Preparation and Thermal Performance Enhancement of Low Temperature Eutectic Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Na2SO4·10H2O
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Preparation of Na2SO4·10H2O Composites
2.3. Characterization
2.3.1. Cooling Curve Test
2.3.2. DSC Analysis
2.3.3. Thermal Conductivity Test
2.3.4. TGA Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Properties of the Na2SO4·10H2O–KCl Eutectic Mixture
3.2. Properties of Na2SO4·10H2O–5 wt.% KCl Eutectics Containing PAM and STD
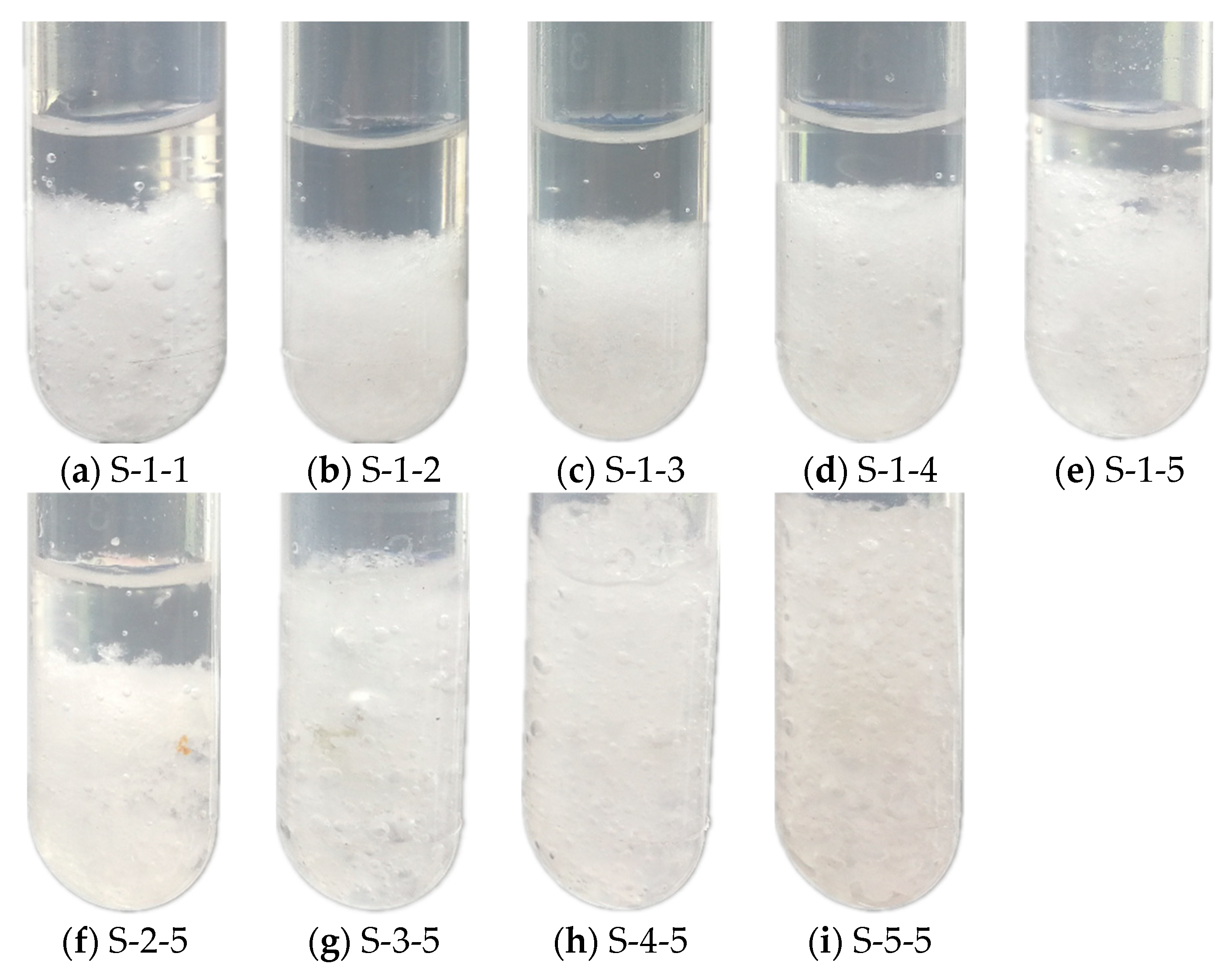
3.2.1. Phase Separation
3.2.2. Thermal Storage and Release Time
3.2.3. Degree of Supercooling
3.3. Thermal Performance of Na2SO4·10H2O Composites with EG
3.3.1. Thermal Conductivity
3.3.2. Cooling Curves
3.3.3. DSC Curves
3.4. Thermal Reliability of Na2SO4·10H2O Eutectic CPCMs
3.4.1. Ambient Temperature
3.4.2. Thermal Cycling Stability
3.4.3. TGA Analysis
4. Conclusions
- The melting temperature of the Na2SO4·10H2O–KCl mixtures decreased as the KCl mass fraction increased. However, KCl addition could not improve the phase separation and supercooling situation of the eutectics.
