Effects of Wet-Pressing and Cross-Linking on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fibers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Methods
2.3. Characterization
3. Results and Discussions
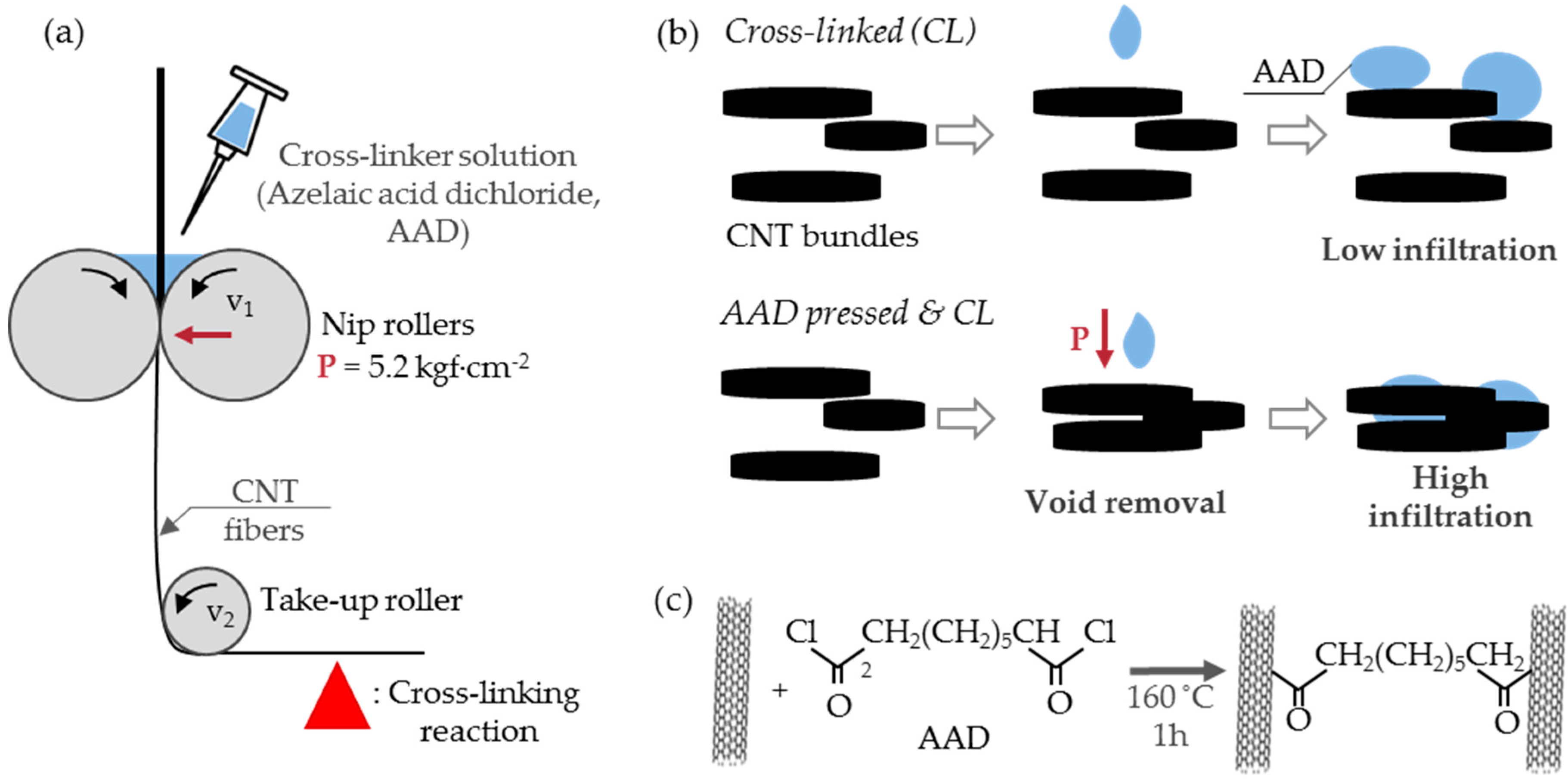
3.1. Physical Effects of Roller Pressing and Liquid Injection
3.2. Chemical Cross-Linking
3.3. Tensile Properties
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thostenson, E.T.; Ren, Z.; Chou, T.-W. Advances in the science and technology of carbon nanotubes and their composites: A review. Compos. Sci. Technol. 2001, 61, 1899–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, B.; Locascio, M.; Zapol, P.; Li, S.; Mielke, S.L.; Schatz, G.C.; Espinosa, H.D. Measurements of near-ultimate strength for multiwalled carbon nanotubes and irradiation-induced crosslinking improvements. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008, 3, 626–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.-L.; Kinloch, I.A.; Windle, A.H. Direct spinning of carbon nanotube fibers from chemical vapor deposition synthesis. Science 2004, 304, 276–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yusof, N.; Ismail, A. Post spinning and pyrolysis processes of polyacrylonitrile (PAN)-based carbon fiber and activated carbon fiber: A review. J. Anal. Appl. Pyrolysis 2012, 93, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vilatela, J.J.; Windle, A.H. Yarn-like carbon nanotube fibers. Adv. Mater. 2010, 22, 4959–4963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, T.Q.; Fan, Z.; Liu, P.; Myint, S.M.; Duong, H.M. Super-strong and highly conductive carbon nanotube ribbons from post-treatment methods. Carbon 2016, 99, 407–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hearle, J. Theoretical analysis of the mechanics of twisted staple fiber yarns. Text. Res. J. 1965, 35, 1060–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, K.-H. Carbon nanotube yarns. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2012, 29, 277–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beese, A.M.; Wei, X.; Sarkar, S.; Ramachandramoorthy, R.; Roenbeck, M.R.; Moravsky, A.; Ford, M.; Yavari, F.; Keane, D.T.; Loutfy, R.O. Key factors limiting carbon nanotube yarn strength: Exploring processing-structure-property relationships. ACS Nano 2014, 8, 11454–11466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duong, H.M.; Gong, F.; Liu, P.; Tran, T.Q. Advanced fabrication and properties of aligned carbon nanotube composites: Experiments and modeling. In Carbon Nanotubes-Current Progress of Their Polymer Composites; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnevis, H.; Tran, T.Q.; Mint, S.M.; Zadhoush, A.; Duong, H.M.; Youssefi, M. Effect of alignment and packing density on the stress relaxation process of carbon nanotube fibers spun from floating catalyst chemical vapor deposition method. Colloid Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2018, 558, 570–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hill, F.A.; Havel, T.F.; Hart, A.J.; Livermore, C. Enhancing the tensile properties of continuous millimeter-scale carbon nanotube fibers by densification. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 7198–7207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miao, M. The role of twist in dry spun carbon nanotube yarns. Carbon 2016, 96, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Sun, Y.; Zhou, R.; Zhu, H.; Wang, J.; Liu, L.; Fan, S.; Jiang, K. Carbon nanotube yarns with high tensile strength made by a twisting and shrinkingmethod. Nanotechnology 2009, 21, 045708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, J.; Fang, S.; Moura, F.A.; Galvão, D.S.; Bykova, J.; Aliev, A.; de Andrade, M.J.; Lepró, X.; Li, N.; Haines, C. Strong, Twist-Stable Carbon Nanotube Yarns and Muscles by Tension Annealing at Extreme Temperatures. Adv. Mater. 2016, 28, 6598–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, C.-D.; Humphries, W.; Smith, S.M.; Huynh, C.; Lucas, S. Improving the tensile strength of carbon nanotube spun yarns using a modified spinning process. Carbon 2009, 47, 2662–2670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miaudet, P.; Badaire, S.; Maugey, M.; Derre, A.; Pichot, V.; Launois, P.; Poulin, P.; Zakri, C. Hot-drawing of single and multiwall carbon nanotube fibers for high toughness and alignment. Nano Lett. 2005, 5, 2212–2215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.; Lee, H.; Oh, E.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.; Park, H.J.; Yoon, S.-B.; Lee, C.-H.; Kwak, G.-H.; Lee, W.J. Hierarchical structure of carbon nanotube fibers, and the change of structure during densification by wet stretching. Carbon 2018, 136, 409–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bishop, R. Crystal Engineering. In Kirk-Othmer Encyclopedia of Chemical Technology; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, J.Y.; Min, J.; McDonnell, J.; Church, J.S.; Easton, C.D.; Humphries, W.; Lucas, S.; Woodhead, A.L. An improved method for functionalisation of carbon nanotube spun yarns with aryldiazonium compounds. Carbon 2012, 50, 4655–4662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.; Cai, J.Y.; Sridhar, M.; Easton, C.D.; Gengenbach, T.R.; McDonnell, J.; Humphries, W.; Lucas, S. High performance carbon nanotube spun yarns from a crosslinked network. Carbon 2013, 52, 520–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, O.-K.; Choi, H.; Jeong, H.; Jung, Y.; Yu, J.; Lee, J.K.; Hwang, J.Y.; Kim, S.M.; Jeong, Y.; Park, C.R. High-modulus and strength carbon nanotube fibers using molecular cross-linking. Carbon 2017, 118, 413–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boncel, S.; Sundaram, R.M.; Windle, A.H.; Koziol, K.K. Enhancement of the mechanical properties of directly spun CNT fibers by chemical treatment. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 9339–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Y.; Chen, H.; Ge, J.; Zhao, J.; Li, Q.; Tang, J.; Cui, Y.; Chen, L. Direct Intertube Cross-Linking of Carbon Nanotubes at Room Temperature. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 6541–6547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, O.