Effect of Healing Agents on Crack Healing of Asphalt and Asphalt Mortar
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
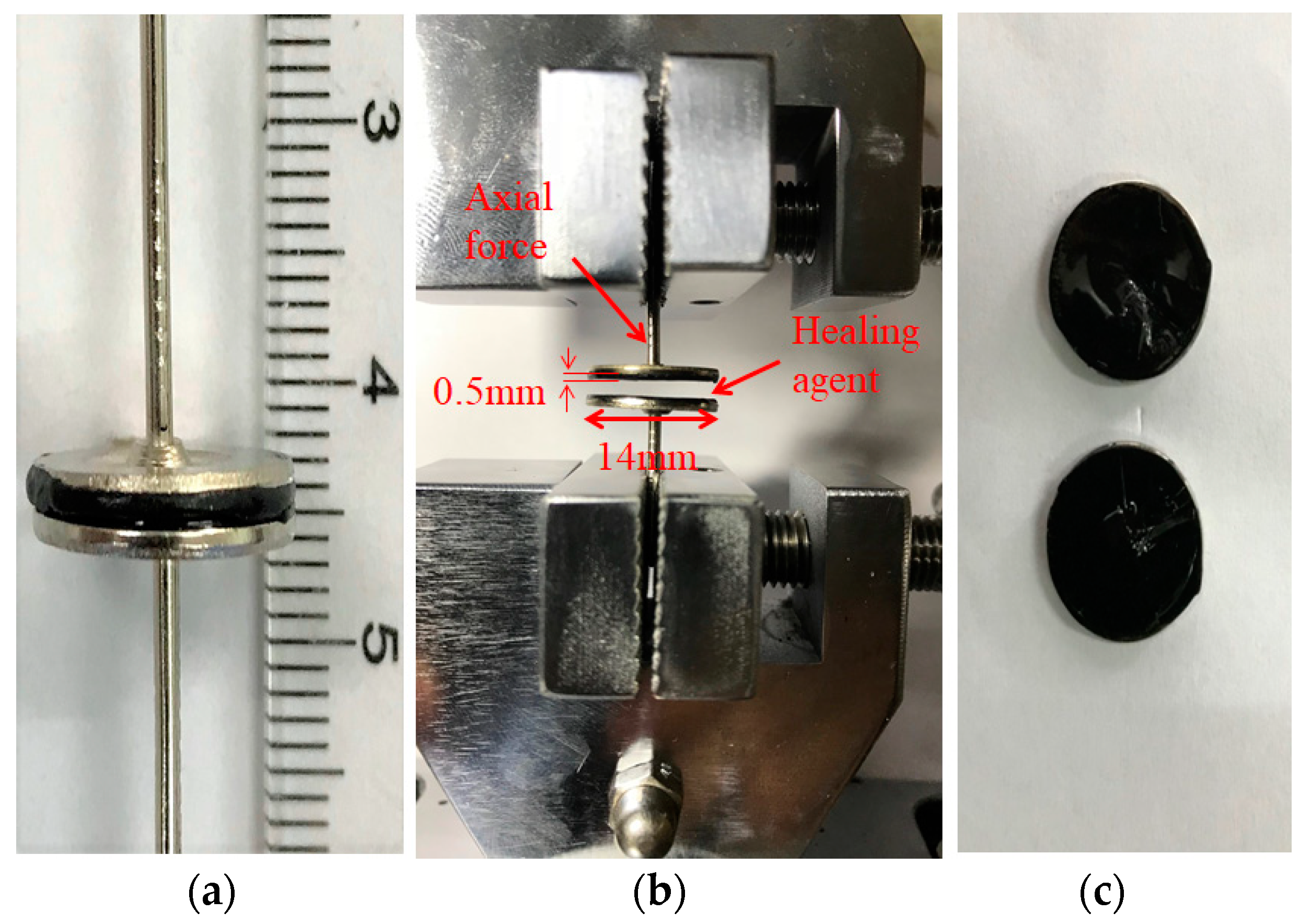
2.2. Sample Fabrication
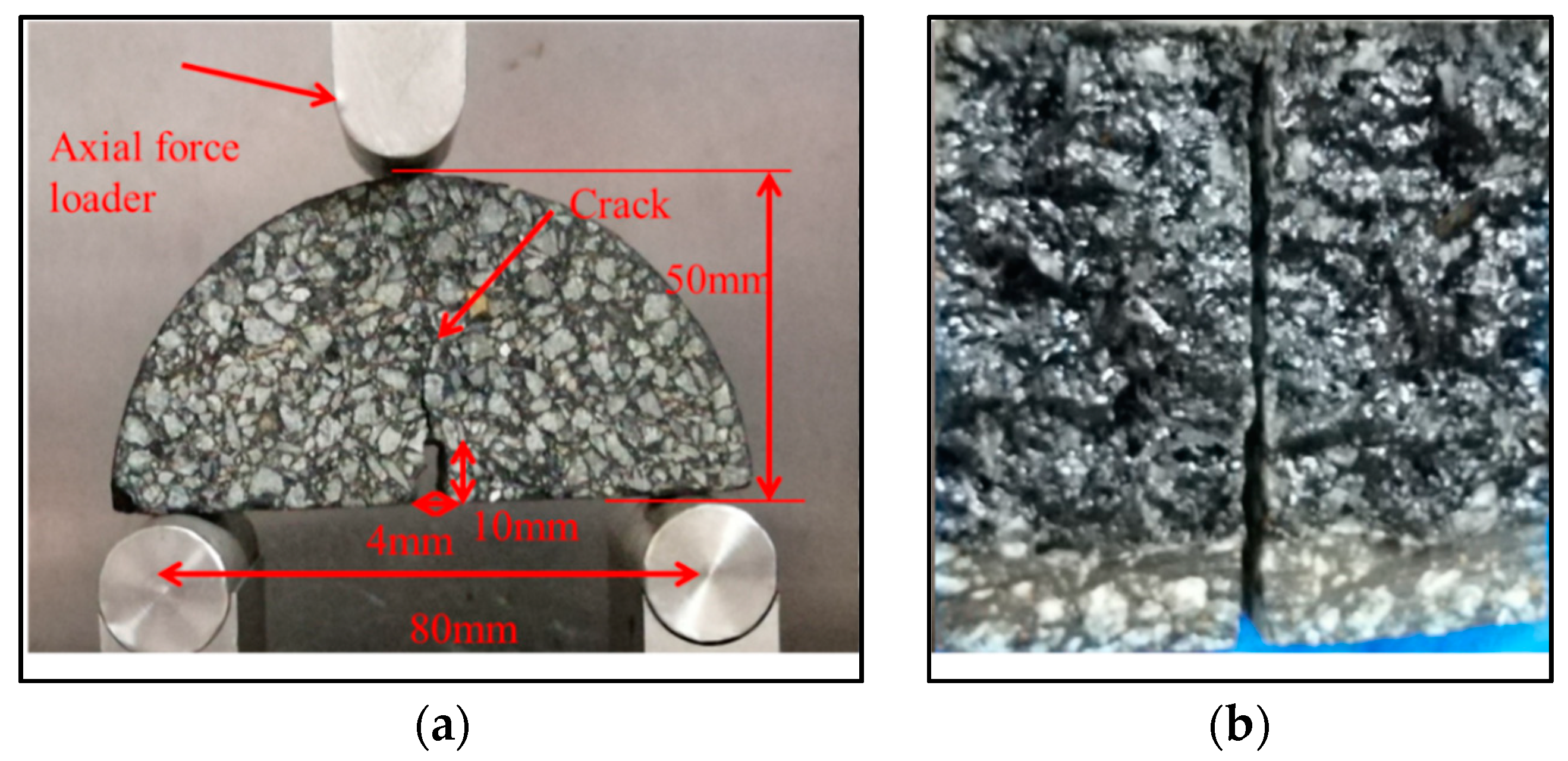
2.3. Test Procedures
- Initial fracture of the SCB samples: The test was conducted at −10 °C with a load rate of 0.5 mm/min. Before starting the test, the samples were kept in an environmental cabinet at −10 °C for 4 h to ensure the test specimens reach the required test temperature. Each sample was loaded until completely broken. The fractured sample was moved to room temperature for at least 2 h to raise the temperature of the sample to around 25 °C.
- Application of the healing agents: A soft brush was used to apply the healing agents on the cracked surfaces at a spreading rate ranging from 0.3 to 0.7 kg/cm3. This rate was appropriate to ensure that the healing agents were fully wetted in the cracked surface without excessive outflow. After the healing agents were applied, the samples were carefully placed together and excess healing agents were wiped. Then they were placed vertically at room temperature.
