Femtosecond Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Fused Silica: The Impact of the Initial Substrate Temperature
Abstract
1. Introduction
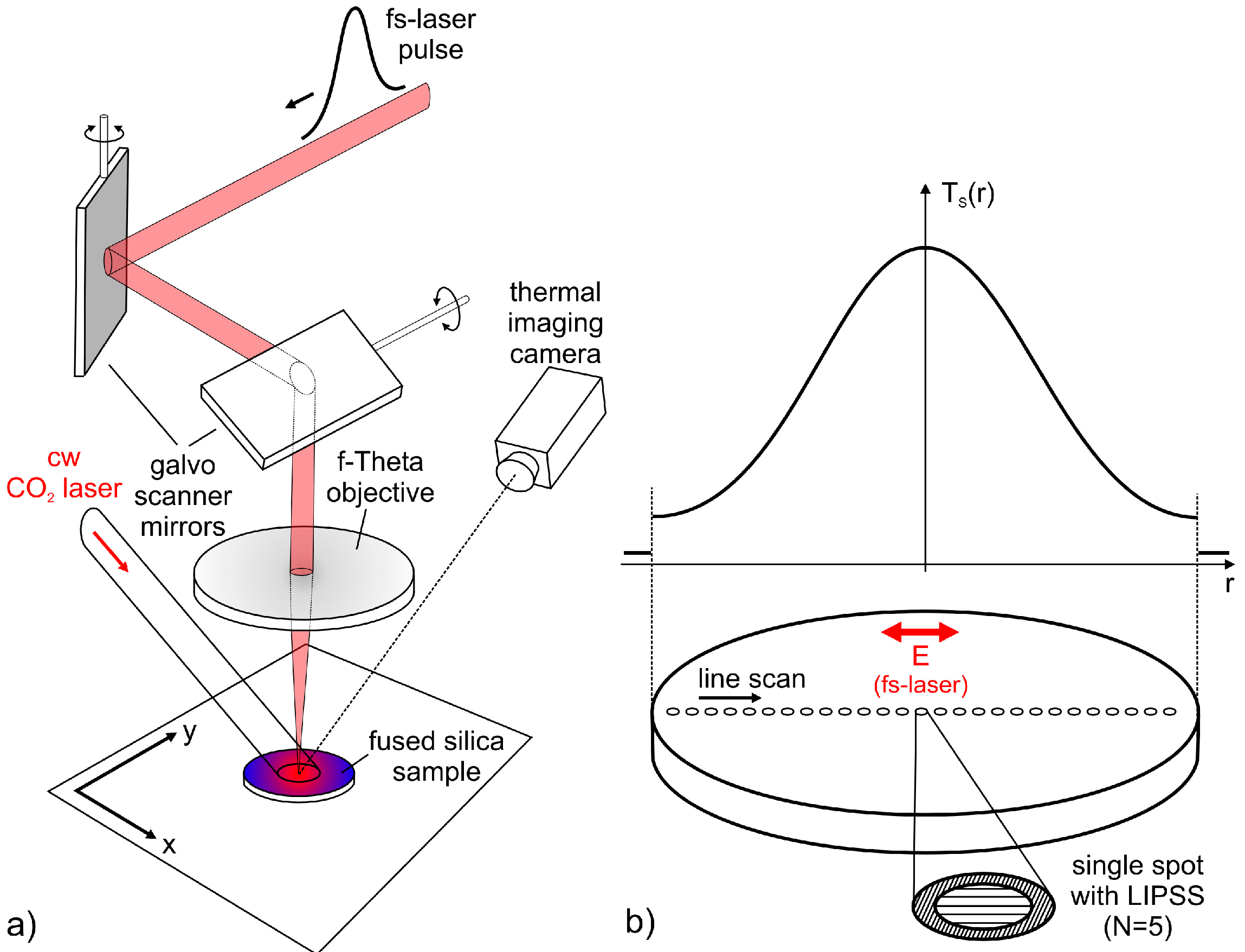
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results and Discussion
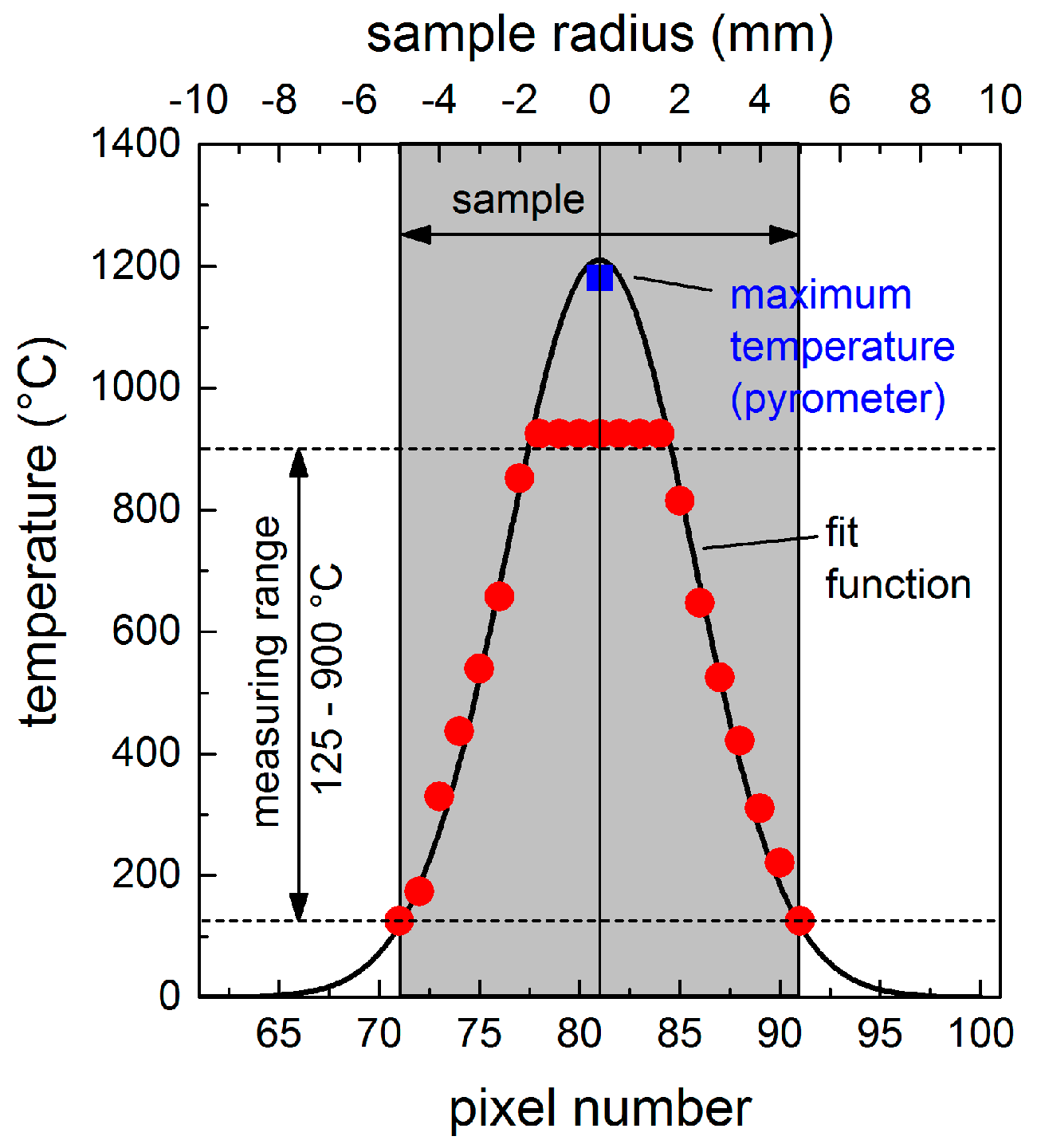
3.1. Temperature Profile
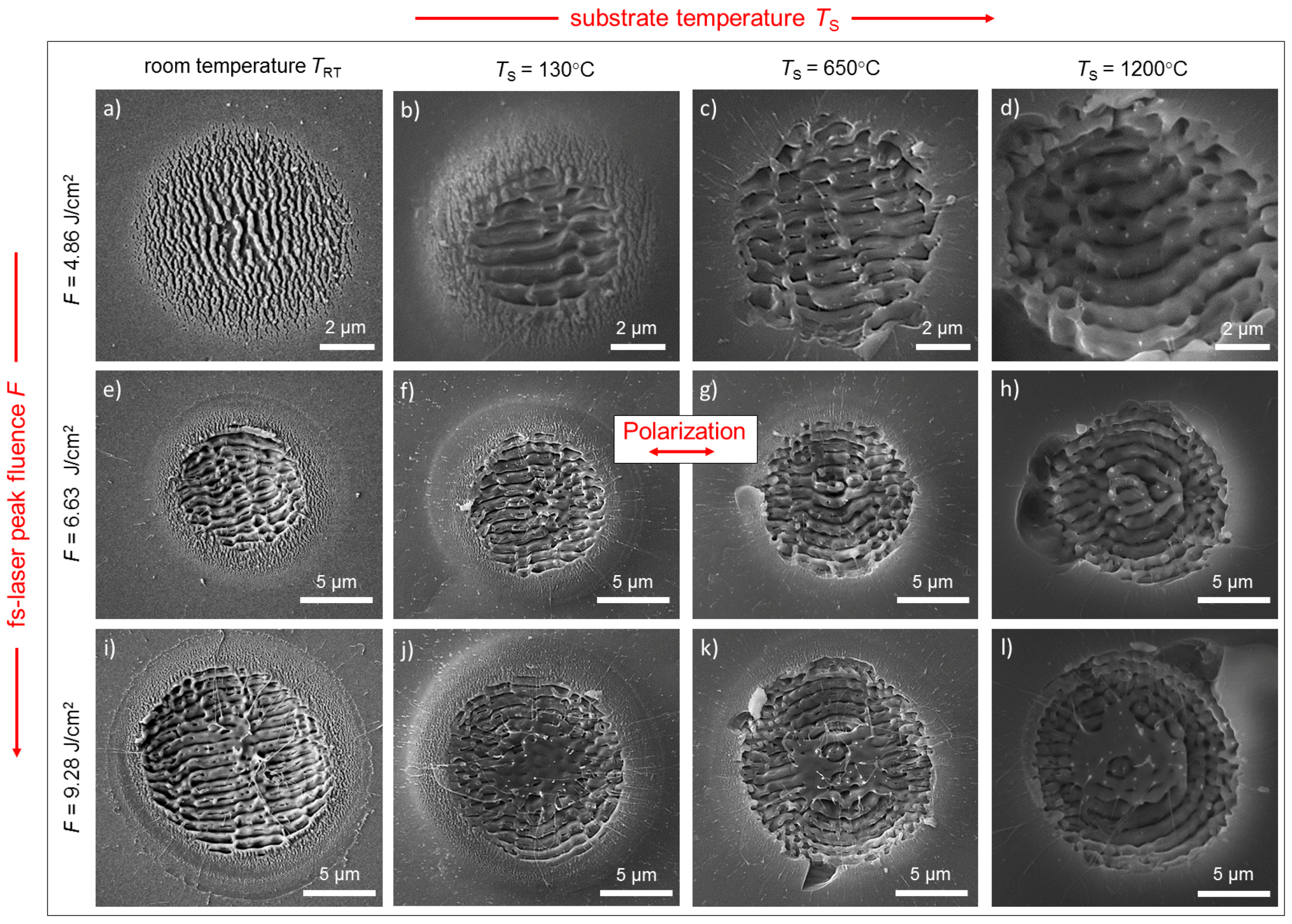
3.2. LIPSS Formation in Dependence of Initial Substrate Temperature
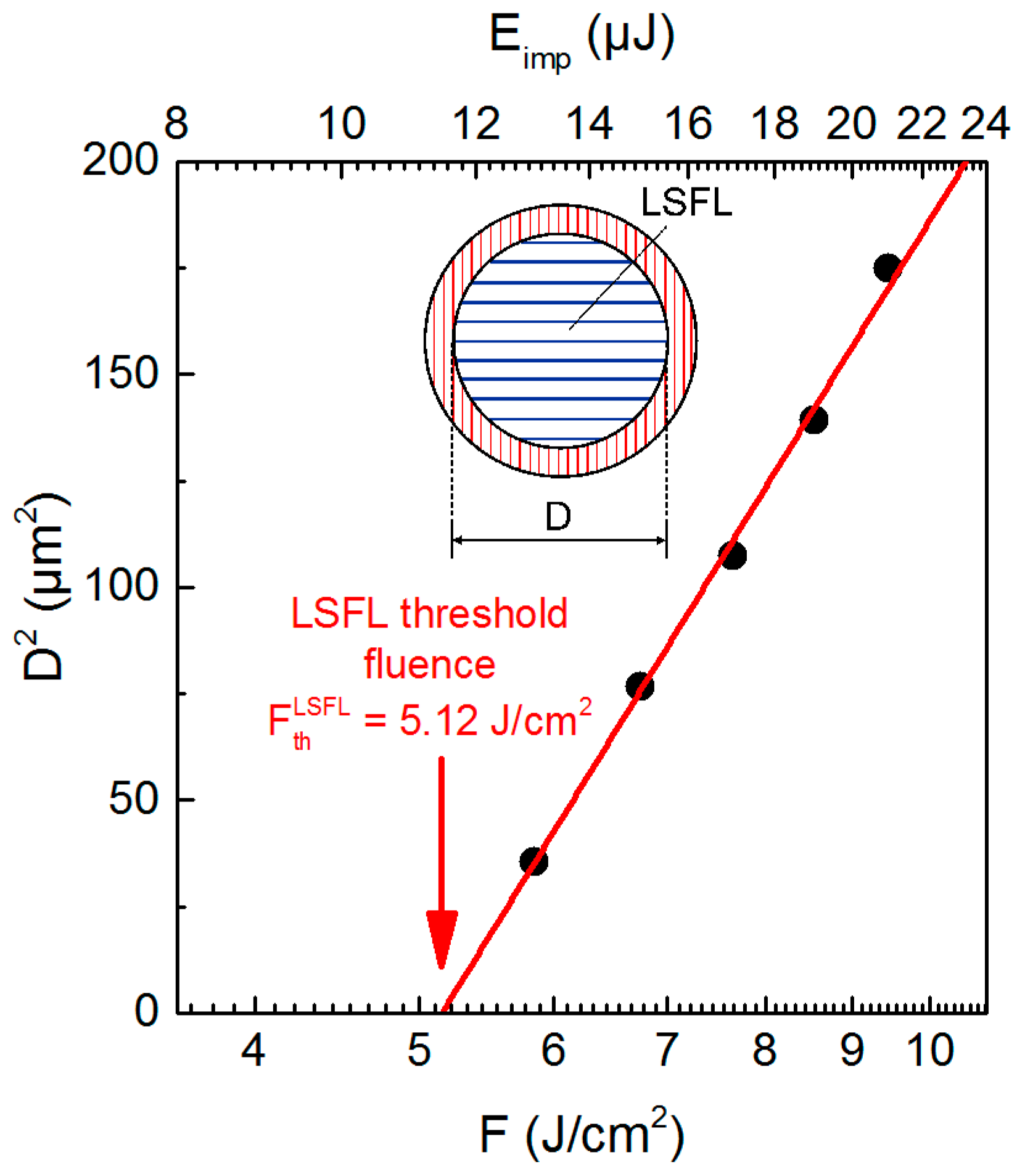
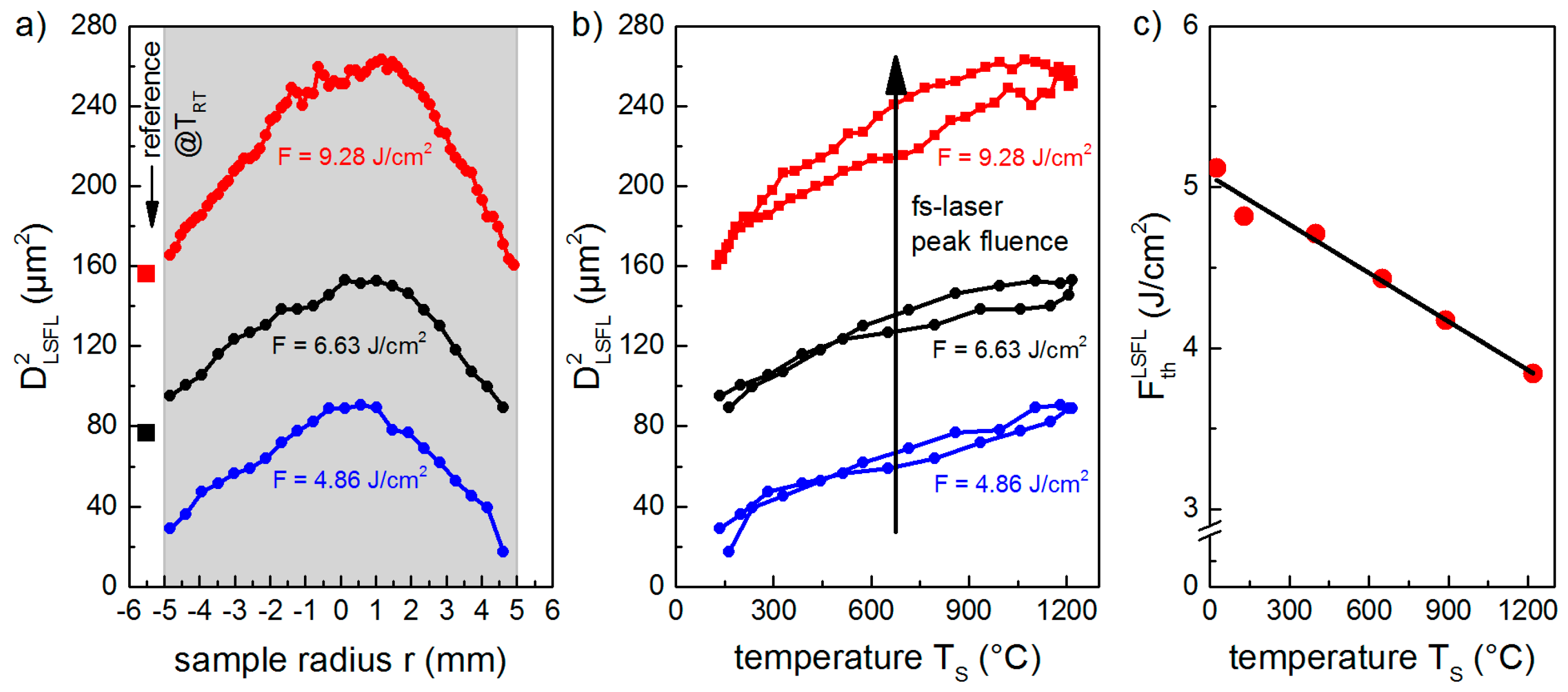
3.2.1. Temperature-Dependency of the LIPSS Formation Threshold
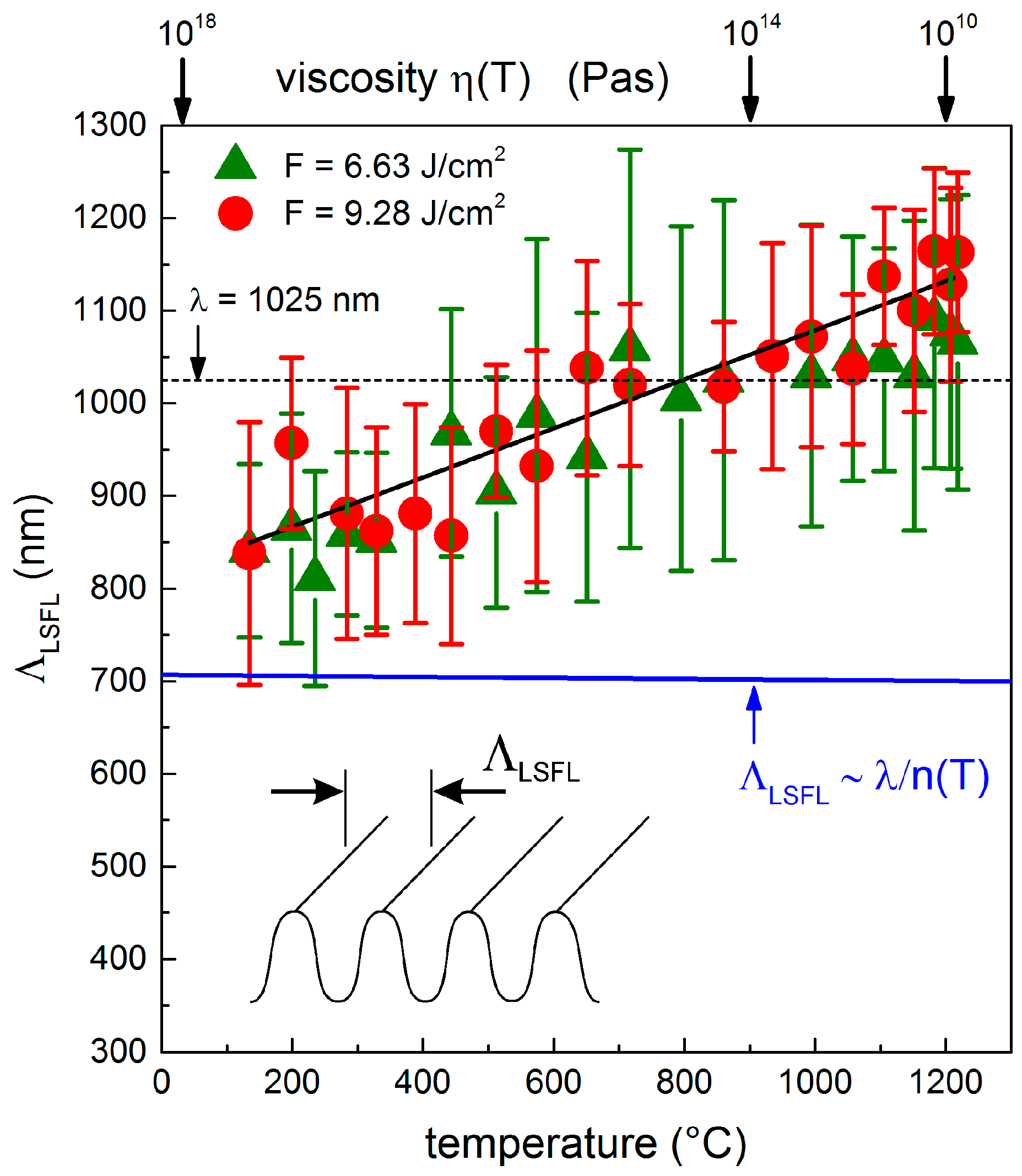
3.2.2. Temperature-Dependency of the LIPSS Spatial Period
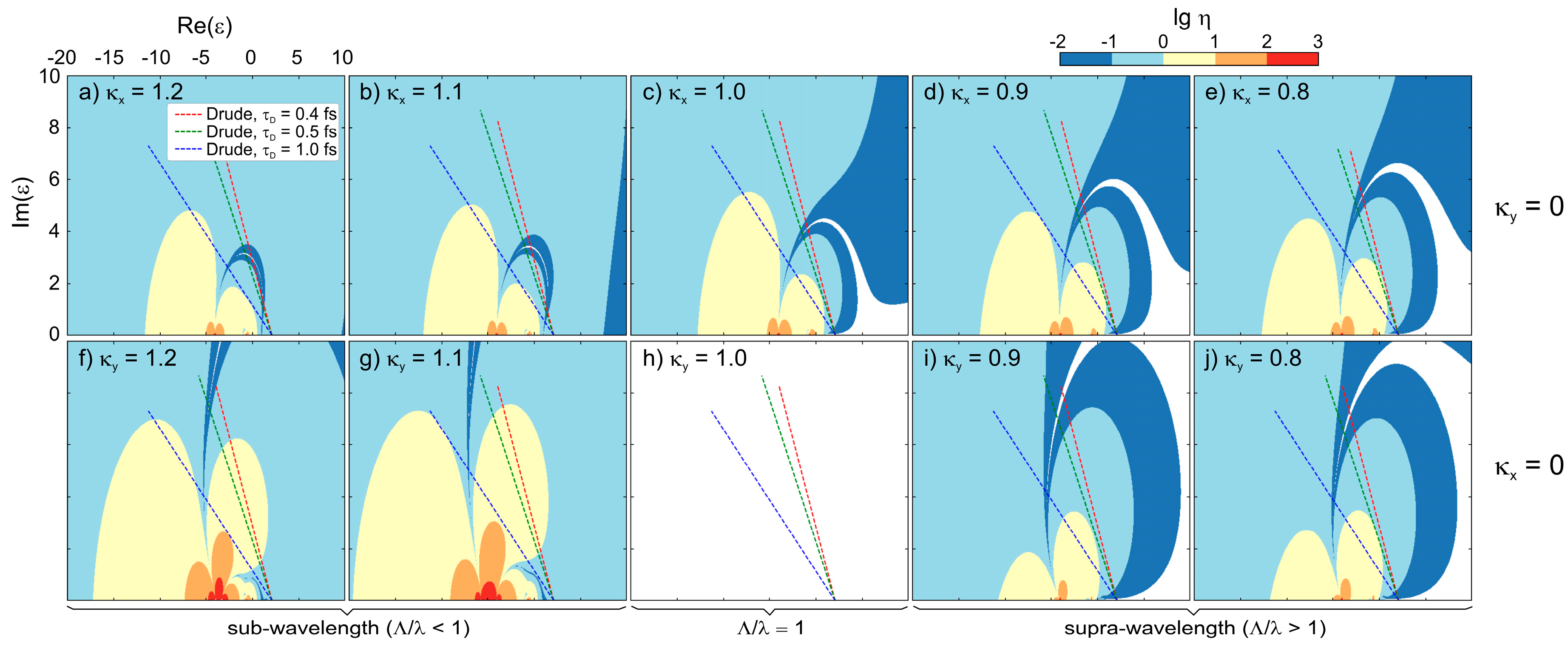
3.3. LIPSS Analysis by Sipe Theory
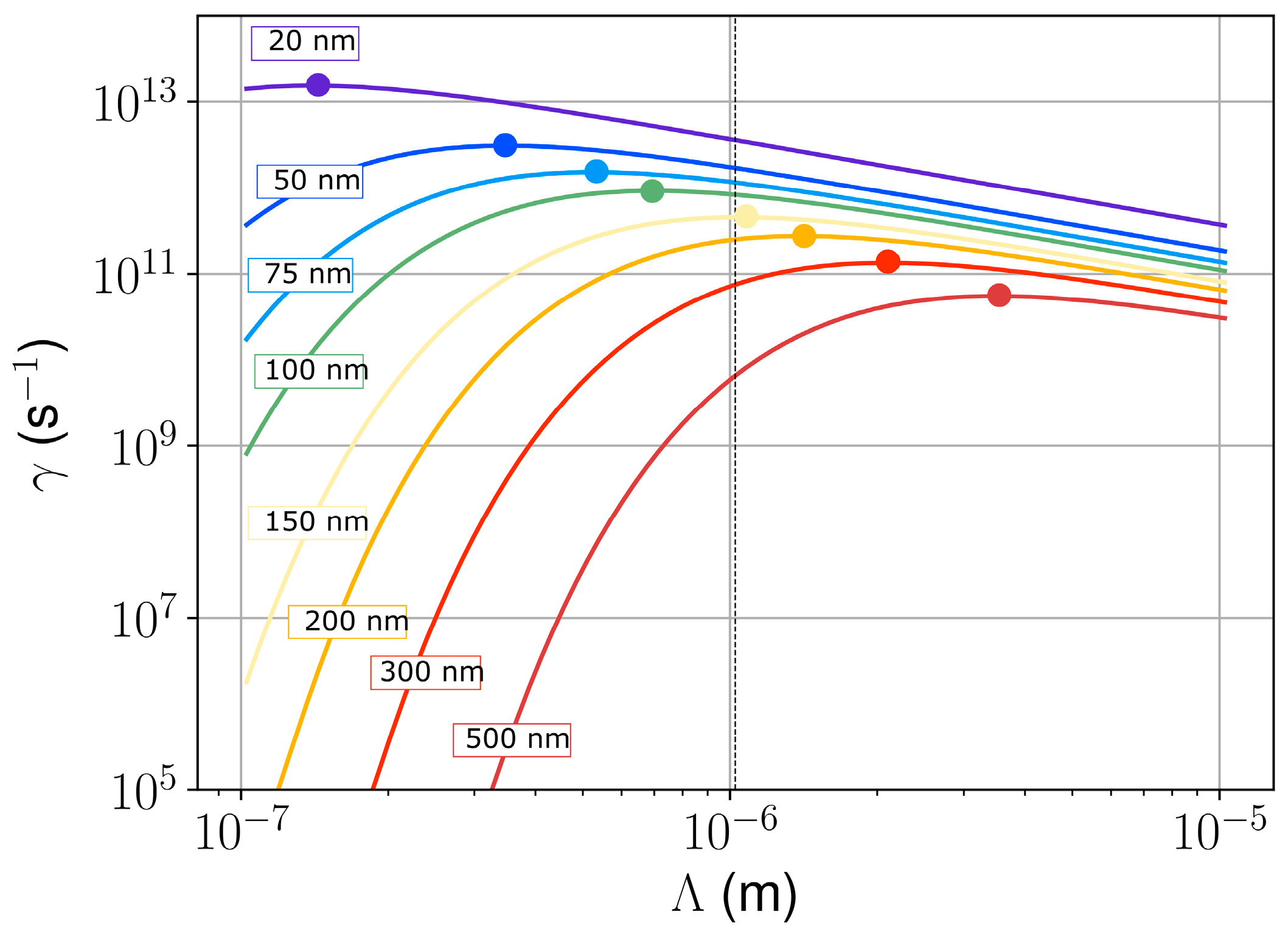
3.4. Hydrodynamic Non-Dimensional Numbers Analysis and Thermo-Capillary Instability
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Quantity | Unity | Quartz | Fused Silica | Liquid Silica |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Volumic mass ρ | kg/m³ | 2.5·10³ | 2.2·10³ | - |
| Fusion temperature Tm | K | 1970 | 1873 | - |
| Heat diffusivity D | m²/s | 8.6·10−4 | 9·10−5 | - |
| Thermal conductivity κ | W/(m·K) | 0.14 [59] | 0.014 [59] | - |
| a3T³ + a2T² + a1T + a0 [38] a3 = 7.06418·10−10, a2 = −3.96976·10⁻⁶, a1 = 7.56664·10−3, a0 = 0.63319 | ||||
| Heat capacity c | J/(g·K) | 0.74 | 0.72 | - |
| Surface tension σ | N/m | aT + b, a = 1.54·10−5, b = 0.267 [60] | ||
| Dynamical viscosity η | kg/(m∙s) | 0.1·exp(10⁴·a/T + b), a = 6.2388, b = −14.6668 [61] | ||
References
- Birnbaum, M. Semiconductor surface damage produced by ruby lasers. J. Appl. Phys. 1965, 36, 3688–3689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Höhm, S.; Kirner, S.V.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Laser-induced periodic surface structures—A scientific evergreen. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 2017, 23, 9000615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Krüger, J.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures. J. Laser Appl. 2012, 24, 042006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, F.A.; Kunz, C.; Gräf, S. Bio-inspired functional surfaces based on laser-induced periodic surface structures. Materials 2016, 9, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonse, J.; Koter, R.; Hartelt, M.; Spaltmann, D.; Pentzien, S.