Superhydrophobic Surface Preparation and Wettability Transition of Titanium Alloy with Micro/Nano Hierarchical Texture
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Experimental Sections
2.1. Preparation of Materials
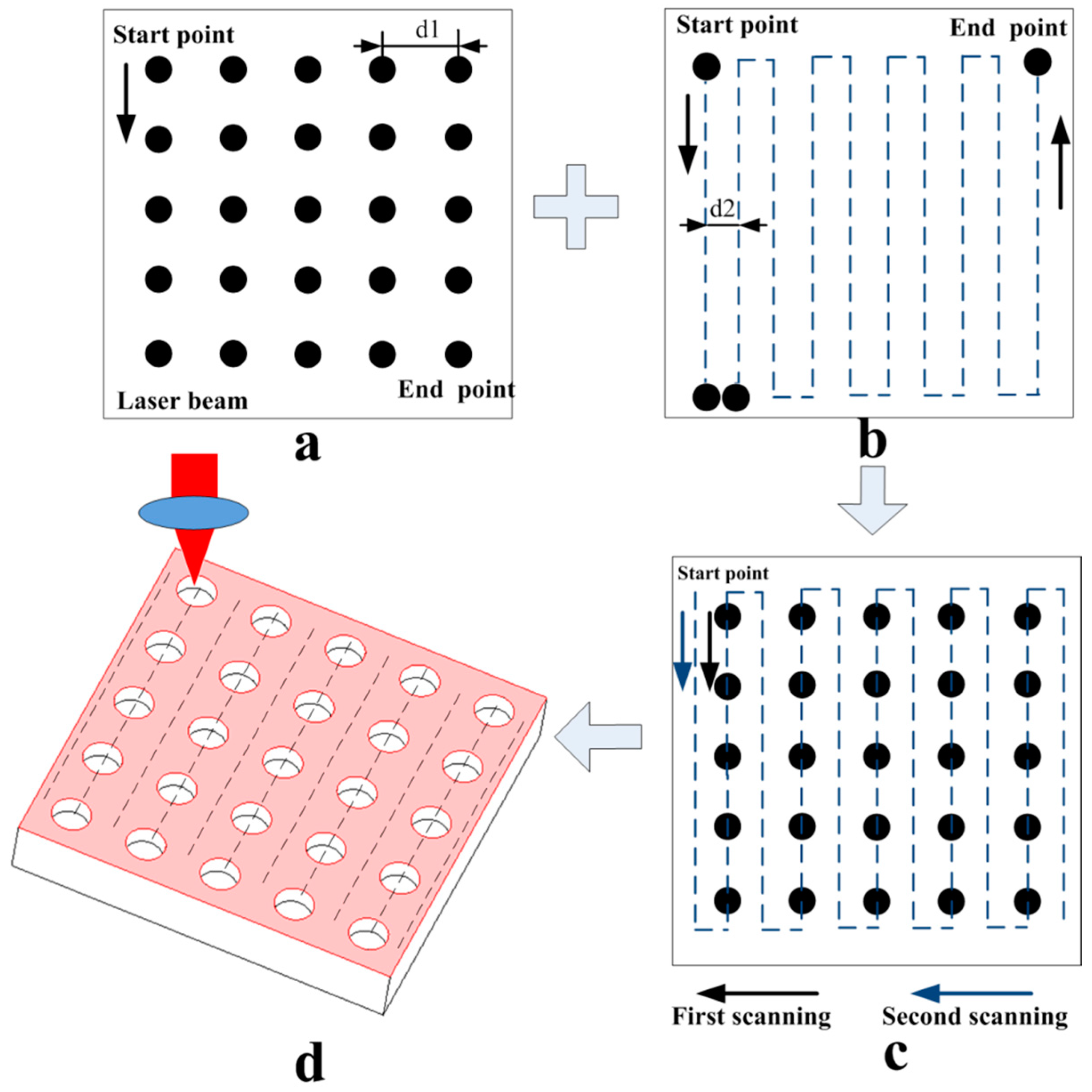
2.2. Equipment and Process Parameters
2.3. Micro/Nanostructure Design
2.4. Low-Temperature Annealing Treatment
2.5. Characterization
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Micro-Dimple Array Fabrication
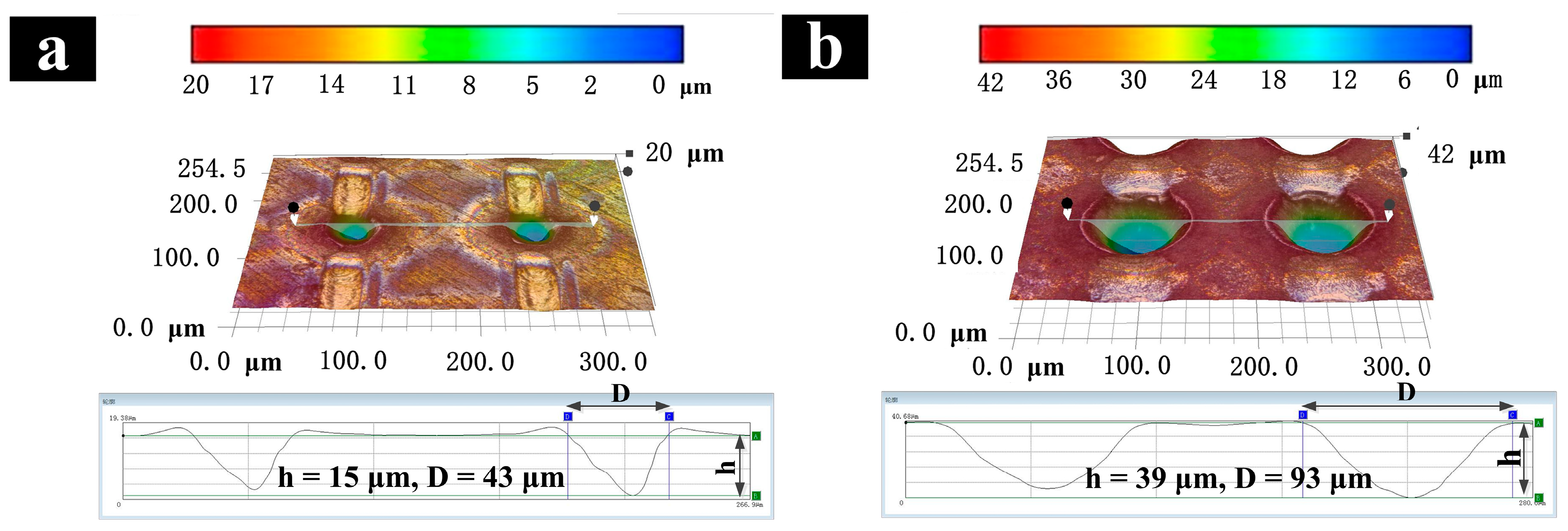
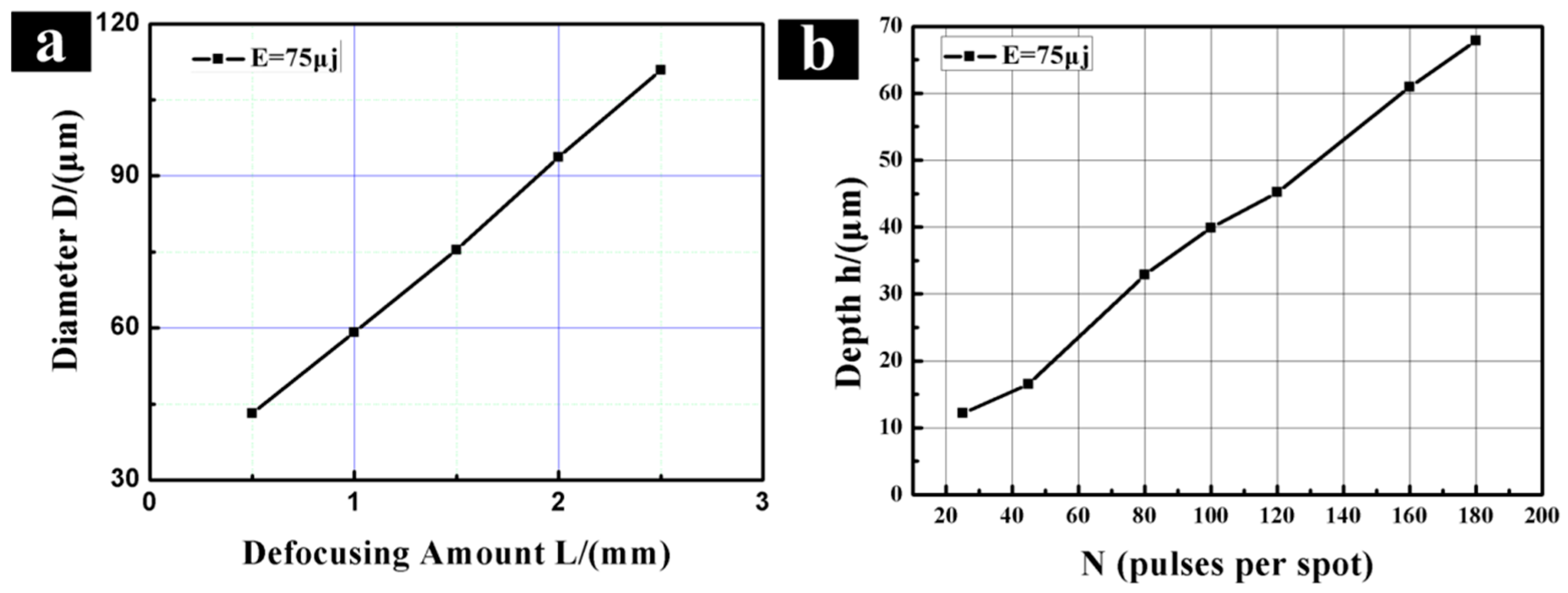
3.1.1. Laser Parameters vs. Structure Parameters
3.1.2. Preparation of Micro-dimple Array Structure
3.2. Nanoscale Pattern Preparation
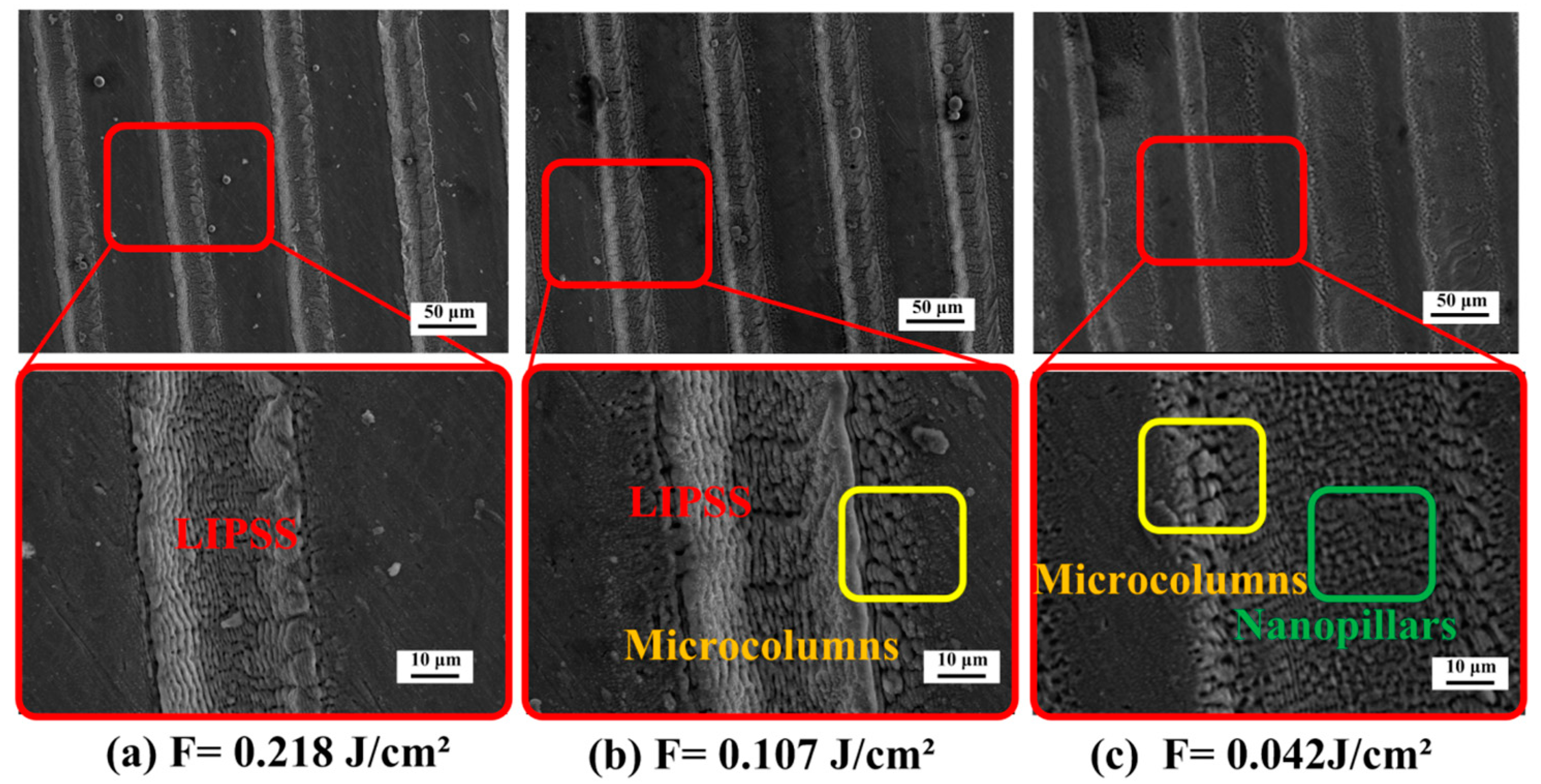
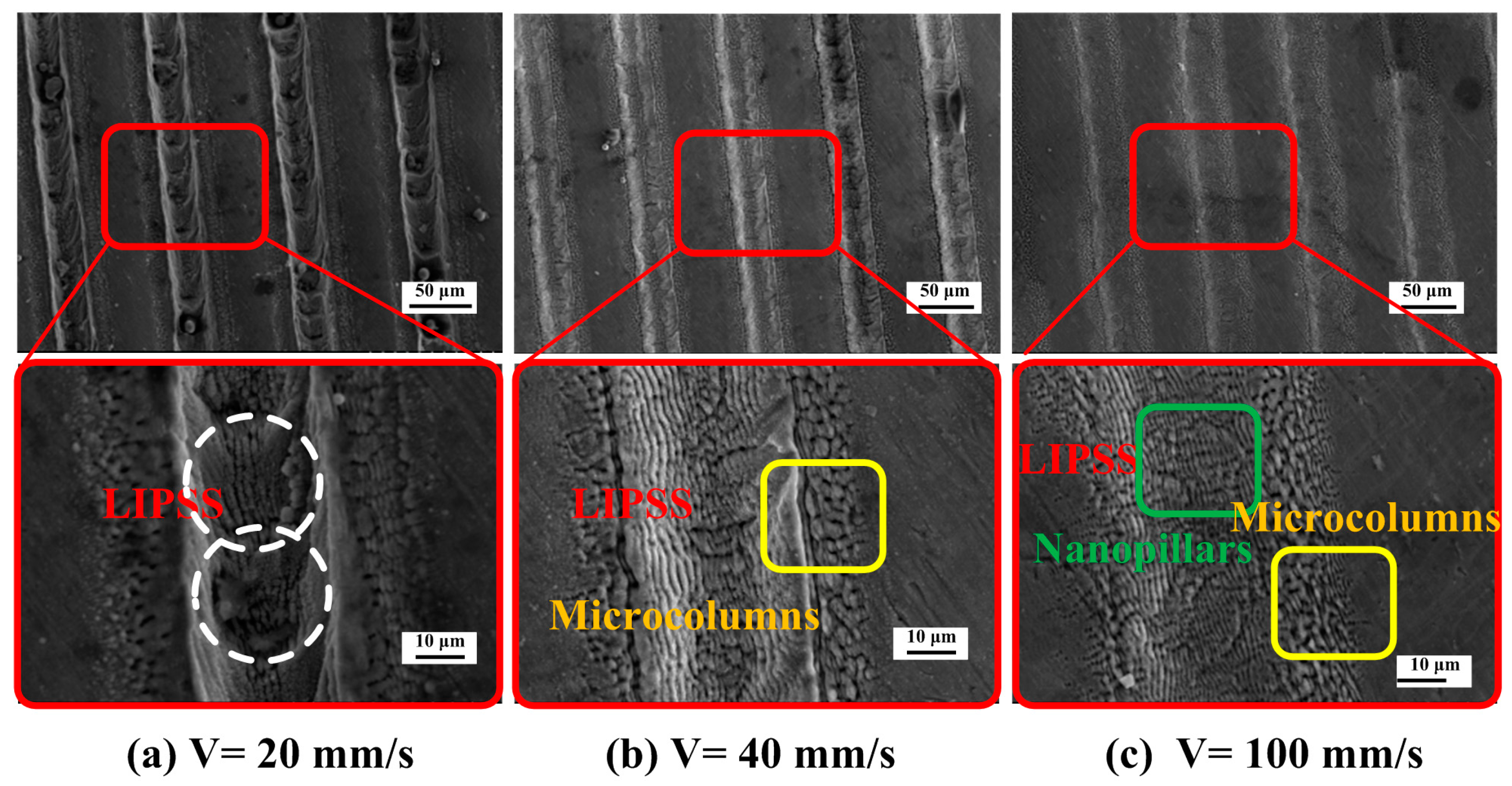
3.2.1. Parameters of LIPSS
3.2.2. Preparation of Micro/Nano Hierarchical Structure
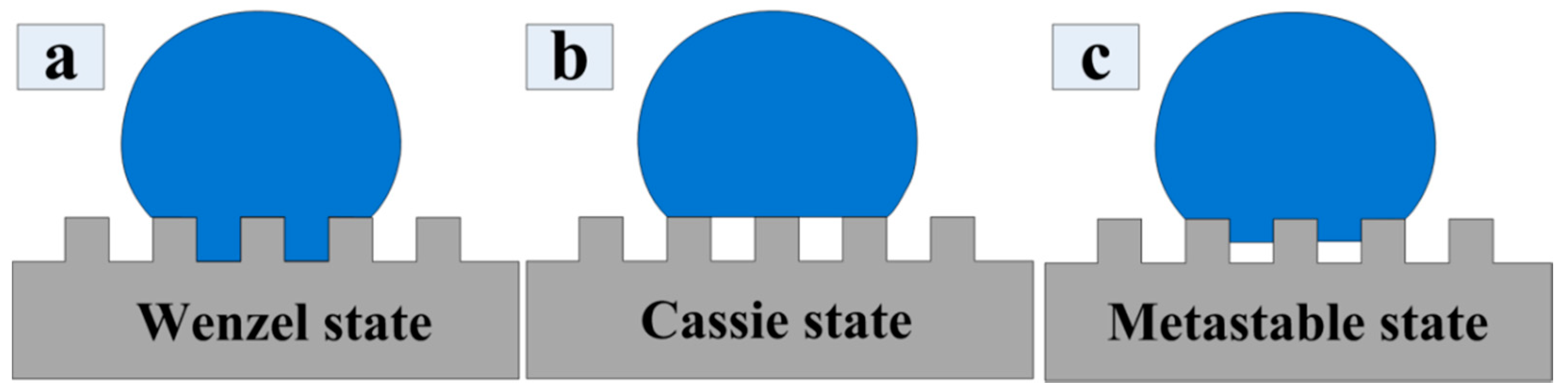
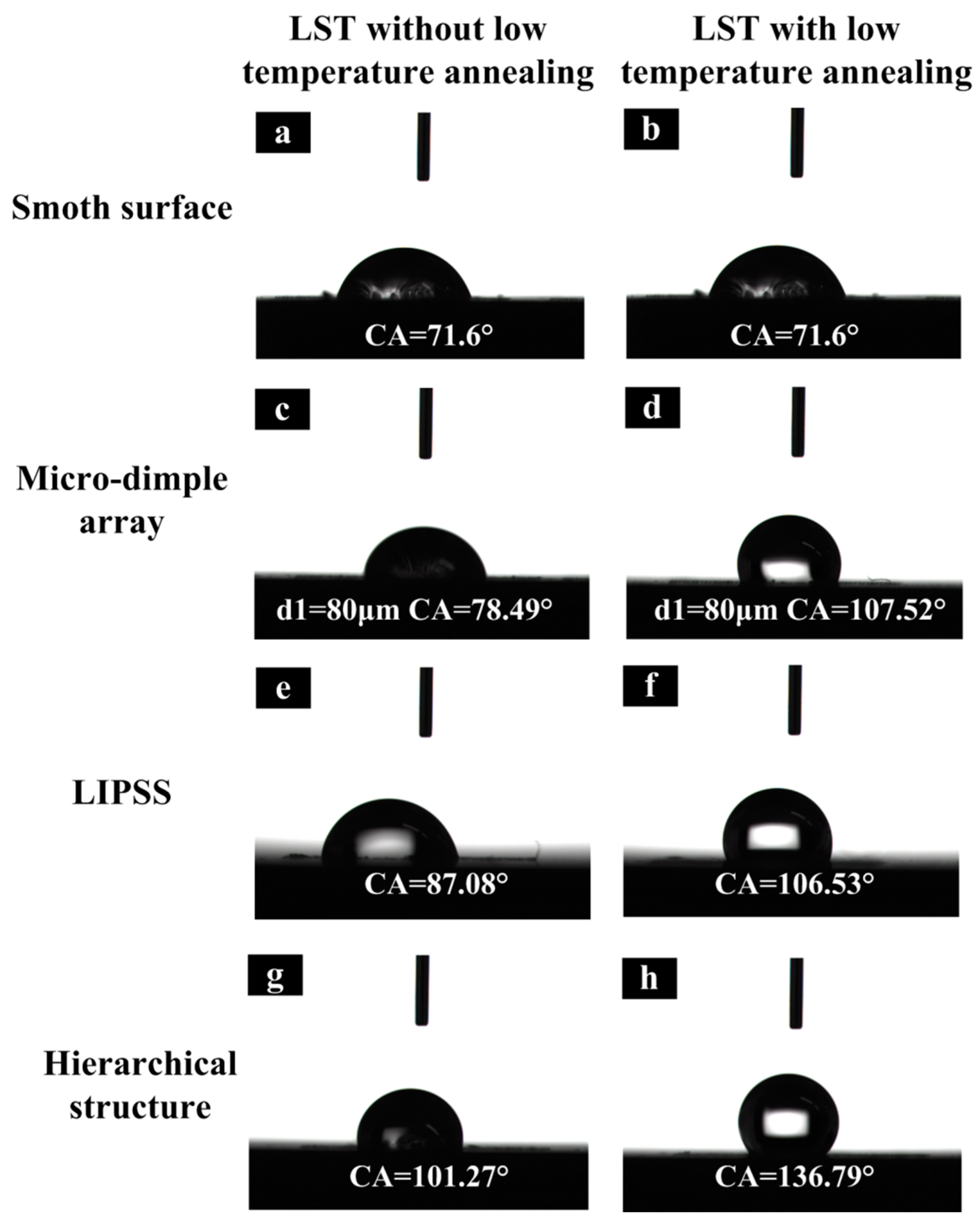
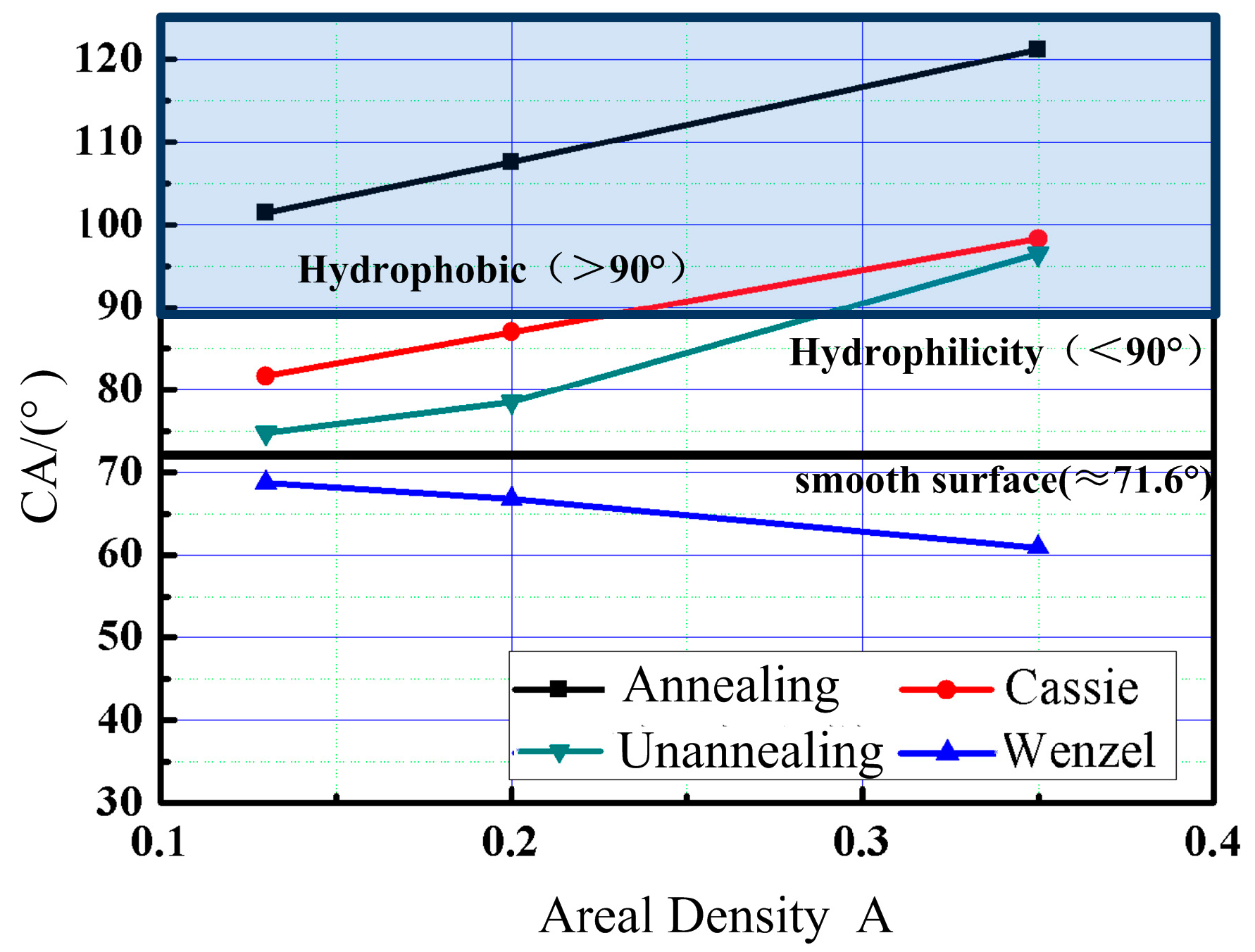
3.3. Wettability Property
3.4. Mechanism of Wettability Transition
3.4.1. Effects of Nano-, Micro-, and Hierarchical Structure on the Contact Angle
3.4.2. Effects of Low-Temperature Annealing on the Contact Angle
4. Conclusions
- (1)
- Micro-dimple arrays with accurate size were achieved by adjusting the pulse energy and the number of pulses. In addition, the dimple array is covered with laser-induced periodic ripple structure (LIPSS). The ripples have a period of about 1100 nm when the energy density and scanning speed is 0.107 J/cm2~0.218 J/cm2 and 30~50 mm/s, respectively. Thus, the micro/nano hierarchical structure is obtained in the Ti-6Al-4V surface.
- (2)
- The contact angle increases significantly with the increase of areal density. Surface wettability of micro and micro/nano hierarchical structure is consistent with the Cassie–Baxter state. At the same time, when the micro-dimple array surface is covered with the LIPSS (periodic ripple structure), contact angle values can reach the maximum value, 144.58°.
- (3)
