CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor: Technology Development toward Commercialization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Fabrication Techniques
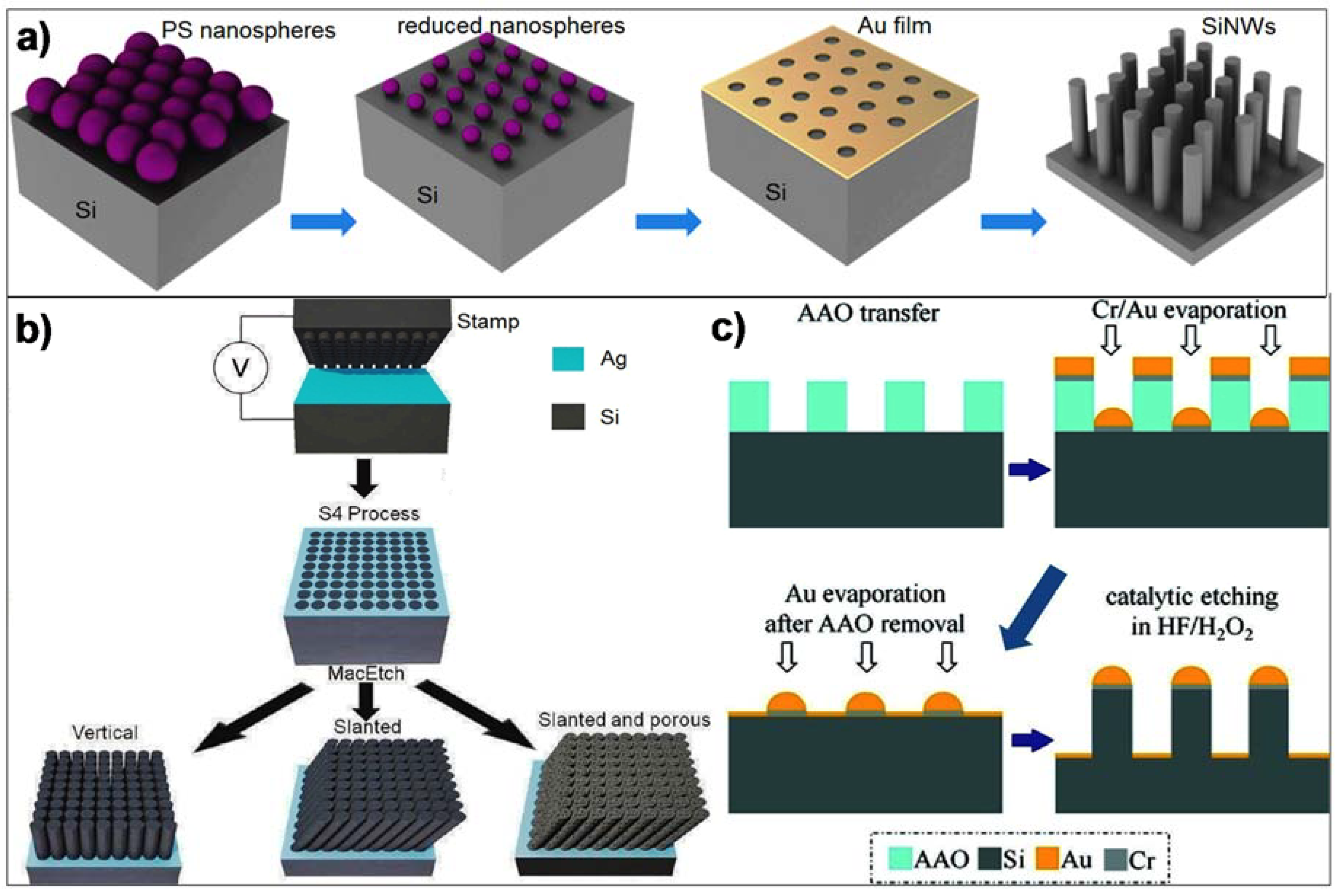
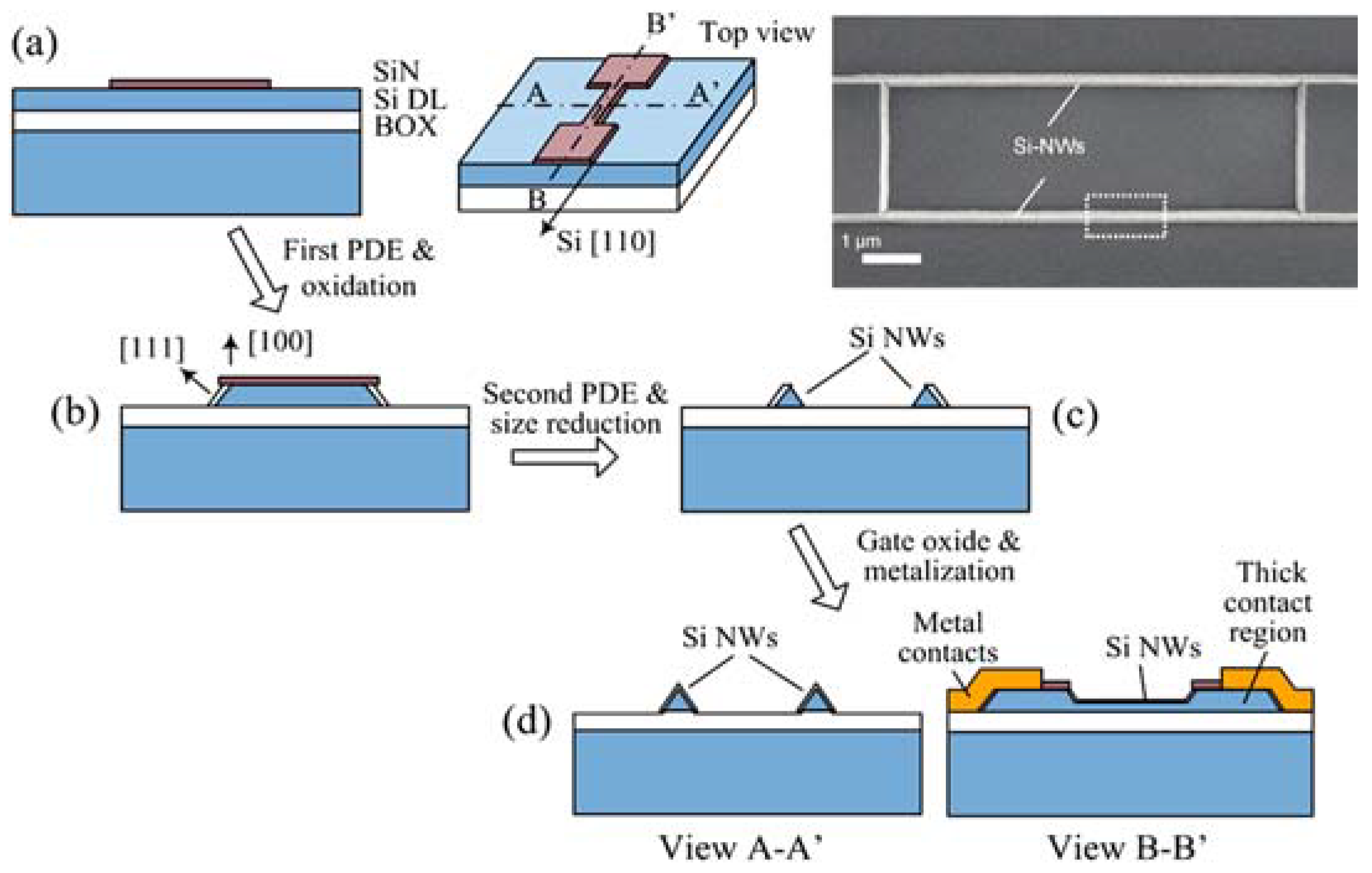
2.1. Vertical SiNWs
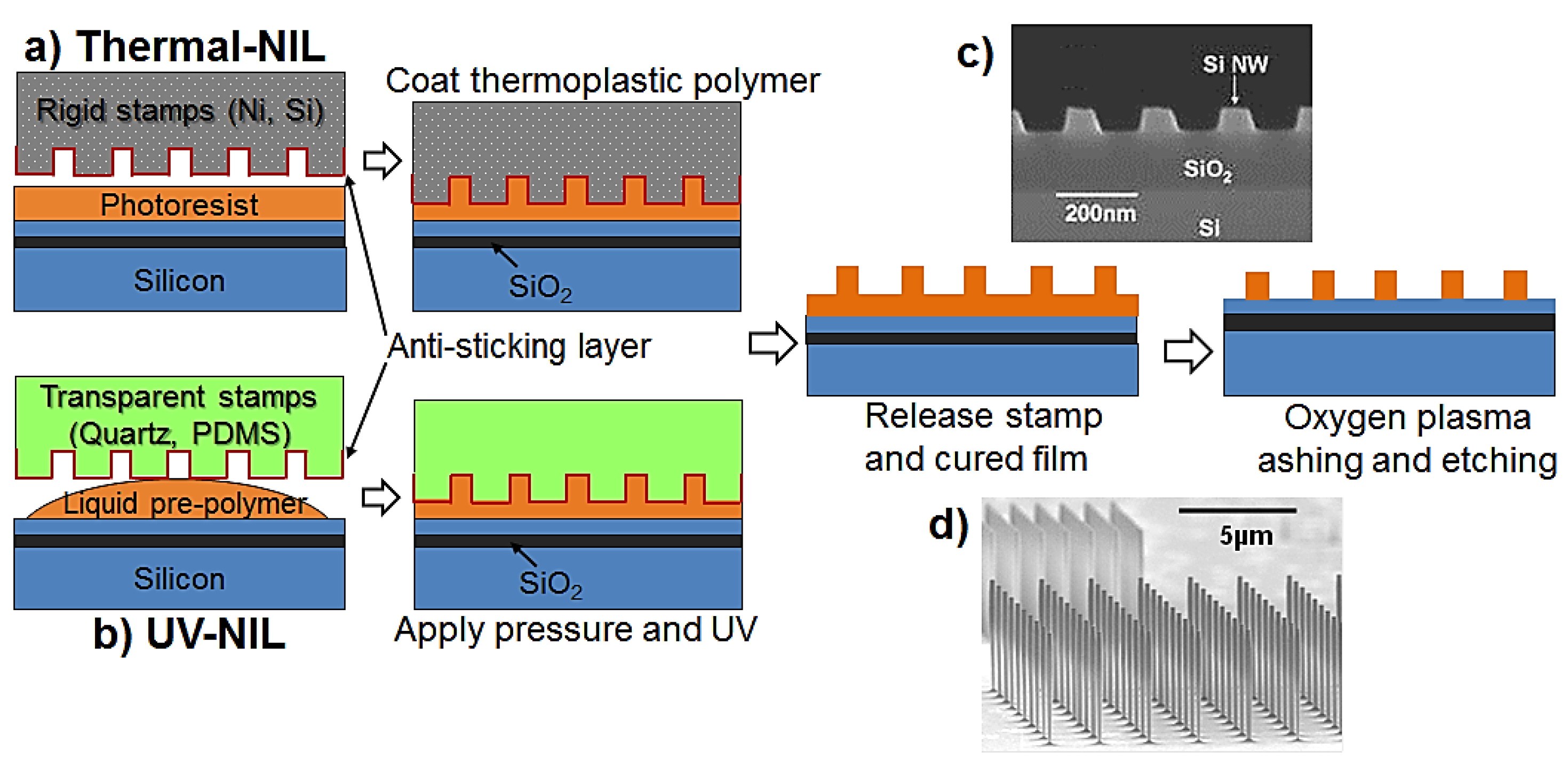
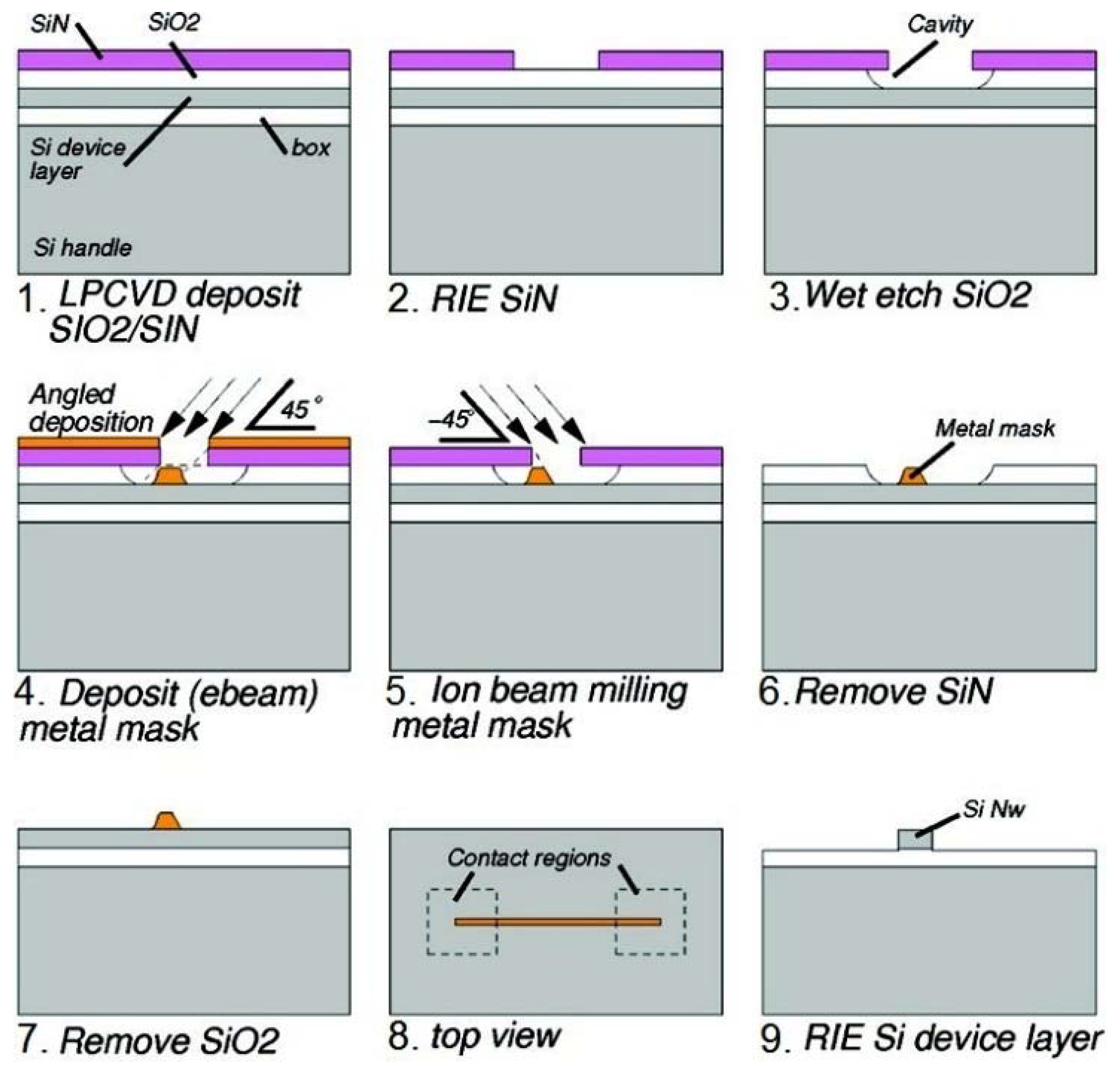
2.2. Horizontal SiNWs
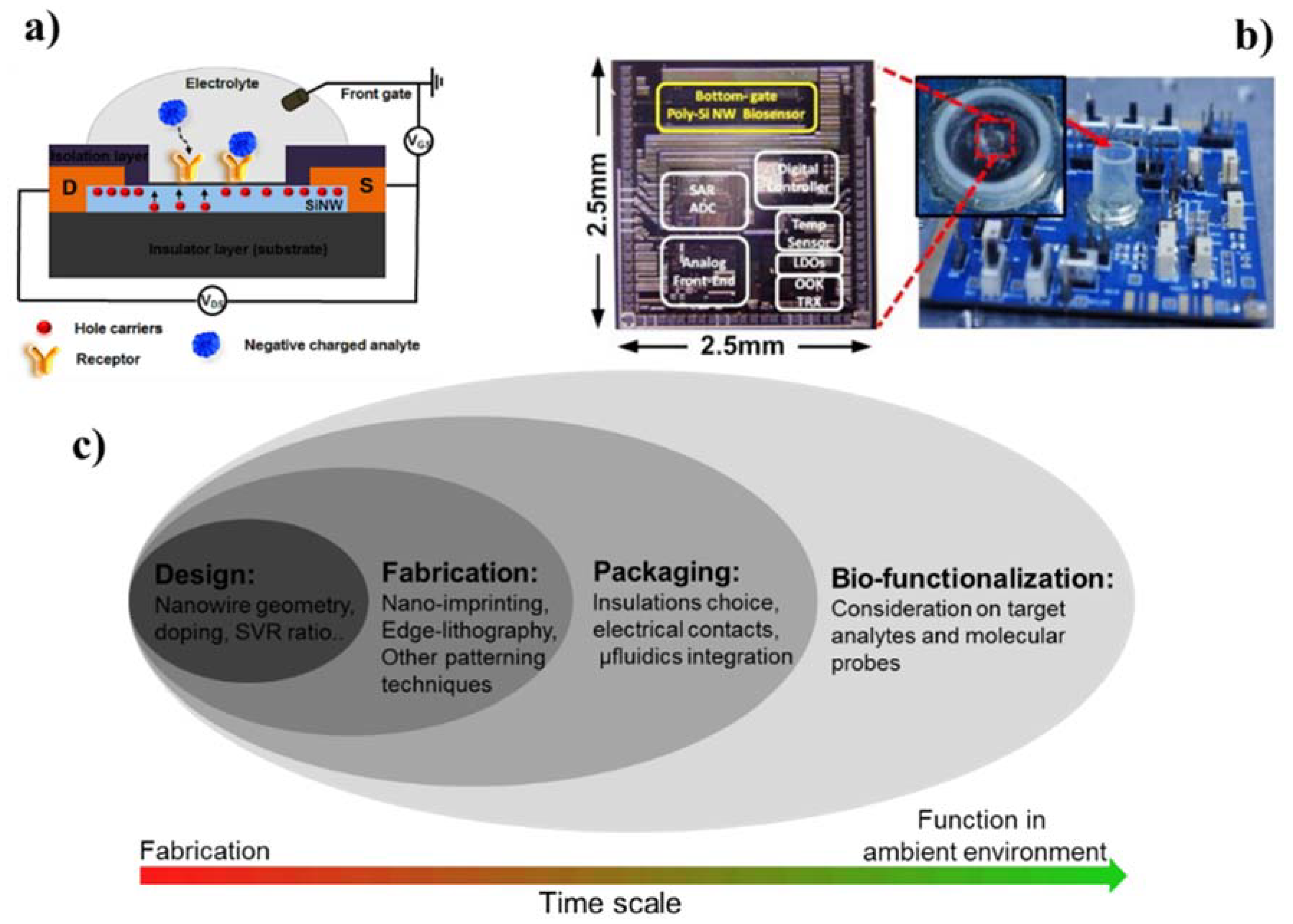
3. Integration of Silicon Nanowires into Functional Devices
3.1. Forming High-Quality Electrical Contacts
3.2. Dielectric Insulation for Silicon Nanowire Device
3.3. Sample Delivery: on-Chip Microfluidics Integration
3.4. Multichannel Electronic Readouts
4. Sensing Performance: Finding the Best Compromise among SiNW FETs Fabrication Aspects
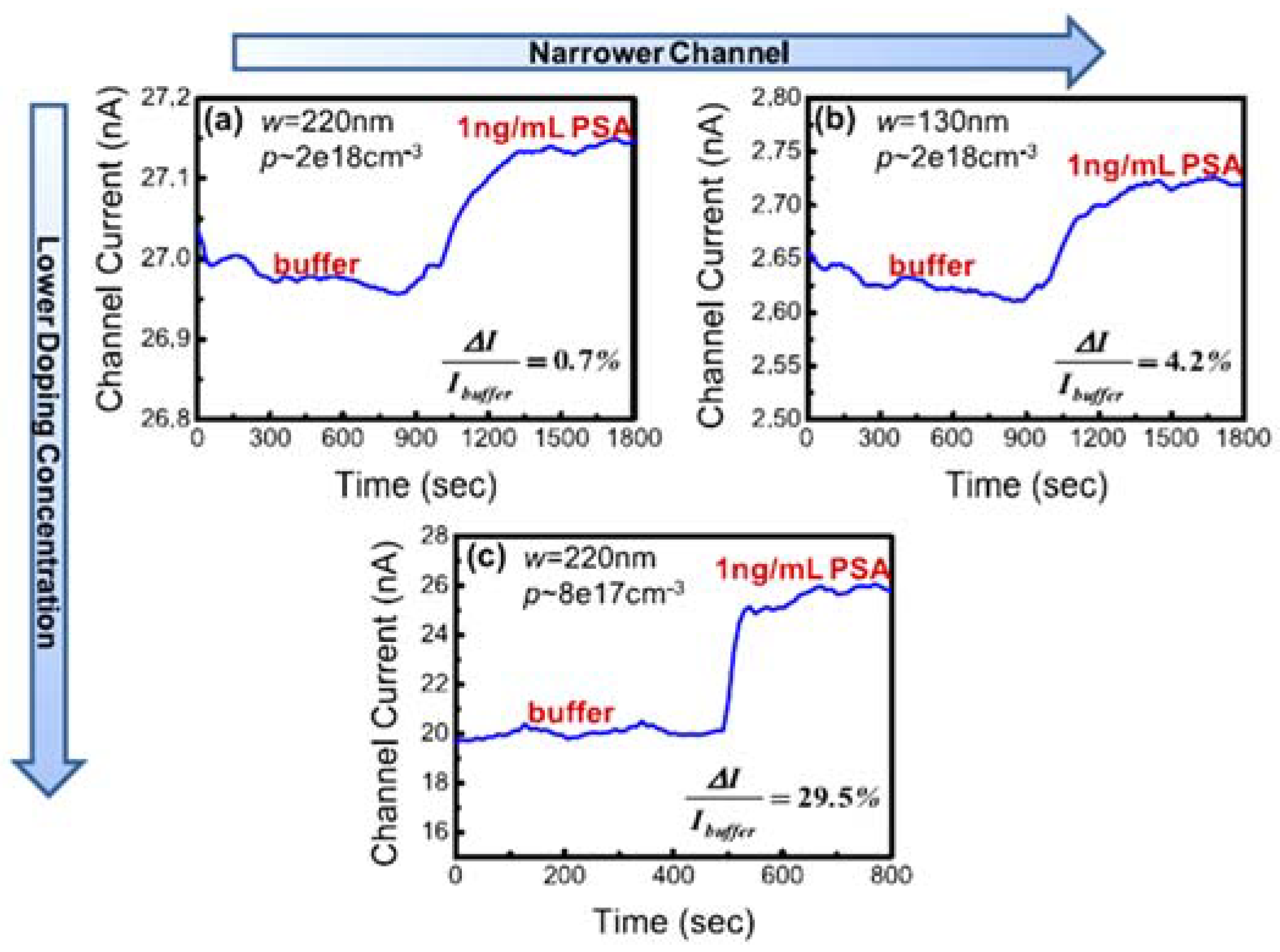
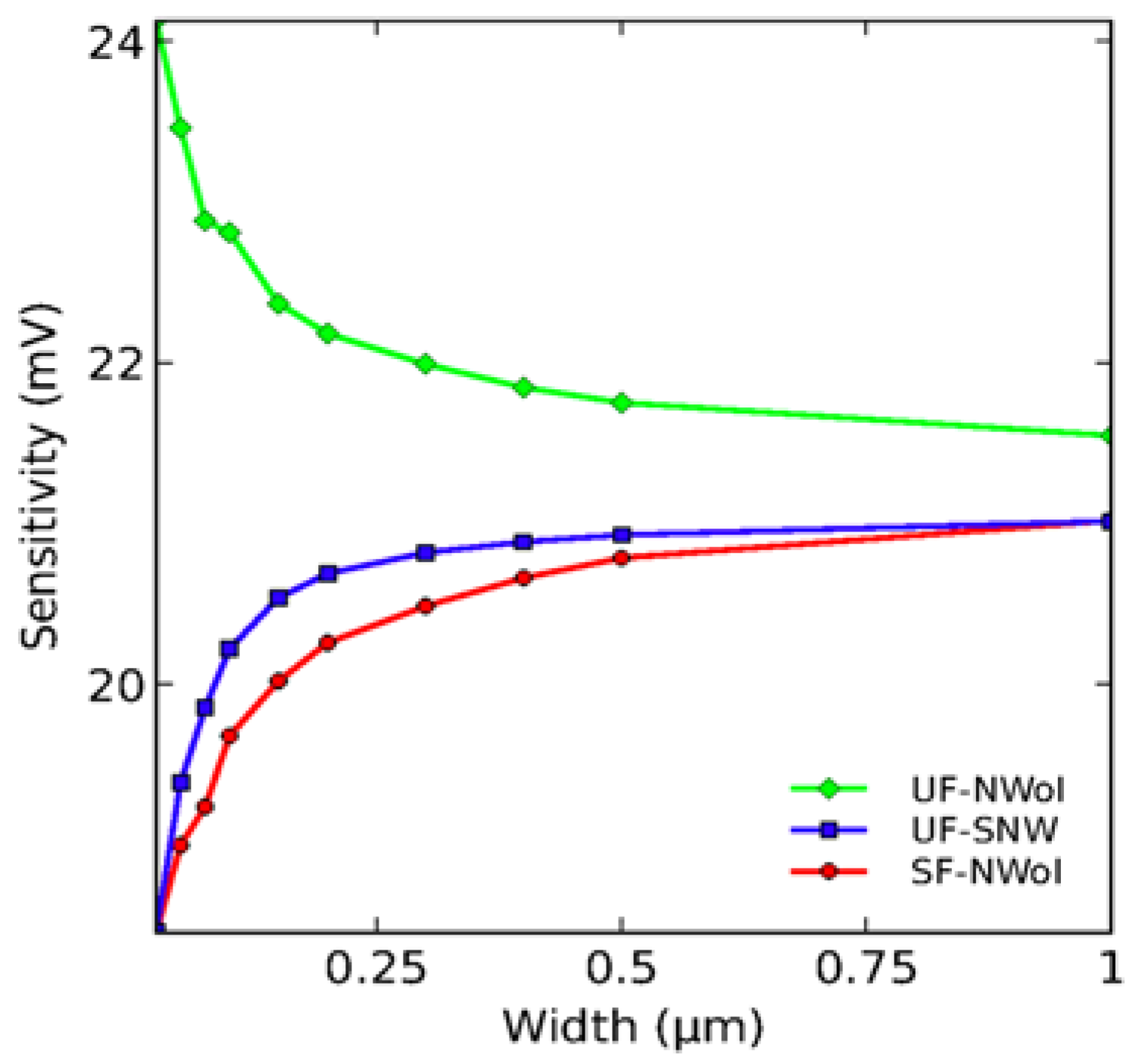
4.1. Impact of the Nanowire Design in Sensing Performance
4.2. Considerations on Fabrication Route and Process-Selection Frame Work
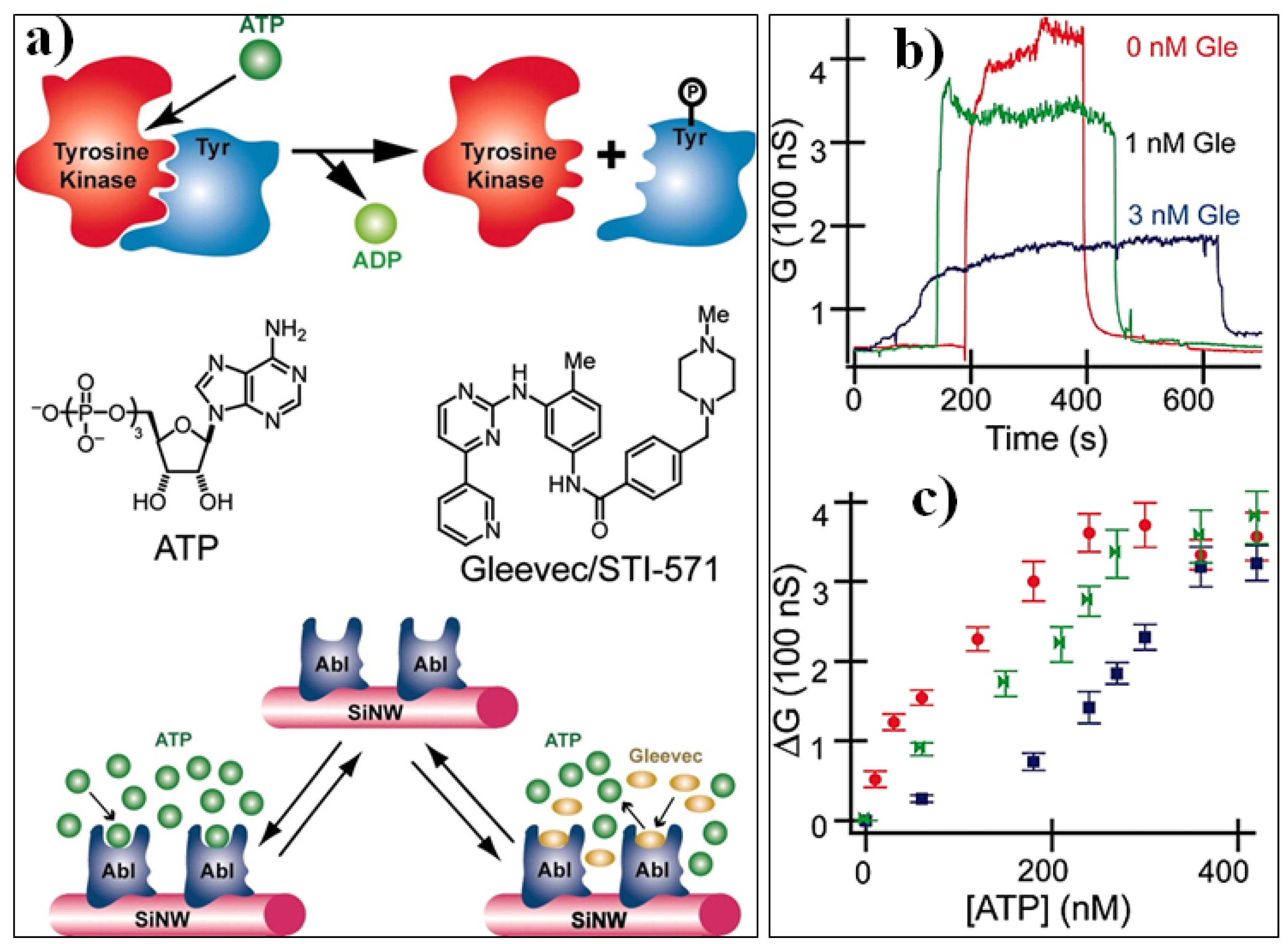
4.3. Molecular Probes and Target Analytes
5. Applications of Silicon Nanowire Biosensor in Biomedical and Environmental Monitoring
5.1. Medical Diagnosis Device Development
5.2. Bio-Pharmaceutical Applications
5.3. Environmental Monitoring
6. Challenges and Opportunities of Silicon Nanowire Biosensor
6.1. Early-Stage Development Platforms
6.2. Challenges and Needs for Commercialization of Silicon Nanowire Biosensor
7. Conclusions and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arlett, J.; Myers, E.; Roukes, M. Comparative advantages of mechanical biosensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 203–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire-Based Biosensors; ACS Publications: Washington, DC, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Maurand, R.; Jehl, X.; Kotekar-Patil, D.; Corna, A.; Bohuslavskyi, H.; Laviéville, R.; Hutin, L.; Barraud, S.; Vinet, M.; Sanquer, M. A cmos silicon spin qubit. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Yan, H.; Das, S.; Klemic, J.F.; Ellenbogen, J.C.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire nanocomputer as a finite-state machine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 2431–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xiang, J.; Qian, F.; Gradecak, S.; Wu, Y.; Yan, H.; Blom, D.A.; Lieber, C.M. Dopant-free gan/aln/algan radial nanowire heterostructures as high electron mobility transistors. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 1468–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, P.; Chettiar, U.K.; Cao, L.; Afshinmanesh, F.; Engheta, N.; Brongersma, M.L. An invisible metal-semiconductor photodetector. Nat. Photonic 2012, 6, 380–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, A.; Kim, H.; Cheng, J.; Lo, Y.-H. Ultrahigh responsivity visible and infrared detection using silicon nanowire phototransistors. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2117–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.P.; Macdonald, T.J.; Wolfrum, B.; Stockmann, R.; Nann, T.; Offenhäusser, A.; Thierry, B. Photoresponsive properties of ultrathin silicon nanowires. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2014, 105, 231116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Floris, F.; Fornasari, L.; Marini, A.; Bellani, V.; Banfi, F.; Roddaro, S.; Ercolani, D.; Rocci, M.; Beltram, F.; Cecchini, M. Self-assembled inas nanowires as optical reflectors. Nanomaterials 2017, 7, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adachi, M.M.; Anantram, M.P.; Karim, K.S. Core-shell silicon nanowire solar cells. Sci. Rep. 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garnett, E.; Yang, P. Light trapping in silicon nanowire solar cells. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.P.; Winter, M.A.; Wolfrum, B.; Stockmann, R.; Yang, C.-T.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Thierry, B. Toward intraoperative detection of disseminated tumor cells in lymph nodes with silicon nanowire field effect transistors. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 2357–2364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-I.; Li, B.-R.; Chen, Y.-T. Silicon nanowire field-effect transistor-based biosensors for biomedical diagnosis and cellular recording investigation. Nano Today 2011, 6, 131–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, X.; Li, Y.; Rajan, N.K.; Routenberg, D.A.; Modis, Y.; Reed, M.A. Quantification of the affinities and kinetics of protein interactions using silicon nanowire biosensors. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012, 7, 401–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Lu, N.; Dai, P.; Li, T.; Pei, H.; Gao, X.; Gong, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C. Silicon-nanowire-based cmos-compatible field-effect transistor nanosensors for ultrasensitive electrical detection of nucleic acids. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 3974–3978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, J.; Liang, D.; Tang, H.; Gao, X.P. Inas nanowire transistors as gas sensor and the response mechanism. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 4348–4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martinez, J.; Martínez, R.V.; Garcia, R. Silicon nanowire transistors with a channel width of 4 nm fabricated by atomic force microscope nanolithography. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3636–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, W.U.; Lieber, C.M. High performance silicon nanowire field effect transistors. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, K.; Mukherjee, S.; Manna, S.; Ray, S.; Raychaudhuri, A. Single si nanowire (diameter ≤ 100 nm) based polarization sensitive near-infrared photodetector with ultra-high responsivity. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 11232–11239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, F.; Tan, M.; Wang, Z.; Yao, M.; Xu, Z.; Wu, Y.; Wang, J.; Guo, X.; Zhu, T. Integrating silicon nanowire field effect transistor, microfluidics and air sampling techniques for real-time monitoring biological aerosols. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 7473–7480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei-Wen, Y.; Che-Wei, H.; Yu-Jie, H.; Min-Cheng, C.; Hsin-Hao, L.; Shey-Shi, L.; Chih-Ting, L. A device design of an integrated cmos poly-silicon biosensor-on-chip to enhance performance of biomolecular analytes in serum samples. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 61, 112–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Makowski, M.S.; Ivanisevic, A. Molecular analysis of blood with micro-/nanoscale field-effect-transistor biosensors. Small 2011, 7, 1863–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Ning, Y. Silicon nanowire biosensor and its applications in disease diagnostics: A review. Anal. Chim. Acta 2012, 749, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobbs, R.G.; Petkov, N.; Holmes, J.D. Semiconductor nanowire fabrication by bottom-up and top-down paradigms. Chem. Mater. 2012, 24, 1975–1991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curreli, M.; Rui, Z.; Ishikawa, F.N.; Hsiao-Kang, C.; Cote, R.J.; Chongwu, Z.; Thompson, M.E. Real-time, label-free detection of biological entities using nanowire-based fets. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2008, 7, 651–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verplanck, N.; Galopin, E.; Camart, J.-C.; Thomy, V.; Coffinier, Y.; Boukherroub, R. Reversible electrowetting on superhydrophobic silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 813–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, V.; Wittemann, J.V.; Senz, S.; Gösele, U. Silicon nanowires: A review on aspects of their growth and their electrical properties. Adv. Mater. 2009, 21, 2681–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zepeda-Ruiz, L.A.; Gilmer, G.H.; Upmanyu, M. Atomistics of vapour–liquid–solid nanowire growth. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 1956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Tran, D.P.; Wolfrum, B.; Stockmann, R.; Pai, J.-H.; Pourhassan-Moghaddam, M.; Offenhäusser, A.; Thierry, B. Complementary metal oxide semiconductor compatible silicon nanowires-on-a-chip: Fabrication and preclinical validation for the detection of a cancer prognostic protein marker in serum. Anal. Chem. 2014, 87, 1662–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, D.P.; Wolfrum, B.; Stockmann, R.; Offenhausser, A.; Thierry, B. Fabrication of locally thinned down silicon nanowires. J. Mater. Chem. C 2014, 2, 5229–5234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Berenschot, E.; Jansen, H.; Tas, N.; Huskens, J.; Elwenspoek, M. Multi-silicon ridge nanofabrication by repeated edge lithography. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 315305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bomer, J.G.; van der Wiel, W.G.; Carlen, E.T.; van den Berg, A. Top-down fabrication of sub-30 nm monocrystalline silicon nanowires using conventional microfabrication. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 3485–3492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, J.; Chiam, S.Y.; Tan, H.H.; Wang, S.; Chim, W.K. Fabrication of silicon nanowires with precise diameter control using metal nanodot arrays as a hard mask blocking material in chemical etching. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 4111–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- In, H.J.; Field, C.R.; Pehrsson, P.E. Periodically porous top electrodes on vertical nanowire arrays for highly sensitive gas detection. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 355501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yeom, J.; Ratchford, D.; Field, C.R.; Brintlinger, T.H.; Pehrsson, P.E. Decoupling diameter and pitch in silicon nanowire arrays made by metal-assisted chemical etching. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, C.Q.; Zheng, W.; Choi, W.; Thompson, C.V. Metal assisted anodic etching of silicon. Nanoscale 2015, 7, 11123–11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, C.; Luo, Z.; Xu, C.; Luo, J.; Liang, R.; Zhu, G.; Wu, W.; Guo, W.; Yan, X.; Xu, J.; et al. Wafer-scale high-throughput ordered arrays of si and coaxial si/si1–xgex wires: Fabrication, characterization, and photovoltaic application. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6629–6636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.; Zheng, M.; Dong, F.; Chen, P.; Xu, L.; Chu, W.; Duan, H. Fabrication of single-crystal silicon nanotubes with sub-10 nm walls using cryogenic inductively coupled plasma reactive ion etching. Nanotechnology 2016, 27, 365302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chern, W.; Hsu, K.; Chun, I.S.; Azeredo, B.P.d.; Ahmed, N.; Kim, K.-H.; Zuo, J.-m.; Fang, N.; Ferreira, P.; Li, X. Nonlithographic patterning and metal-assisted chemical etching for manufacturing of tunable light-emitting silicon nanowire arrays. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 1582–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heath, J.R. Superlattice nanowire pattern transfer (snap). Acc. Chem. Res. 2008, 41, 1609–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Xu, Z.-C.; Deng, S.-R.; Wan, J.; Chen, Y.; Liu, R.; Huq, E.; Qu, X.-P. Silicon nanowires by combined nanoimprint and angle deposition for gas sensing applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 2100–2104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Austin, M. Fabrication of 5 nm linewidth and 14 nm pitch features by nanoimprint lithography. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2004, 84, 5299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talin, A.A.; Hunter, L.L.; Léonard, F.; Rokad, B. Large area, dense silicon nanowire array chemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 89, 153102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferri, M.; Suriano, F.; Roncaglia, A.; Solmi, S.; Cerofolini, G.F.; Romano, E.; Narducci, D. Ultradense silicon nanowire arrays produced via top-down planar technology. Microelectron. Eng. 2011, 88, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, H.D.; Chen, S.; van der Wiel, W.G.; Carlen, E.T.; van den Berg, A. Novel top-down wafer-scale fabrication of single crystal silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1015–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Berenschot, E.; Jansen, H.; Tas, N.; Huskens, J.; Elwenspoek, M. Sub-10 nm silicon ridge nanofabrication by advanced edge lithography for nil applications. Microelectron. Eng. 2008, 86, 832–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menke, E.J.; Thompson, M.A.; Xiang, C.; Yang, L.C.; Penner, R.M. Lithographically patterned nanowire electrodeposition. Nat. Mater. 2006, 5, 914–919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cerofolini, G.F.; Amato, P.; Romano, E. The multi-spacer patterning technique: A non-lithographic technique for terascale integration. Semicond. Sci. Technol. 2008, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jamaa, M.; Cerofolini, G.; Micheli, G.D.; Leblebici, Y. Polysilicon nanowire transistors and arrays fabricated with the multispacer technique. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2011, 10, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Su, C.-J.; Lo, Y.-R.; Lee, C.-C.; Lin, H.-C.; Ko, F.-H.; Huang, T.-Y.; Yang, Y.-S. Novel poly-silicon nanowire field effect transistor for biosensing application. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 1223–1229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.-C.; Chen, H.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Chien, C.-H.; Hsieh, T.-F.; Horng, J.-T.; Qiu, J.-T.; Huang, C.-C.; Ho, C.-H.; Yang, F.-L. A cmos-compatible poly-si nanowire device with hybrid sensor/memory characteristics for system-on-chip applications. Sensors 2012, 12, 3952–3963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, K.-N.; Jung, S.-W.; Shin, K.-S.; Kim, W.-H.; Lee, M.-H.; Seong, W.-K. Fabrication of suspended silicon nanowire arrays. Small 2008, 4, 642–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Min-Hyun, L.; Ki-Bum, K.; Hyo-Sung, L.; Sung-Wook, N.; Park, W. Electrical properties of silicon nanowire fabricated by patterning and oxidation process. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2012, 11, 565–569. [Google Scholar]