- In Na2SO4·10H2O–5 wt.% KCl eutectics with 5 wt.% PAM and 5 wt.% STD, almost no phase separation occurred, and the degree of supercooling reduced to 0.4 °C.
- The results showed that the suitable mass fraction of EG was 3%, and the thermal conductivity increased to 1.35 W/(m·K), approximately 2.4 times that of the pure Na2SO4·10H2O.
- The Na2SO4·10H2O–5 wt.% KCl eutectic CPCMs containing 5 wt.% PAM, 5 wt.% STD, and 3 wt.% EG showed perfect thermal reliability. After 100 thermal cycles, the enthalpy of the CPCMs remained at 104.1 J/g, and the degree of supercooling remained below 2.7 °C. The CPCMs could adapt to most outdoor environmental temperatures (as high as 50 °C), which indicates that the materials can be applied to building energy saving projects and improve personal thermal comfort.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Akeiber, H.; Nejat, P.; Majid, M.Z.A.; Wahid, M.A.; Jomehzadeh, F.; Famileh, I.Z.; Zaki, S.A. A review on phase change material (PCM) for sustainable passive cooling in building envelopes. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 60, 1470–1497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaiyat, N. Energy and economic analysis of a building air-conditioner with a phase change material (PCM). Energy Convers. Manag. 2015, 94, 150–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schossig, P.; Henning, H.M.; Gschwander, S.; Haussmann, T. Micro-encapsulated phase-change materials integrated into construction materials. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2005, 89, 297–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Xie, J.; Liu, J.; Wang, J.; Chen, S. A review on phase change material application in building. Adv. Mech. Eng. 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D.; Zhao, C.Y.; Tian, Y. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials (PCMs) in building applications. Appl. Energy 2012, 92, 593–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Saadi, S.N.; Zhai, Z. Modeling phase change materials embedded in building enclosure: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2013, 21, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abhat, A. Low temperature latent heat thermal energy storage: Heat storage materials. Sol. Energy 1983, 30, 313–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kenisarin, M.M. Thermophysical properties of some organic phase change materials for latent heat storage: A review. Sol. Energy 2014, 107, 553–575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alawadhi, E.M. Thermal analysis of a building brick containing phase change material. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zalba, B.; Marın, J.M.; Cabeza, L.F.; Mehling, H. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change: materials, heat transfer analysis and applications. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2003, 23, 251–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Tao, W.; Cao, X.; He, Y. Fatty acids as phase change materials: A review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2014, 29, 482–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yang, X.; Fang, Y.; Ding, J.; Yan, J. Enhanced thermal conductivity and thermal performance of form-stable composite phase change materials by using β-Aluminum nitride. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 1196–1200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, K.O.; Medina, M.A.; Raith, E.; Sun, X. Assessing the integration of a thin phase change material (PCM) layer in a residential building wall for heat transfer reduction and management. Appl. Energy 2015, 137, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasupathy, A.; Velraj, R. Effect of double layer phase change material in building roof for year round thermal management. Energy Build. 2008, 40, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lane, D.G. Low temperature heat storage with phase change materials. Int. J. Ambient Energy 1980, 1, 155–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuznik, F.; Virgone, J. Experimental assessment of a phase change material for wall building use. Appl. Energy 2009, 86, 2038–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabeza, L.F.; Castellon, C.; Nogues, M.; Medrano, M.; Leppers, R.; Zubillaga, O. Use of microencapsulated PCM in concrete walls for energy savings. Energy Build. 2007, 39, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Q.; Liang, C.; Zhang, L. Experimental study on the thermal storage performance and preparation of paraffin mixtures used in the phase change wall. Sol. Energy Mater. Sol. Cells 2008, 92, 1526–1532. [Google Scholar]