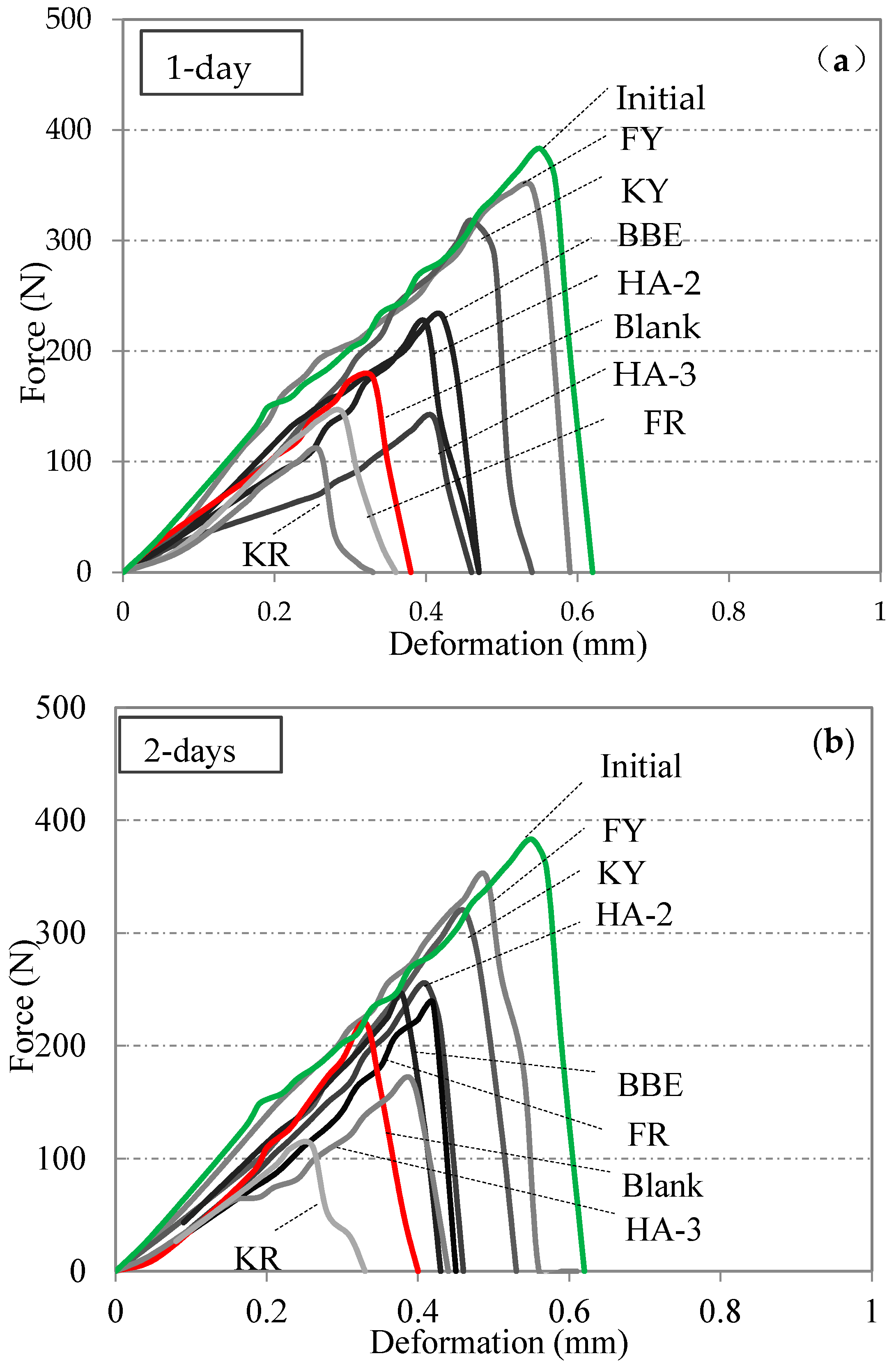
- After 1 day of healing, the samples were tested again. In order to avoid moisture attachment on the cracked surfaces, which would affect the healing of the samples, when they were completely broken, they were put at room temperature for 2 h. The same fractured samples were then put together