Abstract
Using Ti(OC4H9)4 as a precursor, Fe(NO3)3⋅9H2O as the source of iron, and NH4NO3 as the source of nitrogen, an Fe/N codoped TiO2 catalyst was prepared using a sol-gel hydrothermal method. The as-prepared powders were characterized using X-ray powder diffraction, electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, and ultraviolet-visible spectrophotometry. Fe and N codoping resulted in decreased crystallite size and increased specific surface area. Results of the photocatalytic degradation of acid orange 7 (AO7) in a continuous-flow fluidized-bed reactor indicated that the maximum decolorization (more than 90%) of AO7 occurred with the Fe/N-TiO2 catalyst (dosage of 20 g/L) when a combination of visible light irradiation for 10 h HRT (hydraulic retention time), and a heterogeneous system was used. The AO7 degradation efficiency was considerably improved by increasing the hydraulic retention time from 2.5 to 10 h or by reducing the initial AO7 concentration from 300 to 100 mg/L. The reaction rate increased with the light intensity and the maximum value occurred at 35 mW/cm2; moreover, the efficiency of the AO7 degradation increased when the pH decreased with maximum efficiency at pH 3.
1. Introduction
Environmental pollution is a considerable concern in the modern world. An estimated 2% of dyes produced annually are discharged as effluents from manufacturing plants, whereas 10% of dyes are discharged from textile and related industries [1]. Effluents generated from textile manufacturing contain a variety of pollutants characterized by deep coloration, high oxygen demand, high pH, large amounts of suspended solids, and low or nonbiodegradability [2,3]. Many methods have been tested to remove dyes from industrial effluents, including biological processes, adsorption, and coagulation. However, these methods still generate a large amount of sludge or solid waste that requires further treatment.
Advanced oxidation processes are a suitable alternative to traditional methods for solving environmental problems caused by the discharge of textile-dyeing wastewater. Titanium dioxide (TiO2) is a heterogeneous photocatalysts and TiO2 based photocatalysis is a promising technique for wastewater treatment [4], especially for wastewater containing refractory organic compounds. However, the large band gap for highly oriented TiO2 powders with pure anatase structure and rutile are 3.2 and 3.0 eV, respectively. Therefore, pure TiO2 can absorb solar light only in the near ultraviolet (UV) region. To modify this property and shift the excitation threshold toward higher wavenumbers, the recombination time of free radicals must be extended or the phase composition must be changed to significantly affect the optical and electrical properties of the material. Doping with different nonmetallic or metallic elements has often been employed to improve photocatalytic activity [5].
Among nonmetallic dopants, doping TiO2 with N is one of the most effective methods to produce effects from visible light irradiation [6]. However, because the N 2p states are strongly localized at the top of the valence band, the photocatalytic efficiency of N-doped TiO2 decreases. The isolated empty states tend to trap photogenerated electrons, thereby reducing the photogenerated current [7]. Doping TiO2 with two different elements, namely nitrogen and cheaper Fe ions, has attracted interest in computational studies. Several papers have reported that Fe ions can trap holes or electrons at low doping levels, whereas they become recombination centers at high doping levels [8,9,10]. The photocatalytic activities of these powders are approximately two to four times higher than those of pure anatase TiO2 under visible light irradiation. The synthesis of TiO2 nanoparticles by using a combination of sol-gel and hydrothermal methods is another recent innovation. The sol-gel hydrothermal method combines the advantages of the sol-gel method with high-pressure hydrothermal conditions [11]; particle size and morphology can be controlled during the hydrothermal process [11,12].