- Ai, Y.; Huang, R.; Hao, Z.; Fan, C.; Wang, R.; Pu, S.; Wang, Y. Top-down fabrication of shape controllable si nanowires based on conventional cmos process. Phys. E Low-Dimens. Syst. Nanostruct. 2010, 43, 102–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, K.; Yuk, H.; Floresca, H.C.; Kim, M.J.; Hu, W. Quantum confinement induced performance enhancement in sub-5-nm lithographic si nanowire transistors. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 1412–1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanzenboeck, H.D.; Waid, S.; Bertagnolli, E.; Muehlberger, M.; Bergmair, I.; Schoeftner, R. Nanoimprint lithography stamp modification utilizing focused ion beams. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. Part B 2009, 27, 2679–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motayed, A.; Bonevich, J.E.; Krylyuk, S.; Davydov, A.V.; Aluri, G.; Rao, M.V. Correlation between the performance and microstructure of ti/al/ti/au ohmic contacts to p-type silicon nanowires. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 075206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Léonard, F.; Talin, A.A. Electrical contacts to one-and two-dimensional nanomaterials. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011, 6, 773–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vu, X.T.; GhoshMoulick, R.; Eschermann, J.F.; Stockmann, R.; Offenhäusser, A.; Ingebrandt, S. Fabrication and application of silicon nanowire transistor arrays for biomolecular detection. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 144, 354–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reza, S.; Bosman, G.; Islam, M.S.; Kamins, T.I.; Sharma, S.; Williams, R.S. Noise in silicon nanowires. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2006, 5, 523–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajan, N.K. Optimal signal-to-noise ratio for silicon nanowire biochemical sensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2011, 98, 264107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stern, E.; Klemic, J.F.; Routenberg, D.A.; Wyrembak, P.N.; Turner-Evans, D.B.; Hamilton, A.D.; LaVan, D.A.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Label-free immunodetection with cmos-compatible semiconducting nanowires. Nature 2007, 445, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Chen, Y.; Li, X.; Kamins, T.I.; Nauka, K.; Williams, R.S. Sequence-specific label-free DNA sensors based on silicon nanowires. Nano Lett. 2004, 4, 245–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stern, E.; Wagner, R.; Sigworth, F.J.; Breaker, R.; Fahmy, T.M.; Reed, M.A. Importance of the debye screening length on nanowire field effect transistor sensors. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3405–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.U.; Chen, C.; Lin, K.-h.; Fang, Y.; Lieber, C.M. Label-free detection of small-molecule–protein interactions by using nanowire nanosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 3208–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunimovich, Y.L.; Shin, Y.S.; Yeo, W.-S.; Amori, M.; Kwong, G.; Heath, J.R. Quantitative real-time measurements of DNA hybridization with alkylated nonoxidized silicon nanowires in electrolyte solution. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 16323–16331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Lu, K.-C.; Wu, W.-W.; Bai, J.; Chen, L.J.; Tu, K.N.; Huang, Y. Single crystalline ptsi nanowires, ptsi/si/ptsi nanowire heterostructures, and nanodevices. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 913–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Wang, Y.; Dilts, S.; Mayer, T.S.; Mohney, S.E. Silicidation of silicon nanowires by platinum. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 818–824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.-C.; Wu, W.-W.; Chen, L.-J.; Tu, K.-N. Homogeneous nucleation of epitaxial cosi2 and nisi in si nanowires. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 2337–2342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.-C.; Wu, W.-W.; Cheng, S.-L.; Yoo, B.-Y.; Myung, N.; Chen, L.J.; Tu, K.N. In-situ tem observation of repeating events of nucleation in epitaxial growth of nano cosi2 in nanowires of si. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 2194–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, G.; Patolsky, F.; Cui, Y.; Wang, W.U.; Lieber, C.M. Multiplexed electrical detection of cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nat. Biotechnol. 2005, 23, 1294–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellas, N.S.; Liu, B.Z.; Eichfeld, S.M. Nickel and nickel silicide schottky barrier contacts to n-type silicon nanowires. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B Microelectron. Nanometer Struct. 2008, 26, 1592. [Google Scholar]