-K.; Lee, W.; Hwang, J.Y.; You, N.-H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, S.M.; Ku, B.-C. Mechanical and electrical properties of thermochemically cross-linked polymer carbon nanotube fibers. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2016, 91, 222–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, J.; Park, B.; Sa, J.-H.; Jung, A.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Hwang, W.; Lee, K.-H. Improving the tensile strength of carbon nanotube yarn via one-step double [2 + 1] cycloadditions. Korean J. Chem. Eng. 2016, 33, 299–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Im, Y.-O.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, T.; Park, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, K.-H. Utilization of carboxylic functional groups generated during purification of carbon nanotube fiber for its strength improvement. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2017, 392, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Wei, Y.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Fan, S.; Jiang, K. High-strength composite yarns derived from oxygen plasma modified super-aligned carbon nanotube arrays. Nano Res. 2013, 6, 208–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.-M.; Yu, H.; Jeong, H.S.; Kim, S.M.; Lee, K.-H. Accurate measurement of specific tensile strength of carbon nanotube fibers with hierarchical structures by vibroscopic method. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 8575–8580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conroy, D.; Moisala, A.; Cardoso, S.; Windle, A.; Davidson, J. Carbon nanotube reactor: Ferrocene decomposition, iron particle growth, nanotube aggregation and scale-up. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2010, 65, 2965–2977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, P.-C.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Marom, G.; Kim, J.-K. Dispersion and functionalization of carbon nanotubes for polymer-based nanocomposites: A review. Compos. Part A Appl. Sci. Manuf. 2010, 41, 1345–1367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhan, H.; Wang, J.N. High-strength carbon nanotube film from improving alignment and densification. Nano Lett. 2016, 16, 946–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oxtoby, E. Spun Yarn Technology; Butterworth-Heinemann: Oxford, UK, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.J.; Choo, H.; Park, O.-K.; You, N.-H.; Jeong, Y.; Kim, H.C.; Lee, J.K.; Ku, B.-C. Mechanical properties enhanced by solid-state coupling reaction for molecular covalent bridges of carbon nanotube fibers. Mater. Lett. 2018, 211, 243–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Hiremath, N.; Hong, K.; Evora, M.C.; Ranson, V.H.; Naskar, A.K.; Bhat, G.S.; Kang, N.-G.; Mays, J.W. Improving mechanical properties of carbon nanotube fibers through simultaneous solid-state cycloaddition and crosslinking. Nanotechnology 2017, 28, 145603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, D.-M.; Lee, S.-H.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, K.-H.; Kim, S.M. Mathematical model for dynamic mechanical behavior of carbon nanotube yarn in analogy with hierarchically structured bio-materials. 2018; Manuscript in preparation. [Google Scholar]