In this paper, we present a sol-gel hydrothermal method for the fabrication of Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts that respond to visible light. The photocatalytic activity of Fe/N-TiO2 was measured for the degradation of acid orange 7 (AO7) in a continuous-flow fluidized-bed system under visible light irradiation. The effects of operational parameters, such as the catalyst activity, dosage, and solution pH, were also examined.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Sample Preparation
Fe/N-TiO2 was prepared using a sol-gel hydrothermal method. A suitable amount (0.1 mol) of titanium tetra-n-butoxide [Ti(OC4H9)4] (Sigma Aldrich, MO, USA) was dissolved in 100 mL of anhydrous ethanol (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) to obtain solution A. Moreover, 0.0012 mol of iron nitrate [Fe(NO3)3·9H2O] (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) and 0.001 mol of ammonium nitrate (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) were mixed with 2 mL of distilled water and 10 mL of acetic acid (Merck, Darmstadt, Germany) to prepare solution B. Then, solution A was slowly added to solution B at a rate of 2 mL per minute under stirring for up to 48 h. The sample mixture was transferred to a hydrothermal flask to undergo treatment at 100, 150, 175, and 200 °C for 1 h. The resulting Fe/N-TiO2 powder was washed with distilled water until a pH of 7 was established and then dried at 80 °C for 24 h.
2.2. Characterization
The band gap of Fe/N-TiO2 was measured using a UV-visible spectrophotometer (Cary 300 Bio, Varian, Mulgrave, Victoria, Australia) equipped with an integrating sphere for diffuse reflectance spectra. The chemical composition of Fe/N-TiO2 was verified through electron spectroscopy for chemical analysis (ESCA; ESCALAB 250, VG Scientific, UK). Crystal structures were obtained through X-ray diffraction (XRD; Rigaku Co. DMAX 2200VK, Tokyo, Japan) using Cu Kα radiation (λ = 1.5418 Å). All peaks measured through XRD were assigned by comparison with those of the Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards (JCPDS 04-002-2678) [13]. The specific surface area (BET, m2 g−1) was calculated using the BET equation, and total pore volume (Vt, m3 g−1) was evaluated by converting the adsorption amount at P/P0 = 0.95 to the volume of the liquid adsorbate.
2.3. Photocatalytic Experiments
The upflow fluidized-bed system is shown in Figure 1. The photocatalytic activities of Fe/N-TiO2 samples under visible light were evaluated based on the degradation rate of AO7 in a cylindrical quartz reactor (40/30 mm OD/ID; height = 500 mm) containing 20 g of Fe/N-TiO2 and 5 L of a 200 mg/L AO7 aqueous solution. The photoreactor was open to the atmosphere, and the quartz reactor was surrounded by 14 light tubes. The visible light tubes were germicidal lamps with a wavelength of 419 nm (Sankyo Denki, Tokyo, Japan). The light power (approximately 8 mW/cm2) in the center of the reactor in air was measured using a hand-held optical power meter (Model 840-C, Newport, Irvine, CA, USA). The photodegradation rates of AO7 solutions were determined by periodically measuring the absorbance at λ = 484 nm by using a Hach DR 4000 UV-visible spectrophotometer (Hach, Loveland, CO, USA).
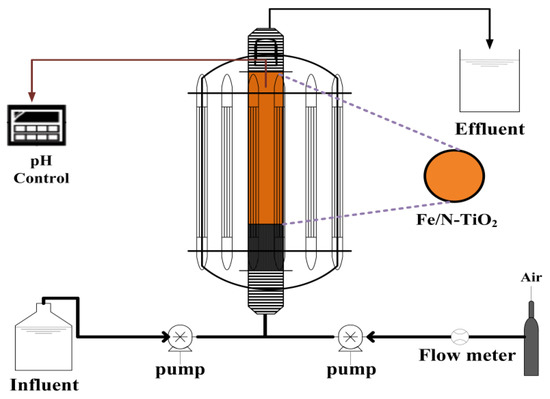
Figure 1.
