Effect of Annealing Temperature on ECD Grown Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Sample Preparation and Methodology
2.1. Materials
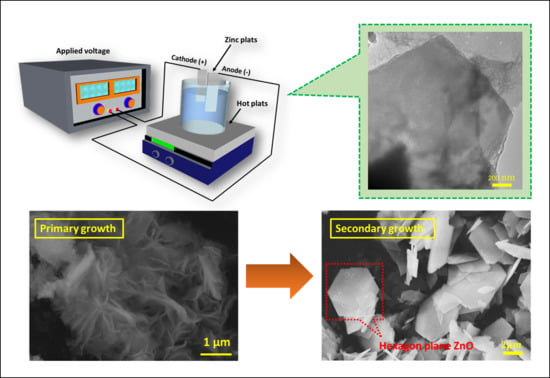
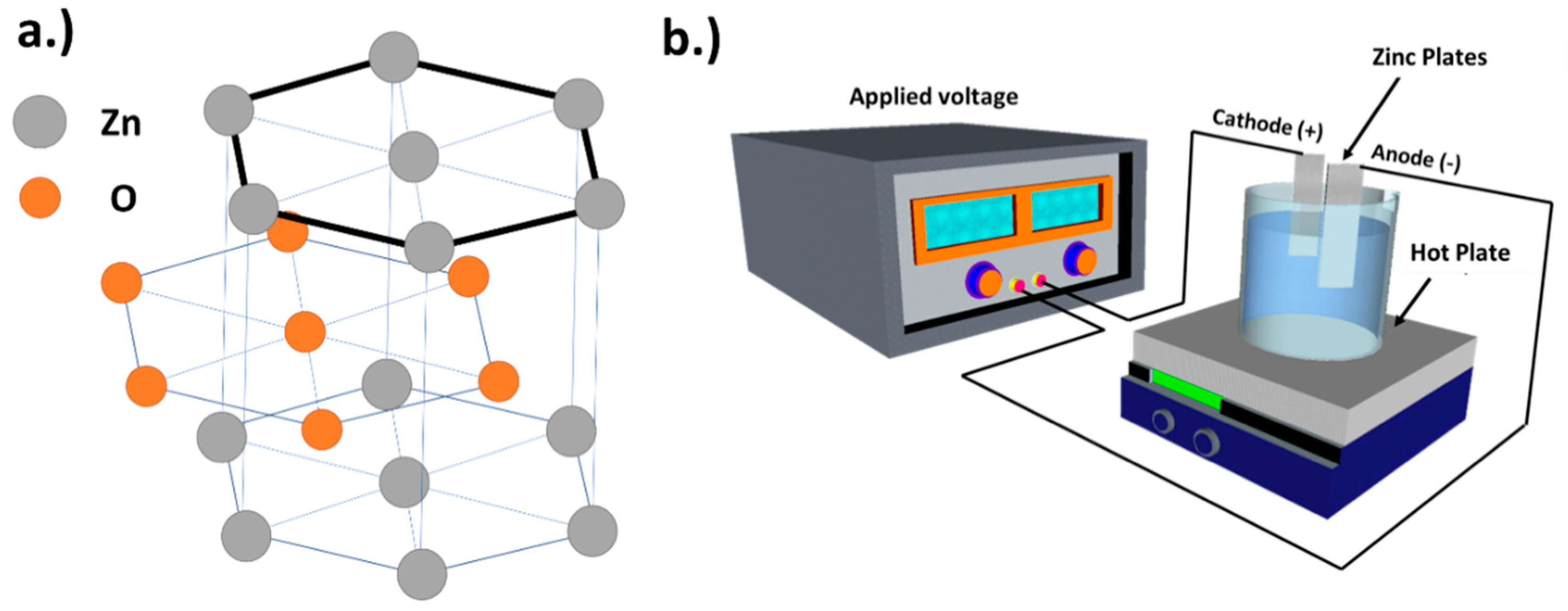
2.2. Preparation of Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide Via Electrochemical Deposition
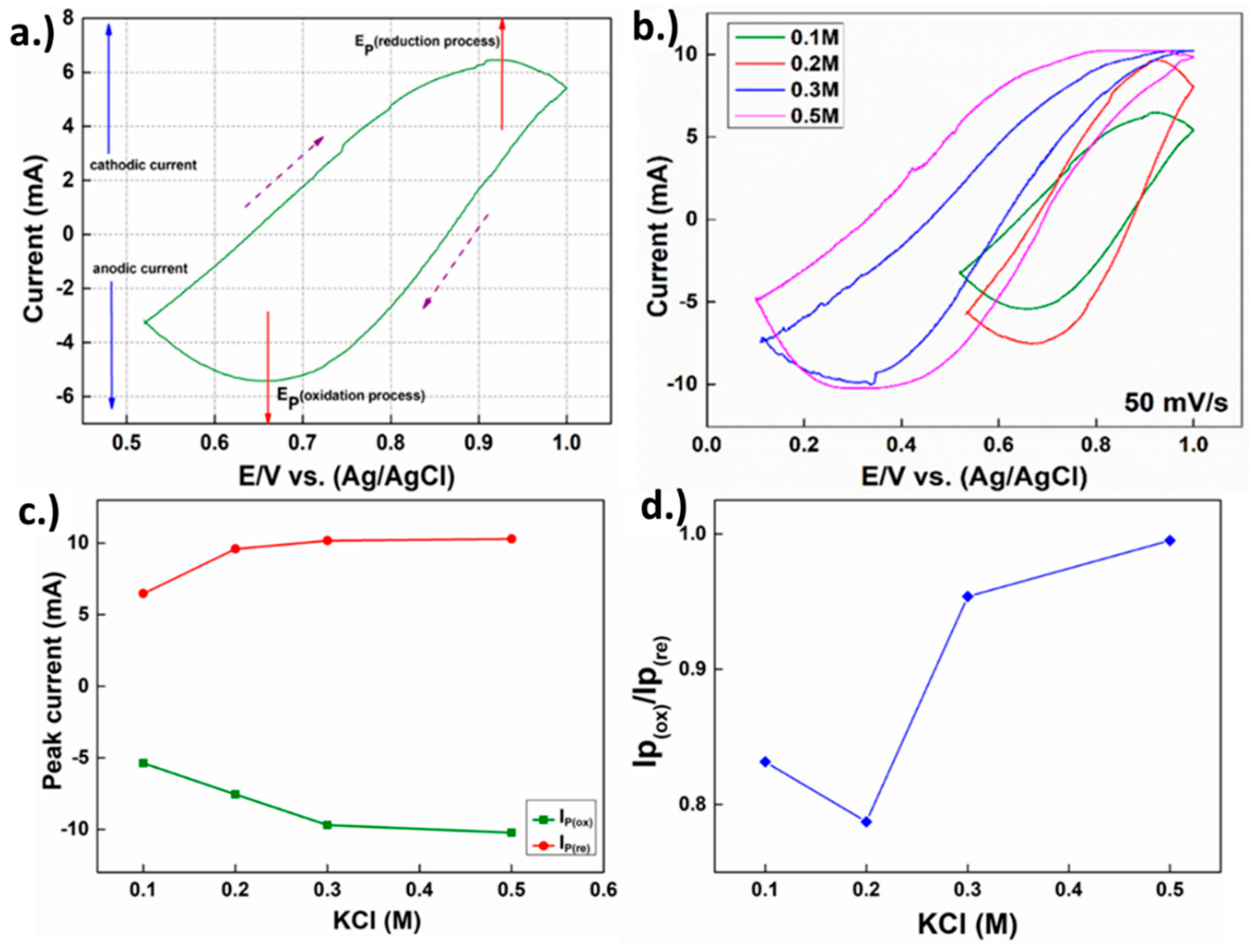
2.3. Characterization and Analysis of the Obtained Materials
3. Growth Mechanism Discussions and Further Annealing
3.1. The Primary ZnO Growth
3.2. The Secondary Growth
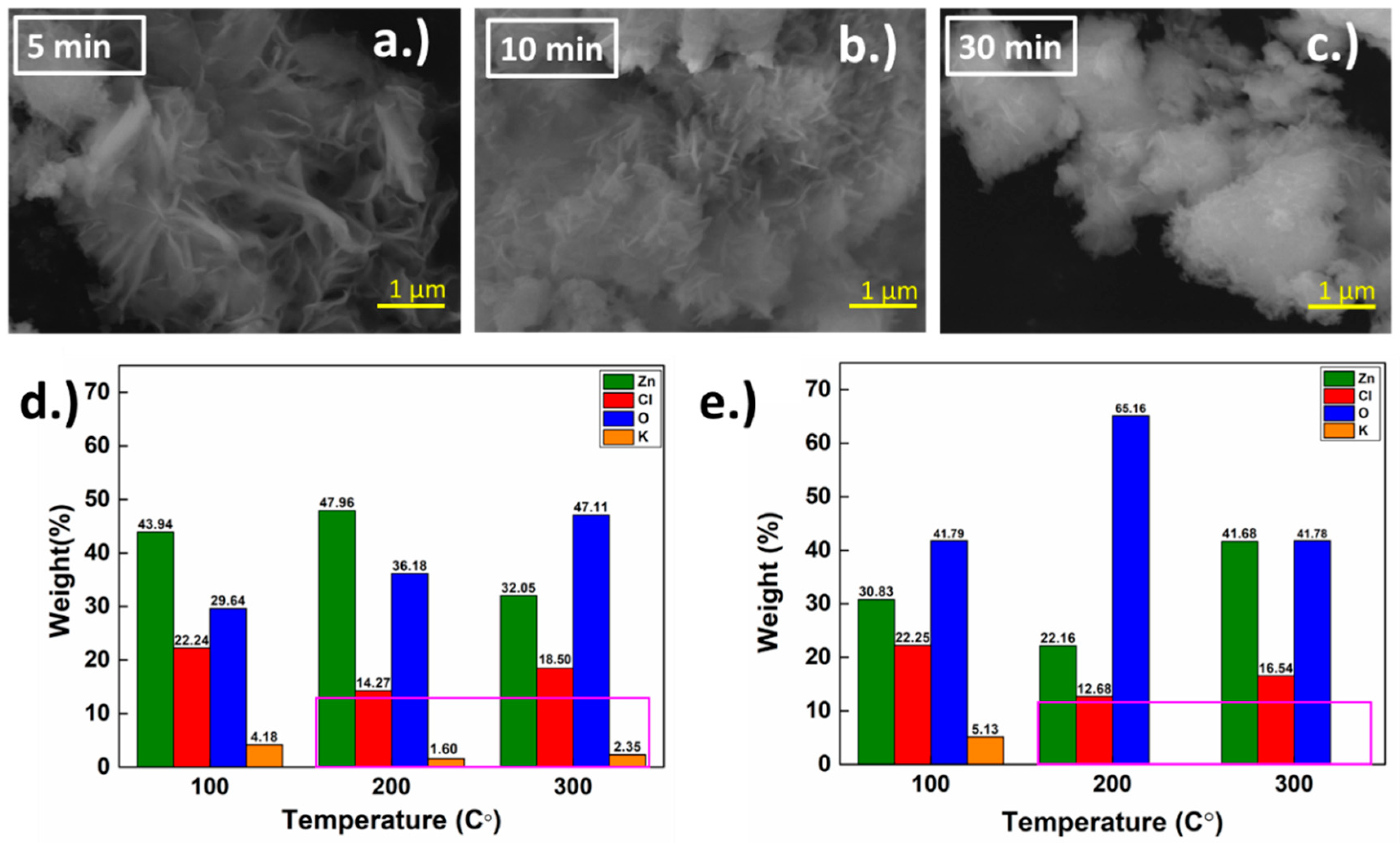
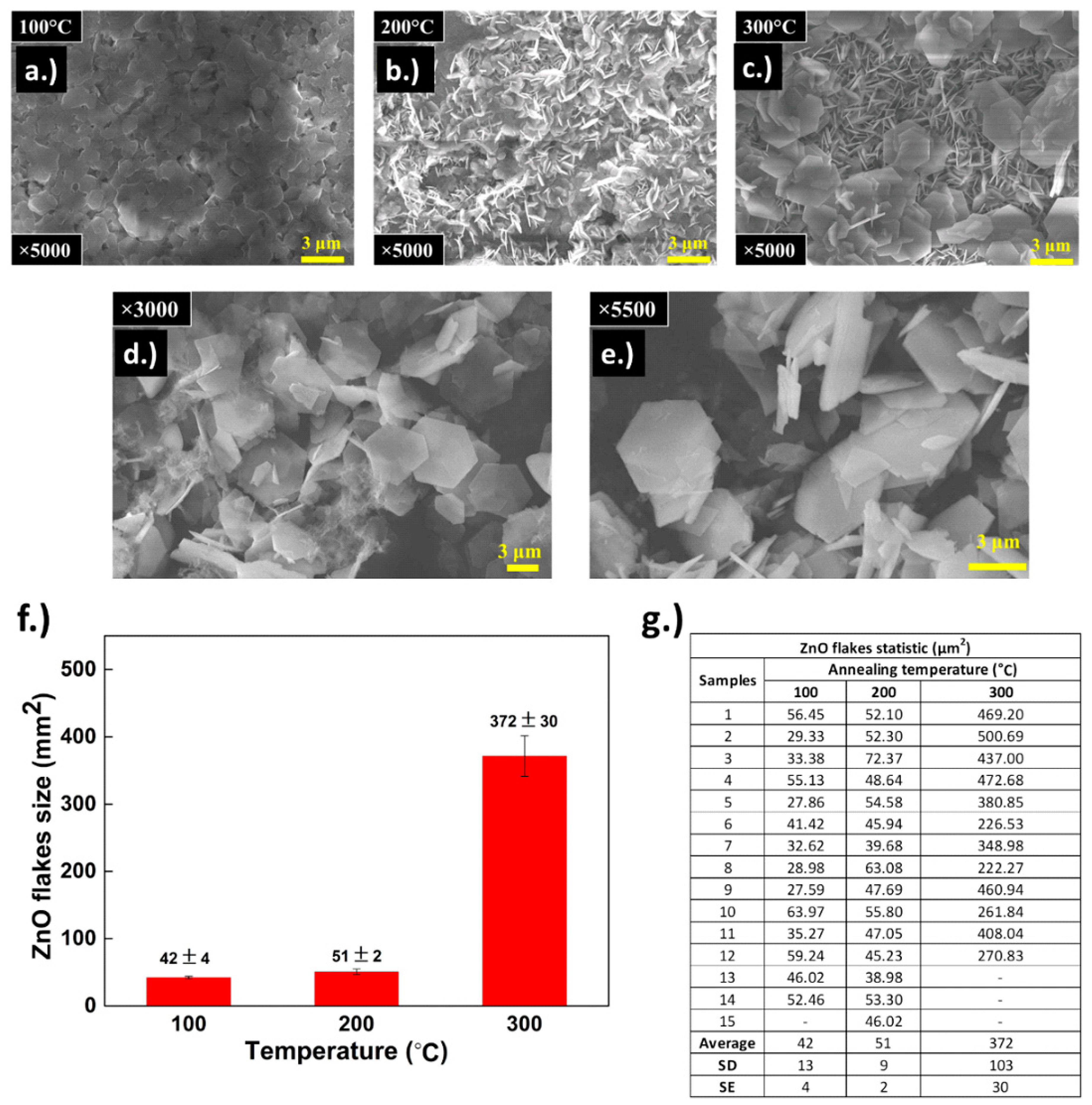
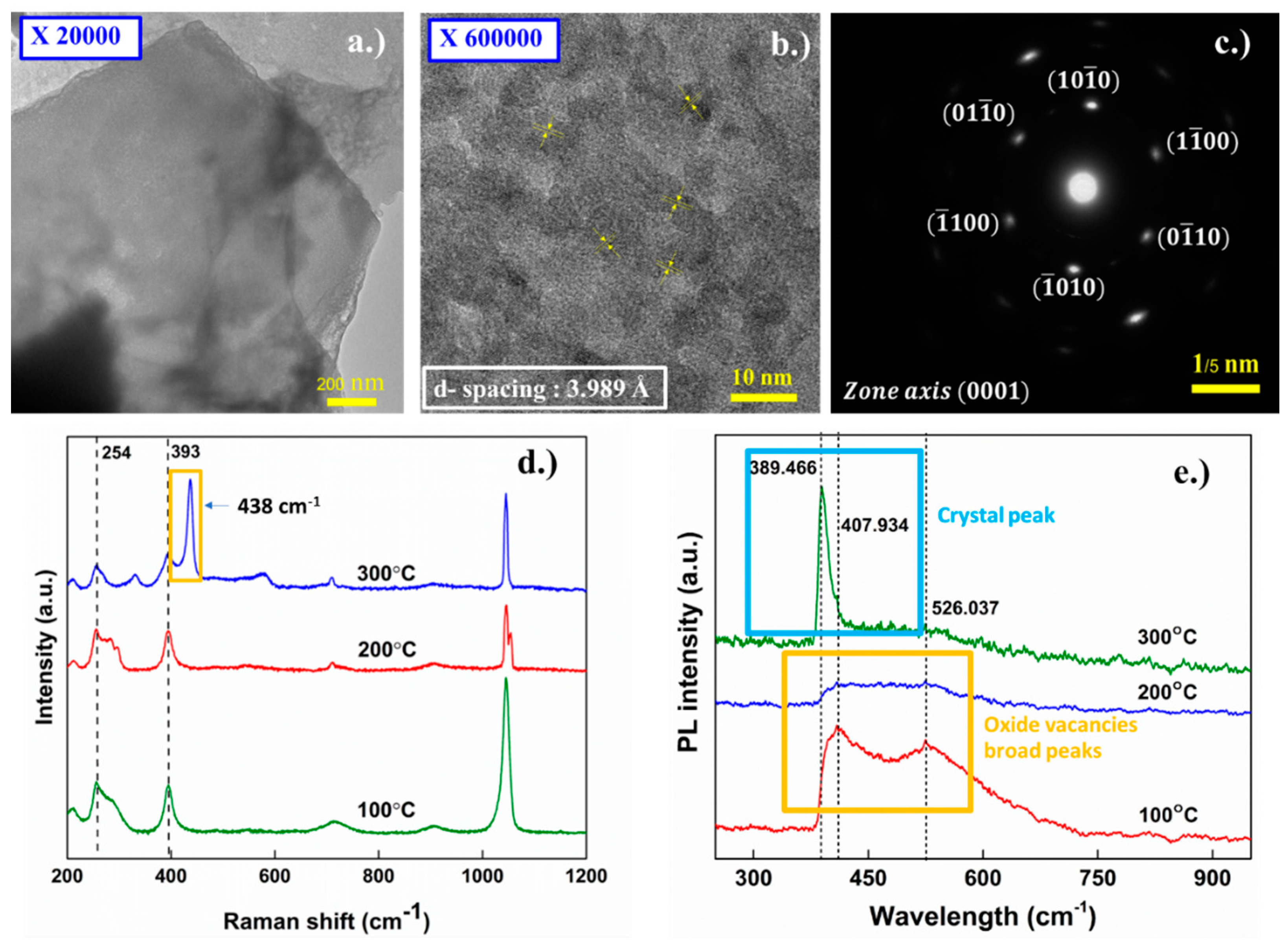
3.3. Annealing of Grown h-ZnO Nanoflakes
3.4. Post-Annealing Characterization
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, J.; Guo, C.; Li, C.M.; Li, Y.; Chi, Q.; Huang, X.; Liao, L.; Yu, T. Carbon-decorated ZnO nanowire array: A novel platform for direct electrochemistry of enzymes and biosensing applications. Electrochem. Commun. 2009, 11, 202–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Mao, S.; Feick, H.; Yan, H.; Wu, Y.; Kind, H.; Weber, E.; Russo, R.; Yang, P. Room-Temperature Ultraviolet Nanowire Nanolasers. Science 2001, 292, 1897–1899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levinson, L.; Philipp, H. ZnO Varistors for Transient Protection. IEEE Trans. Parts Hybrids Packag. 1977, 13, 338–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, H.; Friedrich, M.; Armbrüster, M.; Klötzer, B.; Penner, S. ZnO is a CO2-selective steam reforming catalyst. J. Catal. 2013, 297, 151–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Djurišić, A.B.; Ng, A.M.C.; Chen, X.Y. ZnO nanostructures for optoelectronics: Material properties and device applications. Prog. Quantum Electron. 2010, 34, 191–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, M.S.; Olson, D.C.; Shaheen, S.E.; Kopidakis, N.; Ginley, D.S. Inverted bulk-heterojunction organic photovoltaic device using a solution-derived ZnO underlayer. