Electrospun Produced 3D Matrices for Covering of Vascular Stents: Paclitaxel Release Depending on Fiber Structure and Composition of the External Environment
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Production and Quality Control of Tritium-Labeled Paclitaxel
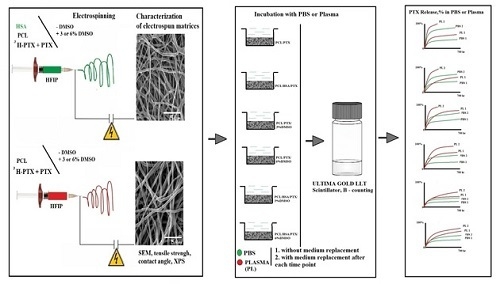
2.2. Preparation of 3D Matrices by Electrospinning
2.3. Characterization of Matrices
2.3.1. Mechanical Testing of Matrices
2.3.2. Study of 3D Matrix Surface Microstructure
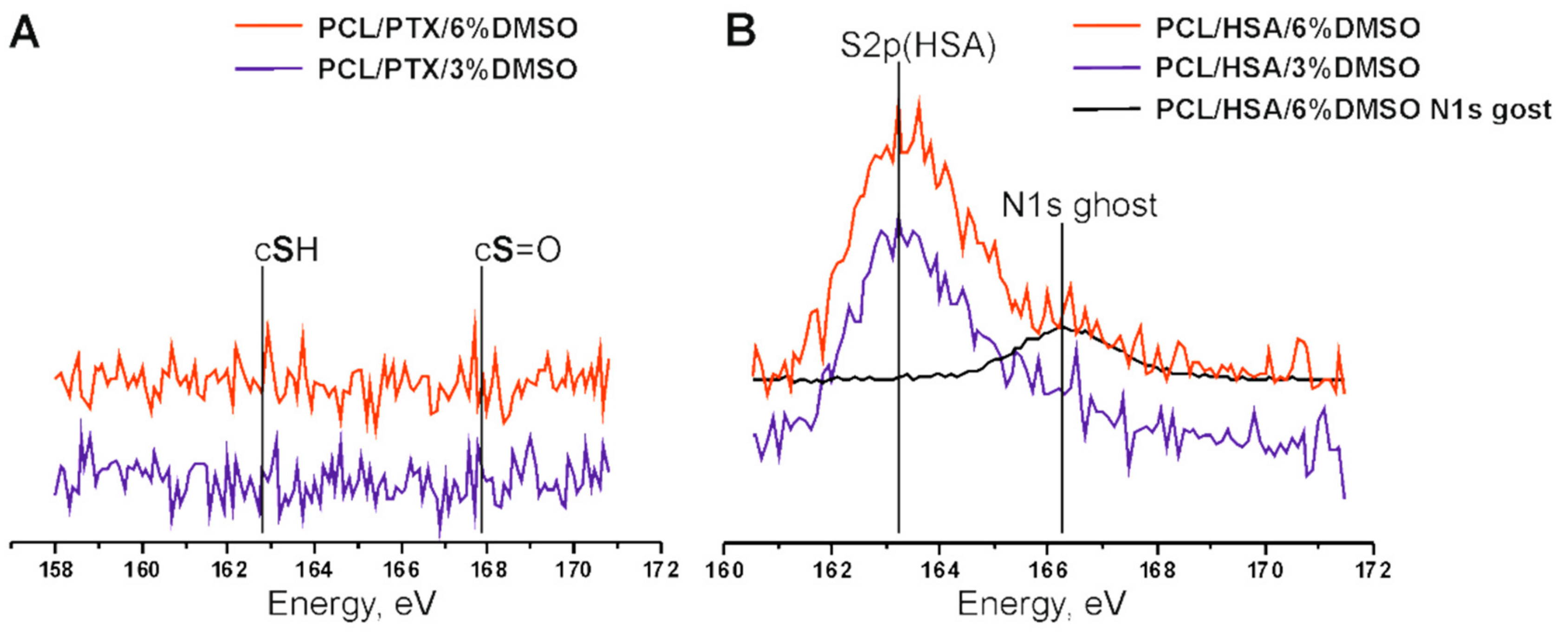
2.3.3. X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy
2.3.4. Additional Physicochemical Characteristics of Matrices
2.4. Assessment of Paclitaxel Release
2.5. Statistical Processing of Data
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Synthesis of Radioactively Labeled PTX
3.2. Electrospinning and Characterization of 3D Matrices Prepared from Different Mixtures of PCL with HSA and Solvents
3.3. PTX Release from Matrices
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sill, T.J.; von Recum, H.A. Electrospinning: Applications in drug delivery and tissue engineering. Biomaterials 2008, 29, 1989–2006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brough, C.; Williams, R.O. Amorphous solid dispersions and nano-crystal technologies for poorly water-soluble drug delivery. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, W.; Li, X.; Zhu, X.; Yu, G.; Zhou, S.; Weng, J. Investigation of drug release and matrix degradation of electrospun poly(DL-lactide) fibers with paracetanol inoculation. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 1623–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seitz, J.M.; Durisin, M.; Goldman, J.; Drelich, J.W. Recent advances in biodegradable metals for medical sutures: A critical review. Adv. Healthc. Mater. 2015, 4, 1915–1936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Li, X.; Cui, W.; Zhou, S.; Tan, R.; Wang, C. Structural stability and release profiles of proteins from core-shell poly (DL-lactide) ultrafine fibers prepared by emulsion electrospinning. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 86, 374–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, H.; Ponticiello, M.S.; Leong, K.W. Fabrication of controlled release biodegradable foams by phase separation. Tissue Eng. 1995, 1, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okuda, T.; Tominag, K.; Kidoak, S. Time-programmed dual release formulation by multilayered drug-loaded nanofiber meshes. J. Control. Release 2010, 143, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosic, R.; Pelipenko, J.; Kristl, J.; Kocbek, P.; Baumgartner, S. Properties: Engineering and applications of polymeric nanofibers: Current research and future advances. Chem. Biochem. Eng. Q. 2012, 26, 417–425. [Google Scholar]