Schematic of the upflow fluidized-bed system.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Characterization of the N/Fe-TiO2 Samples
Figure 2a presents the XRD patterns of undoped (TiO2) and Fe/N-TiO2 particles as a function of the reaction temperature. Fe/N-TiO2 particles were readily indexed to the diffraction peaks of the anatase phase (JCPDS 04-002-2678) and exhibited the presence of an intense peak corresponding to the (101) plane. The major peaks observed corresponded to the (101), (004), (200), (105), and (204) planes of the anatase phase [14]. For 100, 150, 175, and 200 °C Fe/N-TiO2 particles, the crystallite sizes were 10.65, 10.79, 12.11, and 13.46 nm, respectively. Smaller crystallite sizes were obtained for the codoped samples, which indicated that the incorporation of Fe and N ions restricted the growth of TiO2 crystallite and prevented the transformation of anatase to rutile [15]. Deng et al. [16] also investigated the morphology of Fe-doped titania nanotubes synthesized using the sol-gel and hydrothermal methods. They found that the addition of Fe slowed the crystallization process and prevented the growth of crystallite TiO2. The crystallite size of Fe/N-TiO2 particles increased with the reaction temperature (Table 1).
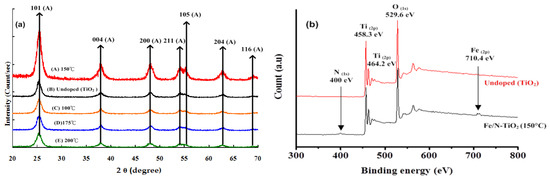
Figure 2.
Fe/N-TiO2 powders prepared using the sol-gel hydrothermal process: (a) XRD patterns of samples A–E, (b) ESCA spectra of the samples.

Table 1.
Physicochemical properties of doped and undoped samples.
To determine whether codoping with Fe/N was successful, the surface of Fe/N-TiO2 composites was examined through ESCA. The ESCA spectra of Ti 2p in Fe/N-TiO2 shown in Figure 2(b) reveal that the Ti 2p1/2 and Ti 2p3/2 peaks at 464.2 and 458.5 eV, respectively, were in a favorable agreement with those previously observed for Ti4+ [17].The presence of N in TiO2 particles was substantiated by the N 1s spectra and significant peaks around 400 eV, which can be attributed to the formation of anionic N in O−Ti−N linkages [18], whereas the iron peak (710 eV) was attributed to Fe3+, indicating the formation of Fe2O3 [19]. Saha and Tompkins [20] investigated N 1s ESCA spectra during the oxidation process of Ti–N and assigned the peaks at 400 eV to be molecularly chemisorbed γ−N2. Kim et al. [15] reported that the ionic radii of Fe3+ (0.64 Å) and Ti4+ (0.68 Å) are similar and that Fe3+ can therefore be incorporated into the lattice of TiO2 to form a Ti–O–Fe bond in Fe/N-TiO2. The results indicate that Fe is present in the form of Fe3+ by replacing Ti4+ in the doped photocatalyst, which may change the charge distribution of atoms on the photocatalyst surface, resulting in enhanced photocatalytic activity. By contrast, the decrease of Ti binding energy upon N-doping could be interpreted as the formation of O–Ti–N in the TiO2 lattice [19], which indicates that nitrogen incorporation can successfully retard the charge recombination at the TiO2/dye/electrolyte interface. Additionally, the concentrations of Fe and N in Fe/N-TiO2 determined using ESCA were 5.58 and 5.48 wt %, respectively, which were consistent with the theoretical expectation.
