Simultaneous Evaluation of Creep Deformation and Recovery of Bulk-Fill Dental Composites Immersed in Food-Simulating Liquids
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
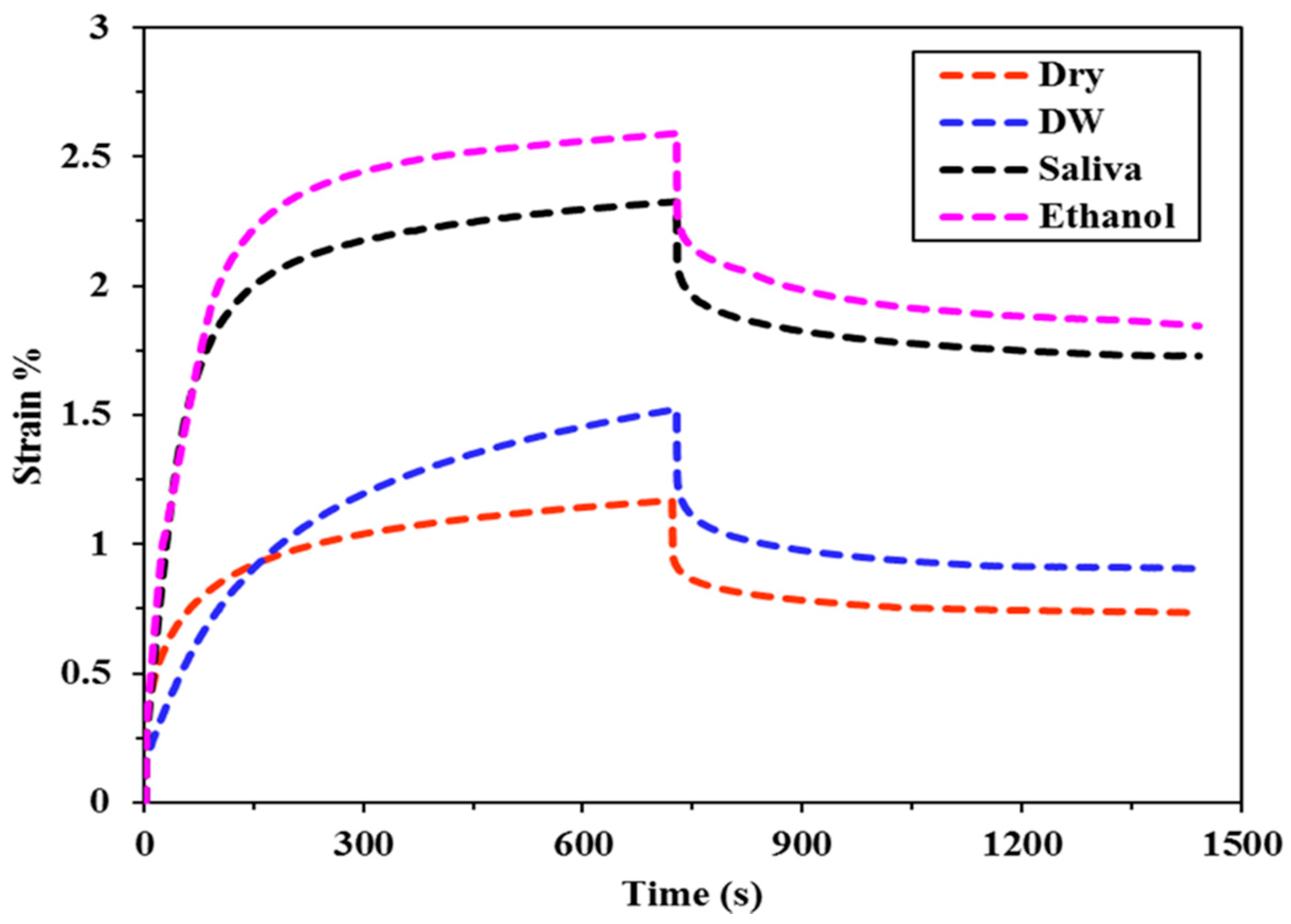
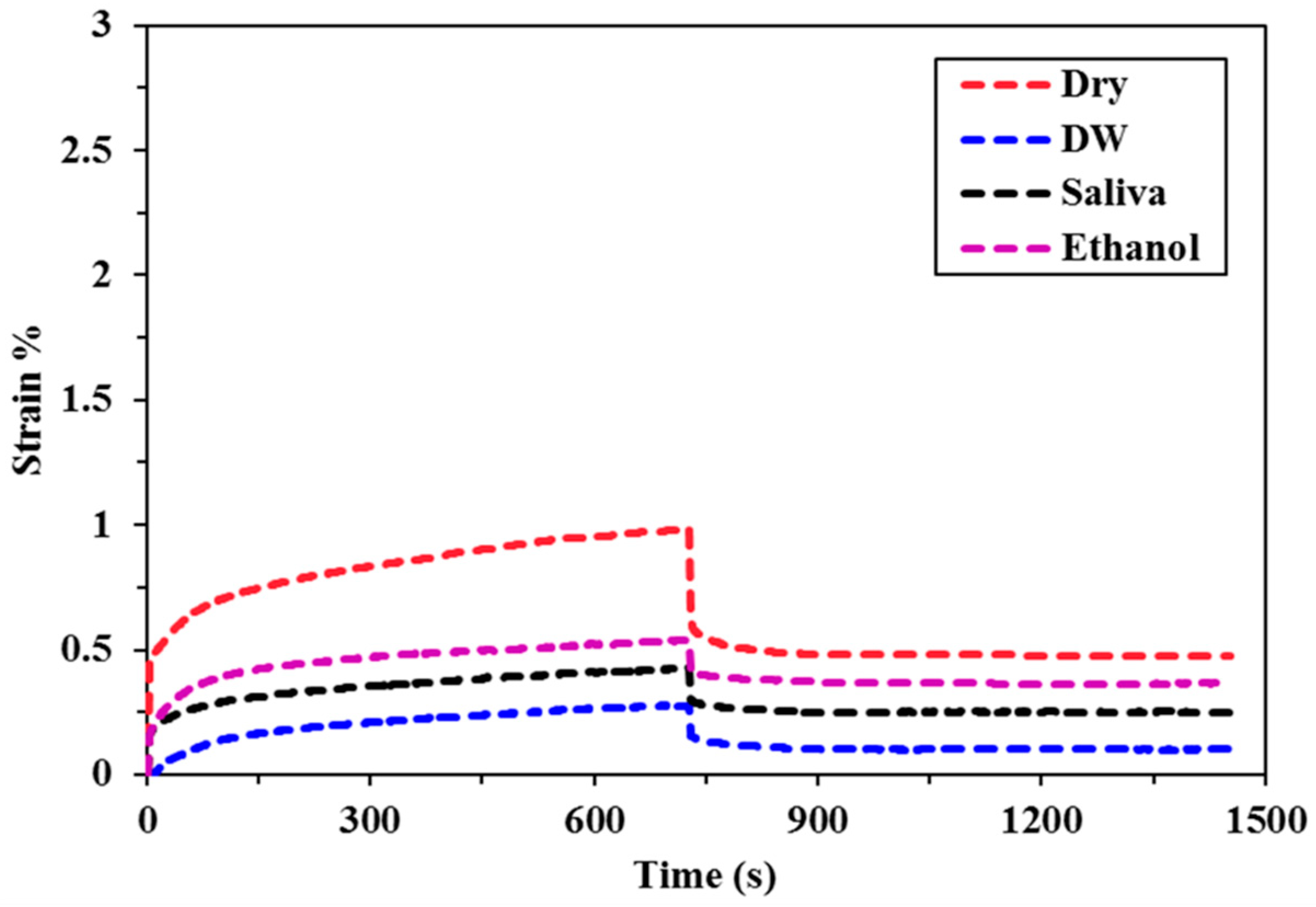
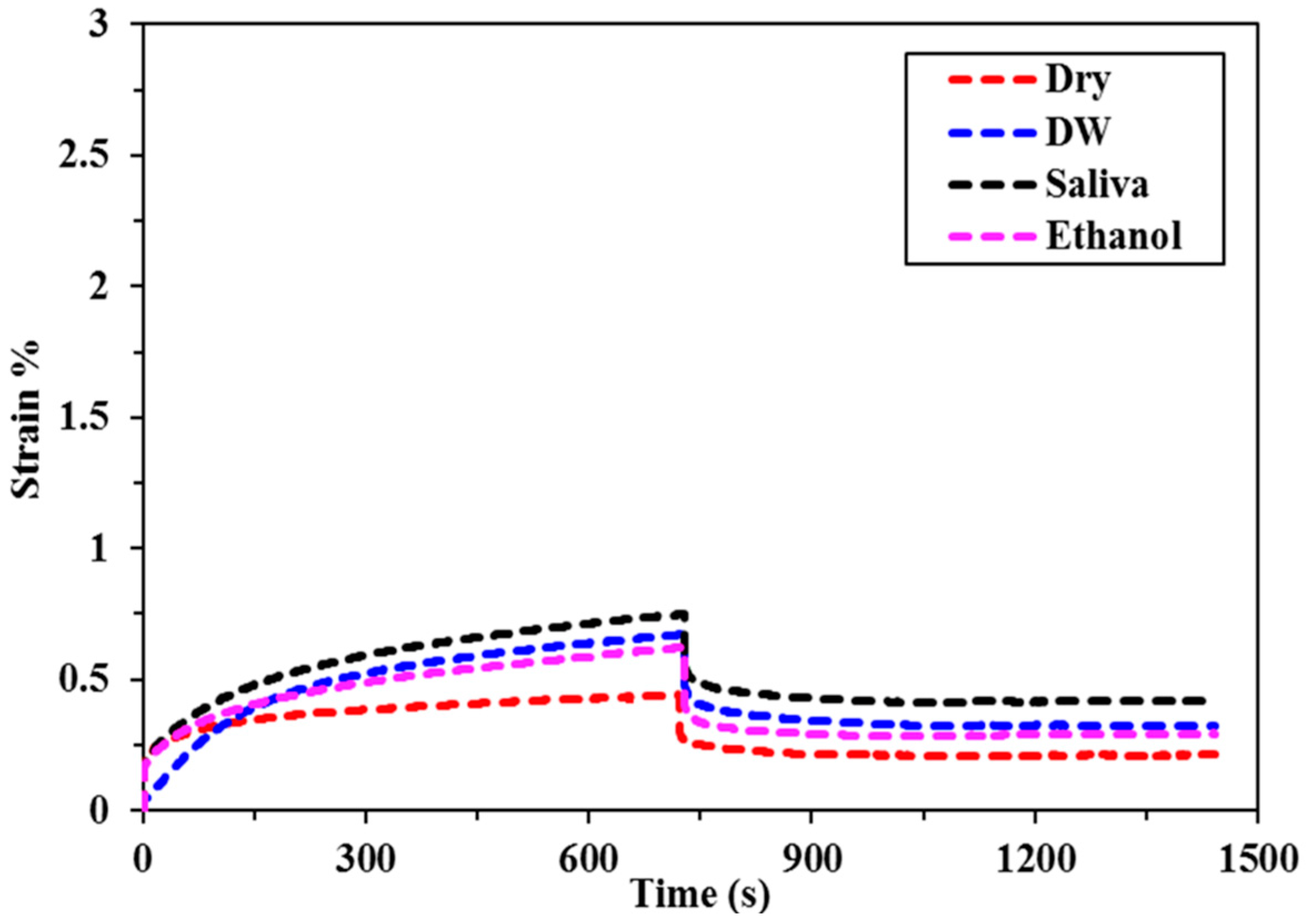
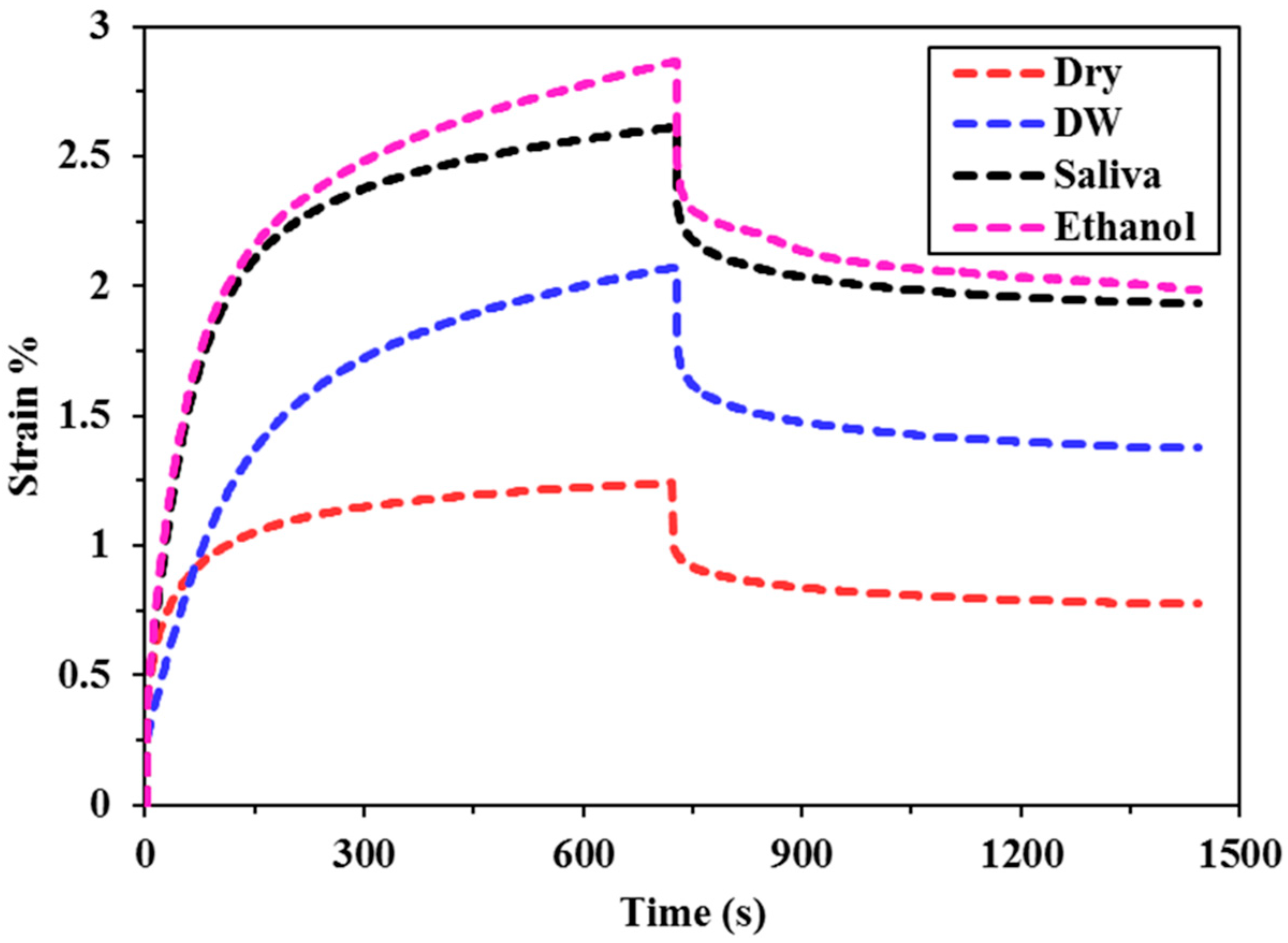
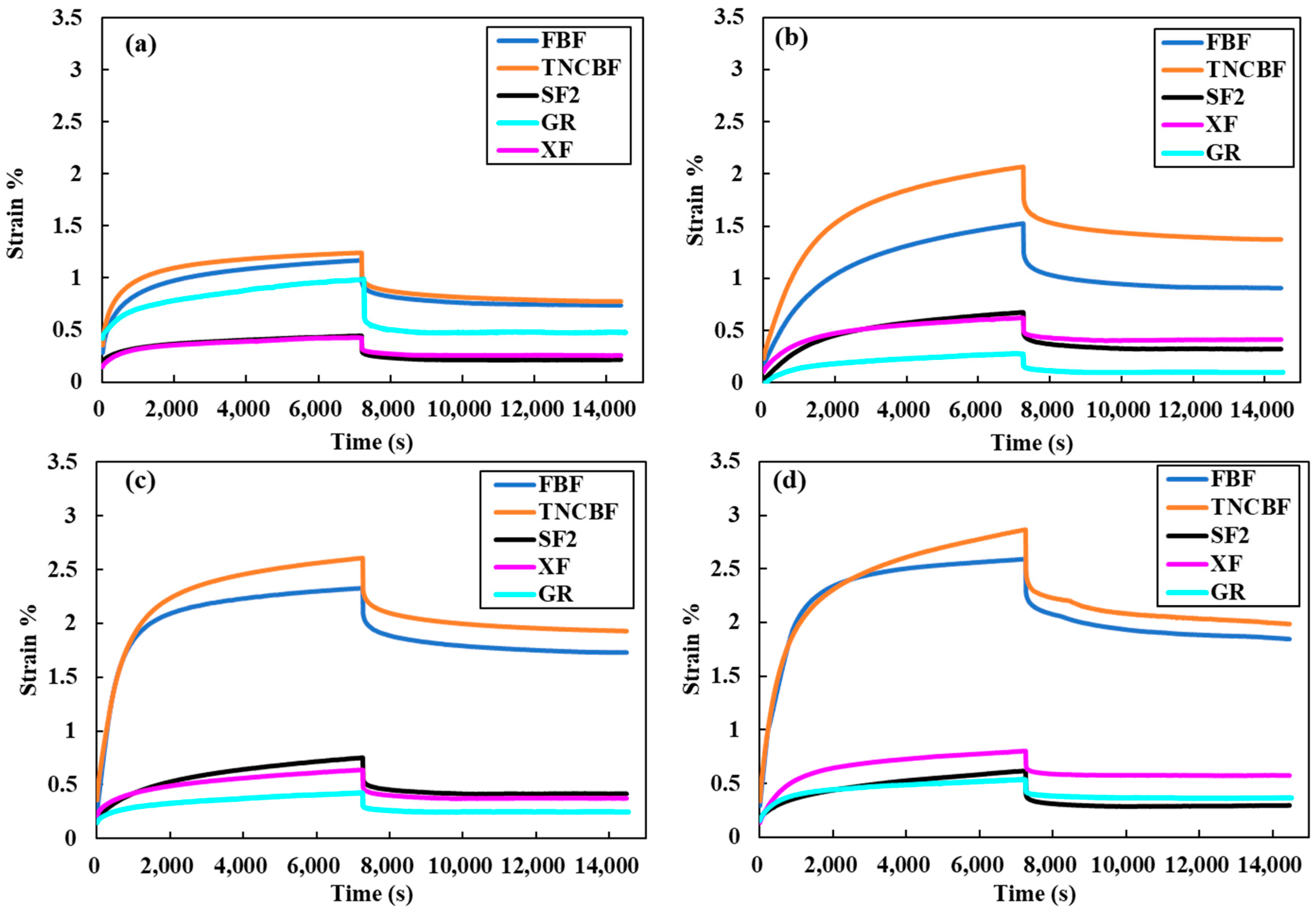
3.1. Creep Strain
3.2. Recovery Strain
3.3. Permanent Set
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benetti, A.R.; Havndrup-Pedersen, C.; Honoré, D.; Pedersen, M.K.; Pallesen, U. Bulk-Fill Resin Composites: Polymerization Contraction, Depth of Cure, and Gap Formation. Oper. Dent. 2014, 40, 190–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alrahlah, A.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Post-cure depth of cure of bulk fill dental resin-composites. Dent. Mater. 2014, 30, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corral-Núnez, C.; Vildósola-Grez, P.; Bersezio-Miranda, C.; Alves-Dos Campos, E.; Fernández Godoy, E. state of the art of bulk-fill resin-based composites: A review. Rev. Fac. Odontol. Univ. Antioq. 2015, 27, 177–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadogiannis, D.; Tolidis, K.; Gerasimou, P.; Lakes, R.; Papadogiannis, Y. Viscoelastic properties, creep behavior and degree of conversion of bulk fill composite resins. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1533–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alshali, R.Z.; Salim, N.A.; Satterthwaite, J.D.; Silikas, N. Post-irradiation hardness development, chemical softening, and thermal stability of bulk-fill and conventional resin-composites. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 209–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jang, K.T.; Chung, D.H.; Shin, D.; García-Godoy, F. Effect of eccentric load cycling on microleakage of Class V flowable and packable composite resin restorations. Oper. Dent. 2001, 26, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yap, A.U.; Tan, S.H.; Wee, S.S.; Lee, C.W.; Lim, E.L.; Zeng, K.Y. Chemical degradation of composite restoratives. J. Oral Rehabil. 2001, 28, 1015–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleem, M.; Khan, A.; Rehman, I.; Wong, F. Effect of Beverages on Viscoelastic Properties of Resin-Based Dental Composites. Materials 2015, 8, 2863–2872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wongkhantee, S.; Patanapiradej, V.; Maneenut, C.; Tantbirojn, D. Effect of acidic food and drinks on surface hardness of enamel, dentine, and tooth-coloured filling materials. J. Dent. 2006, 34, 214–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marghalani, H.Y.; Watts, D.C. Viscoelastic stability of resin-composites aged in food-simulating solvents. Dent. Mater. 2013, 29, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.; Silikas, N.; Akhtar, R.; Watts, D.C. Nanoindentation creep versus bulk compressive creep of dental resin-composites. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1171–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahdal, K.; Ilie, N.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Polymerization kinetics and impact of post polymerization on the degree of conversion of bulk-fill resin-composite at clinically relevant depth. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1207–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilie, N.; Bucuta, S.; Draenert, M. Bulk-fill Resin-based Composites: An in Vitro Assessment of Their Mechanical Performance. Oper. Dent. 2013, 38, 618–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.; Akhtar, R.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Nanomechanical properties of dental resin-composites. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 1292–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Ahdal, K.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Development of viscoelastic stability of resin-composites incorporating novel matrices. Dent. Mater. 2015, 31, 1561–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Correr, G.M.; Bruschi Alonso, R.C.; Baratto-Filho, F.; Correr-Sobrinho, L.; Sinhoreti, M.A.; Puppin-Rontani, R.M. In vitro long-term degradation of aesthetic restorative materials in food-simulating media. Acta Odontol. Scand. 2012, 70, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Creep deformation of restorative resin-composites intended for bulk-fill placement. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, 928–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadogiannis, Y.; Helvatjoglu-Antoniades, M.; Lakes, R. Dynamic mechanical analysis of viscoelastic functions in packable composite resins measured by torsional resonance. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B Appl. Biomater. 2004, 71, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Safty, S.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Temperature-dependence of creep behaviour of dental resin-composites. J. Dent. 2013, 41, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaleem, M.; Masouras, K.; Satterthwaite, J.D.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Viscoelastic stability of resin-composites under static and dynamic loading. Dent. Mater. 2012, 28, e15–e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liou, W.J. Effects of Moisture Content on the Creep Behavior of Nylon-6 Thermoplastic Composites. J. Reinf. Plast. Compos. 1998, 17, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matos, I.C.; Bastos, I.N.; Diniz, M.G.; de Miranda, M.S. Corrosion in artificial saliva of a Ni-Cr-based dental alloy joined by TIG welding and conventional brazing. J. Prosthet. Dent. 2015, 114, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martos, J.; Osinaga, P.W.R.; Oliveira, E.D.; Castro, L.A.S.D. Hydrolytic degradation of composite resins: Effects on the microhardness. Mater. Res. 2003, 6, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshali, R.Z.; Salim, N.A.; Satterthwaite, J.D.; Silikas, N. Long-term sorption and solubility of bulk-fill and conventional resin-composites in water and artificial saliva. J. Dent. 2015, 43, 1511–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Söderholm, K.-J. Degradation of glass filler in experimental composites. J. Dent. Res. 1981, 60, 1867–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halvorson, R.H.; Erickson, R.L.; Davidson, C.L. The effect of filler and silane content on conversion of resin-based composite. Dent. Mater. 