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on steel and titanium alloy for tribological applications. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2014, 117, 103–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, L.T.; Nishii, K.; Namba, Y. Regular subwavelength surface structures induced by femtosecond laser pulses on stainless steel. Opt. Lett. 2009, 34, 1846–1848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sajzew, R.; Schröder, J.; Kunz, C.; Engel, S.; Müller, F.A.; Gräf, S. Femtosecond laser-induced surface structures on carbon fibers. Opt. Lett. 2015, 40, 5734–5737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonse, J.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J. On the role of surface plasmon polaritons in the formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures upon irradiation of silicon by femtosecond-laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 106, 104910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipe, J.E.; Young, J.F.; Preston, J.S.; van Driel, H.M. Laser-induced periodic surface structure. I. Theory. Phys. Rev. B 1983, 27, 1141–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures on silica. J. Appl. Phys. 2012, 112, 014901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gräf, S.; Kunz, C.; Müller, F.A. Formation and properties of laser-induced periodic surface structures on different glasses. Materials 2017, 10, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dufft, D.; Rosenfeld, A.; Das, S.K.; Grunwald, R.; Bonse, J. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures revisited: A comparative study on zno. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105, 034908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganeev, R.A. Optical modification of semiconductor surfaces through the nanoripples formation using ultrashort laser pulses: Experimental aspects. Opt. Spectrosc. 2014, 117, 320–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gregorcic, P.; Sedlacek, M.; Podgornik, B.; Reif, J. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures (lipss) on tool steel by multiple picosecond laser pulses of different polarizations. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 387, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shugaev, M.V.; Gnilitskyi, I.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Zhigilei, L.V. Mechanism of single-pulse ablative generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 96, 205429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, E.L.; Levy, Y.; Gurevich, S.V.; Bulgakova, N.M. Role of the temperature dynamics in formation of nanopatterns upon single femtosecond laser pulses on gold. Phys. Rev. B 2017, 95, 054305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reif, J.; Costache, F.; Henyk, M.; Pandelov, S.V. Ripples revisited: Non-classical morphology at the bottom of femtosecond laser ablation craters in transparent dielectrics. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2002, 197, 891–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borowiec, A.; Haugen, H.K. Subwavelength ripple formation on the surfaces of compound semiconductors irradiated with femtosecond laser pulses. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2003, 82, 4462–4464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-F.; Zhang, C.-Y.; Li, H.; Dai, Q.-F.; Lan, S.; Tie, S.-L. Formation of 100-nm periodic structures on a titanium surface by exploiting the oxidation and third harmonic generation induced by femtosecond laser pulses. Opt. Express 2014, 22, 28086–28099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rudenko, A.; Colombier, J.P.; Höhm, S.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J.; Itina, T.E. Spontaneous periodic ordering on the surface and in the bulk of dielectrics irradiated by ultrafast laser: A shared electromagnetic origin. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgakova, N.M.; Zhukov, V.P.; Meshcheryakov, Y.P. Theoretical treatments of ultrashort pulse laser processing of transparent materials: Toward understanding the volume nanograting formation and “quill” writing effect. Appl. Phys. B Lasers Opt. 2013, 113, 437–449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, E.E.B.; Ashkenasi, D.; Rosenfeld, A. Ultra-short-pulse laser irradiation and ablation of dielectrics. Lasers Mater. Sci. 1999, 301, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rohloff, M.; Das, S.K.; Höhm, S.; Grunwald, R.