Characterization and Corrosion Resistance of Boron-Containing-Austenitic Stainless Steels Produced by Rapid Solidification Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Procedure
2.1. Amorphization Study
2.2. High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Process
2.3. Spray Forming
2.4. Characterization Techniques
2.5. Electrochemical Measurements
3. Results and Discussion
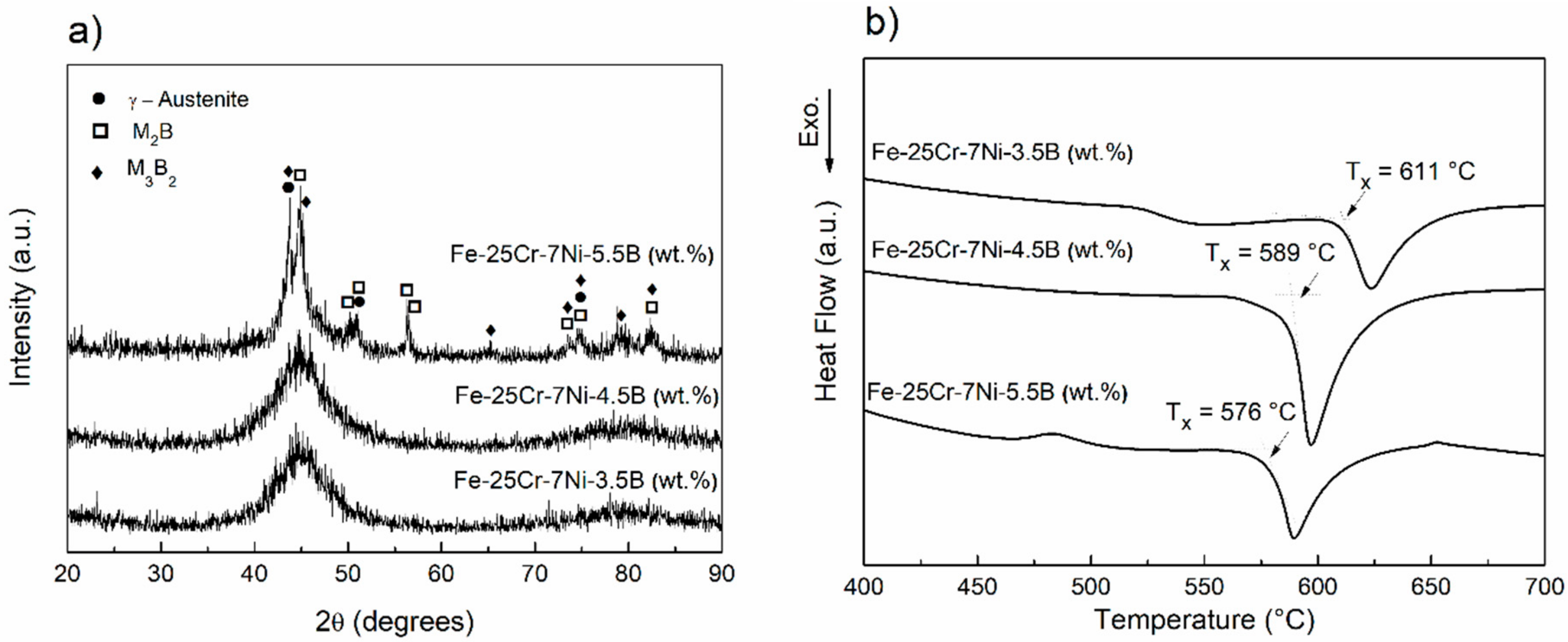
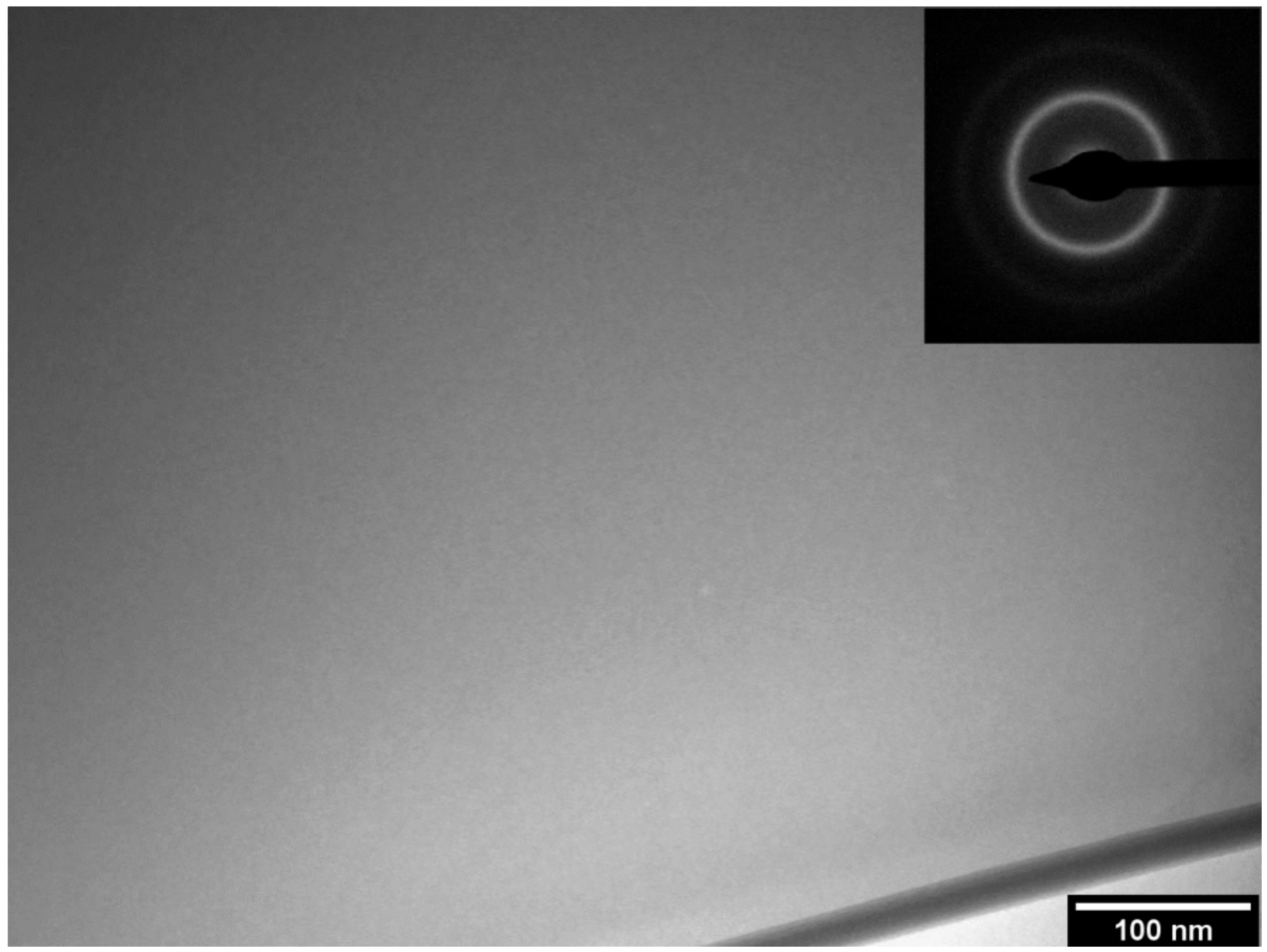
3.1. Amorphization Study of the 68-xFe25Cr7NixB (x = 3.5, 4.5, and 5.5 wt.%) Alloy Compositions
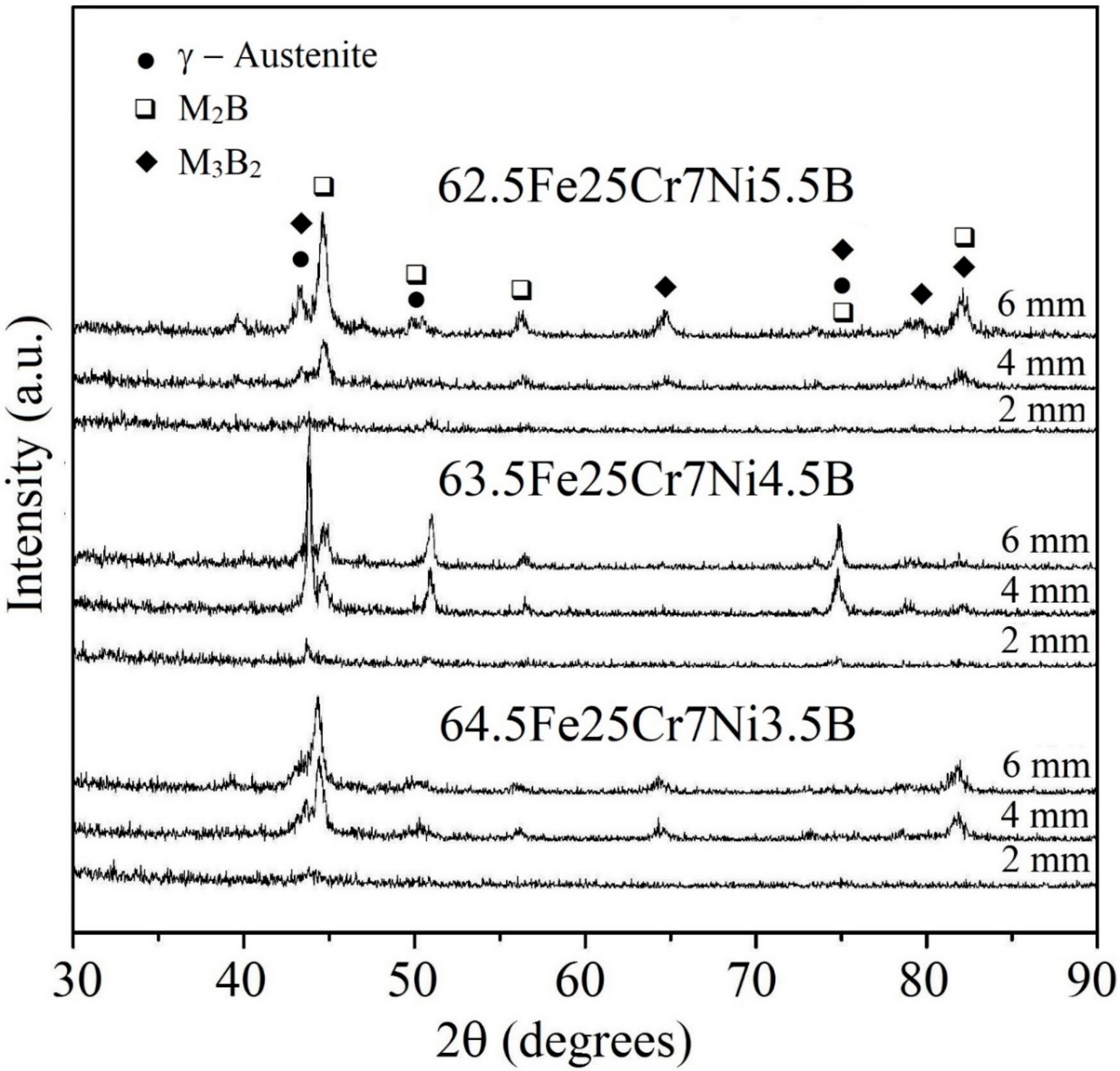
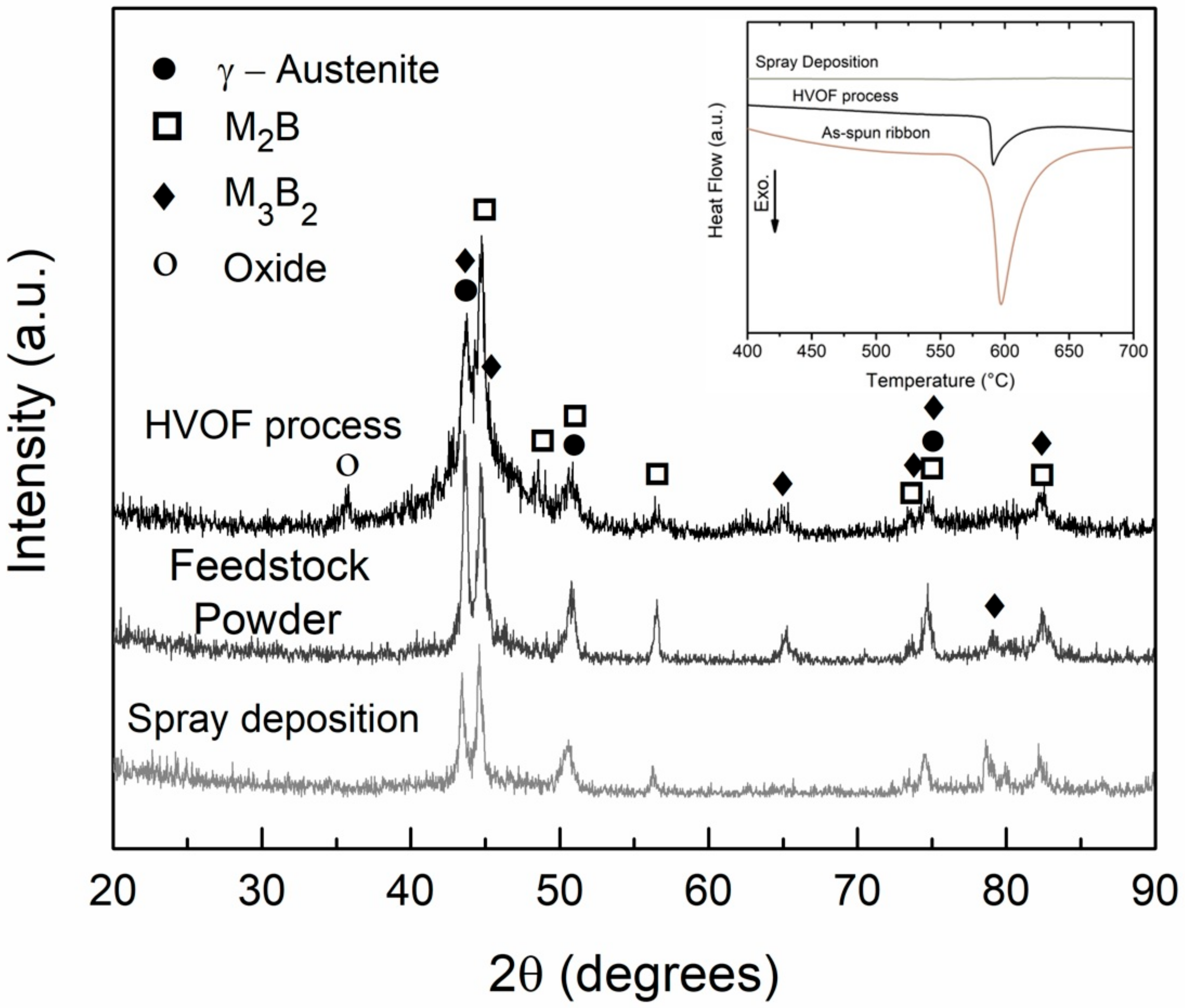