- Weber, W.M.; Geelhaar, L.; Graham, A.P.; Unger, E.; Duesberg, G.S.; Liebau, M.; Pamler, W.; Chèze, C.; Riechert, H.; Lugli, P.; et al. Silicon-nanowire transistors with intruded nickel-silicide contacts. Nano Lett. 2006, 6, 2660–2666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Lieber, C.M. Fabrication of silicon nanowire devices for ultrasensitive, label-free, real-time detection of biological and chemical species. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 1711–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.-C.; Lu, K.-C.; Tu, K. Nucleation and growth of epitaxial silicide in silicon nanowires. Mater. Sci. Eng. R Rep. 2010, 70, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, K.; Ottaviani, G.; Thompson, R.; Mayer, J. Thermal stability and growth kinetics of co2si and cosi in thin-film reactions. J. Appl. Phys. 1982, 53, 4406–4410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chen, Y.; Xu, D.; Huang, Y. Growth of nickel silicides in si and si/siox core/shell nanowires. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 4721–4726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dellas, N.S.; Liu, B.Z.; Eichfeld, S.M.; Eichfeld, C.M.; Mayer, T.S.; Mohney, S.E. Orientation dependence of nickel silicide formation in contacts to silicon nanowires. J. Appl. Phys. 2009, 105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, S.; Spuhler, P.S.; Chiari, M.; Cabodi, M.; Selim Ünlü, M. Quantification of surface etching by common buffers and implications on the accuracy of label-free biological assays. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 36, 222–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dove, P.M.; Han, N.; Wallace, A.F.; De Yoreo, J.J. Kinetics of amorphous silica dissolution and the paradox of the silica polymorphs. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9903–9908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, W.; Dai, X.; Fu, T.-M.; Xie, C.; Liu, J.; Lieber, C.M. Long term stability of nanowire nanoelectronics in physiological environments. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 1614–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Park, I.; Hao, Z.; Holman, H.-Y.; Pisano, A. Quantitative studies of long-term stable, top-down fabricated silicon nanowire ph sensors. Appl. Phys. A 2012, 107, 421–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, T.-E.; Jang, H.-J.; Yang, J.-H.; Cho, W.-J. High performance of silicon nanowire-based biosensors using a high-k stacked sensing thin film. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 5214–5218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, B., Jr.; Dorvel, B.; Go, J.; Nair, P.; Elibol, O.; Credo, G.; Daniels, J.; Chow, E.C.; Su, X.; Varma, M.; et al. High-k dielectric al2o3 nanowire and nanoplate field effect sensors for improved ph sensing. Biomed. Microdevices 2011, 13, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Bomer, J.G.; Carlen, E.T.; van den Berg, A. Al2o3/silicon nanoisfet with near ideal nernstian response. Nano Lett. 2011, 11, 2334–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rothberg, J.M.; Hinz, W.; Rearick, T.M.; Schultz, J.; Mileski, W.; Davey, M.; Leamon, J.H.; Johnson, K.; Milgrew, M.J.; Edwards, M.; et al. An integrated semiconductor device enabling non-optical genome sequencing. Nature 2011, 475, 348–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dorvel, B.R.; Reddy, B.; Go, J.; Duarte Guevara, C.; Salm, E.; Alam, M.A.; Bashir, R. Silicon nanowires with high-k hafnium oxide dielectrics for sensitive detection of small nucleic acid oligomers. ACS Nano 2012, 6, 6150–6164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moselund, K.E.; Bjork, M.T.; Schmid, H.; Ghoneim, H.; Karg, S.; Lortscher, E.; Riess, W.; Riel, H. Silicon nanowire tunnel fets: Low-temperature operation and influence of high-k gate dielectric. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2011, 58, 2911–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sufi, Z.; Christopher, D.E.; Ali, A.; Benjamin, F.; Zhu, Y.; Tak, N. Optimization of ph sensing using silicon nanowire field effect transistors with hfo 2 as the sensing surface. Nanotechnology 2011, 22, 405501. [Google Scholar]
- Masood, M.N.; Chen, S.; Carlen, E.T.; van den Berg, A. All-(111) surface silicon nanowires: Selective functionalization for biosensing applications. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2010, 2, 3422–3428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robertson, J. Interfaces and defects of high-k oxides on silicon. Solid-State Electron. 2005, 49, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafar, S.; Callegari, A.; Gusev, E.; Fischetti, M.V. Charge trapping related threshold voltage instabilities in high permittivity gate dielectric stacks. J. Appl. Phys. 2003, 93, 9298–9303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torii, K.; Mitsuhashi, R.; Ohji, H.; Kawahara, T.; Kitajima, H. Nitrogen profile engineering in the interfacial sion in a hfalo/sion gate dielectric by no re-oxidation. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2006, 53, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilk, G.; Wallace, R. Electrical properties of hafnium silicate gate dielectrics deposited directly on silicon. Appl. Phys. Lett. 1999, 74, 2854–2856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, R.; Regonda, S.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Hu, W. Ultrasensitive protein detection using lithographically defined si multi-nanowire field effect transistors. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 1952–1961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Z.; Agarwal, A.; Trigg, A.D.; Singh, N.; Fang, C.; Tung, C.-H.; Fan, Y.; Buddharaju, K.D.; Kong, J. Silicon nanowire arrays for label-free detection of DNA. Anal. Chem. 2007, 79, 3291–3297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patolsky, F.; Zheng, G.; Hayden, O.; Lakadamyali, M.; Zhuang, X.; Lieber, C.M. Electrical detection of single viruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 14017–14022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahm, J.-i.; Lieber, C.M. Direct ultrasensitive electrical detection of DNA and DNA sequence variations using nanowire nanosensors. Nano Lett. 2003, 4, 51–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmermann, M.; Schmid, H.; Hunziker, P.; Delamarche, E. Capillary pumps for autonomous capillary systems. Lab Chip 2007, 7, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Dai, P.; Lu, N.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Hemmila, S.; Kallio, P. Integration of microfluidic system with silicon nanowires biosensor for multiplexed detection. In Proceedings of the 2013 IEEE International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Suzhou, China, 26–30 August 2013; pp. 333–336. [Google Scholar]