- Khadka, D.B.; Haynie, D.T. Protein- and peptide-based electrospun nanofibers in medical biomaterials. Nanomed. Nanotechnol. Biol. Med. 2012, 8, 1242–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, N.; Kundu, S.C. Electrospinning: A fascinating fiber fabrication technique. Biotechnol. Adv. 2010, 28, 325–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balogh, A.; Domokos, A.; Farkas, B.; Farkas, A.; Rapi, Z.; Kiss, D.; Nyiri, Z.; Eke, Z.; Szarka, G.; Örkényi, R.; et al. Continuous End-to-End Production of Solid Drug Dosage Forms: Coupling Flow Synthesis and Formulation by Electrospinning. Chem. Eng. J. 2018, 350, 290–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Hu, Ch.; Li, B.; Yang, H.; Cheng, Y.; Cui, W. A highly flexible paclitaxel-loaded poly(e-caprolactone) electrospun fibrous-membrane-covered stent for benign cardia stricture. Acta Biomater. 2013, 9, 8328–8336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tefft, B.J.; Uthamaraj, S.; Harburnc, J.J.; Hlinomazd, O.; Lermana, A.; Dragomir-Daescue, D.; Sandhua, G.S. Magnetizable stent-grafts enable endothelial cell capture. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2017, 427, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Papafaklisa, M.I.; Chatzizisis, Y.S.; Naka, K.K.; Giannoglou, G.D.; Michalis, L.K. Drug-eluting stent restenosis: Effect of drug type, release kinetics, hemodynamicsand coating strategy. Pharmacol. Therapeut. 2012, 134, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dangas, G.D.; Claessen, B.E.; Caixeta, A.; Sanidas, E.A.; Mintz, G.S.; Mehran, R. In-stent restenosis in the drug-eluting stent era. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2010, 56, 1897–1907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radke, P.W.; Kaiser, A.; Frost, C.; Sigwar, U. Outcome after treatment of coronary in-stent restenosis: Results from a systematic review using meta-analysis techniques. Eur. Heart J. 2003, 24, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Shim, W.H.; Ho, D.S.; Raizner, A.E.; Park, S.W.; Hong, M.K.; Lee, C.W.; Choi, D.; Jang, Y.; Lam, R.; et al. A paclitaxel-eluting stent for the prevention of coronary restenosis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2003, 348, 1537–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aoki, J.; Kirtane, A.; Martin, S.M.; Leon, B.; Dangas, G. Coronary artery aneurysms after drug-eluting stent implantation. JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2008, 1, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Müller-Hülsbeck, S. Eluvia™ peripheral stent system for the treatment of peripheral lesions above the knee. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2016, 13, 1639–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Schofer, J.; Musiałek, P.; Bijuklic, K.; Kolvenbach, R.; Trystula, M.; Siudak, Z.; Sievert, H. A prospective, multicenter study of a novel mesh-covered carotid stent: The CGuard CARENET trial (carotid embolic protection using MicroNet). JACC Cardiovasc. Interv. 2015, 8, 1229–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Purcell, M.; Neault, J.F.; Tajmir-Riahi, H.A. Interaction of taxol with human serum albumin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2000, 1478, 61–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, M.; Martinson, L.; Wagner, M.S.; Castner, D.G.; Ratner, B.D.; Horbett, T.A. PEO-like plasma polymerized tetraglyme surface interactions with leukocytes and proteins: In vitro and in vivo studies. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 367–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Denizli, F.K.; Guven, O. Competitive adsorption of blood proteins on gamma-irradiated-polycarbonate films. J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 2002, 13, 127–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sidorov, V.N.; Polak, Yu.V.; Laktionov, P.P.; Roshcke, V.V.; Kist, A.G. Method of Production of Tritium Labeled Organic Compounds and the Device for Its Implementation. SU Patent 1823961 A3, 18 January 1991. [Google Scholar]
- Cardiovascular Implants-Tubular Vacuum Prostheses. International Patent Application No. ISO/FDIS 7198:1998, July 1998.
- Chernonosova, V.S.; Kvon, R.I.; Stepanova, A.O.; Larichev, Y.V.; Karpenko, A.A.; Chelobanov, B.P.; Kiseleva, E.V.; Laktionov, P.P. Human serum albumin in electrospun PCL fibers: Structure, release, and exposure on fiber surface. Polym. Adv. Technol. 2017, 28, 819–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulder, J.F.; Stickle, W.F.; Sobol, P.E.; Bomben, K.D. Handbook of X-Ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy; Perkin-Elmer: Eden Prairie, MN, USA, 1992. [Google Scholar]
- Karimi, A.; Navid, M.; Shojaeic, A.; Faghihi, S. Measurement of the uniaxial mechanical properties of healthy and atherosclerotic human coronary arteries. Mater. Sci. Eng. C Mater. Biol. Appl. 2013, 33, 2550–2554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goladkina, A.A.; Kirilova, I.V.; Shychkina, O.A.; Maslaykova, G.N.; Ostrovskii, N.V.; Chelnokova, N.O. Finite-element modeling of ischemic heart disease from the picture of morphofunctional changes of arteries and the heart muscle of the human. Russ. J. Biomech. 2011, 15, 33–46. [Google Scholar]
- Megelski, S.; Stephens, J.S.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Micro- and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 2002, 35, 8456–8466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casper, C.L.; Stephens, J.S.; Tassi, N.G.; Chase, D.B.; Rabolt, J.F. Controlling surface morphology of electrospun polystyrene fibers: Effect of humidity and molecular weight in the electrospinning process. Macromolecules 2004, 37, 573–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsogiannis, K.A.G.; Vladisavljevic’, G.T.; Georgiadou, S. Porous electrospun polycaprolactone fibers: Effect of process parameters. J. Polym. Sci. Part B Polym. Phys. 2016, 54, 1878–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Srikar, R.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M.; Bazilevsky, A.V.; Kelley, E. Desorption-limited mechanism of release from polymer nanofibers. Langmuir 2008, 24, 965–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abouelmagd, S.A.; Sun, B.; Chang, A.C.; Ku, Y.J.; Yeo, Y. Release kinetics study of poorly water-soluble drugs from nanoparticles: Are we doing it right? Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisani, S.; Dorati, R.; Conti, B.; Modena, T.; Bruni, G.; Gentaa, I. Design of copolymer PLA-PCL electrospun matrix for biomedical applications. React. Funct. Polym. 2018, 124, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parmon, V.N. Modern Approaches to the Study and Description of the Processes of Drying Porous Bodies; Siberian Branch of the Russian Academy of Sciences: Novosibirsk, Russia, 2001; 300p. [Google Scholar]
