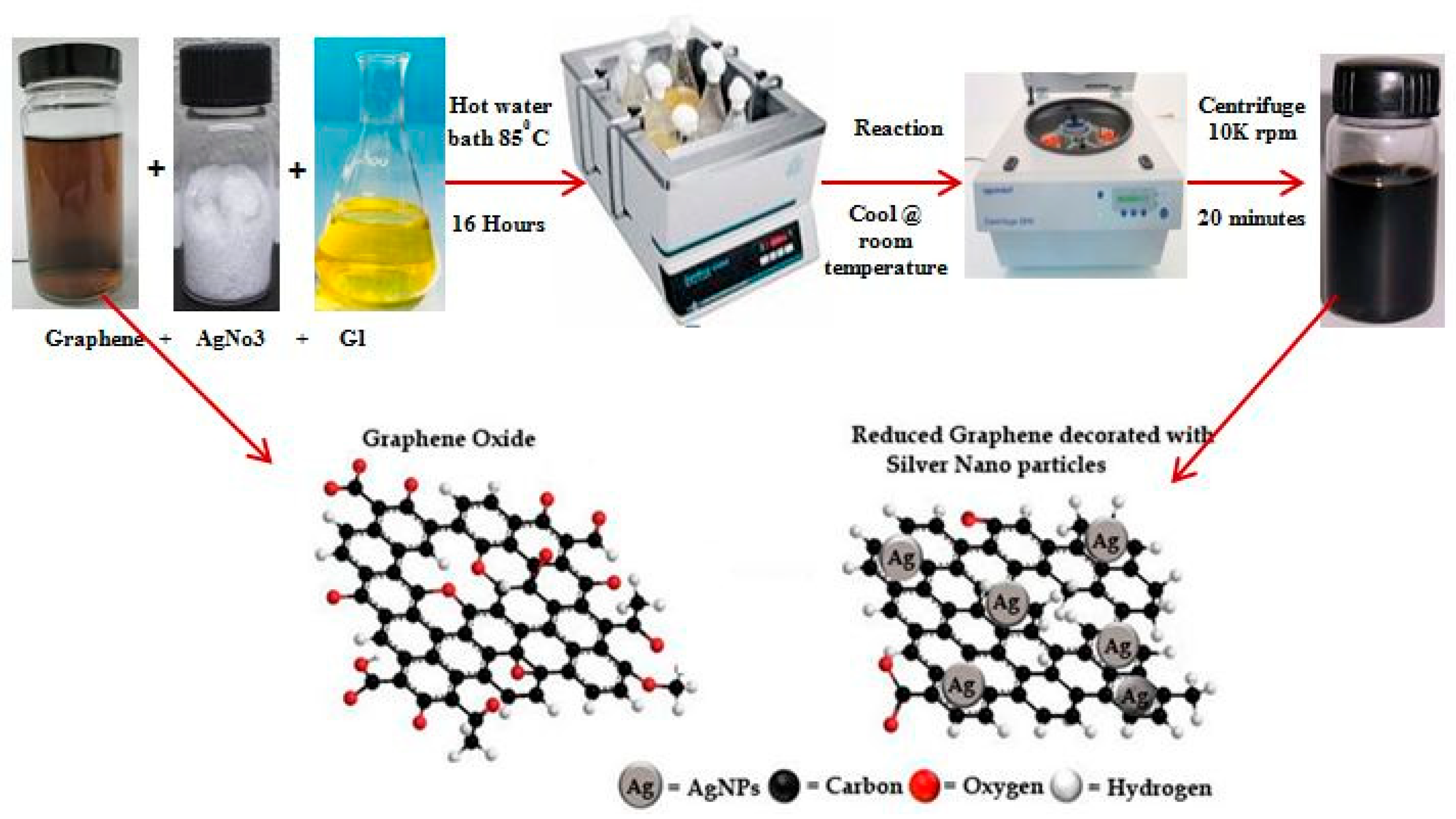
2.1. Preparation of Reducing Agent, G.L. Extract
2.2. Synthesis of GAg Nanocomposite
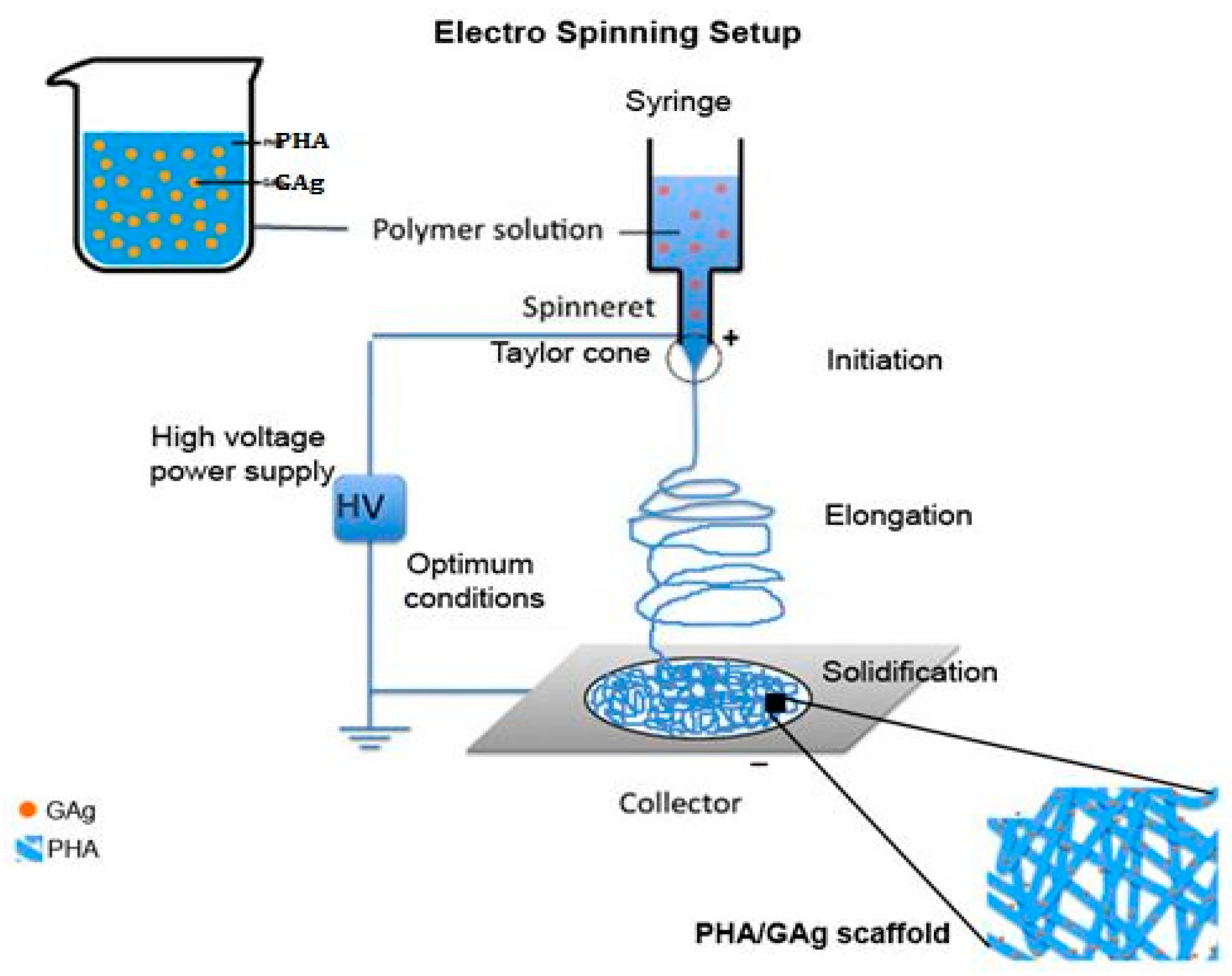
2.3. Fabrication of Electrospun Scaffold (PHA/GAg)
2.4. Antibacterial Culture Preparation
3. Characterization
4. Results
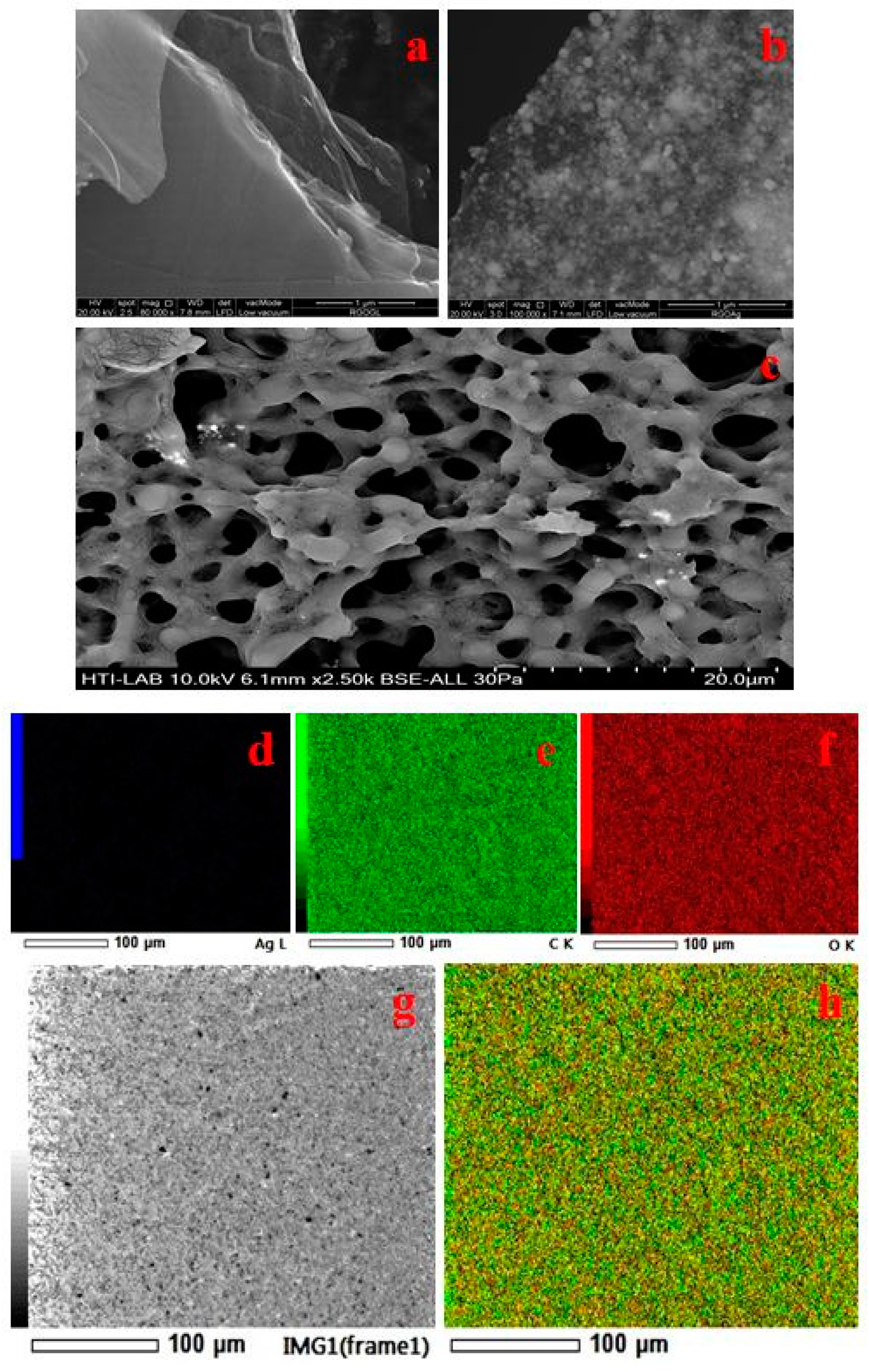
4.1. FESEM and Elemental Analysis
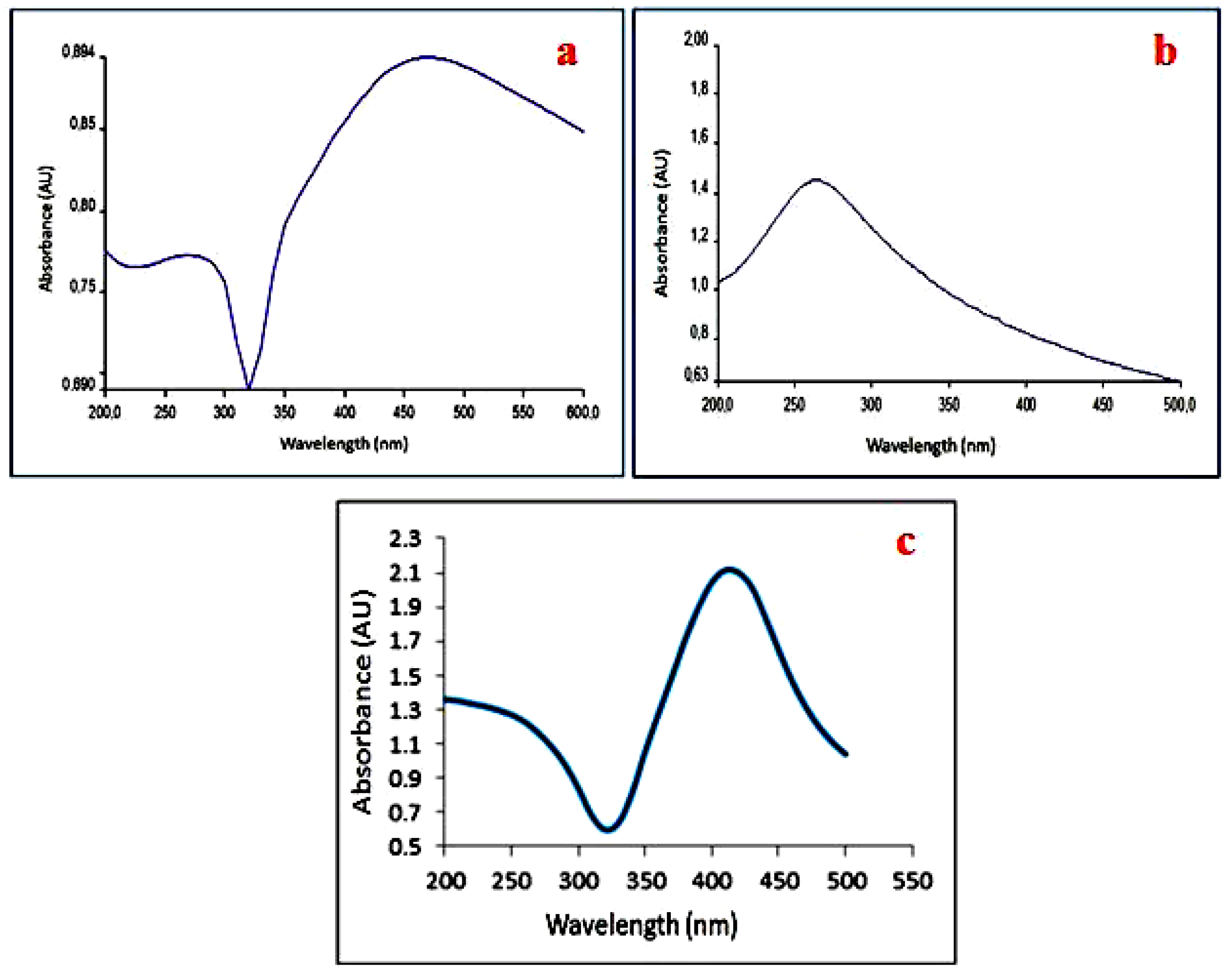
4.2. UV-Vis Analysis
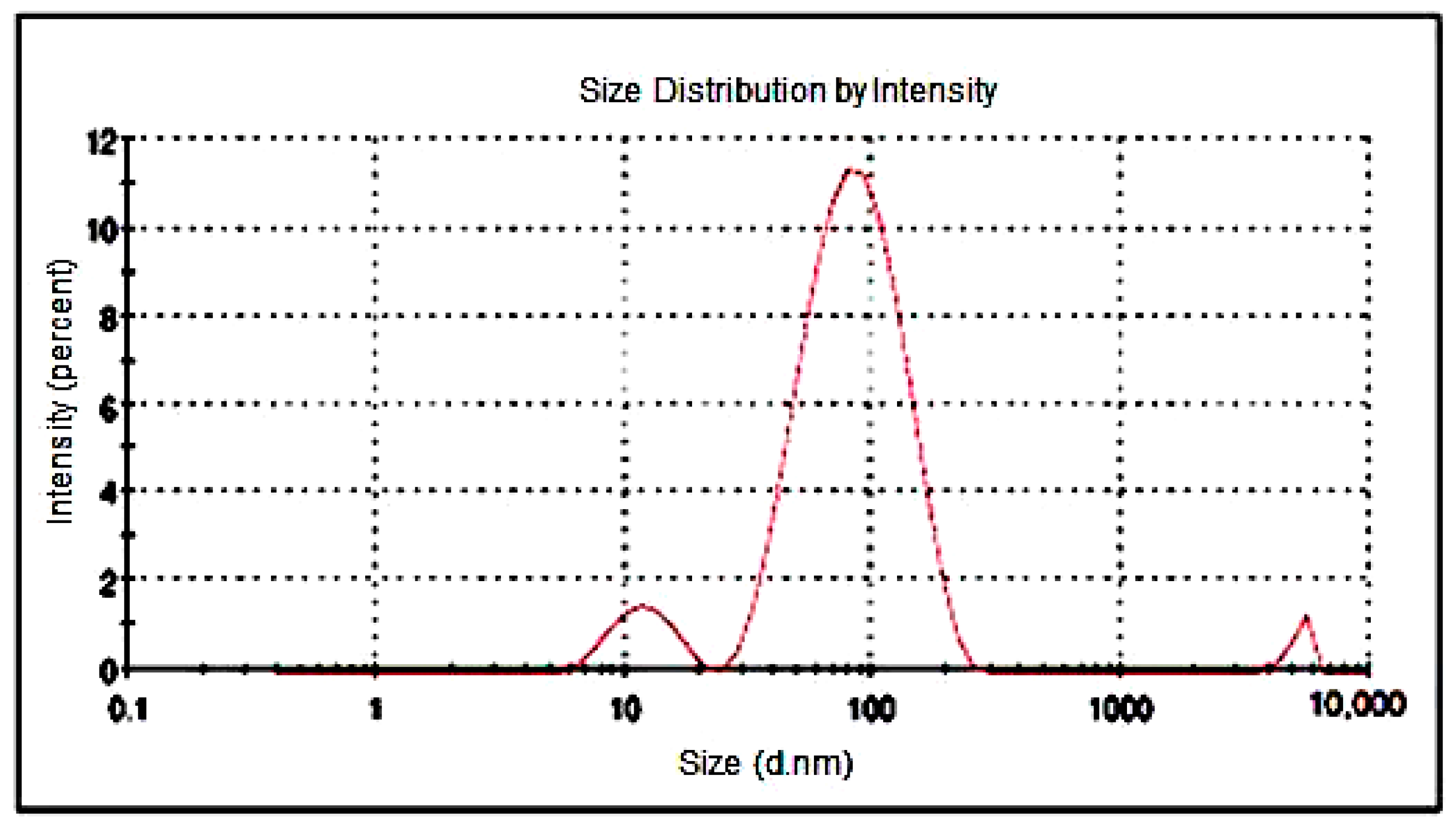
4.3. Particle Size Analysis
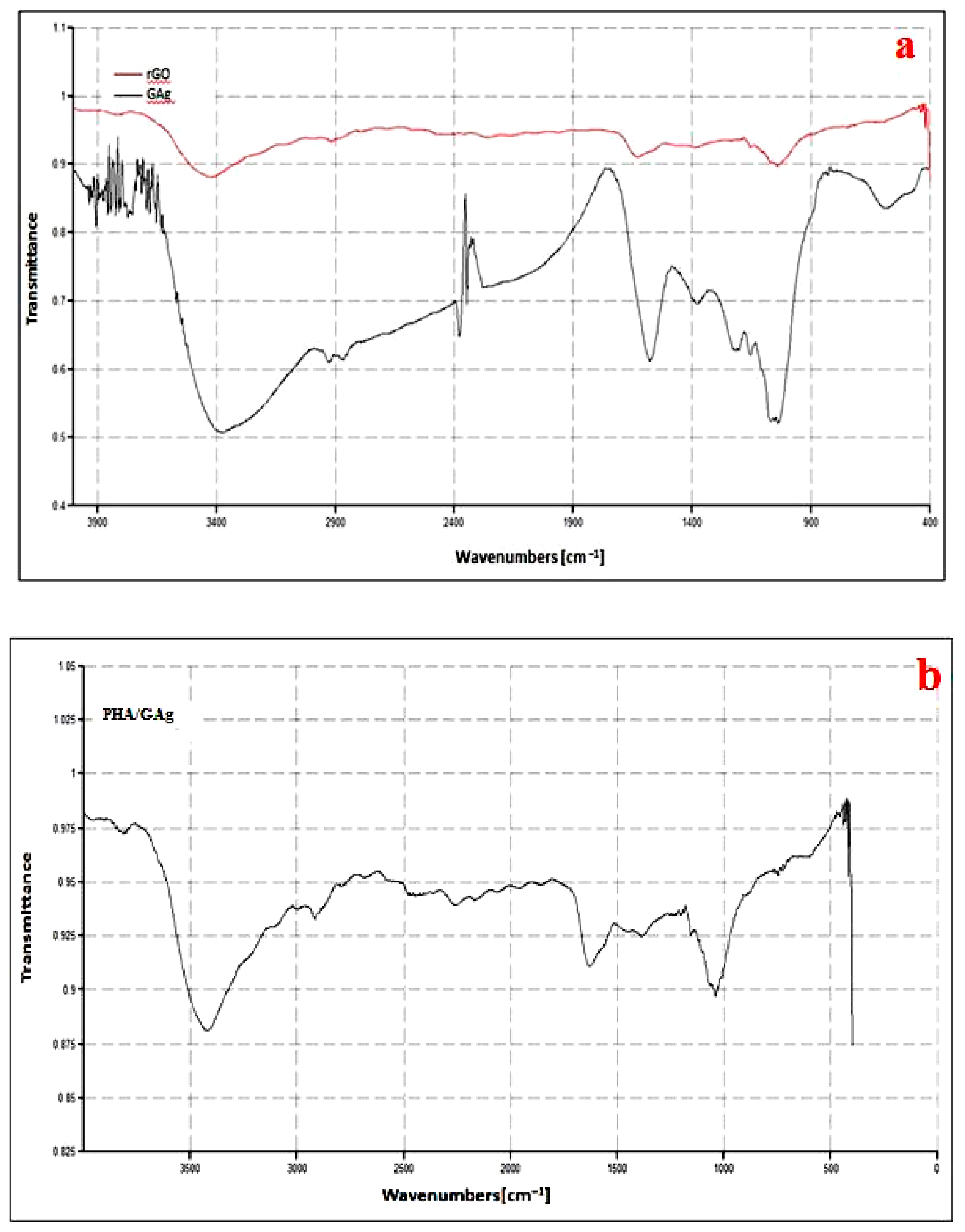
4.4. FTIR Analysis
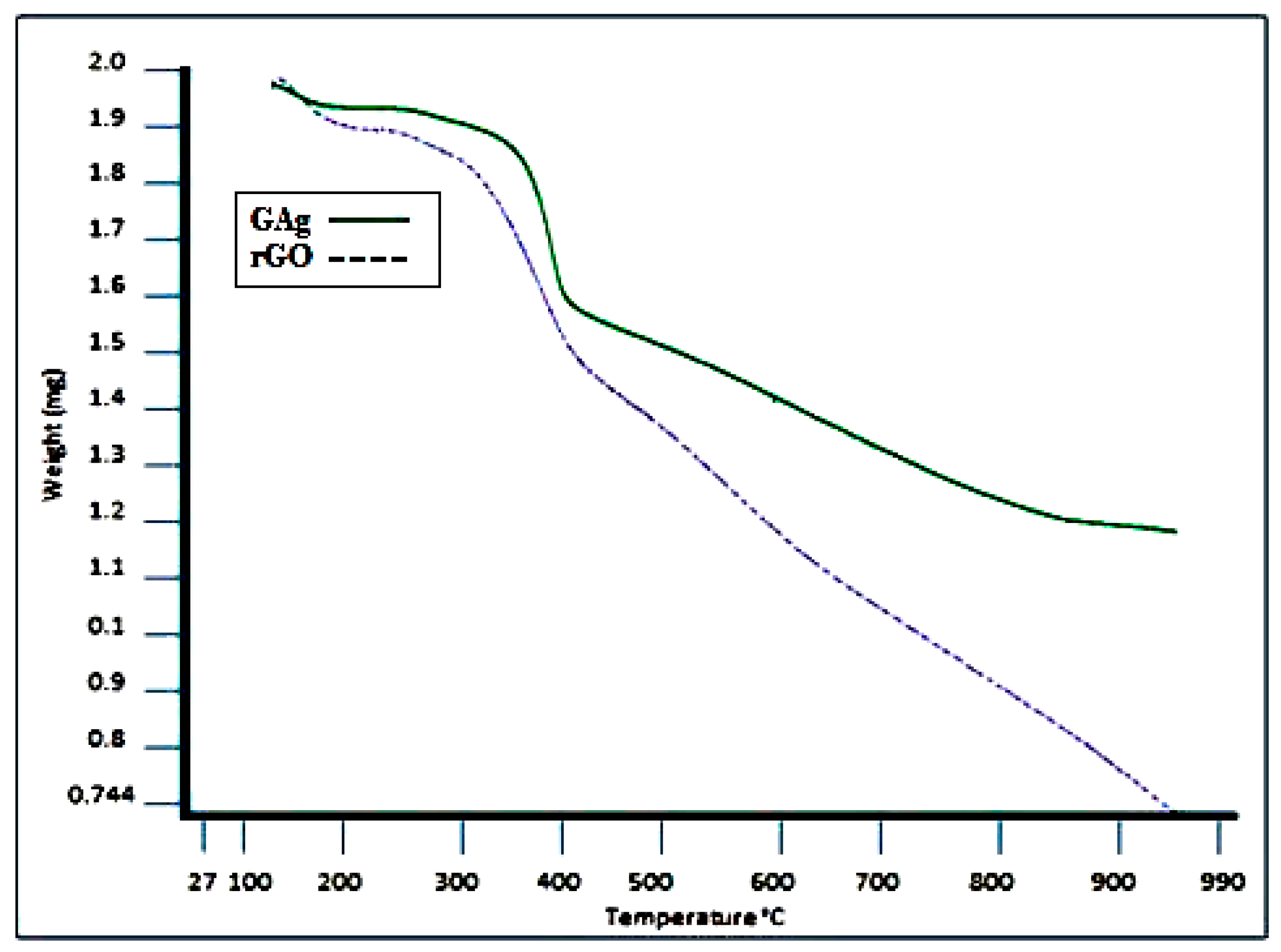
4.5. Thermal Analysis
4.6. Antibacterial Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Walker, B.; Barrett, S.; Polasky, S.; Galaz, V.; Folke, C.; Engström, G.; Ackerman, F.; Arrow, K.; Carpenter, S.; Chopra, K. Looming global-scale failures and missing institutions. Science 2009, 325, 1345–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Organization, W.H. Antimicrobial Resistance: Global Report on Surveillance; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Demain, A.L. Antibiotics: Natural products essential to human health. Med. Res. Rev. 2009, 29, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jayakumar, R.; Prabaharan, M.; Kumar, P.S.; Nair, S.; Tamura, H. Biomaterials based on chitin and chitosan in wound dressing applications. Biotechnol. Adv. 2011, 29, 322–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unnithan, A.R.; Gnanasekaran, G.; Sathishkumar, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kim, C.S. Electrospun antibacterial polyurethane–cellulose acetate–zein composite mats for wound dressing. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 102, 884–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cammas, S.; Bear, M.-M.; Moine, L.; Escalup, R.; Ponchel, G.; Kataoka, K.; Guérin, P. Polymers of malic acid and 3-alkylmalic acid as synthetic phas in the design of biocompatible hydrolyzable devices. Int. J. Boil. Macromol. 