The calculation of the band gap of materials can be conducted using the following formulation: absorption coefficient (a) and the incident photon energy (hν) can be written as a = Bi·(hν−Eg)2/hν, where Bi is the absorption constant for indirect transitions, hν is the photon energy, and Eg is the band gap energy [21]. Plots of (ahν)1/2 versus hν from the spectral data are presented in Figure 3a, which shows the UV-visible spectra of the undoped (TiO2) and Fe/N-TiO2 particles from 250 to 700 nm. Samples A–E exhibited typical UV-visible spectra for semiconductor materials with a band gap absorption onset at 465, 388, 464, 452, and 485 nm, which corresponded to energy bandgaps at 2.67, 3.20, 2.67, 2.74, and 2.55 eV, respectively. These results demonstrate that the absorption of doped TiO2 in the visible light region is significantly enhanced compared with that of undoped TiO2, which in turn may considerably increase the photocatalytic activity of TiO2 under visible light irradiation. Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectrum of the Fe/N-TiO2 prepared using the sol-gel hydrothermal method at 150 °C and the undoped TiO2 over the 400–4000 cm−1 range are shown in Figure 3b. The strong absorption at 3442 and 1640 cm−1 were assigned to the stretching vibration and the bending vibration of OH, respectively, originating from water adsorbed on the samples’ surface [15]. The peaks around 1090 cm−1 were attributed to the N atoms embedded in the TiO2 network. In addition, the small peak observed at 570 cm−1 indicates Fe–O–Ti vibrations [22]. No absorption peak for Fe–N stretching was observed, indicating that Fe did not substitute for Ti at sites where N atoms substituted for O atoms.
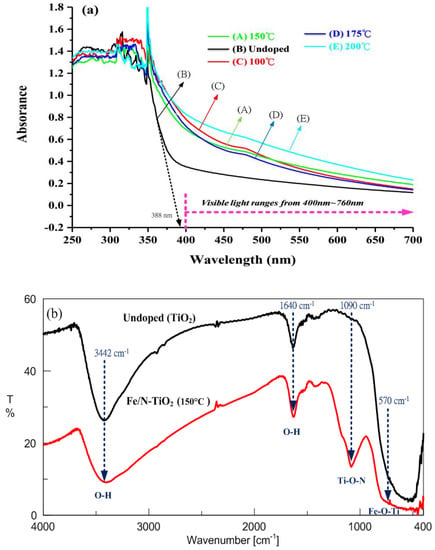
Figure 3.
Fe/N-TiO2 powders prepared using the sol-gel hydrothermal process: (a) UV-visible reflectance spectra of samples A–E, (b) FT-IR spectra of the samples.
The optimal synthesis temperature of Fe/N-TiO2 was determined from batch experiments. Figure 4a shows the photocatalytic AO7 degradation curves for Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts synthesized at different temperatures (see Table 1). The photocatalytic activity evolved as follows: Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C) > Fe/N-TiO2 (175 °C) > Fe/N-TiO2 (200 °C) > Fe/N-TiO2 (100 °C) > undoped TiO2. Fe/N TiO2 (150 °C) exhibited the highest photocatalytic activity and led to 95.2% AO7 degradation in 5 h. In addition, Figure 4b plots ln(C/C0) versus time obtained by assuming first-order kinetics for the degradation reaction. C and C0 are the AO7 concentrations at time t and initial concentration, respectively. The plots were almost linear, indicating that the reactions followed pseudo first-order kinetics. The first-order degradation rate constants (k) for Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C), Fe/N-TiO2 (175 °C), Fe/N-TiO2 (200 °C), Fe/N-TiO2 (100 °C), and undoped TiO2 catalysts were 5.64 × 10−2, 4.57 × 10−2, 2.23 × 10−2, 1.36 × 10−2, and 8.53 × 10−1 min−1, respectively. This suggests that codoping of Fe and N narrows the TiO2 band gap. Cong et al. [23] reported that the overlap of the Ti-d orbital of TiO2 and the doped metal d orbital leads to a narrowing of the TiO2 band gap in TiO2 implanted with metal ions, allowing the absorption of visible light. Therefore, N and Fe were incorporated into the TiO2 framework, narrowing the band gap of TiO2 to 2.67 eV (Table 1) and causing a large red shift, which in turn caused a much narrower band gap and greatly improved photocatalytic activity. By contrast, it inhibits the recombination of photogenerated electrons and holes. Fe ions with a suitable concentration can trap photogenerated electrons, which enhances the utilization efficiency of the photogenerated electron and hole [24]. Consequently, under these experimental conditions, Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C) was optimal for AO7 removal after 5 h of visible light irradiation time.