- Sarı, A.; Alkan, C.; Bilgin, C. Micro/nano encapsulation of some paraffin eutectic mixtures with poly(methyl methacrylate) shell: Preparation, characterization and latent heat thermal energy storage properties. Appl. Energy 2014, 136, 217–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarı, A.; Sarı, H.; Önal, A. Thermal properties and thermal reliability of eutectic mixtures of some fatty acids as latent heat storage materials. Energy Convers. Manag. 2004, 45, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Yuan, Y.; Zhang, N.; Cao, X.; Yang, X. A novel PCM of lauric–myristic–stearic acid/expanded graphite composite for thermal energy storage. Mater. Lett. 2014, 120, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Zhu, N.; Feng, G. Eutectic mixtures of capric acid and lauric acid applied in building wallboards for heat energy storage. Energy Build. 2006, 38, 708–711. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Tyagi, V.V.; Chen, C.R.; Buddhi, D. Review on thermal energy storage with phase change materials and applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2009, 13, 318–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, T.; Kimura, F.; Yamamoto, R. Studies on salt hydrate for latent heat storage, II. Eutectic mixture of pseudo-binary system CH3CO2Na3H2O-CO(NH2)2. Bull. Chem. Soc. Jpn. 2006, 56, 1223–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, M.; Yang, L.; Zhang, Z. Experimental studies on cycling stable characteristics of inorganic phase change material CaCl2·6H2O-MgCl2·6H2O modified with SrCl2·6H2O and CMC. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2018, 108, 022058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Z.; Tie, S. Preparation and thermal properties of Glauber’s salt-based phase-change materials for Qinghai–Tibet Plateau solar greenhouses. Int. J. Mod. Phys. B 2017, 31, 744085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Nian, H.; Zhu, F.; Ren, X.; Dong, O.; Zeng, J. Preparation and thermal energy storage studies of CH3COONa·3H2O–KCl composites salt system with enhanced phase change performance. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2016, 102, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Yuan, Y.; Sun, L.; Cao, X.; Yang, X. Experimental studies on the supercooling and melting/freezing characteristics of nano-copper/sodium acetate trihydrate composite phase change materials. Renew. Energy 2016, 99, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Su, Y.; Ge, X. Prediction of the melting temperature and the fusion heat of (quasi-) eutectic PCM. J. China Univ. Sci. Technol. 1995, 25, 474–478. [Google Scholar]
- Yuan, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, N.; Cao, X.; Yang, X. Investigation on thermal properties of capric–palmitic–stearic acid/activated carbon composite phase change materials for high-temperature cooling application. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 124, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, S.; Yang, H. Stearic acid hybridizing coal-series kaolin composite phase change material for thermal energy storage. Appl. Clay Sci. 2014, 101, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Qin, S.; Wu, X.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y. Preparation and thermal characterization of sodium acetate trihydrate/expanded graphite composite phase change material. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2016, 125, 831–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
















| Samples | PAM and STD Contents | Samples | PAM and STD Contents | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PAM (wt.%) | STD (wt.%) | PAM (wt.%) | STD (wt.%) | ||
| S-0-0 | 0 | 0 | S-3-3 | 3 | 3 |
| S-1-1 | 1 | 1 | S-3-4 | 3 | 4 |
| S-1-2 | 1 | 2 | S-3-5 | 3 | 5 |
| S-1-3 | 1 | 3 | S-4-1 | 4 | 1 |
| S-1-4 | 1 | 4 | S-4-2 | 4 | 2 |
| S-1-5 | 1 | 5 | S-4-3 | 4 | 3 |
| S-2-1 | 2 | 1 | S-4-4 | 4 | 4 |
| S-2-2 | 2 | 2 | S-4-5 | 4 | 5 |
| S-2-3 | 2 | 3 | S-5-1 | 5 | 1 |
| S-2-4 | 2 | 4 | S-5-2 | 5 | 2 |
| S-2-5 | 2 | 5 | S-5-3 | 5 | 3 |
| S-3-1 | 3 | 1 | S-5-4 | 5 | 4 |
| S-3-2 | 3 | 2 | S-5-5 | 5 | 5 |
| KCl Contents | Melting Temperature (°C) | Enthalpy (J/g) | Crystallization Starting Temperature (°C) | Crystallization Temperature (°C) | Degree of Supercooling (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pure | 33.1 | 249.4 | 16.3 | 30.9 | 14.6 |
| 1 wt.% | 29.9 | 145.5 | 13.4 | 30.3 | 16.9 |
| 3 wt.% | 27.8 | 140.9 | 12.9 | 28.6 | 15.7 |
| 5 wt.% | 25.3 | 128.7 | 10.5 | 26.2 | 15.7 |
| 7 wt.% | 24.6 | 82.7 | 8.3 | 24.7 | 16.4 |
| EG Contents | Melting Temperature (°C) | Enthalpy (J/g) | CV (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S-5-5 | 23.9 | 128.2 | 100 |
| 1 wt.% | 23.8 | 127.8 | 99.7 |
| 2 wt.% | 22.3 | 117.4 | 91.6 |
| 3 wt.% | 23.6 | 111.3 | 86.8 |
| 4 wt.% | 22.5 | 106.8 | 83.3 |
| 5 wt.% | 22.8 | 95.2 | 74.3 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hou, P.; Mao, J.; Chen, F.; Li, Y.; Dong, X. Preparation and Thermal Performance Enhancement of Low Temperature Eutectic Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Na2SO4·10H2O. Materials 2018, 11, 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112230
Hou P, Mao J, Chen F, Li Y, Dong X. Preparation and Thermal Performance Enhancement of Low Temperature Eutectic Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Na2SO4·10H2O. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112230
Chicago/Turabian StyleHou, Pumin, Jinfeng Mao, Fei Chen, Yong Li, and Xian Dong. 2018. "Preparation and Thermal Performance Enhancement of Low Temperature Eutectic Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Na2SO4·10H2O" Materials 11, no. 11: 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112230
APA StyleHou, P., Mao, J., Chen, F., Li, Y., & Dong, X. (2018). Preparation and Thermal Performance Enhancement of Low Temperature Eutectic Composite Phase Change Materials Based on Na2SO4·10H2O. Materials, 11(11), 2230. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112230