1999, 25, 273–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudesh, K.; Abe, H.; Doi, Y. Synthesis, structure and properties of polyhydroxyalkanoates: Biological polyesters. Prog. Polym. Sci. 2000, 25, 1503–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valappil, S.P.; Misra, S.K.; Boccaccini, A.R.; Roy, I. Biomedical applications of polyhydroxyalkanoates, an overview of animal testing and In Vivo responses. Expert Rev. Med. Devices 2006, 3, 853–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazer, B. Amphiphilic poly(3-hydroxy alkanoate)s: Potential candidates for medical applications. Int. J. Polym. Sci. 2010, 2010, 423460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.-X.; Sun, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, P. Degradable phbhhx modified by the silk fibroin for the applications of cardiovascular tissue engineering. ISRN Mater. Sci. 2011, 2011, 389872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, V.; Pearson, R.; Lee, D.; Wolowacz, S.; Mc Taggart, S. An investigation of the growth of human dermal fibroblasts on poly-l-lactic acid In Vitro. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Med. 1996, 7, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.-W.; Yang, F.; Wu, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Peter, H.; Chen, J.; Chen, G.-Q. Effect of composition of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) on growth of fibroblast and osteoblast. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 755–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, G.Q.; Wu, Q.; Wang, Y.W.; Zheng, Z. Application of microbial polyesters-polyhydroxyalkanoates as tissue engineering material. Key Eng. Mater. 2005, 288–289, 437–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, M.; Peng, G.; Li, J.; Ma, P.; Wang, Z.; Shu, W.; Peng, S.; Chen, G.-Q. Chondrogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate (PHA) scaffolds coated with PHA granule binding protein PhaP fused with RGD peptide. Biomaterials 2011, 32, 2305–2313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.K.; Ansari, T.I.; Valappil, S.P.; Mohn, D.; Philip, S.E.; Stark, W.J.; Roy, I.; Knowles, J.C.; Salih, V.; Boccaccini, A.R. Poly(3-hydroxybutyrate) multifunctional composite scaffolds for tissue engineering applications. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 2806–2815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kurobe, H.; Maxfield, M.; Naito, Y.; Breuer, C.; Shinoka, T. Stem cells in tissue-engineered blood vessels for cardiac repair. In Cardiac Regeneration and Repair; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; pp. 389–409. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.-Y.; Ciraolo, E.; Stefenia, R.; Chen, G.-Q.; Zhang, Y.; Hirsch, E. Sustained release of PI3K inhibitor from pha nanoparticles and In Vitro growth inhibition of cancer cell lines. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2011, 89, 1423–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, X.-Y.; Li, X.-T.; Peng, S.-W.; Xiao, J.-F.; Liu, C.; Fang, G.; Chen, K.C.; Chen, G.-Q. The behaviour of neural stem cells on polyhydroxyalkanoate nanofiber scaffolds. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 3967–3975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zonari, A.; Martins, T.M.; Paula, A.C.C.; Boeloni, J.N.; Novikoff, S.; Marques, A.P.; Correlo, V.M.; Reis, R.L.; Goes, A.M. Polyhydroxybutyrate-co-hydroxyvalerate structures loaded with adipose stem cells promote skin healing with reduced scarring. Acta Biomater. 2015, 17, 170–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, Y.; Dubonos, S.V.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Firsov, A.A. Electric field effect in atomically thin carbon films. Science 2004, 306, 666–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suk, J.W.; Lee, W.H.; Lee, J.; Chou, H.; Piner, R.D.; Hao, Y.; Akinwande, D.; Ruoff, R.S. Enhancement of the electrical properties of graphene grown by chemical vapor deposition via controlling the effects of polymer residue. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 1462–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.; Wei, X.; Kysar, J.W.; Hone, J. Measurement of the elastic properties and intrinsic strength of monolayer graphene. Science 2008, 321, 385–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loh, K.P.; Bao, Q.; Ang, P.K.; Yang, J. The chemistry of graphene. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2277–2289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akhavan, O.; Ghaderi, E. Toxicity of graphene and graphene oxide nanowalls against bacteria. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 5731–5736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuchowska, A.; Chudy, M.; Dybko, A.; Brzózka, Z. Graphene as a new material in anticancer therapy-In Vitro studies. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2017, 243, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Justino, C.I.; Gomes, A.R.; Freitas, A.C.; Duarte, A.C.; Rocha-Santos, T.A. Graphene based sensors and biosensors. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2017, 91, 53–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Zeng, T.H.; Hofmann, M.; Burcombe, E.; Wei, J.; Jiang, R.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6971–6980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, C.; Xu, B.; Gu, Y.; Xiong, Z.; Sun, J.; Zhao, X. Graphene-based electrodes for electrochemical energy storage. Energy Environ. Sci. 2013, 6, 1388–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Prasad, K.P.; Wang, X.; Pang, H.; Yan, R.; Than, A.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Chen, P. Enzymeless multi-sugar fuel cells with high power output based on 3d graphene–Co3O4 hybrid electrodes. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2013, 15, 9170–9176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.-H.; Cooper, R.C.; An, S.J.; Lee, S.; van der Zande, A.; Petrone, N.; Hammerberg, A.G.; Lee, C.; Crawford, B.; Oliver, W. High-strength chemical-vapor–deposited graphene and grain boundaries. Science 2013, 340, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muthoosamy, K.; Bai, R.G.; Manickam, S. Graphene and graphene oxide as a docking station for modern drug delivery system. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 701–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beyth, N.; Houri-Haddad, Y.; Domb, A.; Khan, W.; Hazan, R. Alternative antimicrobial approach: Nano-antimicrobial materials. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2015, 2015, 246012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, L.; Lu, J.; Xu, H.; Patel, A.; Chen, Z.-S.; Chen, G. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, and therapeutic applications. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 595–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, Q.H.; Le, A.-T. Silver nanoparticles: Synthesis, properties, toxicology, applications and perspectives. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2013, 4, 033001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morones, J.R.; Elechiguerra, J.L.; Camacho, A.; Holt, K.; Kouri, J.B.; Ramírez, J.T.; Yacaman, M.J. The bactericidal effect of silver nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rai, M.; Deshmukh, S.; Ingle, A.; Gade, A. Silver nanoparticles: The powerful nanoweapon against multidrug-resistant bacteria. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2012, 112, 841–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karunamuni, R.; Naha, P.C.; Lau, K.C.; Al-Zaki, A.; Popov, A.V.; Delikatny, E.J.; Tsourkas, A.; Cormode, D.P.; Maidment, A.D. Development of silica-encapsulated silver nanoparticles as contrast agents intended for dual-energy mammography. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3301–3309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, W.K.; Koo, H.C.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, S.; Kim, S.H.; Park, Y.H. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action of the silver ion in staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2008, 74, 2171–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Liu, X.; Min, H.; Dong, G.; Feng, Q.; Zuo, S. Preparation, characterization, and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide nanocomposite. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 6966–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Men, B.; Sun, Y.; Tang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Chen, Y.; Wan, P.; Pan, J. Highly dispersed ag-functionalized graphene electrocatalyst for oxygen reduction reaction in energy-saving electrolysis of sodium carbonate. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2015, 54, 7415–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Liu, J. Enhanced antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles/halloysite nanotubes/graphene nanocomposites with sandwich-like structure. Sci. Rep. 2014, 4, 4551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, W.-P.; Zhang, L.-C.; Li, J.-P.; Lu, Y.; Li, H.-H.; Ma, Y.-N.; Wang, W.-D.; Yu, S.-H. Facile synthesis of silver@ graphene oxide nanocomposites and their enhanced antibacterial properties. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 4593–4597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Marri, A.H.; Khan, M.; Shaik, M.R.; Mohri, N.; Adil, S.F.; Kuniyil, M.; Alkhathlan, H.Z.; Al-Warthan, A.; Tremel, W.; Tahir, M.N. Green synthesis of Pd@graphene nanocomposite: Catalyst for the selective oxidation of alcohols. Arab. J. Chem. 2016, 9, 835–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iravani, S. Green synthesis of metal nanoparticles using plants. Green Chem. 2011, 13, 2638–2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, A.; Parida, S.; Böhm, S. One step eco-friendly synthesis of ag–reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite by phytoreduction for sensitive nitrite determination. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 100383–100391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muthoosamy, K.; Bai, R.G.; Abubakar, I.B.; Sudheer, S.M.; Lim, H.N.; Loh, H.-S.; Huang, N.M.; Chia, C.H.; Manickam, S. Exceedingly biocompatible and thin-layered reduced graphene oxide nanosheets using an eco-friendly mushroom extract strategy. Int. J. Nanomed. 2015, 10, 1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontogiannopoulos, K.N.; Assimopoulou, A.N.; Tsivintzelis, I.; Panayiotou, C.; Papageorgiou, V.P. Electrospun fiber mats containing shikonin and derivatives with potential biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 409, 216–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.-L.; Lin, C.-C.; Su, H.-L.; Chen, P.-Y.; Sun, Y.-M. Processing and characterization of electrospun poly(3-hydroxybutyrate-co-3-hydroxyhexanoate) nanofibrous membranes. Polymer 2008, 49, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schniepp, H.C.; Li, J.-L.; McAllister, M.J.; Sai, H.; Herrera-Alonso, M.; Adamson, D.H.; Prud’homme, R.K.; Car, R.; Saville, D.A.; Aksay, I.A. Functionalized single graphene sheets derived from splitting graphite oxide. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 8535–8539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, P.; Zhu, X.; Liang, S.; Li, Z.; Yang, W.; Wang, H. Large reversible capacity of high quality graphene sheets as an anode material for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochim. Acta 2010, 55, 3909–3914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukman, A.I.; Gong, B.; Marjo, C.E.; Roessner, U.; Harris, A.T. Facile synthesis, stabilization, and anti-bacterial performance of discrete ag nanoparticles using medicago sativa seed exudates. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2011, 353, 433–444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurunathan, S.; Han, J.W.; Dayem, A.A.; Eppakayala, V.; Kim, J.-H. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in pseudomonas aeruginosa. Int. J. Nanomed. 2012, 7, 5901–5914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Zhang, J.-J.; Cheng, F.-F.; Zheng, T.-T.; Wang, C.; Zhu, J.-J. Green and facile synthesis of highly biocompatible graphene nanosheets and its application for cellular imaging and drug delivery. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 12034–12040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdock, R.C.; Braydich-Stolle, L.; Schrand, A.M.; Schlager, J.J.; Hussain, S.M. Characterization of nanomaterial dispersion in solution prior to In Vitro exposure using dynamic light scattering technique. Toxicol. Sci. 2008, 101, 239–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bykkam, S.; Rao, K.; Chakra, C.; Thunugunta, T. Synthesis and characterization of graphene oxide and its antimicrobial activity against klebseilla and staphylococus. Int. J. Adv. Biotechnol. Res. 2013, 4, 142–146. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, H.-L.; Wang, X.-F.; Qian, Q.-Y.; Wang, F.-B.; Xia, X.-H. A green approach to the synthesis of graphene nanosheets. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 2653–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.W.; Gurunathan, S.; Jeong, J.-K.; Choi, Y.-J.; Kwon, D.-N.; Park, J.-K.; Kim, J.-H. Oxidative stress mediated cytotoxicity of biologically synthesized silver nanoparticles in human lung epithelial adenocarcinoma cell line. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salim, Y.S.; Chan, C.H.; Sudesh, K.; Gan, S.N. Influence of thermal treatment on the molecular weights of polyhydroxyalkanoate containing 3-hydroxyhexanoate. Adv. Mater. Res. 2013, 812, 250–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamala, T.; Divyashree, M.; Davis, R.; Kumari, K.S.L.; Vijayendra, S.V.; Raj, B. Production and characterization of bacterial polyhydroxyalkanoate copolymers and evaluation of their blends by fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and scanning electron microscopy. Indian J. Microbiol. 