| Code | Sample Name | Roller Pressing | Solvent Infiltration | Cross-Linking Reaction (Temperature) | Related Figures |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Pristine | no | no | no | – |
| 1 | CL100 | no | yes (AAD) | yes (100 °C) | Figure 1b (up) |
| 1 | CL130 | no | yes (AAD) | yes (130 °C) | Figure 1b (up) |
| 1 | CL160 | no | yes (AAD) | yes (160 °C) | Figure 1b (up) |
| 2 | Pressed | yes | no | no | – |
| 3 | Acetone pressed | yes | yes (Acetone) | no | – |
| 4 | AAD pressed and CL | yes | yes (AAD) | yes (160 °C) | Figure 1a,b (down) |
| Liquid | Surface Tension (mN·m−1) | Contact Angle θ (°) | (mN·m−1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water | 72.0 | 106.7 | −20.7 |
| Acetone | 22.9 | 9.0 | 22.6 |
| AAD | 36.5 | 27.3 | 32.4 |
| Factors | Unit | Sample Name | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pristine | CL160 | Pressed | Acetone Pressed | AAD Pressed and CL | ||
| Specific strength | N/tex | 0.40 ± 0.05 | 0.36 ± 0.04 | 0.47 ± 0.01 | 0.49 ±0.03 | 0.67 ± 0.04 |
| Tensile strength | MPa | 180 ± 20 | 180 ± 10 | 680 ± 20 | 350 ± 20 | 380 ± 20 |
| Load at break | cN | 2.83 ± 0.25 | 1.94 ± 0.15 | 4.41 ± 0.16 | 2.98 ± 0.18 | 3.61 ± 0.22 |
| Linear density | tex | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.07 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.00 | 0.05 ± 0.00 |
| Cross-sectional area | μm2 | 160 | 110 | 66 | 85 | 96 |
| Strain at break | % | 3.4 ± 0.6 | 3.6 ± 0.6 | 4.3 ± 0.2 | 3.7 ± 0.4 | 3.5 ± 0.4 |
| Toughness | N/tex | 0.74 ± 0.05 | 0.90 ± 0.29 | 1.43 ± 0.09 | 1.31 ± 0.20 | 1.36 ± 0.22 |
| Maximum tangent modulus | N/tex | 0.26 ± 0.01 | 0.25 ± 0.02 | 0.32 ±0.02 | 0.31 ± 0.02 | 0.37 ± 0.03 |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, H.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.; Lee, S.-H.; Park, J.; Lee, C.-H.; Lee, K.-H. Effects of Wet-Pressing and Cross-Linking on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fibers. Materials 2018, 11, 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112170
Cho H, Lee J, Lee H, Lee S-H, Park J, Lee C-H, Lee K-H. Effects of Wet-Pressing and Cross-Linking on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fibers. Materials. 2018; 11(11):2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112170
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Hyunjung, Jinwoo Lee, Haemin Lee, Sung-Hyun Lee, Junbeom Park, Cheol-Hun Lee, and Kun-Hong Lee. 2018. "Effects of Wet-Pressing and Cross-Linking on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fibers" Materials 11, no. 11: 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112170
APA StyleCho, H., Lee, J., Lee, H., Lee, S.-H., Park, J., Lee, C.-H., & Lee, K.-H. (2018). Effects of Wet-Pressing and Cross-Linking on the Tensile Properties of Carbon Nanotube Fibers. Materials, 11(11), 2170. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11112170