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 143517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravirajan, P.; Peiró, A.M.; Nazeeruddin, M.K.; Graetzel, M.; Bradley, D.D.C.; Durrant, J.R.; Nelson, J. Hybrid Polymer/Zinc Oxide Photovoltaic Devices with Vertically Oriented ZnO Nanorods and an Amphiphilic Molecular Interface Layer. J. Phys. Chem. B 2006, 110, 7635–7639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.C.; Piris, J.; Collins, R.T.; Shaheen, S.E.; Ginley, D.S. Hybrid photovoltaic devices of polymer and ZnO nanofiber composites. Thin Solid Films 2006, 496, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izaki, M.; Shinagawa, T.; Mizuno, K.-T.; Ida, Y.; Inaba, M.; Tasaka, A. Electrochemically constructed p-Cu 2 O/n-ZnO heterojunction diode for photovoltaic device. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 3326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrier, J.; Demchenko, D.O.; Lin, W.; Alivisatos, A.P. Optical Properties of ZnO/ZnS and ZnO/ZnTe Heterostructures for Photovoltaic Applications. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2377–2382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takanezawa, K.; Hirota, K.; Wei, Q.-S.; Tajima, K.; Hashimoto, K. Efficient Charge Collection with ZnO Nanorod Array in Hybrid Photovoltaic Devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 7218–7223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leschkies, K.S.; Divakar, R.; Basu, J.; Enache-Pommer, E.; Boercker, J.E.; Carter, C.B.; Kortshagen, U.R.; Norris, D.J.; Aydil, E.S. Photosensitization of ZnO Nanowires with CdSe Quantum Dots for Photovoltaic Devices. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 1793–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olson, D.C.; Lee, Y.-J.; White, M.S.; Kopidakis, N.; Shaheen, S.E.; Ginley, D.S.; Voigt, J.A.; Hsu, J.W.P. Effect of Polymer Processing on the Performance of Poly(3-hexylthiophene)/ZnO Nanorod Photovoltaic Devices. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16640–16645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Z.; Wang, D.; Chang, P.-C.; Tseng, W.-Y.; Lu, J.G. ZnO nanowire field-effect transistor and oxygen sensing property. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 85, 5923–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.C.; Yu, D.P.; Zhang, B.; Fang, W.; Feng, S.Q. Ultraviolet-emitting ZnO nanowires synthesized by a physical vapor deposition approach. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2001, 78, 407–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, L.E.; Law, M.; Tan, D.H.; Montano, M.; Goldberger, J.; Somorjai, G.; Yang, P. General Route to Vertical ZnO Nanowire Arrays Using Textured ZnO Seeds. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 1231–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lorenz, M.; Kaidashev, E.M.; Rahm, A.; Nobis, T.; Lenzner, J.; Wagner, G.; Spemann, D.; Hochmuth, H.; Grundmann, M. MgxZn1−xO(0⩽x<0.2) nanowire arrays on sapphire grown by high-pressure pulsed-laser deposition. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2005, 86, 143113. [Google Scholar]
- Cao, B.Q.; Lorenz, M.; Rahm, A.; Von Wenckstern, H.; Czekalla, C.; Lenzner, J.; Benndorf, G.; Grundmann, M. Phosphorus acceptor doped ZnO nanowires prepared by pulsed-laser deposition. Nanotechnology 2007, 18, 455707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baruah, S.; Dutta, J. Hydrothermal growth of ZnO nanostructures. Sci. Technol. Adv. Mater. 2009, 10, 013001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; George Ndifor-Angwafor, N.; Jason Riley, D.; Ashfold, M.N.R. Synthesis and photoluminescence of ultra-thin ZnO nanowire/nanotube arrays formed by hydrothermal growth. Chem. Phys. Lett. 2006, 431, 352–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.D.; Chan, Y.F.; Wang, N. Formation of ZnO nanostructures by a simple way of thermal evaporation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2002, 81, 757–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.H.; Wu, Y.; Feick, H.; Tran, N.; Weber, E.; Yang, P. Catalytic Growth of Zinc Oxide Nanowires by Vapor Transport. Adv. Mater. 2001, 13, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, S.C.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, C.J.; Ruh, H.; Lee, H.J. Low-Temperature Growth of ZnO Nanowire Array by a Simple Physical Vapor-Deposition Method. Chem. Mater. 