carefully without the re-application of the healing agents. After 2 days of healing, the same specimen was tested. By the fracture and re-heal method, the effect of 4, 8, 30, and 60 days on crack healing was evaluated. In this test, at least three replicate samples in each group were conducted, and the mean value of test result was used for data analysis.
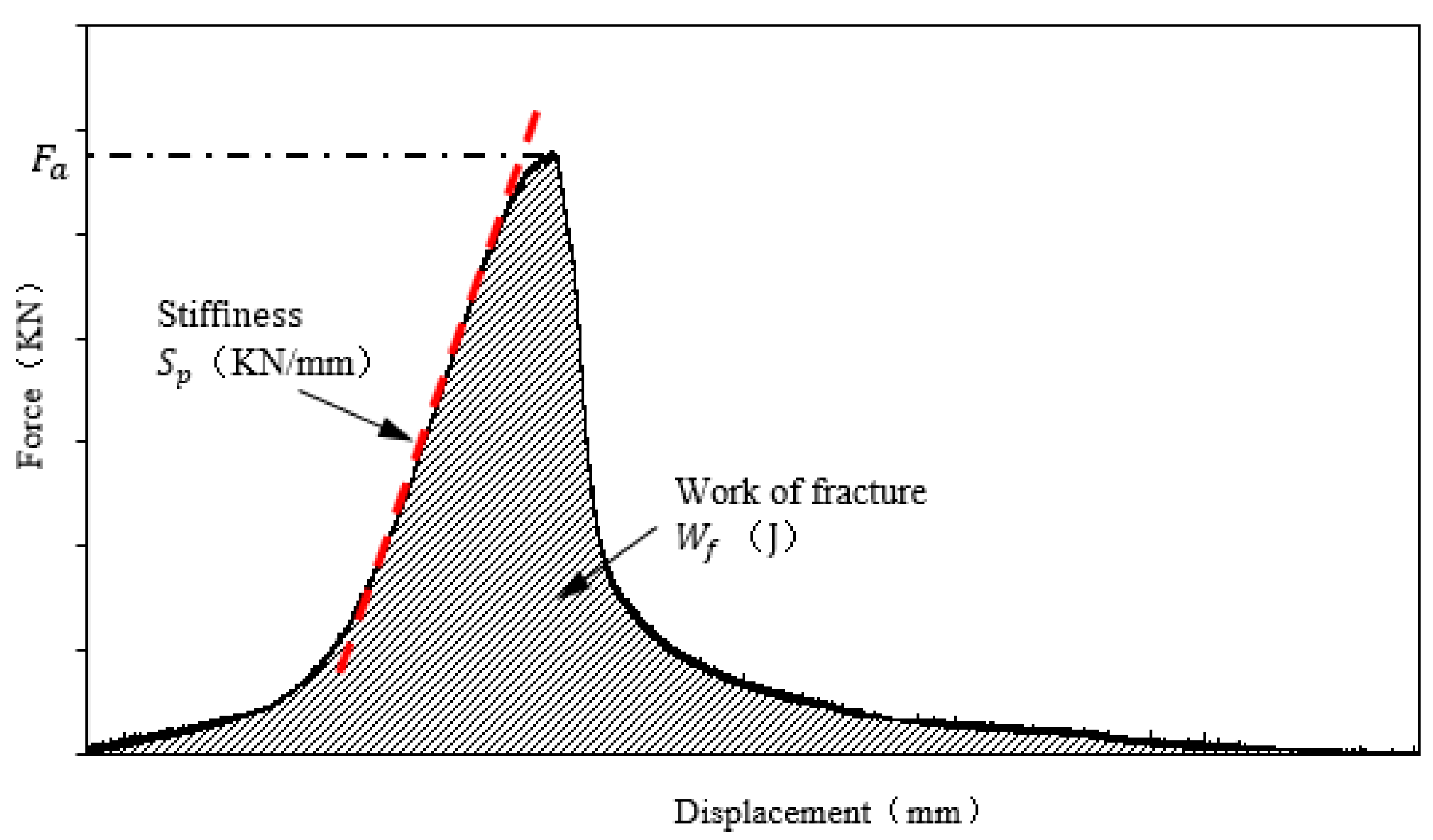
2.4. Healing Indicators
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Healing Agents on Asphalt
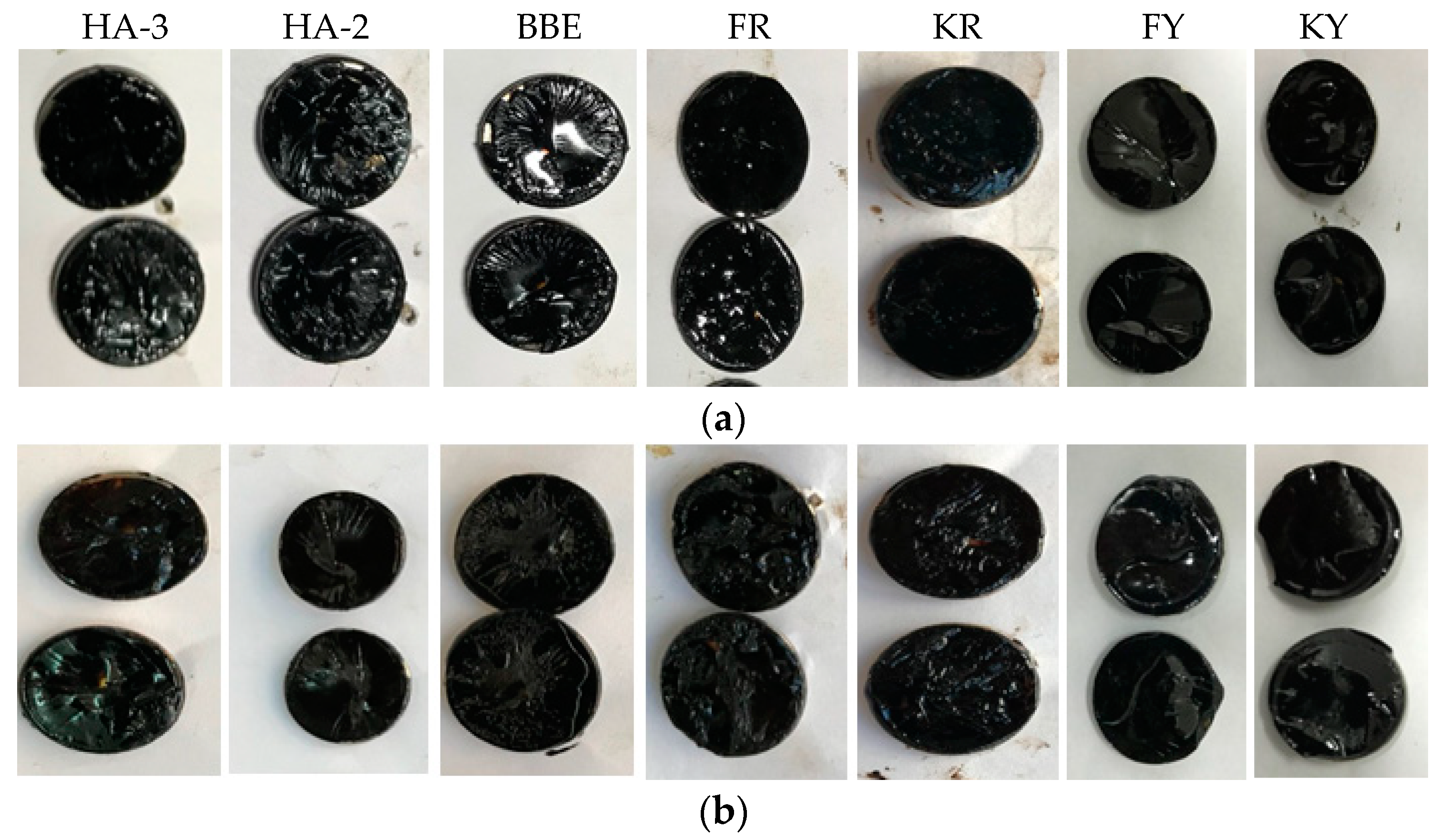
3.2. Appearance of Fractured Surface for Asphalt
3.3. Healing of Asphalt Mortar
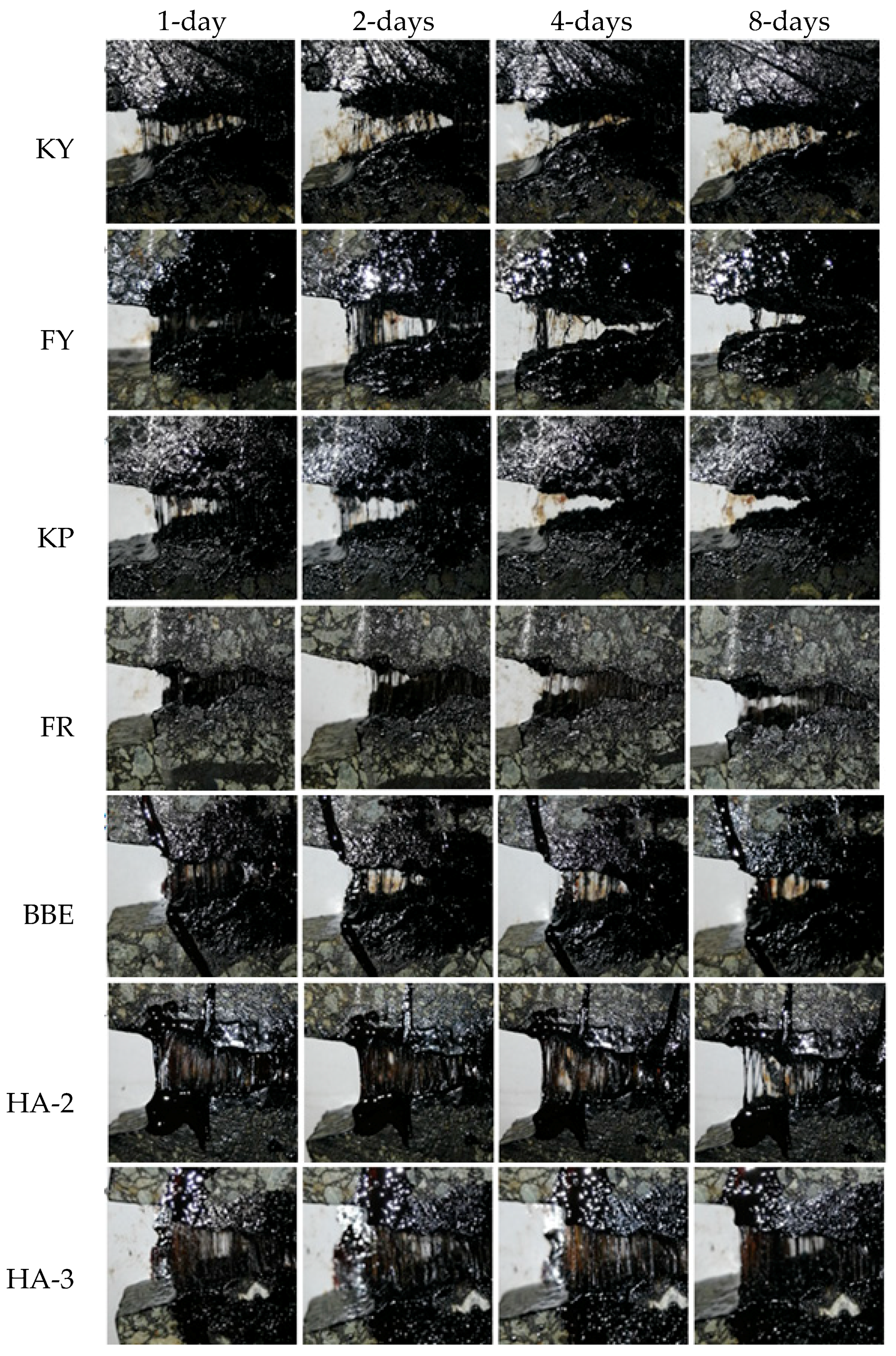