2003, 19, 327–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fouad, H.; Elleithy, R. High density polyethylene/graphite nano-composites for total hip joint replacements: Processing and in vitro characterization. J. Mech. Behav. Biomed. Mater. 2011, 4, 1376–1383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fouad, H.; Elleithy, R.; Alothman, O.Y. Thermo-mechanical, Wear and Fracture Behavior of High-density Polyethylene/Hydroxyapatite Nano Composite for Biomedical Applications: Effect of Accelerated Ageing. J. Mater. Sci. Technol. 2013, 29, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayne, S.C.; Thompson, J.Y.; Swift, E.J.; Stamatiades, P.; Wilkerson, M. A characterization of first-generation flowable composites. J. Am. Dent. Assoc. 1998, 129, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labella, R.; Lambrechts, P.; Van Meerbeek, B.; Vanherle, G. Polymerization shrinkage and elasticity of flowable composites and filled adhesives. Dent. Mater. 1999, 15, 128–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprince, J.G.; Palin, W.M.; Vanacker, J.; Sabbagh, J.; Devaux, J.; Leloup, G. Physico-mechanical characteristics of commercially available bulk-fill composites. J. Dent. 2014, 42, 993–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayad, N.M.; Bahgat, H.A.; Al Kaba, E.H.; Buholayka, M.H. Food Simulating Organic Solvents for Evaluating Crosslink Density of Bulk Fill Composite Resin. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soh, M.; Yap, A.U. Influence of curing modes on crosslink density in polymer structures. J. Dent. 2004, 32, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sih, G.C.; Shih, M.T.; Chou, S.C. Transient hygrothermal stresses in composites: Coupling of moisture and heat with temperature varying diffusivity. Int. J. Eng. Sci. 1980, 18, 19–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Brauer, G. Solvent effects on bonding organo-silane to silica surfaces. J. Dent. Res. 1982, 61, 1439–1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baroudi, K.; Silikas, N.; Watts, D.C. Time-dependent visco-elastic creep and recovery of flowable composites. Eur. J. Oral Sci. 2007, 115, 517–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sideridou, I.; Tserki, V.; Papanastasiou, G. Study of water sorption, solubility and modulus of elasticity of light-cured dimethacrylate-based dental resins. Biomaterials 2003, 24, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feilzer, A.; Dauvillier, B. Effect of TEGDMA/BisGMA ratio on stress development and viscoelastic properties of experimental two-paste composites. J. Dent. Res. 2003, 82, 824–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
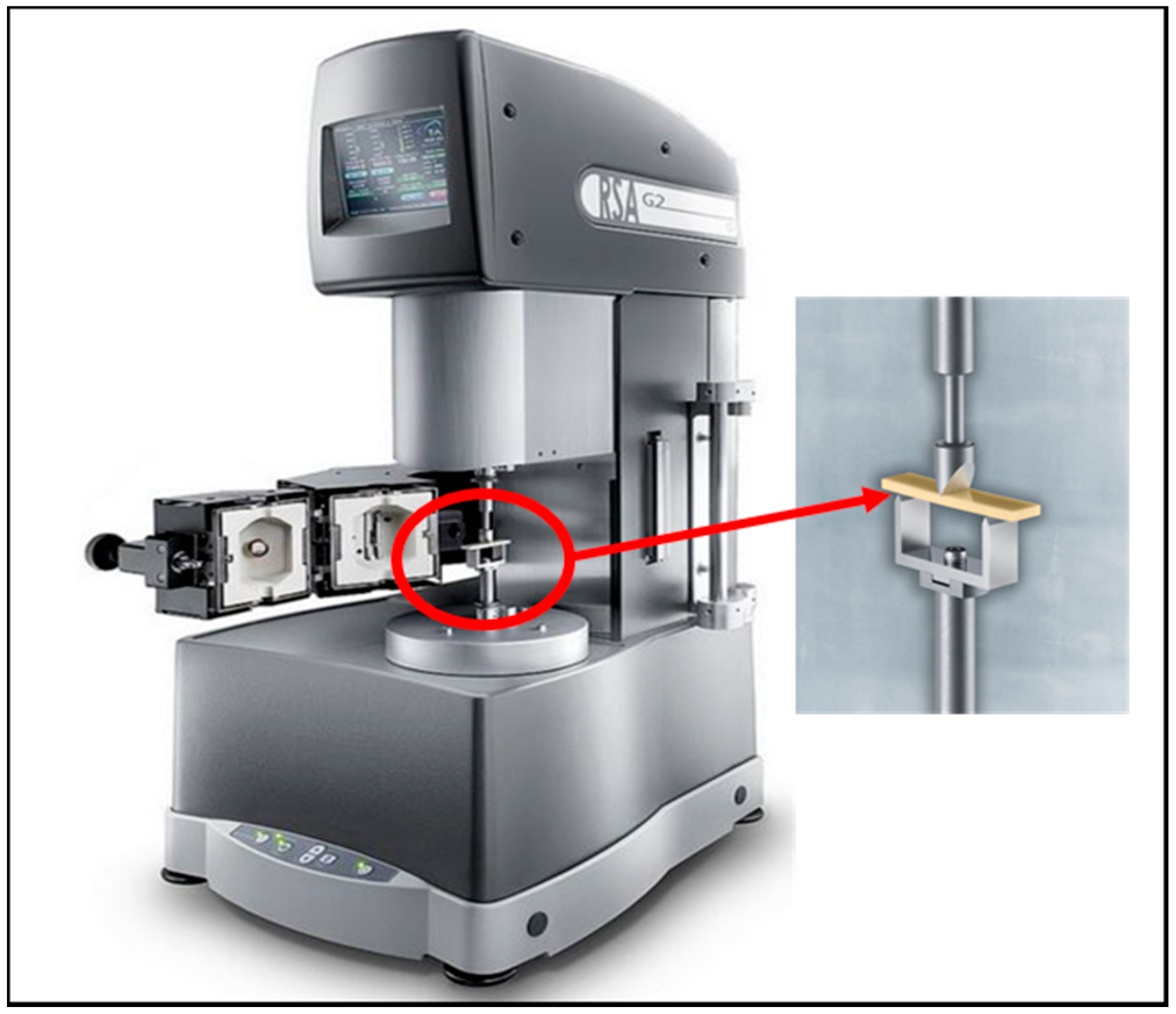

| Material | Code | Type | Manufacturer Increment Thickness (mm) | Matrix | Filler (wt %) | Manufacturer |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetric N-ceram Bulk Fill | TNCBF | Bulk fill | 4 | Bis-GMA, Bis-EMA, UDMA | 78 | Ivoclar Vivadent AG, Schaan, Liechtenstein |
| FiltekTM Bulk Fill | FBF | Bulk fill | 4 | AUDMA, AFM, DDDMA, UDMA | 76.5 | 3 M ESPE GmbH, Seefeld, Germany |
| SonicFillTM2 | SF2 | Sonic-activated, bulk fill | 5 | Bis-GMA, TEGDMA, Bis-EMA, SIMA | 83.5 | Kerr Corp, Orange, USA |
| X-tra fil | XF | Bulk fill | 4 | Bis-GMA, UDMA, TEGDMA | 86 | Voco GmbH Cuxhaven, Germany |