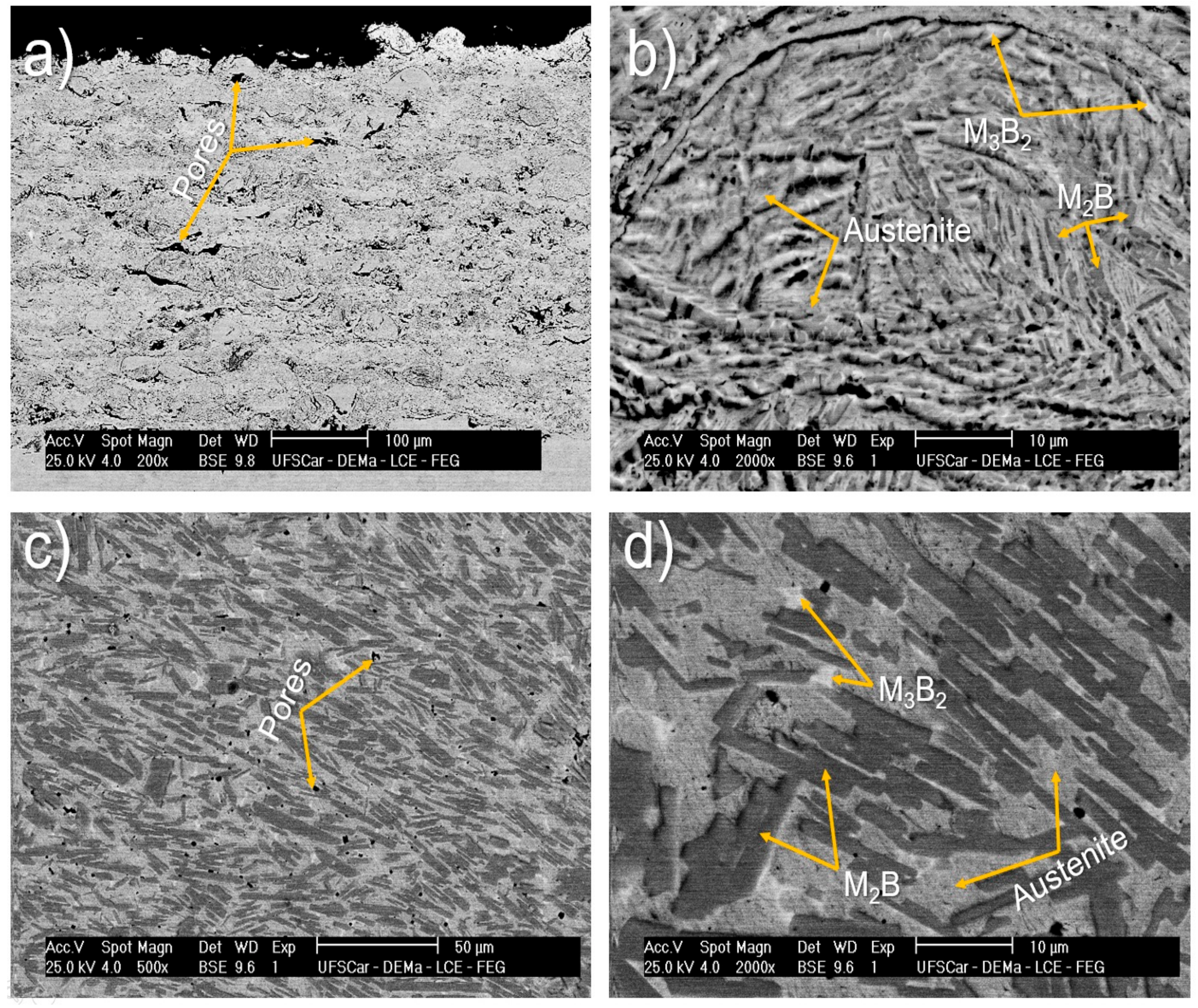
3.2. Microstructure Characterization of 63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B HVOF Coatings and Spray Formed Deposits
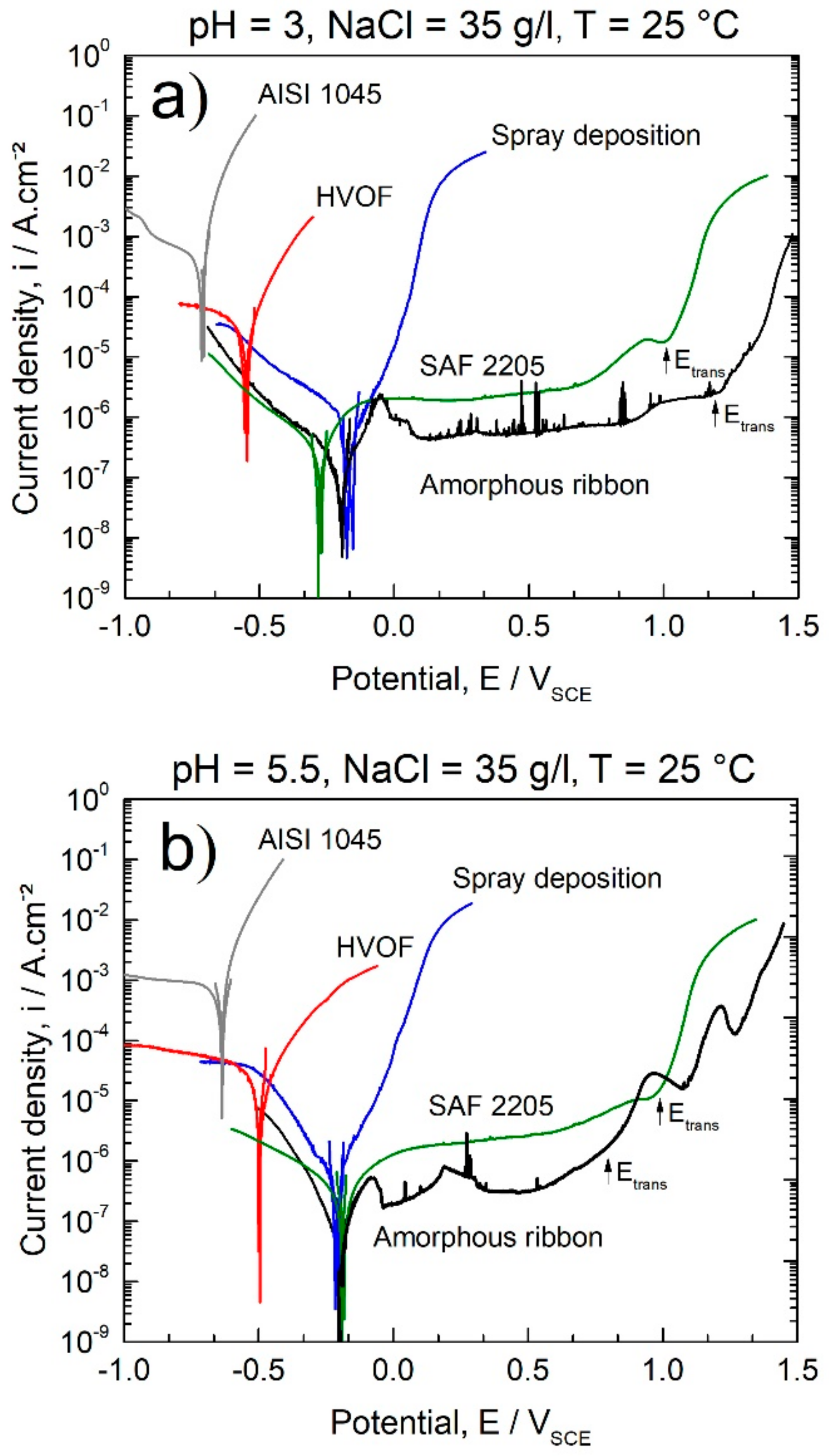
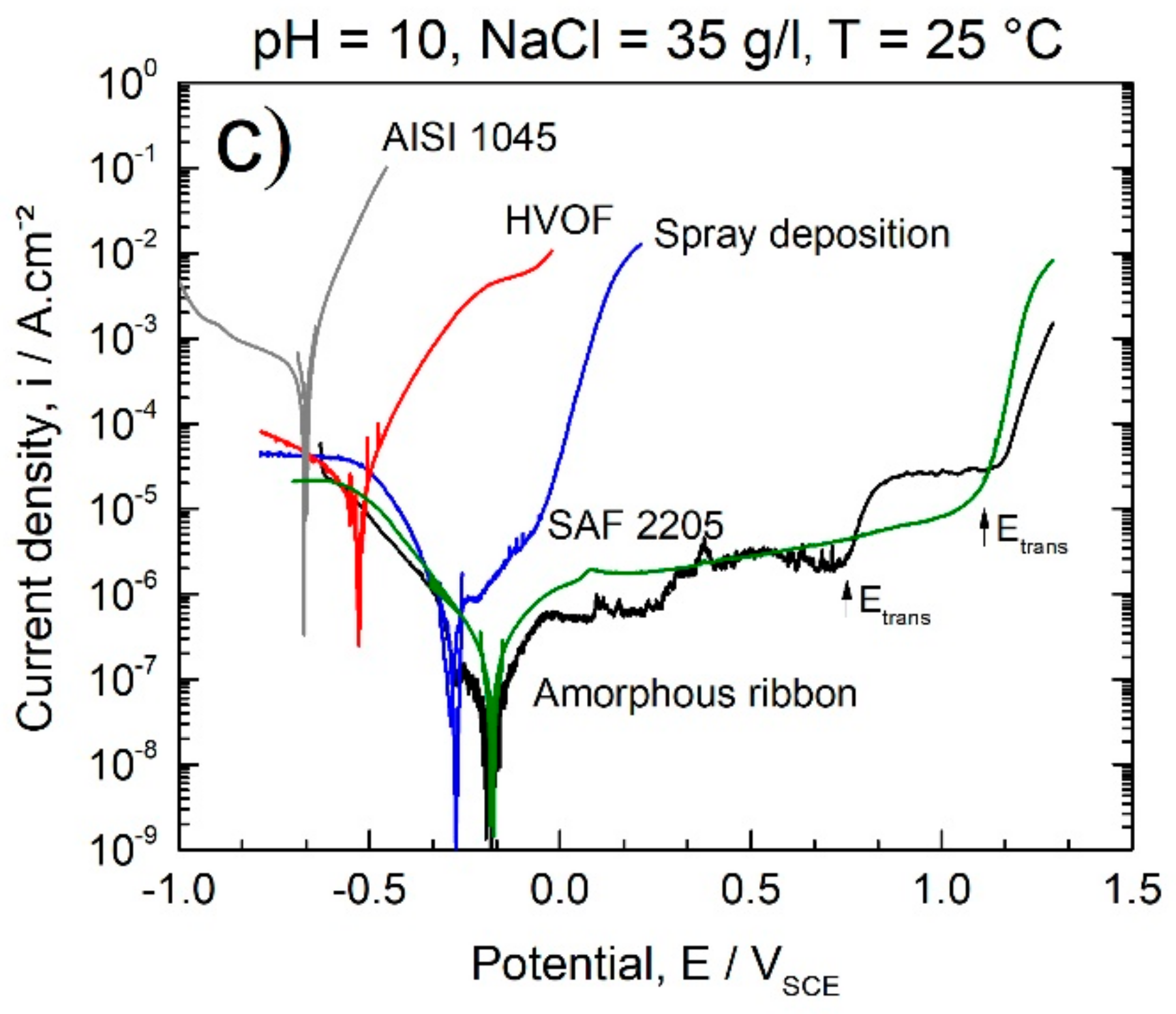
3.3. Corrosion Behavior
4. Conclusions