3.4. Appearance of Fractured Surface for Asphalt Mortar
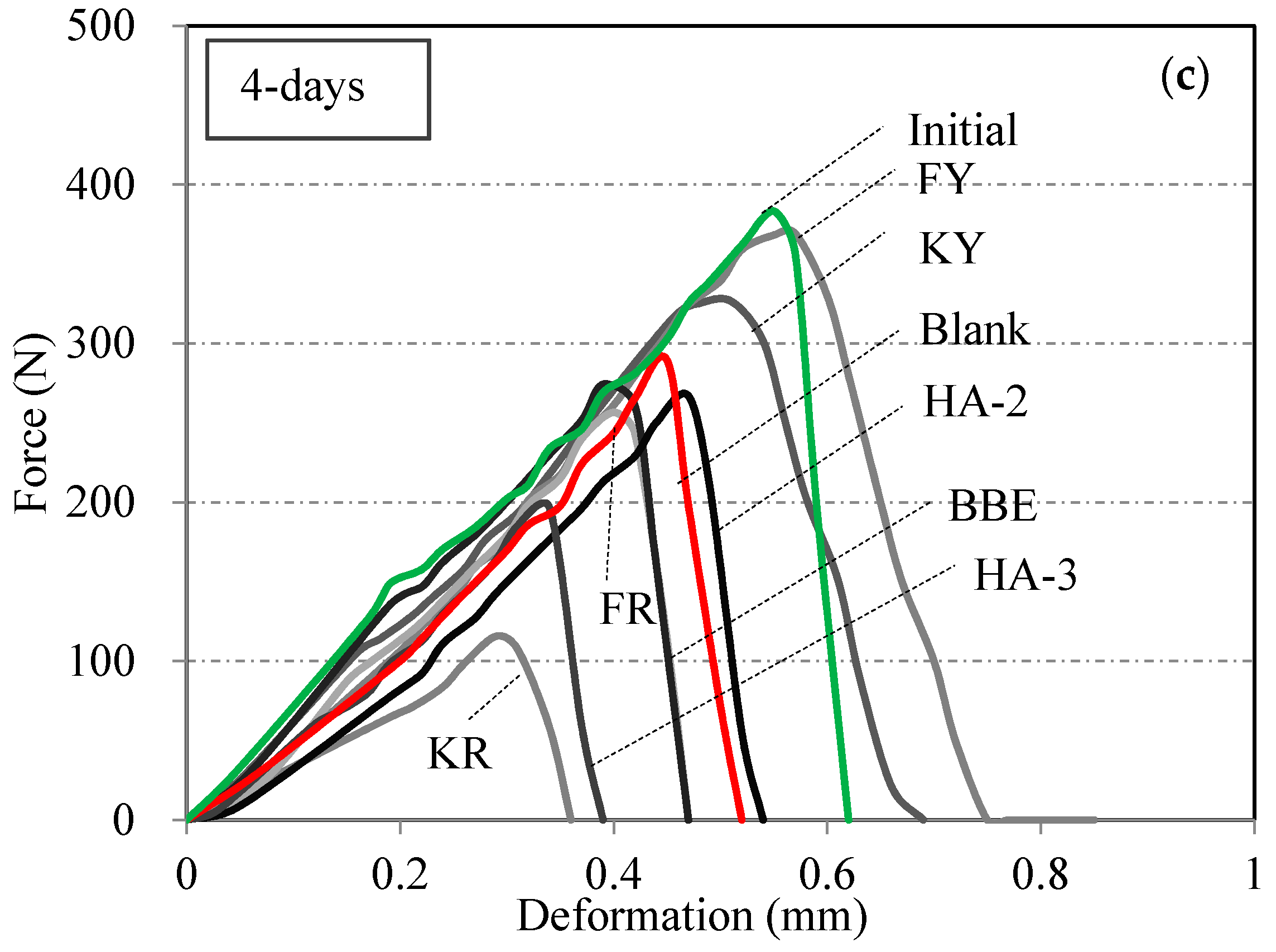
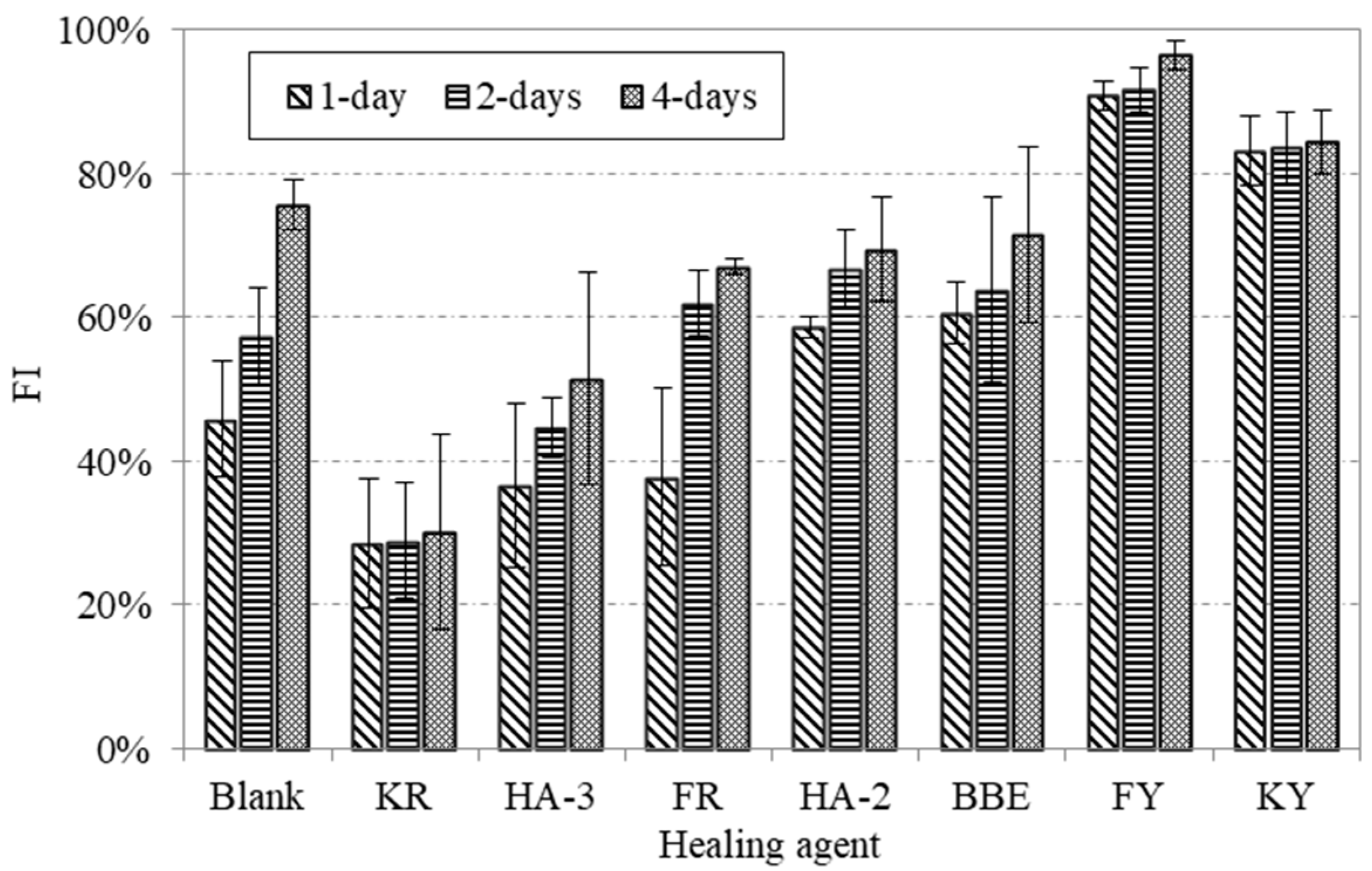
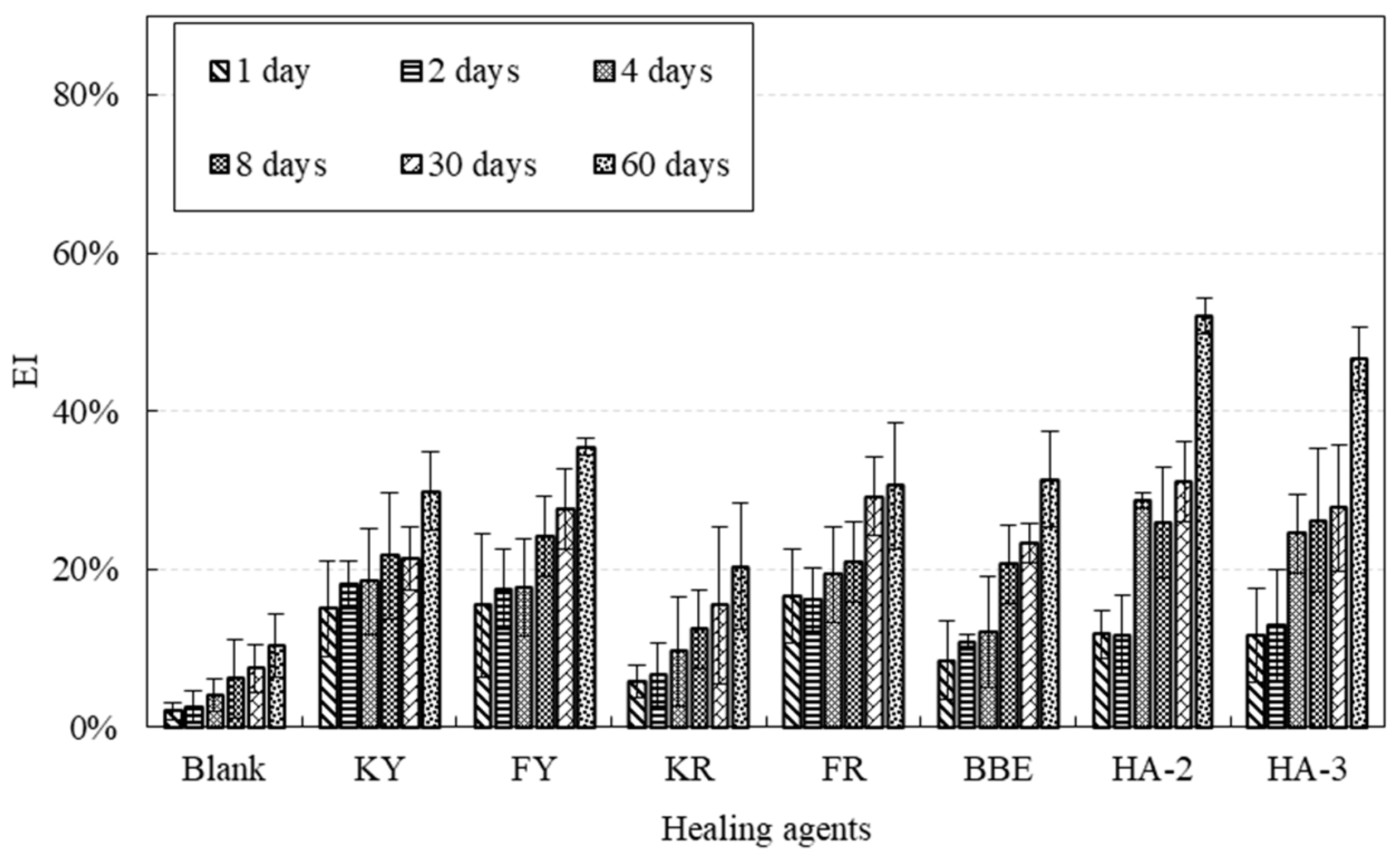
3.5. Effect of Healing Agents on Fracture Energy Healing Index
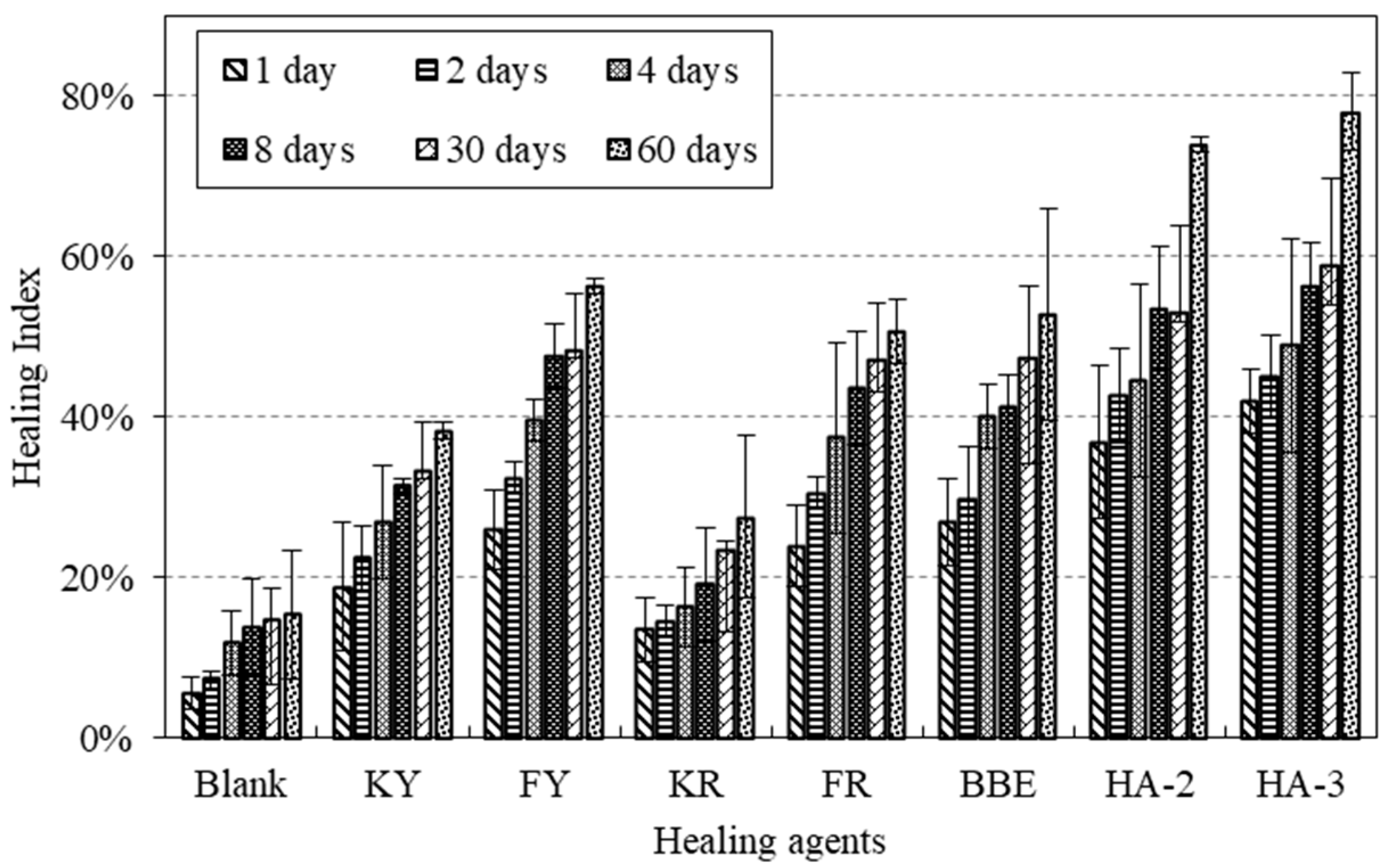
3.6. Effect of Healing Agents on Strength Healing Index