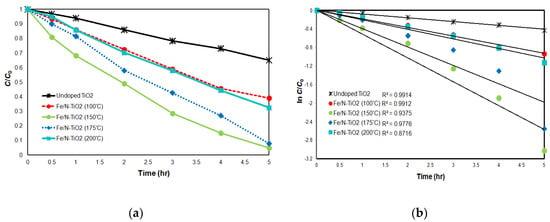
Figure 4.
(a) AO7 degradation curves for Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts synthesized at different temperatures; (b) logarithmic AO7 decay as a function of time. (Experimental condition: pH = 3, initial AO7 concentration = 10 mg/L, catalyst dosage = 0.1 g/L).
3.2. Degradation of AO7 in a Continuous-Flow Fluidized-Bed System
The optimal Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C) catalyst was selected for photocatalytic activity tests of the degradation of AO7. The effect of the initial AO7 concentration on the photocatalytic degradation efficiency was examined for concentrations ranging from 100 to 300 mg/L with an Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C) dosage of 20 g/L, a hydraulic retention time (HRT) of 10 h, a pH of 3, and a visible light intensity of 35 mW/cm2. Figure 5a shows the AO7 removal efficiency and observed rate constant (Kobs) as a function of the initial AO7 concentration at a pH of 3 and with an HRT of 10 h. The degradation rate of AO7 decreased when the initial AO7 concentration increased. The number of photons decreased because of the decreasing intensity of the visible light, leading to a decrease in the formation of hydroxyl radicals, which ultimately reduced AO7 removal efficiency [25]. Moreover, the reaction rate also increased when the visible light intensity increased, and the maximum rate was reached for an irradiation of 35 mW/cm2, as illustrated in Figure 5b. This indicates that the rate of photons per unit area of catalyst powder increased with the light intensity [26], and there was a corresponding increase in photocatalytic degradation rate of AO7.
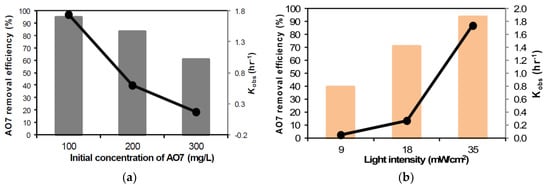
Figure 5.
(a) AO7 removal efficiency and Kobs as a function of initial concentration, (b) effect of visible light intensity on AO7 removal efficiency and Kobs (Experimental condition: pH = 3, HRT = 10 h, catalyst dosage = 20 g/L).
To study the effect of pH on degradation efficiency, experiments were performed under visible light at pH values from 3 to 10 with constant concentrations of AO7 and Fe/N-TiO2 (150 °C) catalyst. The results in Figure 6a indicate that the photodegradation efficiency for AO7 increased as the pH decreased, with maximum efficiency (88%) at pH 3. The degradation rates for the continuous-flow photoreactor evolved as follows: pH 3 > pH 7 > pH 10. In addition, increasing the HRT from 2.5 to 10 h increased the AO7 removal efficiency from 32% to 88% at pH 3. Explaining the effect of pH on the dye photodegradation efficiency is difficult because of the multiple roles of H+ ions, but pH change is related to the charge in the functionalized surface of the solid catalyst according to the following reactions [27]:
TiOH + H+ ←→ TiOH2+, pH < pHζ
TiOH + OH− ←→ TiO− + H2O, pH > pHζ
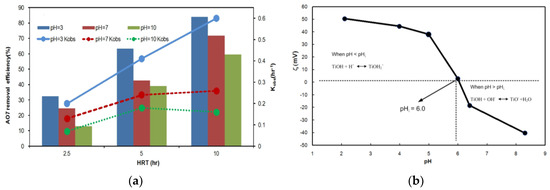
Figure 6.