- The change of hydroxyl groups on the surface is the main cause of surface hydrophobicity. Low-temperature annealing treatment can accelerate the transition of wettability.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Lessons from nature–an overview. Philos. Trans. R.Soc. Lon-don A Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2009, 367, 1445–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bixler, G.D.; Bhushan, B. Biofouling: Lessons from nature. Philos. Trans. A. Math. Phys. Eng. Sci. 2012, 370, 2381–2417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhushan, B. Biomimetics: Bioinspired Hierarchical-Strctured Surfaces for Green Science and Technology; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Wenzel, R.N. Resistance of solid surfaces to wetting by water. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 1936, 28, 988–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassie, A.B.D.; Baxter, S. Wettability of porous surfaces. Trans. Faraday Soc. 1944, 40, 546–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Y.; Pan, L.; Fan, P.X.; Gong, D.W.; Jiang, D.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, L.; Zhong, M.L. Cassie-State Stability of Metallic Superhydrophobic Surfaces with Various Micro/Nanostructures Produced by a Femtosecond Laser. Langmuir 2016, 32, 1065–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.Y.; Fan, P.X.; Gong, D.W.; Jiang, D.F.; Zhang, H.J.; Li, L.; Zhong, M.L. Superhydrophobic Surfaces Fabricated by Femtosecond Laser with Tunable Water Adhesion From Lotus Leaf to Rose Petal. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2015, 7, 9858–9865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, C.Y.; Chen, Z.Y.; Tiwari, M.K. All-organic superhydrophobic coatings with mechanochemical robustness and liquid impalement resistance. Nat. Mater. 2018, 17, 355–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilhelm, P.; Renu, K.; Heino, B.; Tim, S.; Jyotsna, D.M. Laser surface textured titanium alloy (Ti–6Al–4V): Part II—Studies on bio-compatibility. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 750–758. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, K.; Yang, H.; Xue, W.; He, A.; Zhu, D.H.; Liu, W.W.; Adeyemi, K.; Cao, Y. Anti-biofouling superhydrophobic surface fabricated by picosecond laser texturing of stainless steel. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 436, 263–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilbas, B.S.; Ali, H.; Al-Sharafi, A.; Al-Aqeeli, N. Laser gas assisted texturing and formation of nitride and oxynitride compounds on alumina surface: Surface response to environmental dust. Opt. Laser Eng. 2018, 102, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, C.; O’Hare, P.; O’Leary, N.D. Deposition of substituted apatites with anti-colonizing properties onto titanium surfaces using a novel blasting process. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. Part B 2010, 95, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katona, B.; Bognár, E.; Berta, B. Chemical etching of nitinol stents. Acta Bioeng. Biomech. 2013, 15, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pratap, T.; Patra, K. Mechanical micro-texturing of Ti-6Al-4V surfaces for improved wettability and bio-tribological performances. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2018, 349, 71–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadipour, M.; Hafezi, M.; Hesaraki, S. Preparation and characterization of plasma-sprayed nanostructured-merwinite coating on Ti-6Al-4V. J. Ceram. Process. Res. 2015, 16, 287–290. [Google Scholar]
- Jokinen, V.; Sainiemi, L.; Franssila, S. Complex Droplets on Chemically Modified Silicon Nanograss. Adv. Mater. 2008, 20, 3453–3456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiu, Y.; Zhu, L.; Hess, D.W.; Wong, C.P. Hierarchical Silicon Etched Structures for Controlled Hydrophobicity/Superhydrophobicity. Nano Lett. 2007, 7, 3388–3393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Wang, L.; Yu, X.; Feng, Y. Tantalum coating on porous Ti6Al4V scaffold using chemical vapor deposition and preliminary biological evaluation. Mater. Sci. Eng. C. 2013, 33, 2987–2994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bryan, E.J.; Lee, H.E.; Arnaud, W.; Kathryn, G. Characterization and evaluation of femtosecond laser-induced sub-micron periodic structures generated on titanium to improve osseointegration of implants. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 441, 1034–1042. [Google Scholar]
- Rafieazad, M.; Jaffer, J.A.; Cui, C.; Duan, X.L.; Nasiri, A. Nanosecond Laser Fabrication of Hydrophobic Stainless Steel Surfaces: The Impact on Microstructure and Corrosion Resistance. Materials 2018, 11, 1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chichkove, B.N.; Momma, C.N. Femtosecond, picosecond and nanosecond laser ablation of solids. Appl. Phys. A 1996, 63, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar-Morales, A.I.; Alamri, S.; Lasagnia, A.F. Micro-fabrication of high aspect ratio periodic structures on stainless steel by picosecond direct laser interference patterning. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 2018, 252, 313–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ta, V.D.; Dunn, A.; Wasley, T.J.; Li, J. Laser textured superhydrophobic surfaces and their applications for homogeneous spot deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 365, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhao, S.C.; Du, F.; Zhou, Y.L.; Yu, H.D. One-step fabrication of superhydrophobic surfaces with different adhesion via laser processing. J. Alloys Compd. 2018, 739, 489–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Tian, Y.L.; Yang, C.J.; Zhang, D.W. Laser-induced hydrophobicity on Ti-6Al-4V surface. In Proceedings of the 2015 International Conference on Manipulation, Manufacturing and Measurement on the Nanoscale (3M-NANO), Changchun, China, 5–9 October 2015; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2015; pp. 153–158. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Tiana, Y.L.; Yang, C.J.; Wang, F.J.; Liu, X.P. Modifcation of wetting property of Inconel 718 surface by nanosecond laser texturing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 414, 313–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, X.Q.; Wang, L.; Lv, D.H. Fabrication of hierarchical structures for stable superhydrophobicity on metallic planar and cylindrical inner surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 325, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.T.; Nivas, J.J.; Anoop, K.K. Surface structures induced by ultrashort laser pulses: Formation mechanisms of ripples and grooves. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 353, 1214–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.Y.; Zhong, M.L.; Zhang, H.J.; Fan, P.X. Superhydrophilicity to superhydrophobicity transition of picosecond laser microstructured aluminum in ambient air. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2015, 441, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rukosuyev, M.V.; Lee, J.; Cho, S.J.; Martin, G.L.; Jun, B.G. One-step fabrication of superhydrophobic hierarchical structures by femtosecond laser ablation. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 313, 411–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.J.; Li, H.; Huang, L.J.; Ren, N.F.; Kong, X. Femtosecond pulsed laser textured titanium surfaces with stable superhydrophilicity and superhydrophobicity. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2016, 389, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duong, V.T.; Andrew, D.; Thomas, J.W.; Robert, W.K.; Jonathan, S.; Patrick, J.S.; Colm, C.; Jonathan, D.S. Nanosecond laser textured superhydrophobic metallic surfaces and their chemical sensing applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 357, 48–254. [Google Scholar]
- Guan, Y.C.; Luo, F.F.; Lim, G.C.; Hong, M.H.; Zheng, H.Y.; Qi, B.J. Fabrication of metallic surfaces with long-term superhydrophilic property using one-stop laser method. Mater. Des. 2015, 78, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.J.; Mei, X.S.; Tian, Y.L.; Zhang, D.W.; Li, Y.; Liu, X.P. Modification of wettability property of titanium by laser texturing. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Tech. 2016, 87, 5–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, B.; Lupton, C.; Spanrad, S. Fatigue crack growth in laser-shock-peened Ti-6Al-4V aerofoil specimens due to foreign object damage. Int. J. Fatigue 2014, 59, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kietzig, A.M.; Hatzikiriakos, S.G.; Englezos, P. Patterned Superhydrophobic Metallic Surfaces. Langmuir 2009, 25, 4821–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Long, J.Y.; Zhong, M.L.; Fan, P.X.; Gong, D.W.; Zhang, H.J. Wettability conversion of ultrafast laser structured copper surface. J. Laser Appl. 2015, 27, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.P.; Mohamed, R.; Rashid, B.A.; Khew, S.Y.; Li, F.P.; Hong, M.H. Wettability transition of laser textured brass surfaces inside different mediums. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2018, 427, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Wang, F.J.; Li, W.L. Reversible wettability between superhydrophobicity and superhydrophilicity of Ag surface. Sci. China Mater. 2016, 59, 348–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qing, Y.Q.; Yang, C.N.; Yu, N.N. Superhydrophobic TiO2/polyvinylidene fluoride composite surface with reversible wettability switching and corrosion resistance. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 290, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, D.M.; Ngo, C.V.; Lee, K.M. Fast fabrication of superhydrophobic metallic surface using nanosecond laser texturing and low-temperature annealing. CIRP Ann. Manuf. Technol. 2016, 65, 519–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngo, C.V.; Chun, D.M. Fast wettability transition from hydrophilic to superhydrophobic laser-textured stainless steel surfaces under low-temperature annealing. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 409, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Z.Y.; Fu, Y.H.; Yin, B.F. Characterization of partitioned alienation surface texturing on cylinder bore. J. JIANGSU U.: Nat. Sci. Ed. 2015, 36, 93–98. [Google Scholar]