- The GFA of boron-modified duplex stainless steel, 68-xFe25Cr7NixB (x = 3.5, 4.5, and 5.5 wt.%) was investigated. The 63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B alloy composition presented the higher GFA, and fully amorphous ribbons were obtained by melt-spinning.
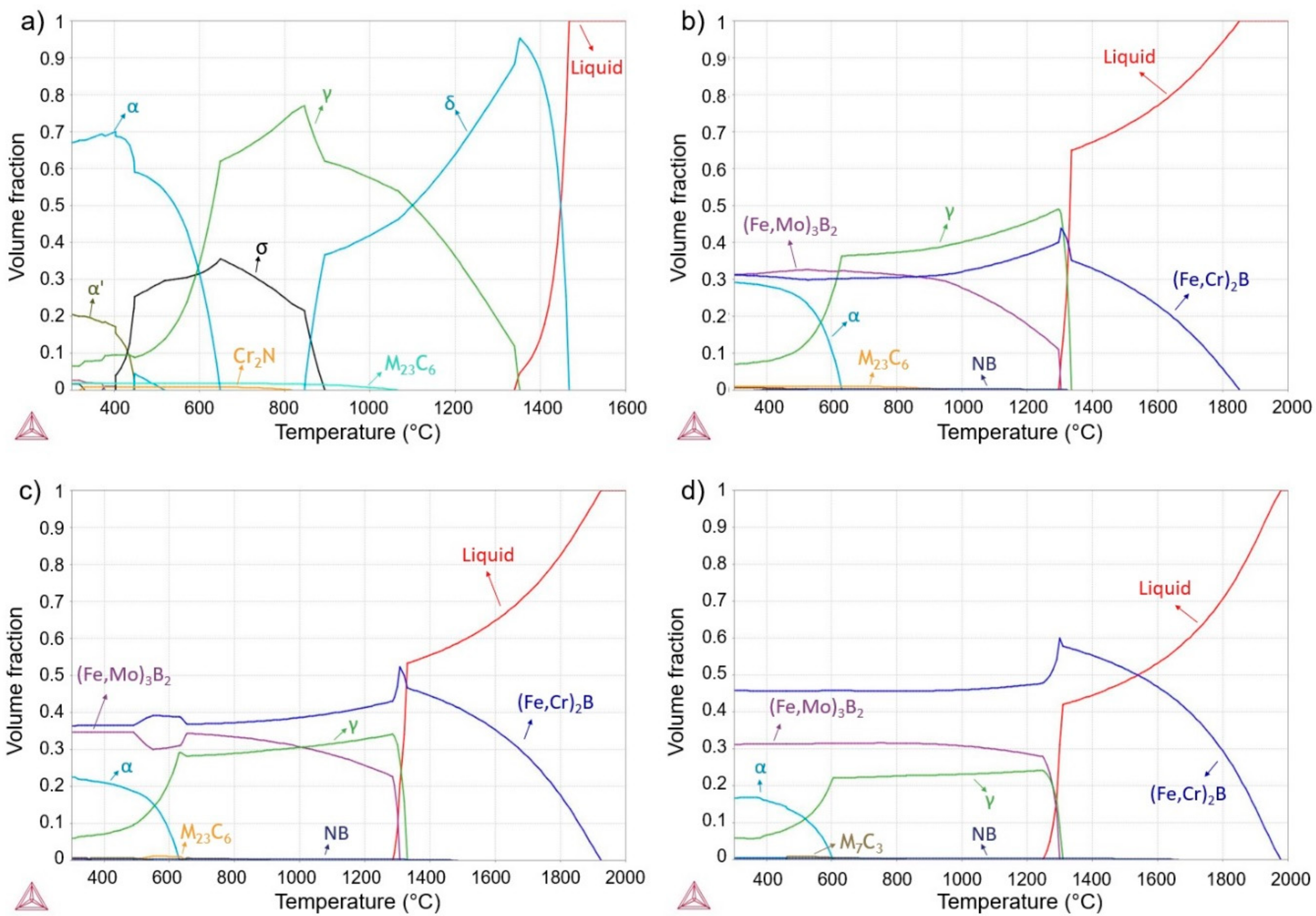
- The thermodynamic calculations predicted the stable phases, and from this result, it was possible to understand the microstructure evolution of the copper mold cast alloys for different cooling rates. These results were also of importance to understand the formed microstructure from the HVOF and spray deposition processes.