- Randall, G.C.; Doyle, P.S. Permeation-driven flow in poly (dimethylsiloxane) microfluidic devices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 10813–10818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woias, P. Micropumps—Past, progress and future prospects. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2005, 105, 28–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Zheng, X. Numerical characterization and optimization of the microfluidics for nanowire biosensors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 3233–3237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Lao, I.; Ji, H.; Agarwal, A.; Balasubramanian, N.; Kwong, D. Microfluidic design for bio-sample delivery to silicon nanowire biosensor-a simulation study. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2006, 34, 626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.R.; Lee, C.H.; Zheng, X. Probing flow velocity with silicon nanowire sensors. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 1984–1988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Xie, Y.; De, A.; van den Berg, A.; Carlen, E.T. Electrical shielding for silicon nanowire biosensor in microchannels. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2013, 103, 173702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorvel, B.; Reddy, B.; Bashir, R. Effect of biointerfacing linker chemistries on the sensitivity of silicon nanowires for protein detection. Anal. Chem. 2013, 85, 9493–9500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Stern, E.; Vacic, A.; Rajan, N.K.; Criscione, J.M.; Park, J.; Ilic, B.R.; Mooney, D.J.; Reed, M.A.; Fahmy, T.M. Label-free biomarker detection from whole blood. Nat Nano 2010, 5, 138–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, J.-R. Label-free attomolar detection of proteins using integrated nanoelectronic and electrokinetic devices. Small 2010, 6, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-C.; Ko, F.-H.; Yang, Y.-S.; Hsia, D.-L.; Lee, B.-S.; Su, T.-S. Label-free biosensing of a gene mutation using a silicon nanowire field-effect transistor. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 25, 820–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, A.; Ah, C.S.; Yu, H.Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Baek, I.-B.; Ahn, C.-G.; Park, C.W.; Jun, M.S.; Lee, S. Ultrasensitive, Label-Free, and Real-Time Immunodetection Using Silicon Field-Effect Transistors; AIP: New York, NY, USA, 2007; Volume 91, p. 103901. [Google Scholar]
- Eschermann, J.F.; Stockmann, R.; Hueske, M.; Vu, X.T.; Ingebrandt, S.; Offenhausser, A. Action potentials of hl-1 cells recorded with silicon nanowire transistors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 95, 083703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Kang, T.G.; Je, M. A pa multichannel asic readout system for silicon nanowire biosensor applications. In Proceedings of the APSIPA Annual Summit and Conference (ACS), Biopolis, Singapore, 14–17 December 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Chai, K.T.C.; Luo, H.Z.H.; Huang, J.M.; Tay, I.G.K.; Lim, A.E.-J.; Je, M. Multiplexed detection of cardiac biomarkers in serum with nanowire arrays using readout asic. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2012, 35, 218–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elfström, N.; Juhasz, R.; Sychugov, I.; Engfeldt, T.; Karlström, A.E.; Linnros, J. Surface charge sensitivity of silicon nanowires: Size dependence. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 2608–2612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhang, Y.; To, S.; You, L.; Sun, Y. Effect of nanowire number, diameter, and doping density on nano-fet biosensor sensitivity. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 6661–6668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, C.W.; Ahn, C.G.; Yang, J.H.; Baek, I.B.; Ah, C.S.; Kim, A.; Kim, T.Y.; Sung, G.Y. Control of channel doping concentration for enhancing the sensitivity of ‘top-down’ fabricated si nanochannel fet biosensors. Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 475501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Performance limits of nanobiosensors. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2006, 88, 233120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Screening-limited response of nanobiosensors. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 1281–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.R.; Alam, M.A. Design considerations of silicon nanowire biosensors. IEEE Trans. Electron Devices 2007, 54, 3400–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, D.; Zhang, G.; Li, B. A universal expression of band gap for silicon nanowires of different cross-section geometries. Nano Lett. 2008, 8, 4557–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rurali, R. Colloquium: Structural, electronic, and transport properties of silicon nanowires. Rev. Mod. Phys. 2010, 82, 427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.-A.; Yang, L.; Chou, M.Y. Size and orientation dependence in the electronic properties of silicon nanowires. Phys. Rev. B 2007, 76, 115319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shoorideh, K.; Chui, C.O. On the origin of enhanced sensitivity in nanoscale fet-based biosensors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5111–5116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheehan, P.E.; Whitman, L.J. Detection limits for nanoscale biosensors. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squires, T.M.; Messinger, R.J.; Manalis, S.R. Making it stick: Convection, reaction and diffusion in surface-based biosensors. Nat. Biotechnol. 2008, 26, 417–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Stelzner, T.; Dirawi, R.; Assad, O.; Shehada, N.; Christiansen, S.; Haick, H. Field-effect transistors based on silicon nanowire arrays: Effect of the good and the bad silicon nanowires. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2012, 4, 4251–4258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.-Y.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, S.; Kim, G.-T.; Duesberg, G.S. Electrical properties of high density arrays of silicon nanowire field effect transistors. J. Appl. Phys. 2013, 114, 144503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, B.; Liu, J.; Dvir, T.; Jin, L.; Tsui, J.H.; Qing, Q.; Suo, Z.; Langer, R.; Kohane, D.S.; Lieber, C.M. Macroporous nanowire nanoelectronic scaffolds for synthetic tissues. Nat. Mater. 2012, 11, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tian, B.; Cohen-Karni, T.; Qing, Q.; Duan, X.; Xie, P.; Lieber, C.M. Three-dimensional, flexible nanoscale field-effect transistors as localized bioprobes. Science 2010, 329, 830–834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.X.; Johnson, A.T.; Hone, J.; Smith, W.F. Simple fabrication of molecular circuits by shadow mask evaporation. Nano Lett. 2003, 3, 1371–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.S.; Chen, C.C.; Sheu, J.T.; Li, Y.-K. Detection of an uncharged steroid with a silicon nanowire field-effect transistor. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2009, 138, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAlpine, M.C.; Agnew, H.D.; Rohde, R.D.; Blanco, M.; Ahmad, H.; Stuparu, A.D.; Goddard, W.A.; Heath, J.R. Peptide−nanowire hybrid materials for selective sensing of small molecules. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 9583–9589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Wang, X.; Hong, M.; Erramilli, S.; Mohanty, P. Surface-modified silicon nano-channel for urea sensing. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2008, 133, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephanopoulos, N.; Francis, M.B. Choosing an effective protein bioconjugation strategy. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011, 7, 876–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- YoungáJeong, J.; HyunáChung, B. Recent advances in immobilization methods of antibodies on solid supports. Analyst 2008, 133, 697–701. [Google Scholar]