| Grandio | GR | Nano-Hybrid | 2 | Bis-GMA, TEDMA, UDMA | 87 | Voco GmbH Cuxhaven, Germany |
| Ingredients | Concentration (G/100 ML) |
|---|---|
| KH2PO4 | 0.3402 |
| Na2HPO4 | 0.4450 |
| HKCO3 | 1.5017 |
| NaCl | 0.5844 |
| MgCl2 + 6H2O | 0.0305 |
| Citric Acid | 0.5224 |
| CaCl2 | 0.2205 |
| Materials Code | Dry | Dw | Saliva | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBF | 1.17 (0.10) a, c, A | 1.52 (0.11) a, A | 2.33 (0.15) a, B | 2.59 (0.08) a, B |
| SF2 | 0.44 (0.07) b, A | 0.67 (0.08) b, A | 0.75 (0.13) b, A | 0.62 (0.11) b, c, A |
| XF | 0.43 (0.14) b, A | 0.62 (0.16) b, A | 0.64 (0.10) b, A | 0.80 (0.14) b, A |
| TNC BF | 1.24 (0.05) a, A | 2.07 (0.19) c, B | 2.61 (0.09) a, C | 2.87 (0.18) a, C |
| GR | 0.98 (0.03) c, A | 0.28 (0.07) d, B | 0.43 (0.05) c, B, C | 0.54 (0.06) c, C |
| Materials Code | Dry | Dw | Saliva | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBF | 0.45 | 0.73 | 1.49 | 1.55 |
| SF2 | 0.02 | 0.28 | 0.24 | 0.13 |
| XF | 0.11 | 0.31 | 0.17 | 0.44 |
| TNC BF | 0.42 | 1.14 | 1.58 | 1.65 |
| GR | 0.06 | 0.09 | 0.10 | 0.22 |
| Materials Code | Dry | Dw | Saliva | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBF | 61.14 | 51.91 | 35.88 | 40.10 |
| SF2 | 94.59 | 59.03 | 67.91 | 79.35 |
| XF | 73.99 | 50.20 | 72.59 | 45.31 |
| TNC BF | 66.24 | 45.10 | 39.74 | 42.52 |
| GR | 94.14 | 64.19 | 76.67 | 60.06 |
| Materials Code | Dry | Dw | Saliva | Ethanol |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBF | 0.72 (0.12) a, A | 0.79 (0.01) a, A | 0.83 (0.10) a, A, B | 1.04 (0.07) a, B |
| SF2 | 0.42 (0.05) b, A | 0.39 (0.04) b, A | 0.51 (0.09) b, A | 0.49 (0.18) b, A |