- HVOF and spray depositions were performed in the alloy with higher glass forming ability (63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B). In both cases, the cooling rates were not high enough to ensure fully amorphization. The crystalline phases formed were primary (Fe,Cr)2B and eutectic (Fe,Mo)3B2 borides in an austenitic matrix. The microstructure of the HVOF coating was more refined than that of the sprayed deposits, however, with higher levels of porosity.
- Fully amorphous 63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B ribbons exhibited excellent corrosion resistance in chloride-rich alkaline and acid media with icorr of about 10−8 A/cm2 and broad passivation plateau.
- Coatings and deposits of the same composition as for the ribbons (63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B) produced by the HVOF process and spray deposition, respectively, exhibited lower corrosion resistance due to the presence of porosity and crystalline defects. However, their corrosion resistance was higher than that of the AISI 1045 steel used as substrate, with the advantage of being reinforced with hard borides, resulting in a composite microstructure promising to be resistant against wear.
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lavernia, E.J.; Srivatsan, T.S. The rapid solidification processing of materials: Science, principles, technology, advances, and applications. J. Mater. Sci. 2010, 45, 287–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Takeuchi, A. Recent development and application products of bulk glassy alloys. Acta Mater. 2011, 59, 2243–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, P.H.; Xiao, A.C.; Li, J.B.; Jang, J.S.C.; Chu, J.P.; Huang, J.C. Prominent Fe-based bulk amorphous steel alloy with large supercooled liquid region and superior corrosion resistance. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 586, 94–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Kong, F.L.; Man, Q.K.; Shen, B.L.; Li, R.W.; Al-Marzouki, F. Development and applications of Fe- and Co-based bulk glassy alloys and their prospects. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S2–S8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, X.; Du, D.; Wang, K.; Hong, Y.; Chang, B. Microstructure and Wear Resistance of Fe-Cr-Mo-Co-C-B Amorphous Composite Coatings Synthesized by Laser Cladding. Metals 2018, 8, 622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suryanarayana, C.; Inoue, A. Iron-based bulk metallic glasses. Int. Mater. Rev. 2013, 58, 131–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Li, Z.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, G.; Zheng, W. Highly Ductile and Ultra-Thick P-Doped FeSiB Amorphous Alloys with Excellent Soft Magnetic Properties. Materials 2018, 11, 1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, N.; Wang, F.; Qin, F.; Tang, W.; Dan, Z. Enhanced Azo-Dyes Degradation Performance of Fe-Si-B-P Nanoporous Architecture. Materials 2017, 10, 1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboki, T. Development of Fe-B Based Bulk Metallic Glasses: Morphology of Residual Phases in Fe50Ni16Mo6B18Zr10 Glass. Metals 2013, 3, 159–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lu, Z.P.; Liu, C.T. Role of minor alloying additions in formation of bulk metallic glasses: A Review. J. Mater. Sci. 2004, 39, 3965–3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.T.; Lu, Z.P. Effect of minor alloying additions on glass formation in bulk metallic glasses. Intermetallics 2005, 13, 415–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inoue, A.; Wang, X.M. Bulk amorphous FC20 (Fe-C-Si) alloys with small amounts of B and their crystallized structure and mechanical properties. Acta Mater. 2000, 48, 1383–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheney, J.; Vecchio, K. Development of quaternary Fe-based bulk metallic glasses. Mater. Sci. Eng. A 2008, 492, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wang, L.; Wang, F.C.; Zhang, H.F.; Liu, Y.B.; Xu, S.H. Formation and corrosion behavior of Fe-based amorphous metallic coatings by HVOF thermal spraying. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2009, 204, 563–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, G.Y.; Nogueira, R.P.; Roche, V.; Yavari, A.R.; Melle, A.K.; Gallego, J.; Bolfarini, C.