- Sassolas, A.; Blum, L.J.; Leca-Bouvier, B.D. Immobilization strategies to develop enzymatic biosensors. Biotechnol. Adv. 2012, 30, 489–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, V.; Zharnikov, M.; Gulino, A.; Gupta, T. DNA immobilization, delivery and cleavage on solid supports. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 10602–10618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, S.; Obubuafo, A.; Soper, S.A.; Spivak, D.A. Surface immobilization methods for aptamer diagnostic applications. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2008, 390, 1009–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, Y.; Wei, Q.; Park, H.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selective detection of biological and chemical species. Science 2001, 293, 1289–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.-H.; Hung, C.-H.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-C.; Ko, F.-H.; Yang, Y.-S. Poly-silicon nanowire field-effect transistor for ultrasensitive and label-free detection of pathogenic avian influenza DNA. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashim, U.; Arshad, M.M.; Kasjoo, S.; Rahman, S.; Ruslinda, A.; Fathil, M.; Adzhri, R.; Shahimin, M. Electrical detection of dengue virus (denv) DNA oligomer using silicon nanowire biosensor with novel molecular gate control. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2016, 83, 106–114. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, N.N.; Maki, W.C.; Cameron, E.; Nelson, R.; Winterrowd, P.; Rastogi, S.K.; Filanoski, B.; Maki, G.K. Ultra-sensitive detection of bacterial toxin with silicon nanowire transistor. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 868–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elnathan, R.; Kwiat, M.; Pevzner, A.; Engel, Y.; Burstein, L.; Khatchtourints, A.; Lichtenstein, A.; Kantaev, R.; Patolsky, F. Biorecognition layer engineering: Overcoming screening limitations of nanowire-based fet devices. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5245–5254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.P.; Lee, B.Y.; Hong, S.; Sim, S.J. Ultrasensitive carbon nanotube-based biosensors using antibody-binding fragments. Anal. Biochem. 2008, 381, 193–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miersch, S.; Sidhu, S. Synthetic antibodies: Concepts, potential and practical considerations. Methods 2012, 57, 486–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheu, J.T.; Chen, C.C.; Chang, K.S.; Li, Y.K. A possibility of detection of the non-charge based analytes using ultra-thin body field-effect transistors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1883–1886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Zou, N.; Dai, P.; Lu, N.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Mao, H. Signal-to-noise ratio enhancement of silicon nanowires biosensor with rolling circle amplification. Nano Lett. 2013, 13, 4123–4130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.H.; Jeon, K.J.; Lee, W.; Choi, A.; Jung, H.-I.; Kim, C.-J.; Jo, M.-H. P-type si-nanowire-based field-effect transistors for electric detection of a biomarker: Matrix metalloproteinase-9. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 2009, 55, 232–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.-Y.; Li, B.-R.; Li, Y.-K. Silicon nanowire field-effect-transistor based biosensors: From sensitive to ultra-sensitive. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2014, 60, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudholter, E.; De Smet, L.; Mescher, M.; Uliien, D. Organic surface modification of silicon nanowire-based sensor devices. In Nanowires—Implementations and Applications; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kuan, D.-H.; Wang, I.-S.; Lin, J.-R.; Yang, C.-H.; Huang, C.-H.; Lin, Y.-H.; Lin, C.-T.; Huang, N.-T. A microfluidic device integrating dual cmos polysilicon nanowire sensors for on-chip whole blood processing and simultaneous detection of multiple analytes. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 3105–3113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.; Dai, P.; Li, T.; Gao, X.; Wang, Y.; Fan, C. Enhanced sensing of nucleic acids with silicon nanowire field effect transistor biosensors. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 5262–5268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krivitsky, V.; Hsiung, L.-C.; Lichtenstein, A.; Brudnik, B.; Kantaev, R.; Elnathan, R.; Pevzner, A.; Khatchtourints, A.; Patolsky, F. Si nanowires forest-based on-chip biomolecular filtering, separation and preconcentration devices: Nanowires do it all. Nano Lett. 2012, 12, 4748–4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAlpine, M.C.; Ahmad, H.; Wang, D.; Heath, J.R. Highly ordered nanowire arrays on plastic substrates for ultrasensitive flexible chemical sensors. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 379–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, C.; Deng, S.-R.; Wan, J.; Lu, B.-R.; Liu, R.; Huq, E.; Qu, X.-P.; Chen, Y. 22nm silicon nanowire gas sensor fabricated by trilayer nanoimprint and wet etching. Microelectron. Eng. 2010, 87, 927–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shehada, N.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Pariente, E.S.; Brönstrup, G.; Christiansen, S.; Johnson, D.W.; Leja, M.; Davies, M.P.; Liran, O. Silicon nanowire sensors enable diagnosis of patients via exhaled breath. ACS Nano 2016, 10, 7047–7057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Haick, H. Effect of functional groups on the sensing properties of silicon nanowires toward volatile compounds. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 2289–2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knopfmacher, O.; Tarasov, A.; Fu, W.; Wipf, M.; Niesen, B.; Calame, M.; Schönenberger, C. Nernst limit in dual-gated si-nanowire fet sensors. Nano Lett. 2010, 10, 2268–2274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.-W.; Hsieh, P.-J.; Lin, C.-L.; Fang, Y.-Y.; Yang, J.-X.; Tsai, C.-C.; Chiang, P.-L.; Pan, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T. Label-free detection of protein-protein interactions using a calmodulin-modified nanowire transistor. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1047–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, A.; Liu, C.-R.; Chou, A.-C.; Hsu, W.-H.; Ulaganathan, R.K.; Lin, Y.-C.; Dai, C.-A.; Tseng, F.-G.; Pan, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T. Detection of k+ efflux from stimulated cortical neurons by an aptamer-modified silicon nanowire field-effect transistor. ACS Sens. 2017, 2, 69–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X. Silicon-based nanochannel glucose sensor. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2008, 92, 013903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.-C.; Liao, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y.-T.; Yeh, H.-I.; Wu, C.-C. Multiple silicon nanowires with enzymatic modification for measuring glucose concentration. Micromachines 2015, 6, 1135–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Afzali, A.; You, K.-D.; Kisslinger, K.; Stach, E.; Shahrjerdi, D. Glucose sensing using dual-gated biofets with 5nm-thick silicon body. In Proceedings of the 2017 75th Annual Device Research Conference (DRC), South Bend, IN, USA, 25–28 June 2017; pp. 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.-H.; Hsiao, C.-Y.; Hung, C.-H.; Lo, Y.-R.; Lee, C.-C.; Su, C.-J.; Lin, H.-C.; Ko, F.-H.; Huang, T.-Y.; Yang, Y.-S. Ultrasensitive detection of dopamine using a polysilicon nanowire field-effect transistor. Chem. Commun. 2008, 5749–5751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.-R.; Hsieh, Y.-J.; Chen, Y.-X.; Chung, Y.-T.; Pan, C.-Y.; Chen, Y.-T. An ultrasensitive nanowire-transistor biosensor for detecting dopamine release from living pc12 cells under hypoxic stimulation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 16034–16037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Chua, J.H.; Chee, R.-E.; Agarwal, A.; Wong, S.M.; Buddharaju, K.D.; Balasubramanian, N. Highly sensitive measurements of pna-DNA hybridization using oxide-etched silicon nanowire biosensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2008, 23, 1701–1707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.-I.; Pan, C.-Y.; Li, K.-H.; Huang, Y.-C.; Lu, C.-W.; Tang, C.-Y.; Su, Y.-W.; Tseng, L.-W.; Tseng, K.-C.; Lin, C.-Y. Isolation and identification of post-transcriptional gene silencing-related micro-rnas by functionalized silicon nanowire field-effect transistor. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 17375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, A.; Lu, N.; Dai, P.; Fan, C.; Wang, Y.; Li, T. Direct ultrasensitive electrical detection of prostate cancer biomarkers with cmos-compatible n-and p-type silicon nanowire sensor arrays. Nanoscale 2014, 6, 13036–13042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.-J.; Zhang, L.; Huang, M.J.; Luo, Z.H.H.; Tay, G.K.I.; Lim, E.-J.A.; Kang, T.G.; Chen, Y. Silicon nanowire biosensor for highly sensitive and rapid detection of dengue virus. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2010, 146, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Xu, L.; Gao, R.; Mai, L.; Lieber, C.M. Free-standing kinked nanowire transistor probes for targeted intracellular recording in three dimensions. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2014, 9, 142–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pui, T.-S.; Agarwal, A.; Ye, F.; Balasubramanian, N.; Chen, P. Cmos-compatible nanowire sensor arrays for detection of cellular bioelectricity. Small 2009, 5, 208–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timko, B.P.; Cohen-Karni, T.; Yu, G.; Qing, Q.; Tian, B.; Lieber, C.M. Electrical recording from hearts with flexible nanowire device arrays. Nano Lett. 2009, 9, 914–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qing, Q.; Pal, S.K.; Tian, B.; Duan, X.; Timko, B.P.; Cohen-Karni, T.; Murthy, V.N.; Lieber, C.M. Nanowire transistor arrays for mapping neural circuits in acute brain slices. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 1882–1887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, H.; Kim, J.-Y.; Choi, Y.-K.; Nam, Y. Feasibility study of extended-gate-type silicon nanowire field-effect transistors for neural recording. Sensors 2017, 17, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Chen, R.; Elthakeb, A.T.; Lee, S.H.; Hinckley, S.; Khraiche, M.L.; Scott, J.; Pre, D.; Hwang, Y.; Tanaka, A. High density individually addressable nanowire arrays record intracellular activity from primary rodent and human stem cell derived neurons. Nano Lett. 2017, 17, 2757–2764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engel, Y.; Elnathan, R.; Pevzner, A.; Davidi, G.; Flaxer, E.; Patolsky, F. Supersensitive detection of explosives by silicon nanowire arrays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2010, 49, 6830–6835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Cancilla, J.C.; Torrecilla, J.S.; Haick, H. Artificial sensing intelligence with silicon nanowires for ultraselective detection in the gas phase. Nano Lett. 2014, 14, 933–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paska, Y.; Stelzner, T.; Christiansen, S.; Haick, H. Enhanced sensing of nonpolar volatile organic compounds by silicon nanowire field effect transistors. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 5620–5626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, X.; Agarwal, A.; Yang, K.-L. Oligopeptide-modified silicon nanowire arrays as multichannel metal ion sensors. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2009, 24, 3248–3251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, L.; Jie, J.; Zhang, W.; He, Z.; Wang, J.; Yuan, G.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.C.M.; Lee, S.-T. Silicon nanowire sensors for hg2+ and cd2+ ions. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2009, 94, 193101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vista Therapeutics. Available online: http://www.vistatherapeutics.org (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- QuantuMDx. Available online: http://www.quantumdx.com/ (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- Nanosens. Available online: http://nanosens.nl (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- INanoBio. Available online: http://www.inanobio.com (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- Tracense. Available online: http://www.tracense.com (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- Availsmedical. Available online: http://www.availsmedical.com (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- Nanoivd. Available online: http://www.nanoivd.com (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- MiDiagnostics. Available online: http://www.midiagnostics.com/ (accessed on 11 May 2018).