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on fused silica upon multiple cross-polarized double-femtosecond-laser-pulse irradiation sequences. J. Appl. Phys. 2011, 110, 014910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenfeld, A.; Rohloff, M.; Höhm, S.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on fused silica upon multiple parallel polarized double-femtosecond-laser-pulse irradiation sequences. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 9233–9236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höhm, S.; Herzlieb, M.; Rosenfeld, A.; Krüger, J.; Bonse, J. Formation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on fused silica upon two-color double-pulse irradiation. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 254101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, S.; Rung, S.; Hellmann, R. Generation of laser-induced periodic surface structures on transparent material-fused silica. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2016, 108, 181607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, Z.; Zhao, Y.A.; Shao, J.D. Femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structure on fused silica surface. Optik 2016, 127, 1171–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, D.; Arines, J.; O’connor, G.M.; Flores-Arias, M.T. Single-pulse laser ablation threshold of borosilicate, fused silica, sapphire, and soda-lime glass for pulse widths of 500 fs, 10 ps, 20 ns. Appl. Opt. 2015, 54, 8596–8601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yahng, J.S.; Nam, J.R.; Jeoung, S.C. The influence of substrate temperature on femtosecond laser micro-processing of silicon, stainless steel and glass. Opt. Lasers Eng. 2009, 47, 815–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bude, J.; Guss, G.; Matthews, M.; Spaeth, M.L. The effect of lattice temperature on surface damage in fused silica optics. In Proceedings of the 2007 SPIE Conference, Boulder, CO, USA, 24–26 September 2007; p. 672009. [Google Scholar]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Grambow, C.; Kietzig, A.