2003, 15, 3294–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thepnurat, M.; Chairuangsri, T.; Hongsith, N.; Ruankham, P.; Choopun, S. Realization of Interlinked ZnO Tetrapod Networks for UV Sensor and Room-Temperature Gas Sensor. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 24177–24184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.S.; Venkateswarlu, P.; Rao, V.R.; Rao, G.N. Synthesis, characterization and optical properties of zinc oxide nanoparticles. Int. Nano Lett. 2013, 3, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.-H.; Oh, E.; Lee, K.-H.; Yang, Y.; Park, C.G.; Park, W.; Jeong, S.-H. Sonochemical Preparation of Shape-Selective ZnO Nanostructures. Cryst. Growth Des. 2008, 8, 265–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Li, Q.; Wang, T. Sonochemical Synthesis, Optical Properties, and Electrical Properties of Core/Shell-Type ZnO Nanorod/CdS Nanoparticle Composites. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 887–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Chen, Q.; Xu, D. Hierarchical ZnO Nanostructures Obtained by Electrodeposition. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 11560–11565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tena-Zaera, R.; Elias, J.; Wang, G.; Lévy-Clément, C. Role of Chloride Ions on Electrochemical Deposition of ZnO Nanowire Arrays from O2 Reduction. J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 16706–16711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Kumar, M.; Ando, Y.; Leung, K.T. One-Dimensional and Two-Dimensional ZnO Nanostructured Materials on a Plastic Substrate and Their Field Emission Properties. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 7093–7096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, S.; Lévy-Clément, C.; Ivanova, V. Electrochemical Deposition of ZnO Thin Films and Nanowires for Photovoltaic Applications. J. Electrochem. Soc. 2012, 159, D705–D712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novoselov, K.S.; Geim, A.K.; Morozov, S.V.; Jiang, D.; Katsnelson, M.I.; Grigorieva, I.V.; Dubonos, S.V.; Firsov, A.A. Two-dimensional gas of massless Dirac fermions in graphene. Nature 2005, 438, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pradhan, D.; Leung, K.T. Vertical Growth of Two-Dimensional Zinc Oxide Nanostructures on ITO-Coated Glass: Effects of Deposition Temperature and Deposition Time. J. Phys. Chem. C 2008, 112, 1357–1364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Kumar, M.; Ando, Y.; Leung, K.T. Fabrication of ZnO Nanospikes and Nanopillars on ITO Glass by Templateless Seed-Layer-Free Electrodeposition and Their Field-Emission Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2009, 1, 789–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tusche, C.; Meyerheim, H.L.; Kirschner, J. Observation of Depolarized ZnO(0001) Monolayers: Formation of Unreconstructed Planar Sheets. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2007, 99, 026102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonardi, S.G. Two-Dimensional Zinc Oxide Nanostructures for Gas Sensor Applications. Chemosensors 2017, 5, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.-W.; Hong, Y.-Y.; Lin, Z.-D.; Liu, L.-M.; Zhang, X.-W. Enhanced formaldehyde gas sensing properties of ZnO nanosheets modified with graphene. Electron. Mater. Lett. 2017, 13, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-M.; Lin, K.-F.; Hsu, H.-C.; Hsieh, W.-F. Size dependence of photoluminescence and resonant Raman scattering from ZnO quantum dots. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 261909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-H.; Yue, L.-J.; Gong, F.-L.; Li, F.; Zhang, H.-L.; Chen, J.-L. Highly enhanced H2S gas sensing and magnetic performances of metal doped hexagonal ZnO monolayer. Vacuum 2017, 141, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Zhao, Y.; Lu, N.; Kan, E.; Zeng, X.C.; Wu, X.; Yang, J. Tunable Magnetism in a Nonmetal-Substituted ZnO Monolayer: A First-Principles Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 11336–11342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illy, B.; Shollock, B.A.