- Diagnostics—Research Teams—BioMed X. Available online: https://bio.mx/research-teams/diagnostics/ (accessed on 11 May 2018).
| Step | Selection | Possible Options and Their Characteristics | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Option A | Option B | ||
| 1 | Silicon crystallization type | Monocrystalline. Mostly available on SOI wafer, expensive, best electronics properties and uniformity | Polycrystalline. Require deposition and thermal annealing. Cheap, relative good electronic properties, uniformity depend on deposition and annealing process |
| 2 | Nanowire designs | Low-concentration doping (<1017 cm−3) yields higher detection sensitivity | High-concentration doping (>1017 cm−3) yields lower detection sensitivity |
| Smaller NWs yield higher SVR and hence more sensitivity to charge detection | Larger cross-sectional NWs result in lower SVR and lower detection sensitivity | ||
| Single NW: Theoretically better LODs but prone to large detection signal variation and batch to batch variation | NW arrays: Better reliability but lower limit of detections (LODs) | ||
| 3 | Top-down fabrication routes | Horizontal NWs: High density, good control over quality and uniformity, compatible to packaging and integration but require advanced facility and have high fabrication cost. | Vertical silicon NWs: High aspect ratio, high density, good uniformity and low cost but challenging in regard to integration, packaging and sample delivery |
| 3’ | Horizontal SiNW fabrication approaches | Edge transfer lithography: Compatible with standard microfabrication facilities, low cost but lengthy process and high risk of contamination | Nanoimprinting and advanced nanolithography: Require advanced facilities but have low contamination risk and good fabrication throughput and high cost |
| 4 | Dielectric insulation | Thermal SiO2: Compatible with standard fabrication process, low intrinsic defects but unstable in long-term measurement in liquid | High-k materials: Additional fabrication complexity and prone to interface defects but excellent durability and stability in long-term measurement |
| 5 | Electrical contact formation | Ohmic contacts: Standard process, requires ion-implantation at the contact areas and sensitive to temperature | Silicide contacts: Require stringent control in metal deposition and annealing steps but provide excellent electrical contacts and no requirement for ion-implantation |
| 6 | Microfluidics integration | Active microfluidics: Simple fabrication, operation and integration with SiNW FETs but require external power source or pump | Passive microfluidics: Compatible with POC applications, low cost, low or zero energy consumption but careful design and fabrication required to control sample flow and integration with NW FETs |
| 8 | Readout | Multi channels: Multiplexed sensing capabilities. Mainly custom built based on the specific specification of the SiNW FETs. Require compromise between resolution/functionality and cost | Single channel: Commercial read out available offering high resolution and universal functionality but bulky, expensive and not compatible for multiplex and POC sensing |
| Sensing Type | Fabrication Approach | Probe | Analyte | LOD | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gas, VOCs | Nano imprinting, bottom-up synthesis | Bare, Silane | NO2, VOCs | 20 ppb | [155,156,157,158] |
| Ions | Advanced lithography, nanoimprinting | Bare, chelated protein, aptamer | H+, Ca2+, K+ | 1 µM | [29,159,160,161] |
| Small molecules | Size reduction, advanced lithography, edge transfer | Glucose oxidase, benzylphosphonic acid-4-boronic acid pinnacol ester, phenylboronic acid, aptamer | Glucose, dopamine | 1 fM | [162,163,164,165,166] |
| Genetic materials | Size reduction, advanced lithography | DNA, PNA, aptamer | DNA, cDNA, RNA | 0.1 fM | [148,153,167,168] |
| Protein markers | Nanoimprinting, Size reduction, advanced lithography | Antibody | Protein | 30 aM | [12,108,169] |
| Pathogen | Advanced lithography, bottom-up synthesis | Antibody | Bacteria toxin, virus materials, virus particles | 1 fM | [97,141,142,143,170] |
| Cell, tissue, organ | Nanoimprinting, bottom-up synthesis | Fibronectin, silane | Cardiac cells, neural cell/tissue, heart | N/A | [112,171,172,173,174] |
| Company | Product | Detection Targets | Format | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vista therapeutics, Inc. (US) | NanoBioSensor™ | Cancer markers, viruses, biological toxin, DNA/RNA | Sample collection/Prep Kits; NanoCards; Readout devices | [182] |
| QuantuMDx, (UK) | Q-POC™ | Cancer marker, bacteria, virus, DNA/RNA | Sample cartridge; readout device | [183] |
| Nanosens, B.V. (The Netherlands) | Nanowire in various materials, nanowire on-chip | Under development | Wafer-scale nanowires; chip-unit | [184] |
| Inanobio, LLC. (US) | Fully depleted exponentially coupled SiNW FET on-chip | Under development. Co-develop with medical devices company | Wafer-scale nanowires; chip-unit | [185] |
| Tracense (Israel) | TESS explosives trace detector | Gas sensing platforms for explosive, chemical and biological warfare agents detection | Detection unit: nanowire chip; readout device | [186] |
| Avails Medical, Inc. (US) | Under-development | Drug monitoring in saliva | Under-development | [187] |
| NanoIVD, Inc. (US) | Under-development | Genetic mutation detection | Test cartridge | [188] |
| miDIAGNOSTICS (Belgium) | Under-development | Proteins, nucleic acids, and small molecules | Under-development | [189] |
| BiomedX | Under-development | electrolytes, proteins, and blood gases | Under-development | [190] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tran, D.P.; Pham, T.T.T.; Wolfrum, B.; Offenhäusser, A.; Thierry, B. CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor: Technology Development toward Commercialization. Materials 2018, 11, 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050785
Tran DP, Pham TTT, Wolfrum B, Offenhäusser A, Thierry B. CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor: Technology Development toward Commercialization. Materials. 2018; 11(5):785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050785
Chicago/Turabian StyleTran, Duy Phu, Thuy Thi Thanh Pham, Bernhard Wolfrum, Andreas Offenhäusser, and Benjamin Thierry. 2018. "CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor: Technology Development toward Commercialization" Materials 11, no. 5: 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050785
APA StyleTran, D. P., Pham, T. T. T., Wolfrum, B., Offenhäusser, A., & Thierry, B. (2018). CMOS-Compatible Silicon Nanowire Field-Effect Transistor Biosensor: Technology Development toward Commercialization. Materials, 11(5), 785. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11050785