- Garrelie, F.; Colombier, J.P.; Pigeon, F.; Tonchev, S.; Faure, N.; Bounhalli, M. Evidence of surface pasmon resonance in ultrafast laser-induced ripples. Opt. Express 2011, 19, 9035–9043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gnilitskyi, I.; Derrien, T.J.Y.; Levy, Y. High-speed manufacturing of highly regular femtosecond laser-induced periodic surface structures: Physical origin of regularity. Sci. Rep. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, M.C.; Wang, J. Surface Quality Analysis of Titanium and Nickel-based Alloys Using Pico-second Laser. Procedia CIRP. 2014, 13, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drzymala, J. Hydrophobicity and collectorless flotation of inorganic materials. Adv. Colloid Interface Sci. 1994, 50, 143–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, M.A. An HREELS and TPD study of water on TiO2(110): The extent of molecular versus dissociative adsorption. Surf. Sci. 1996, 355, 151–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Nobuyuki, S.; Akira, F. Studies of Surface Wettability Conversion on TiO2 Single-Crystal Surfaces. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 2188–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pant, R.; Singha, S.; Bandyopadhyay, A. Investigation of static and dynamic wetting transitions of UV responsive tunable wetting surface. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2014, 292, 777–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Liu, X.; Tian, Y. Insights into the wettability transition of nanosecond laser ablated surface under ambient air exposure. J. Colloid Interf. Sci. 2018, 533, 268–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Cao, L.; Zhao, W. Insights into the superhydrophobicity of metallic surfaces prepared by electrodeposition involving spontaneous adsorption of airborne hydrocarbons. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2015, 324, 576–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafrin, E.; Zisman, W. Critical surface tension for spreading on a liquid substrate. J. Phys. Chem. 1967, 71, 1309–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