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L.; Ryan, M.P. Electrochemical growth of ZnO nanoplates. Nanotechnology 2005, 16, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, Y.; Zou, X.P.; Meng, X.M.; Teng, G.Q. 2-D ZnO Nanostructures on Aluminum by Solution Method. Adv. Mater. Res. 2010, 123–125, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kissinger, P.T.; Heineman, W.R. Cyclic voltammetry. J. Chem. Educ. 1983, 60, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walsh, F.C.; Herron, M.E. Electrocrystallization and electrochemical control of crystal growth: Fundamental considerations and electrodeposition of metals. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 1991, 24, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambali, N.A.; Hashim, A.M. Synthesis of Zinc Oxide Nanostructures on Graphene/Glass Substrate via Electrochemical Deposition: Effects of Potassium Chloride and Hexamethylenetetramine as Supporting Reagents. Nano-Micro Lett. 2015, 7, 317–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hambali, N.; Yahaya, H.; Mahmood, M.; Terasako, T.; Hashim, A. Synthesis of zinc oxide nanostructures on graphene/glass substrate by electrochemical deposition: Effects of current density and temperature. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.S.; Nishiyama, T.; Rusli, N.I.; Mahmood, M.R.; Yasui, K.; Hashim, A.M. Seedless growth of zinc oxide flower-shaped structures on multilayer graphene by electrochemical deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, N.S.; Mahmood, M.R.; Yasui, K.; Hashim, A.M. Seed/catalyst-free vertical growth of high-density electrodeposited zinc oxide nanostructures on a single-layer graphene. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2014, 9, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownson, D.A.C.; Banks, C.E. Interpreting Electrochemistry. In The Handbook of Graphene Electrochemistry; Springer: London, UK, 2014; pp. 23–77. [Google Scholar]
- Illy, B.N.; Ingham, B.; Ryan, M.P. Effect of Supersaturation on the Growth of Zinc Oxide Nanostructured Films by Electrochemical Deposition. Cryst. Growth Des. 2010, 10, 1189–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.Y.; No, Y.S.; Kim, J.Y.; Kim, T.W. Effect of Potassium Chloride Concentration on the Structural and Optical Properties of ZnO Nanorods Grown on Glass Substrates Coated with Indium Tin Oxide Film. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 51, 06FG13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pradhan, D.; Sindhwani, S.; Leung, K.T. Parametric Study on Dimensional Control of ZnO Nanowalls and Nanowires by Electrochemical Deposition. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 5, 1727–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salih, E.; Mekawy, M.; Hassan, R.Y.A.; El-Sherbiny, I.M. Synthesis, characterization and electrochemical-sensor applications of zinc oxide/graphene oxide nanocomposite. J. Nanostruct. Chem. 2016, 6, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruth, M.; Meier, C. Scaling coefficient for three-dimensional grain coalescence of ZnO on Si(111). Phys. Rev. B 2012, 86, 224108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Phillips, M.R.; Ton-That, C. Coalescence of ZnO nanowires grown from monodisperse Au nanoparticles. CrystEngComm 2015, 17, 4987–4991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, J.S.; Lee, J.Y.; Cho, J.H.; Suh, H.J.; Lee, C.J. Single-Crystalline ZnO Microtubes Formed by Coalescence of ZnO Nanowires Using a Simple Metal-Vapor Deposition Method. Chem. Mater. 2005, 17, 2752–2756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Shen, Z.; Liu, J.; Kerisit, S.N.; Bowden, M.E.; Sushko, M.L.; De Yoreo, J.J.; Rosso, K.M. Direction-specific interaction forces underlying zinc oxide crystal growth by oriented attachment. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choopun, S.; Hongsith, N.; Wongrat, E. Metal-Oxide Nanowires by Thermal Oxidation Reaction Technique. In Nanowires; InTech: Munich, Germany, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Wong, M.H.; Berenov, A.; Qi, X.; Kappers, M.J.; Barber, Z.H.; Illy, B.; Lockman, Z.; Ryan, M.P.; MacManus-Driscoll, J.L. Electrochemical growth of ZnO nano-rods on polycrystalline Zn foil. Nanotechnology 2003, 14, 968–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manzoor, U.; Tuz Zahra, F.; Rafique, S.; Moin, M.T.; Mujahid, M. Effect of Synthesis Temperature, Nucleation Time, and Postsynthesis Heat Treatment of ZnO Nanoparticles and Its Sensing Properties. J. Nanomater. 