-M. Fabrication of micro/nano structures on metals by femtosecond laser micromachining. Micromachines 2014, 5, 1219–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, G.L.; Feng, G.Y.; Liu, K.; Zhou, S.H. Temperature dependence of laser-induced micro/nanostructures for femtosecond laser irradiation of silicon. Appl. Opt. 2014, 53, 3004–3009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsibidis, G.D.; Skoulas, E.; Papadopoulos, A.; Stratakis, E. Convection roll-driven generation of supra-wavelength periodic surface structures on dielectrics upon irradiation with femtosecond pulsed lasers. Phys. Rev. B 2016, 94, 081305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.M. Simple technique for measurements of pulsed gaussian-beam spot sizes. Opt. Lett. 1982, 7, 196–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gräf, S.; Staupendahl, G.; Gerling, P.; Müller, F.A. Optical constants n and k of various technical and optical glasses at l = 10.59 µm. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 113, 013101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Munz, M.; Sturm, H. Structure formation on the surface of indium phosphide irradiated by femtosecond laser pulses. J. Appl. Phys. 2005, 97, 013538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunz, C.; Büttner, T.N.; Naumann, B.; Boehm, A.V.; Gnecco, E.; Bonse, J.; Neumann, C.; Turchanin, A.; Müller, F.A.; Gräf, S. Large-area fabrication of low- and high-spatial-frequency laser-induced periodic surface structures on carbon fibers. Carbon 2018, 133, 176–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wray, J.H.; Neu, J.T. Refractive index of several glasses as a function of wavelength and temperature. J. Opt. Soc. Am. 1969, 59, 774–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudrie, L.; Couairon, A.; Franco, M.; Lamouroux, B.; Prade, B.; Tzortzakis, S.; Mysyrowicz, A. Femtosecond laser-induced damage and filamentary propagation in fused silica. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2002, 89, 186601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgakova, N.M.; Stoian, R.; Rosenfeld, A.; Hertel, I.V.; Marine, W.; Campbell, E.E.B. A general continuum approach to describe fast electronic transport in pulsed laser irradiated materials: The problem of coulomb explosion. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2005, 81, 345–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temnov, V.V. Ultrafast Laser-Induced Phenomena in Solids Studied by Time-Resolved Interferometry. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Duisburg-Essen, Duisburg, Germany, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Wachter, G.; Lemell, C.; Burgdorfer, J.; Sato, S.A.; Tong, X.M.; Yabana, K. Ab initio simulation of electrical currents induced by ultrafast laser excitation of dielectric materials. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2014, 113, 087401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnilitskyi, I.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Levy, Y.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Mocek, T.; Orazi, L. High-speed manufacturing of highly regular femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures: Physical origin of regularity. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ben-Yakar, A.; Harkin, A.; Ashmore, J.; Byer, R.L.; Stone, H.A. Thermal and fluid processes of a thin melt zone during femtosecond laser ablation of glass: The formation of rims by single laser pulses. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 2007, 40, 1447–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ursu, I.; Mihailescu, I.N.; Nistor, L.C.; Teodorescu, V.S.; Prokhorov, A.M.; Konov, V.I.; Tokarev, V.N. Periodic structures on the surface of fused-silica under multipulse 10.6-mu-m laser irradiation. Appl. Opt. 1985, 24, 3736–3739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emelyanov, V.I.; Konov, V.I.; Tokarev, V.N.; Seminogov, V.N. Formation of periodic surface ripples under the action of pulsed carbon-dioxide laser-radiation on fused-silica. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B Opt. Phys. 1989, 6, 104–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokarev, V.N.; Kaplan, A.F.H. An analytical modeling of time dependent pulsed laser melting. J. Appl. Phys. 1999, 86, 2836–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonse, J.; Bachelier, G.; Siegel, J.; Solis, J. Time- and space-resolved dynamics of melting, ablation, and solidification phenomena induced by femtosecond laser pulses in germanium. Phys. Rev. B 2006, 74, 134106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Gurevich, E.L.; Mocek, T. Relaxation dynamics of femtosecond-laser-induced temperature modulation on the surfaces of metals and semiconductors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Mocek, T. Laser-induced periodic surface structures formation: Investigation of the effect of nonlinear absorption of laser energy in different materials. In Nonlinear Optics and Applications X; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2017; Volume 10228. [Google Scholar]