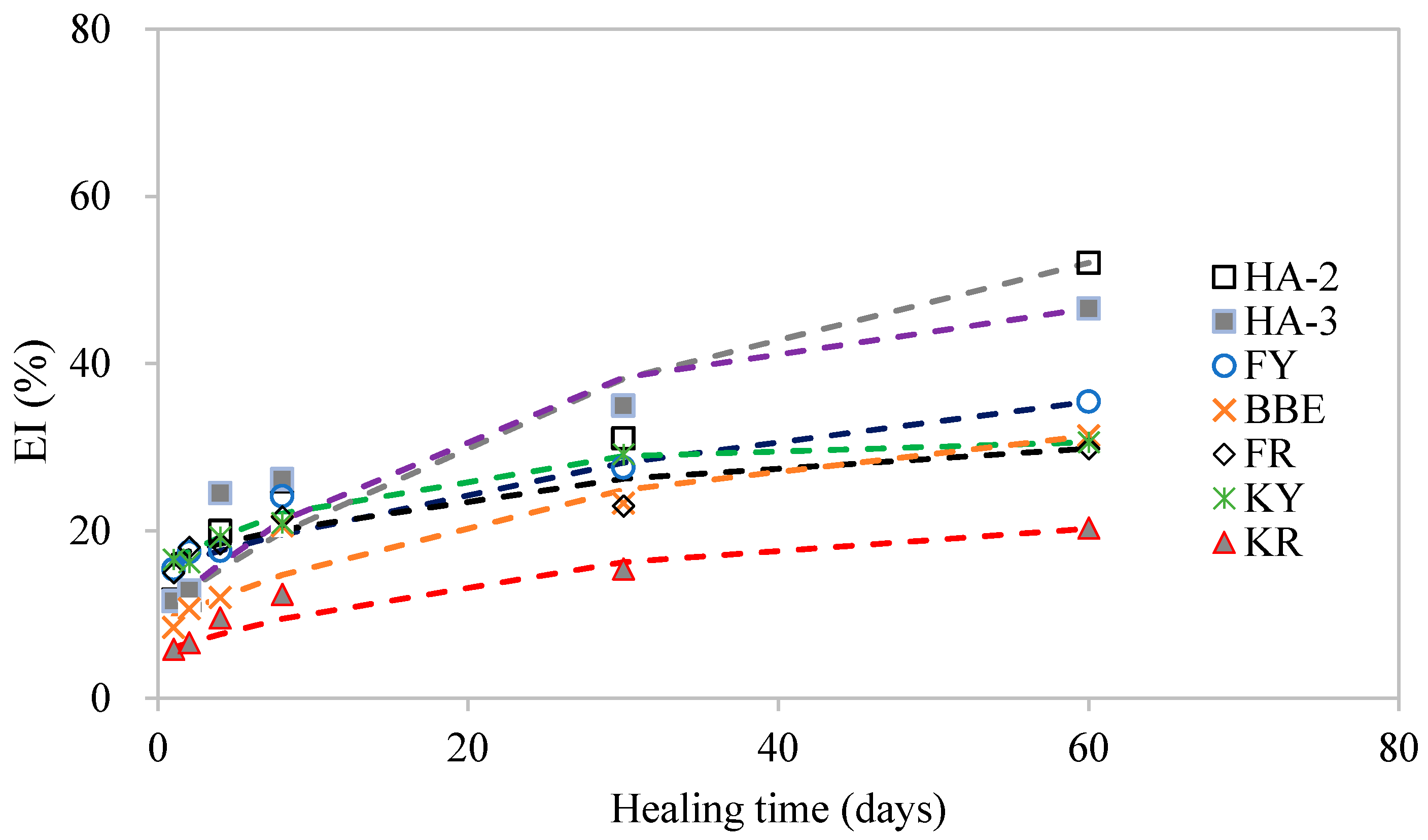
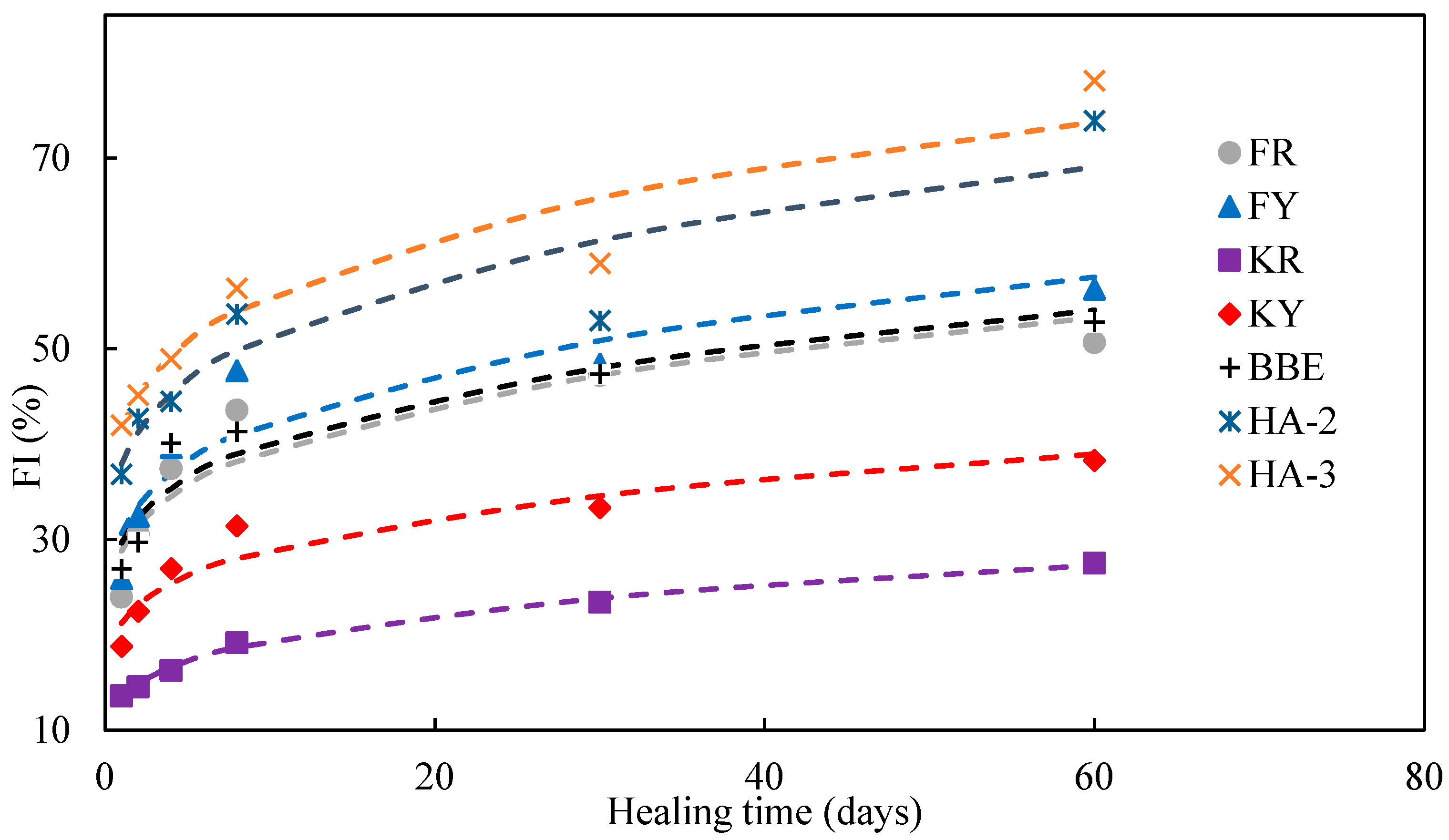
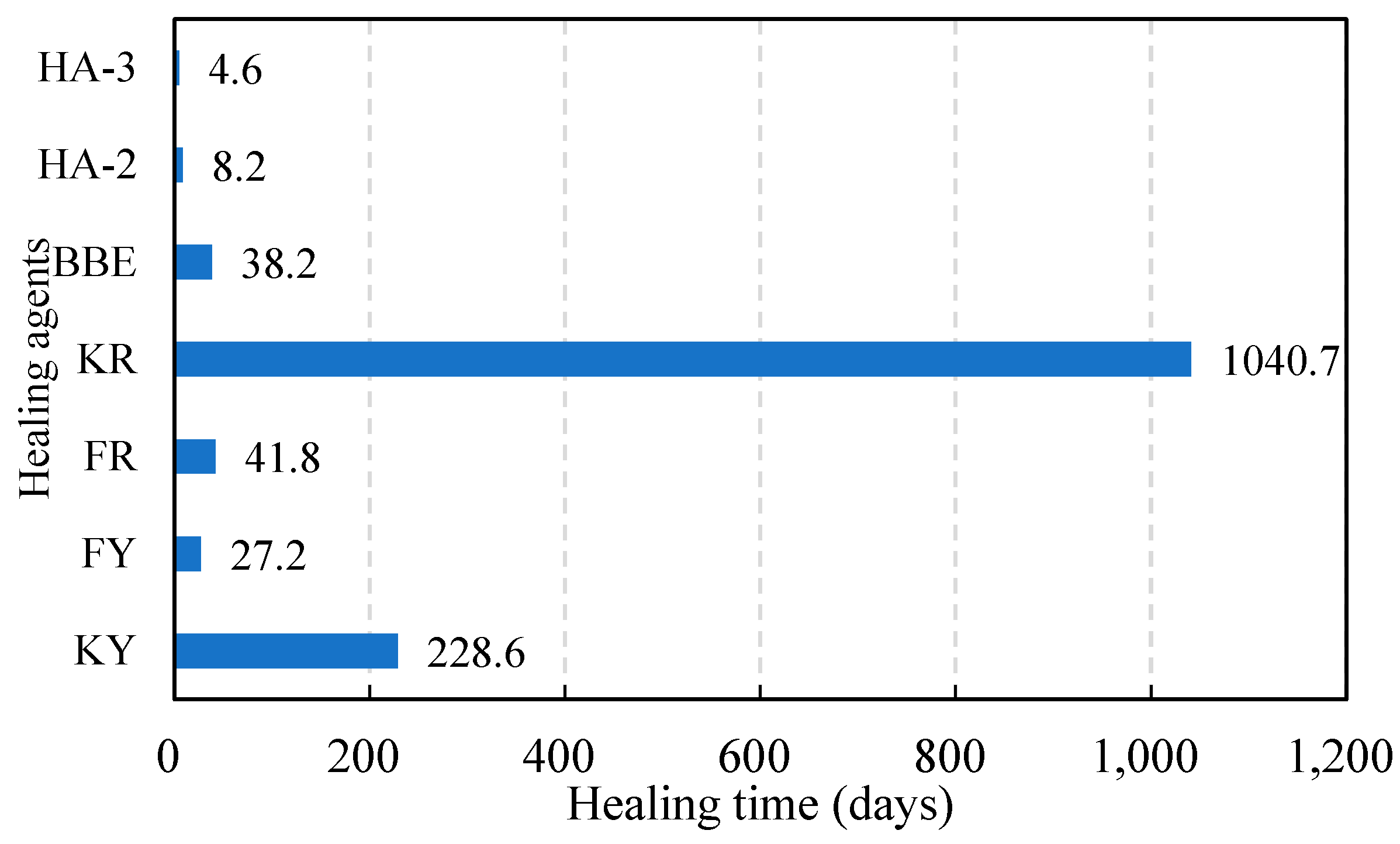
3.7. Modelling of Healing Development
4. Conclusions
- Asphalt could have high self-healing ability even after subjecting to long-term aging. The crack healing of asphalt can be well improved by using oil agents but not emulsion agents.