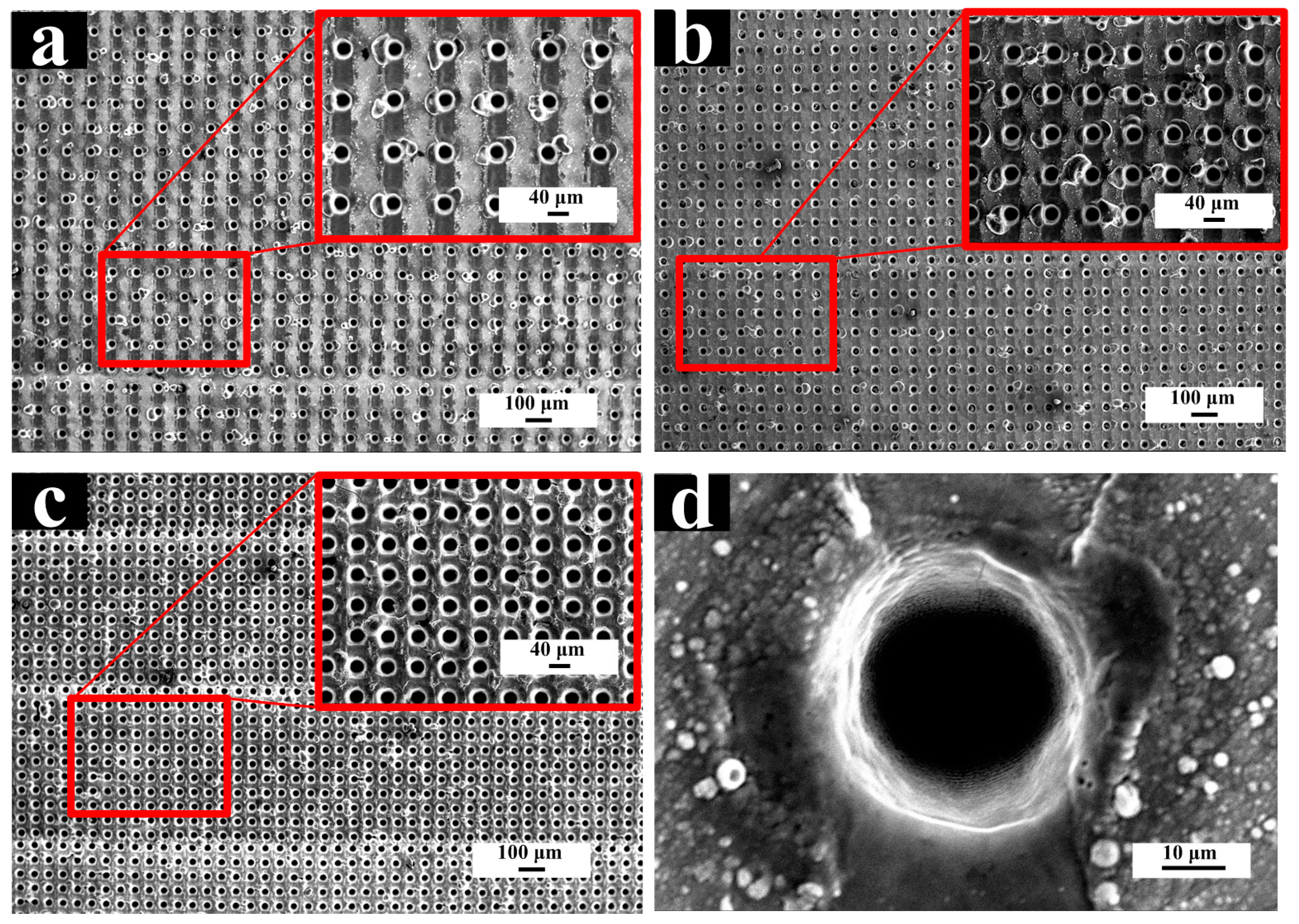



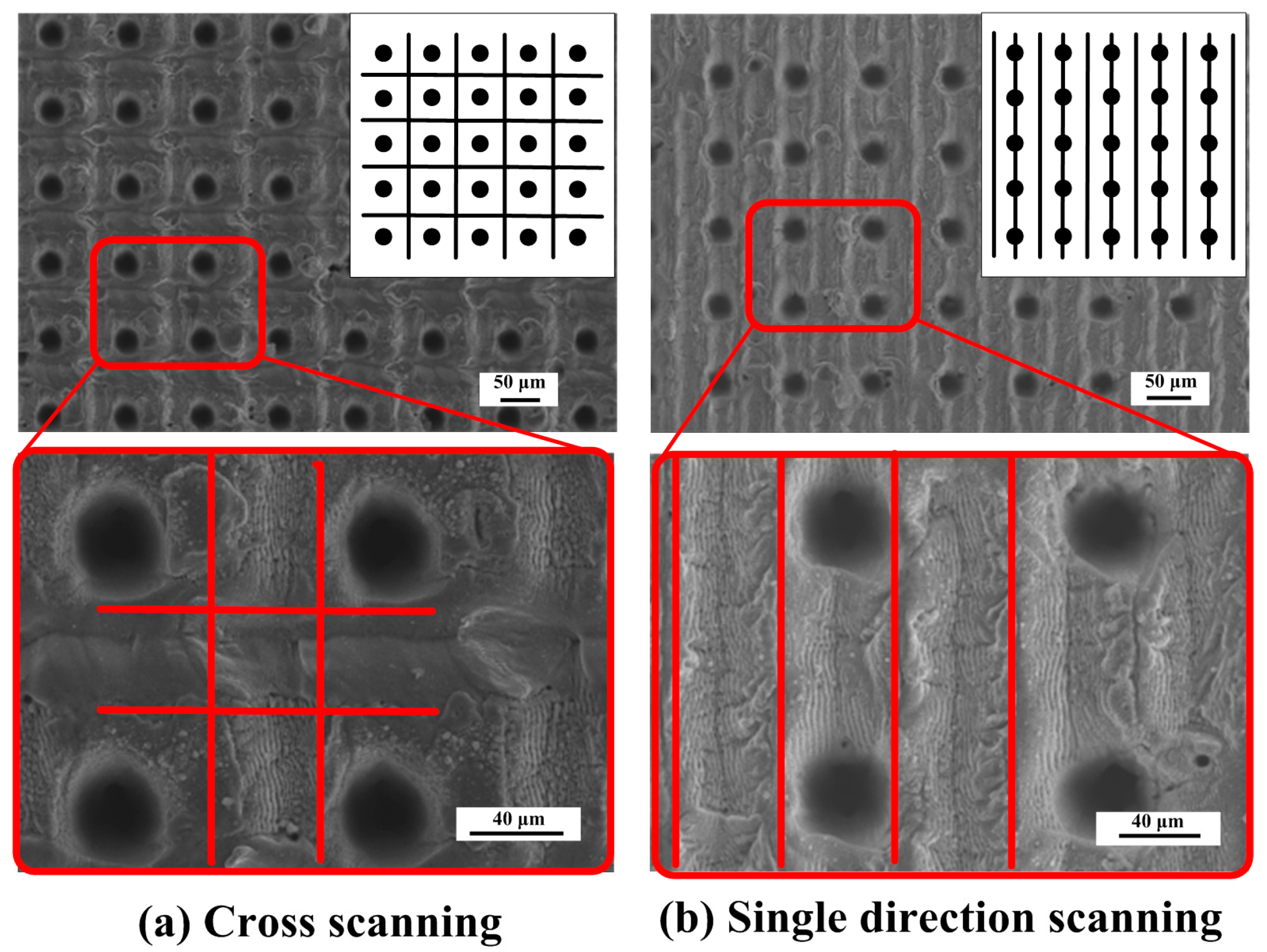

| a Micro-Dimple Array | b LIPSS | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Single-pulse energy | 75 μJ | Single-pulse energy | 75 μJ |
| Pulse frequency | 400 kHz | Pulse frequency | 100 kHz |
| Scanning speed | 300 mm/s | Scanning speed | 20 mm/s~100 mm/s |
| Defocusing amount | 0~2.5 mm | Defocusing amount | 0~4 mm |
| Pulse number | 20~200 | Scanning times | 1 |
| Energy density | 6.68~16.7 J/cm2 | Energy density | 0.02~ 66.8 J/cm2 |
| Accumulated fluence | 334~1336 J/cm2 | ||
| Main Elements | C | N | O | Al | Ti |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Untreated sample | 1.24 | 3.7 | 3.41 | 6.34 | 81.7 |
| LST without low temperature annealing | 2.2 | 2.32 | 40.88 | 4.01 | 50.6 |
| LST with low temperature annealing | 3.11 | 0.09 | 42.6 | 3.85 | 50.35 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Yang, Z.; Zhu, C.; Zheng, N.; Le, D.; Zhou, J. Superhydrophobic Surface Preparation and Wettability Transition of Titanium Alloy with Micro/Nano Hierarchical Texture. Materials 2018, 11, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112210
Yang Z, Zhu C, Zheng N, Le D, Zhou J. Superhydrophobic Surface Preparation and Wettability Transition of Titanium Alloy with Micro/Nano Hierarchical Texture. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112210
Chicago/Turabian StyleYang, Zhiru, Chongchong Zhu, Nan Zheng, Dezheng Le, and Jianzhong Zhou. 2018. "Superhydrophobic Surface Preparation and Wettability Transition of Titanium Alloy with Micro/Nano Hierarchical Texture" Materials 11, no. 11: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112210
APA StyleYang, Z., Zhu, C., Zheng, N., Le, D., & Zhou, J. (2018). Superhydrophobic Surface Preparation and Wettability Transition of Titanium Alloy with Micro/Nano Hierarchical Texture. Materials, 11(11), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112210