- Gurevich, E.L. Mechanisms of femtosecond lipss formation induced by periodic surface temperature modulation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 374, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gurevich, E.L. Self-organized nanopatterns in thin layers of superheated liquid metals. Phys. Rev. E 2011, 83, 031604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berthier, J.; Silberzan, P. Microfluidics for Biotechnology; Artech House: Norwood, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Levchenko, E.B.; Chernyakov, A.L. Instability of surface-waves in a nonuniformly heated liquid. JETP 1981, 81, 202–209. [Google Scholar]
- Mirza, I.; Bulgakova, N.M.; Tomastik, J.; Michalek, V.; Haderka, O.; Fekete, L.; Mocek, T. Ultrashort pulse laser ablation of dielectrics: Thresholds, mechanisms, role of breakdown. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulgakova, N.M.; Bulgakov, A.V. Pulsed laser ablation of solids: Transition from normal vaporization to phase explosion. Appl. Phys. A Mater. Sci. Process. 2001, 73, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Zhigilei, L.V. Microscopic mechanisms of laser spallation and ablation of metal targets from large-scale molecular dynamics simulations. Appl. Phys. A 2014, 114, 11–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povarnitsyn, M.; Itina, T.; Sentis, M.; Khishchenko, K.; Levashov, P. Material decomposition mechanism in femtosecond laser interactions with metals. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 75, 235414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bäuerle, D.W. Laser Processing and Chemistry; Springer: Heidelberg, Germany, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Boyd, K.; Ebendorff-Heidepriem, H.; Monro, T.M.; Munch, J. Surface tension and viscosity measurement of optical glasses using a scanning CO2 laser. Opt. Mater. Express 2012, 2, 1101–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbain, G.; Bottinga, Y.; Richet, P. Viscosity of liquid silica, silicates and alumino-silicates. Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 1982, 46, 1061–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Process | Definition | Magnitude | Regime |