- The healing ability for cracked asphalt mortar without any healing agents was low. The application of healing agent could significantly promote the crack healing. The strength recovery could well distinguish the healing ability of mortar cracks.
- The crack healing of asphalt and its mortar strongly depended on the type of agent used and the dependency was not in agreement with each other, indicating the difference of healing mechanisms of these two materials. Asphalt was much easier to heal compared with its mortar. The diffusion, softening, and reconstitution effects of the healing agent were important for crack healing.
- The healing development of mortar crack can be divided into the initial phase of rapid increase and a steady state. The diffusion and softening effects due to the application of the healing agent contributed to the initial low strength recovery. Long-term healing benefited the bonding reconstitution in the cracks and, thus, improved the final strength.
- Results on the fracture surfaces indicated that the behavior of crack healing was similar to asphalt rejuvenation. Therefore, it could provide a way to optimize the components of healing agent to achieve maximum strength recovery to resist crack, as well as sufficient re-healing ability to deal with crack opening and closing.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflicts of Interest
References
- JTG D20-2017 Standard of Highway Asphalt Pavement Design; People’s Republic of China Communication Press: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Sol-Sánchez, M.; Fiume, A.; Moreno-Navarro, F.; Rubio-Gámez, M.C. Analysis of fatigue cracking of warm mix asphalt. influence of the manufacturing technology. Int. J. Fatigue 2018, 110, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Li, L.; Li, P.; Saboundjian, S. Low temperature cracking analysis of asphalt binders and mixtures. Cold Reg. Sci. Technol. 2017, 141, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Luo, H.; Zhu, H. The feasibility of continuous construction of the base and asphalt layers of asphalt pavement to solve the problem of reflective cracks. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 119, 80–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kakar, M.R.; Hamzah, M.O.; Valentin, J. A review on moisture damages of hot and warm mix asphalt and related investigations. J. Clean. Prod. 2015, 99, 39–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Van de Ven, M.F.C.; Wu, S.; Molenaar, A. Investigating self-healing behavior of pure bitumen using dynamic shear rheometer. Fuel 2011, 90, 2710–2720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.; Van de Ven, M.F.C.; Molenaar, A. Crack-healing investigation in bituminous materials. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2013, 25, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sun, G.; Zhu, X.; Pang, Q.; Yu, F.; Lin, T. Identification of wetting and molecular diffusion stages during self-healing process of asphalt binder via fluorescence microscope. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 132, 230–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Q.; Huang, W.; Xiao, F. Laboratory evaluation of self-healing properties of various modified asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 136, 192–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Storey, L.; Schlangene, E. Self-healing properties of recycled asphalt mixtures containing metal waste: An approach through microwave radiation heating. J. Environ. Manag. 2018, 214, 242–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- García, Á.; Schlangen, E.; Van de Ven, M. Properties of capsules containing rejuvenators for their use in asphalt concrete. Fuel 2011, 90, 583–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pamulapati, Y.; Elseifi, M.A.; Cooper, S.B.; Mohammad, L.N.; Elbagalati, O. Evaluation of self-healing of asphalt concrete through induction heating and metallic fibers. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 146, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Micaelo, R.; Garcia, A. Self-healing of asphalt mastic by the action of polymeric capsules containing rejuvenators. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 330–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Mansoori, T.; Micaelo, R.; Artamendi, I.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Garcia, A. Microcapsules for self-healing of asphalt mixture without compromising mechanical performance. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 155, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ba, H.D.; Park, D.W.; Le, T.H.M. Effect of rejuvenators on the crack healing performance of recycled asphalt pavement by induction heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 164, 246–254. [Google Scholar]
- Apostolidis, P.; Liu, X.; Scarpas, A.; Kasbergen, C.; van de Ven, M.F.C. Advanced evaluation of asphalt mortar for induction healing purposes. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 126, 9–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Yalcin, E.; Garcia, A.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Yilmaz, M.; Hudson-Griffiths, R. Effect of mixing and ageing on the mechanical and self-healing properties of asphalt mixtures containing polymeric capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 175, 254–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, Q.; Wang, Z.; Hasan, M.R.M. Investigation of induction healing effects on electrically conductive asphalt mastic and asphalt concrete beams through fracture-healing tests. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 49, 729–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallego, J.; del Val, M.A.; Contreras, V.; Paez, A. Heating asphalt mixtures with microwaves to promote self-healing. Constr. Build. Mater. 2013, 42, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vila-Cortavitarte, M.; Jato-Espino, D.; Castro-Fresno, D.; Calzada-Pérez, M.Á. Self-healing capacity of asphalt mixtures including by-products both as aggregates and heating inductors. Materials 2018, 11, 800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.M.; Jahanbakhsh, H.; Jahangiri, B.; Nejad, F.M. Induced heating-healing characterization of activated carbon modified asphalt concrete under microwave radiation. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 178, 254–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Wu, S.; Liu, Q.; Zeng, W.; Chen, Z.; Ye, Q.; Pan, P. Self-healing performance of asphalt mixtures through heating fibers or aggregate. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 150, 673–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Norambuena-Contreras, J.; Storey, L.; Schlangen, E. Effect of RAP and fibers addition on asphalt mixtures with self-healing properties gained by microwave radiation heating. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 159, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, A.; Jelfs, J.; Austin, C.J. Internal asphalt mixture rejuvenation using capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 101, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Micaelo, R.; Al-Mansoori, T.; Garcia, A. Study of the mechanical properties and self-healing ability of asphalt mixture containing calcium-alginate capsules. Constr. Build. Mater. 2016, 123, 734–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tabaković, A.; Liu, X.; Schlangen, E. Calcium alginate capsules encapsulating rejuvenator as healing system for asphalt mastic. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 379–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, B.; Wang, H.; Pei, J.; Li, R.; Zhang, J.; Fan, Z. Study on self-healing microcapsule containing rejuvenator for asphalt. Constr. Build. Mater. 2017, 135, 641–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Hong, J.; Huang, C.; Liu, J.; Wu, S. Effectiveness of rejuvenator seal materials on performance of asphalt pavement. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 55, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riara, M.; Tang, P.; Mo, L.; Javilla, B.; Wu, S. Investigation into crack healing of asphalt mixtures using healing agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 161, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Xiao, Y.; Wu, S.; Pan, P. The rejuvenating effect in hot asphalt recycling by mortar transfer ratio and image analysis. Materials 2017, 10, 574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- ASTM D6521-18 Standard Practice for Accelerated Aging of Asphalt Binder Using a Pressurized Aging Vessel (PAV); ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2018.