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Corrosion properties of Fe–Cr–Nb–B amorphous alloys and coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2014, 254, 238–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.B.; Zheng, Y.G.; Sun, W.H.; Wang, J.Q. Erosion–corrosion of HVOF-sprayed Fe-based amorphous metallic coating under impingement by a sand-containing NaCl solution. Corros. Sci. 2013, 76, 337–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, G.Y.; Schulz, R.; Savoie, S.; Nascimento, A.R.C.; Drolet, Y.; Bolfarini, C.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Microstructure and wear behavior of Fe-based amorphous HVOF coatings produced from commercial precursors. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2017, 309, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, P.S. Solidification in spray forming. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2007, 38, 1520–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rios, C.T.; Afonso, C.R.M.; Bolfarini, C.; Botta Filho, W.J.; Kiminami, C.S. Characterization of Glass Forming Alloy Fe43.2Co28.8B19.2Si4.8Nb4 Processed by Spray Forming and Wedge Mold Casting Techniques. Mater. Sci. Forum 2011, 691, 23–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Processing of glass former alloys by spray forming. Herstellung von Legierungen für Glasformen durch Sprühkompaktieren. Materwiss. Werksttech. 2010, 41, 513–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, M.J.; Klemm, J.; Klemm, S.O.; Mayrhofer, K.J.J.; Stratmann, M.; Borodin, S.; Romero, A.H.; Madinehei, M.; Crespo, D.; Serrano, J.; et al. Element-resolved corrosion analysis of stainless-type glass-forming steels. Science 2013, 341, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Habazaki, H. Corrosion of amorphous and nanograined alloys. In Shreir’s Corrosion; Cottis, B., Graham, M., Lindsay, R., Lyon, S., Richardson, T., Scantlebury, D., Stott, H., Eds.; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2010; pp. 2192–2204. ISBN 9780444527875. [Google Scholar]
- Madinehei, M.; Bruna, P.; Duarte, M.J.; Pineda, E.; Klemm, J.; Renner, F.U. Glass-formation and corrosion properties of Fe–Cr–Mo–C–B glassy ribbons with low Cr content. J. Alloys Compd. 2014, 615, S128–S131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pang, S.J.; Zhang, T.; Asami, K.; Inoue, A. Bulk glassy Fe-Cr-Mo-C-B alloys with high corrosion resistance. Corros. Sci. 2002, 44, 1847–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarshan, T.S.; Srivatsan, T.S. Rapid Solidification Technology: An Engineering Guide, 1st ed.; Technomic Publishing Company, Inc.: Lancaster, PA, USA, 1993; ISBN 9780877629269. [Google Scholar]
- Zepon, G.; Nogueira, R.P.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Electrochemical Corrosion Behavior of Spray-Formed Boron-Modified Supermartensitic Stainless Steel. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2017, 48, 2077–2089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Koga, G.Y.; Jorge, A.M.; Savoie, S.; Schulz, R.; Kiminami, C.S.; Bolfarini, C.; Botta, W.J. Microstructural investigation of Fe-Cr-Nb-B amorphous/nanocrystalline coating produced by HVOF. Mater. Des. 2016, 111, 608–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koga, G.Y.; Jorge Junior, A.M.; Roche, V.; Nogueira, R.P.; Schulz, R.; Savoie, S.; Melle, A.K.; Loable, C.; Bolfarini, C.; Kiminami, C.S.; et al. Production and Corrosion Resistance of Thermally Sprayed Fe-Based Amorphous Coatings from Mechanically Milled Feedstock Powders. Metall. Mater. Trans. A 2018, 49, 4860–4870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundman, B.; Jansson, B.; Andersson, J.O. The Thermo-Calc databank system. Calphad 1985, 9, 153–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, Y.; Si, L.; Tan, H.; Li, Y. Boron content dependence of crystallization, glass forming ability and magnetic properties in amorphous Fe-Zr-B-Nb alloys. J. Alloys Compd. 2004, 370, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, P.K. Non-crystalline solids: Glasses and amorphous solids. J. Non-Cryst. Solids 1996, 195, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farmer, J.C.; Haslam, J.J.; Day, S.D.; Lian, T.; Saw, C.K.; Hailey, P.D.; Choi, J.-S.; Rebak, R.B.; Yang, N.; Payer, J.H.; et al. Corrosion resistance of thermally sprayed high-boron iron-based amorphous-metal coatings: Fe49.7Cr17.7Mn1.9Mo7.4W1.6B15.2C3.8Si2.4. J. Mater. Res. 2007, 22, 2297–2311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soyama, J.; Zepon, G.; Lopes, T.P.; Beraldo, L.