2015, 2015, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Gong, F.; Jiu, B.; Li, F. Large scale synthesis of hexagonal simonkolleit nanosheets for ZnO gas sensors with enhanced performances. Mater. Lett. 2017, 186 (Suppl. C), 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minami, T.; Sato, H.; Nanto, H.; Takata, S. Group III Impurity Doped Zinc Oxide Thin Films Prepared by RF Magnetron Sputtering. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys. 1985, 24, L781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavelko, R.G.; Yuasa, M.; Kida, T.; Shimanoe, K.; Yamazoe, N. Impurity level in SnO2 materials and its impact on gas sensing properties. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2015, 210, 719–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.; An, S.; Ko, H.; Jin, C.; Lee, C. Synthesis of Nanograined ZnO Nanowires and Their Enhanced Gas Sensing Properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 3650–3656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, M.-H.; Chu, M.-J. Synthesis of hexagonal ZnO nanodrums, nanosheets and nanowires by the ionic effect during the growth of hexagonal ZnO crystals. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 6675–6682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sucharitakul, S.; Panyathip, R.; Choopun, S. Effect of Annealing Temperature on ECD Grown Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide. Materials 2018, 11, 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081360
Sucharitakul S, Panyathip R, Choopun S. Effect of Annealing Temperature on ECD Grown Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081360
Chicago/Turabian StyleSucharitakul, Sukrit, Rangsan Panyathip, and Supab Choopun. 2018. "Effect of Annealing Temperature on ECD Grown Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide" Materials 11, no. 8: 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081360
APA StyleSucharitakul, S., Panyathip, R., & Choopun, S. (2018). Effect of Annealing Temperature on ECD Grown Hexagonal-Plane Zinc Oxide. Materials, 11(8), 1360. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081360