| XF | 0.32 (0.10) b, A | 0.31 (0.11) b, c, A | 0.46 (0.13) b, A | 0.36 (0.08) b, A |
| TNC BF | 0.82 (0.09) c, a, A | 0.93 (0.14) a, A | 1.04 (0.06) c, A, B | 1.22 (0.11) a, B |
| GR | 0.93 (0.07) c, A | 0.18 (0.03) c, B | 0.33 (0.09) b, B | 0.32 (0.03) b, B |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alrahlah, A.; Khan, R.; Alotaibi, K.; Almutawa, Z.; Fouad, H.; Elsharawy, M.; Silikas, N. Simultaneous Evaluation of Creep Deformation and Recovery of Bulk-Fill Dental Composites Immersed in Food-Simulating Liquids. Materials 2018, 11, 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071180
Alrahlah A, Khan R, Alotaibi K, Almutawa Z, Fouad H, Elsharawy M, Silikas N. Simultaneous Evaluation of Creep Deformation and Recovery of Bulk-Fill Dental Composites Immersed in Food-Simulating Liquids. Materials. 2018; 11(7):1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071180
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlrahlah, Ali, Rawaiz Khan, Khalid Alotaibi, Ziad Almutawa, H. Fouad, Mohamed Elsharawy, and Nikolaos Silikas. 2018. "Simultaneous Evaluation of Creep Deformation and Recovery of Bulk-Fill Dental Composites Immersed in Food-Simulating Liquids" Materials 11, no. 7: 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071180
APA StyleAlrahlah, A., Khan, R., Alotaibi, K., Almutawa, Z., Fouad, H., Elsharawy, M., & Silikas, N. (2018). Simultaneous Evaluation of Creep Deformation and Recovery of Bulk-Fill Dental Composites Immersed in Food-Simulating Liquids. Materials, 11(7), 1180. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11071180