2009, 49, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, N.; Gao, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chai, J.; Yang, Z.; Kong, E.S.-W.; Zhang, Y. The preparation and characterization of non-covalently functionalized graphene. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 12, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, B.G.; Park, H.; Park, T.J.; Yang, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Jang, S.-Y.; Heo, N.S.; Lee, S.Y.; Kong, J.; Hong, W.H. Solution chemistry of self-assembled graphene nanohybrids for high-performance flexible biosensors. ACS Nano 2010, 4, 2910–2918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Test Samples | Antibacterial Activity against E. coli | Antibacterial Activity against S. aureus |
|---|---|---|
| PHA | − | − |
| PHA/rGO | + | + |
| PHA/GAg | + | + |
| Gentamicin | + | + |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mukheem, A.; Muthoosamy, K.; Manickam, S.; Sudesh, K.; Shahabuddin, S.; Saidur, R.; Akbar, N.; Sridewi, N. Fabrication and Characterization of an Electrospun PHA/Graphene Silver Nanocomposite Scaffold for Antibacterial Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091673
Mukheem A, Muthoosamy K, Manickam S, Sudesh K, Shahabuddin S, Saidur R, Akbar N, Sridewi N. Fabrication and Characterization of an Electrospun PHA/Graphene Silver Nanocomposite Scaffold for Antibacterial Applications. Materials. 2018; 11(9):1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091673
Chicago/Turabian StyleMukheem, Abdul, Kasturi Muthoosamy, Sivakumar Manickam, Kumar Sudesh, Syed Shahabuddin, Rahman Saidur, Noor Akbar, and Nanthini Sridewi. 2018. "Fabrication and Characterization of an Electrospun PHA/Graphene Silver Nanocomposite Scaffold for Antibacterial Applications" Materials 11, no. 9: 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091673
APA StyleMukheem, A., Muthoosamy, K., Manickam, S., Sudesh, K., Shahabuddin, S., Saidur, R., Akbar, N., & Sridewi, N. (2018). Fabrication and Characterization of an Electrospun PHA/Graphene Silver Nanocomposite Scaffold for Antibacterial Applications. Materials, 11(9), 1673. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091673