- Chernonosova, V.S.; Gostev, A.A.; Gao, Y.; Chesalov, Y.A.; Shutov, A.V.; Pokushalov, E.A.; Karpenko, A.A.; Laktionov, P.P. Mechanical properties and biological behavior of 3D matrices produced by electrospinning from protein-enriched polyurethane. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 1380606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yasukawa, T.; Ogura, Y.; Sakurai, E.; Tabata, Y.; Kimura, H. Intraocular sustained drug delivery using implantable polymeric devices. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2005, 57, 2033–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppas, N.A.; Narasimhan, B. Mathematical models in drug delivery: How modeling has shaped the way we design new drug delivery systems. J. Control. Release 2014, 190, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandhi, M.; Srikar, R.; Yarin, A.L.; Megaridis, C.M.; Gemeinhart, R.A. Mechanistic examination of protein release from polymer nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2009, 6, 641–647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Creel, C.J.; Lovich, M.A.; Edelman, E.R. Arterial paclitaxel distribution and deposition. Circ. Res. 2000, 28, 879–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.D.; Vukmirovic, N.; Hwang, C.W.; Edelman, E.R. Specific binding to intracellular proteins determines arterial transport properties for rapamycin and paclitaxel. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 9463–9467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Baldwin, A.L.; Secomb, T.W.; Simon, B.R. Convection and diffusion of albumin through artery walls: Implications for local drug delivery. In Bioengineering Division; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: New York, NY, USA, 1997; Volume 35, pp. 93–94. [Google Scholar]
- Goriely, A.R.; Baldwin, A.L.; Secom, T.W. Transient diffusion of albumin in aortic walls: Effects of binding to medial elastin layers. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2007, 292, 2195–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sirianni, R.W.; Kremer, J.; Guler, I.; Chen, Y.L.; Keeley, F.W.; Saltzman, W.M. Effect of extracellular matrix elements on the transport of paclitaxel through an arterial wall tissue mimic. Biomacromolecules 2008, 10, 2792–2798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axel, D.I.; Kunert, W.; Göggelmann, C.; Oberhoff, M.; Herdeg, C.; Küttner, A.; Wild, D.H.; Brehm, B.R.; Riessen, R.; Köveker, G.; et al. Paclitaxel inhibits arterial smooth muscle cell proliferation and migration in vitro and in vivo using local drug delivery. Circulation 1997, 15, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Matrix Composition | Electrospinning Parameters | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Voltage, kV | Feed Rate of the Solution, mL/h | Distance between Electrodes, cm | |
| PCL/PTX | 23.0 | 1.2 | 20 |