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Microstructure formation and abrasive wear resistance of a boron-modified superduplex stainless steel produced by spray forming. J. Mater. Res. 2016, 31, 2987–2993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay, N.; Pujar, M.G.; Das, C.R.; Mallika, C.; Mudali, U.K. Pitting corrosion studies on solution-annealed borated type 304l stainless steel using electrochemical noise technique. Corrosion 2014, 70, 781–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, K.; Tjong, S. Effect of Secondary Phase Precipitation on the Corrosion Behavior of Duplex Stainless Steels. Materials 2014, 7, 5268–5304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Wang, Y.; Jiang, S.L.; Zheng, Y.G.; Ke, W.; Sun, W.H.; Wang, J.Q. Effect of porosity sealing treatments on the corrosion resistance of high-velocity oxy-fuel (HVOF)-sprayed Fe-based amorphous metallic coatings. Surf. Coat. Technol. 2011, 206, 1307–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.D.; Wu, J.; Qi, W.B.; Wang, J.Q. Effect of porosity defects on the long-term corrosion behaviour of Fe-based amorphous alloy coated mild steel. Corros. Sci. 2016, 110, 57–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zepon, G.; Nascimento, A.R.C.; Kasama, A.H.; Nogueira, R.P.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J.; Bolfarini, C. Design of wear resistant boron-modified supermartensitic stainless steel by spray forming process. Mater. Des. 2015, 83, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

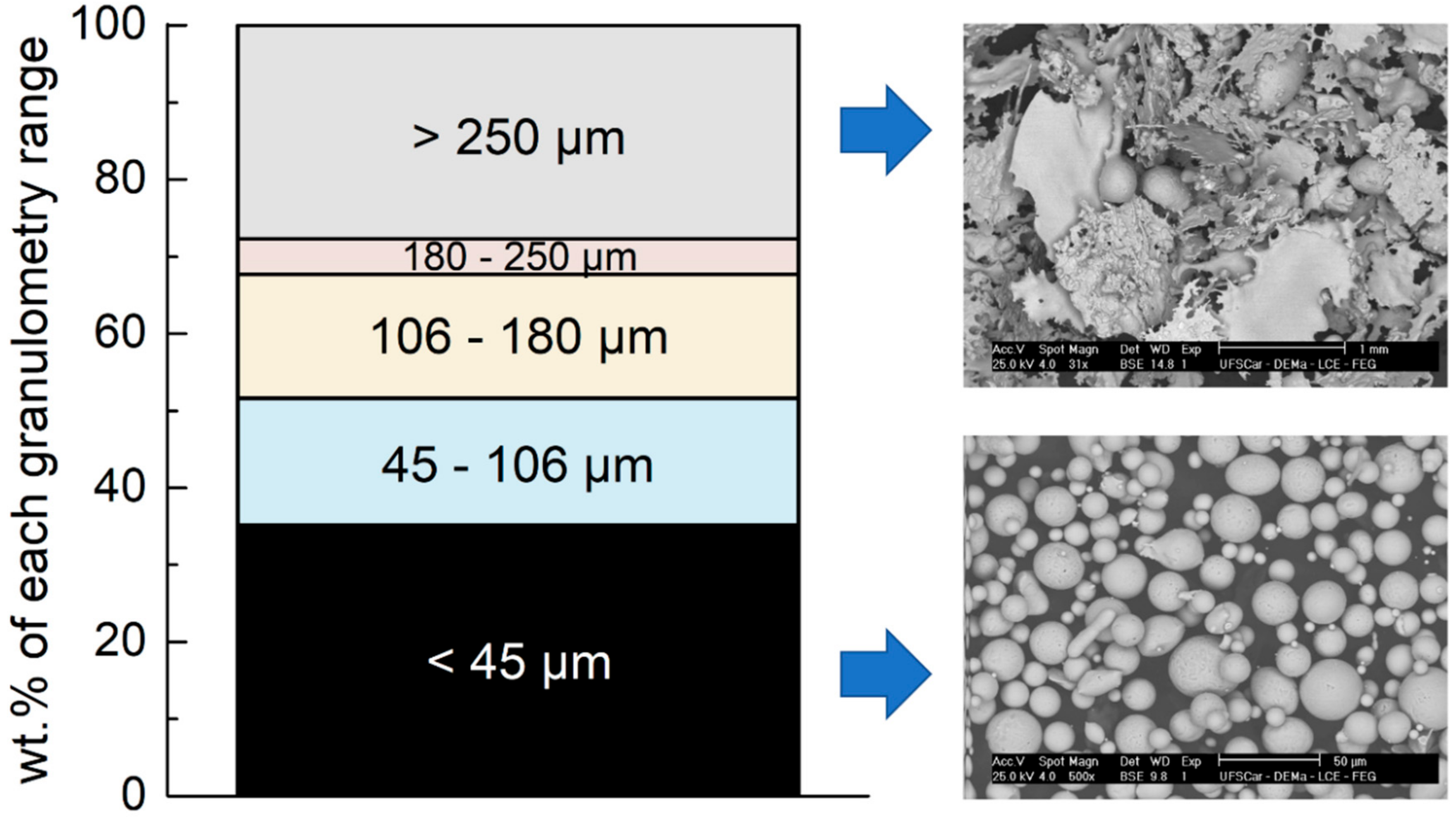
| Alloy/wt.% | C | Si | Mn | Cr | Ni | Mo | S | N | P | B | Fe |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 64.5Fe25Cr7Ni3.5B | 0.08 | 0.35 | 1.02 | 25 | 7 | 1.67 | <0.01 | 0.08 | 0.009 | 3.5 | bal. |
| 63.5Fe25Cr7Ni4.5B | 0.09 | 0.35 | 0.82 | 25 | 7 | 1.47 | <0.01 | 0.07 | 0.007 | 4.5 | bal. |
| 62.5Fe25Cr7Ni5.5B | 0.11 | 0.36 | 0.78 | 25 | 7 | 1.29 | <0.01 | 0.06 | 0.006 | 5.5 | bal. |
| SAF 2205 | 0.02 | 0.35 | 1.57 | 22.60 | 5.38 | 2.58 | 0.01 | 0.13 | 0.010 | - | bal. |
| AISI 1045 | 0.47 | 0.15 | 0.63 | 0.055 | 0.04 | 0.02 | 0.02 | - | 0.014 | - | bal. |
| Samples | Media: pH = 10.0 | Media: pH = 5.5 | Media: pH = 3.0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr (mV) | icorr (µA/cm2) | Ecorr (mV) | icorr (µA/cm2) | Ecorr (mV) | icorr (µA/cm2) | |
| HVOF coating | −530 ± 10 | 30 ± 5 | −480 ± 3 | 30 ± 6 | −530 ± 5 | 20 ± 9 |
| Spray deposition | −310 ± 30 | 0.52 ± 0.04 | −230 ± 20 | 0.7 ± 0.1 | −180 ± 30 | 2.0 ± 0. 8 |
| Amorphous ribbon | −120 ± 25 | 0.05 ± 0.01 | −200 ± 10 | 0.07 ± 0.02 | −190 ± 20 | 0.16 ± 0.03 |
| SAF 2205 | −183 ± 21 | 0.2 ± 0.1 | −181 ± 36 | 0.3 ± 0.2 | −281 ± 12 | 0.3 ± 0.1 |
| AISI 1045 | −666 ± 15 | 500 ± 80 | −632 ± 20 | 800 ± 100 | −715 ± 11 | 400 ± 20 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Koga, G.Y.; Otani, L.B.; Silva, A.M.B.; Roche, V.; Nogueira, R.P.; Jorge, A.M., Jr.; Bolfarini, C.; Kiminami, C.S.; Botta, W.J. Characterization and Corrosion Resistance of Boron-Containing-Austenitic Stainless Steels Produced by Rapid Solidification Techniques. Materials 2018, 11, 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112189
Koga GY, Otani LB, Silva AMB, Roche V, Nogueira RP, Jorge AM Jr., Bolfarini C, Kiminami CS, Botta WJ. Characterization and Corrosion Resistance of Boron-Containing-Austenitic Stainless Steels Produced by Rapid Solidification Techniques. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112189
Chicago/Turabian StyleKoga, Guilherme Y., Lucas B. Otani, Ana M. B. Silva, Virginie Roche, Ricardo P. Nogueira, Alberto M. Jorge, Jr., Claudemiro Bolfarini, Claudio S. Kiminami, and Walter J. Botta. 2018. "Characterization and Corrosion Resistance of Boron-Containing-Austenitic Stainless Steels Produced by Rapid Solidification Techniques" Materials 11, no. 11: 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112189
APA StyleKoga, G. Y., Otani, L. B., Silva, A. M. B., Roche, V., Nogueira, R. P., Jorge, A. M., Jr., Bolfarini, C., Kiminami, C. S., & Botta, W. J. (2018). Characterization and Corrosion Resistance of Boron-Containing-Austenitic Stainless Steels Produced by Rapid Solidification Techniques. Materials, 11(11), 2189. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112189








