Recent Hydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Applications
Abstract
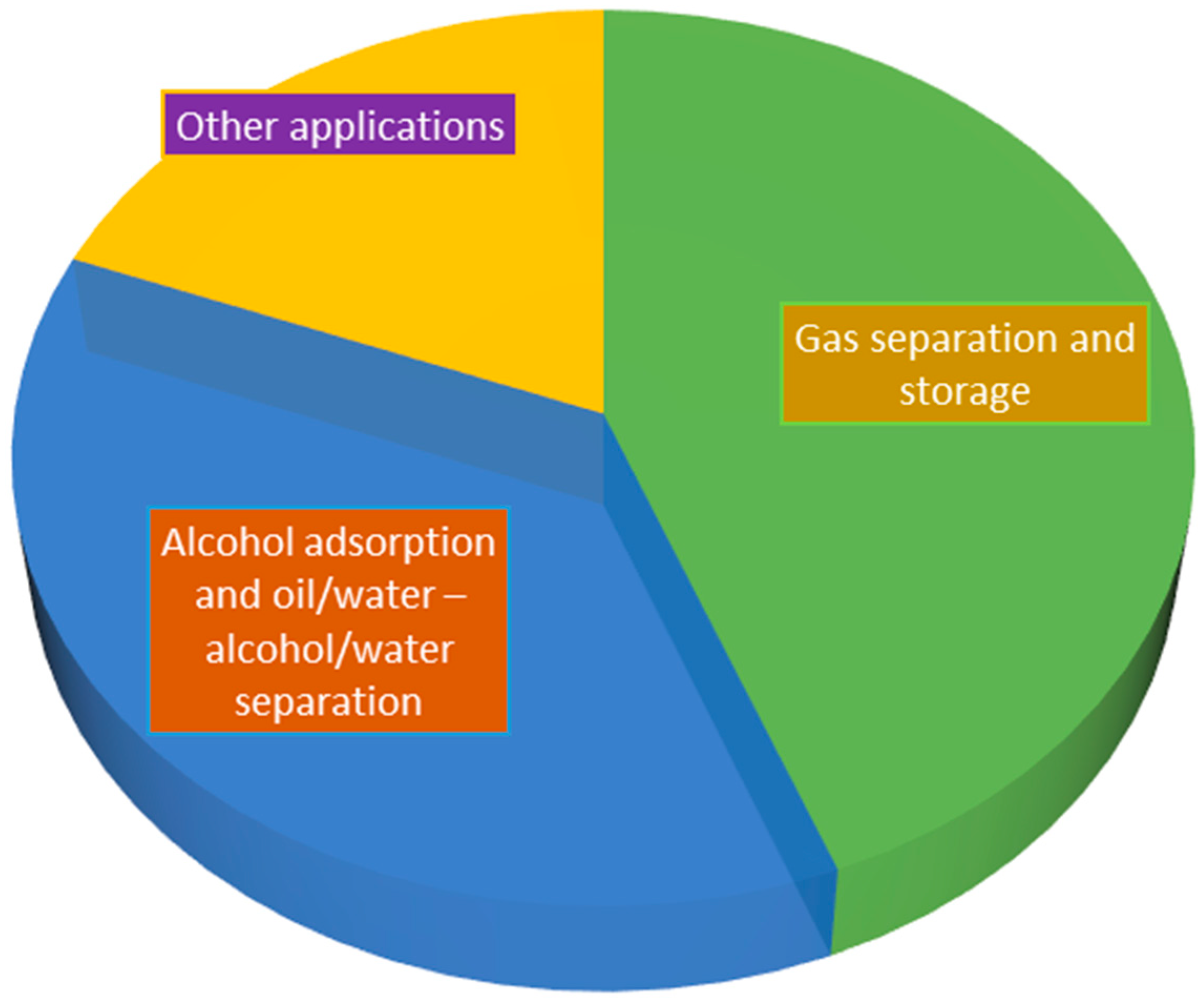
:1. Introduction
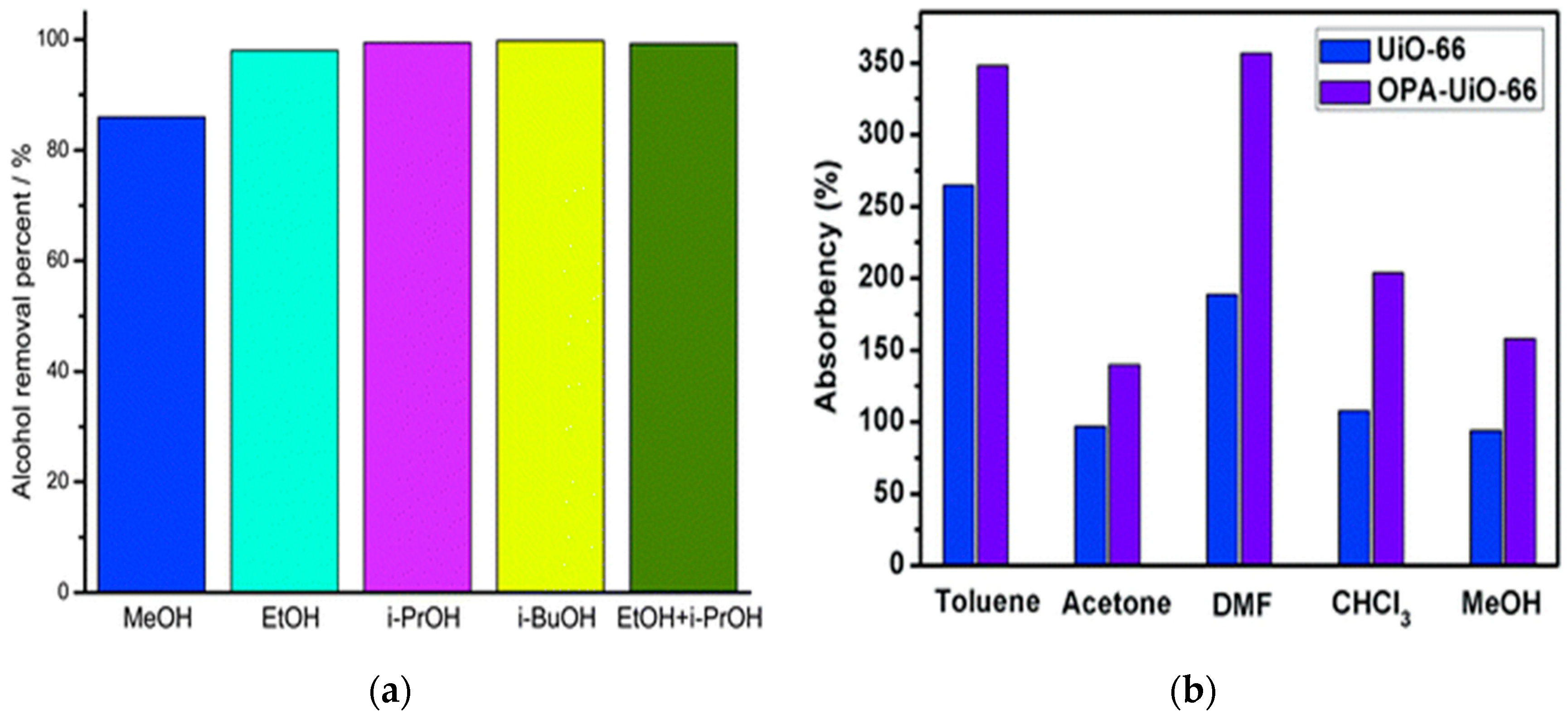
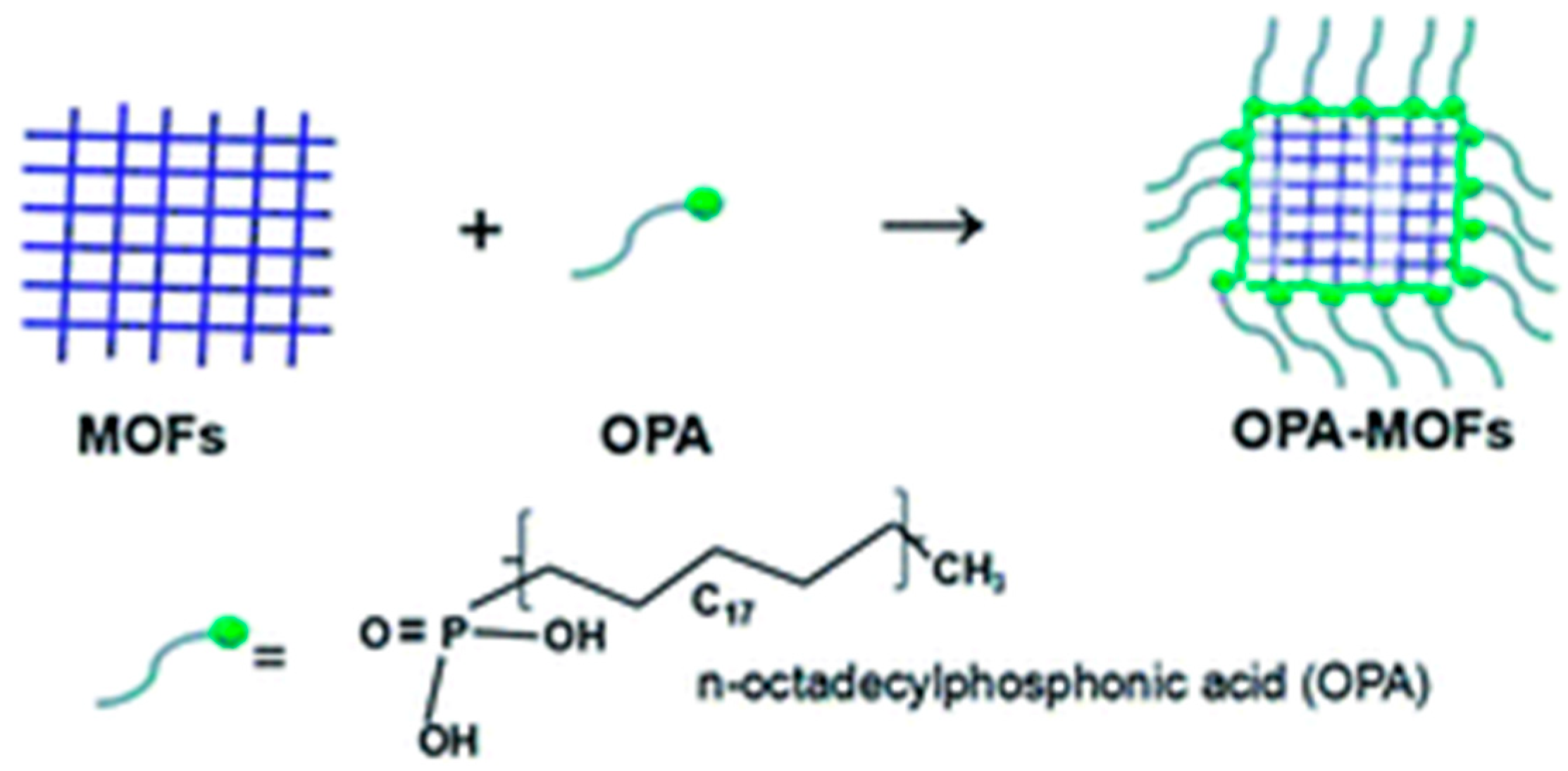
2. Alcohol Adsorption and Oil/Water-Alcohol/Water Separation
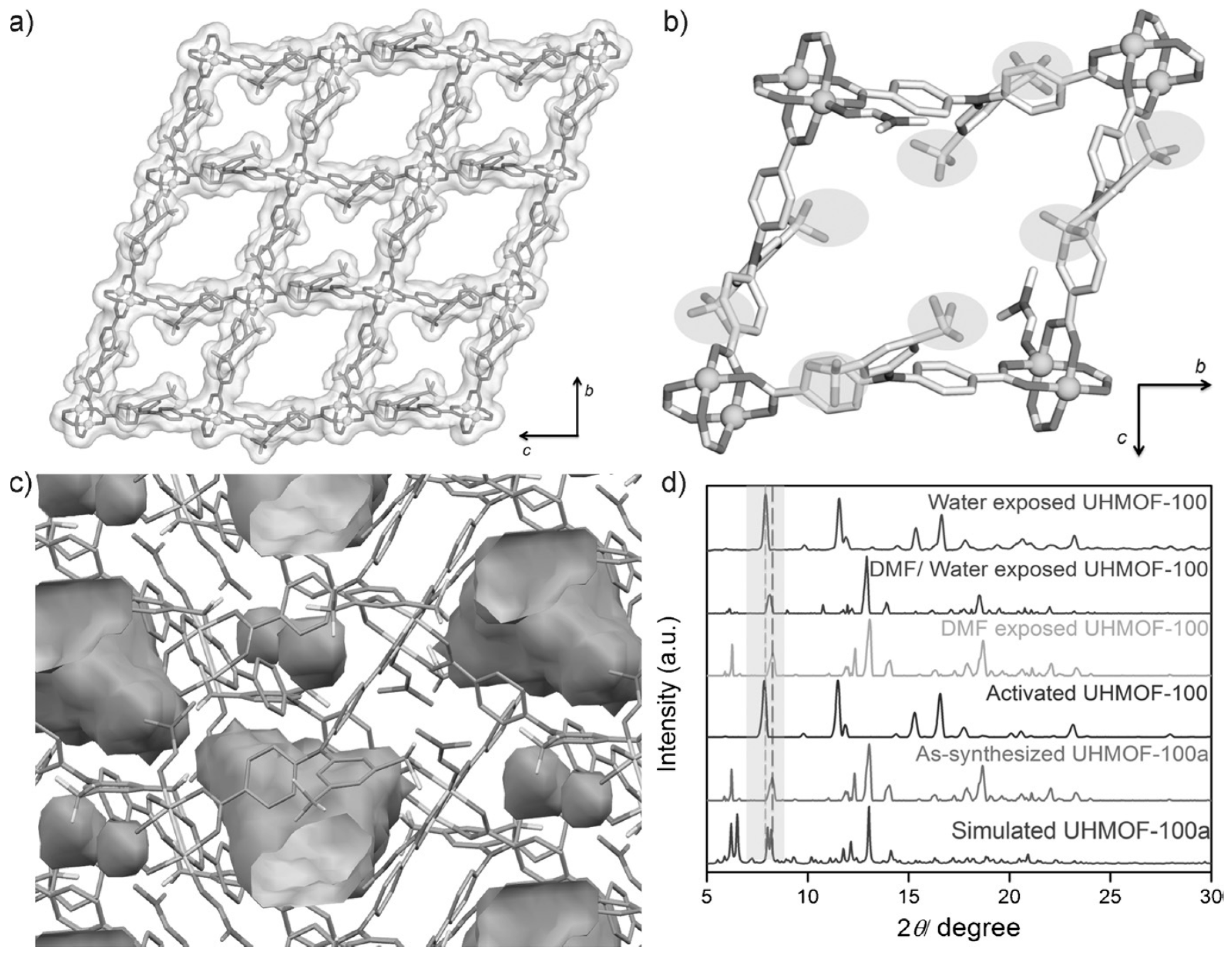
3. Gas Separation and Storage
4. Other Applications
4.1. Self-Cleaning
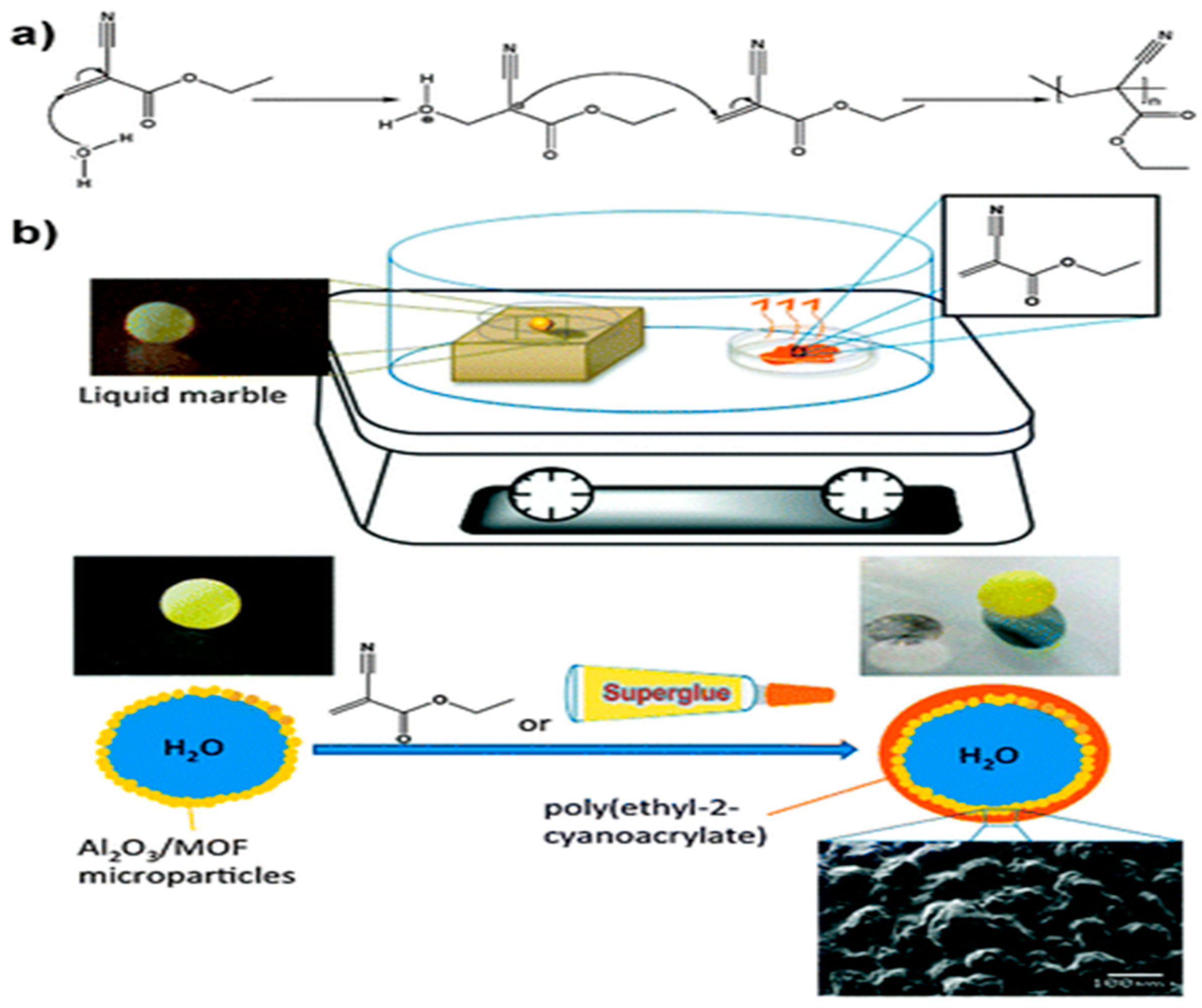
4.2. Liquid Marbles
5. Summary and Outlook
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhu, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, S. Assembly of a Metal-Organic Framework into 3 D Hierarchical Porous Monoliths Using a Pickering High Internal Phase Emulsion Template. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 8751–8755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Zhu, H.; Zhu, S. Reversibly Dispersible/Collectable Metal-Organic Frameworks Prepared by Grafting Thermally Responsive and Switchable Polymers. Macromol. Mater. Eng. 2015, 300, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, H.; Cordova, K.E.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. The Chemistry and Applications of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, S.; Zhou, H.-C. Gas storage in porous metal-organic frameworks for clean energy applications. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 44–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sibo, W.; Xinchen, W. Multifunctional Metal-Organic Frameworks for Photocatalysis. Small 2015, 11, 3097–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasan, Z.; Jhung, S.H. Removal of hazardous organics from water using metal-organic frameworks (MOFs): Plausible mechanisms for selective adsorptions. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 283, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meek, S.T.; Greathouse, J.A.; Allendorf, M.D. Metal-Organic Frameworks: A Rapidly Growing Class of Versatile Nanoporous Materials. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 249–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, J.; Jiang, F.; Wu, M.; Liu, C.; Su, K.; Lu, W.; Yuan, D.; Hong, M. A porous metal-organic framework with ultrahigh acetylene uptake capacity under ambient conditions. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Farha, O.K.; Özgür Yazaydın, A.; Eryazici, I.; Malliakas, C.D.; Hauser, B.G.; Kanatzidis, M.G.; Nguyen, S.T.; Snurr, R.Q.; Hupp, J.T. De novo synthesis of a metal–organic framework material featuring ultrahigh surface area and gas storage capacities. Nat. Chem. 2010, 2, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, H.; Liu, H.; Zhitomirsky, I.; Zhu, S. Preparation of metal–organic framework films by electrophoretic deposition method. Mater. Lett. 2015, 142, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Liang, C.; Yang, J.; Contreras, D.S.; Clancy, Y.L.; Lobkovsky, E.B.; Yaghi, O.M.; Dai, S. A Microporous Metal-Organic Framework for Gas-Chromatographic Separation of Alkanes. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 1390–1393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, T.-H.; Lee, J.S.; Qiu, W.; Koros, W.J.; Jones, C.W.; Nair, S. A High-Performance Gas-Separation Membrane Containing Submicrometer-Sized Metal–Organic Framework Crystals. Angew. Chem. 2010, 122, 10059–10062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamon, L.; Llewellyn, P.L.; Devic, T.; Ghoufi, A.; Clet, G.; Guillerm, V.; Pirngruber, G.D.; Maurin, G.; Serre, C.; Driver, G.; et al. Co-adsorption and Separation of CO2−CH4 Mixtures in the Highly Flexible MIL-53(Cr) MOF. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17490–17499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Sun, F.; Zhang, F.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, R.; Wang, C.; Qiu, S. In situ growth of continuous thin metal-organic framework film for capacitive humidity sensing. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 3775–3778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stassen, I.; Burtch, N.; Talin, A.; Falcaro, P.; Allendorf, M.; Ameloot, R. An updated roadmap for the integration of metal–organic frameworks with electronic devices and chemical sensors. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3185–3241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondloch, J.E.; Katz, M.J.; Isley Iii, W.C.; Ghosh, P.; Liao, P.; Bury, W.; Wagner, G.W.; Hall, M.G.; DeCoste, J.B.; Peterson, G.W.; et al. Destruction of chemical warfare agents using metal–organic frameworks. Nat. Mater. 2015, 14, 512–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corma, A.; García, H.; Llabrés i Xamena, F.X. Engineering Metal Organic Frameworks for Heterogeneous Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 2010, 110, 4606–4655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Farha, O.K.; Roberts, J.; Scheidt, K.A.; Nguyen, S.T.; Hupp, J.T. Metal-organic framework materials as catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1450–1459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shultz, A.M.; Farha, O.K.; Hupp, J.T.; Nguyen, S.T. A Catalytically Active, Permanently Microporous MOF with Metalloporphyrin Struts. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 4204–4205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogge, S.M.; Bavykina, A.; Hajek, J.; Garcia, H.; Olivos-Suarez, A.I.; Sepúlveda-Escribano, A.; Vimont, A.; Clet, G.; Bazin, P.; Kapteijn, F. Metal-organic and covalent organic frameworks as single-site catalysts. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 3134–3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, Y.; Liu, H.; Liu, Z. Fabrication of porous metal-organic frameworks via a mixed-ligand strategy for highly selective and efficient dye adsorption in aqueous solution. Cryst. Eng. Comm. 2015, 17, 6037–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimizu, G.K.H.; Taylor, J.M.; Kim, S. Proton Conduction with Metal-Organic Frameworks. Science 2013, 341, 354–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horcajada, P.; Chalati, T.; Serre, C.; Gillet, B.; Sebrie, C.; Baati, T.; Eubank, J.F.; Heurtaux, D.; Clayette, P.; Kreuz, C.; et al. Porous metal-organic-framework nanoscale carriers as a potential platform for drug delivery and imaging. Nat. Mater. 2010, 9, 172–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canivet, J.; Fateeva, A.; Guo, Y.; Coasne, B.; Farrusseng, D. Water adsorption in MOFs: Fundamentals and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5594–5617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Low, J.J.; Benin, A.I.; Jakubczak, P.; Abrahamian, J.F.; Faheem, S.A.; Willis, R.R. Virtual High Throughput Screening Confirmed Experimentally: Porous Coordination Polymer Hydration. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 15834–15842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolleboyina, J.; Ramanatha, D.K.K.; Christoph, R.; Martin, P.; Michal, O.; Radek, Z.; Fischer, R.A. Biomimetic Superhydrophobic/Superoleophilic Highly Fluorinated Graphene Oxide and ZIF-8 Composites for Oil–Water Separation. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 1178–1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prabhakara, R.K.; Masakazu, H.; Kenji, S.; Shuhei, F.; Jingui, D.; Susumu, K. Design of Superhydrophobic Porous Coordination Polymers through the Introduction of External Surface Corrugation by the Use of an Aromatic Hydrocarbon Building Unit. Angew. Chem. 2014, 126, 8364–8369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Miller, S.A.; Ploskonka, A.M.; DeCoste, J.B.; Cohen, S.M. Polymer-Metal-Organic Frameworks (polyMOFs) as Water Tolerant Materials for Selective Carbon Dioxide Separations. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 920–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Ge, J.; Jiang, H.-L.; Yu, S.-H. A Facile and General Coating Approach to Moisture/Water-Resistant Metal-Organic Frameworks with Intact Porosity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2014, 136, 16978–16981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, J.G.; Cohen, S.M. Moisture-Resistant and Superhydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks Obtained via Postsynthetic Modification. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 4560–4561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-H.; Popov, I.; Zenasni, O.; Daugulis, O.; Miljanic, O.S. Superhydrophobic perfluorinated metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 6846–6848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukherjee, S.; Kansara, A.M.; Saha, D.; Gonnade, R.; Mullangi, D.; Manna, B.; Desai, A.V.; Thorat, S.H.; Singh, P.S.; Mukherjee, A.; et al. An Ultrahydrophobic Fluorous Metal-Organic Framework Derived Recyclable Composite as a Promising Platform to Tackle Marine Oil Spills. Chem. A Eur. J. 2016, 22, 10937–10943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez-Hermida, S.; Tsang, M.Y.; Vignatti, C.; Stylianou, K.C.; Guillerm, V.; Pérez-Carvajal, J.; Teixidor, F.; Viñas, C.; Choquesillo-Lazarte, D.; Verdugo-Escamilla, C. Switchable Surface Hydrophobicity-Hydrophilicity of a Metal-Organic Framework. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2016, 55, 16049–16053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bae, J.; Lee, E.J.; Jeong, N.C. Metal coordination and metal activation abilities of commonly unreactive chloromethanes toward metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2018, 54, 6458–6471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, J.; Choi, J.S.; Hwang, S.; Yun, W.S.; Song, D.; Lee, J.; Jeong, N.C. Multiple Coordination Exchanges for Room-Temperature Activation of Open-Metal Sites in Metal-Organic Frameworks. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 24743–24752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.S.; Bae, J.; Lee, E.J.; Jeong, N.C. A Chemical Role for Trichloromethane: Room-Temperature Removal of Coordinated Solvents from Open Metal Sites in the Copper-Based Metal–Organic Frameworks. Inorg. Chem. 2018, 57, 5225–5231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, A.P.; Farha, O.K.; Mulfort, K.L.; Hupp, J.T. Supercritical processing as a route to high internal surface areas and permanent microporosity in metal-organic framework materials. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 131, 458–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.-S.; Chen, C.-Y.; Chung, T.-Y.; Su, C.-J.; Su, C.-H.; Chen, H.-L.; Jeng, U.-S.; Yu, M.-S.; Liao, P.-Y.; Lin, K.-F. Structural Analysis and Thermal Behavior of Pore Networks in High-Surface-Area Metal-Organic Framework. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 7014–7020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Shukla, P.; Wang, S.; Rudolph, V.; Chen, X.-M.; Zhu, Z. Significant improvement of surface area and CO2 adsorption of Cu-BTC via solvent exchange activation. RSC Adv. 2013, 3, 17065–17072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic Methods for the Functionalization of Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2012, 112, 970–1000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1315–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cohen, S.M. Modifying MOFs: New chemistry, new materials. Chem. Sci. 2010, 1, 32–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanabe, K.K.; Cohen, S.M. Postsynthetic modification of metal-organic frameworks—A progress report. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2011, 40, 498–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, J.A. A realizable renewable energy future. Science 1999, 285, 687–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, A.; Sun, H.-X.; Tan, D.-Z.; Fan, W.-J.; Wen, S.-H.; Qing, X.-J.; Li, G.-X.; Li, S.-Y.; Deng, W.-Q. Superhydrophobic conjugated microporous polymers for separation and adsorption. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2062–2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pollard, S.J.T.; Fowler, G.D.; Sollars, C.J.; Perry, R. Low-cost adsorbents for waste and wastewater treatment: A review. Sci. Total Environ. 1992, 116, 31–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ono, T.; Sugimoto, T.; Shinkai, S.; Sada, K. Lipophilic polyelectrolyte gels as super-absorbent polymers for nonpolar organic solvents. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lively, R.P.; Noel, J.D.; Dose, M.E.; McCool, B.A.; Chance, R.R.; Koros, W.J. Adsorption of water and ethanol in MFI-type zeolites. Langmuir 2012, 28, 8664–8673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Lively, R.P.; Dose, M.E.; Li, L.; Koros, W.J.; Ruthven, D.M.; McCool, B.A.; Chance, R.R. Diffusion of water and ethanol in silicalite crystals synthesized in fluoride media. Microporous Mesoporous Mater. 2013, 170, 259–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, K.; Lively, R.P.; Dose, M.E.; Brown, A.J.; Zhang, C.; Chung, J.; Nair, S.; Koros, W.J.; Chance, R.R. Alcohol and water adsorption in zeolitic imidazolate frameworks. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 3245–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, K.; Gupta, K.M.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, J. Biofuel purification in GME zeolitic-imidazolate frameworks: From ab initio calculations to molecular simulations. AIChE J. 2015, 61, 2763–2775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, X.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L. Applications of bio-inspired special wettable surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Liang, W.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic super-lyophobic and super-lyophilic materials applied for oil/water separation: A new strategy beyond nature. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 336–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, T.; Guo, Z.; Liu, W. Biomimetic superoleophobic surfaces: focusing on their fabrication and applications. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 1811–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebajo, M.O.; Frost, R.L.; Kloprogge, J.T.; Carmody, O.; Kokot, S. Porous materials for oil spill cleanup: A review of synthesis and absorbing properties. J. Porous Mater. 2003, 10, 159–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hayase, G.; Kanamori, K.; Hasegawa, G.; Maeno, A.; Kaji, H.; Nakanishi, K. A superamphiphobic macroporous silicone monolith with marshmallow-like flexibility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2013, 52, 10788–10791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, P. Smart surfaces with switchable superoleophilicity and superoleophobicity in aqueous media: Toward controllable oil/water separation. NPG Asia Mater. 2012, 4, e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Seeger, S. Polyester materials with superwetting silicone nanofilaments for oil/water separation and selective oil absorption. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 4699–4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, X.; Wei, J.; Wang, K.; Cao, A.; Zhu, H.; Jia, Y.; Shu, Q.; Wu, D. Carbon nanotube sponges. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 617–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sohn, K.; Na, Y.J.; Chang, H.; Roh, K.-M.; Jang, H.D.; Huang, J. Oil absorbing graphene capsules by capillary molding. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 5968–5970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Zhang, Z.; Mai, Z.; Ma, Y.; Liu, B.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. A Super-Hydrophobic and Super-Oleophilic Coating Mesh Film for the Separation of Oil and Water. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2012–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Sun, Q.; Huang, H.; Aguila, B.; Niu, Z.; Perman, J.A.; Ma, S. A molecular-level superhydrophobic external surface to improve the stability of metal-organic frameworks. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 18770–18776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Liu, Q.; Huang, A. A superhydrophobic zeolitic imidazolate framework (ZIF-90) with high steam stability for efficient recovery of bioalcohols. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 3400–3402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Suresh, V.M.; Maji, T.K. Self-cleaning MOF: Realization of extreme water repellence in coordination driven self-assembled nanostructures. Chem. Sci. 2016, 7, 2251–2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Xin, X.; Xiao, Z.; Wang, R.; Zhang, L.; Sun, D. A multi-aromatic hydrocarbon unit induced hydrophobic metal-organic framework for efficient C2/C1 hydrocarbon and oil/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 1168–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Sun, F.; Sun, J.; Wu, H.; Xiao, F.; Wu, X.; Zhu, G. Imparting surface hydrophobicity to metal-organic frameworks using a facile solution-immersion process to enhance water stability for CO2 capture. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 2003–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modena, M.M.; Wang, Y.; Riedel, D.; Burg, T.P. Resolution enhancement of suspended microchannel resonators for weighing of biomolecular complexes in solution. Lab Chip 2014, 14, 342–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Modena, M.M.; Hirschle, P.; Wuttke, S.; Burg, T.P. Mass Measurements Reveal Preferential Sorption of Mixed Solvent Components in Porous Nanoparticles. Small 2018, 1800826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wuttke, S.; Dietl, C.; Hinterholzinger, F.M.; Hintz, H.; Langhals, H.; Bein, T. Turn-on fluorescence triggered by selective internal dye replacement in MOFs. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 3599–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilmer, C.E.; Leaf, M.; Lee, C.Y.; Farha, O.K.; Hauser, B.G.; Hupp, J.T.; Snurr, R.Q. Large-scale screening of hypothetical metal-organic frameworks. Nat. Chem. 2011, 4, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnobrich, J.K.; Lebel, O.; Cychosz, K.A.; Dailly, A.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Linker-Directed Vertex Desymmetrization for the Production of Coordination Polymers with High Porosity. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 13941–13948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Yadian, B.; Wu, R.; Long, Y.; Zhou, K.; Zhu, B.; Huang, Y. Structure stability of metal-organic framework MIL-53 (Al) in aqueous solutions. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2013, 38, 16710–16715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, X.; Zhong, Z.; Yadian, B.; Wu, J.; Zhou, K.; Teo, J.S.-K.; Chen, L.; Long, Y.; Huang, Y. Loading MIL-53 (Al) with Ag nanoparticles: Synthesis, structural stability and catalytic properties. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2014, 39, 14496–14502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, C.; Liu, Y.; Xu, H.; Li, S.; Zhang, W.; Cui, P.; Huo, F. Self-Assembled Metal-Organic Frameworks Crystals for Chemical Vapor Sensing. Small 2014, 10, 3672–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, R.; Qian, X.; Law, A.W.-K.; Zhou, K. Coordination polymer-derived mesoporous Co3O4 hollow nanospheres for high-performance lithium-ions batteries. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 50846–50850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, G.; Cui, C.; Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Huo, F. Synthesis and Self-Assembly of Monodispersed Metal-Organic Framework Microcrystals. Chem. Asian J. 2013, 8, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cadiau, A.; Adil, K.; Bhatt, P.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Eddaoudi, M. A metal-organic framework-based splitter for separating propylene from propane. Science 2016, 353, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chi, L.; Lu, G. Defect-Controlled Preparation of UiO-66 Metal-Organic Framework Thin Films with Molecular Sieving Capability. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, B.; Zhang, J.; Han, B. Assembling Metal-Organic Frameworks in Ionic Liquids and Supercritical CO2. Chem. Asian J. 2016, 11, 2610–2619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.-M.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Cui, Y.; Wang, H.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. A microporous metal-organic framework with lewis basic nitrogen sites for high C2H2 storage and significantly enhanced C2H2/CO2 separation at ambient conditions. Inorg. Chem. 2016, 55, 7214–7218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.; Adil, K.; Weseliński, Ł.J.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Eddaoudi, M. A supermolecular building layer approach for gas separation and storage applications: The eea and rtl MOF platforms for CO2 capture and hydrocarbon separation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2015, 3, 6276–6281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, D.-X.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Shekhah, O.; Jiang, H.; Adil, K.; Cairns, A.J.; Eddaoudi, M. Tunable rare earth fcu-MOF platform: Access to adsorption kinetics driven gas/vapor separations via pore size contraction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2015, 137, 5034–5040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Cai, J.; Cui, Y.; Yang, Y.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. A microporous metal-organic framework with both open metal and Lewis basic pyridyl sites for highly selective C2H2/CH4 and C2H2/CO2 gas separation at room temperature. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 77–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Ramirez-Cuesta, A.J.; Newby, R.; Garcia-Sakai, V.; Manuel, P.; Callear, S.K.; Campbell, S.I.; Tang, C.C.; Schröder, M. Supramolecular binding and separation of hydrocarbons within a functionalized porous metal-organic framework. Nat. Chem. 2014, 7, 121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duan, J.; Jin, W.; Kitagawa, S. Water-resistant porous coordination polymers for gas separation. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2017, 332, 48–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luebke, R.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Weseliński, Ł.J.; Cairns, A.J.; Alkordi, M.; Norton, G.; Wojtas, Ł.; Adil, K.; Eddaoudi, M. Versatile rare earth hexanuclear clusters for the design and synthesis of highly-connected ftw-MOFs. Chem. Sci. 2015, 6, 4095–4102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Assen, A.H.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Adil, K.; Bhatt, P.M.; Xue, D.X.; Jiang, H.; Eddaoudi, M. Ultra-Tuning of the Rare-Earth fcu-MOF Aperture Size for Selective Molecular Exclusion of Branched Paraffins. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 14353–14358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Yu, J.; Wang, H.; Duan, X.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, C.; Cui, Y.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Z.; Chen, B. A Noninterpenetrated Metal-Organic Framework Built from an Enlarged Tetracarboxylic Acid for Small Hydrocarbon Separation. Cryst. Growth Des. 2015, 15, 4071–4074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, H.-M.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Wu, C.; Alfooty, K.; Krishna, R.; Chen, B. A microporous metal–organic framework with rare lvt topology for highly selective C2H2/C2H4 separation at room temperature. Chem. Commun. 2015, 51, 5610–5613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Xiang, S.; Rao, X.; Zheng, Q.; Fronczek, F.R.; Qian, G.; Chen, B. A rod packing microporous metal–organic framework with open metal sites for selective guest sorption and sensing of nitrobenzene. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 7205–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Millward, A.R.; Yaghi, O.M. Metal-organic frameworks with exceptionally high capacity for storage of carbon dioxide at room temperature. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2005, 127, 17998–17999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furukawa, H.; Ko, N.; Go, Y.B.; Aratani, N.; Choi, S.B.; Choi, E.; Yazaydin, A.Ö.; Snurr, R.Q.; O’Keeffe, M.; Kim, J. Ultrahigh porosity in metal-organic frameworks. Science 2010, 329, 424–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Xiang, S.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, L.; Bai, J.; Chen, B. A new MOF-505 analog exhibiting high acetylene storage. Chem. Commun. 2009, 48, 7551–7553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wen, H.-M.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Krishna, R.; Chen, B. High acetylene/ethylene separation in a microporous zinc(ii) metal-organic framework with low binding energy. Chem. Commun. 2016, 52, 1166–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.-P.; Chen, X.-M. Optimized Acetylene/Carbon Dioxide Sorption in a Dynamic Porous Crystal. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5516–5521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tian, J.; Thallapally, P.K.; McGrail, B.P. Selective CO2 Capture from Flue Gas Using Metal-Organic Frameworks―A Fixed Bed Study. J. Phys. Chem. C 2012, 116, 9575–9581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kizzie, A.C.; Wong-Foy, A.G.; Matzger, A.J. Effect of Humidity on the Performance of Microporous Coordination Polymers as Adsorbents for CO2 Capture. Langmuir 2011, 27, 6368–6373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burtch, N.C.; Jasuja, H.; Walton, K.S. Water Stability and Adsorption in Metal-Organic Frameworks. Chem. Rev. 2014, 114, 10575–10612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Liu, X.; Akbulut, O.; Hu, J.; Suib, S.L.; Kong, J.; Stellacci, F. Superwetting nanowire membranes for selective absorption. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, X.; Ren, Q.; Wu, X.; Sun, J.; Wu, H.; Lei, J. Enhanced Water Stability in Zn-Doped Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-67 (ZIF-67) for CO2 Capture Applications. Chem. Sel. 2018, 3, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furukawa, Y.; Ishiwata, T.; Sugikawa, K.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Nano-and Microsized Cubic Gel Particles from Cyclodextrin Metal-Organic Frameworks. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10718–10721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsotsalas, M.; Liu, J.; Tettmann, B.; Grosjean, S.; Shahnas, A.; Wang, Z.; Azucena, C.; Addicoat, M.; Heine, T.; Lahann, J. Fabrication of highly uniform gel coatings by the conversion of surface-anchored metal-organic frameworks. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 136, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishiwata, T.; Furukawa, Y.; Sugikawa, K.; Kokado, K.; Sada, K. Transformation of metal-organic framework to polymer gel by cross-linking the organic ligands preorganized in metal-organic framework. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Kaseda, T.; Kitagawa, S. Controlled synthesis of anisotropic polymer particles templated by porous coordination polymers. Chem. Mater. 2013, 25, 3772–3776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Distefano, G.; Suzuki, H.; Tsujimoto, M.; Isoda, S.; Bracco, S.; Comotti, A.; Sozzani, P.; Uemura, T.; Kitagawa, S. Highly ordered alignment of a vinyl polymer by host–guest cross-polymerization. Nat. Chem. 2013, 5, 335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, I.H.; Medishetty, R.; Lee, H.H.; Mulijanto, C.E.; Quah, H.S.; Lee, S.S.; Vittal, J.J. Formation of a Syndiotactic Organic Polymer Inside a MOF by a [2 + 2] Photo-Polymerization Reaction. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 7313–7317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Kitaura, R.; Ohta, Y.; Nagaoka, M.; Kitagawa, S. Nanochannel-promoted polymerization of substituted acetylenes in porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2006, 45, 4112–4116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Hiramatsu, D.; Kubota, Y.; Takata, M.; Kitagawa, S. Topotactic linear radical polymerization of divinylbenzenes in porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2007, 46, 4987–4990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uemura, T.; Yanai, N.; Kitagawa, S. Polymerization reactions in porous coordination polymers. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 1228–1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ding, N.; Li, H.; Feng, X.; Wang, Q.; Wang, S.; Ma, L.; Zhou, J.; Wang, B. Partitioning MOF-5 into confined and hydrophobic compartments for carbon capture under humid conditions. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2016, 138, 10100–10103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wisdom, K.M.; Watson, J.A.; Qu, X.; Liu, F.; Watson, G.S.; Chen, C.-H. Self-cleaning of superhydrophobic surfaces by self-propelled jumping condensate. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 201210770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blossey, R. Self-cleaning surfaces—Virtual realities. Nat. Mater. 2003, 2, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, A.; Seeger, S. Nepenthes pitcher inspired anti-wetting silicone nanofilaments coatings: Preparation, unique anti-wetting and self-cleaning behaviors. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2014, 24, 1074–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-M.; Reinhoudt, D.; Crego-Calama, M. What do we need for a superhydrophobic surface? A review on the recent progress in the preparation of superhydrophobic surfaces. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2007, 36, 1350–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.; Yao, X.; Jiang, L. Recent developments in bio-inspired special wettability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 3240–3255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roach, P.; Shirtcliffe, N.J.; Newton, M.I. Progess in superhydrophobic surface development. Soft Matter 2008, 4, 224–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.; Feng, L.; Gao, X.; Jiang, L. Bioinspired surfaces with special wettability. Acc. Chem. Res. 2005, 38, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xin, B.; Hao, J. Reversibly switchable wettability. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2010, 39, 769–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuteja, A.; Choi, W.; Ma, M.; Mabry, J.M.; Mazzella, S.A.; Rutledge, G.C.; McKinley, G.H.; Cohen, R.E. Designing superoleophobic surfaces. Science 2007, 318, 1618–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dyett, B.P.; Wu, A.H.; Lamb, R.N. Mechanical Stability of Surface Architecture—Consequences for Superhydrophobicity. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 18380–18394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, T.; Kim, C.-J. Turning a surface superrepellent even to completely wetting liquids. Science 2014, 346, 1096–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Verho, T.; Bower, C.; Andrew, P.; Franssila, S.; Ikkala, O.; Ras, R.H. Mechanically durable superhydrophobic surfaces. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 673–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiou, N.-R.; Lu, C.; Guan, J.; Lee, L.J.; Epstein, A.J. Growth and alignment of polyaniline nanofibres with superhydrophobic, superhydrophilic and other properties. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2007, 2, 354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, L.; Li, S.; Li, H.; Zhai, J.; Song, Y.; Jiang, L.; Zhu, D. Super-hydrophobic surface of aligned polyacrylonitrile nanofibers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2002, 41, 1221–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahner, D.; Abagat, J.; Svec, F.; Fréchet, J.M.; Levkin, P.A. A facile approach to superhydrophilic-superhydrophobic patterns in porous polymer films. Adv. Mater. 2011, 23, 3030–3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belman, N.; Jin, K.; Golan, Y.; Israelachvili, J.N.; Pesika, N.S. Origin of the contact angle hysteresis of water on chemisorbed and physisorbed self-assembled monolayers. Langmuir 2012, 28, 14609–14617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genzer, J.; Efimenko, K. Creating long-lived superhydrophobic polymer surfaces through mechanically assembled monolayers. Science 2000, 290, 2130–2133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, Y.C.; Bhushan, B. Mechanically durable carbon nanotube-composite hierarchical structures with superhydrophobicity, self-cleaning, and low-drag. ACS Nano 2009, 3, 4155–4163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, X.; Chen, J.; Ma, Y.; Wang, J.; Chan-Park, M.B.; Liu, X.; Wang, L.; Huang, W.; Chen, P. Superhydrophobic and superoleophilic hybrid foam of graphene and carbon nanotube for selective removal of oils or organic solvents from the surface of water. Chem. Commun. 2012, 48, 10660–10662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobaku, S.P.; Kota, A.K.; Lee, D.H.; Mabry, J.M.; Tuteja, A. Patterned Superomniphobic-Superomniphilic Surfaces: Templates for Site-Selective Self-Assembly. Angew. Chem. 2012, 124, 10256–10260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geyer, F.L.; Ueda, E.; Liebel, U.; Grau, N.; Levkin, P.A. Superhydrophobic–superhydrophilic micropatterning: towards genome-on-a-chip cell microarrays. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2011, 50, 8424–8427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.; Lin, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, J.; Zhuang, H.; Sun, L. Superhydrophilic–superhydrophobic micropattern on TiO2 nanotube films by photocatalytic lithography. Electrochem. Commun. 2008, 10, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Tuominen, M.T.; Rothstein, J.P. Hierarchical superhydrophobic surfaces fabricated by dual-scale electron-beam-lithography with well-ordered secondary nanostructures. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2011, 21, 3715–3722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maji, T.K.; Matsuda, R.; Kitagawa, S. A flexible interpenetrating coordination framework with a bimodal porous functionality. Nat. Mater. 2007, 6, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Eddaoudi, M.; O’Keeffe, M.; Yaghi, O.M. Design and synthesis of an exceptionally stable and highly porous metal-organic framework. Nature 1999, 402, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitagawa, S.; Kitaura, R.; Noro, S.I. Functional porous coordination polymers. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 2334–2375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herm, Z.R.; Wiers, B.M.; Mason, J.A.; van Baten, J.M.; Hudson, M.R.; Zajdel, P.; Brown, C.M.; Masciocchi, N.; Krishna, R.; Long, J.R. Separation of hexane isomers in a metal-organic framework with triangular channels. Science 2013, 340, 960–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Chakraborty, A.; Maji, T.K. Lanthanide-organic frameworks for gas storage and as magneto-luminescent materials. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2014, 273, 139–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haldar, R.; Matsuda, R.; Kitagawa, S.; George, S.J.; Maji, T.K. Amine-Responsive Adaptable Nanospaces: Fluorescent Porous Coordination Polymer for Molecular Recognition. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 11772–11777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Nguyen, H.T.H.; Miller, S.A.; Cohen, S.M. PolyMOFs: A Class of Interconvertible Polymer-Metal-Organic-Framework Hybrid Materials. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2015, 54, 6152–6157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, R.A. Meta-Organic Frameworks—The New Jack of All Trades for (Inorganic) Chemists. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2014, 53, 5716–5717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heine, J.; Müller-Buschbaum, K. Engineering metal-based luminescence in coordination polymers and metal–organic frameworks. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 9232–9242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seo, Y.K.; Yoon, J.W.; Lee, J.S.; Hwang, Y.K.; Jun, C.H.; Chang, J.S.; Wuttke, S.; Bazin, P.; Vimont, A.; Daturi, M. Porous Materials: Energy-Efficient Dehumidification over Hierachically Porous Metal-Organic Frameworks as Advanced Water Adsorbents. Adv. Mater. 2012, 24, 710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Li, B.; O’Keeffe, M.; Chen, B. Multifunctional metal–organic frameworks constructed from meta-benzenedicarboxylate units. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2014, 43, 5618–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aussillous, P.; Quéré, D. Liquid marbles. Nature 2001, 411, 924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Dai, L.; Feng, L.; Wang, X.; Lin, T. Magnetic Liquid Marbles: A “Precise” Miniature Reactor. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4814–4818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Balter, R.; Aurbach, D. Micropump based on liquid marbles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 2010, 97, 091908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, S.; Kameyama, S.; Armes, S.P.; Dupin, D.; Suzaki, M.; Nakamura, Y. pH-responsive liquid marbles stabilized with poly(2-vinylpyridine) particles. Soft Matter 2010, 6, 635–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Arbatan, T.; Li, X.; Shen, W. Liquid marble for gas sensing. Chem. Commun. 2010, 46, 4734–4736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bormashenko, E.; Musin, A. Revealing of water surface pollution with liquid marbles. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 6429–6431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, J.M.; Reithofer, M.R.; Tan, T.T.Y.; Menon, A.G.; Chen, E.Y.; Chow, C.A.; Hor, A.T.S.; Xu, J. Supergluing MOF liquid marbles. Chem. Commun. 2013, 49, 493–495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, Y.; Sun, G.; Ngai, T. Dopamine polymerization in liquid marbles: A general route to Janus particle synthesis. Langmuir 2016, 32, 3122–3129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




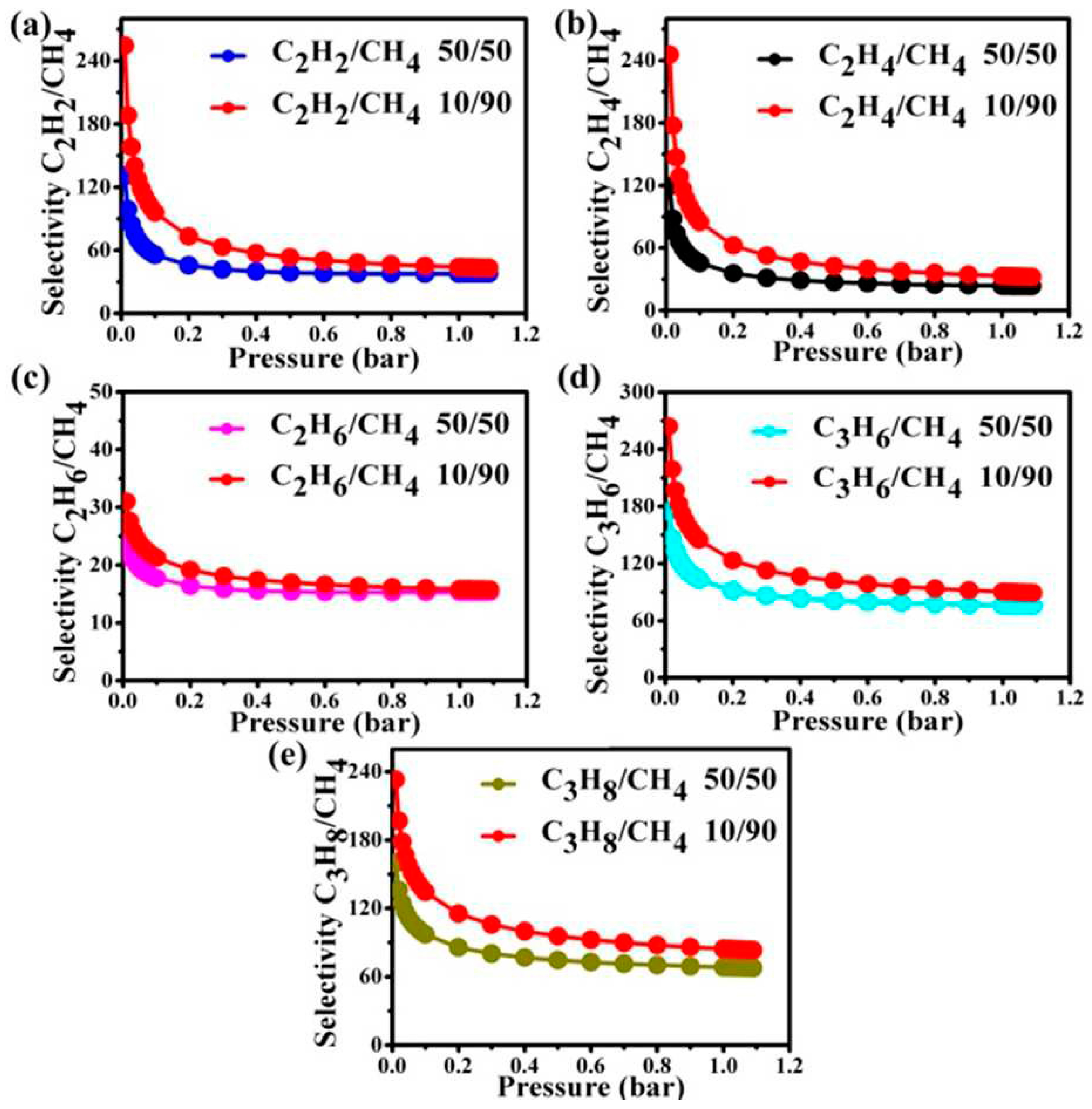
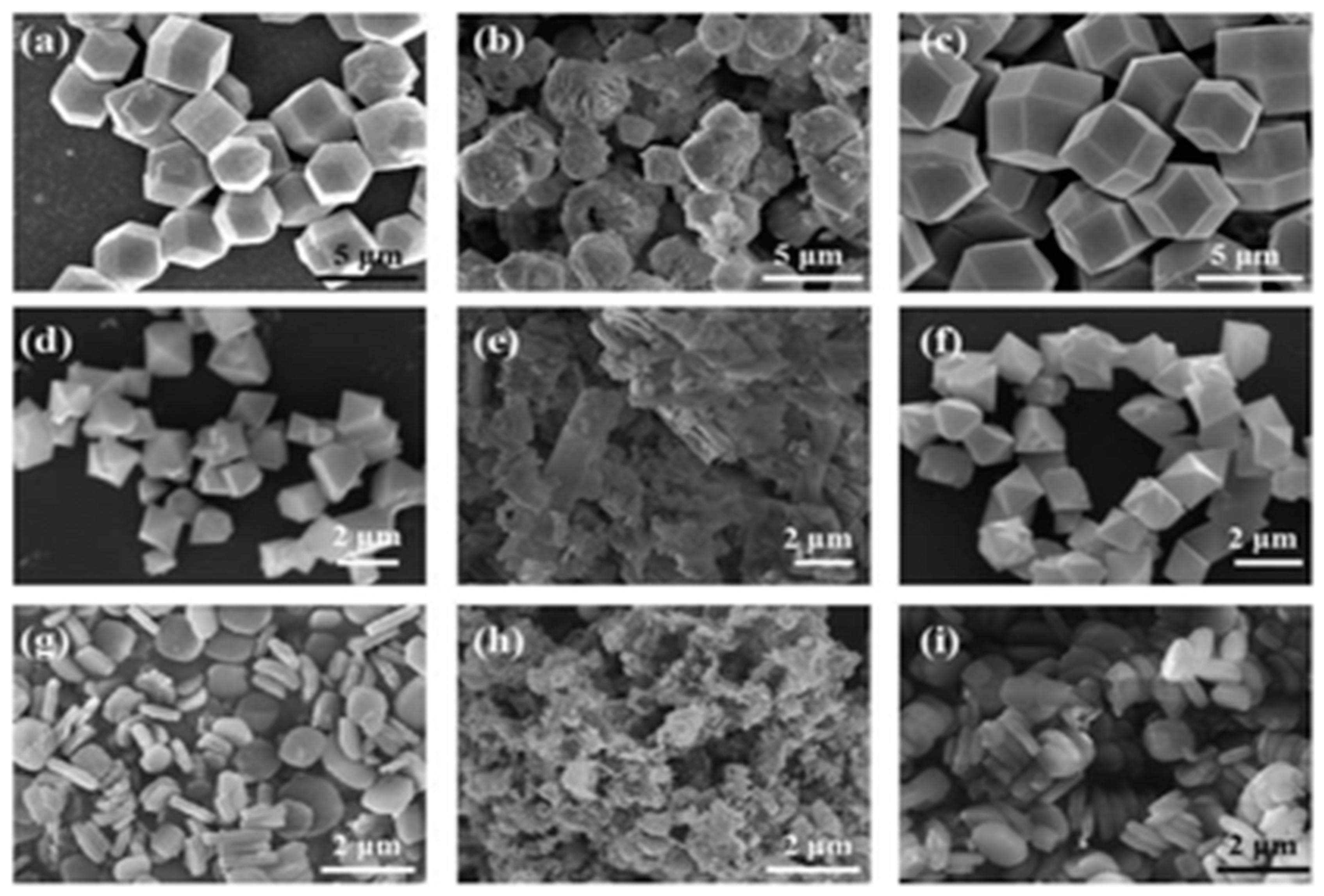
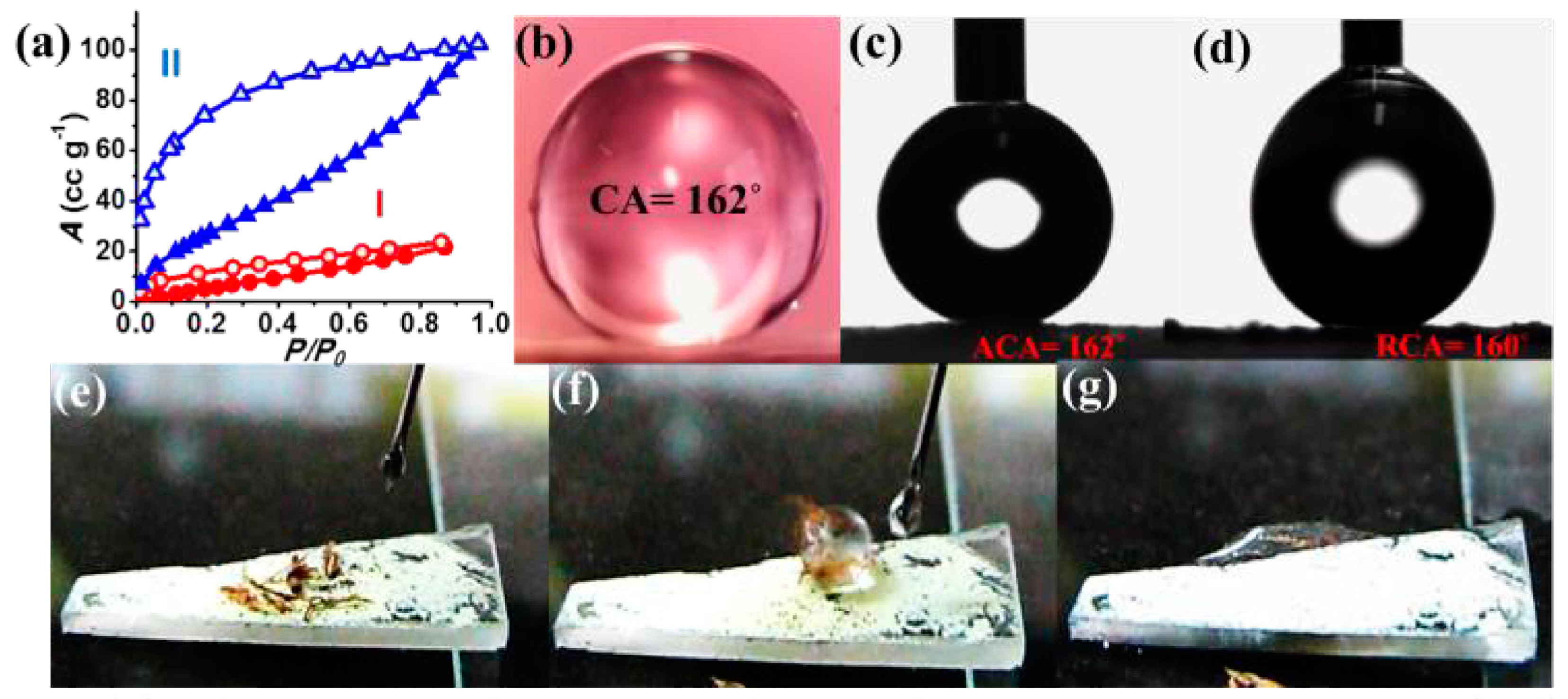
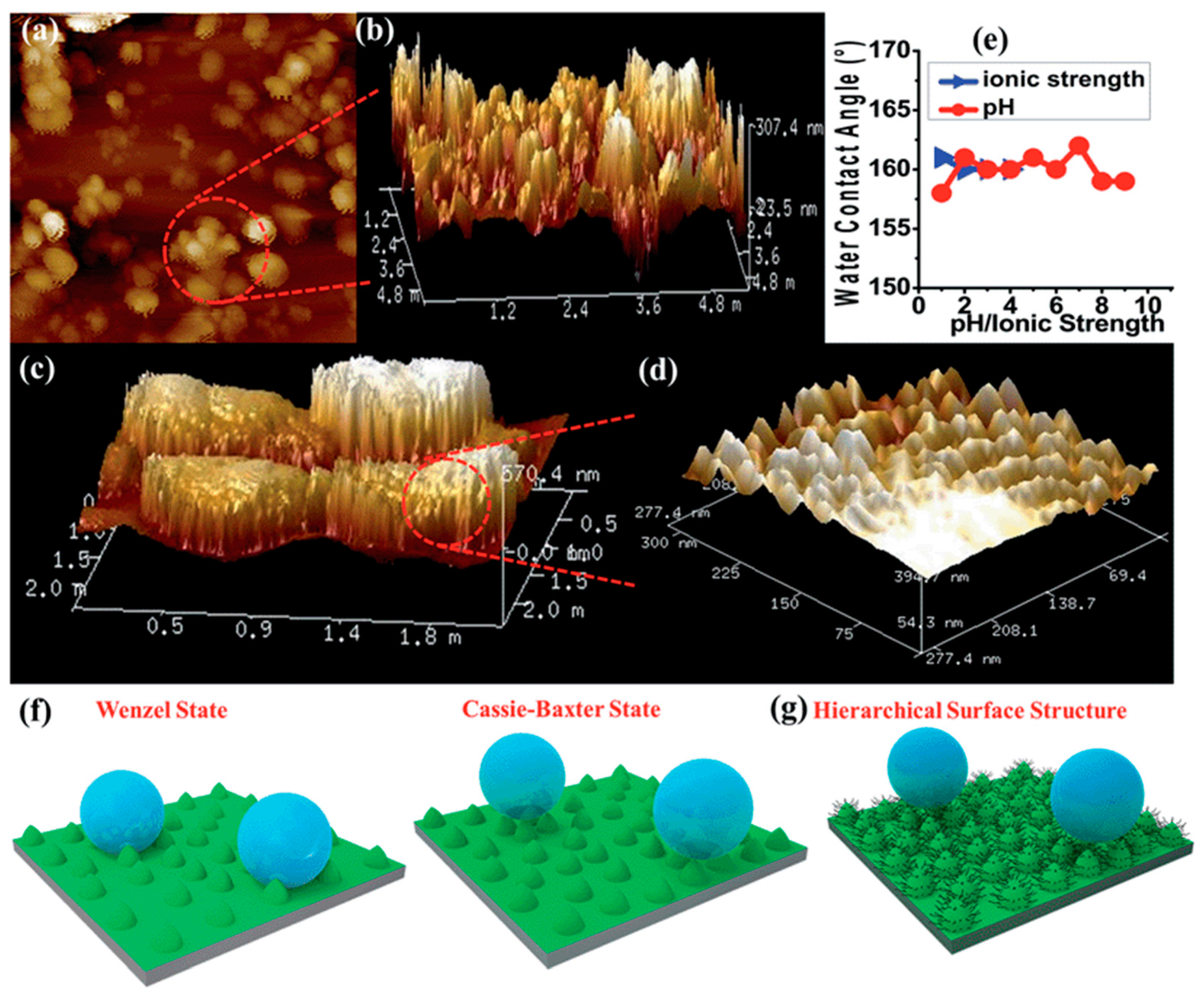
| MOF | CA (°) | PSM | SC | pH SR | MS | TS | ISSR | BET SA (m2·g−1) | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SH ZIF-90 | 152.4 | Yes | - | - | Yes | Yes | - | 1182 | [63] |
| OPA-UiO-66 | 160 | Yes | - | 1–11 | Yes | - | 1–2 | 1068 | [62] |
| OPA-UiO-66-SO3H | ˃150 | Yes | - | 1–11 | Yes | - | 1–2 | 1148 | [62] |
| OPA-PCN-222 | ˃150 | Yes | - | 1–11 | Yes | - | 1–2 | 1618 | [62] |
| UHMOF-100 | 176 | No | - | - | Yes | Yes | - | 469.2 | [32] |
| NMOF-1 | 162 | No | Yes | 1–9 | Yes | Yes | 1–4 | - | [64] |
| UPC-21 | ≥145 | No | - | - | Yes | - | - | 1725.1 | [65] |
| SH NH2-MIL-125(Ti) | ≥146 | Yes | - | - | Yes | - | - | ≈1134 | [66] |
| SH ZIF-67 | ≥146 | Yes | - | - | Yes | - | - | ≈1587 | [66] |
| SH HKUST-1 | ≥146 | Yes | - | - | Yes | - | - | ≈1386 | [66] |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Antwi-Baah, R.; Liu, H. Recent Hydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Applications. Materials 2018, 11, 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112250
Antwi-Baah R, Liu H. Recent Hydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Applications. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112250
Chicago/Turabian StyleAntwi-Baah, Ruth, and Heyang Liu. 2018. "Recent Hydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Applications" Materials 11, no. 11: 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112250
APA StyleAntwi-Baah, R., & Liu, H. (2018). Recent Hydrophobic Metal-Organic Frameworks and Their Applications. Materials, 11(11), 2250. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112250