| PCL/PTX/10% HSA | 23.5 | 1.3 | 20 |
| PCL/PTX/3% DMSO | 23.0 | 1.3 | 20 |
| PCL/PTX/6% DMSO | 24.5 | 1.3 | 20 |
| PCL/PTX/10% HSA/3%DMSO | 24.5 | 1.4 | 20 |
| PCL/PTX/10% HSA/6% DMSO | 25.0 | 1.4 | 20 |
| No | Sample | Fiber Diameter, µm | Pore Diameter, µm | Porosity, % * | Contact Angle, ° ** | Water Absorption, % | Weight Loss, % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 5% PCL/PTX | 0.31 ± 0.04 | 5.72 ± 2.42 | 78/54.1 | 127.33 (±1.30)° | 294 ± 7 | 0 |
| 2 | 5% PCL/PTX/10% HSA | 0.56 ± 0.09 | 2.66 ± 1.21 | 77/61.4 | 88.89 (±3.03)° | 589 ± 16 | 0 |
| 3 | 5% PCL/PTX/3% DMSO | 0.19 ± 0.03 | 2.01 ± 0.73 | 78/65 | 128.30 (±2.18)° | 400 ± 11 | 0 |
| 4 | 5% PCL/PTX/6% DMSO | 0.13 ± 0.02 | 0.97 ± 0.32 | 80/76.6 | 132.35 (±3.11)° | 238 ± 9 | 0 |
| 5 | 5% PCL/PTX/3% DMSO/HSA | 0.37 ± 0.08 | 1.97 ± 0.52 | 77/71 | 124.73 (±3.49)° | 750 ± 13 | 0 |
| 6 | 5% PCL/PTX/6% DMSO/HSA | 0.16 ± 0.03 | 1.35 ± 0.40 | 79/61.3 | 120.52 (±2.66)° | 883 ± 15 | 0 |
| No | Sample of 3D Matrix | Concentration of HSA or PTX, % | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial Matrix | Matrix after Incubation in PBS | ||
| 1 | PCL/10% HSA | 20 * | 24 * |
| 2 | 5%PCL/10%HSA/3%DMSO | 18.9 | 27.1 |
| 3 | 5%PCL/10%HSA/6%DMSO | 16.3 | 21.5 |
| 4 | 5%PCL/PTX | 21.1 | 23.4 |
| 5 | 5%PCL/PTX/3%DMSO | 15.1 | 23.9 |
| 6 | 5%PCL/PTX/6%DMSO | 3.7 | 13.7 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kuznetsov, K.A.; Stepanova, A.O.; Kvon, R.I.; Douglas, T.E.L.; Kuznetsov, N.A.; Chernonosova, V.S.; Zaporozhchenko, I.A.; Kharkova, M.V.; Romanova, I.V.; Karpenko, A.A.; et al. Electrospun Produced 3D Matrices for Covering of Vascular Stents: Paclitaxel Release Depending on Fiber Structure and Composition of the External Environment. Materials 2018, 11, 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112176
Kuznetsov KA, Stepanova AO, Kvon RI, Douglas TEL, Kuznetsov NA, Chernonosova VS, Zaporozhchenko IA, Kharkova MV, Romanova IV, Karpenko AA, et al. Electrospun Produced 3D Matrices for Covering of Vascular Stents: Paclitaxel Release Depending on Fiber Structure and Composition of the External Environment. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112176
Chicago/Turabian StyleKuznetsov, Konstantin A., Alena O. Stepanova, Ren I. Kvon, Timothy E. L. Douglas, Nikita A. Kuznetsov, Vera S. Chernonosova, Ivan A. Zaporozhchenko, Maria V. Kharkova, Irina V. Romanova, Andrey A. Karpenko, and et al. 2018. "Electrospun Produced 3D Matrices for Covering of Vascular Stents: Paclitaxel Release Depending on Fiber Structure and Composition of the External Environment" Materials 11, no. 11: 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112176
APA StyleKuznetsov, K. A., Stepanova, A. O., Kvon, R. I., Douglas, T. E. L., Kuznetsov, N. A., Chernonosova, V. S., Zaporozhchenko, I. A., Kharkova, M. V., Romanova, I. V., Karpenko, A. A., & Laktionov, P. P. (2018). Electrospun Produced 3D Matrices for Covering of Vascular Stents: Paclitaxel Release Depending on Fiber Structure and Composition of the External Environment. Materials, 11(11), 2176. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112176