- Kuang, D.; Jiao, Y.; Ye, Z.; Lu, Z.; Chen, H.; Yu, J.; Liu, N. Diffusibility enhancement of rejuvenator by epoxidized soybean oil and its influence on the performance of recycled hot mix asphalt mixtures. Materials 2018, 11, 833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, M.; Wu, S.; Liu, J.; Amirkhanian, S. Analysis of the relationships between waste cooking oil qualities and rejuvenated asphalt properties. Materials 2017, 10, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qu, X.; Liu, Q.; Wang, C.; Wang, D.; Oeser, M. Effect of co-Production of renewable biomaterials on the performance of asphalt binder in macro and micro perspectives. Materials 2018, 11, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaumanis, M.; Mallick, R.B.; Poulikakos, L.; Frank, R. Influence of six rejuvenators on the performance properties of reclaimed asphalt pavement (RAP) binder and 100% recycled asphalt mixtures. Constr. Build. Mater. 2014, 71, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, T.; Huang, X.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, Y. Evaluation of the diffusion and distribution of the rejuvenator for hot asphalt recycling. Constr. Build. Mater. 2015, 98, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2140-08 Standard Practice for Calculating Carbon-Type Composition of Insulating Oils of Petroleum Origin; ASTM International: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- JTG F40-2004 Technical Specification for Construction of Highway Asphalt Pavements; People’s Republic of China Ministry of Transport: Beijing, China, 2004.
- Dunn, K.; Chilingarian, G.V.; Lian, H.; Wang, Y.; Yen, T.F. Analysis of asphalt and its components by thin-layer chromatography. In Asphaltenes and Asphalts, 2nd ed.; Yen, T.F., Chilingarian, G.V., Eds.; Elsevier Science: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2000; Volume 40B, pp. 305–317. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, P. Effect of Crack Healing of Bituminous Mortar and Concrete with Healing Agents. Master’s Thesis, Wuhan University of Technology, Wuhan, China, May 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Riara, M.; Tang, P.; Mo, L.; Hong, W.; Chen, M.; Wu, S. Evaluation of moisture and temperature effect on crack healing of asphalt mortar and mixtures using healing agents. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 177, 388–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AASHTO TP105 Standard Method of Test for Determining the Fracture Energy of Asphalt Mixtures Using the Semicircular Bend Geometry (SCB); AASHTO: Washington, DC, USA, 2015.
- Guo, M. Study on Mechanism and Multiscale Evaluation Method of Interfacial Interaction between Asphalt Binder and Mineral Aggregate. Ph.D. Thesis, Harbin Institute of Technology, Harbin, China, December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wool, R.P.; O’Connor, K.M. A theory crack healing in polymers. J. Appl. Phys. 1981, 52, 5953–5963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Sieve Size (mm) | Upper Limitation (%) | Lower Limitation (%) | Passing Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 4.75 | 100 | 100 | 100 |
| 2.36 | 100 | 48 | 66.8 |
| 1.18 | 76 | 30 | 50.2 |
| 0.6 | 56 | 20 | 32.8 |
| 0.3 | 40 | 14 | 22.5 |
| 0.15 | 30 | 10 | 14.5 |
| 0.075 | 16 | 8 | 9.6 |
| Healing Agents | Chemical Composition (%) | Viscosity | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Saturates | Aromatics | Resins | Asphaltenes | Residue at 60 °C (Pa s) | Emulsion at 25 °C (cp) | |
| KY | 1.5 | 86.3 | 10.0 | 2.2 | 0.5–5 | – |
| FY | 7.3 | 84.5 | 3.3 | 4.9 | 30–50 | – |
| KR | 1.5 | 86.3 | 10.0 | 2.2 | 0.5–5 | 30–50 |
| FR | 7.3 | 84.5 | 3.3 | 4.9 | 30–50 | 40–60 |
| HA-2 | 18.1 | 48.6 | 22.2 | 11.1 | 140–160 | 50–70 |
| HA-3 | 12.2 | 70.1 | 11.2 | 6.5 | 100–120 | 45–65 |
| BBE | 14.1 | 29.6 | 43.5 | 12.8 | 210–230 | 150–170 |
| Healing Agents | Healing Time (days) | Strength (kN) | Stiffness (N/mm) | Fracture Energy (J/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Blank (pure asphalt) | Initial | 3.15 | 9.47 | 4.35 |
| 1 | 0.18 | 0.80 | 0.09 | |
| 2 | 0.23 | 0.93 | 0.11 | |
| 4 | 0.38 | 2.87 | 0.18 | |
| 8 | 0.44 | 2.99 | 0.27 | |
| KY oil | Initial | 3.27 | 9.34 | 3.90 |
| 1 | 0.62 | 5.92 | 0.56 | |
| 2 | 0.74 | 6.39 | 0.67 | |
| 4 | 0.88 | 7.06 | 0.69 | |
| 8 | 1.03 | 6.87 | 0.81 | |
| FY oil | Initial | 2.92 | 11.81 | 3.97 |
| 1 | 0.76 | 4.83 | 0.56 | |
| 2 | 0.95 | 6.91 | 0.63 | |
| 4 | 1.16 | 7.58 | 0.70 | |
| 8 | 1.39 | 5.34 | 0.87 | |
| KR emulsion | Initial | 3.41 | 8.90 | 4.55 |
| 1 | 0.46 | 2.65 | 0.27 | |
| 2 | 0.50 | 2.99 | 0.30 | |
| 4 | 0.55 | 2.37 | 0.44 | |
| 8 | 0.65 | 3.08 | 0.57 | |
| FR emulsion | Initial | 2.74 | 9.26 | 3.63 |
| 1 | 0.66 | 3.11 | 0.60 | |
| 2 | 0.84 | 5.52 | 0.59 | |
| 4 | 1.02 | 7.43 | 0.70 | |
| 8 | 1.19 | 5.21 | 0.76 |
| Healing Agents | Healing Time (days) | Strength (kN) | Stiffness (N/mm) | Fracture Energy (J/m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBE emulsion | Initial | 3.20 | 9.19 | 4.21 |
| 1 | 0.86 | 7.82 | 0.36 | |
| 2 | 0.95 | 7.30 | 0.45 | |
| 4 | 1.28 | 9.93 | 0.51 | |
| 8 | 1.32 | 5.85 | 0.87 | |
| HA-2 emulsion | Initial | 2.99 | 6.67 | 3.86 |
| 1 | 1.10 | 3.66 | 0.45 | |
| 2 | 1.28 | 2.94 | 0.45 | |
| 4 | 1.33 | 8.86 | 1.11 | |
| 8 | 1.60 | 8.63 | 1.00 | |
| HA-3 emulsion | Initial | 3.16 | 8.85 | 4.20 |
| 1 | 1.33 | 3.90 | 0.49 | |
| 2 | 1.43 | 8.87 | 0.54 | |
| 4 | 1.55 | 6.04 | 1.03 | |
| 8 | 1.78 | 7.45 | 1.10 |
| Healing Agents | A | B | A − B | t0 | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| KR | 22.7 | 17.1 | 5.5 | 30.4 | 0.94 |
| KY | 30.9 | 15.3 | 15.6 | 14.4 | 0.99 |
| FR | 32.0 | 15.4 | 16.6 | 30.3 | 0.89 |
| FY | 45.5 | 30.0 | 15.5 | 54.9 | 0.94 |
| BBE | 35.8 | 26.7 | 9.0 | 33.2 | 0.91 |
| HA-2 | 66.0 | 55.5 | 10.5 | 43.4 | 0.92 |
| HA-3 | 51.0 | 40.0 | 10.0 | 24.3 | 0.90 |
| Healing Agents | Fitting Function | Correlation Coefficients |
|---|---|---|
| KY | R2 = 0.91 | |
| FY | R2 = 0.87 | |
| FR | R2 = 0.87 | |
| KR | R2 = 0.99 | |
| BBE | R2 = 0.91 | |
| HA-2 | R2 = 0.87 | |
| HA-3 | R2 = 0.92 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pan, C.; Tang, P.; Riara, M.; Mo, L.; Li, M.; Guo, M. Effect of Healing Agents on Crack Healing of Asphalt and Asphalt Mortar. Materials 2018, 11, 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081373
Pan C, Tang P, Riara M, Mo L, Li M, Guo M. Effect of Healing Agents on Crack Healing of Asphalt and Asphalt Mortar. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081373
Chicago/Turabian StylePan, Changluan, Ping Tang, Martin Riara, Liantong Mo, Mingliang Li, and Meng Guo. 2018. "Effect of Healing Agents on Crack Healing of Asphalt and Asphalt Mortar" Materials 11, no. 8: 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081373
APA StylePan, C., Tang, P., Riara, M., Mo, L., Li, M., & Guo, M. (2018). Effect of Healing Agents on Crack Healing of Asphalt and Asphalt Mortar. Materials, 11(8), 1373. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081373