(a) Effect of pH on AO7 removal efficiency and Kobs as a function of HRT, (b) Zeta potential (ζ) of Fe/N-TiO2 (initial AO7 concentration = 200 mg/L, catalyst dosage = 20 g/L, visible light intensity = 35mW/cm2).
According to Equation (1), when TiO2 is suspended in an acidic solution (pH < point of zero charge, pHζ), the surface charge of TiO2 becomes positive. Conversely, when TiO2 is suspended in a basic solution (pH > pHζ), the surface charge becomes negative, as shown in Equation (2). Figure 6b shows that pHζ for the Fe/N-TiO2 was 6. Therefore, the surface of the catalyst was positively charged at pH < 6 and negatively charged at pH > 6. AO7 is an anionic dye and was negatively charged under the experimental conditions used because of the SO32− groups. Therefore, electrostatic interactions between the Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts and the sulfonate groups resulted in adsorption at pH < 6 and enhanced degradation efficiency. Conversely, adsorption of AO7 onto Fe/N-TiO2 surfaces was weak at pH > 6 because of Coulombic repulsion between the negatively charged Fe/N-TiO2 and the AO7 molecules. Therefore, the degradation efficiency decreased.
4. Conclusions
Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts were synthesized using a combination of sol-gel and hydrothermal processes. The average size and distribution of the Fe/N-TiO2 particles synthesized was approximately 10–15 nm. The average size of the particles synthesized increased with the reaction temperature, and the absorption edge of Fe/N-TiO2 catalysts was red-shifted toward 480 nm. The Fe/N-TiO2 photocatalyst exhibited favorable photocatalytic activity for the degradation of AO7 in a continuous-flow fluidized-bed system under visible light. The experimental results revealed that the optimal dosage of Fe/N-TiO2 was 20 g/L, and that AO7 degradation efficiency was substantially improved by increasing HRT from 2.5 to 10 h or by reducing initial AO7 concentration from 300 to 100 mg/L. Additionally, the degradation efficiency of AO7 increased as the pH decreased, with a maximum efficiency at pH 3.
Author Contributions
All the authors have contributed equally to the realization of work.
Funding
This study was supported by grant from Hsuteng Consulting International Co., Ltd.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge experimental apparatus support from Institute of Environment Engineering and Management, National Taipei University of Technology.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Easton, J.R.; Waters, B.D.; Churchley, J.H.; Harrison, J. Colour in dyehouse effluent. In Society of Dyers and Colourists; Cooper, P., Ed.; The Alden Press: Oxford, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, C.C.; Hsieh, Y.H.; Lai, P.F.; Li, C.H.; Kao, C.L. Photodegradation treatment of azo dye wastewater by UV/TiO2 process. Dyes Pigm. 2006, 68, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Yang, B.; Chen, J.; Sun, R. Treatment of wastewater containing azo dye reactive brilliant red X-3B using sequential ozonation and upflow biological aerated filter process. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 161, 241–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jothiramalingam, R.; Wang, M.K. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic activity of porous manganese oxide doped titania for toluene decomposition. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 562–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Society for Testing and Material. Powder Diffraction Files; Joint Committee on Powder Diffraction Standards: Swarthmore, PA, USA, 1999; pp. 3–888. [Google Scholar]
- McManamon, C.; Delaney, P.; Morris, M.A. Photocatalytic properties of metal and non-metal doped novel sub 10 nm titanium dioxide nanoparticles on methyl orange. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2013, 411, 169–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Irie, H.; Watanabe, Y.; Hashimoto, K. Nitrogen-concentration dependence on photocatalytic activity of TiO2−xNx powders. J. Phys. Chem. B 2003, 107, 5483–5486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Z.; Orlov, A.; Lambert, R.M.; Payne, M.C. New Insights into the origin of visible light photocatalytic activity of nitrogen-foped and oxygen-feficient snatase TiO2. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 20948–20952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Yu, J.; Cheng, B. Effects of Fe-doping on the photocatalytic activity of mesoporous TiO2 powders prepared by an ultrasonic method. J. Hazard. Mater. 2006, 137, 1838–1847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Xiang, Q.; Zhou, M. Preparation, characterization and visible-light-driven photocatalytic activity of Fe-doped titania nanorods and first-principles study for electronic structures. Appl. Catal. B 2009, 90, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, L.; Liu, B.; Zhao, X.; Kazuya, N.; Taketoshi, M.; Akira, F. Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalysis of Fe-doped TiO2: A combined experimental and theoretical study. Int. J. Photoenergy 2012, 2012, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Dang, T.M.H.; Trinh, V.D.; Bui, D.H.; Phan, M.H.; Huynh, D.C. Sol-gel hydrothermal synthesis of strontium hexaferrite nanoparticles and the relation between their crystal structure and high coercivity properties. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2012, 2, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.J.; Bae, S.B.; Bae, D.S. Synthesis and characterization of Ru doped TiO2 nanoparticles by a sol-gel and a hydrothermal process. J Mater. 2010, 9, 9–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bickley, R.I.; Gonzalez-Carreno, T.; Lees, J.S.; Palmisano, L.; Tilley, R.J.D. A structural investigation of titanium dioxide photocatalysts. J. Solid State Chem. 1991, 92, 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, T.H.; Rodríguez-González, V.; Gyawali, G.; Cho, S.H.; Sekino, T.; Lee, S.W. Synthesis of solar light responsive Fe, N codoped TiO2 photocatalyst by sonochemical method. Catal. Today 2013, 212, 75–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, L.; Wang, S.; Liu, D. Synthesis, characterization of Fe-doped TiO2 nanotubes with high photocatalytic activity. Catal. Lett. 2009, 129, 513–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.H.; Chen, S.S.; Cheng, Y.W.; Tseng, W.L.; Wang, Y.H. Liquid-phase non-thermal plasma-prepared N-doped TiO2 for azo dye degradation with the catalyst separation system by ceramic membranes. Water Sci. Technol. 2010, 62, 1060–1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, G.; Jiang, Z.; Shi, H.; Xiao, T.; Yan, Z. Preparation of highly visible-light active N-doped TiO2 photocatalyst. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 5301–5309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, B.C.; Chen, S.S.; Su, C.C.; Li, Y.C. Preparation and characterization of nanocrystalline Fe/N Codoped titania. Ferroelectrics 2009, 381, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saha, N.C.; Saha, H.G. Titanium nitride oxidation chemistry: An X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy study. J. Appl. Phys. 1992, 72, 3072–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, F.; Wu, Z.; Tong, Y.; Wu, Z.; Cravotto, G. Microwave-assisted synthesis of carbon-based (N, Fe)-codoped TiO2 for the photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2010, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishii, M.; Nakahira, M.; Yamanaka, T. Infrared absorption spectra and cation distributions in (Mn, Fe)3O4. Solid State Commun. 1972, 1, 209–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Anpo, M.; He, D. Preparation, photocatalytic activity, and mechanism of nano-TiO2 Codoped with nitrogen and iron (III). J. Phys. Chem. C 2007, 111, 10618–10623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.N.; Nguyen, N.K.T.; Nguyen, P.H. Hydrothermal synthesis of Fe-doped TiO2 nanostructure photocatalys. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2011, 2, 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Daneshvar, N.; Aber, S.; Hosseinzadeh, F. Study of C.I. acid orange 7 removal in contaminated water by photo oxidation processes. Glob. Nest J. 2008, 10, 16–23. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, R.; Heda, L.C.; Ameta, S.C.; Sharma, S. Use of zinc oxide as photocatalyst for photodegradation of copper soap derived from azadirecta indica (neem) oil. Res. J. Pharm. Biol. Chem. Sci. 2013, 4, 537–548. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, W.Y.; Ku, Y. Effect of solution pH on the adsorption and photocatalytic reaction behaviors of dyes using TiO2 and Nafion-coated TiO2. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2007, 302, 261–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).