|---|---|---|---|
| momentum damping | τdiff = ρ·L2·η−1 | 10−15 s | strong viscosity dissipates the liquid momentum |
| ambient-pressure-induced deformation of the interface | vp = pout·L/η τp = L/vp | 10−9 m/s ∞ | negligible |
| surface tension driven deformation of the interface | vσ = 2·σ·h/(L·η) τσ = L/vσ | 10−8 m/s ∞ | negligible |
| non-linear transport induced by recoil pressure | vNL = (pout/ρ)1/2 tNL = L/vNL | 2 m/s 500 ns | considerable effect |
| non-linear transport due to surface tension gradient | vNLSTG = (2·σ·h/(ρ·L2))1/2 tNLSTG = L/vNLSTG | 1–6 m/s 0.2–1 µs | considerable effect |
| Reynolds number | Re = ρ·v·L/η | 10−8 | inertial transport is negligible |
| Capillary number | Ca = η·v/σ | 107–1012 | surface tension dominates over materials viscosity, capillary effects must act at the free surface |
| Reech number | Ri = g·L/v2 | <5·10−5 | the influence of gravity is negligible |
| Peclet number | Pe = η·cl/κ | ~1016 | thermal convection dominates over diffusion |
| Weber number | We = ρ·v2·L/σ | 0.1–0.4 | inertial forces and surface tension are competing |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gräf, S.; Kunz, C.; Engel, S.; Derrien, T.J.-Y.; Müller, F.A. Femtosecond Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Fused Silica: The Impact of the Initial Substrate Temperature. Materials 2018, 11, 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081340
Gräf S, Kunz C, Engel S, Derrien TJ-Y, Müller FA. Femtosecond Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Fused Silica: The Impact of the Initial Substrate Temperature. Materials. 2018; 11(8):1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081340
Chicago/Turabian StyleGräf, Stephan, Clemens Kunz, Sebastian Engel, Thibault J. -Y. Derrien, and Frank A. Müller. 2018. "Femtosecond Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Fused Silica: The Impact of the Initial Substrate Temperature" Materials 11, no. 8: 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081340
APA StyleGräf, S., Kunz, C., Engel, S., Derrien, T. J.-Y., & Müller, F. A. (2018). Femtosecond Laser-Induced Periodic Surface Structures on Fused Silica: The Impact of the Initial Substrate Temperature. Materials, 11(8), 1340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11081340





